fuel pressure MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1990 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1990, Model line: ECLIPSE, Model: MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1990Pages: 391, PDF Size: 15.27 MB
Page 142 of 391

14-30SELF-DIAGNOSISFUEL SYSTEM- Engine Control Unit
There are 16 diagnosis items, as listed below; the
diagnosis results are stored in computer memory.The diagnosis memory is maintained by backup
The stored results can be ready by connecting apower from the battery (not by way of the ignition
circuit tester or voltmeter to the diagnosis
connec-switch) so that it will not be lost even if the ignition
switch is turned OFF.
tor.
DiagnosisOutput pattern
codeEl
None
lP
@ 11l-l
@ 12n@ 13
@ 14
@ 21Ul n
Diagnosis items
Faulty computer in the engine control unitMalfunction of the air/fuel ratio control system
Open or short circuit in the oxygen sensor circuit
Open or short circuit in the air flow sensor circuit
Open or short circuit in the intake air temperature sensor
circuit
Open or short circuit in the throttle position sensor circuit
Open or short circuit in the engine coolant temperature sensor
circuit
022u1 nn
No voltage change of the crank angle sensor signal
,
@
23
u u-inn
No voltage change of the TDC sensor signal
24uu-uvinnnnNo voltage change of the vehicle speed sensor signal
Q25uuuuuunnnnnOpen or short circuit in the barometric pressure sensor
2 31I-~-~---~ nOpen circuit in the detonation sensor circuit
@ 41uuul nOpen circuit in the injection circuit
042UUuLJul
Malfunction of the control relayOpen or short circuit in the fuel pump drive circuit
z 43UUULnlulMalfunction of the
EGR system
Open or short circuit in the EGR temperature sensor circuit
%4u u u uvinnOpen circuit in either of ignition coil circuit
0nNormal (with none of above faults)
. IA-r-NUltl 1:
Page 144 of 391

__.-~-..- -
FUEL SYSTEM- Ermine Control Unit
FAIL-SAFE AND BACKUP FUNCTiON
(1) The fail-safe function controls the system so
that passenger and vehicle safety can be
maxi-
mized. in the event of failure of sens.ors or other
parts.If a sensor related to
ISC fails, for example, the
engine control unit is programmed to prevent
sharp increases in the engine speed.(2) The backup function of the engine control unit
ignores the output signal of a failed sensor and
instead uses a built-in program or set of values
so that the vehicle may continue to function. The
operating state when the backup function is
