ESP LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 374 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-37
In the case of a catalytic converter failure the following failure symptoms may be apparent:
lMIL light on after 2 driving cycles (NAS market only).
lHigh exhaust back pressure if catalyst partly melted.
lExcessive emissions
lStrong smell of H
2S (rotten eggs).
Oxygen sensor voltages can be monitored using 'Testbook', the approximate output voltage from the heated oxygen
sensors with a warm engine at idle and with closed loop fuelling active are shown in the table below:
Mass air flow sensor and air temperature sensor
The engine management ECM uses the mass air flow sensor to measure the mass of air entering the intake and
interprets the data to determine the precise fuel quantity which needs to be injected to maintain the stoichiometric
air:fuel ratio for the exhaust catalysts. If the mass air flow sensor fails, lambda control and idle speed control will be
affected and the emission levels will not be maintained at the optimum level. If the device should fail and the ECM
detects a fault, it invokes a software backup strategy.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.
The air temperature sensor is used by the engine management ECM to monitor the temperature of the inlet air. If the
device fails, catalyst monitoring will be affected. The air temperature sensor in integral to the mass air flow sensor.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.
Throttle position sensor
If the engine management ECM detects a throttle position sensor failure, it may indicate a blocked or restricted air
intake filter. Failure symptoms may include:
lPoor engine running and throttle response
lEmission control failure
lNo closed loop idle speed control
lAltitude adaption is incorrect
If a signal failure should occur, a default value is derived using data from the engine load and speed.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Description - engine
management.
Atmospheric pressure will vary with altitude and have a resulting influence on the calculations performed by the ECM
in determining the optimum engine operating conditions to minimise emissions. The following are approximate
atmospheric pressures for the corresponding altitudes:
l0.96 bar at sea level
l0.70 bar at 2,750 m (9,000 ft.)
Measurement Normal catalyst Defective catalyst
Pre-catalytic heated oxygen sensors ~ 100 to 900 mV switching @ ~ 0.5
Hz~ 100 to 900 mV switching @ ~ 0.5 Hz
Post-catalytic heated oxygen sensors ~ 200 to 650 mV, static or slowly
changing~ 200 to 850 mV, changing up to same
frequency as pre-catalytic heated oxygen
sensors
Amplitude ratio (LH HO
2 sensors & RH
HO
2 sensors)<0.3 seconds >0.6 seconds (needs to be approximately
0.75 seconds for single catalyst fault)
Number of speed/load monitoring areas
exceeded (LH & RH)0 >1 (needs to be 3 for fault storage)
Page 376 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 17-2-39
Possible symptoms associated with a purge valve or associated pipework failure is listed below:
lEngine may stall on return to idle if purge valve is stuck open.
lPoor idling quality if the purge valve is stuck open
lFuelling adaptions forced excessively lean if the EVAP canister is clear and the purge valve is stuck open.
lFuelling adaptions forced excessively rich if the EVAP canister is saturated and the purge valve is stuck open.
lSaturation of the EVAP canister if the purge valve is stuck closed.
To maintain driveability and effective emission control, EVAP canister purging must be closely controlled by the
engine management ECM, as a 1% concentration of fuel vapour from the EVAP canister in the air intake may shift
the air:fuel ratio by as much as 20%. The ECM must purge the fuel vapour from the EVAP canister at regular intervals
as its storage capacity is limited and an excessive build up of evaporated fuel pressure in the system could increase
the likelihood of vapour leaks. Canister purging is cycled with the fuelling adaptation as both cannot be active at the
same time. The ECM alters the PWM signal to the purge valve to control the rate of purging of the canister to maintain
the correct stoichiometric air:fuel mixture for the engine.
Fuel leak detection system (vacuum type) – NAS only
The advanced evaporative loss control system used on NAS vehicles is similar to the standard system, but also
includes a CVS valve and fuel tank pressure sensor and is capable of detecting holes in the fuel evaporative system
down to 1 mm (0.04 in.). The test is carried out in three parts. First the purge valve and the canister vent solenoid
valve closes off the storage system and the vent pressure increases due to the fuel vapour pressure level in the tank.
