Ignition MITSUBISHI 380 2005 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: 380, Model: MITSUBISHI 380 2005Pages: 1500, PDF Size: 47.87 MB
Page 986 of 1500

CHARGING SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-9
Required Special Tool:
: Diagnostic Tool (MUT-III)
MB991824: V.C.I.
MB991827: MUT-III USB Cable
MB991910: MUT-III Main Harness A
This test determines whether the alternator outputs
normal current. For best results, use a charging sys-
tem tester. If not available, follow the steps below.
Battery posts, terminals and related acces-
sories contain lead and lead compounds.
WASH HANDS AFTER HANDLING.
1. Before the test, always be sure to check the
following.
Alternator installation
Battery (Refer to GROUP 54A, Chassis Electrical
Battery On-vehicle Service Battery Check
P.54A-5.)
NOTE: The battery to be used should be slightly
discharged. The load in a fully-charged battery
will be insufficient and the test may not be able to
be carried out correctly.
Alternator drive belt tension (Refer to GROUP 00,
General
Maintenance Service Drive Belts
(For Alternator, Power Steering Pump and Air
Conditioning) (Check) P.00-39.)
Fusible link
Abnormal noise from the alternator while the
engine is running.
2. Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF)
position.
3. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
Never use clips to connect the wire. Loose
connections (for example, using clips) will
lead to a serious accident because of high
current.
4. Connect a clamp-type DC test ammeter with a
range of 0
120 A to the alternator "B" terminal
output wire.
5. Connect a voltmeter with a range of 0
20 V
between the alternator "B" terminal and ground.
(Connect the positive lead of the voltmeter to the
"B" terminal, and then connect the negative lead
of the voltmeter to ground.)
6. Connect the negative battery cable.
7. Connect an engine tachometer or diagnostic tool.
8. Leave the hood open.9. Check to be sure that the reading on the voltmeter
is equal to the battery positive voltage.
NOTE: If the voltage is 0 V, the cause is probably
an open circuit in the wire or fusible link between
the alternator "B" terminal and the battery positive
terminal or malfunctioning voltmeter.
10.After turning on the headlights, start the engine.
NOTE: Because the current from the battery will
soon drop after the engine is started, step 11
should be carried out as quickly as possible in
order to obtain the maximum current output value.
11.Immediately after setting the headlights to high
beam and turning the heater blower switch to the
highest position, increase the engine speed to
2,500 r/min and read the maximum current output
value displayed on the ammeter.
Limit value: 70 % of nominal current output
NOTE: For the nominal current output, refer to the
Alternator Specifications.
NOTE: The current output value will depend on
the electrical load and the temperature of the
alternator body.
NOTE: If the electrical load is small while testing,
the specified level of current may not be output
even though the alternator is normal. In such
cases, increase the electrical load by leaving the
headlights turned on for some time to discharge
the battery or by using the lighting system in
another vehicle, and then test again.
NOTE: The specified level of current also may not
be output if the temperature of the alternator body
or the ambient temperature is too high. In such
cases, cool the alternator and then test again.
12.The reading on the ammeter should be above the
limit value. If the reading is below the limit value
and the alternator output wire is normal, remove
the alternator from the engine and check the
alternator.
13.Run the engine at idle speed after the test.
14.Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF)
position.
15.Disconnect the engine tachometer or diagnostic
tool.
16.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
17.Disconnect the ammeter and voltmeter .
18.Connect the negative battery cable.
19.Run the engine for 10 minutes at an idle.
