oil type MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1990 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 1990, Model line: ECLIPSE, Model: MITSUBISHI ECLIPSE 1990Pages: 391, PDF Size: 15.27 MB
Page 126 of 391

14-14
.._~- ---.FUEL SYSTEM
- Sensors
SENSORSRlUGENERAL DESCRIPTION
The types and functions of the sensors are as listedsend corresponding signals to the engine control
below. These sensors detect engine conditions and
unit.
SENSORSFUNCTION
AIR FLOW SENSOR
fSenses the intake arr volume with a Karman vortex flow meter.
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE
SENSORSenses the Intake air temperature (temperature of air at
the point of entry into the air cleaner).I
BAROMETRIC PRESSURE
SENSORISenses the barometric pressure faltrtude) wrth a
semiconductor diffusion type pressure sensor.
$;;OOf;T TEMPERATURESenses the engine coolant tern
THROTTLE
POSITISenses the throttle
tI
IDLE POSITION SWITCHSenses whether or not the accelerator pedal is being
operated with a contact switch.
Senses the top dead center on compression stroke of
NO. 1 and No. 4 cylinders with an LED and photo diode pair.
CRANK ANGLE SENSORSenses the crank angle of each cylinder with an LED
and photo diodepair.
T
OXYGEN SENSORSenses
actrvation of the air con
POWER STEERING OIL
PRESSURE SWITCHc-lSenses the power steering ‘load with a contact switch.
IGNITION SWITCHSenses ON/OFF
posrtion of the ignition switch.I
Senses engine cranking.
,
IGNITION TIMING
ADJUSTMENT TERMINALWhen this terminal is shorted, the ignition timing and idle
speed control servo is set in the adjustrng mode by the enginecontrol unit.
INHIBITOR SWITCHSenses the *P” and “N” positthe automatic transaxle.Senses.
by pieto-electric element,. cylinder block
vibrations that occur when there ISengineknocking.
CONTROL RELAY
(Fuel pump drive signal)
lFnorne ianitron sianal!Senses ignrtton coil prIman/ voltage.
Page 157 of 391
3-d__- .
FUEL SYSTEM
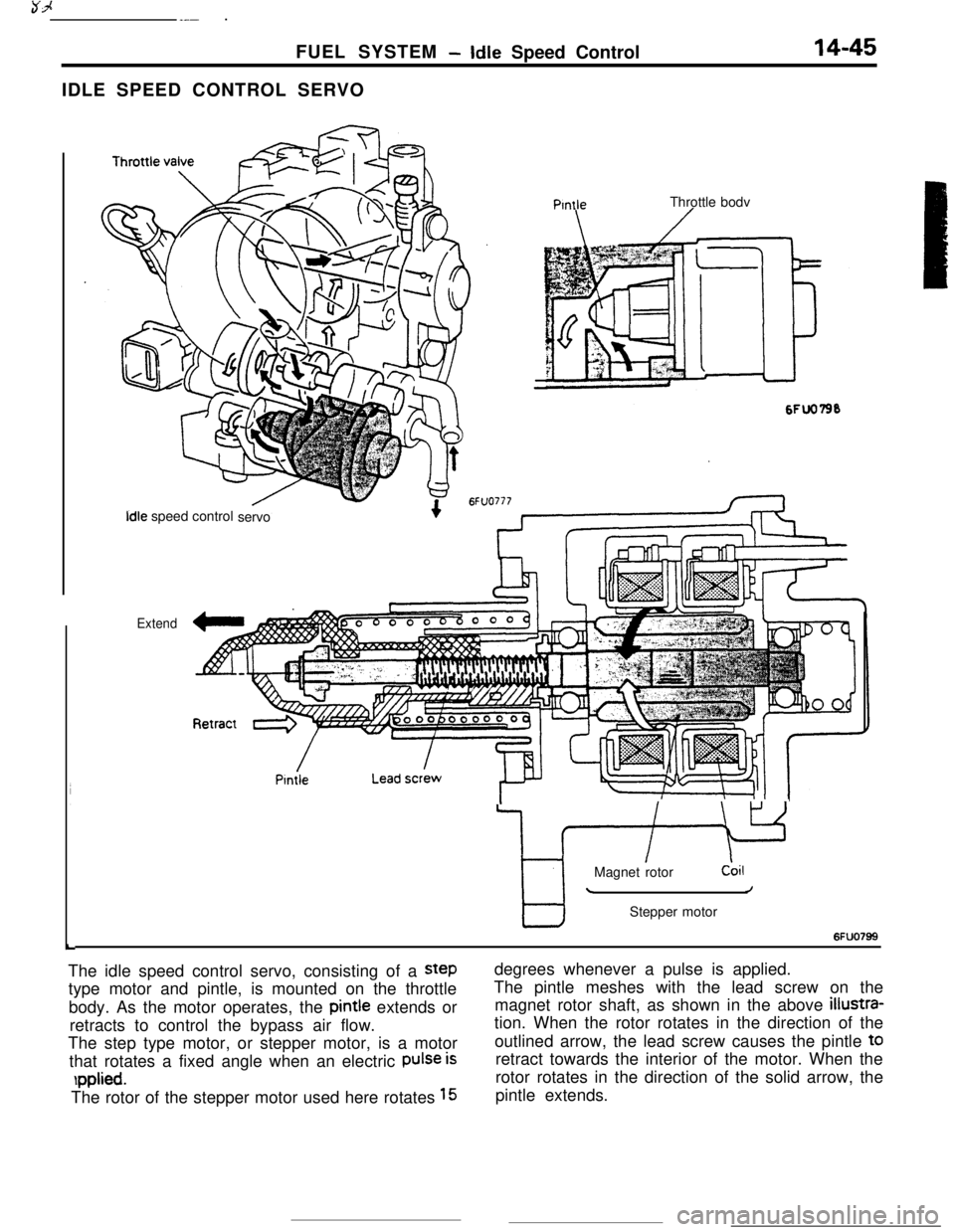
-Idle Speed Control14-45IDLE SPEED CONTROL SERVO
L
PtntleThrottle bodv
Idle speed control
servo
Extend
7 -IMagnet rotordoil
/Stepper motor
6FUO799The idle speed control servo, consisting of a
steptype motor and pintle, is mounted on the throttle
body. As the motor operates, the pintie extends or
retracts to control the bypass air flow.
The step type motor, or stepper motor, is a motor
