check engine MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1991, Model line: 3000GT, Model: MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991Pages: 1146, PDF Size: 76.68 MB
Page 108 of 1146

13-2
Boost Meter
Components Location........................................................36
Crank Angle Sensor
............................................................72Detonation Sensor................................................................84EGR Control Solenoid Valve
EGR Temperature Sensor
Fuel Pump Operation Check................................................137Fuel Pump Relay No. 2........................................................53Fuel Pump Resistor............................................................53
Idle Position Switch............................................................68Idle Speed Control Servo (Stepper Motor Type)............1 IOIgnition Coil and Power Transistor....................................115Ignition Switch-ST and Inhibitor Switch ................76Ignition Switch-ST
Injectors
94
Oxygen Sensor
Power Steering Oil Pressure Switch................................80Power Supply and Ignition Switch-IG................................41
Purge Control Solenord Valve............................................1 19Release of Residual Pressure from High
Pressure Fuel Hose............................................................137Throttle Position Sensor....................................................65Top Dead Center Sensor....................................................70Variable Induction Control Servo (DC Motor)
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES............................31
Adjustment of Fixed SAS....................................................35Adjustment of Idle Position Switch and
Throttle Position Sensor (TPS)............................................33Basic Idle Speed Adjustment............................................31Throttle Body (Throttle Valve Area) Cleaning....................33
SPECIAL TOOLS........................................................................8
SPECIFICATIONS
....................................................................6
General Specifications........................................................6Sealant....................................................................................7Service Specifications........................................................7
THROlTLE BODY....................................................................143
TROUBLESHOOTING............................................................9
Check Chart Classified by Problem Symptoms................16Circuit Diagram....................................................................18Engine Warning Light (Malfunction Indicator Light)........11Explanation and Cautions about Harness Check............10Explanation of Troubleshooting Procedures....................9Fuel Tank and Fuel Line........................................................30
Problem Symptoms Table (For Your Information)............17Self-diagnosis........................................................................12)
I
Page 115 of 1146
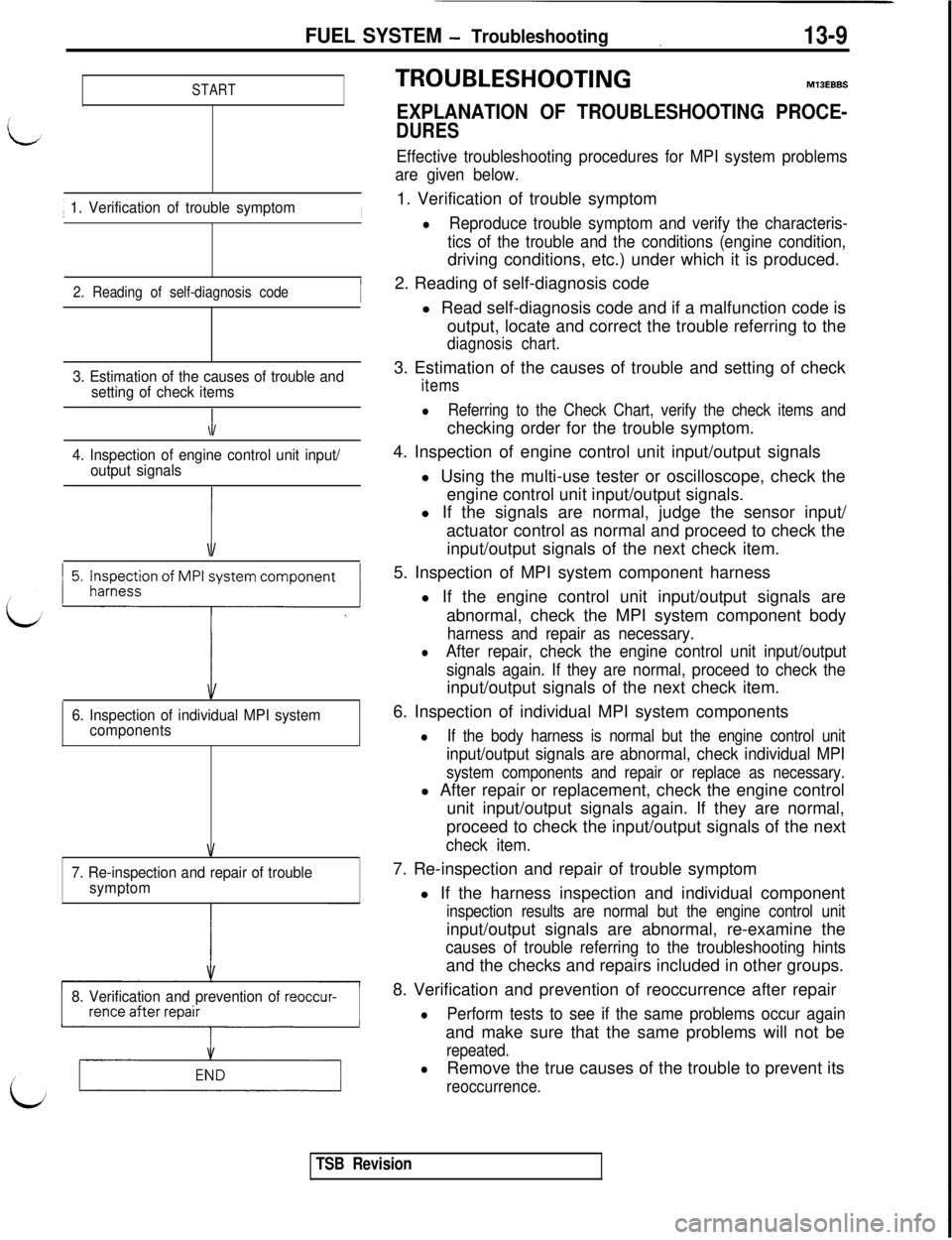
FUEL SYSTEM - Troubleshooting13-9
START1
1. Verification of trouble symptomI
2. Reading of self-diagnosis code
3. Estimation of the causes of trouble and
setting of check items
\1
4. Inspection of engine control unit input/
output signals
