Exhaust MITSUBISHI 380 2005 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: 380, Model: MITSUBISHI 380 2005Pages: 1500, PDF Size: 47.87 MB
Page 706 of 1500
AUTO A/C DIAGNOSIS
HEATER, AIR CONDITIONING AND VENTILATION55-5
AUTO A/C DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTIONM1554006200062
After air is taken in through the damper, it is fed to
the evaporator by the blower fan and motor and
cooled. The air cooled by the air mix damper is
mixed appropriately with the warmed air to achieve a
comfortable temperature. If the A/C does not operate
or the cooled air is not discharged, the system com-
ponents or relay may be faulty.
AUTOMATIC AIR CONDITIONING TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGYM1554004700157
Use these steps to plan your diagnostic strategy. If
you follow them carefully, you will be sure that you
have exhausted most of the possible ways to find a
heater, air conditioning and ventilation fault.
1. Gather information from the customer.2. Verify that the condition described by the
customer exists.
3. Find the malfunction by following the Symptom
Chart.
4. Verify malfunction is eliminated.
DIAGNOSTIC FUNCTIONM1552019800046
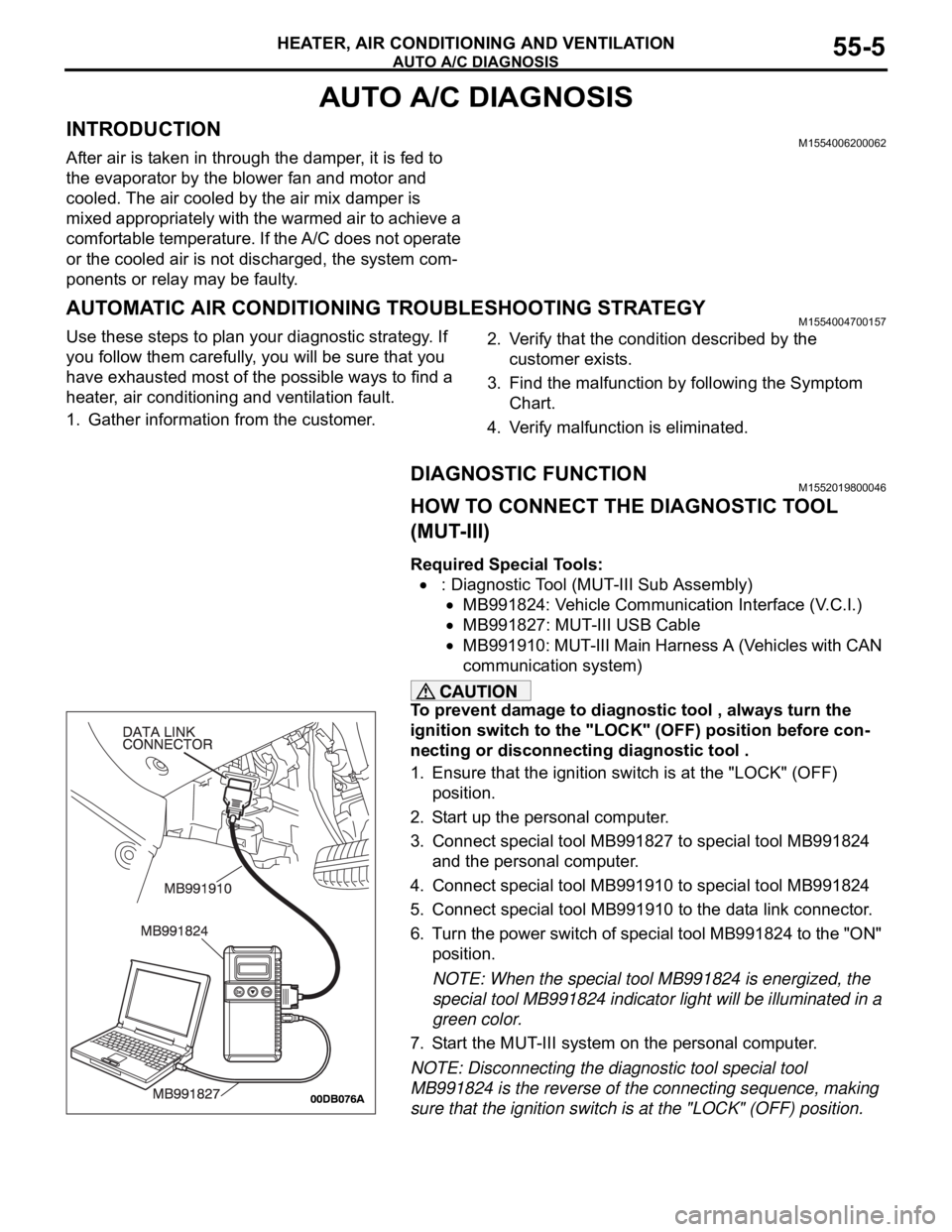
HOW TO CONNECT THE DIAGNOSTIC TOOL
(MUT-III)
Required Special Tools:
: Diagnostic Tool (MUT-III Sub Assembly)
MB991824: Vehicle Communication Interface (V.C.I.)
