check engine MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1991, Model line: 3000GT, Model: MITSUBISHI 3000GT 1991Pages: 1146, PDF Size: 76.68 MB
Page 86 of 1146
11-36ENGINE - Cylinder Head and Valve
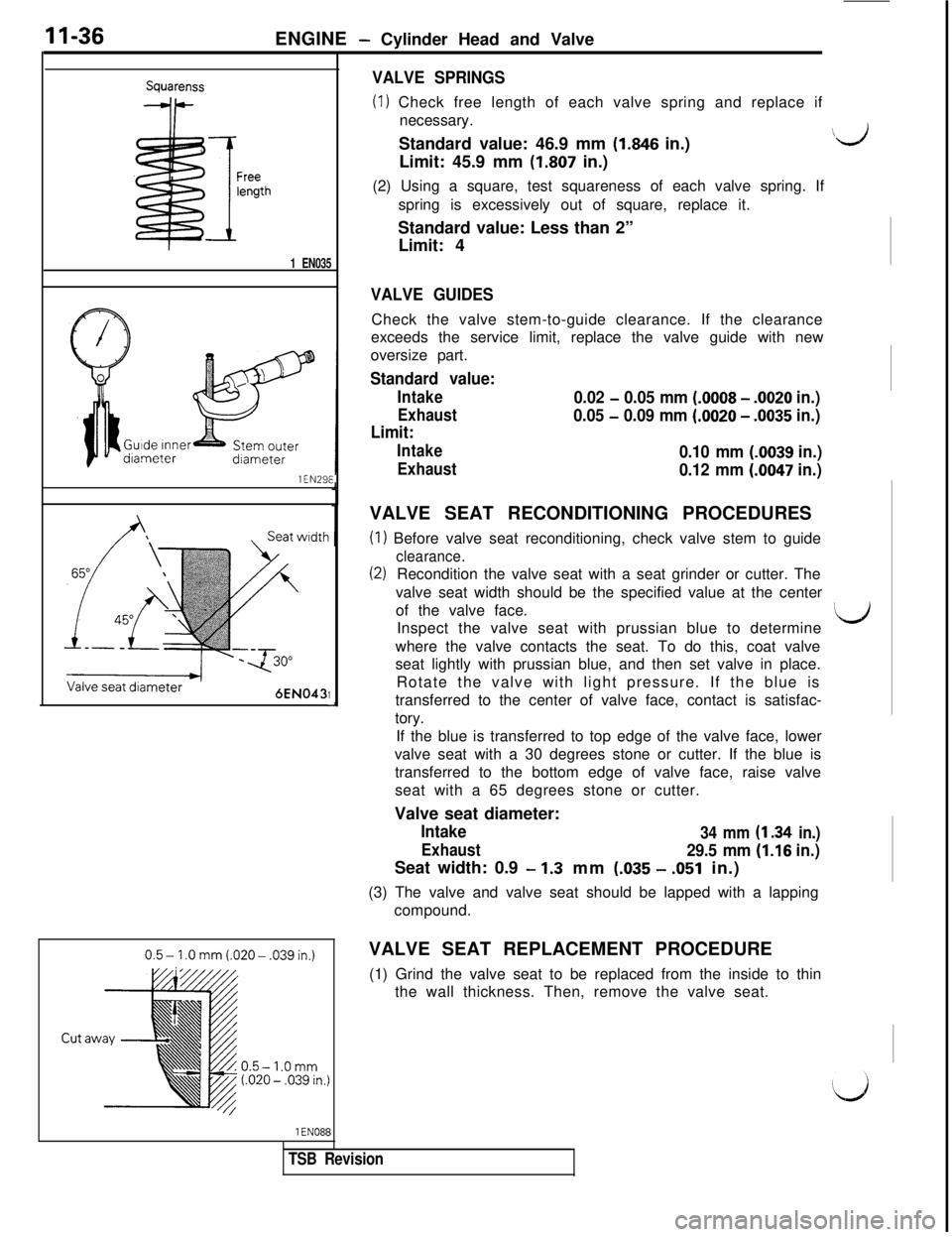
SquarenssVALVE SPRINGS
(1) Check free length of each valve spring and replace if
necessary.
!
FreelengthStandard value: 46.9 mm
(1.846 in.)\bJLimit: 45.9 mm
(1.807 in.)
(2) Using a square, test squareness of each valve spring. If
spring is excessively out of square, replace it.
Standard value: Less than 2”
Limit: 4
1 EN035
VALVE GUIDES
1 EN29ECheck the valve stem-to-guide clearance. If the clearance
exceeds the service limit, replace the valve guide with new
oversize part.
Standard value:
Intake
Exhaust0.02 - 0.05 mm (0008 - .0020 in.)
Limit:0.05
- 0.09 mm (.0020 - .0035 in.)
Intake
Exhaust0.10 mm (0039 in.)
0.12 mm (0047
in.)6EN043
1AVALVE SEAT RECONDITIONING PROCEDURES
(I 1 Before valve seat reconditioning, check valve stem to guide
clearance.
(2)Recondition the valve seat with a seat grinder or cutter. The
valve seat width should be the specified value at the center
of the valve face.
Inspect the valve seat with prussian blue to determine
LJwhere the valve contacts the seat. To do this, coat valve
seat lightly with prussian blue, and then set valve in place.
Rotate the valve with light pressure. If the blue is
transferred to the center of valve face, contact is satisfac-
tory.
If the blue is transferred to top edge of the valve face, lower
valve seat with a 30 degrees stone or cutter. If the blue is
transferred to the bottom edge of valve face, raise valve
seat with a 65 degrees stone or cutter.
Valve seat diameter:
Intake34 mm (I .34 in.)
ExhaustSeat width: 0.9
29.5 mm (1.16 in.)
- 1.3 mm (035 - .051 in.)
(3) The valve and valve seat should be lapped with a lapping
compound.