being used, is termed the emergency mode, and
the engine, control unit keeps the engine warn-
ing light ON during this mode.
Fail-safe/Backup Function
Control contentsFaulty system
Fuel injection control
Idle speed controlIgnition timing control
Air flow sensor
Uses throttle position sensorFixes stepper motor atUses throttle position sensorsignal for control.
position wider than idle.signal for control.
Intake air
temper-Provides control with intake
Provides control with intakeProvides control with intake
ature sensorair temperature assumed to
be 25°C (77°F).air temperature assumed toair temperature assumed tobe 25°C (77°F).be 25°C (77°F).Throttle position
-Does not perform driving and-sensor
acceleration/deceleration
control.
Engine coolantProvides control with engine
Provides control with engineProvides control with engine
temperaturecoolant temperature
coolant temperaturecoolant temperature
sensorassumed to be 80°C (176°F)assumed to be 80°C (176°F).assumed to be 80°C (176°F).BarometricProvides control with
baro-Provides control with baro-Provides control with baro-pressure sensormetric pressure assumed to
be 760
mmHg (30 in.HgI.metric pressure assumed tometric pressure assumed tobe 760 mmHg (30 in.Hg).be 760 mmHg (30 in.Hg).Detonation sensor
-Retarded about 3 degree.Ignition coil
Fuel not injection to a cylinder-whose ignition signal is
abnormal.
TDC sensorOxygen sensor
No fuel injection.-
Feedback control of air/fuel-
ratio by oxygen sensor signal
is not made.
Page 146 of 391
-
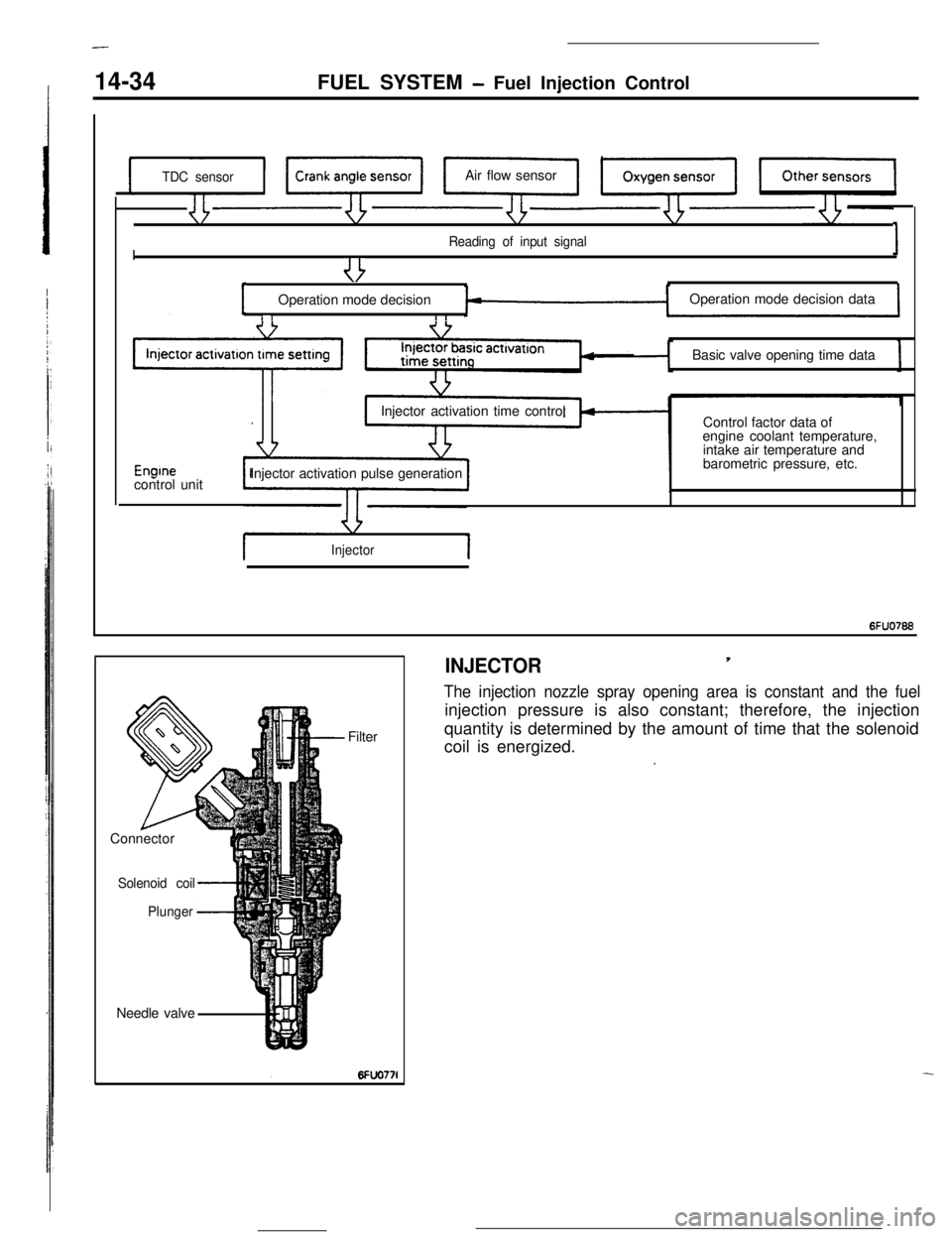
14-34FUEL SYSTEM - Fuel Injection Control
TDC sensorAir flow sensor
I
Reading of input signal1
I ,,
uOperation mode decisionOperation mode decision data
I rBasic valve opening time data
Enginecontrol unitInjector activation time control
Injector activation pulse generationControl factor data of
engine coolant temperature,
intake air temperature and
barometric pressure, etc.
Injector1
6FUO766Needle valveFilter
Connector
Solenoid coil
Plunger
-4
INJECTOR,
The injection nozzle spray opening area is constant and the fuelinjection pressure is also constant; therefore, the injection
quantity is determined by the amount of time that the solenoid
coil is energized.
.
Page 152 of 391
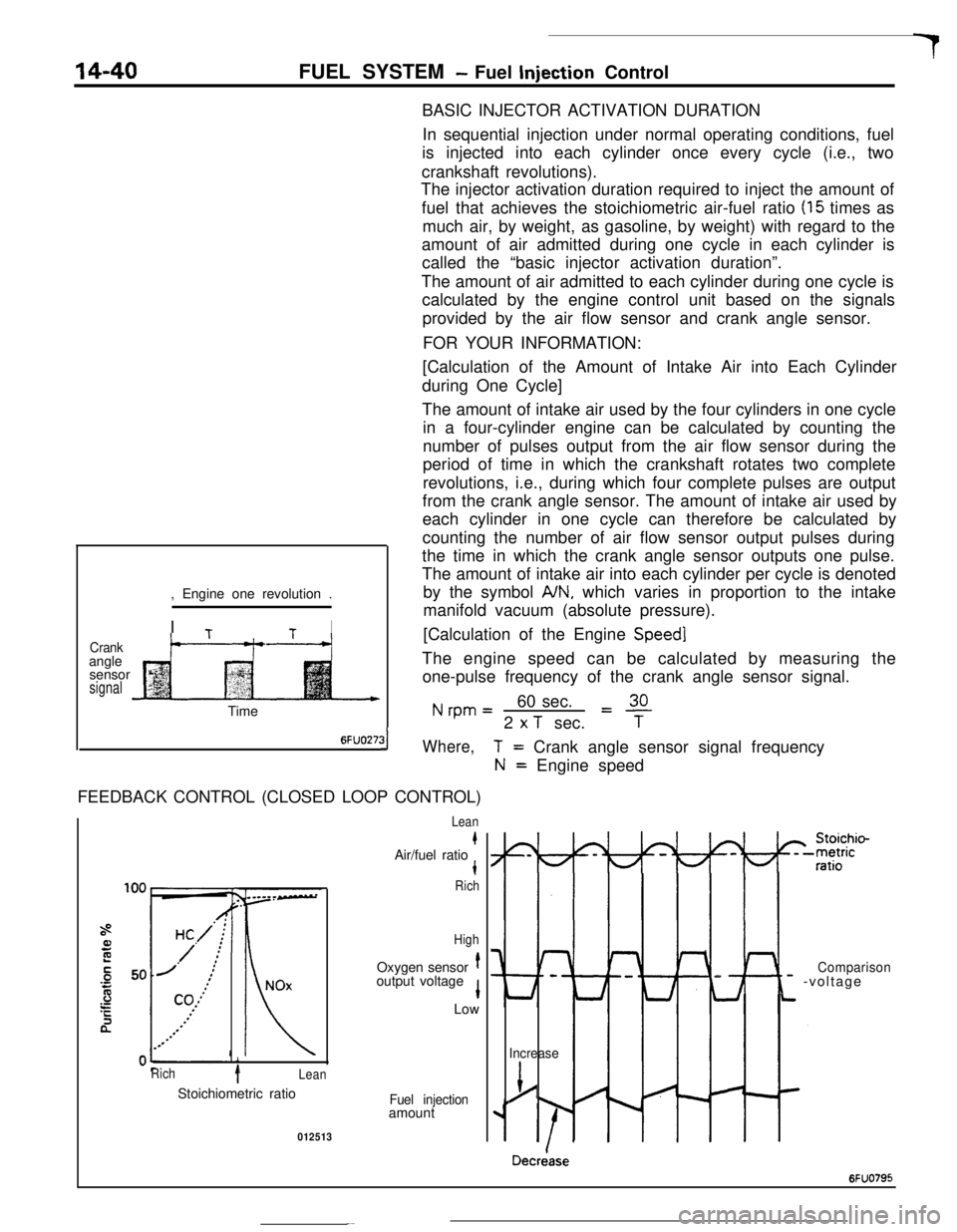
14-40FUEL SYSTEM - Fuel Injection Control
BASIC INJECTOR ACTIVATION DURATION
In sequential injection under normal operating conditions, fuel
is injected into each cylinder once every cycle (i.e., two
crankshaft revolutions).