\1
5. Inspection of MPI system component
LL
6. Inspection of individual MPI system
components
7. Re-inspection and repair of trouble
symptom
8. Verification and prevention of
reoccur-
TROUBLESHO.OTlNGMlBEBBS
EXPLANATION OF TROUBLESHOOTING PROCE-
DURES
Effective troubleshooting procedures for MPI system problems
are given below.1. Verification of trouble symptom
lReproduce trouble symptom and verify the characteris-
tics of the trouble and the conditions (engine condition,driving conditions, etc.) under which it is produced.
2. Reading of self-diagnosis code
l Read self-diagnosis code and if a malfunction code is
output, locate and correct the trouble referring to the
diagnosis chart.3. Estimation of the causes of trouble and setting of check
items
lReferring to the Check Chart, verify the check items andchecking order for the trouble symptom.
4. Inspection of engine control unit input/output signals
l Using the multi-use tester or oscilloscope, check the
engine control unit input/output signals.
l If the signals are normal, judge the sensor input/
actuator control as normal and proceed to check the
input/output signals of the next check item.
5. Inspection of MPI system component harness
l If the engine control unit input/output signals are
abnormal, check the MPI system component body
harness and repair as necessary.
lAfter repair, check the engine control unit input/output
signals again. If they are normal, proceed to check theinput/output signals of the next check item.
6. Inspection of individual MPI system components
lIf the body harness is normal but the engine control unit
input/output signals are abnormal, check individual MPI
system components and repair or replace as necessary.l After repair or replacement, check the engine control
unit input/output signals again. If they are normal,
proceed to check the input/output signals of the next
check item.7. Re-inspection and repair of trouble symptom
l If the harness inspection and individual component
inspection results are normal but the engine control unitinput/output signals are abnormal, re-examine the
causes of trouble referring to the troubleshooting hintsand the checks and repairs included in other groups.
8. Verification and prevention of reoccurrence after repair
lPerform tests to see if the same problems occur againand make sure that the same problems will not be
repeated.
lRemove the true causes of the trouble to prevent its
reoccurrence.
TSB Revision
Page 117 of 1146
FUEL SYSTEM - Troubleshooting13-11
L
L
Sensor side6FU1215
Malfunctionl
If the sensor impressed voltage is abnormal, check the wire
for an open circuit or short-circuit to ground and repair as
necessary. If the wire is normal, replace the engine control
unit and check again.l To check the voltage, use a digital voltmeter (or circuit
tester) as a rule.
[However, use an analog voltmeter for checking the power
transistor drive voltage.]ENGINE WARNING LIGHT (MALFUNCTION IN-
DICATOR LIGHT)
Among the self-diagnosis items, a malfunction indicator lightcomes on to notify the driver of the emission control items
when an irregurality is detected.
However, when an irregular signal returns to normal and theengine control unit judges that it has returned to normal, the
malfunction indicator light goes out.
Moreover, when the ignition switch is turned off, the light goes
out. Even if the ignition switch is turned on again, the light doesnot come on until the irregularity is detected.