VALVE SEAT REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE
(1) Grind the valve seat to be replaced from the inside to thin
the wall thickness. Then, remove the valve seat.
1 ENOE18
TSB Revision
Page 91 of 1146
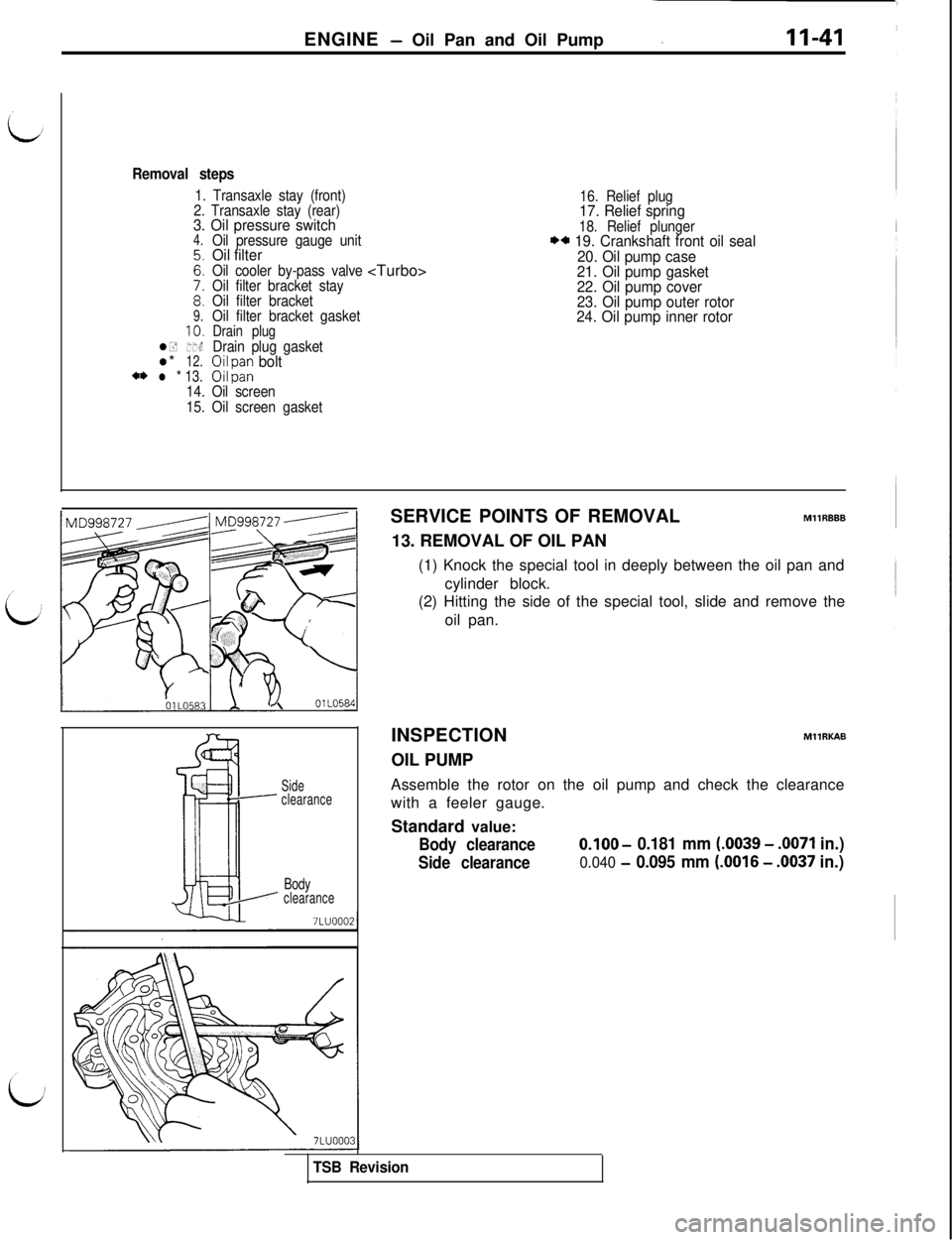
ENGINE - Oil Pan and Oil Pump
Removal steps
1. Transaxle stay (front)
2. Transaxle stay (rear)
3. Oil pressure switch4.
Z:
;:9.10.l+11.l*12.** l * 13.
Oil pressure gauge unitOil filterOil cooler by-pass valve
Oil filter bracket stay
Oil filter bracket
Oil filter bracket gasket
Drain plugDrain plug gasket0; y; boltI
16. Relief plug17. Relief spring18. Relief plunger** 19. Crankshaft front oil seal
20. Oil pump case
21. Oil pump gasket
22. Oil pump cover
23. Oil pump outer rotor
24. Oil pump inner rotor
14. Oil screen
15. Oil screen gasket
Side
clearance
BodyclearanceSERVICE POINTS OF REMOVALMllRBBB
13. REMOVAL OF OIL PAN
(1) Knock the special tool in deeply between the oil pan and
cylinder block.
(2) Hitting the side of the special tool, slide and remove the
oil pan.
INSPECTION
OIL PUMPMllRKAB
Assemble the rotor on the oil pump and check the clearance
with a feeler gauge.
Standard value:
Body clearanceO.lOO- 0.181 mm (.0039 - .0071 in.)
Side clearance0.040 - 0.095 mm (.0016 - .0037 in.)
TSB Revision
Page 95 of 1146
ENGINE - Piston and. Connectina RodII-45
LJ
Front mark
-
MD998764
lEN0113
lEN0114
v5EN057
,, Push in by thepiston.