Page 987 of 1500
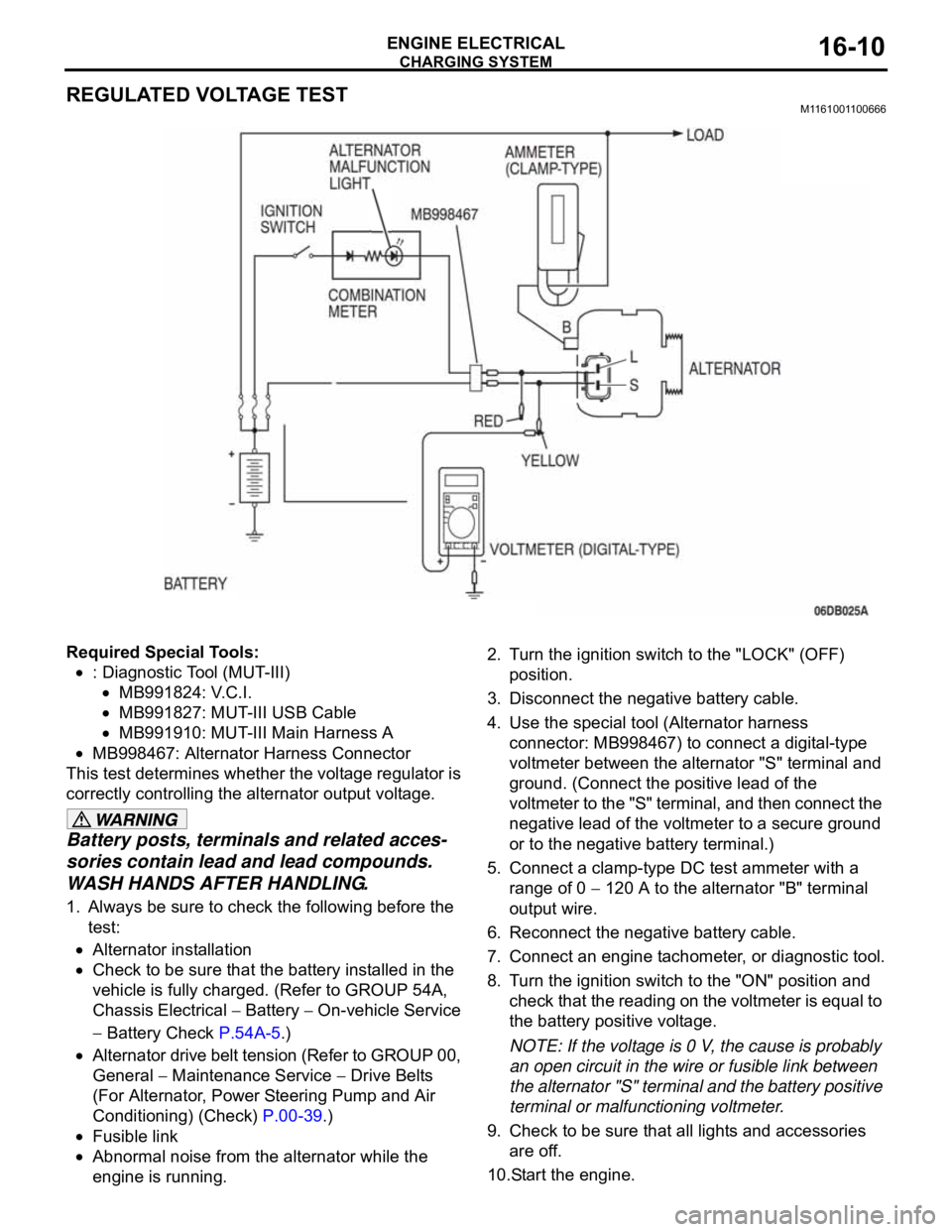
CHARGING SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-10
REGULATED VOLTAGE TESTM1161001100666
Required Special Tools:
: Diagnostic Tool (MUT-III)
MB991824: V.C.I.
MB991827: MUT-III USB Cable
MB991910: MUT-III Main Harness A
MB998467: Alternator Harness Connector
This test determines whether the voltage regulator is
correctly controlling the alternator output voltage.
Battery posts, terminals and related acces-
sories contain lead and lead compounds.
WASH HANDS AFTER HANDLING.
1. Always be sure to check the following before the
test:
Alternator installation
Check to be sure that the battery installed in the
vehicle is fully charged. (Refer to GROUP 54A,
Chassis Electrical
Battery On-vehicle Service
Battery Check P.54A-5.)
Alternator drive belt tension (Refer to GROUP 00,
General
Maintenance Service Drive Belts
(For Alternator, Power Steering Pump and Air
Conditioning) (Check) P.00-39.)
Fusible link
Abnormal noise from the alternator while the
engine is running.2. Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF)
position.
3. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
4. Use the special tool (Alternator harness
connector: MB998467) to connect a digital-type
voltmeter between the alternator "S" terminal and
ground. (Connect the positive lead of the
voltmeter to the "S" terminal, and then connect the
negative lead of the voltmeter to a secure ground
or to the negative battery terminal.)
5. Connect a clamp-type DC test ammeter with a
range of 0
120 A to the alternator "B" terminal
output wire.
6. Reconnect the negative battery cable.
7. Connect an engine tachometer, or diagnostic tool.
8. Turn the ignition switch to the "ON" position and
check that the reading on the voltmeter is equal to
the battery positive voltage.
NOTE: If the voltage is 0 V, the cause is probably
an open circuit in the wire or fusible link between
the alternator "S" terminal and the battery positive
terminal or malfunctioning voltmeter.
9. Check to be sure that all lights and accessories
are off.
10.Start the engine.
Page 988 of 1500
CHARGING SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-11
11.Increase the engine speed to 2,500 r/min.
