ABS LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: LAND ROVER, Model Year: 2002, Model line: DISCOVERY, Model: LAND ROVER DISCOVERY 2002Pages: 1672, PDF Size: 46.1 MB
Page 617 of 1672

COOLING SYSTEM - V8
26-2-16 REPAIRS
8.Remove 6 scrivets and remove LH and RH air
deflectors from front panel. Disconnect
multiplug of gearbox oil temperature sensor
(arrowed).
9.Remove nut and move horn aside. 10.Remove 2 bolts securing radiator LH and RH
upper mounting brackets to body panel and
remove brackets.
11.Remove 4 screws securing air conditioning
condenser LH and RH upper mounting
brackets to condenser.
12.Remove brackets with rubber mounts from
radiator extension brackets.
13.Position absorbent cloth under each cooler
hose to collect oil spillage.
14.Push against coupling release rings and
disconnect hoses from gearbox oil cooler.
CAUTION: Always fit plugs to open
connections to prevent contamination.
15. If fitted: Push against coupling release rings
and disconnect hoses from engine oil cooler.
Page 625 of 1672

MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS - TD5
30-1-4 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Front pipe assembly
The front pipe is of welded and fabricated tubular construction. The front pipe is connected to a flange on the
turbocharger and secured with three flanged nuts and sealed with a metal laminated gasket. The front pipe
incorporates a flexible pipe near the connection with the turbocharger and terminates in a flanged connection with the
intermediate pipe.
The flexible pipe is formed into a concertina shape with woven metal strands around its outer diameter. The flexible
pipe allows for ease of exhaust system alignment and also absorbs engine vibration. The woven metal strands also
increase the longevity of the flexible pipe.
The front pipe is attached via a bracket and a mounting rubber to the chassis. The mounting rubber allows ease of
alignment and vibration absorption.
Intermediate pipe and silencer
The intermediate pipe is of welded and fabricated tubular construction. It connects at its forward end to the front pipe
flange. Two captive studs on the intermediate pipe flange allow for attachment to the front pipe with locknuts. The rear
section of intermediate pipe connects to the tail pipe assembly via a flanged joint, sealed with a metal gasket and
secured with locknuts and studs.
The forward and rear sections are joined by a silencer. The silencer is fabricated from stainless steel sheet to form
the body of the silencer. An end plate closes each end of the silencer and is attached to the body with seam joints.
Perforated baffle tubes, inside the silencer, are connected to the inlet and outlet pipes on each end plate. Internal
baffle plates support the baffle tubes and, together with a stainless steel fibre packing, absorb combustion noise as
the exhaust gases pass through the silencer.
The intermediate pipe is attached by two brackets, positioned at each end of the silencer, and two mounting rubbers
to the chassis. The mounting rubber allows for ease of alignment and vibration absorption.
Tail pipe assembly
The tail pipe is of welded and fabricated construction. The tail pipe connects to the intermediate pipe with a flanged
joint secured with locknuts and sealed with a metal gasket. The pipe is shaped to locate above the rear axle allowing
clearance for axle articulation. The pipe is also curved to clear the left hand side of the fuel tank which has a reflective
shield to protect the tank from heat generated from the pipe.
A fabricated silencer is located at the rear of the tail pipe. The silencer is circular in section and is constructed from
stainless steel sheet. A baffle tube is located inside the silencer and the space around the baffle tube is packed with
a stainless steel fibre. The holes in the baffle tube allow the packing to further reduce combustion noise from the
engine. The tail pipe from the silencer is curved downwards at the rear of the vehicle and directs exhaust gases
towards the ground. The curved pipe allows the exhaust gases to be dissipated by the airflow under the vehicle and
prevents the gases from being drawn behind the vehicle.
The tail pipe is attached by a bracket, positioned forward of the silencer, and a mounting rubber to the chassis. The
mounting rubber allows ease of alignment and vibration absorption.