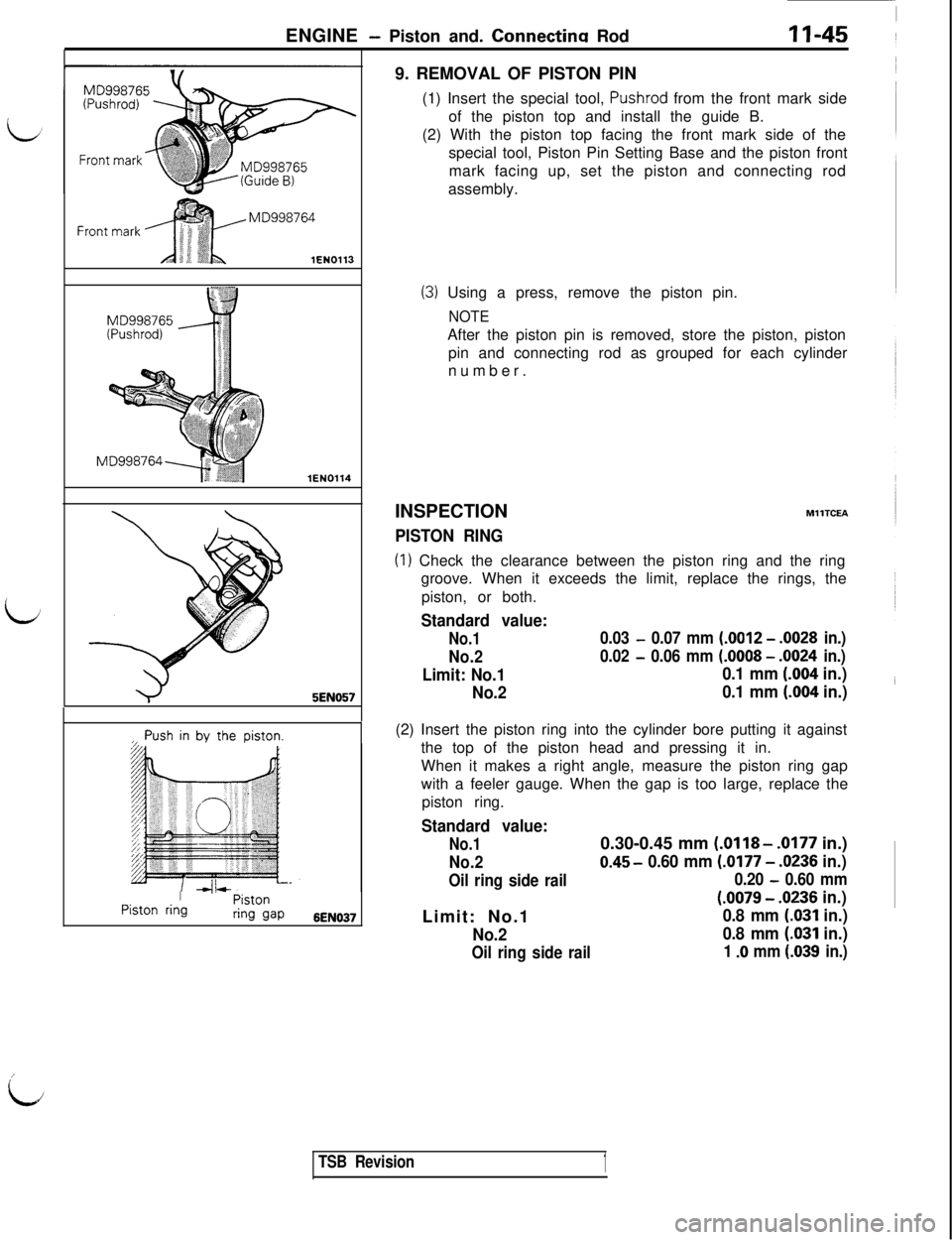
IPiston ringPistonring gap6EN0379. REMOVAL OF PISTON PIN
(1) Insert the special tool,
Pushrod from the front mark side
of the piston top and install the guide B.
(2) With the piston top facing the front mark side of the
special tool, Piston Pin Setting Base and the piston front
mark facing up, set the piston and connecting rod
assembly.
(3) Using a press, remove the piston pin.
NOTEAfter the piston pin is removed, store the piston, piston
pin and connecting rod as grouped for each cylinder
number.
INSPECTION
PISTON RING
MllTCEA
(1) Check the clearance between the piston ring and the ring
groove. When it exceeds the limit, replace the rings, the
piston, or both.
Standard value:
No.10.03 - 0.07 mm (.0012 - .0028 in.)
No.20.02
- 0.06 mm (.OOOS - ‘0024 in.)
Limit: No.10.1 mm (.004 in.)
No.20.1 mm
(.004 in.)(2) Insert the piston ring into the cylinder bore putting it against
the top of the piston head and pressing it in.
When it makes a right angle, measure the piston ring gap
with a feeler gauge. When the gap is too large, replace the
piston ring.
Standard value:
No.10.30-0.45 mm (.0118- .0177 in.)
No.20.45- 0.60 mm (.0177 - .0236 in.)
Oil ring side rail0.20 - 0.60 mmLimit: No.1
(.0079 - .0236 in.)
0.8 mm
(.031 in.)
No.20.8 mm
(.031 in.)
Oil ring side rail1 .O mm (.039 in.)