If the pressure level is greater than the acceptable limit, the test will abort because a false leak test response will
result. In part two of the test, the purge valve is opened and the fuel tank pressure will decrease due to the depression
from the intake manifold, evident at the purge port of the EVAP canister during purge operation. In part three of the
test, the leak measurement test is performed. The pressure response of the tests determines the level of leak, and if
this is greater than the acceptable limit on two consecutive tests, the ECM stores the fault in diagnostic memory and
the MIL light on the instrument pack is illuminated. The test is only carried out at engine idle with the vehicle stationary,
and a delay of 15 minutes after engine start is imposed before diagnosis is allowed to commence.
Page 377 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-40 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
EVAP system, leak detection diagnostic (vacuum type)
The EVAP system leak detection is performed as follows:
1The ECM checks that the signal from the fuel tank pressure sensor is within the expected range. If the signal is
not within range, the leakage test will be cancelled.
2Next the purge valve is held closed and the canister vent solenoid (CVS) valve is opened to atmosphere. If the
ECM detects a rise in pressure with the valves in this condition, it indicates there is a blockage in the fuel
evaporation line between the CVS valve and the EVAP canister, or that the CVS valve is stuck in the closed
position and thus preventing normalisation of pressure in the fuel evaporation system. In this instance, the
leakage test will be cancelled.
3The CVS valve and the purge valve are both held in the closed position while the ECM checks the fuel tank
pressure sensor. If the fuel tank pressure sensor detects a decline in pressure, it indicates that the purge valve
is not closing properly and vapour is leaking past the valve seat face under the influence of the intake manifold
depression. In this instance, the leakage test will be cancelled.
4If the preliminary checks are satisfactory, a compensation measurement is determined next. Variations in fuel
level occur within the fuel tank, which will influence the pressure signal detected by the fuel tank pressure
sensor. The pressure detected will also be influenced by the rate of change in the fuel tank pressure, caused by
the rate of fuel evaporation which itself is dependent on the ambient temperature conditions. Because of these
variations, it is necessary for the ECM to evaluate the conditions prevailing at a particular instance when testing,
to ensure that the corresponding compensation factor is included in its calculations.
The CVS valve and purge valves are both closed while the ECM checks the signal from the fuel tank pressure
sensor. The rise in fuel pressure detected over a defined period is used to determine the rate of fuel evaporation
and the consequent compensation factor necessary.
5With the CVS valve still closed, the purge valve is opened. The inlet manifold depression present while the purge
valve is open, decreases EVAP system pressure and sets up a small vacuum in the fuel tank. The fuel tank
pressure sensor is monitored by the ECM and if the vacuum gradient does not increase as expected, a large
system leak is assumed by the ECM (e.g. missing or leaking fuel filler cap) and the diagnostic test is terminated.
If the EVAP canister is heavily loaded with hydrocarbons, purging may cause the air:fuel mixture to become
excessively rich, resulting in the upstream oxygen sensors requesting a leaner mix from the ECM to bring the
mixture back to the stoichiometric ideal. This may cause instability in the engine idle speed and consequently
the diagnostic test will have to be abandoned. The ECM checks the status of the upstream oxygen sensors
during the remainder of the diagnostic, to ensure the air:fuel mixture does not adversely affect the engine idle
speed.
6When the fuel tank pressure sensor detects that the required vacuum has been reached (-800 Pa), the purge
valve is closed and the EVAP system is sealed. The ECM then checks the change in the fuel tank pressure
sensor signal (diminishing vacuum) over a period of time, and if it is greater than expected (after taking into
consideration the compensation factor due to fuel evaporation within the tank, determined earlier in the
diagnostic), a leak in the EVAP system is assumed. If the condition remains, the MIL warning light will be turned
on after two drive cycles.
The decrease in vacuum pressure over the defined period must be large enough to correspond to a hole
equivalent to 1 mm (0.04 in.) diameter or greater, to be considered significant enough to warrant the activation
of an emissions system failure warning.
The diagnostic test is repeated at regular intervals during the drive cycle, when the engine is at idle condition. The
diagnostic test will not be able to be performed under the following conditions:
lDuring EVAP canister purging
lDuring fuelling adaption
lIf excess slosh in the fuel tank is detected (excess fuel vapour will be generated, invalidating the result)
Page 379 of 1672

EMISSION CONTROL - V8
17-2-42 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Secondary air injection system
When the engine is started, the engine control module checks the engine coolant temperature and if it is below 55°
C, the ECM grounds the electrical connection to the coil of the secondary air injection (SAI) pump relay.