12.Read the value displayed on the voltmeter when
the current output by the alternator becomes 10 A
or less.
13.If the voltage reading conforms to the value in the
voltage regulation table, then the voltage regulator
is operating normally.
If the voltage is outside the standard value, there
is a malfunction of the voltage regulator or the
alternator (Refer to the following table).14.After the test, lower the engine speed to idle.
15.Turn the ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF)
position.
16.Disconnect the engine tachometer or diagnostic
tool .
17.Disconnect the negative battery cable.
18.Disconnect the ammeter and voltmeter.
19.Connect the negative battery cable.
20.Run the engine for 10 minutes at an idle.
VOLTAGE REGULATION TABLE
WAVE PATTERN CHECK USING AN
OSCILLOSCOPE
M1161001200180.
MEASUREMENT METHOD
Connect the oscilloscope special patterns pick-up to the
alternator "B" terminal.
.
STANDARD WAVEFORM
INSPECTION TERMINAL VOLTAGE REGULATOR
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE [
C
(
F)]STANDARD VALUE (V)
Te r m i n a l " S "
20 (4)14.2 15.4
20 (68) 13.9
14.9
60 (140) 13.4
14.5
80 (176) 13.1
14.2
Observation Conditions
FUNCTION SPECIAL PATTERNS
Pattern height Variable
Variable knob Adjust while viewing the wave
pattern
Pattern selector Raster
Engine revolutions Curb idle speed
Page 997 of 1500
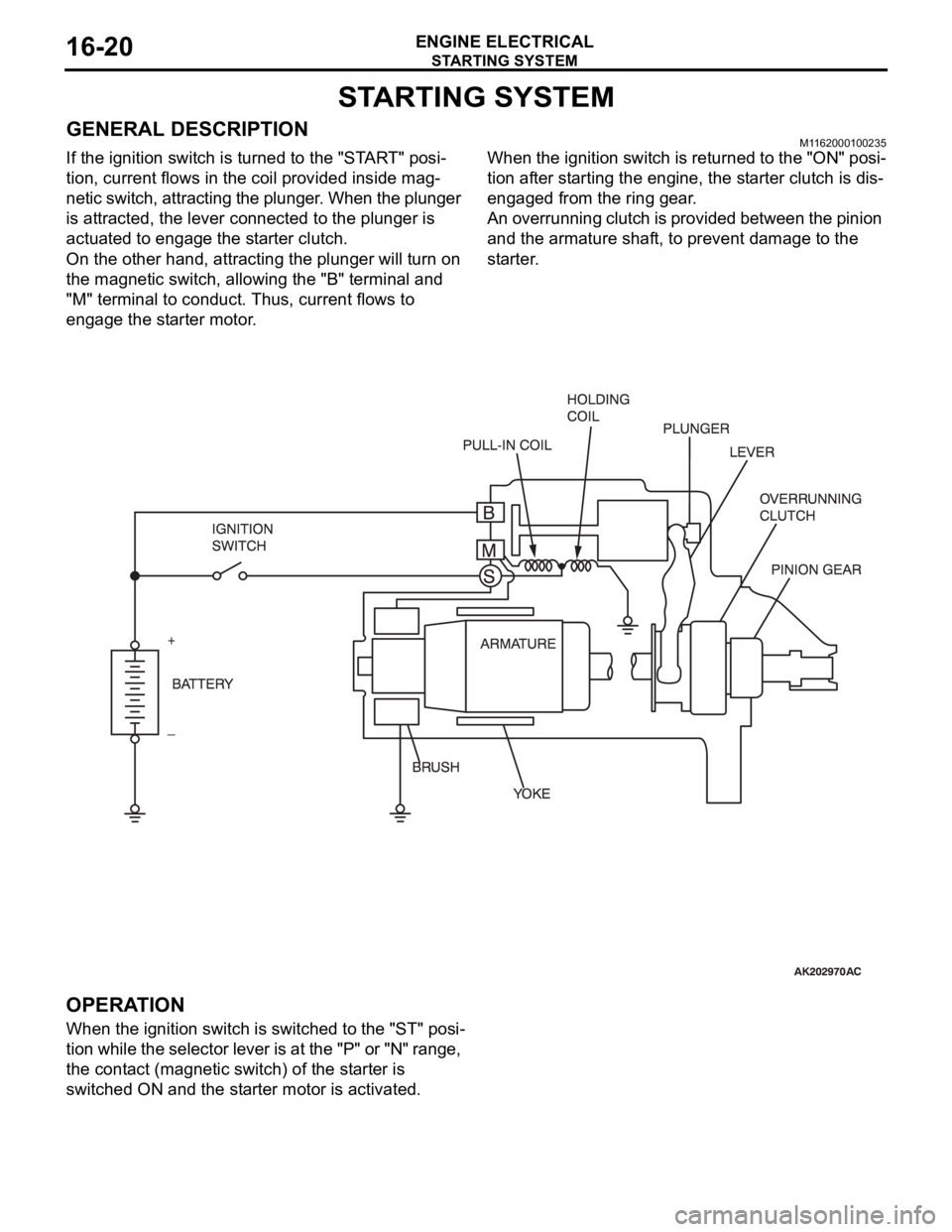
STARTING SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-20
STARTING SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTIONM1162000100235
If the ignition switch is turned to the "START" posi-
tion, current flows in the coil provided inside mag-
netic switch, attracting the plunger. When the plunger
is attracted, the lever connected to the plunger is
actuated to engage the starter clutch.
