ECU LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 951 of 1672
FRONT SUSPENSION
60-12 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
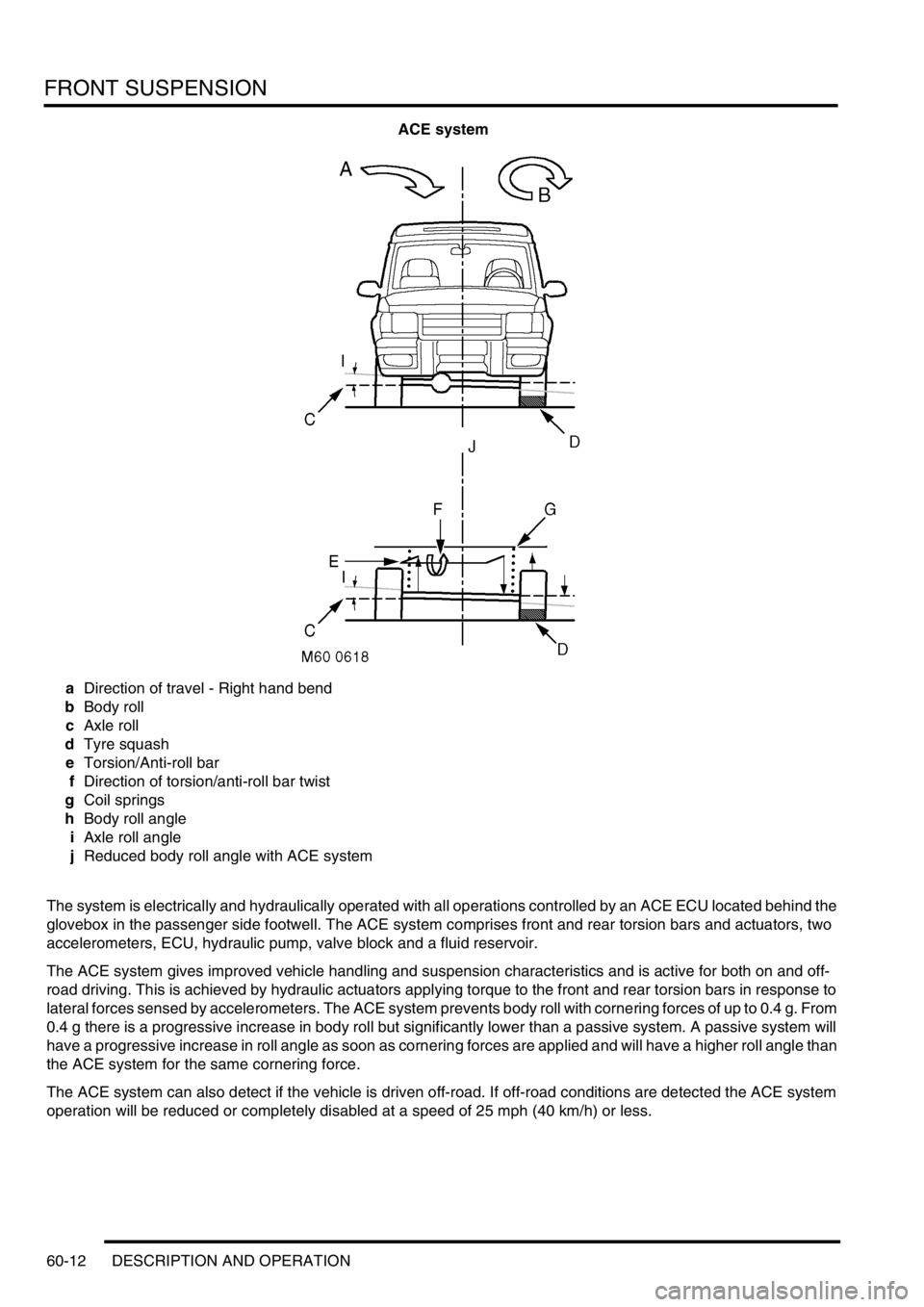
ACE system
aDirection of travel - Right hand bend
bBody roll
cAxle roll
dTyre squash
eTorsion/Anti-roll bar
fDirection of torsion/anti-roll bar twist
gCoil springs
hBody roll angle
iAxle roll angle
jReduced body roll angle with ACE system
The system is electrically and hydraulically operated with all operations controlled by an ACE ECU located behind the
glovebox in the passenger side footwell. The ACE system comprises front and rear torsion bars and actuators, two
accelerometers, ECU, hydraulic pump, valve block and a fluid reservoir.