A 12V battery supply is fed to the inertia switch via fuse 13 in the engine compartment fusebox. When the inertia
switch contacts are closed, the feed passes through the switch and is connected to the coil of the Main relay. An earth
connection from the Main relay coil is connected to the ECM. When the ECM completes the earth path, the coil
energises and closes the contacts of the Main relay.
The Main and Secondary Air Injection (SAI) pump relays are located in the engine compartment fusebox. When the
contacts of the Main relay are closed, a 12V battery supply is fed to the coil of the SAI pump relay. An earth connection
from the coil of the SAI pump relay is connected to the ECM. When the ECM completes the earth path, the coil
energises and closes the contacts of the SAI pump relay to supply 12V to the SAI pump via fusible link 2 in the engine
compartment fusebox. The SAI pump starts to operate, and will continue to do so until the ECM switches off the earth
connection to the coil of the SAI pump relay.
The SAI pump remains operational for a period determined by the ECM and depends on the starting temperature of
the engine, or for a maximum operation period determined by the ECM if the target engine coolant temperature has
not been reached in the usual time.
When the contacts of the main relay are closed, a 12V battery supply is fed to the SAI solenoid valve via Fuse 2 in
the engine compartment fusebox.
The ECM grounds the electrical connection to the SAI vacuum solenoid valve at the same time as it switches on the
SAI pump motor. When the SAI vacuum solenoid valve is energised, a vacuum is provided to the operation control
ports on both of the vacuum operated SAI control valves at the exhaust manifolds. The control vacuum is sourced
from the intake manifold depression and routed to the SAI control valves via a vacuum reservoir and the SAI vacuum
solenoid valve.
The vacuum reservoir is included in the vacuum supply circuit to prevent vacuum fluctuations caused by changes in
the intake manifold depression affecting the operation of the SAI control valves.
When a vacuum is applied to the control ports of the SAI control valves, the valves open to allow pressurised air from
the SAI pump to pass through to the exhaust ports in the cylinder heads for combustion.
When the ECM has determined that the SAI pump has operated for the desired duration, it switches off the earth paths
to the SAI pump relay and the SAI vacuum solenoid valve. With the SAI vacuum solenoid valve de-energised, the
valve closes, cutting off the vacuum supply to the SAI control valves. The SAI control valves close immediately and
completely to prevent any further pressurised air from the SAI pump entering the exhaust manifolds.
The engine coolant temperature sensor incurs a time lag in respect of detecting a change in temperature and the SAI
pump automatically enters a 'soak period' between operations to prevent the SAI pump overheating. The ECM also
compares the switch off and start up temperatures, to determine whether it is necessary to operate the SAI pump.
This prevents the pump running repeatedly and overheating on repeat starts.
Other factors which may prevent or stop SAI pump operation include the prevailing engine speed / load conditions.
Page 403 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-10 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Mass Air Flow (MAF) sensor
The MAF sensor is located in the intake system between the air filter housing and the turbocharger. The ECM uses
the information generated by the MAF to control exhaust gas recirculation (EGR).
The MAF sensor works on the hot film principal. The MAF sensor has 2 sensing elements contained within a film. One
element is controlled at ambient temperature e.g. 25
°C (77 °F) while the other is heated to 200 °C (392 °F) above
this temperature e.g. 225
°C (437 °F). As air passes through the MAF sensor the hot film will be cooled. The current
required to keep the constant 200
°C (392 °F) difference provides a precise although non-linear signal of the air drawn
into the engine. The MAF sensor sends a voltage between 0 and 5 volts to the ECM proportional to the mass of the
incoming air. This calculation allows the ECM to set the EGR ratio for varying operating conditions.
Input/Output
The MAF sensor receives battery voltage from the main relay in the engine compartment fuse box. Signal output from
the MAF sensor to the ECM is a variable voltage proportional to air drawn into the engine.
Input to the MAF sensor is via pin 5 of connector C0570 at the engine compartment fuse box. This 12 volt supply is
provided by the main relay via fuse 2 in the engine compartment fuse box. The MAF sensor receives the input voltage
at pin 3 of the sensor connector.
Output from the MAF sensor is measured at pin 11 of the ECM connector C0158. The earth path is via pin 20 of the
ECM connector C0158.
The MAF sensor can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lContaminated sensor element.
lDamaged sensor element.
lDamaged in wiring harness.
lMAF supplies incorrect signal (due to air leak or air inlet restriction).