On the other hand, attracting the plunger will turn on
the magnetic switch, allowing the "B" terminal and
"M" terminal to conduct. Thus, current flows to
engage the starter motor.When the ignition switch is returned to the "ON" posi-
tion after starting the engine, the starter clutch is dis-
engaged from the ring gear.
An overrunning clutch is provided between the pinion
and the armature shaft, to prevent damage to the
starter.
OPERATION
When the ignition switch is switched to the "ST" posi-
tion while the selector lever is at the "P" or "N" range,
the contact (magnetic switch) of the starter is
switched ON and the starter motor is activated.
Page 998 of 1500

STARTING SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-21
STARTING SYSTEM DIAGNOSISM1162000700293
TROUBLESHOOTING HINTS
The starter motor does not operate at all.
Battery posts, terminals and related accessories con-
tain lead and lead compounds. WASH HANDS AFTER
HANDLING.
Check the starter (coil).
Check for poor contact at the battery terminals and
starter.
Check the transmission range switch.
The starter motor doesn't stop
Check the starter (magnetic switch).
TROUBLESHOOTING GUIDE
The starting system troubleshooting guide is shown in the fol-
lowing steps.
Battery posts, terminals and related accessories con-
tain lead and lead compounds. WASH HANDS AFTER
HANDLING.
STEP 1.
Q: Is the battery in good condition? (Refer to GROUP 54A,
Chassis Electrical
Battery On-vehicle Service
Battery Check P.54A-5.)
YES : Go to Step 2.
NO : Charge or replace the battery.
STEP 2.
Disconnect the starter motor S (solenoid) terminal connec-
tor.
Using a jumper wire, apply battery positive voltage to the
starter motor S (solenoid) terminal.
Check the engine condition.
OK: Turns normally
Q: Dose the starter motor operate normally?
YES :
Check the ignition switch (Refer to GROUP 54A,
Chassis Electrical
Ignition Switch Ignition
Switch
Inspection P.54A-44.)
Check the transmission range switch. (Refer to
GROUP 23A, Automatic Transaxle
On-vehicle
Service
Essential Service Transmission Range
Switch Check P.23A-294.)
Check the wire between the battery and starter
motor S (solenoid) terminal.
NO : Go to Step 3.
Page 1007 of 1500
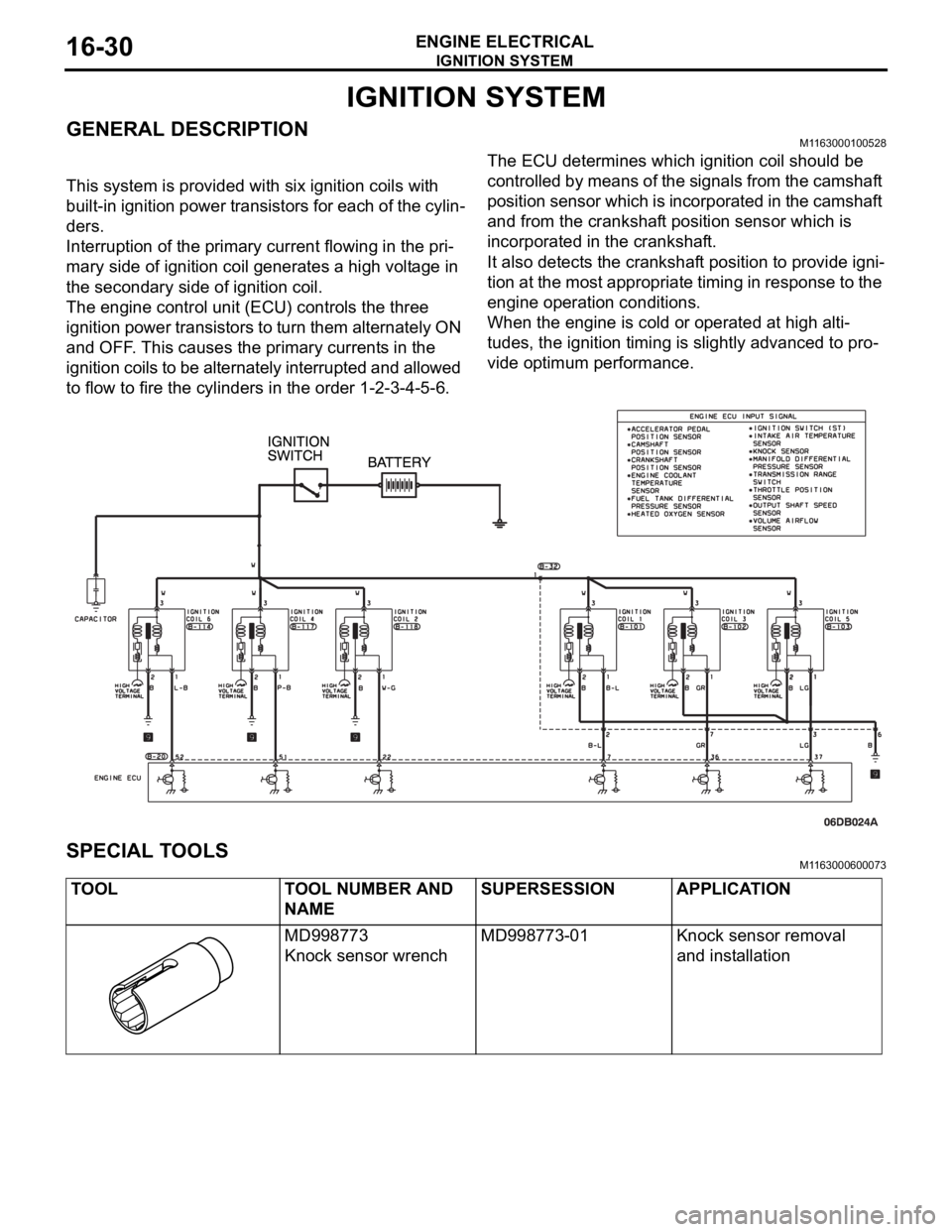
IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-30
IGNITION SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTIONM1163000100528