I
LJ
TSB Revision1
Page 97 of 1146
ENGINE - Piston and Connecting RodII-47
6EN0223
Side rail
Side rail end
7EN249
7EN250
ldentiftcation mark embossed
No. 1
7Barrel
weldenthcation mark
Tapered
we7EN013i
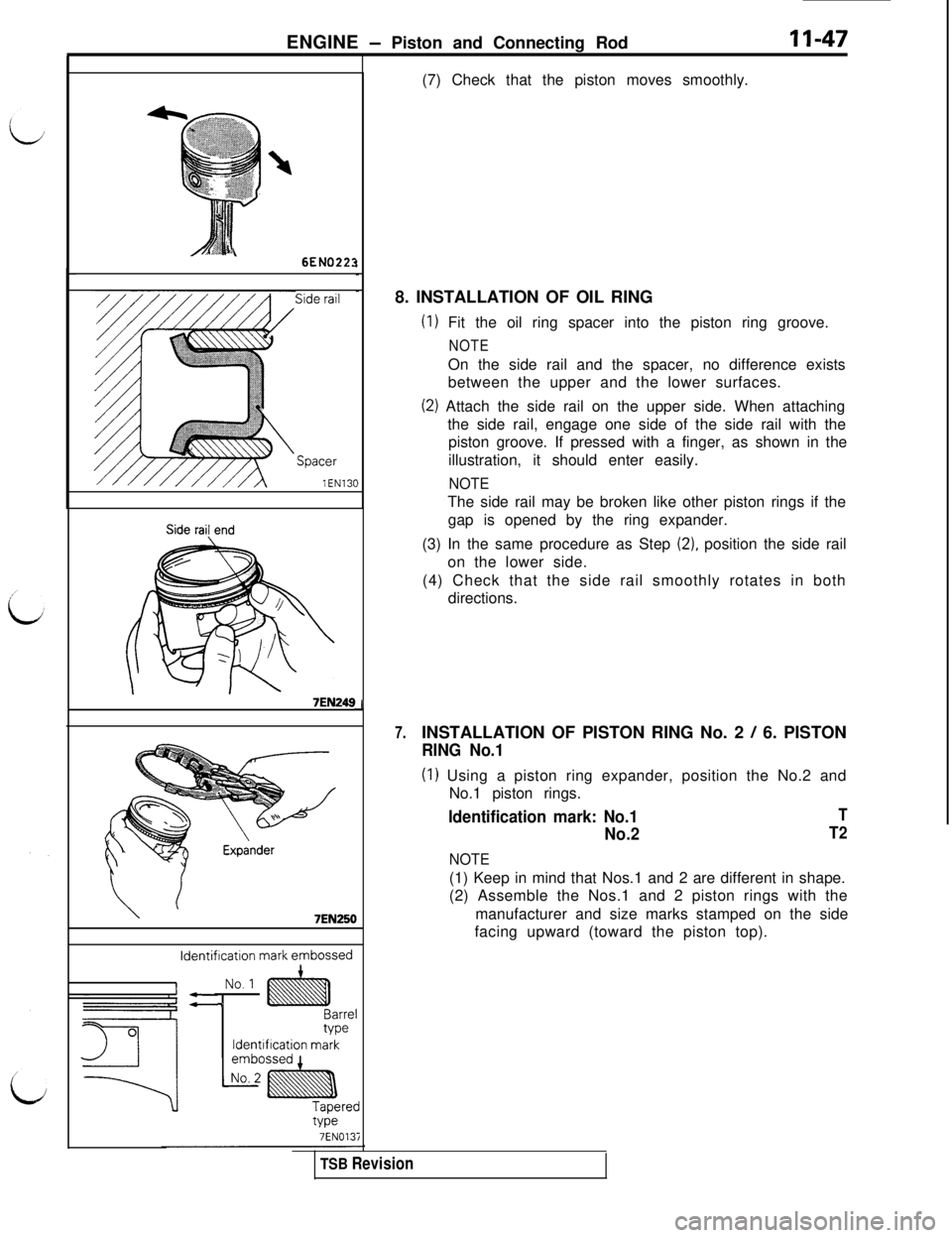
LI(7) Check that the piston moves smoothly.
8. INSTALLATION OF OIL RING
(1) Fit the oil ring spacer into the piston ring groove.
NOTEOn the side rail and the spacer, no difference exists
between the upper and the lower surfaces.
(2) Attach the side rail on the upper side. When attaching
the side rail, engage one side of the side rail with the
piston groove. If pressed with a finger, as shown in the
illustration, it should enter easily.
NOTEThe side rail may be broken like other piston rings if the
gap is opened by the ring expander.
(3) In the same procedure as Step
(2), position the side rail
on the lower side.
(4) Check that the side rail smoothly rotates in both
directions.
7.INSTALLATION OF PISTON RING No. 2 / 6. PISTON
RING No.1
(1) Using a piston ring expander, position the No.2 and
No.1 piston rings.
Identification mark: No.1
No.2
NOTE
T
T2(1) Keep in mind that Nos.1 and 2 are different in shape.
(2) Assemble the Nos.1 and 2 piston rings with the
manufacturer and size marks stamped on the side
facing upward (toward the piston top).