MB991827: MUT-III USB Cable
MB991910: MUT-III Main Harness A (Vehicles with CAN
communication system)
To prevent damage to diagnostic tool , always turn the
ignition switch to the "LOCK" (OFF) position before con-
necting or disconnecting diagnostic tool .
1. Ensure that the ignition switch is at the "LOCK" (OFF)
position.
2. Start up the personal computer.
3. Connect special tool MB991827 to special tool MB991824
and the personal computer.
4. Connect special tool MB991910 to special tool MB991824
5. Connect special tool MB991910 to the data link connector.
6. Turn the power switch of special tool MB991824 to the "ON"
position.
NOTE: When the special tool MB991824 is energized, the
special tool MB991824 indicator light will be illuminated in a
green color.
7. Start the MUT-III system on the personal computer.
NOTE: Disconnecting the diagnostic tool special tool
MB991824 is the reverse of the connecting sequence, making
sure that the ignition switch is at the "LOCK" (OFF) position.
Page 847 of 1500

ON-VEHICLE SERVICE
HEATER, AIR CONDITIONING AND VENTILATION55-146
Sharper bends will reduce the flow of refrigerant. The flexible
hose lines should be routed so that they are at least 80 mm
(3.1 inches) from the exhaust manifold. It is good practice to
inspect all flexible hose lines at least once a year to make sure
they are in good condition and properly routed.
On standard plumbing fittings with O-rings, these O-rings are
not reusable.
AIR CONDITIONING NOISE TEST
You must first know the conditions when the noise occurs.
These conditions are: weather, vehicle speed, in gear or neu-
tral, engine temperature or any other special conditions.
Noises that develop during A/C operation can often be mislead-
ing. For example: what sounds like a failed front bearing or
connecting rod, may be caused by loose bolts, nuts, mounting
brackets, or a loose clutch assembly. Verify accessory drive
belt tension (power steering or generator).
Improper accessory drive belt tension can cause a misleading
noise when the compressor is engaged and little or no noise
when the compressor is disengaged.
Drive belts are speed-sensitive. That is, at different engine
speeds, and depending upon belt tension, belts can develop
unusual noises that are often mistaken for mechanical prob-
lems within the compressor.
Normal air conditioning operation will generate some level of
operational noise. To judge what is normal and abnormal,
requires an understanding of the air conditioning system. This
test is to detail the most common noise complaints and the
repair methods.
VEHICLE CONDITION
1. Ensure the system is not over or under charged.(Refer to
P.55-142).
2. Tighten all compressor mounting bolts, clutch mounting
bolts and compressor drive belt.
3. Inspect layout of the system is correct, ie no interference
between hoses and all retaining clamps are in place.
Page 910 of 1500
HOW TO DIAGNOSE
GENERAL
CABLES AND WIRES CHECKM1001005100041
1. Check connections for looseness, rust, and stains.
2. Check terminals and wires for corrosion.
3. Check terminals and wires for open circuit or impending
open circuit.
4. Check wire insulation and coating for damage, cracks, and
wear.
5. Check conductive parts of terminals for contact with other
metallic parts (vehicle body and other parts).
6. Check grounding parts to verify that there is complete
continuity between attaching bolt(s) and vehicle body.
7. Check for incorrect wiring.
8. Check that harnesses are secured to prevent contact with
sharp edges and corners or hot parts (exhaust manifold,
pipe, etc.).
9. Check that harnesses are secured firmly to provide enough
clearance from the fan pulley, fan belt, and other rotating or
moving parts.
10.Check that the harnesses between fixed parts (such as the
vehicle body) and vibrating parts (such as the engine) are
long enough to allow for vibration and movement.
BATTERY HANDLINGM1001005200048
Battery posts, terminals and related accessories con-
tain lead and lead compounds. WASH HANDS AFTER
HANDLING.
When checking or servicing does not require power from the
vehicle battery, be sure to disconnect the cable from the battery
(
) terminal. This will prevent problems that could be caused by
a short circuit. Disconnect the (
) battery terminal first and
reconnect it last.
GENERAL ELECTRICAL SYSTEM CHECKM1001005300045
A circuit consists of the power supply, switch, relay, load,
ground, etc. There are various methods to check a circuit
including an overall check, voltage check, short-circuit check,
and continuity check. Each of the methods briefly described
below applies only to circuits similar to the illustration.