This system is provided with six ignition coils with
built-in ignition power transistors for each of the cylin-
ders.
Interruption of the primary current flowing in the pri-
mary side of ignition coil generates a high voltage in
the secondary side of ignition coil.
The engine control unit (ECU) controls the three
ignition power transistors to turn them alternately ON
and OFF. This causes the primary currents in the
ignition coils to be alternately interrupted and allowed
to flow to fire the cylinders in the order 1-2-3-4-5-6.The ECU determines which ignition coil should be
controlled by means of the signals from the camshaft
position sensor which is incorporated in the camshaft
and from the crankshaft position sensor which is
incorporated in the crankshaft.
It also detects the crankshaft position to provide igni-
tion at the most appropriate timing in response to the
engine operation conditions.
When the engine is cold or operated at high alti-
tudes, the ignition timing is slightly advanced to pro-
vide optimum performance.
SPECIAL TOOLSM1163000600073
TOOL TOOL NUMBER AND
NAMESUPERSESSION APPLICATION
MD998773
Knock sensor wrenchMD998773-01 Knock sensor removal
and installation
Page 1008 of 1500

IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-31
ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
KNOCK CONTROL SYSTEM CHECKM1163001800081
Check the knock sensor circuit if diagnostic trouble code, No.
P0325 is shown.
Refer to GROUP 13B, Multiport Fuel Injection (MPI)
Multiport
Fuel Injection (MPI) Diagnosis
Diagnostic Trouble Code Pro-
cedures
DTC P0325 : Knock Sensor Circuit 13A-346.
IGNITION COIL CHECK M1163001200380
Check by the following procedure, and replace the coil if there
is a malfunction.
.
PRIMARY COIL AND IGNITION POWER
TRANSISTOR CONTINUITY CHECK
NOTE: No test can be performed on the Primary side of coil.
.
SECONDARY COIL CHECK
NOTE: It is impossible to check the secondary coil through the
continuity check as a diode is integrated in the secondary coil
circuit of this ignition coil. Accordingly, check the secondary coil
in the following procedure.
1. Disconnect the ignition coil connector.
2. Remove the ignition coil and install a new spark plug to the
ignition coil.
3. Connect the ignition coil connector.
4. Disable vehicle fuel pump by removing fuel pump relay or
disconnecting fuel pump connector D-18 (under rear seat).