TSB Revision
Page 98 of 1146
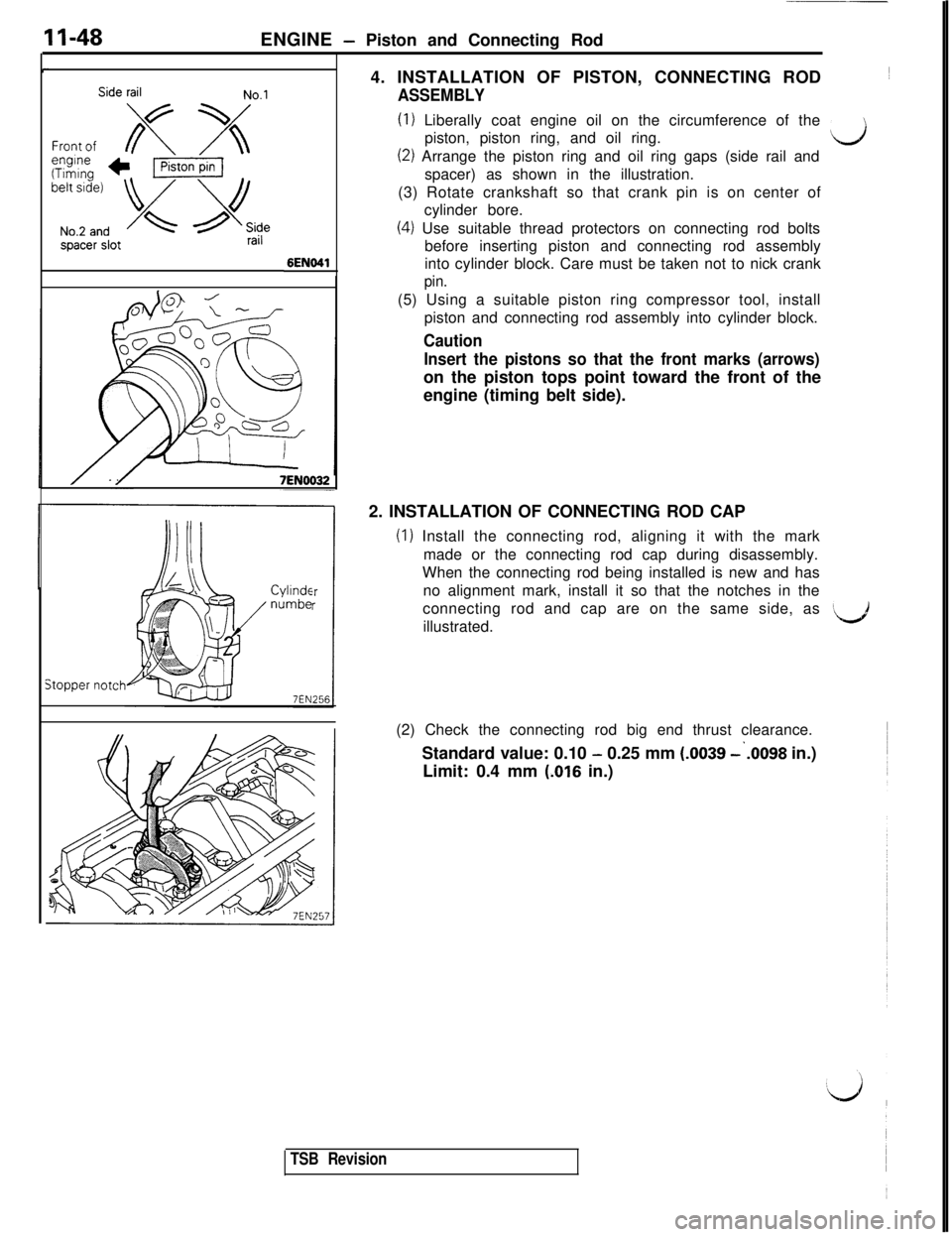
11-48ENGINE - Piston and Connecting Rod
Side railNo.1
spacer slotrail
6ENO41
7EN0032
Cylindcnumbe
Stopper notch4. INSTALLATION OF PISTON, CONNECTING ROD~
ASSEMBLY
(1) Liberally coat engine oil on the circumference of the
piston, piston ring, and oil ring.
d
(2) Arrange the piston ring and oil ring gaps (side rail and
spacer) as shown in the illustration.
(3) Rotate crankshaft so that crank pin is on center of
cylinder bore.
(4) Use suitable thread protectors on connecting rod bolts
before inserting piston and connecting rod assembly
into cylinder block. Care must be taken not to nick crank
pin.(5) Using a suitable piston ring compressor tool, install
piston and connecting rod assembly into cylinder block.
Caution
Insert the pistons so that the front marks (arrows)on the piston tops point toward the front of the
engine (timing belt side).
2. INSTALLATION OF CONNECTING ROD CAP
(1) Install the connecting rod, aligning it with the mark
made or the connecting rod cap during disassembly.
When the connecting rod being installed is new and has
no alignment mark, install it so that the notches in the
connecting rod and cap are on the same side, as
illustrated.
‘d(2) Check the connecting rod big end thrust clearance.
Standard value: 0.10
- 0.25 mm (.0039 -‘.0098 in.)
Limit: 0.4 mm
(-016 in.)
TSB Revision
Page 100 of 1146
II-50ENGINE - Crankshaft, FlYwheel and Drive Plate
\7EN262
7EN261INSPECTION
MllUCHAFLYWHEEL (engine with a manual transaxle)
(I) Make a visual inspection of the clutch disc. If stepped wear, :streaking, or seizure are apparent, replace it.\J(2) If flywheel run out exceeds the limit, replace it.
Limit: 0.13 mm
t.0051 in.)
RING GEAR (engine with a manual transaxle)
When there is wear, cracks, or other damage to the ring gear
teeth, replace the ring gear by the following procedure. Check
the starter motor pinion.
Ring gear replacement procedure:
(1) Tap around the ring gear to loosen and remove it from the
flywheel..
CautionThe ring gear cannot be removed while it is hot.
(2) Heat the ring gear to 300°C (572°F) and install it into the
flywheel.
CRANKSHAFTInspect out-of-roundness and taper of crankshaft journal and
pin.
Limit:Out-of-roundness of journal and pin:
LJ
0.003 mm (.00012 in.)Taper of journal and pin: 0.005 mm
(.00020 in.)
OIL CLEARANCE MEASUREMENT
(I) To check the oil clearance, measure the outside diameter of
the crankshaft journal and the crank pin and the inside
diameter of the bearing. The clearance can be obtained by
calculating the difference between the measured outside
and inside diameters.
Standard value: 0.019
- 0.044 mm i.0007 - .0017 in.)
Limit: 0.1 mm
(.004 in.)
(2) If the oil clearance exceeds the limit, replace the bearing,
and crankshaft if necessary.