The ACE system gives improved vehicle handling and suspension characteristics and is active for both on and off-
road driving. This is achieved by hydraulic actuators applying torque to the front and rear torsion bars in response to
lateral forces sensed by accelerometers. The ACE system prevents body roll with cornering forces of up to 0.4 g. From
0.4 g there is a progressive increase in body roll but significantly lower than a passive system. A passive system will
have a progressive increase in roll angle as soon as cornering forces are applied and will have a higher roll angle than
the ACE system for the same cornering force.
The ACE system can also detect if the vehicle is driven off-road. If off-road conditions are detected the ACE system
operation will be reduced or completely disabled at a speed of 25 mph (40 km/h) or less.
Page 952 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-13
Lateral acceleration of the body is sensed by two accelerometers and signals are transmitted to the ECU. The engine
driven hydraulic pump supplies a constant hydraulic flow to the valve block. Two directional control valves are
solenoid operated by the ECU and these supply fluid to the applicable side of each actuator to apply an equal and
opposite force to the torsion bar. In operation the ACE system maintains the attitude of the vehicle body when
cornering.
The ACE system uses a semi-synthetic hydraulic fluid which is the same as the fluid used for the PAS system. The
total capacity of the ACE system is 1.62 litres (0.42 US Gallons).
CAUTION: The ACE hydraulic system is extremely sensitive to the ingress of dirt or debris. The smallest
amount could render the system unserviceable. It is imperative that the following precautions are taken.
lACE components are thoroughly cleaned externally before work commences;
lall opened pipe and module ports are capped immediately;
lall fluid is stored in and administered through clean containers.
In the event of an ECU or hydraulic failure the system will fail safe to a 'locked bars' condition. The 'locked bars'
condition will allow the torsion bars to operate in a similar manner as conventional 'passive' anti-roll bars. Prolonged
cornering forces will allow a progressive increase in roll angle due to hydraulic leakage through the actuators and
valve block. Failures will be relayed to the driver by the illumination of the ACE warning lamp in the instrument pack.
Faults are recorded by the ECU and can be retrieved using TestBook.
When the ignition switch is moved to position II, the warning lamp will illuminate for two seconds to check functionality.
The warning lamp functionality can also be checked using TestBook.
TestBook must also be used to perform a bleeding procedure after maintenance operations have been performed to
ensure that complete system bleeding is performed. Trapped air in the system can seriously reduce the system
performance.
Fluid reservoir
The moulded plastic fluid reservoir is mounted on the left hand side of the engine compartment on a bracket which is
attached to the inner wing. The reservoir is dual purpose, being divided into two separate chambers; one for the ACE
system and one for the PAS system. Each chamber has its own filler neck and cap and is identified by moulded
lettering on the reservoir adjacent to each filler.
A non-serviceable filter assembly is fitted in the base of each chamber. The filter is made from fine stainless steel
mesh which is moulded into the body of the reservoir. The filter removes particulate matter from the fluid before it is
drawn into the hydraulic pump.
Upper and lower fluid level marks are moulded onto the reservoir body. The capacity of the ACE reservoir chamber
to the upper level mark is 0.5 litre (0.13 US Gallon).
Page 956 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-17
The valve block directs hydraulic pressure to the actuators via solenoid operated directional control valves. A solenoid
operated pressure control valve regulates the required pressure to the actuators. The three valve solenoids are
controlled by signals received from the ACE ECU. A pressure transducer monitors the pressure delivered by the
pump. A replacable high pressure filter is installed into the lower face of the valve block and filters fluid before it
reaches the valves.
The valve block is located on the outside of the right hand chassis longitudinal. The valve block is secured to the
chassis with three bolts and rubber bushes. The rubber bushes isolate the valve block from the chassis, preventing
hydraulic noise from the valve block transmitting through the chassis and body.
The two solenoid operated directional control valves (DCV's) are fitted to ports in the top face of the valve block. The
DCV's are screwed into the valve block and sealed with O ring seals. Each DCV has a solenoid for electrical operation
of the valve. The solenoid is sealed to the DCV with two O ring and secured with a cap. The cap, coil and O rings are
serviceable items. The DCV's are non-serviceable and failure of a DCV requires the replacement of the valve block
assembly.
The pressure control valve is fitted to a port in the rear face of the valve block. The pressure control valve is screwed
into the valve block and sealed with O rings. The pressure control valve has a coil for electrical operation. The coil is
sealed to the pressure control valve with two O rings and secured with a cap. The cap, coil and O rings are serviceable
items. The pressure control valve is non-serviceable and failure requires replacement of the valve block assembly.
The pressure transducer is fitted to a port in the forward face of the valve block. The pressure transducer is screwed
into the valve block and sealed with an O ring seal. The pressure transducer is a serviceable item.