Page 635 of 1672

MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS - V8
30-2-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Inlet plenum
The plenum is mounted transversely on the front of the upper manifold. The plenum divides into two galleries which
connect with the galleries on the upper manifold. The plenum is secured to the upper manifold with four bolts and
sealed with a coated metal gasket.
The plenum provides attachment for the throttle housing, which is secured with four bolts and sealed with a coated
metal gasket. The plenum also has vacuum connections for brake servo, rocker cover breather and fuel vapour from
the charcoal canister. A port on the top of the plenum connects via a hose to the IAC valve.
Exhaust manifolds
Two handed, cast iron exhaust manifolds are used on the V8 engine. Each manifold has four ports which merge into
one flanged outlet positioned centrally on the manifold.
Each manifold is attached to its cylinder head with eight Torx bolts. Each bolt is fitted with a 'cotton reel' shaped spacer
which allows for a longer bolt resulting in increased torque loading on each bolt. Two laminated metal gaskets seal
each manifold to its cylinder head. The flanged outlet on each manifold provides the attachment for the front pipe of
the exhaust system.
Exhaust system
The exhaust system comprises a front pipe assembly with two front pipes each incorporating a catalytic converter, an
intermediate pipe incorporating a silencer and a tail pipe assembly which also has a silencer. The exhaust system is
constructed mainly of 63 mm (2.48 in) diameter extruded pipe with a 1.5 mm (0.06 in) wall thickness. All pipes are
aluminized to resist corrosion and the silencers are fabricated from stainless steel sheet.
Front pipe assembly
The front pipe assembly is of welded and fabricated construction. A front pipe from each exhaust manifold merges
into one flanged connection. Two captive studs on the flange provide attachment to the intermediate pipe with
locknuts. Each front pipe has a welded flange which is attached to each manifold and secured with three studs and
flanged nuts and sealed with a metal laminated gasket. The gasket comprises a heat resistant fibre between two thin
metallic layers to enhance the sealing properties of the gasket.
A catalytic converter is located in each front pipe. The catalytic converters are different shapes to allow clearance
between the body and transmission. Both catalytic converters are of similar internal construction.
+ EMISSION CONTROL - V8, DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION, Emission Control Systems.
CAUTION: Ensure the exhaust system is free from leaks. Exhaust gas leaks upstream of the catalytic
converter could cause internal damage to the catalytic converter.
From the catalytic converters, the front pipes merge into one pipe which terminates at a flanged joint. The flange
connects with the intermediate pipe, sealed with an olive and secured with studs and locknuts.
Intermediate pipe and silencer
The intermediate pipe is of welded and fabricated tubular construction. It connects at its forward end with a flange on
the front pipe assembly and is secured with locknuts to captive studs in the front pipe assembly flange. The rear
section of the intermediate pipe connects to the tail pipe assembly via a flanged joint, sealed with a metal gasket and
secured with locknuts and studs.
The forward and rear sections are joined by a silencer. The silencer is fabricated from stainless steel sheet to form
the body of the silencer. An end plate closes each end of the silencer and is attached to the body with seam joints.
Perforated baffle tubes inside the silencer are connected to the inlet and outlet pipes on each end plate. Internal baffle
plates support the baffle tubes and together with a stainless steel fibre absorb combustion noise as the exhaust gases
pass through the silencer.
The intermediate pipe is attached by two brackets, positioned at each end of the silencer, and mounting rubbers to
the chassis. The mounting rubbers allow ease of alignment and vibration absorption. The two mounting rubbers are
fitted with removable heat deflectors to prevent heat from the silencer damaging the material.
Page 636 of 1672

MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS - V8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 30-2-7
Tail pipe assembly
The tail pipe is of welded and fabricated construction. It connects to the intermediate pipe with a flanged joint secured
with studs and locknuts and sealed with a metal gasket. The pipe is shaped to locate above the rear axle allowing
clearance for axle articulation. The pipe is also curved to clear the left hand side of the fuel tank which has a reflective
shield to protect the tank from heat generated from the pipe.