TSB Revision
Page 102 of 1146
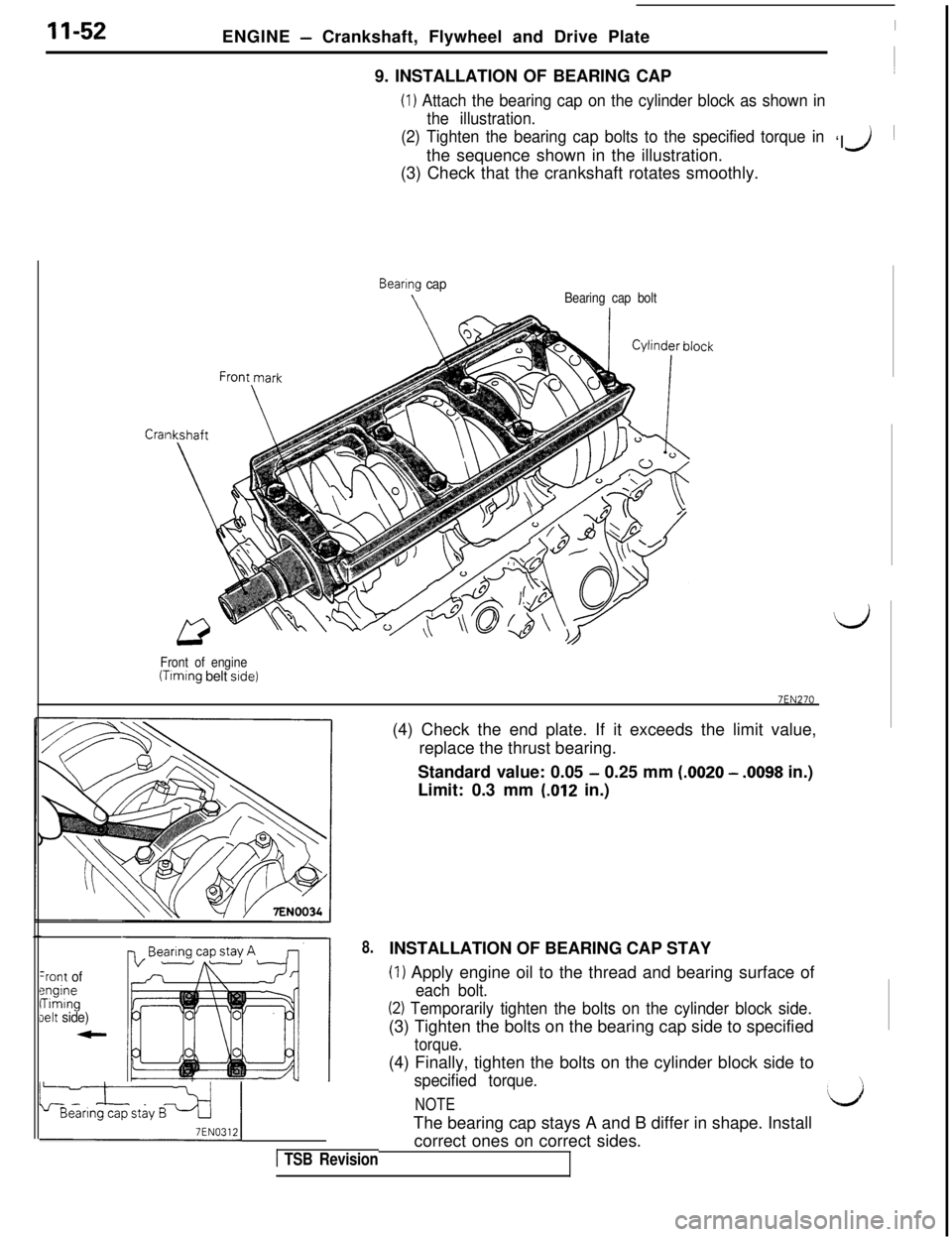
11-52ENGINE - Crankshaft, Flywheel and Drive Plate
9. INSTALLATION OF BEARING CAP
(1) Attach the bearing cap on the cylinder block as shown in
the illustration.
(2) Tighten the bearing cap bolts to the specified torque in‘I
the sequence shown in the illustration.
J ~
(3) Check that the crankshaft rotates smoothly.
Cral
Bearing cap
\Bearing cap bolt
Front of engine
(Timing belt side)
7EN270(4) Check the end plate. If it exceeds the limit value,
replace the thrust bearing.
Standard value: 0.05
- 0.25 mm (.0020 - .0098 in.)
Limit: 0.3 mm
(.012 in.)
-rent ofengineTimingIelt side)
8.
LLiN03,ij
1 TSB RevisionINSTALLATION OF BEARING CAP STAY
(1) Apply engine oil to the thread and bearing surface of
each bolt.
(2) Temporarily tighten the bolts on the cylinder block side.(3) Tighten the bolts on the bearing cap side to specified
torque.(4) Finally, tighten the bolts on the cylinder block side to
specified torque.