In the event of a MAF sensor signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lDuring driving engine speed may dip, before recovering.
lDifficult starting.
lEngine stalls after starting.
lDelayed throttle response.
lEGR inoperative.
lReduced engine performance.
lMAF signal out of parameters.
The MIL will not illuminate in a MAF sensor failure, and the ECM will use a fixed default value from its memory.
Page 409 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-16 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Crankshaft speed and Position (CKP) sensor
The CKP is located in the transmission housing with its tip adjacent to the outer circumference of the flywheel. The
CKP sensor works on the variable reluctance principle, which sends a signal back to the ECM in the form of an ac
voltage.
The ECM uses the signal from the CKP for the following functions:
lTo calculate engine speed.
lTo determine engine crank position.
lTo determine fuel injection timing.
The CKP sensor works as a Variable Reluctance Sensor (VRS). It uses an electromagnet and a target ring to generate
a signal. As the target ring passes the tip of the CKP sensor the magnetic field produced by the sensor is cut and then
re-instated. The ECM measures the signal as an ac voltage.
The outer circumference of the flywheel acts as the target ring for the sensor. The flywheel is divided into 36 segments
each of 10
°. 31 segments have drilled holes and 5 segments are spaces. This equals 360° or one engine revolution.
The 5 spaces correspond to the TDC position of the 5 cylinders, this allows the ECM to control fuel injection timing
for each of the cylinders.
Input/Output
The two pins on the sensor are both outputs. The ECM processes the outputs of the sensor. To protect the integrity
of the CKP signal an earth shield or screen is used.
The ECM measures the outputs from the CKP. The ECM measures the positive signal from the CKP at pin 13 of ECM
connector C0158. The ECM measures the negative signal from the CKP at pin 36 of ECM connector C0158. The earth