A fabricated silencer is located at the rear of the tail pipe. The silencer is circular in section and is constructed from
stainless steel sheet. A baffle tube is located inside the silencer and the space around the baffle tube is packed with
a stainless steel fibre. The holes in the baffle tube allow the packing to further reduce combustion noise from the
engine. The tail pipe from the silencer is curved downwards at the rear of the vehicle and directs exhaust gases
towards the ground. The curved pipe allows the exhaust gases to be dissipated by the airflow under the vehicle and
prevents gases being drawn behind the vehicle.
The tail pipe is attached by a bracket, positioned forward of the silencer, and a mounting rubber to the chassis. The
mounting rubber allows ease of alignment and vibration absorption.
Page 643 of 1672
MANIFOLDS AND EXHAUST SYSTEMS - V8
30-2-14 REPAIRS
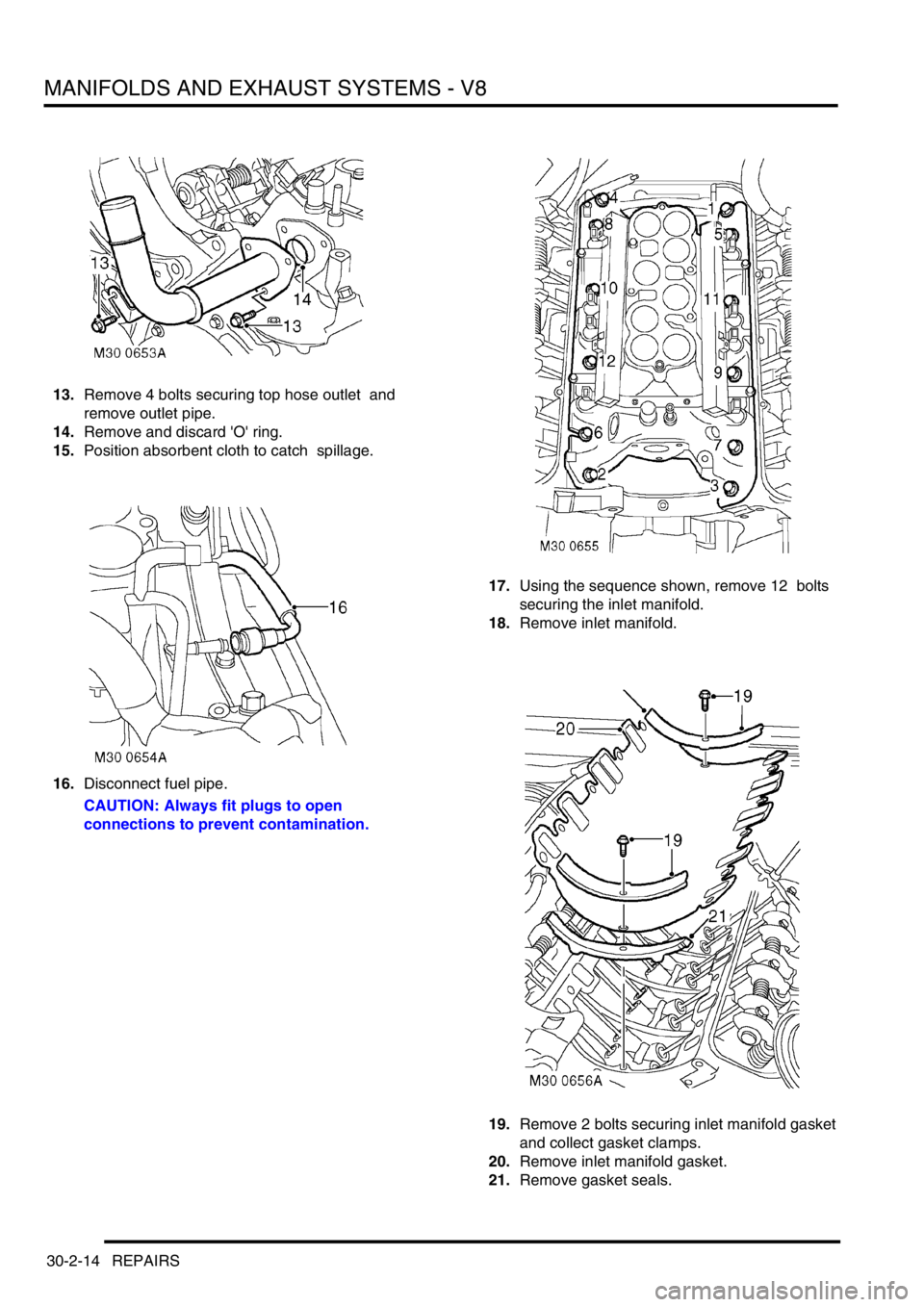
13.Remove 4 bolts securing top hose outlet and
remove outlet pipe.