The high pressure filter locates in a port on the lower face of the valve block. The gauze and fibre filter is sealed in
the port with O ring seals. A threaded cap secures the filter in the valve block and is also sealed with an O ring seal.
A threaded hole on the lower face of the filter allows a bolt to be fitted to remove the filter from the port. If a system
component is replaced, the filter must be changed.
Four ports are located on the forward face of the valve block and two ports on the rear. Each port is fitted with a seal
pack which contains two O ring seals and backing rings. The ACE pipes locate and seal in the seal packs and are
secured to the valve block with the studs and nuts located on the forward and rear faces.
Actuators
Two actuators are used for the ACE system and are attached to the front and rear torsion bars. The actuators apply
hydraulically generated force to the torsion bar to oppose lateral forces caused by the vehicle cornering.
Each actuator is a conventional double-acting cylinder. A piston is attached to a rod and moves within the cylinder
when hydraulic pressure is applied. The rod is sealed at the point where it exits the cylinder. The outer end of the rod
is threaded and locates in a bush in the ACE long arm and secured with a nut. A rubber gaiter covers the rod and
prevents dirt and moisture from damaging the rod surface and cylinder seals. The cylinder has a forked attachment
which locates on the short arm bush and secured with a bolt and nut.
Two banjo connections provide for the attachment of the hydraulic hoses from the ACE valve block. The connections
provide hydraulic flow to each side of the piston to extend or retract the rod.
Page 958 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-19
The right hand end of the torsion bar has a machined spigot which provides for the attachment of the forged steel
short and long arms. The spigot for the short arm is splined and mates with splines in the short arm. The short arm is
located in a specific position on the splines and clamped to the spigot with a Torx bolt and locknut. The short arm is
not a serviceable item other than the actuator attachment bush. The smaller spigot diameter locates the long arm.
The long arm is fitted with a slipper bush which is located on the spigot and secured with a large washer and a special
bolt. The slipper bush comprises two inner and two outer bushes which are installed from each side of the long arm.
The outer bushes have three lugs which locate in the long arm to prevent the bush from rotating. The long arm also
provides the attachment point for the actuator piston rod and the anti-roll bar link.
The actuator has a forked end which locates on the bush in the short arm and is secured with a bolt and nut. The
piston rod of the actuator locates through a hole in a cast boss on the long arm which is fitted with a special bush. A
shoulder on the piston rod seats in a hole in the bush and a locknut on the end of the piston rod secures the rod to
the long arm and bush.
The front torsion bar is attached to the front chassis cross member. Two rubber bushes are fitted to the torsion bar
and are located in clamp plates. The clamp plates are located in slots in the cross member and secured with bolts.
The rear torsion bar is attached to the tubular cross member at the rear section of the chassis. Two rubber bushes
are fitted to the torsion bar and are located in clamp plates. The clamp plates are located in fabricated brackets
attached to the tubular cross-member and secured with bolts.
Two anti-roll bar links are mounted on brackets on the front and rear axles. Each anti-roll bar link is fitted with a
spherical bearing at each end. One bearing is attached to the link at a 90
° angle. The threaded shank of the bearing
is located through a hole in a bracket on the axle and secured with a locknut; a washer is installed on the threaded
shank between the bearing and the bracket. The second spherical bearing is attached in-line with the link and locates
in the torsion bar on the left hand side and the long arm on the right hand side. The front anti-roll bar links are longer
than the rear links and are not interchangeable.
Accelerometers
Two accelerometers are used for the ACE system. The upper accelerometer is mounted on a bracket, behind the
headlining adjacent to the rear view mirror and the sunroof ECU. The lower accelerometer is located on a bracket on
the inner sill panel under the RH front floor.
The lower accelerometer is the primary sensor used to measure lateral acceleration of the vehicle for roll control. The
upper accelerometer is used by the ECU for roll correction and fault detection in conjunction with the lower
accelerometer.
Each accelerometer is a solid state capacitive acceleration sensor and operates on a 5 V supply from the ECU. The
upper and lower sensors can measure acceleration in the range of
± 1.10 g and return an output to the ECU of
between 0.5 and 4.5 V.
Failures of an accelerometer are recorded by the ECU and can be retrieved using TestBook. A special tool is required
to remove and replace a sensor in the bracket.