The injector activation duration required to inject the amount of
fuel that achieves the stoichiometric air-fuel ratio
(15 times as
much air, by weight, as gasoline, by weight) with regard to the
amount of air admitted during one cycle in each cylinder is
called the “basic injector activation duration”.
The amount of air admitted to each cylinder during one cycle is
calculated by the engine control unit based on the signals
provided by the air flow sensor and crank angle sensor.
FOR YOUR INFORMATION:
Crankangle
sensor
signal, Engine one revolution .
I
TtI
t--“---t-+[Calculation of the Amount of Intake Air into Each Cylinder
during One Cycle]
The amount of intake air used by the four cylinders in one cycle
in a four-cylinder engine can be calculated by counting the
number of pulses output from the air flow sensor during the
period of time in which the crankshaft rotates two complete
revolutions, i.e., during which four complete pulses are output
from the crank angle sensor. The amount of intake air used by
each cylinder in one cycle can therefore be calculated by
counting the number of air flow sensor output pulses during
the time in which the crank angle sensor outputs one pulse.
The amount of intake air into each cylinder per cycle is denoted
by the symbol
A/N, which varies in proportion to the intake
manifold vacuum (absolute pressure).
[Calculation of the Engine
Speed]The engine speed can be calculated by measuring the
one-pulse frequency of the crank angle sensor signal.
Nrpm=60 sec.L!!L2
x T sec.TTime
6FUO27:31Where,FEEDBACK CONTROL (CLOSED LOOP CONTROL)
i
Rich1Lean
T= Crank angle sensor signal frequency
N= Engine speed
Lean
kAir/fuel ratiot
Rich
HighOxygen sensor
toutput voltage
1Low
Stoichiometric ratio
Fuel injectionamount
012513
I-
Lt
Comparison- -voltage
Increase
j/
Decriase
6FUO795
Page 154 of 391
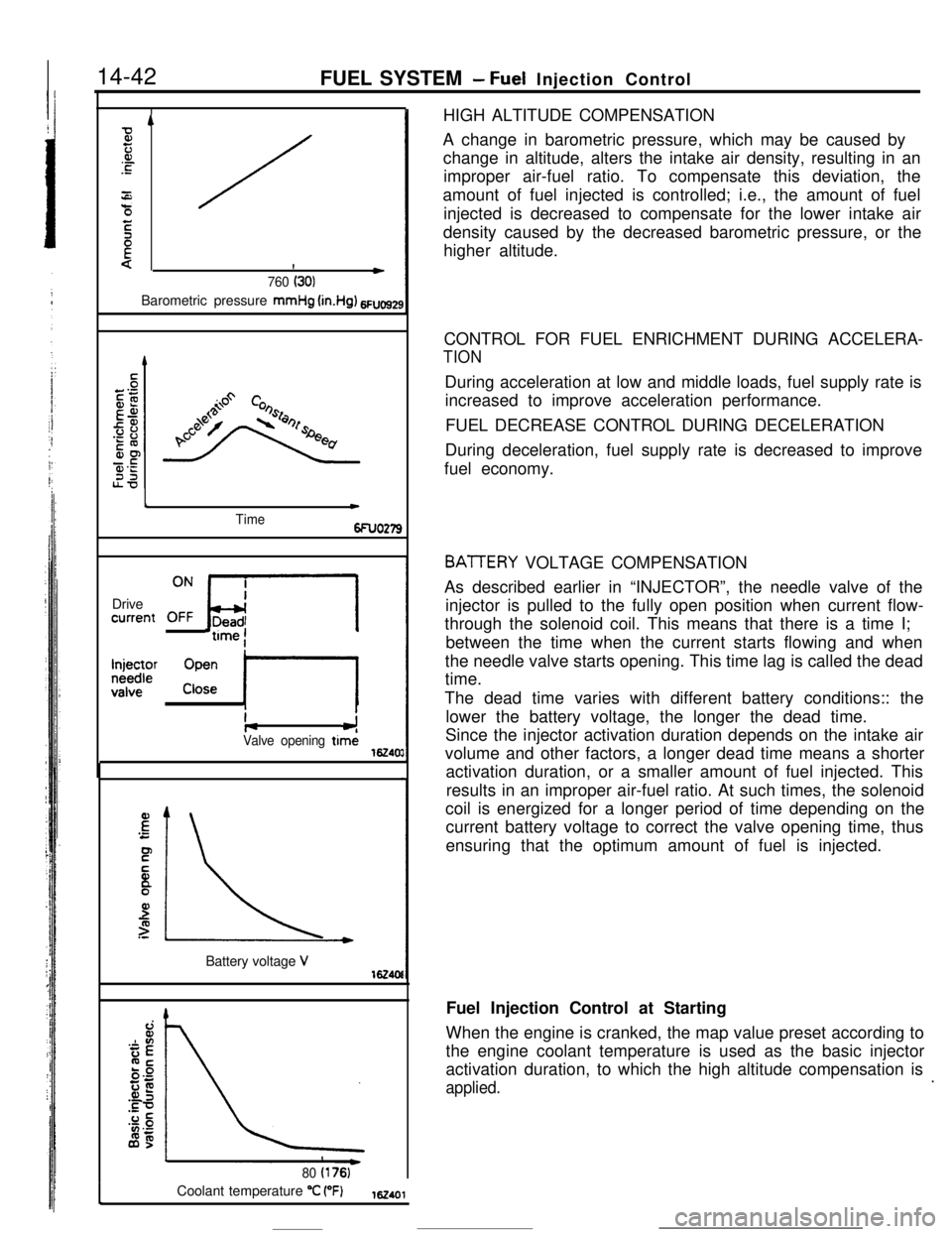
14-42
FUEL SYSTEM- Fuel Injection Control
4
Fz.or.c
4:0/
E
{!*760 (301Barometric pressure
mmHg (in.Hg) 6Fuo9z
c
Timet
6FUO279Drivecurrent
0: bri
F2JJ’ ipe; II
I+-JValve opening timi16240:
E‘C
F
.-
is
3
3:\Battery voltage
V162406
80 (176)Coolant temperature
“C (“F)162401HIGH ALTITUDE COMPENSATION
A change in barometric pressure, which may be caused by
change in altitude, alters the intake air density, resulting in an
improper air-fuel ratio. To compensate this deviation, the
amount of fuel injected is controlled; i.e., the amount of fuel
injected is decreased to compensate for the lower intake air
density caused by the decreased barometric pressure, or the
higher altitude.