path is via pin 16 of ECM connector C0158.
Voltage generation from the CKP sensor is relative to engine speed. The values expected from a good CKP sensor
are as follows:
l2 to 3 volts with engine cranking.
lRising to 6 to 6.5 volts from 1000 rev/min upwards.
The above readings are dependent upon correct air gap between the tip of the CKP sensor and the passing teeth of
the reluctor ring.
Page 411 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-18 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
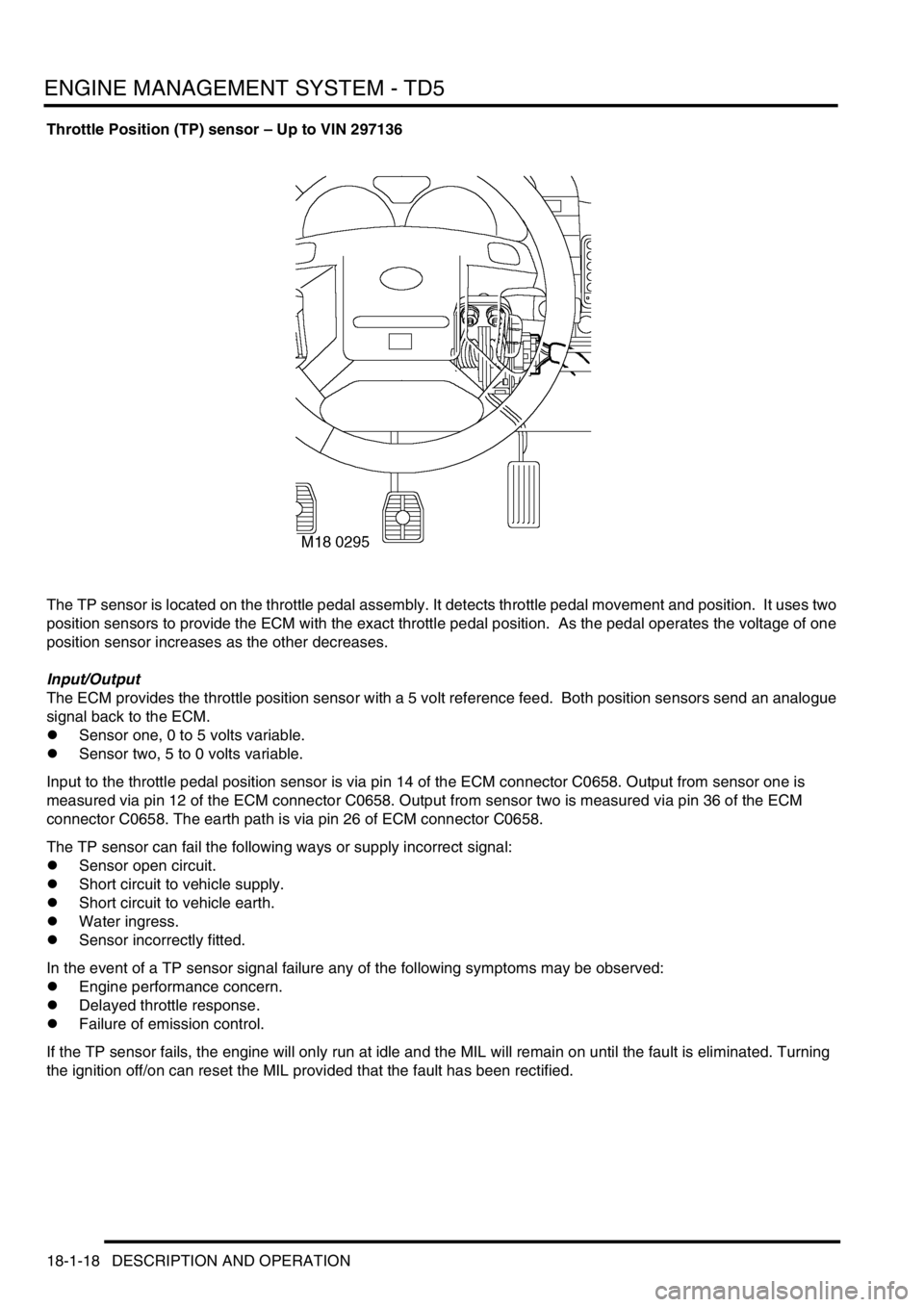
Throttle Position (TP) sensor – Up to VIN 297136
The TP sensor is located on the throttle pedal assembly. It detects throttle pedal movement and position. It uses two
position sensors to provide the ECM with the exact throttle pedal position. As the pedal operates the voltage of one
position sensor increases as the other decreases.
Input/Output
The ECM provides the throttle position sensor with a 5 volt reference feed. Both position sensors send an analogue
signal back to the ECM.
lSensor one, 0 to 5 volts variable.
lSensor two, 5 to 0 volts variable.
Input to the throttle pedal position sensor is via pin 14 of the ECM connector C0658. Output from sensor one is
measured via pin 12 of the ECM connector C0658. Output from sensor two is measured via pin 36 of the ECM
connector C0658. The earth path is via pin 26 of ECM connector C0658.
The TP sensor can fail the following ways or supply incorrect signal:
lSensor open circuit.
lShort circuit to vehicle supply.
lShort circuit to vehicle earth.
lWater ingress.
lSensor incorrectly fitted.
In the event of a TP sensor signal failure any of the following symptoms may be observed:
lEngine performance concern.
lDelayed throttle response.
lFailure of emission control.
If the TP sensor fails, the engine will only run at idle and the MIL will remain on until the fault is eliminated. Turning
the ignition off/on can reset the MIL provided that the fault has been rectified.