14.Remove and discard 'O' ring.
15.Position absorbent cloth to catch spillage.
16.Disconnect fuel pipe.
CAUTION: Always fit plugs to open
connections to prevent contamination.17.Using the sequence shown, remove 12 bolts
securing the inlet manifold.
18.Remove inlet manifold.
19.Remove 2 bolts securing inlet manifold gasket
and collect gasket clamps.
20.Remove inlet manifold gasket.
21.Remove gasket seals.
Page 657 of 1672

CLUTCH - TD5
33-1-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
The clutch system is a diaphragm type clutch operated by a hydraulic cylinder. The drive plate is of the rigid centre
type with no integral damping springs. The flywheel is of the dual mass type with damping springs integral with the
flywheel. The clutch requires no adjustment to compensate for wear.
Hydraulic clutch
The hydraulic clutch comprises a master cylinder, slave cylinder and a hydraulic reservoir. The master and slave
cylinders are connected to each other hydraulically by plastic and metal pipes. The plastic section of the pipe allows
ease of pipe routing and also absorbs engine movements and vibrations.
The master cylinder comprises a body with a central bore. Two ports in the body connect the bore to the hydraulic
feed pipe to the slave cylinder and the fluid reservoir. The bore is also connected to a damper which prevents engine
pulses being transferred hydraulically to the clutch pedal. A piston is fitted in the bore and has an external rod which
is attached to the clutch pedal with a pin. Two coil springs on the clutch pedal reduce the effort required to depress
the pedal.
The master cylinder is mounted on the bulkhead and secured with two bolts. The cylinder is connected to the shared
brake/clutch reservoir on the brake servo by a braided connecting hose.
The slave cylinder is located on the left hand side of the gearbox housing and secured with two bolts. A heat shield
is fitted to protect the underside of the slave cylinder from heat generated from the exhaust system. The slave cylinder
comprises a cylinder with a piston and a rod. A port in the cylinder body provides the attachment for the hydraulic feed
pipe from the master cylinder. A second port is fitted witha bleed nipple used for removing air from the hydraulic
system after servicing. The piston rod locates on a clutch release lever located in the gearbox housing. The rod is
positively retained on the release lever with a clip.
Clutch mechanism
The clutch mechanism comprises a flywheel, drive plate, pressure plate, release lever and a release bearing. The
clutch mechanism is fully enclosed at the rear of the engine by the gearbox housing.
A clutch release bearing sleeve is attached in the gearbox housing with two bolts and located on two dowels. A spigot
with a ball end is formed on the release bearing sleeve and provides amounting and pivot point for the clutch release
lever. A dished pivot washer is located on the ball of the spigot. When the release lever is located on the ball, the pivot
washer seats against the rear face of the release lever. A spring clip is located on the lever and the pivot washer and
secures the lever on the spigot. A small bolt retains the spring clip in position.
The release lever is forked at its inner end and locates on the clutch release bearing carrier. The outer end of the
release lever has a nylon seat which locates the slave cylinder piston rod. A second nylon seat, positioned centrally
on the release lever, locates on the ball spigot of the release bearing sleeve and allows the release lever to pivot freely
around the ball.