Page 959 of 1672
FRONT SUSPENSION
60-20 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
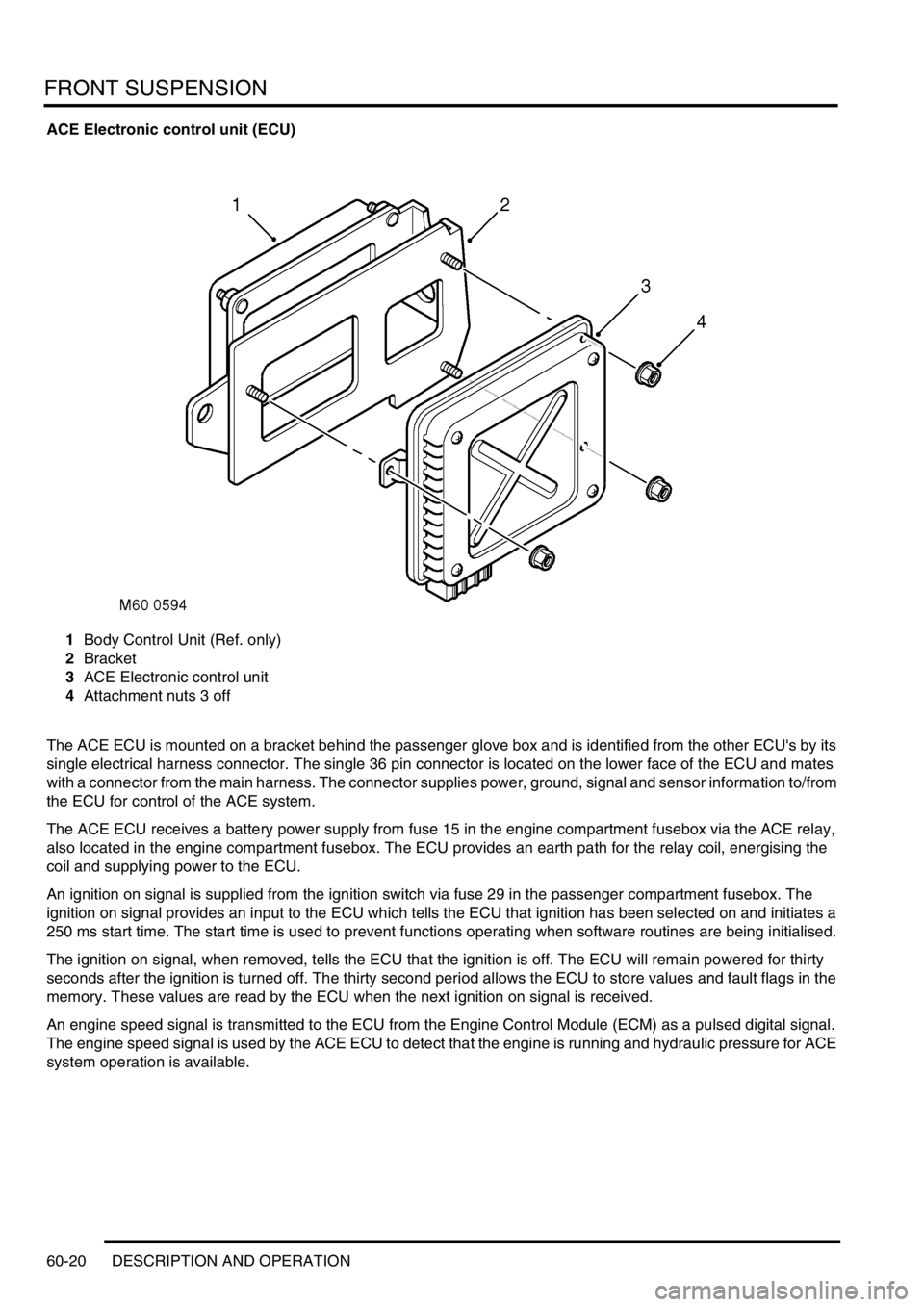
ACE Electronic control unit (ECU)
1Body Control Unit (Ref. only)
2Bracket
3ACE Electronic control unit
4Attachment nuts 3 off
The ACE ECU is mounted on a bracket behind the passenger glove box and is identified from the other ECU's by its
single electrical harness connector. The single 36 pin connector is located on the lower face of the ECU and mates
with a connector from the main harness. The connector supplies power, ground, signal and sensor information to/from
the ECU for control of the ACE system.
The ACE ECU receives a battery power supply from fuse 15 in the engine compartment fusebox via the ACE relay,
also located in the engine compartment fusebox. The ECU provides an earth path for the relay coil, energising the
coil and supplying power to the ECU.
An ignition on signal is supplied from the ignition switch via fuse 29 in the passenger compartment fusebox. The
ignition on signal provides an input to the ECU which tells the ECU that ignition has been selected on and initiates a
250 ms start time. The start time is used to prevent functions operating when software routines are being initialised.
The ignition on signal, when removed, tells the ECU that the ignition is off. The ECU will remain powered for thirty
seconds after the ignition is turned off. The thirty second period allows the ECU to store values and fault flags in the
memory. These values are read by the ECU when the next ignition on signal is received.