Here, immediately after the ignition switch is turned on, the
malfunction indicator light is lit for 5 seconds to indicate that
the malfunction indicator light operates normally.
ITEMS INDICATED BY THE MALFUNCTION INDICATOR
LIGHT
Engine control unit
Oxygen sensor
Air flow sensor
Intake air temperature sensor
Throttle position sensor
Engine coolant temperature sensor
Crank angle sensor
Top dead center sensor
Barometric pressure sensor
Detonation sensor
Ignition timing adjustment signal
Injector
EGR system
Ignition coil, power transistor unit
Caution
The malfunction indicator light comes on when the line ofthe ignition timing adjustment terminal is shorted to
ground. Therefore, the light also comes on when the
ignition timing adjustment terminal is grounded to adjust
the ignition timing, but this does not show any abnormal-
ity.
TSB Revision
Page 118 of 1146

13-12FUEL SYSTEM - Troubleshooting
MALFUNCTION INDICATOR LIGHT INSPECTION
(1) Check that when the ignition switch is turned on, the lightilluminates for about 5 seconds and then goes out.
(2) If the light does not illuminate, check for open circuit in
dharness, blown fuse and blown bulb.
SELF-DIAGNOSIS
The engine control unit monitors the input/output signals (some
signals at all times and the others under specified conditions) ofthe engine control unit.
When it is noticed that an irregularity has continued for a
specified time or longer from when the irregular signal is
initially monitored, passing a certain number, the engine controlunit judges that an irregularity has occurred, memorizes the
malfunction code, and outputs the signal to the self-diagnosis
output terminal.
There are 21 diagnosis items, including the normal state, andthe diagnosis results can be read out with a voltmeter or
multi-use tester.Moreover, since memorization of the malfunction codes is
backed up directly by the battery, the diagnosis results are
memorized even if the ignition key is turned off. The malfunc-
tion codes will, however, be erased when the battery terminalor the engine control unit connector is disconnected.
The malfunction code can also be erased by turning on the
ignition switch and sending the malfunction code erase signalfrom the multi-use tester to the engine control unit.
CautionIf the sensor connector is disconnected with the ignition
_ _switch turned on, the malfunction code is memorized. Ind
this case, send the malfunction code erase signal from themulti-use tester to the engine control unit or disconnect
the battery terminal
(-) for 10 seconds or more, and the
diagnosis memory will be erased.
The 21 diagnosis items are provided as follows, and if plural