Page 960 of 1500

15-1
GROUP 15
INTAKE AND
EXHAUST
CONTENTS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION. . . . . . . . .15-2
INTAKE AND EXHAUST DIAGNOSIS15-2
INTRODUCTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-2
TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGY . . . . . . 15-2
SYMPTOM CHART. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-2
SYMPTOM PROCEDURES . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-2
SPECIAL TOOLS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-3
AIR CLEANER . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-4
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . 15-4
INTAKE MANIFOLD PLENUM . . . . .15-5
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION . . . . . . . 15-5
INTAKE MANIFOLD . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . 15-7
INSPECTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-9
EXHAUST MANIFOLD . . . . . . . . . . . .15-10
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . 15-10
INSPECTION. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-13
EXHAUST PIPE AND MAIN MUFFLER15-14
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION . . . . . . . . 15-14
SPECIFICATIONS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .15-16
FASTENER TIGHTENING SPECIFICATIONS15-16
SERVICE SPECIFICATION . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-18
SEALANTS . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . 15-18
Page 961 of 1500

GENERAL DESCRIPTION
INTAKE AND EXHAUST15-2
GENERAL DESCRIPTIONM1151000100446
The exhaust pipe is divided into four parts.
INTAKE AND EXHAUST DIAGNOSIS
INTRODUCTIONM1151006900321
Intake leaks usually create driveability issues that
are not obviously related to the intake system.
Exhaust leaks or abnormal noise is caused by
cracks, gaskets and fittings, or by exhaust pipe or
muffler damage due to impacts during travel. The
exhaust leaks from these sections and causes the
exhaust noise to increase. There may be cases
when the system contacts the body and vibration
noise is generated.
TROUBLESHOOTING STRATEGYM1151007000321
Use these steps to plan your diagnostic strategy. If
you follow them carefully, you will be sure that you
have exhausted most of the possible ways to find an
intake or exhaust system fault.
1. Gather information from the customer.2. Verify that the condition described by the
customer exists.
3. Find the malfunction by following the Symptom
Chart.
4. Verify malfunction is eliminated.
SYMPTOM CHARTM1151007100328
SYMPTOM PROCEDURES
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 1: Exhaust Leakage
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Start the engine. Have an assistant stay
in the driver’s seat. Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
Have the assistant rev the engine while
searching for exhaust leaks.
Q: Is the exhaust leaking?
YES :
Go to Step 2.
NO : The procedure is complete.
STEP 2. Check the gasket for cracks, damage.
Q: Is the gasket damaged?
YES :
Replace the gasket, then go Step 1.
NO : Go to Step 3.
STEP 3. Check for loose coupling sections.
Q: Are there any loose each sections?
YES :
Tighten, then go to Step 1.
NO : There is no action to be taken. SYMPTOM INSPECTION PROCEDURE REFERENCE PAGE
Exhaust Leakage 1
P.15-2
Abnormal Noise 2
P.15-3
Page 962 of 1500
SPECIAL TOOLS
INTAKE AND EXHAUST15-3
INSPECTION PROCEDURE 2: Abnormal Noise
DIAGNOSIS
STEP 1. Start the engine. Have an assistant stay
in the drivers seat. Raise the vehicle on a hoist.
Have the assistant rev the engine while
searching for exhaust leaks.
Q: Is any abnormal noise generated?
YES :
Go to Step 2.
NO : The procedure is complete.
STEP 2. Check for missing parts in the muffler.
Tap the muffler lightly to check for loose baffles,
etc.
Q: Are there any missing parts in the muffler?
YES :
Replace, then go to Step 1.
NO : Go to Step 3.
STEP 3. Check the hanger for cracks.
Q: Is the hanger cracked?
YES :
Replace, then go to Step 1.
NO : Go to Step 4.
STEP 4. Check for interference of the pipes and
muffler with the body.
Q: Are the pipes and muffler interfering with the
body?
YES :
Repair, then go to Step 1.
NO : Go to Step 5.
STEP 5. Check the heat protectors.
Q: Are any heat protectors loose or damaged?
YES :
Tighten or replace, then go to Step 1.
NO : Go to Step 6.
STEP 6. Check the pipes and muffler for damage.
Q: Are the pipes and muffler damaged?
YES :
Replace, then go to Step 1.
NO : There is no action to be taken.