An engine speed signal is transmitted to the ECU from the Engine Control Module (ECM) as a pulsed digital signal.
The engine speed signal is used by the ACE ECU to detect that the engine is running and hydraulic pressure for ACE
system operation is available.
Page 960 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-21
A road speed signal is transmitted to the ACE ECU as a pulsed digital signal from the Self-levelling/Anti-lock Braking
System (SLABS) ECU. The road speed signal is used by the ACE ECU for on and off-road roll compensation.
When reverse gear is selected, an input is received from the reverse lamp switch. When the ACE ECU detects that
reverse gear has been selected, the ACE system reverts to a 'locked bars' condition until reverse gear is disengaged.
The diagnostic connection allows diagnostic interrogation of the ACE ECU. The diagnostic socket allows diagnostic
equipment to be connected to interrogate the ACE ECU for fault codes.
When system faults are detected by the ECU, the ACE warning lamp in the instrument pack is illuminated by the ECU
continuously in amber for minor faults or flashing red with an audible warning for faults which require the driver to stop
the vehicle immediately.
The ACE ECU supplies a control current to the pressure control valve in the valve block. The current supplied by the
ECU is determined by a number of input signals from the upper and lower accelerometers, road speed etc.. The
pressure control valve controls the hydraulic pressure supplied to the actuators proportional to the current supplied
by the ECU.
Power is supplied to the two solenoid operated directional control valves (DCV's) in the valve block by the ECU.
Together, the DCV's control the direction of flow of hydraulic fluid to the actuators. When the ECU supplies power to
the solenoids the valves open allowing hydraulic fluid to flow to the actuators. When power is removed the valves
close.
The pressure transducer in the valve block receives a 5 V supply from the ECU. The pressure transducer measures
hydraulic pressures in the range of 0 to 180 bar (0 to 2610 lbf.in
2) and returns a linear output voltage to the ECU
dependent on hydraulic pressure.
The ECU supplies a 5 V current to each of the accelerometers. Each accelerometer is capable of measuring lateral
acceleration in the range of
± 1.10 g. An analogue input to the ECU of between 0.5 and 4.5 V relative to the lateral
acceleration sensed is returned by each accelerometer. The ECU processes the two signals received to produce a
'pure' lateral acceleration signal which is then used as the main control signal for the ACE system.
ACE ECU connector pin details
Pin No. Description Input/Output
1 Not used -
2 Not used -
3SpareInput
4 Not used -
5 Road speed Input
6 ARC relay Output
7 to 9 Not used -
10 K line (diagnostics) -
11 Ignition switch Input
12 Accelerometer - lower (supply) Output
13 Pressure transducer (supply) Output
Page 961 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
60-22 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Failure modes
Failures where the vehicle can still be driven safely are indicated by the ACE warning lamp illuminating continuously
with an amber colour. The amber warning lamp will remain illuminated until the ignition is turned off. For all faults the
warning lamp will only illuminate again if the fault is still present. Failures which require the driver to stop the vehicle
immediately are indicated by the ACE warning lamp flashing with a red colour and an audible warning. All faults are
recorded by the ACE ECU and can be retrieved with diagnostic equipment.
The following tables show the type of system failures and their effects on the system operation. Torsion bar 'floppy'
means that fluid is allowed to circulate freely through the system. With no pressure in the actuators the torsion bar will
have no effect on vehicle roll. 'Locked bars' means that all pump flow is directed through the valve block and returns
to the reservoir. Both DCV's close and fluid is trapped in the actuators but can flow from one actuator to the other via
the valve block. In this condition the torsion bar will perform similar to a conventional anti-roll bar, resisting roll but still
allowing the axles to articulate.