The clutch release bearing locates on the clutch release lever and release bearing sleeve. The bearing is retained on
a carrier which has two flats to prevent the carrier rotating on the release lever. A clip retains the release lever on the
carrier. The bearing and carrier are not serviceable individually.
Page 673 of 1672

CLUTCH - V8
33-2-6 DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
Description
General
The clutch system is a conventional diaphragm type clutch operated by a hydraulic cylinder. The clutch requires no
adjustment to compensate for wear.
Hydraulic clutch
The hydraulic clutch comprises a master cylinder, slave cylinder and a hydraulic reservoir, which is also shared with
the braking system. The master and slave cylinders are connected to each other hydraulically by plastic and metal
pipes. The plastic section of the pipe allows ease of pipe routing and also absorbs engine movements and vibrations.
The master cylinder comprises a body with a central bore. Two ports in the body connect the bore to the hydraulic
feed pipe to the slave cylinder and the brake/clutch fluid reservoir. A piston is fitted in the bore and has an external
rod which is attached to the clutch pedal with a pin. Two coiled springs on the clutch pedal reduce the effort required
to depress the pedal.
The master cylinder is mounted on the bulkhead in the engine compartment and secured with two bolts. The cylinder
is connected to the shared brake/clutch reservoir on the brake servo by a braided connecting hose.
The slave cylinder is located on the left hand side of the gearbox housing and secured with two bolts. A heat shield
protects the underside of the cylinder from heat generated from the exhaust system. The slave cylinder comprises a
cylinder with a piston and a rod. A port in the cylinder body provides the attachment for the hydraulic feed pipe from
the master cylinder. A second port is fitted with a bleed nipple for removing air from the hydraulic system after
servicing. The piston rod locates on a clutch release lever located in the gearbox housing. The rod is positively
retained on the release lever with a clip.
Clutch mechanism
The clutch mechanism comprises a flywheel, drive plate, pressure plate, release lever and a release bearing. The
clutch mechanism is fully enclosed at the rear of the engine by the gearbox housing.
A clutch release bearing sleeve is attached in the gearbox housing with two bolts and located on two dowels. A spigot
with a ball end is formed on the release bearing sleeve and provides a mounting and pivot point for the clutch release
lever. A dished pivot washer is located on the ball of the spigot. When the release lever is located on the ball, the pivot
washer seats against the rear face of the release lever. A spring clip is located on the lever and the pivot washer and
secures the lever on the spigot. A small bolt retains the spring clip in position.
The release lever is forked at its inner end and locates on the clutch release bearing carrier. The outer end of the
release lever has a nylon seat which locates the slave cylinder piston rod. A second nylon seat, positioned centrally
on the release lever, locates on the ball spigot of the release bearing sleeve and allows the release lever to pivot freely
around the ball.
The clutch release bearing locates on the clutch release lever and the release bearing sleeve. The bearing is retained
on a carrier which has two flats to prevent the carrier rotating on the release lever. A clip retains the release lever on
the carrier. The bearing and carrier are not serviceable individually.
Page 705 of 1672

MANUAL GEARBOX - R380
37-22 REPAIRS
Refit
1.Using a suitable solvent clean seal housing
mating faces.
2.Clean seal recess, bearings and bearing races.
3.Lubricate new oil seal and fit using a suitable
mandrel into housing.
4.Fit input shaft front bearing track using a press
and suitable mandrel.
5.Apply sealant, Part No. STC 4404 to seal
housing.
6.Position seal housing, fit new bolts and tighten
by diagonal selection to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
7.Clean bell housing mating faces, dowels and
dowel holes.
8.Position bell housing, fit bolts and tighten to 75
Nm (55 lbf.ft).
9.Clean release bearing sleeve mating faces,
dowel and dowel holes.
10.Position release bearing sleeve, fit bolts and
tighten to 25 Nm (18 lbf.ft).
11.Examine clutch release fork pivot points for
wear and replace as required.
12.Apply a smear of Molybdenum disulphide
grease to pivot points and position release
fork.