items are activated, they are all indicated sequentially from the
smallest code number.
CautionThe malfunction code for the ignition timing adjustment
signal is output when the line of the ignition timing
adjustment terminal is shorted to ground. Therefore, the
malfunction code is also output when the ignition timing
adjustment terminal is grounded to adjust the ignition
timing, but this does not show any abnormality.
TSB Revision
Page 119 of 1146
FUEL SYSTEM - Troubleshootinn
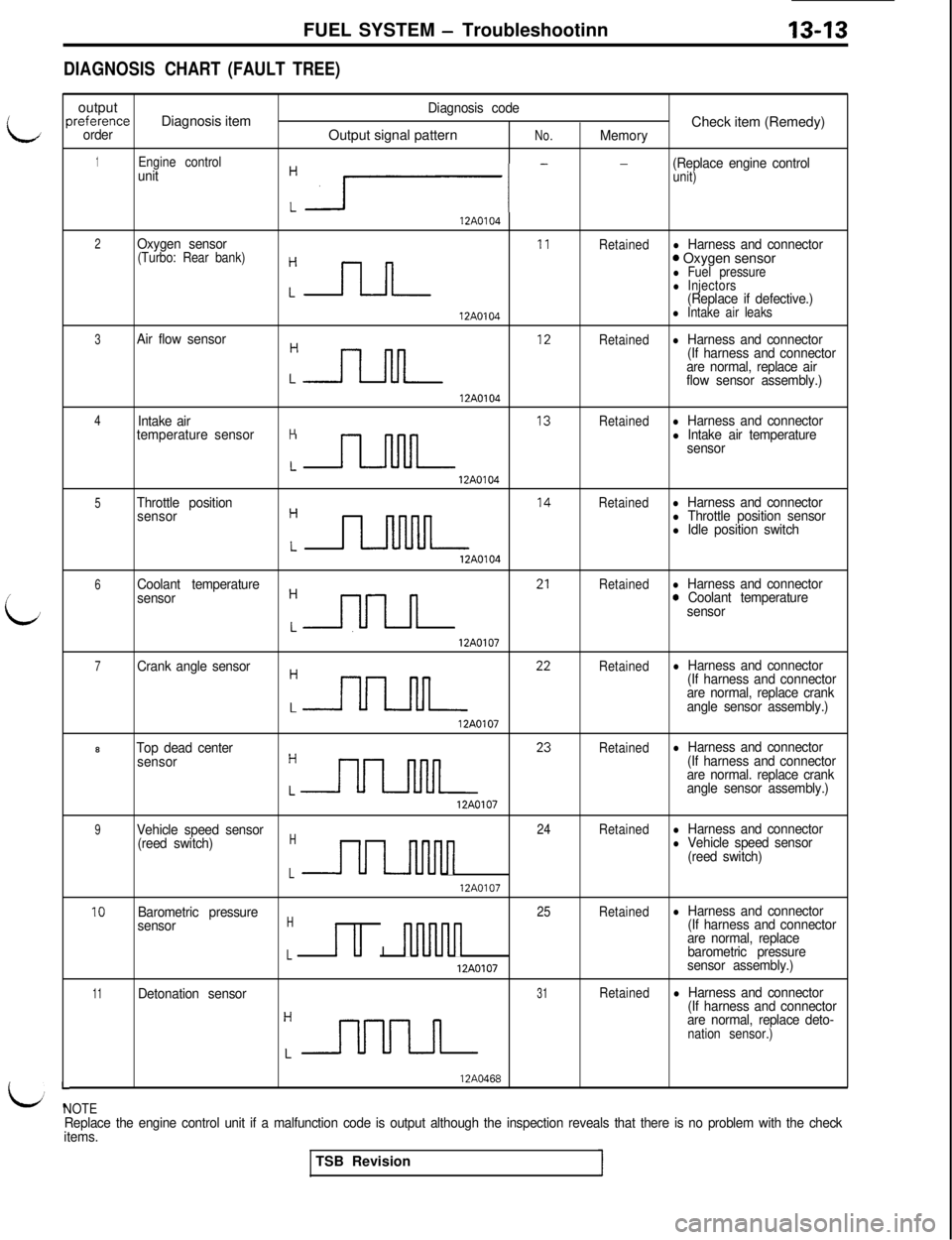
DIAGNOSISCHART (FAULT TREE)
i
L
Foutput
Diagnosis codeIreferenceDiagnosis item
Check item (Remedy)orderOutput signal patternNo.Memory
1Engine controlunit
:r- -
(Replace engine controlunit)
12A0104
2Oxygen sensorRetainedl Harness and connector(Turbo: Rear bank)
Cnn I’
0 Oxygen sensorl Fuel pressurel Injectors(Replace if defective.)
12A0104l Intake air leaks
3Air flow sensor
:n ‘*
Retainedl Harness and connector
(If harness and connector
are normal, replace air
flow sensor assembly.)
12A0104
4Intake airRetainedl Harness and connector
temperature sensorH
Ln I3
l Intake air temperature
sensor
12A0104
5Throttle position
sensor
:n I4
Retainedl Harness and connectorl Throttle position sensorl Idle position switch
12AO104
6Coolant temperature
:nn 21
Retainedl Harness and connector
sensor0 Coolant temperature
sensor12A0107
7Crank angle sensor
:nn 22
Retainedl Harness and connector
(If harness and connector
are normal, replace crank
angle sensor assembly.)
12A01078
Top dead centerRetainedl Harness and connector
sensor
:nn 23
(If harness and connector
are normal. replace crank
angle sensor assembly.)
12A0107
9Vehicle speed sensor24Retainedl Harness and connector
(reed switch)H
UInnnn
l Vehicle speed sensor
(reed switch)
L12A0107
10Barometric pressure25Retainedl Harness and connector
sensorHu I
nnluln
(If harness and connector
are normal, replace
Lbarometric pressure
12A0107sensor assembly.)
11Detonation sensor31Retainedl Harness and connector
:-r-uuuL
(If harness and connector
are normal, replace deto-
nation sensor.)
L-NOTE
12A0468
Replace the engine control unit if a malfunction code is output although the inspection reveals that there is no problem with the check
items.TSB Revision
Page 120 of 1146

13-14FUEL SYSTEM - Troubleshooting
routput
preference
order
7Diannosis item
Diagnosis code
IOutput signal patternNo.
36
39
121 Ignition timing
adjustment signalH
L
13Oxygen sensor ’(Turbo: Front bank)HRetainedl Harness and connectorl Oxygen sensorl Fuel pressurel Injectors (Replaceif defective)l Intake air leaks
Retained
l Harness and connectorl Injector coil resistance
5
I--
Injector12AOlO!