NOTEThe bearing cap stays A and B differ in shape. Install
correct ones on correct sides.d
Page 104 of 1146
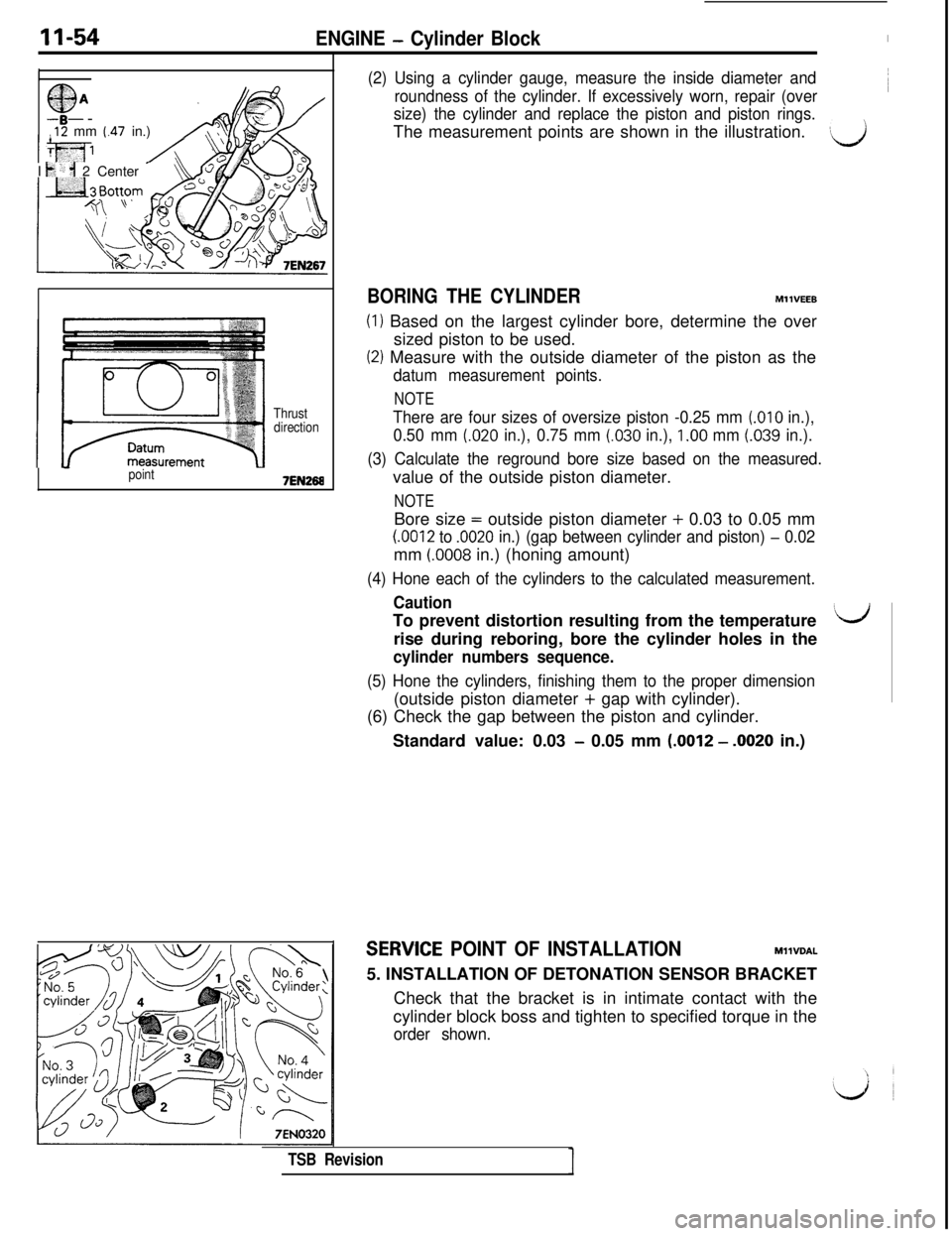
11-54ENGINE - Cylinder Block
I
$jA A@/
,12 mm (.47 in.)
I
t+ ‘: ;I 2 Center -
Thrust
direction
-point7EN268
(2) Using a cylinder gauge, measure the inside diameter and
roundness of the cylinder. If excessively worn, repair (over~
size) the cylinder and replace the piston and piston rings.The measurement points are shown in the illustration.
)d
BORING THE CYLINDERMllVEEB
(1) Based on the largest cylinder bore, determine the over
sized piston to be used.
(2) Measure with the outside diameter of the piston as the
datum measurement points.
NOTE
There are four sizes of oversize piston -0.25 mm (.OlO in.),
0.50 mm
(.020 in.), 0.75 mm (.030 in.), 1.00 mm (.039 in.).
(3) Calculate the reground bore size based on the measured.value of the outside piston diameter.
NOTEBore size = outside piston diameter + 0.03 to 0.05 mm
(.0012 to .0020 in.) (gap between cylinder and piston) - 0.02mm (0008 in.) (honing amount)
(4) Hone each of the cylinders to the calculated measurement.
CautionTo prevent distortion resulting from the temperature‘drise during reboring, bore the cylinder holes in the
cylinder numbers sequence.
(5) Hone the cylinders, finishing them to the proper dimension(outside piston diameter + gap with cylinder).
(6) Check the gap between the piston and cylinder.
Standard value: 0.03
- 0.05 mm (.0012 - .0020 in.)
SERWCE POINT OF INSTALLATIONMllVDAL
5. INSTALLATION OF DETONATION SENSOR BRACKET
Check that the bracket is in intimate contact with the
cylinder block boss and tighten to specified torque in the
order shown.