CONTROL FOR FUEL ENRICHMENT DURING ACCELERA-
TIONDuring acceleration at low and middle loads, fuel supply rate is
increased to improve acceleration performance.
FUEL DECREASE CONTROL DURING DECELERATION
During deceleration, fuel supply rate is decreased to improve
fuel economy.
BATTERY VOLTAGE COMPENSATION
As described earlier in “INJECTOR”, the needle valve of the
injector is pulled to the fully open position when current flow-
through the solenoid coil. This means that there is a time I;
between the time when the current starts flowing and when
the needle valve starts opening. This time lag is called the dead
time.
The dead time varies with different battery conditions:: the
lower the battery voltage, the longer the dead time.
Since the injector activation duration depends on the intake air
volume and other factors, a longer dead time means a shorter
activation duration, or a smaller amount of fuel injected. This
results in an improper air-fuel ratio. At such times, the solenoid
coil is energized for a longer period of time depending on the
current battery voltage to correct the valve opening time, thus
ensuring that the optimum amount of fuel is injected.
Fuel Injection Control at Starting
When the engine is cranked, the map value preset according to
the engine coolant temperature is used as the basic injector
activation duration, to which the high altitude compensation is
applied..
Page 155 of 391
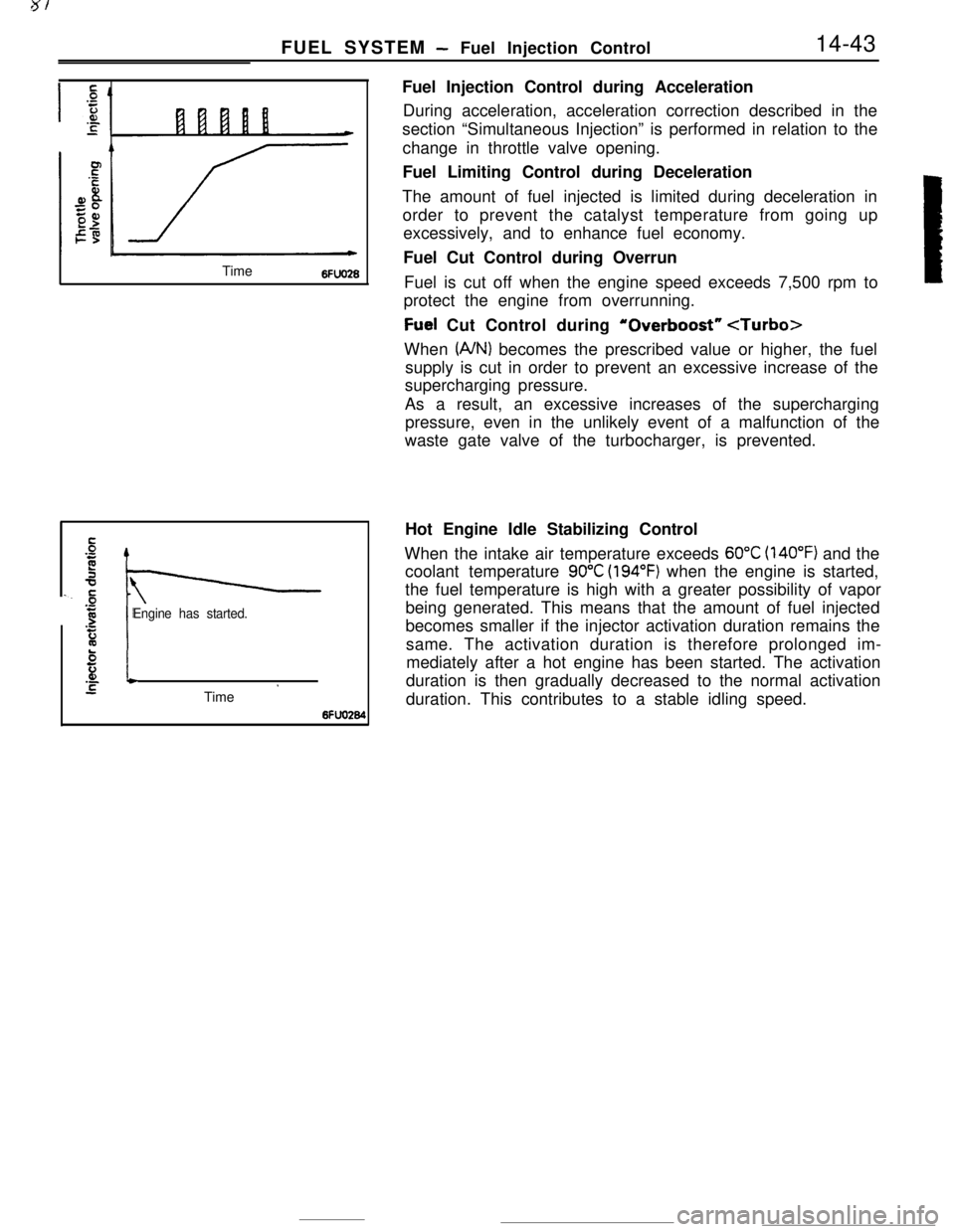
FUEL SYSTEM - Fuel Injection Control14-43
Time
6FUO26
Engine has started.