:nnnn
EGR
12A0105
14
41
Retainedl Harness and connectorl EGR thermo-sensorl EGRvalvel EGR control solenoidvalvel EGR valve controlvacuum
Retainedl Harness and connectorl Ignition coill Power transistor unit
16
lqnition coil,
12A0105
52power transistor unitINO. 2-5 cylinder)H
Lu Lnll
‘qnition coil.
12AO105
18Retainedl Harness and connectorl Ignition coill Power transistor unit
Retainedl Harness and connector(If harness and connector
are normal, replace only
transaxle control unit.)
Retainedl Harness and connector(If harness, connector
and induction control
valve are normal,
replace air intake
plenum assembly.)
--
Tower transistor unitH‘NO. 3-6 cylinder)
Ln
12A0105
A cable from trans-
axle control unit,Hfor transmission
of torque reductionLUUUUUI n
signal 12A0105
Induction control
valve position
61
62
sensorH
12A0105
Normal stateH-
NOTE-Replace the engine control unit if a malfunction code is output although the inspection reveals that there is no problem with the check
items.TSB Revision
Page 121 of 1146
FUEL SYSTEM - Troubleshooting13-15READ OUT OF MALFUNCTION CODE
Precautions for Operation
(1) When battery voltage is low, no detection of failure is
possible. Be sure to check the battery for voltage and otherconditions before starting the test.
(2) Diagnosis item is erased if the battery or the engine controlunit connector is disconnected. Do not disconnect the
battery before the diagnosis result is completely read.
Using Multi-Use Tester
(I) Read and record the self-diagnosis output.
(2) Referring to the diagnosis chart, repair the faulty part.
(3) Turn the ignition switch OFF and then turn it ON.
(4) Erase the malfunction code.(5) Recheck that a normal code is output.
7FUO999
r MPI diagnosis
L Ground
EC165(Using Voltmeter(I) Connect an analog voltmeter between the self-diagnosis
output terminal of the diagnosis connector and ground
terminal.(2) Turn on the ignition switch.
(3) Read the diagnosis output pattern from the voltmeter and