Page 415 of 1672
ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-22 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
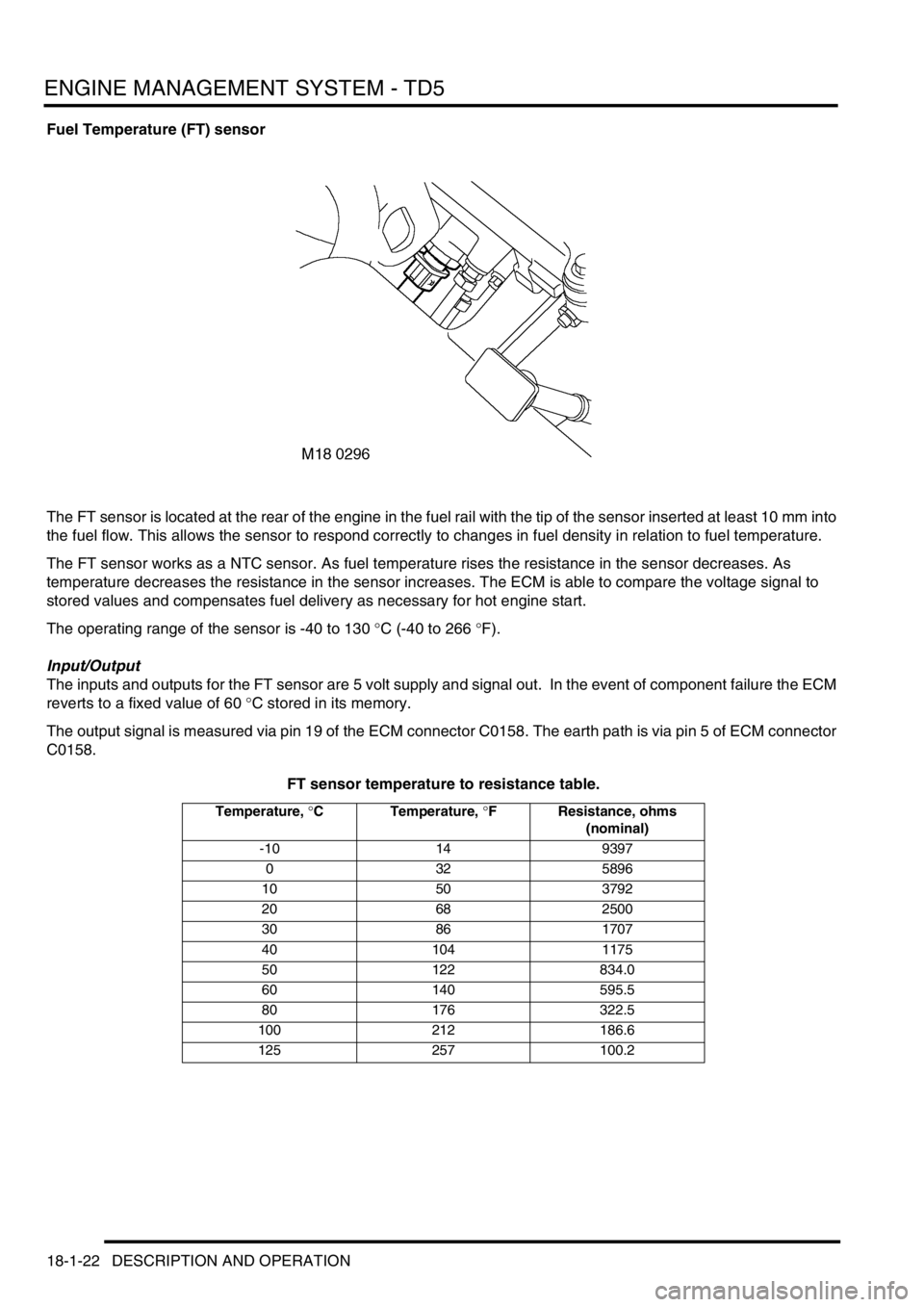
Fuel Temperature (FT) sensor
The FT sensor is located at the rear of the engine in the fuel rail with the tip of the sensor inserted at least 10 mm into
the fuel flow. This allows the sensor to respond correctly to changes in fuel density in relation to fuel temperature.
The FT sensor works as a NTC sensor. As fuel temperature rises the resistance in the sensor decreases. As
temperature decreases the resistance in the sensor increases. The ECM is able to compare the voltage signal to
stored values and compensates fuel delivery as necessary for hot engine start.
The operating range of the sensor is -40 to 130
°C (-40 to 266 °F).
Input/Output
The inputs and outputs for the FT sensor are 5 volt supply and signal out. In the event of component failure the ECM
reverts to a fixed value of 60
°C stored in its memory.
The output signal is measured via pin 19 of the ECM connector C0158. The earth path is via pin 5 of ECM connector
C0158.
FT sensor temperature to resistance table.
Temperature, °C Temperature, °F Resistance, ohms
(nominal)
-10 14 9397
0325896
10 50 3792
20 68 2500
30 86 1707
40 104 1175
50 122 834.0
60 140 595.5
80 176 322.5
100 212 186.6
125 257 100.2
Page 431 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-38 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Operation
Engine management
The ECM controls the operation of the engine using stored information within its memory. This guarantees optimum
performance from the engine in terms of torque delivery, fuel consumption and exhaust emissions in all operating
conditions, while still giving optimum driveability.
The ECM will receive information from its sensors under all operating conditions, especially during:
lCold starting.
lHot starting.
lIdle.
lWide open throttle.
lAcceleration.
lAdaptive strategy.
lBackup strategy for sensor failures.