El.-*STime ’6fFuel Injection Control during Acceleration
During acceleration, acceleration correction described in the
section “Simultaneous Injection” is performed in relation to the
change in throttle valve opening.
Fuel Limiting Control during Deceleration
The amount of fuel injected is limited during deceleration in
order to prevent the catalyst temperature from going up
excessively, and to enhance fuel economy.
Fuel Cut Control during Overrun
Fuel is cut off when the engine speed exceeds 7,500 rpm to
protect the engine from overrunning.
Fuel Cut Control during ‘Overboost”
(A/N) becomes the prescribed value or higher, the fuel
supply is cut in order to prevent an excessive increase of the
supercharging pressure.
As a result, an excessive increases of the supercharging
pressure, even in the unlikely event of a malfunction of the
waste gate valve of the turbocharger, is prevented.
Hot Engine Idle Stabilizing Control
When the intake air temperature exceeds
60°C (140°F) and the
coolant temperature
90°C (194°F) when the engine is started,
the fuel temperature is high with a greater possibility of vapor
being generated. This means that the amount of fuel injected
becomes smaller if the injector activation duration remains the
same. The activation duration is therefore prolonged im-
mediately after a hot engine has been started. The activation
duration is then gradually decreased to the normal activation
duration. This contributes to a stable idling speed.
Page 156 of 391
- __..--
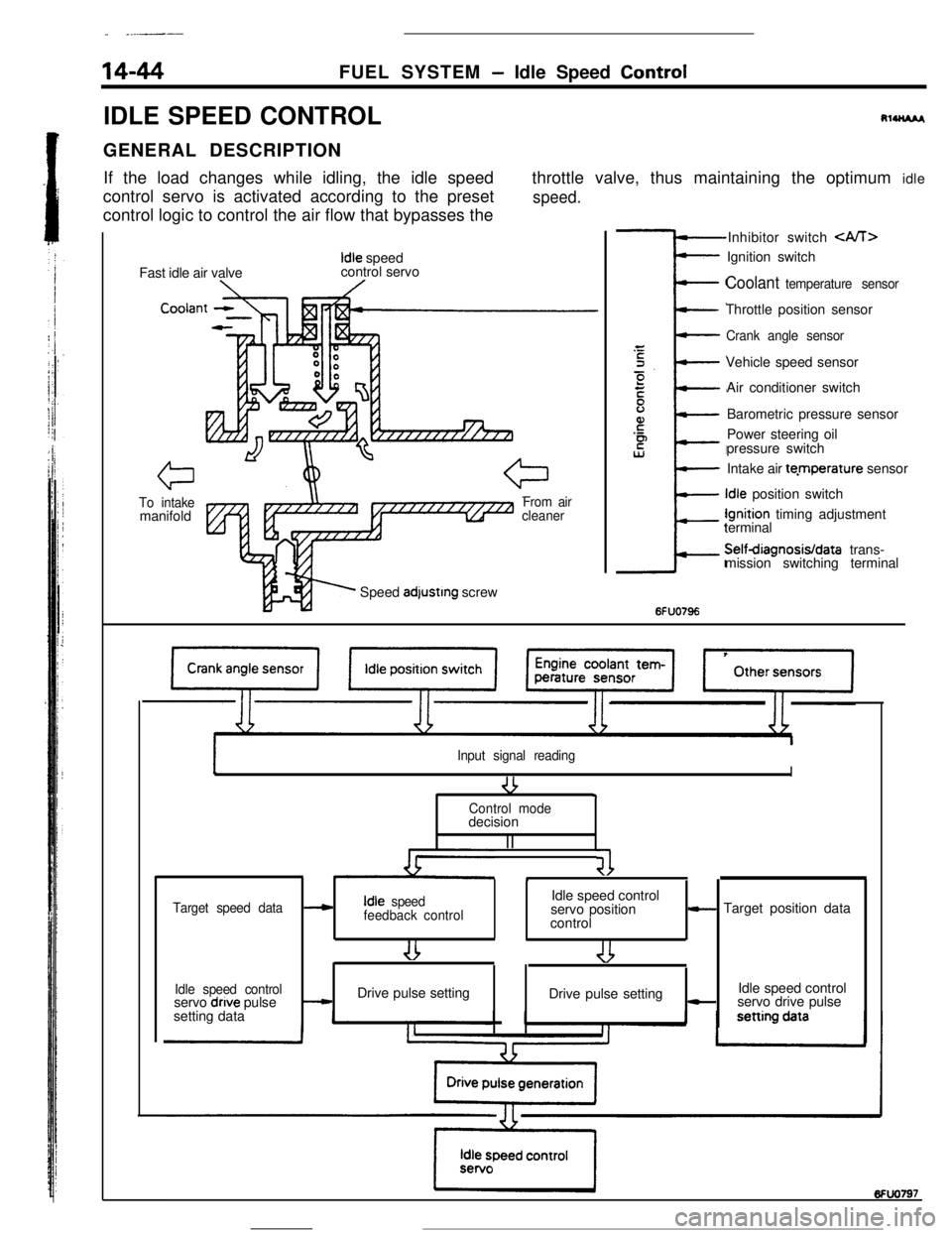
14-44FUEL SYSTEM- Idle Speed Control
IDLE SPEED CONTROL
RlUU*I,GENERAL DESCRIPTION
If the load changes while idling, the idle speed
control servo is activated according to the preset
control logic to control the air flow that bypasses thethrottle valve, thus maintaining the optimum idle
speed.Fast idle air valve
Idle speed
control servo
Cooiar
To intakemanifoldFrom air
cleanerSpeed
adjustrng screwInhibitor switch
Coolant temperature sensorThrottle position sensor
Crank angle sensorVehicle speed sensor