record it.(4) Referring to the diagnosis chart, repair the faulty part.
(5) Erase the malfunction code using the following procedure.
@ Turn OFF the ignition switch.
@ Disconnect the negative battery cable from the battery
terminal for
10 seconds or more and then reconnect it.
@ Turn ON the ignition switch and read the self-diagnosiscode to check that a normal code is output.
Diagnosis by DIAGNOSIS 2 MODE
(1) Using the multi-use tester, changeover the diagnosis modeof the engine control unit to DIAGNOSIS 2 MODE.
(2) Road test the vehicle.
(3) Read the diagnosis code in the same manner as “READ
OUT OF MALFUNCTION CODE” and repair the malfunc-
tioning part.(4) Remove the multi-use tester.
NOTERemoval of the multi-use tester
.will erase all the self-’
diagnosis malfunction codes in the engine control unit and
changeover the diagnosis mode from DIAGNOSIS 2 MODEto DIAGNOSIS 1 MODE.
TSB Revision
Page 122 of 1146
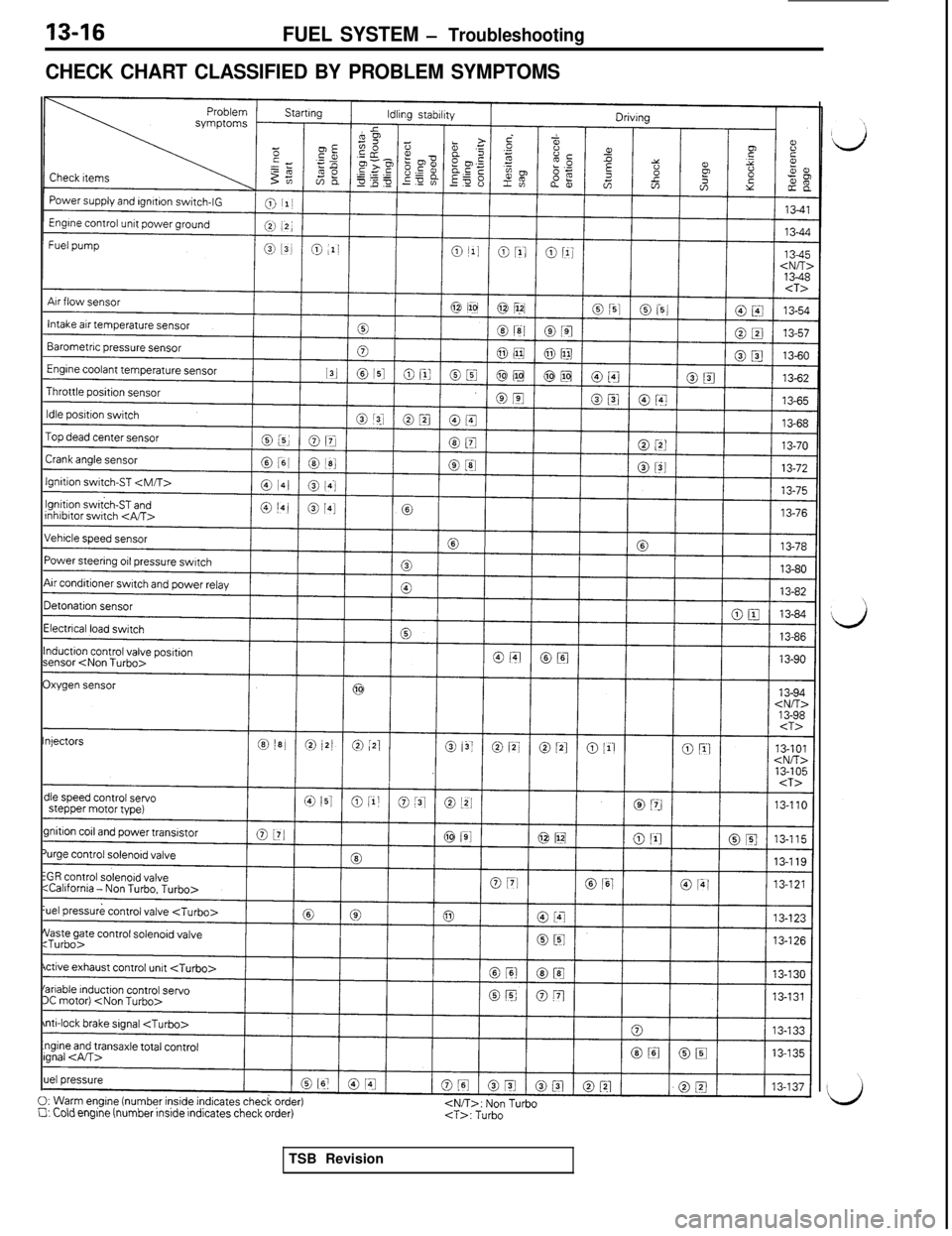
13-16FUEL SYSTEM - Troubleshooting
CHECK CHART CLASSIFIED BY PROBLEM SYMPTOMSstepper motor type)
0:Warmen,gine (number inside indicates check order)Cl: Cold engine (number inside indicates check order)
Page 137 of 1146
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES
MlBFHSU
BASIC IDLE SPEED ADJUSTMENT
NOTE(1) The basic idle speed has been factory-adjusted with the
speed adjusting screw (SAS) and does not normally require
adjustment.(2) If the adjustment is required, first check that the ignition
plug, injector,
ISC servo, and compression pressure are
normal.
(1) Before starting the inspection and adjustment procedures,set the vehicle in the following conditions:
l
Engine coolant temperature: 80 to 95°C (176 to 205°F)l Lights, electric cooling fan, accessories: OFF
lTransaxle: Neutral (P range on vehicles with automatic
transaxle)l Steering wheel: Straightforward position
(2) When using the multi-use tester, connect it to the diagnosis
connector.
NOTEThe connection of the multi-use tester grounds the
self-
diagnosis/data transmission selector terminal.