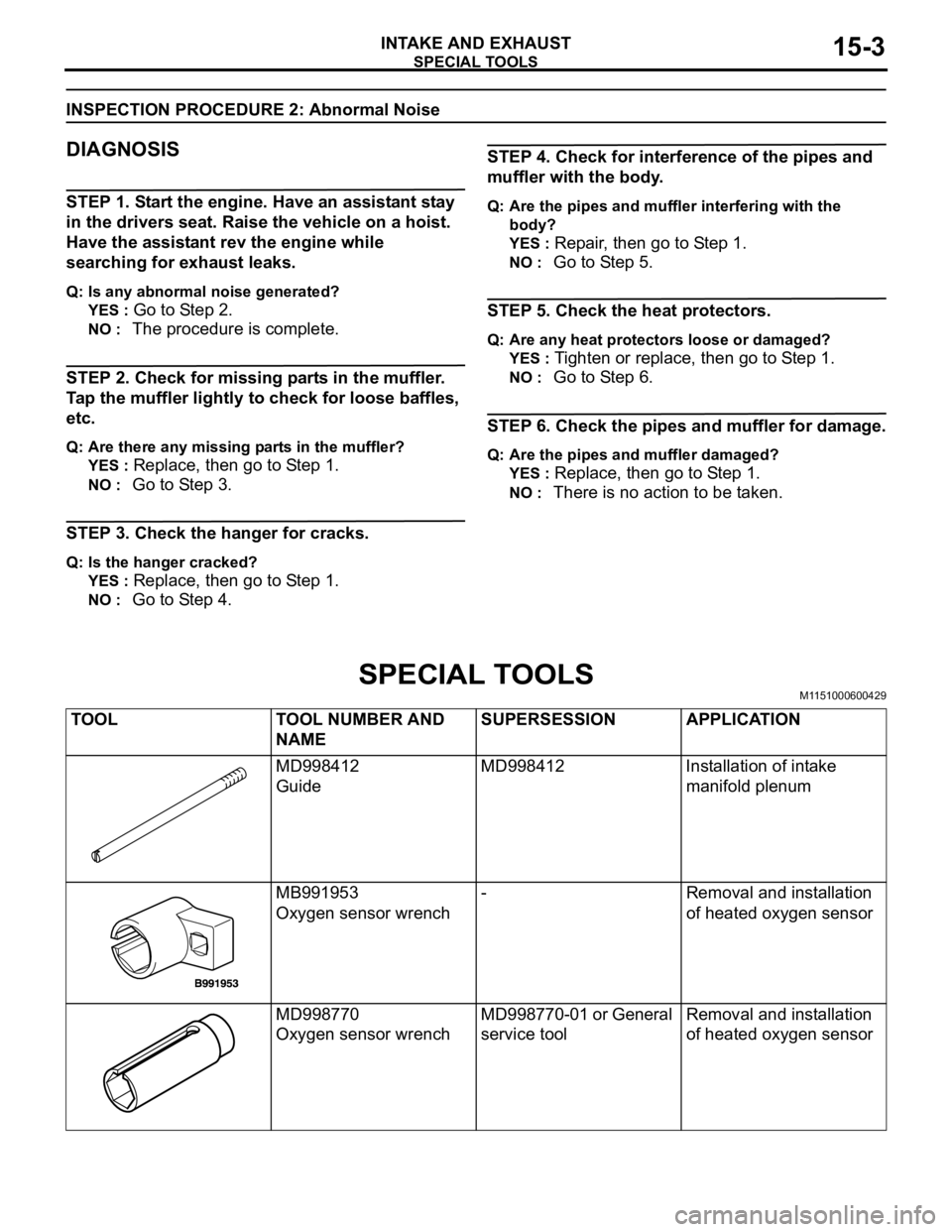
SPECIAL TOOLSM1151000600429
TOOL TOOL NUMBER AND
NAMESUPERSESSION APPLICATION
MD998412
GuideMD998412 Installation of intake
manifold plenum
MB991953
Oxygen sensor wrench- Removal and installation
of heated oxygen sensor
MD998770
Oxygen sensor wrenchMD998770-01 or General
service toolRemoval and installation
of heated oxygen sensor
Page 963 of 1500
AIR CLEANER
INTAKE AND EXHAUST15-4
AIR CLEANER
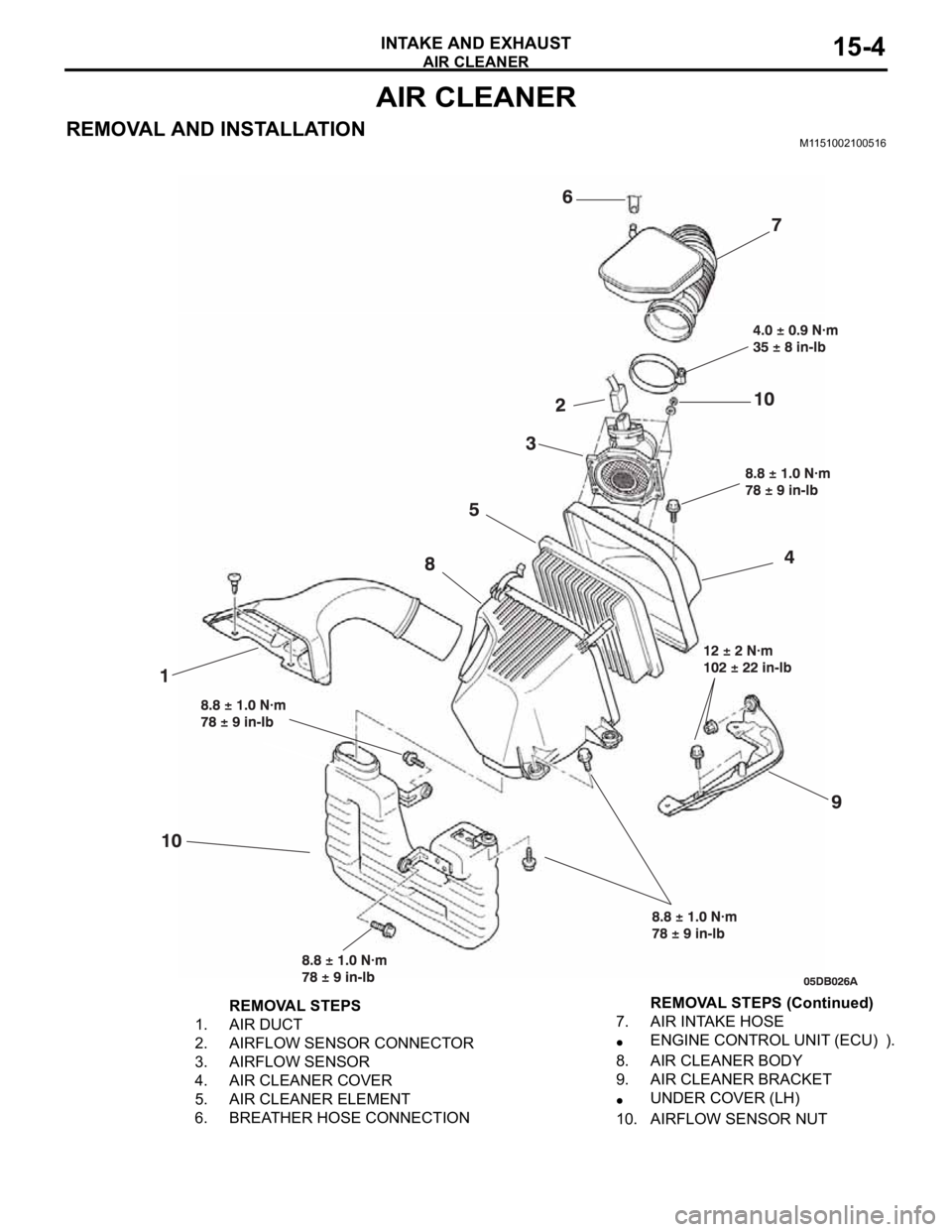
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATIONM1151002100516
REMOVAL STEPS