Air conditioner switch
Barometric pressure sensor
Power steering oil
pressure switch
Intake air te.mperature sensorIdle position switchIgnition timing adjustment
terminalSelfdiagnosisIdata trans-
mission switching terminal
6FUO796
Input signal reading
-3I9Control modedecision
II
41*
Target speed dataIdle speed control---cIdle speed
feedback controlservo position- Target position data
control
Idle speed controlIdle speed control
servo dnve pulse-Drive pulse setting
Drive pulse setting-servo drive pulse
setting data
Page 161 of 391
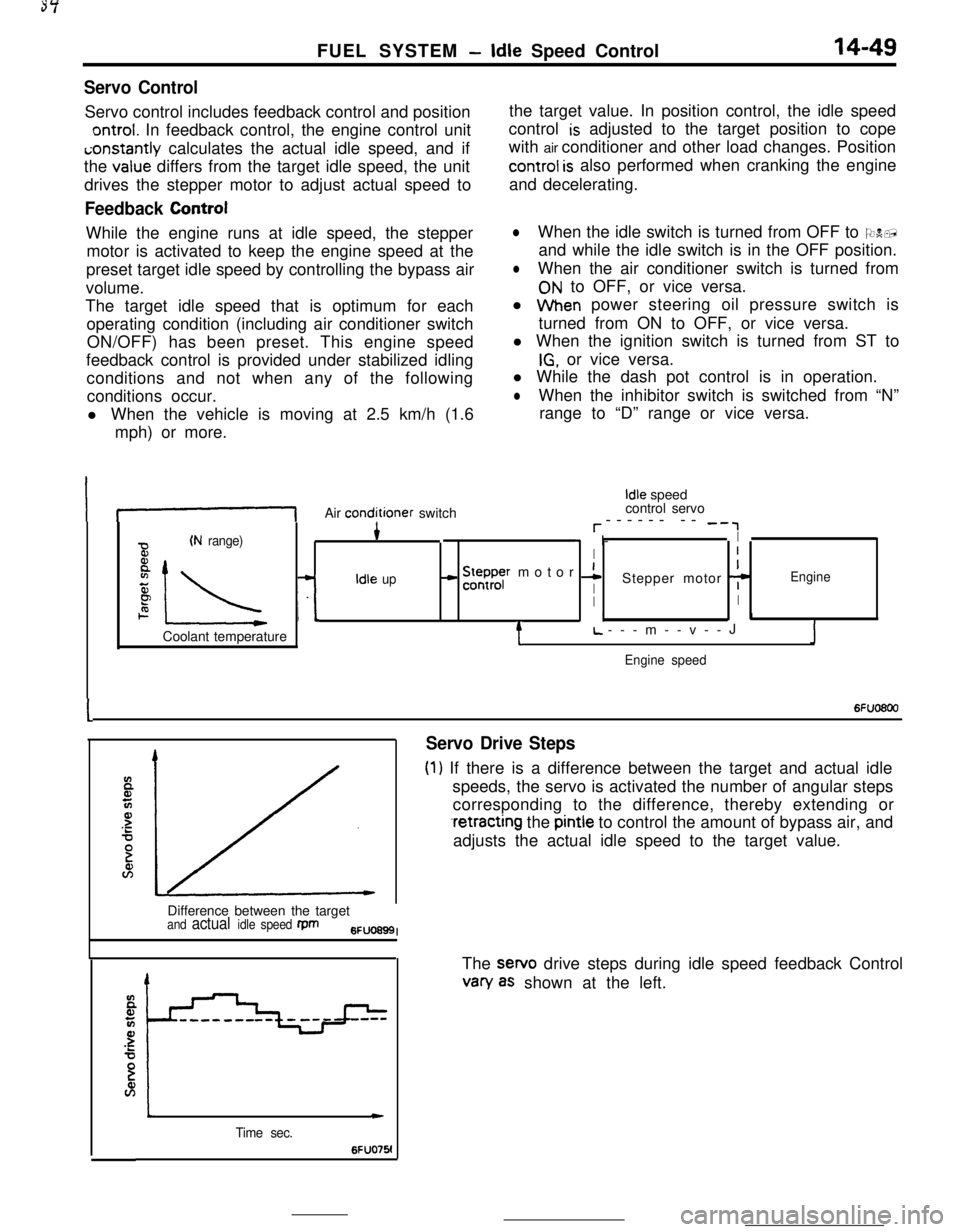
FUEL SYSTEM -Idle Speed Control14-49
Servo ControlServo control includes feedback control and position
ontrol. In feedback control, the engine control uniti;onstantly calculates the actual idle speed, and if
the
value differs from the target idle speed, the unit
drives the stepper motor to adjust actual speed to
Feedback ControlWhile the engine runs at idle speed, the stepper
motor is activated to keep the engine speed at the
preset target idle speed by controlling the bypass air
volume.
The target idle speed that is optimum for each
operating condition (including air conditioner switch
ON/OFF) has been preset. This engine speed
feedback control is provided under stabilized idling
conditions and not when any of the following
conditions occur.
l When the vehicle is moving at 2.5 km/h (1.6
mph) or more.the target value. In position control, the idle speed
control
is adjusted to the target position to cope
with air conditioner and other load changes. Position
control is also performed when cranking the engine
and decelerating.
lWhen the idle switch is turned from OFF to ON,
and while the idle switch is in the OFF position.
lWhen the air conditioner switch is turned from
ON to OFF, or vice versa.
l When power steering oil pressure switch is
turned from ON to OFF, or vice versa.
l When the ignition switch is turned from ST to
IG, or vice versa.
l While the dash pot control is in operation.
lWhen the inhibitor switch is switched from “N”
range to “D” range or vice versa.