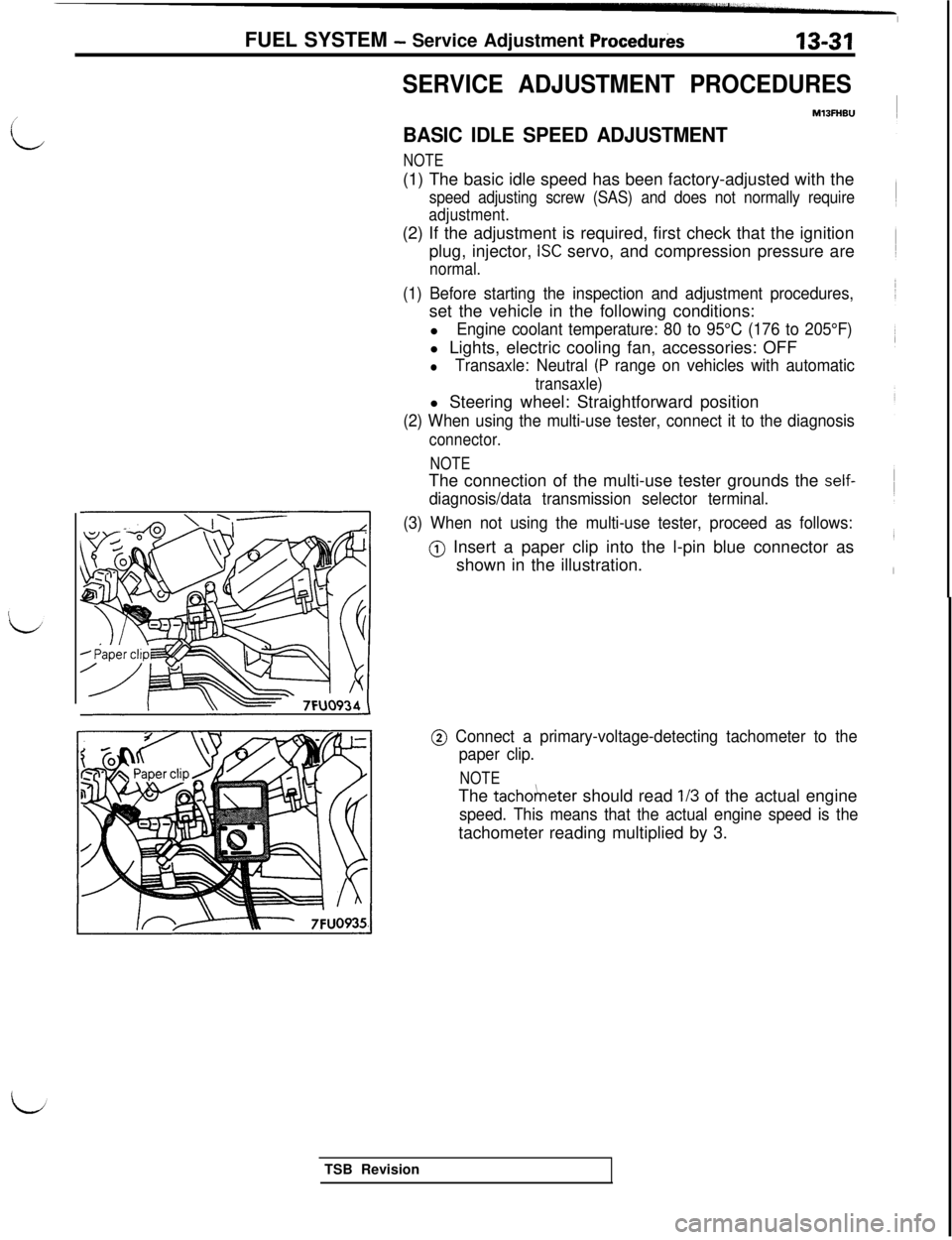
(3) When not using the multi-use tester, proceed as follows:
@) Insert a paper clip into the l-pin blue connector as
shown in the illustration. FUEL SYSTEM
- Service Adjustment Procedurks13-31
i
@ Connect a primary-voltage-detecting tachometer to the
paper clip.
NOTEThe
tacho/neter should read l/3 of the actual engine
speed. This means that the actual engine speed is thetachometer reading multiplied by 3.