1. AIR DUCT
2. AIRFLOW SENSOR CONNECTOR
3. AIRFLOW SENSOR
4. AIR CLEANER COVER
5. AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
6. BREATHER HOSE CONNECTION7. AIR INTAKE HOSE
ENGINE CONTROL UNIT (ECU) ).
8. AIR CLEANER BODY
9. AIR CLEANER BRACKET
UNDER COVER (LH)
10. AIRFLOW SENSOR NUTREMOVAL STEPS (Continued)
Page 964 of 1500
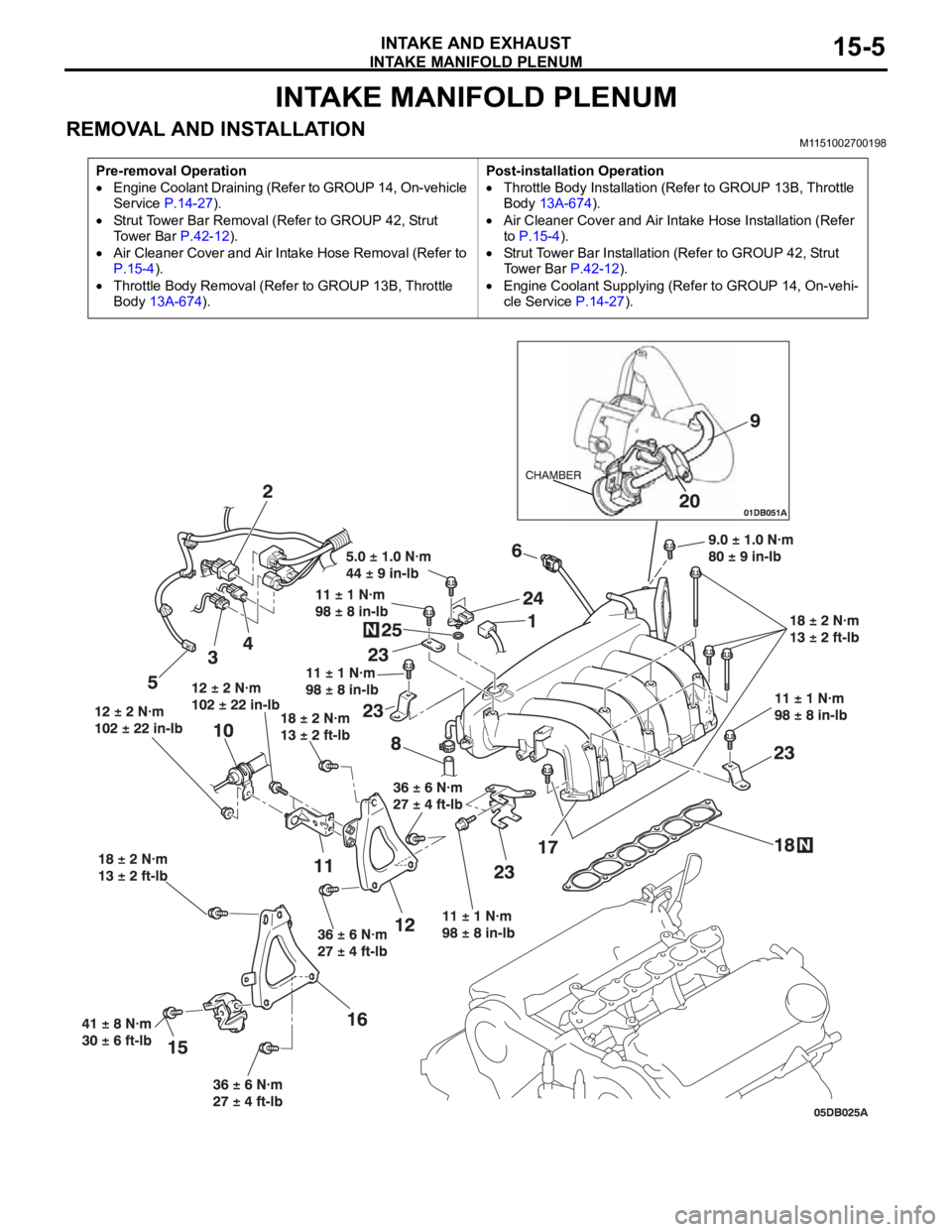
INTAKE MANIFOLD PLENUM
INTAKE AND EXHAUST15-5
INTAKE MANIFOLD PLENUM
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION M1151002700198
Pre-removal Operation
Engine Coolant Draining (Refer to GROUP 14, On-vehicle
Service P.14-27).
Strut Tower Bar Removal (Refer to GROUP 42, Strut
To w e r B a r P.42-12).
Air Cleaner Cover and Air Intake Hose Removal (Refer to
P.15-4).
Throttle Body Removal (Refer to GROUP 13B, Throttle
Body 13A-674).Post-installation Operation
Throttle Body Installation (Refer to GROUP 13B, Throttle
Body 13A-674).
Air Cleaner Cover and Air Intake Hose Installation (Refer
to P.15-4).
Strut Tower Bar Installation (Refer to GROUP 42, Strut
Tower Bar P.42-12).
Engine Coolant Supplying (Refer to GROUP 14, On-vehi-
cle Service P.14-27).