If-1Air conditioner switch
Idle speed
control servo
r------ -- -‘,
(N range)4* I-I
BI
8
IL -L
- !5ysr motor 1I
zIdle upIStepper motor 7Engine
PII2. I.1Coolant temperature
tL.---m--v--JJ
Engine speed
I6Fuo6oo
Servo Drive Steps
(1) If there is a difference between the target and actual idle
speeds, the servo is activated the number of angular steps
corresponding to the difference, thereby extending or
.retracting the pintle to control the amount of bypass air, and
adjusts the actual idle speed to the target value.
Difference between the target
and actual idle speed fpm6FUO699I
Time sec.
c
6FUO76!The sewo drive steps during idle speed feedback Control
van/ as shown at the left.
Page 162 of 391
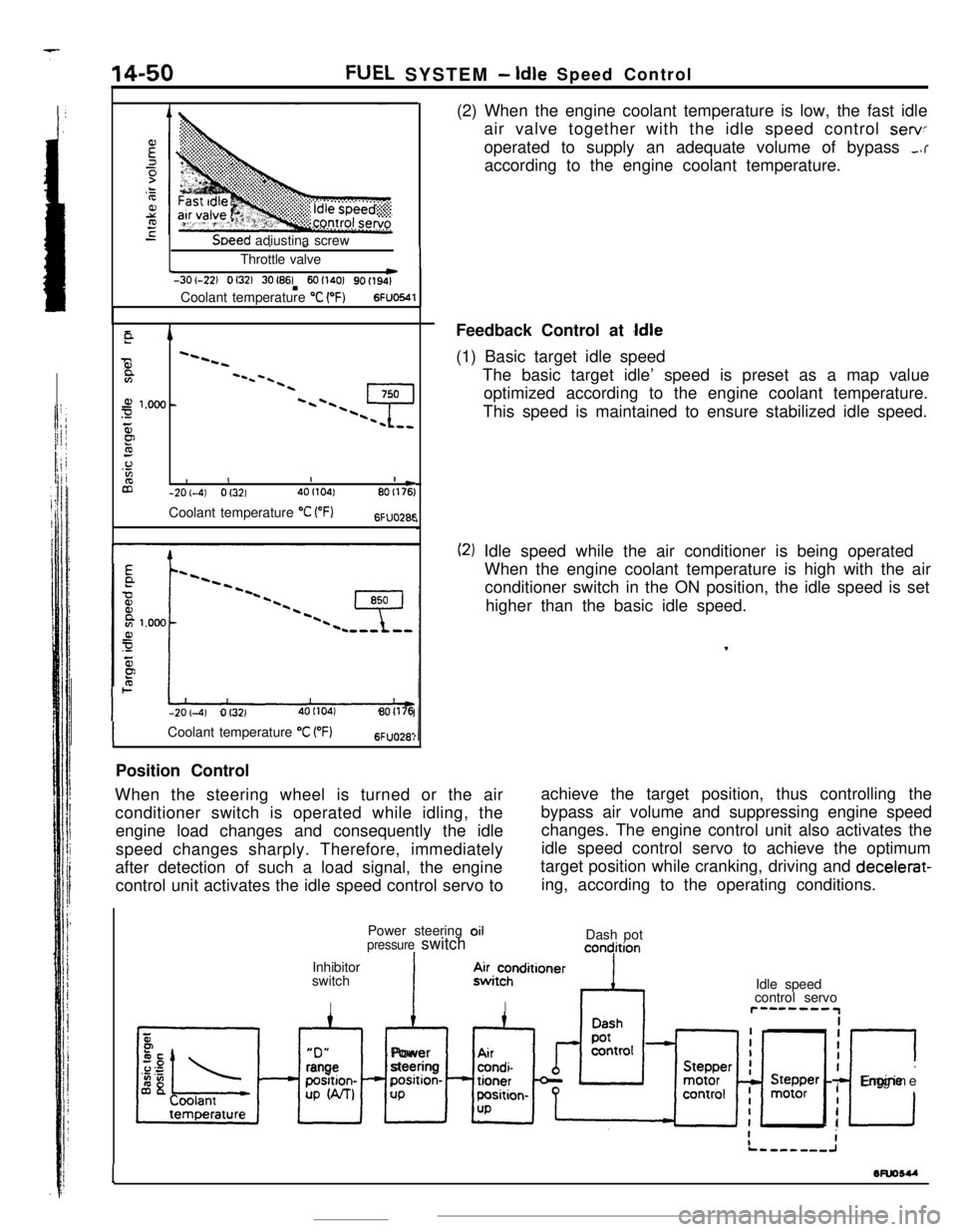
14-50FUEL SYSTEM- Idle Speed Control
SDeed adiustina screwI -Throttle valve
Lw-3O(-22) 0132) 30(86! 601140) 9ofl94)Coolant temperature
“C (OF)6FUO641
E94
72--2--I
Q--.-.-z
3201.000 --4-\-\
5P9.o%IIIaI L-2O(-41 Of3214Of104)801176)Coolant temperature
“C VF)6FU028E
-201-4) Of3214OI104180(176(2) When the engine coolant temperature is low, the fast idle
air valve together with the idle speed control
servoperated to supply an adequate volume of bypass
,.raccording to the engine coolant temperature.
Feedback Control at
Idle(1) Basic target idle speed
The basic target idle’ speed is preset as a map value
optimized according to the engine coolant temperature.
This speed is maintained to ensure stabilized idle speed.
(2) Idle speed while the air conditioner is being operated
When the engine coolant temperature is high with the air
conditioner switch in the ON position, the idle speed is set
higher than the basic idle speed.
,
ICoolant temperature “C VF)6FUO28:Position Control
When the steering wheel is turned or the air
conditioner switch is operated while idling, theachieve the target position, thus controlling the
engine load changes and consequently the idlebypass air volume and suppressing engine speed
changes. The engine control unit also activates the
speed changes sharply. Therefore, immediately
after detection of such a load signal, the engine
control unit activates the idle speed control servo toidle speed control servo to achieve the optimum
target position while cranking, driving and decelerat-
ing, according to the operating conditions.