TSB Revision
Page 105 of 1146
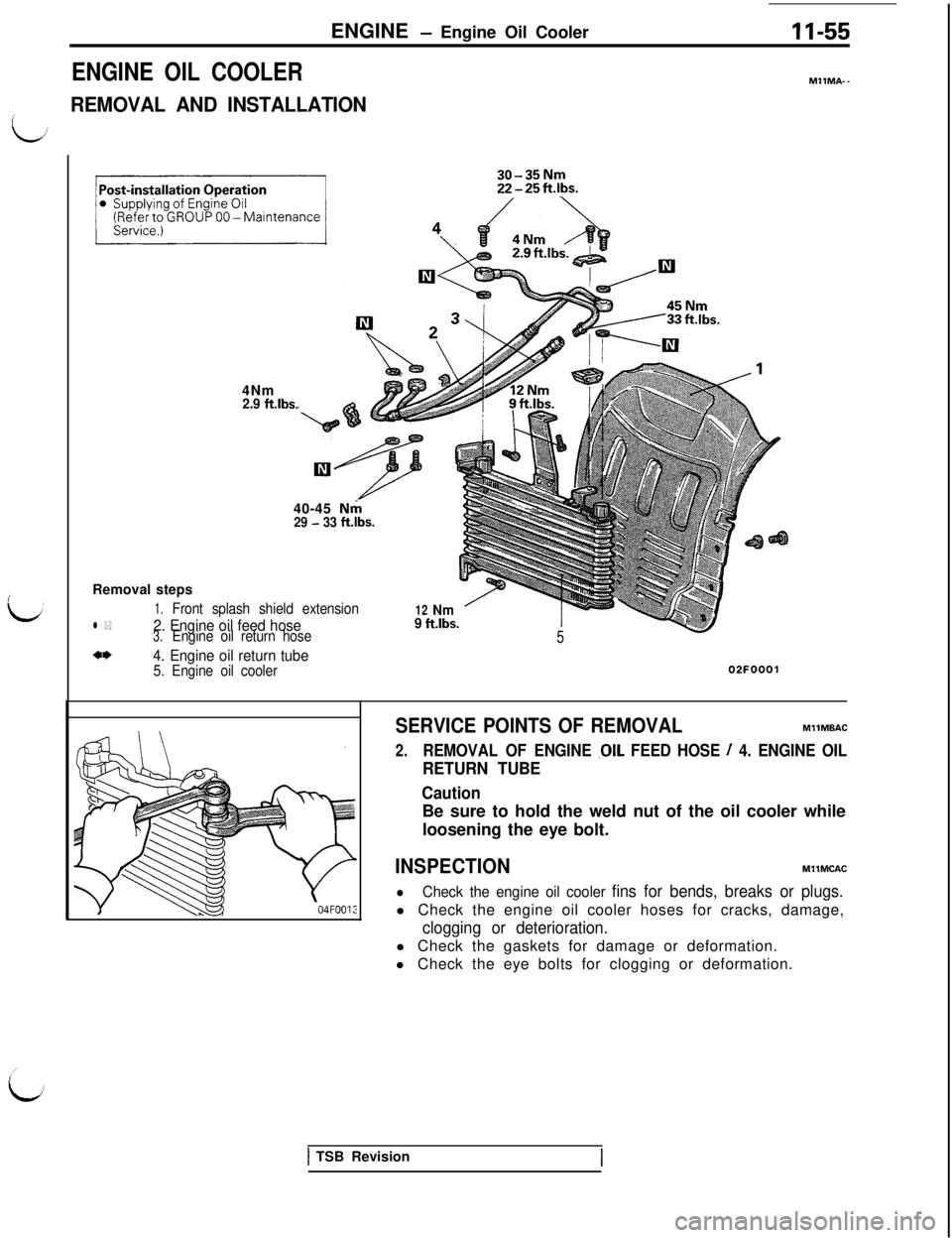
ENGINE - Engine Oil Cooler
ENGINE OIL COOLER
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
11-55
MllMA-.4Nm
2.9 ft.lbs.40-45
Nrh
29 - 33 ft.lbs.Removal steps
1.Front splash shield extensionl *2. Engine oil feed hose3.Engine oil return hose
4*4. Engine oil return tube5. Engine oil cooler
12Nm
9 ft.lbs.5
02FOOOi
SERVICE POINTS OF REMOVALMllMBAC
2.REMOVAL OF ENGINE .OIL FEED HOSE / 4. ENGINE OIL
RETURN TUBE
CautionBe sure to hold the weld nut of the oil cooler while
loosening the eye bolt.
INSPECTIONMllMCAC
l
Check the engine oil cooler fins for bends, breaks or plugs.l Check the engine oil cooler hoses for cracks, damage,
clogging or deterioration.l Check the gaskets for damage or deformation.
l Check the eye bolts for clogging or deformation.
1 TSB Revision
Page 107 of 1146

FUEL
SYSTEM
CONTENTSM13AA- _
CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .158SPECIFICATIONS. . . . . . . .._._....................................................155
CRUISE CONTROL SYSTEM*................................................185
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES............................178
Cruise Control Cables Inspection and Adjustment........178Cruise Control SystemInspection....................................179individual Parts Inspection....................................................181
SPECIAL TOOLS........................................................................159
SPECIFICATIONS....................................................................158
General Specifications........................................................158Service Specifications........................................................158
TROUBLESHOOTING............................................................159
Check Chart............................................................................163Harness and Components Layout....................................176Preliminary Inspection........................................................159Self-diagnosis Checking........................................................172Troubleshooting Quick Reference Chart............................159
ENGINE CONTROL............................................155
ENGINE CONTROL................................................................157
SERVICE ADJUSTMENT PROCEDURES............................156
Accelerator Cable Inspection and Adjustment................156Accelerator Switch Inspection and Adjustment................156
Service Specifications........................................................
155
TROUBLESHOOTING............................................................
155
Accelerator Cable and Accelerator Pedal........................155
FUEL SYSTEM....................................................3
DETONATION SENSOR........................................................154
FUEL FILTER............................................................................
153
FUEL LINE AND VAPOR LINE................................................151
FUEL PUMP AND FUEL GAUGE UNIT ASSEMBLYAND OVERFILL LIMITER (TWO-WAY VALVE)................149
FUEL TANK.................................................................................146
GENERAL INFORMATION
....................................................
3
MPI System Diagram............................................................3
INJECTOR................................................................................141
ON-VEHICLE INSPECTION OF MPI COMPONENTS........36
Active Exhaust Control Unit
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS)
(1)A Supplemental Restraint System (SRS), which uses a driver-side air bag, has been installed in the 3000GT.(2)The SRS includes the following components: impact sensors, SRS diagnosis unit: SRS warning light, air bagmodule, clock spring, interconnecting wiring. Other SRS-related components (that may have to be
removed/installed in connection with SRS service or maintenance) are indicated in the table of contents byan asterisk (*).
WARNING!(I)Improper service or maintenance of any component of the SRS, or any SRS-related component, can lead to
personal injury or death to service personnel (from inadvertent firing of the air bag) or to the driver (from
rendering the SRS inoperative).
(2) Service or maintenance of any SRS component or SRS-related component must be performed only at anauthorized MITSUBISHI dealer.
(3) MITSUBISHI dealer personnel must thoroughly review this manual, and especially its GROUP
528 -Supplemental Restraint System (SRS), before beginning any service or maintenance of any component of theSRS or any SRS-related component.