13.Fit retaining clip ensuring it locates over pivot
point washer, fit release fork bolt and tighten to
10 Nm (7 lbf.ft).
14.Clean release bearing and bearing sleeve
mating faces.
15.Apply smear of Molybdenum disulphide grease
to release bearing sleeve.
16.Fit release bearing and secure with retaining
peg.
17.Fit gearbox assembly.
+ MANUAL GEARBOX - R380,
REPAIRS, Gearbox - V8.
Cooler - oil - gearbox - Diesel
$% 37.24.02
Remove
1.Remove intercooler.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
Td5, REPAIRS, Intercooler.
2.Position absorbent cloth under each gearbox
oil cooler hose connection to collect spillage.
3.Push against coupling release ring and
disconnect both fluid hoses from oil cooler.
CAUTION: Always fit plugs to open
connections to prevent contamination.
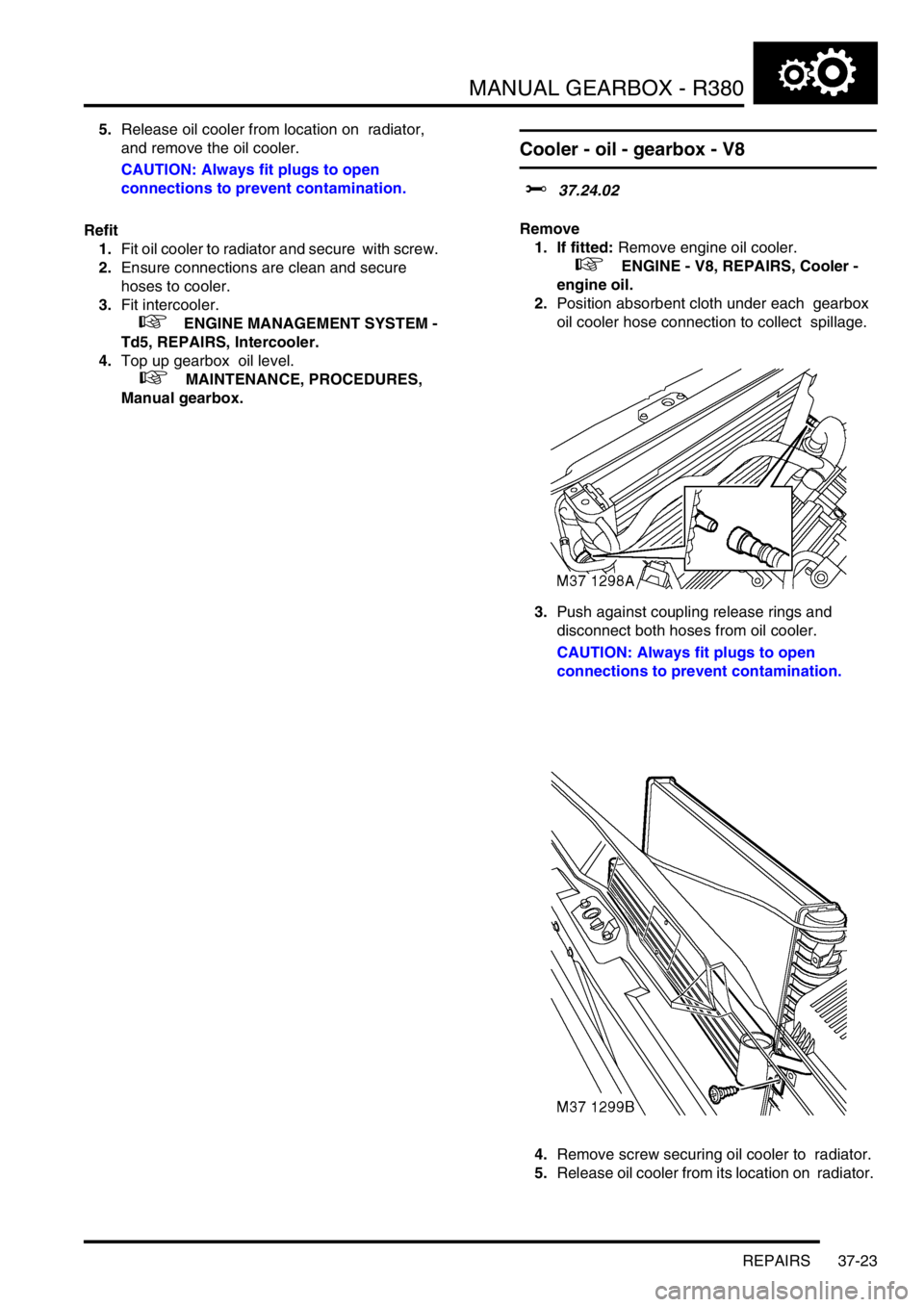
4.Remove screw securing oil cooler to radiator.