Acceleration sensors
Pressure transducer
14 Reverse switch Input
15 Accelerometer - lower (signal) Input
16 Pressure transducer (signal) Input
17 Accelerometer - upper (signal) Input
18 Accelerometer - upper (supply) Output
19 Engine speed Input
20 Main earth 1 -
21 Pressure transducer (earth) Input
22 DCV 2 (earth) Input
23 DCV 1 (earth) Input
24 DCV 1 & 2 (supply) Output
25 Pressure control valve (earth) Input
26 Not used -
27 Pressure control valve (supply) Output
28 Main supply (+ V Batt) Input
29 to 31 Not used -
32 Main earth 2 -
33 Accelerometer - lower (signal) Input
34 Accelerometer - upper (signal) Input
35 Not used -
36 Warning lamp Output
Failure Effect
Valve stuck closed No ACE control
Short circuit - Ground No ACE control
Short circuit - VBatt No ACE control
Loose sensor Erractic ACE activity when driving in straight line
Failure Effect
Short circuit - VBatt Large sensor dead band - possible random movementsPin No. Description Input/Output
Page 962 of 1672
FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-23
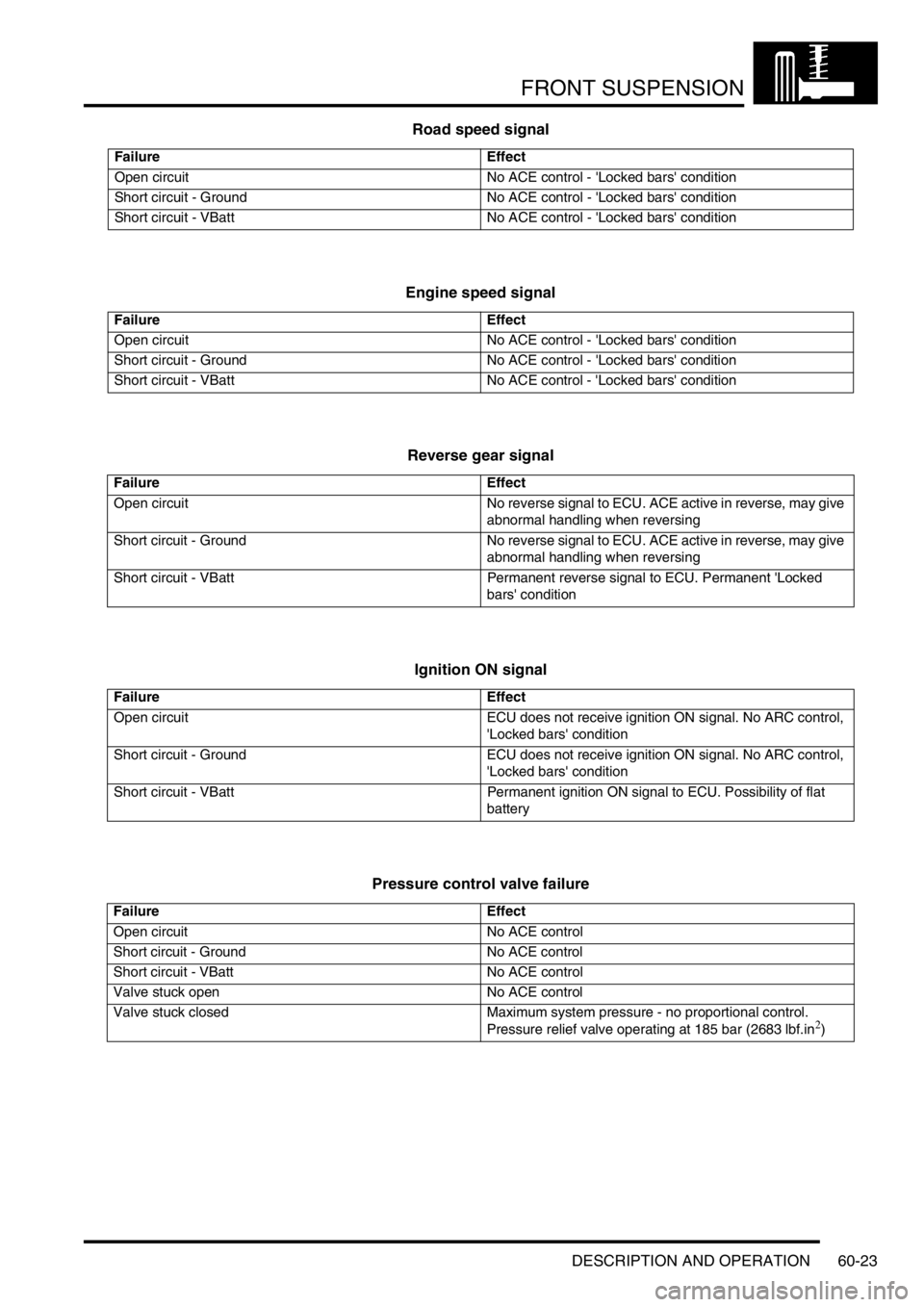
Road speed signal
Engine speed signal
Reverse gear signal
Ignition ON signal
Pressure control valve failure
Failure Effect
Open circuit No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - Ground No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - VBatt No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Failure Effect
Open circuit No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - Ground No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - VBatt No ACE control - 'Locked bars' condition
Failure Effect
Open circuit No reverse signal to ECU. ACE active in reverse, may give
abnormal handling when reversing
Short circuit - Ground No reverse signal to ECU. ACE active in reverse, may give
abnormal handling when reversing
Short circuit - VBatt Permanent reverse signal to ECU. Permanent 'Locked
bars' condition
Failure Effect
Open circuit ECU does not receive ignition ON signal. No ARC control,
'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - Ground ECU does not receive ignition ON signal. No ARC control,
'Locked bars' condition
Short circuit - VBatt Permanent ignition ON signal to ECU. Possibility of flat
battery
Failure Effect
Open circuit No ACE control
Short circuit - Ground No ACE control
Short circuit - VBatt No ACE control
Valve stuck open No ACE control
Valve stuck closed Maximum system pressure - no proportional control.