Page 965 of 1500
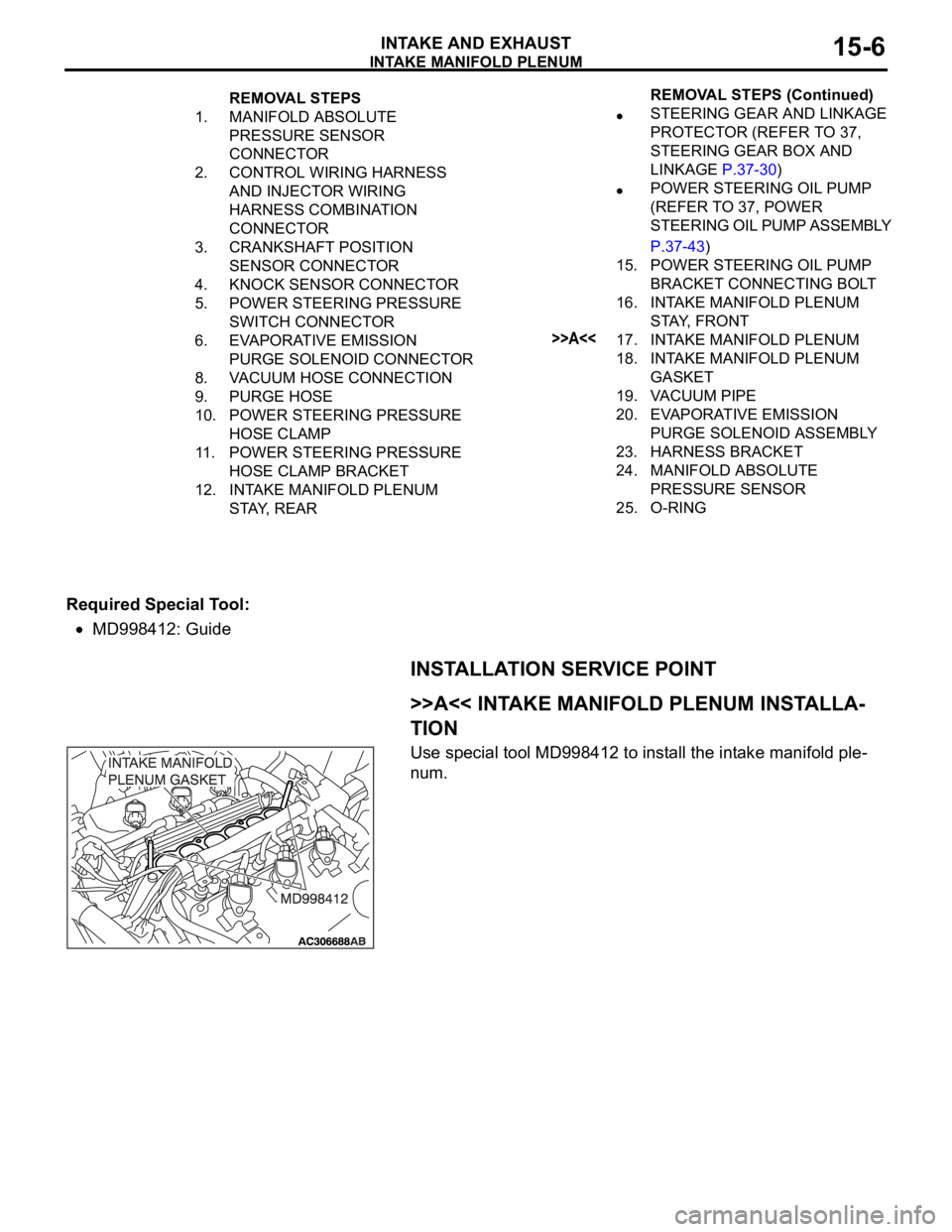
INTAKE MANIFOLD PLENUM
INTAKE AND EXHAUST15-6
Required Special Tool:
MD998412: Guide
INSTALLATION SERVICE POINT
.
>>A<< INTAKE MANIFOLD PLENUM INSTALLA-
TION
Use special tool MD998412 to install the intake manifold ple-
num.
REMOVAL STEPS
1. MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE SENSOR
CONNECTOR
2. CONTROL WIRING HARNESS
AND INJECTOR WIRING
HARNESS COMBINATION
CONNECTOR
3. CRANKSHAFT POSITION
SENSOR CONNECTOR
4. KNOCK SENSOR CONNECTOR
5. POWER STEERING PRESSURE
SWITCH CONNECTOR
6. EVAPORATIVE EMISSION
PURGE SOLENOID CONNECTOR
8. VACUUM HOSE CONNECTION
9. PURGE HOSE
10. POWER STEERING PRESSURE
HOSE CLAMP
11. POWER STEERING PRESSURE
HOSE CLAMP BRACKET
12. INTAKE MANIFOLD PLENUM
STAY, REARSTEERING GEAR AND LINKAGE
PROTECTOR (REFER TO 37,
STEERING GEAR BOX AND
LINKAGE P.37-30)
POWER STEERING OIL PUMP
(REFER TO 37, POWER
STEERING OIL PUMP ASSEMBLY
P.37-43)
15. POWER STEERING OIL PUMP
BRACKET CONNECTING BOLT
16. INTAKE MANIFOLD PLENUM
STAY, FRONT
>>A<<17. INTAKE MANIFOLD PLENUM
18. INTAKE MANIFOLD PLENUM