The ECM receives information from various sensors to determine the current operating state of the engine. The ECM
then refers this information to stored values in its memory and makes any necessary changes to optimise air/fuel
mixture and fuel injection timing. The ECM controls the air/fuel mixture and fuel injection timing via the Electronic Unit
Injectors (EUI), by the length of time the EUI's are to inject fuel into the cylinder. This is a rolling process and is called
adaptive strategy. By using this adaptive strategy the ECM is able to control the engine to give optimum driveability
under all operating conditions.
During cold start conditions the ECM uses ECT information to allow more fuel to be injected into the cylinders, this
combined with the glow plug timing strategy supplied by the ECM facilitates good cold starting.
During hot start conditions the ECM uses ECT and FT information to implement the optimum fuelling strategy to
facilitate good hot starting.
During idle and wide open throttle conditions the ECM uses mapped information within its memory to respond to input
information from the throttle pedal position sensor to implement the optimum fuelling strategy to facilitate idle and wide
open throttle.
To achieve an adaptive strategy for acceleration the ECM uses input information from the CKP sensor, TP sensor,
ECT sensor, MAP/ IAT sensor, and the FT sensor. This is compared to mapped information within its memory to
implement the optimum fuelling strategy to facilitate acceleration.
Immobilisation system
When the starter switch is turned on, the BCU sends a unique security code to the ECM. The ECM must accept this
code before it will allow the engine to operate. If the ECM receives no security code or the ECM receives the incorrect
security code, then the ECM allows the engine to run for 0.5 seconds only. During this operation all other ECM
functions remain as normal.
The ECM operates immobilisation in three states:
l'New.'
l'Secure'.
l'No Code'.
When an ECM is unconfigured it will operate in the 'New' state. When an unconfigured ECM is installed the engine
can be started and operated once only, then the ECM has to be re-configured to either 'secure' or 'no code'
configuration depending on whether a security system is fitted to the vehicle. This is achieved by using TestBook.
Page 435 of 1672

ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM - TD5
18-1-42 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Cruise control resumption
Cruise control can be resumed at the previously set speed, provided the set speed has not been erased from the
ECM's memory as described above.
To resume cruise control operation to the previously set speed, depress the RES switch once when the following
conditions are met:
lA set speed is stored in the ECM.
lVehicle speed is above 22 mph (35 km/h).
lThe brake pedal is not pressed.
lThe clutch pedal is not pressed (manual transmission only).
lThe transmission is not in Park, Reverse or Neutral (automatic transmission only).
The ECM activates the cruise control system at the stored speed.
Accelerating while cruise control is active
There are three ways of increasing vehicle speed when cruise control is active:
lTemporarily increase vehicle speed (e.g. when overtaking another vehicle).
lIncrease vehicle set speed in 1 mph (1.5 km/h) increments.
lIncrease vehicle set speed.
To temporarily increase vehicle speed press the accelerator pedal until the desired speed is reached.
When the accelerator pedal is released, the vehicle coasts back to the set speed. When it reaches the set speed,
cruise control operation continues.
To increase the vehicle set speed in 1 mph (1.5 km/h) increments, tap the SET+ switch. Each tap on the switch
increases vehicle speed.
To increase the vehicle set speed, press and hold the SET+ switch until the desired set speed is reached.
Vehicle set speed will increase if the following conditions are met:
lThe vehicle is under cruise control operation.
lVehicle speed is above 22 mph (35 km/h).
lThe brake pedal is not pressed.
lThe clutch pedal is not pressed (manual transmission only).
lThe transmission is not in Park, Reverse or Neutral (automatic transmission only).
The vehicle responds as follows:
lIf the driver accelerates using the throttle pedal, the ECM increases vehicle speed using the TP sensor signal.
When the driver releases the accelerator pedal, the vehicle returns to the set speed.
lIf the SET+ switch is tapped the stored speed and vehicle speed increases by 1 mph (1.5 km/h) per tap on the
switch.
lIf the driver presses and holds the SET+ switch the vehicle speed will increase and will hold the speed when the
switch is released.
Switching off cruise control
Switching off cruise control allows the driver to regain control of vehicle speed, and erases the set road speed from
the ECM's memory.
To switch off cruise control, press the cruise control master switch to the off position.
When the cruise control master switch is switched off, the ECM deactivates cruise control and the driver regains
control of vehicle speed.