Pressure relief valve operating at 185 bar (2683 lbf.in
2)
Page 964 of 1672
FRONT SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 60-25
Operation
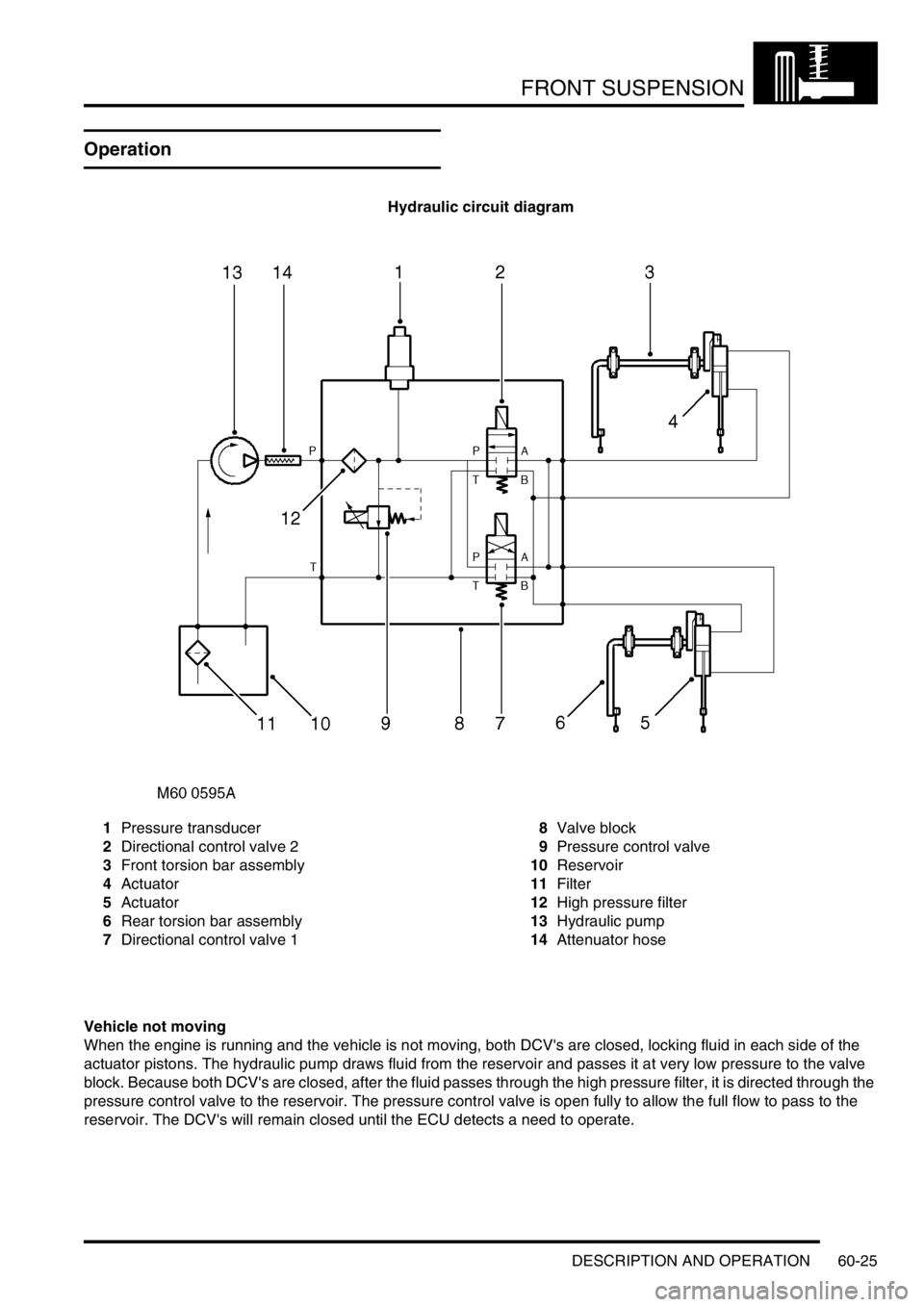
Hydraulic circuit diagram
1Pressure transducer
2Directional control valve 2
3Front torsion bar assembly
4Actuator
5Actuator
6Rear torsion bar assembly
7Directional control valve 18Valve block
9Pressure control valve
10Reservoir
11Filter
12High pressure filter
13Hydraulic pump
14Attenuator hose
Vehicle not moving
When the engine is running and the vehicle is not moving, both DCV's are closed, locking fluid in each side of the
actuator pistons. The hydraulic pump draws fluid from the reservoir and passes it at very low pressure to the valve
block. Because both DCV's are closed, after the fluid passes through the high pressure filter, it is directed through the
pressure control valve to the reservoir. The pressure control valve is open fully to allow the full flow to pass to the
reservoir. The DCV's will remain closed until the ECU detects a need to operate.