5. Ground the side electrode of the spark plug and crank the
engine.
6. Check that spark is produced between the electrodes of the
spark plug.
7. If no spark is produced, replace the ignition coil with a new
one and recheck.
8. If spark is produced with the new ignition coil, replace the
old one as it is faulty. If no spark is produced again, the
ignition circuit is suspected as faulty. Check the ignition
circuit.
Page 1009 of 1500
IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-32
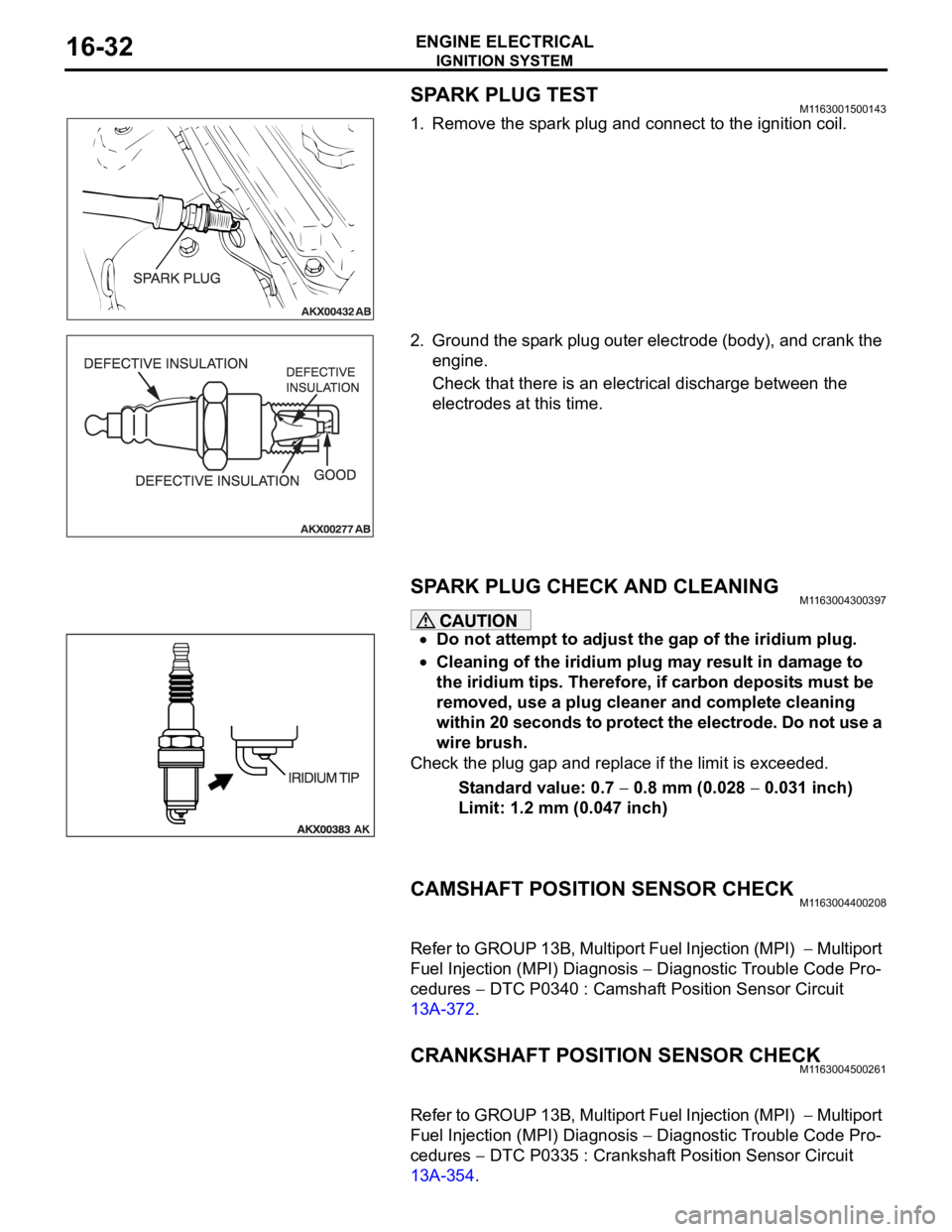
SPARK PLUG TESTM1163001500143
1. Remove the spark plug and connect to the ignition coil.
2. Ground the spark plug outer electrode (body), and crank the
engine.
Check that there is an electrical discharge between the
electrodes at this time.
SPARK PLUG CHECK AND CLEANING M1163004300397
Do not attempt to adjust the gap of the iridium plug.