GASKET
19. VACUUM PIPE
20. EVAPORATIVE EMISSION
PURGE SOLENOID ASSEMBLY
23. HARNESS BRACKET
24. MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE
PRESSURE SENSOR
25. O-RINGREMOVAL STEPS (Continued)
Page 966 of 1500
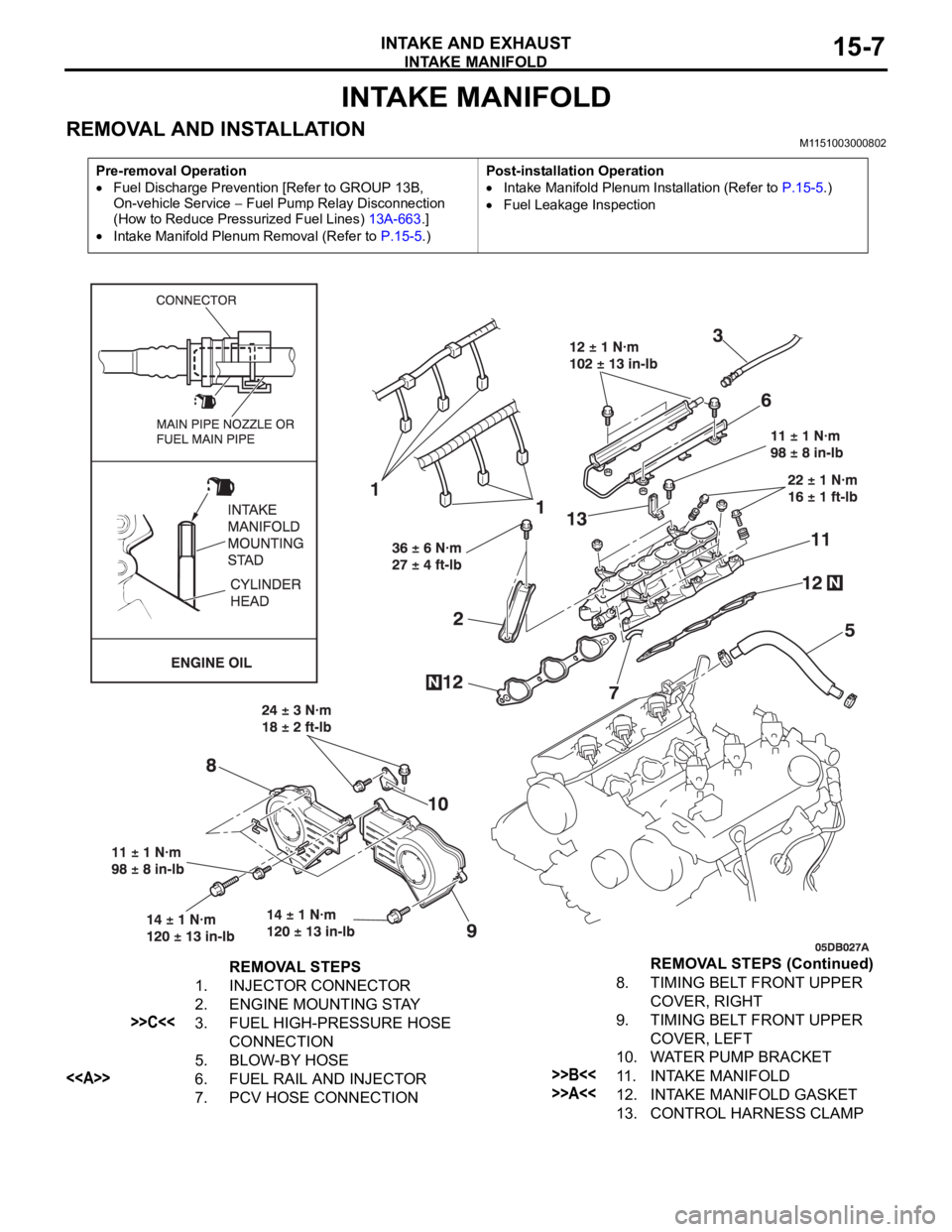
INTAKE MANIFOLD
INTAKE AND EXHAUST15-7
INTAKE MANIFOLD
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION M1151003000802
Pre-removal Operation
Fuel Discharge Prevention [Refer to GROUP 13B,
On-vehicle Service
Fuel Pump Relay Disconnection
(How to Reduce Pressurized Fuel Lines) 13A-663.]
Intake Manifold Plenum Removal (Refer to P.15-5.)Post-installation Operation
Intake Manifold Plenum Installation (Refer to P.15-5.)
Fuel Leakage Inspection
REMOVAL STEPS
1. INJECTOR CONNECTOR
2. ENGINE MOUNTING STAY
>>C<<3. FUEL HIGH-PRESSURE HOSE
CONNECTION
5. BLOW-BY HOSE
<>6. FUEL RAIL AND INJECTOR
7. PCV HOSE CONNECTION8. TIMING BELT FRONT UPPER
COVER, RIGHT
9. TIMING BELT FRONT UPPER
COVER, LEFT
10. WATER PUMP BRACKET>>B<<11. INTAKE MANIFOLD
>>A<<12. INTAKE MANIFOLD GASKET
13. CONTROL HARNESS CLAMPREMOVAL STEPS (Continued)