Page 965 of 1672

FRONT SUSPENSION
60-26 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Vehicle moving and turning left
When the vehicle is turning left, the accelerometers detect the cornering forces applied and transmit signals to the
ECU. The ECU determines that an opposing force must be applied to the torsion bars to counter the cornering forces.
The ECU supplies a current to the solenoid of the DCV2. Simultaneously, a current is sent from the ECU to the
pressure control valve which operates to restrict the flow of fluid returning to the reservoir.
The restriction causes the hydraulic pressure in the system to rise and the pressure is sensed by the pressure
transducer which sends a signal to the ECU. The ECU determines from the inputs it receives what pressure is required
and adjusts the pressure control valve accordingly.
The pressure in the system is applied to the annulus of each actuator, applying an opposing force to the torsion bar
and minimising the cornering effect on the vehicle and maintaining the vehicle attitude. The fluid displaced from the
full area of the actuator is returned to the reservoir via the valve block.
As the cornering force is removed when the vehicle straightens up, the ECU opens the pressure control valve to
reduce the pressure in the system. The fluid bleeds from the actuator back into the system as the cornering force is
reduced, removing the force from the torsion bar. When the vehicle is moving in a straight line DCV 2 closes.
Vehicle moving and turning right
When the vehicle is turning right, the accelerometers detect the cornering forces applied and transmit signals to the
ECU. The ECU determines that an opposing force must be applied to the torsion bars to counter the cornering forces.
The ECU supplies a current to the solenoid of the DCV1. Simultaneously, a current is sent from the ECU to the
pressure control valve which operates to restrict the flow of fluid through the by-pass gallery.
The restriction causes the hydraulic pressure in the system to rise and the pressure is sensed by the pressure
transducer which sends a signal corresponding to the pressure to the ECU. The ECU determines from the inputs it
receives what pressure is required and adjusts the pressure control valve accordingly.
The pressure in the system is applied to the full area of each actuator, applying an opposing force to the torsion bar
and minimising the cornering effect on the vehicle and maintaining the vehicle attitude. The fluid displaced from the
annulus of the actuator is returned to the reservoir via the valve block.
As the cornering force is removed when the vehicle straightens up, the ECU opens the pressure control valve to
reduce the pressure in the system. The fluid bleeds from the actuator back into the system as the cornering force is
reduced, removing the force from the torsion bar. When the vehicle is moving in a straight line the DCV 1 closes.
Vehicle moving in a straight line
The ECU is constantly monitoring the signals received from the accelerometers and operates the DCV's and pressure
control valve to maintain the vehicle attitude when the vehicle is moving.
Off-road driving
Off-road detection is achieved by the ECU by monitoring the signals from the upper and lower accelerometers for
varying degrees of body movement. Off-road driving generates differing signals to the accelerometers which in turn
produce differing outputs due to their vertical separation and the location of the roll centre of the vehicle. The two
signals are passed through a filter to remove any offset caused by the vehicle leaning or the terrain. The ECU then
uses this signal to calculate the percentage of road roughness.
Below 25 mph (40 km/h) the percentage of road roughness calculated is used by the ECU to limit the operation of the
ACE system. The system is completely inoperative at speeds below 2 mph (3 km/h). At speeds above 25 mph (40
km/h) the system disables the percentage road roughness signal and full ACE system assistance is restored.
Side slope detection
The ECU uses side slope detection when the upper and lower accelerometers detect an average acceleration of more
than
± 0.2 g and a road speed of less than 25 mph (40 km/h).
When side slope is detected both DCV's close to provide a 'locked bars' condition. This condition increases stability
and gives a consistent vehicle response. As the road speed increases up to 25 mph (40 km/h), the level of average
lateral acceleration must also increase and be maintained for the system to recognise that the vehicle is on a side
slope. If the side slope angle is steep and the road speed is low, the ECU will detect the side slope in a short time.