TSB Revision
Page 138 of 1146
13-32FUEL SYSTEM - Service Adjustment Procedures
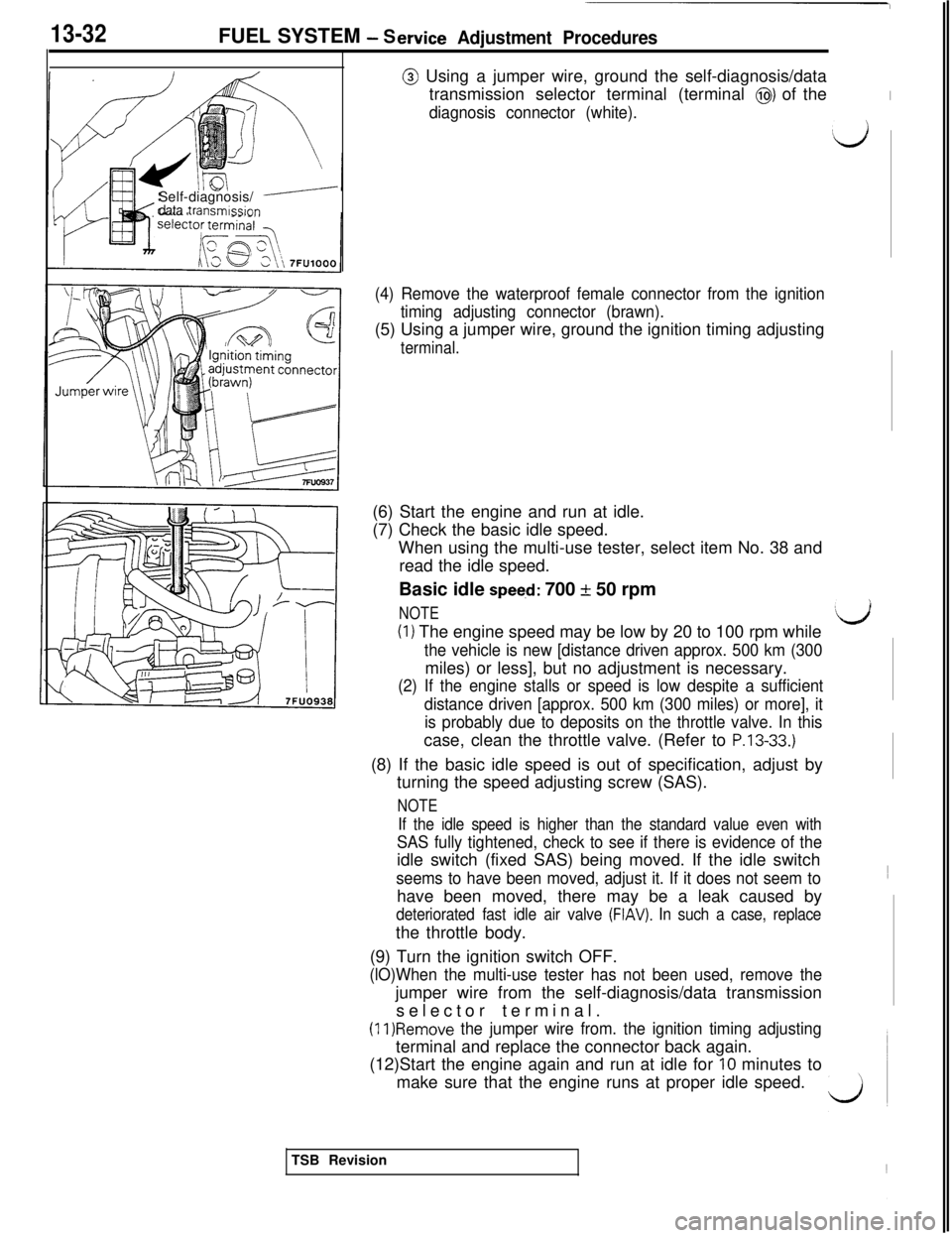
@ Using a jumper wire, ground the self-diagnosis/data
transmission selector terminal (terminal
@) of theI
diagnosis connector (white).
dSelf-diagnosis/
ydata transmission
(4) Remove the waterproof female connector from the ignition
timing adjusting connector (brawn).(5) Using a jumper wire, ground the ignition timing adjusting
terminal.(6) Start the engine and run at idle.
(7) Check the basic idle speed.
When using the multi-use tester, select item No. 38 and
read the idle speed.
Basic idle
speeci: 700 + 50 rpm
NOTE(I) The engine speed may be low by 20 to 100 rpm while
the vehicle is new [distance driven approx. 500 km (300miles) or less], but no adjustment is necessary.
(2) If the engine stalls or speed is low despite a sufficient
distance driven [approx. 500 km (300 miles) or more], it
is probably due to deposits on the throttle valve. In thiscase, clean the throttle valve. (Refer to
P.13-33.)(8) If the basic idle speed is out of specification, adjust by
turning the speed adjusting screw (SAS).
NOTE
If the idle speed is higher than the standard value even with
SAS fully tightened, check to see if there is evidence of theidle switch (fixed SAS) being moved. If the idle switch
seems to have been moved, adjust it. If it does not seem tohave been moved, there may be a leak caused by
deteriorated fast idle air valve (FIAV). In such a case, replacethe throttle body.
(9) Turn the ignition switch OFF.
(lO)When the multi-use tester has not been used, remove thejumper wire from the self-diagnosis/data transmission
selector terminal.
(11)Remove the jumper wire from. the ignition timing adjustingterminal and replace the connector back again.
(12)Start the engine again and run at idle for
10 minutes to
make sure that the engine runs at proper idle speed.
‘dTSB Revision