Power steering oil
pressure switchIInhibitor
switch
IDash pot
concjition“D”
xl
rangeposition-
UP W-U
IAlPower
steeringposition-
UP.4~i~hnditioner
IIdle speed
control servor”--““IiiI
I
c
IEngine
I
I
1wuosu
-
Page 163 of 391
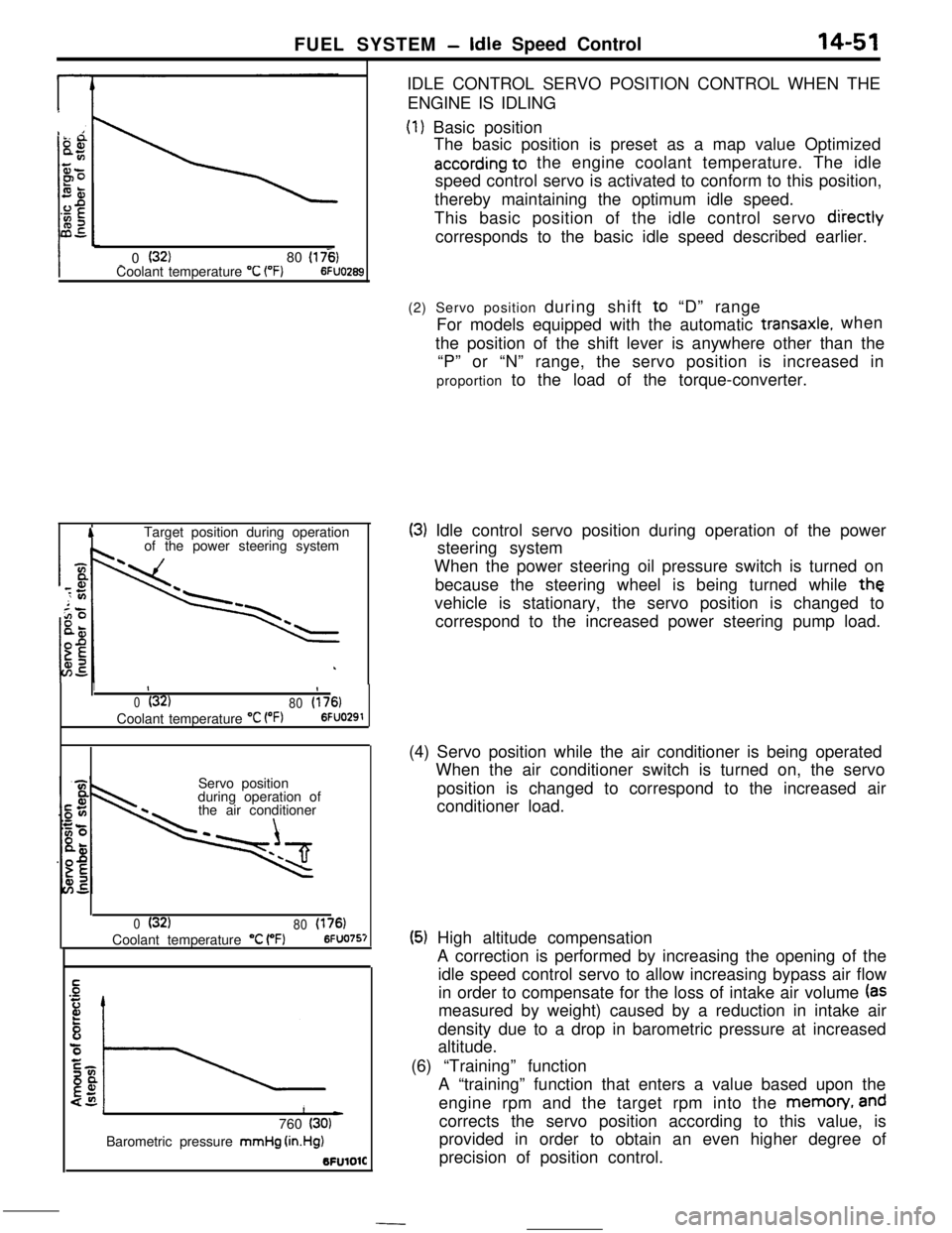
FUEL SYSTEM -Idle Speed Control14-51
_ 0 (32)80 (175)Coolant temperature “C (“F)6FUO2653
ATarget position during operation
of the power steering systemIDLE CONTROL SERVO POSITION CONTROL WHEN THE
ENGINE IS IDLING
(1) Basic position
The basic position is preset as a map value Optimized
according to the engine coolant temperature. The idle
speed control servo is activated to conform to this position,
thereby maintaining the optimum idle speed.
This basic position of the idle control servo
diiectlycorresponds to the basic idle speed described earlier.
1II
0(32)
80(176)Coolant temperature
“C VW6FUO291Servo position
during operation of
the air conditioner
0(32)
80(176)Coolant temperature “C (“F)6FUO757
1L)760 (30)Barometric pressure mmHg
(in.Hg)BFUlOlC(2) Servo position during shift to “D” range
For models equipped with the automatic
transaxle.when
the position of the shift lever is anywhere other than the
“P” or “N” range, the servo position is increased in
proportion to the load of the torque-converter.
(3) Idle control servo position during operation of the power
steering system
When the power steering oil pressure switch is turned on
because the steering wheel is being turned while
thevehicle is stationary, the servo position is changed to
correspond to the increased power steering pump load.
(4) Servo position while the air conditioner is being operated
When the air conditioner switch is turned on, the servo
position is changed to correspond to the increased air
conditioner load.
(5) High altitude compensation
A correction is performed by increasing the opening of the
idle speed control servo to allow increasing bypass air flow
in order to compensate for the loss of intake air volume
(asmeasured by weight) caused by a reduction in intake air
density due to a drop in barometric pressure at increased
altitude.
(6) “Training” function
A “training” function that enters a value based upon the
engine rpm and the target rpm into the memon/,
andcorrects the servo position according to this value, is
provided in order to obtain an even higher degree of
precision of position control.