Cleaning of the iridium plug may result in damage to
the iridium tips. Therefore, if carbon deposits must be
removed, use a plug cleaner and complete cleaning
within 20 seconds to protect the electrode. Do not use a
wire brush.
Check the plug gap and replace if the limit is exceeded.
Standard value: 0.7
0.8 mm (0.028 0.031 inch)
Limit: 1.2 mm (0.047 inch)
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR CHECKM1163004400208
Refer to GROUP 13B, Multiport Fuel Injection (MPI) Multiport
Fuel Injection (MPI) Diagnosis
Diagnostic Trouble Code Pro-
cedures
DTC P0340 : Camshaft Position Sensor Circuit
13A-372.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR CHECKM1163004500261
Refer to GROUP 13B, Multiport Fuel Injection (MPI) Multiport
Fuel Injection (MPI) Diagnosis
Diagnostic Trouble Code Pro-
cedures
DTC P0335 : Crankshaft Position Sensor Circuit
13A-354.
Page 1010 of 1500
IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-33
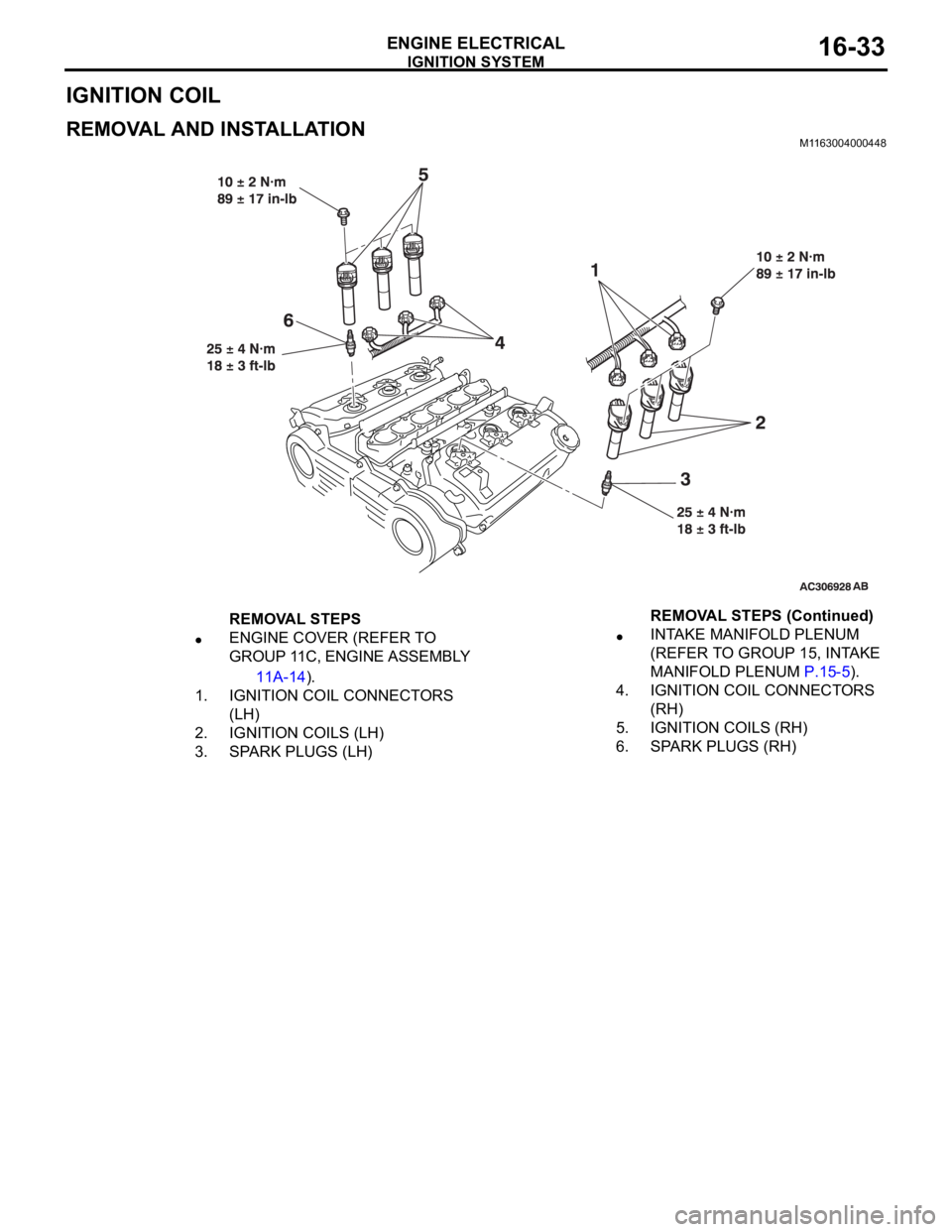
IGNITION COIL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION M1163004000448
REMOVAL STEPS
ENGINE COVER (REFER TO
GROUP 11C, ENGINE ASSEMBLY
11A-14).