Page 706 of 1672
MANUAL GEARBOX - R380
REPAIRS 37-23
5.Release oil cooler from location on radiator,
and remove the oil cooler.
CAUTION: Always fit plugs to open
connections to prevent contamination.
Refit
1.Fit oil cooler to radiator and secure with screw.
2.Ensure connections are clean and secure
hoses to cooler.
3.Fit intercooler.
+ ENGINE MANAGEMENT SYSTEM -
Td5, REPAIRS, Intercooler.
4.Top up gearbox oil level.
+ MAINTENANCE, PROCEDURES,
Manual gearbox.
Cooler - oil - gearbox - V8
$% 37.24.02
Remove
1. If fitted: Remove engine oil cooler.
+ ENGINE - V8, REPAIRS, Cooler -
engine oil.
2.Position absorbent cloth under each gearbox
oil cooler hose connection to collect spillage.
3.Push against coupling release rings and
disconnect both hoses from oil cooler.
CAUTION: Always fit plugs to open
connections to prevent contamination.
4.Remove screw securing oil cooler to radiator.
5.Release oil cooler from its location on radiator.
Page 748 of 1672

TRANSFER BOX - LT230SE
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION 41-15
High/low detect switch
A high/low detect switch is fitted in the front output housing and connects to earth when low is selected. The switch is
connected to the engine ECM, the SLABS ECU and the EAT ECU. The purpose of the switch is to enable selection
of the hill descent feature and to modify the engine fuelling and automatic gearbox gearshift maps stored within the
respective ECM's and ECU's.
Differential lock - Fitted to certain vehicles only
The differential lock selector housing is bolted to the top of the front output housing, the selector finger passes through
the housing, locating in a slot in the differential lock selector shaft. The differential lock selector shaft passes through
the selector fork which is located beneath a plate bolted to the side of the output housing. The selector fork engages
the dog clutch sleeve with the differential rear shaft when the splines of the sleeve and differential rear shaft are
aligned. A spring loaded detent ball fitted in the output housing locates in grooves in the shaft.
Functionality – Vehicles up to 03 model year only
The function of the differential lock used in previous applications is performed on this vehicle by the Electronic Traction
Control System. However, for the purposes of 2 wheel rolling road testing , the differential lock components are
retained. For all driving conditions however, the differential lock must be set in the unlocked position.
Up to 03 model year specification shown
The differential lock must only be engaged for 2 wheel rolling road testing as engagement of the lock disables the
traction control feature and inhibits correct operation of the electronic brake distribution and hill descent features. It
will also be necessary to disconnect the propeller shaft from the transfer box output shaft driving the axle whose
wheels are NOT on the rolling road. The lock may be engaged/disengaged by using a 10 mm open ended spanner
on the flats (arrowed) machined on the differential lock selector shaft.
Vehicles not fitted with a differential lock may be identified by there being no cover or selector shaft (arrowed) on the
front output housing.
WARNING: VEHICLES NOT FITTED WITH A DIFFERENTIAL LOCK MUST NOT BE TESTED ON A ROLLING
ROAD WHERE THE ROLLERS ARE DRIVEN BY THE VEHICLE.