1. IGNITION COIL CONNECTORS
(LH)
2. IGNITION COILS (LH)
3. SPARK PLUGS (LH)INTAKE MANIFOLD PLENUM
(REFER TO GROUP 15, INTAKE
MANIFOLD PLENUM P.15-5).
4. IGNITION COIL CONNECTORS
(RH)
5. IGNITION COILS (RH)
6. SPARK PLUGS (RH)REMOVAL STEPS (Continued)
Page 1011 of 1500
IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-34
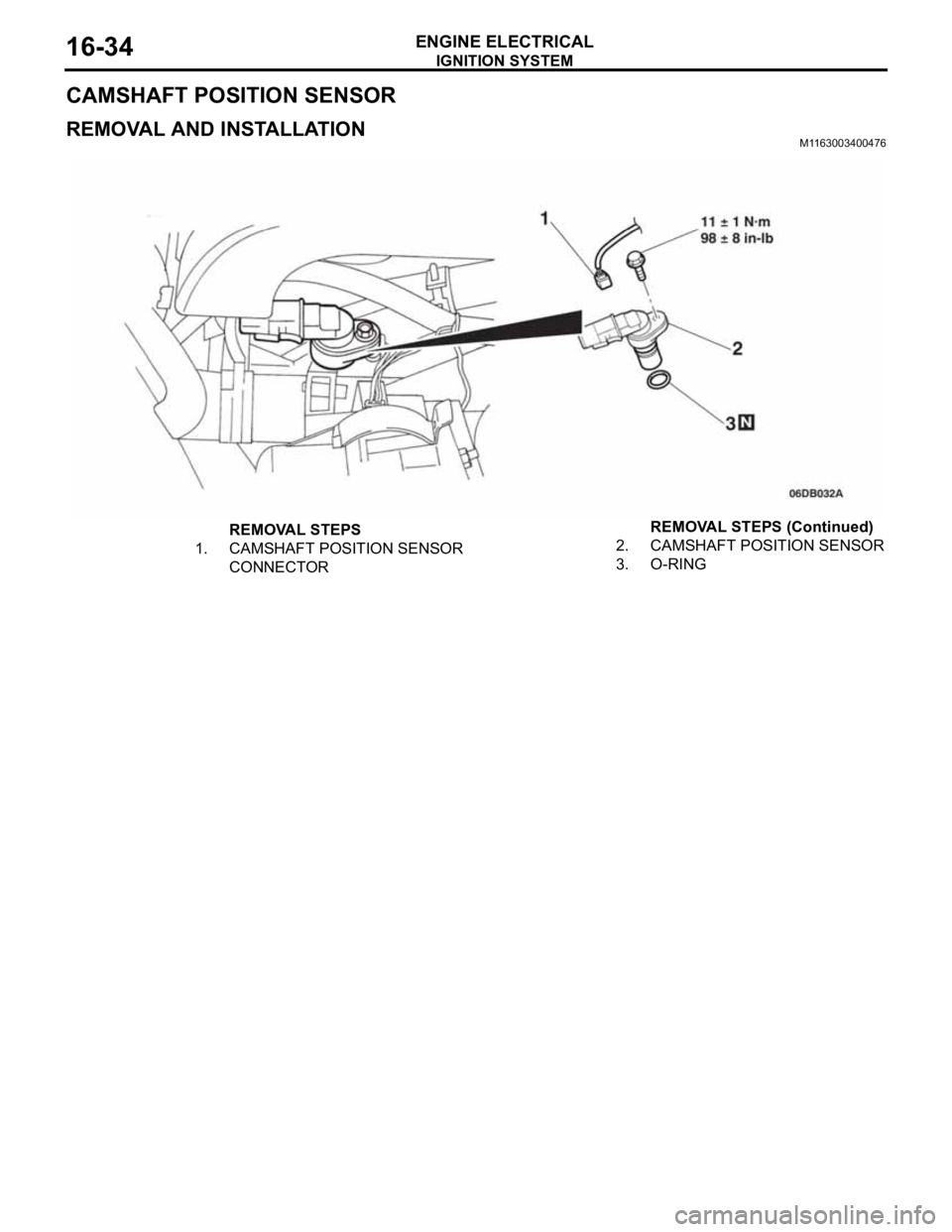
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION M1163003400476
REMOVAL STEPS
1. CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
CONNECTOR2. CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
3. O-RINGREMOVAL STEPS (Continued)