that rotates a fixed angle when an electric
Pulse is
rpplied.The rotor of the stepper motor used here rotates
15degrees whenever a pulse is applied.
The pintle meshes with the lead screw on the
magnet rotor shaft, as shown in the above
illustra-tion. When the rotor rotates in the direction of the
outlined arrow, the lead screw causes the pintle t0
retract towards the interior of the motor. When the
rotor rotates in the direction of the solid arrow, the
pintle extends.
Page 186 of 391
14-74
_ ,.-..FUEL SYSTEM
- Auto-cruise Control System
When Canceled by the Stop Light Switch (broad
solid-line arrows)
The stop light switch is a four-pole type that
integrates the switch for the stop light (NO) with
that for the auto-cruise control (NC).
When the brake pedal is depressed, the contacts forthe auto-cruise control (NC) open, cutting off the
circuit to energize the electromagnetic clutch coil.
At the same time, the contacts for the stop light
(NO) close to allow a cancel signal to be input from
the
12-V power supply of the control unit to the
cancel circuit and to the microcomputer. As a result,the transistor which energizes the actuator electro-
magnetic clutch coil turns OFF and the electro-
magnetic clutch coil grounding circuit is cut off, thus
canceling the auto-cruise control mode.
When Canceled by the Clutch Switch (thin
solid-line arrows)
When the clutch pedal is depressed, the clutch
switch is turned ON and the battery voltage is
applied to the cancel circuit of the control unit. then,a cancel signal is input to the microcomputer.
causing the transistor that energizes the actuator
electromagnetic clutch coil to turn OFF. This results
in the electromagnetic clutch coil grounding circuit
bma$ndge cut off, which cancels the auto-cruise control
When Canceled by the Selector Lever (position“N”) (dotted-line arrows)
When the transaxle control selector lever is placed
in the “N” (neutral) position, the inhibitor switch is
turned ON and, as a result, current flows from the
control unit to the inhibitor switch, starter, and
ground. Then, a cancel signal is input from the
cancel circuit to the control unit, causing the
transistor which energizes the actuator electro-
magnetic clutch coil to be turned OFF. As a result,
the electromagnetic clutch coil grounding circuit is
cut off and the auto-cruise control mode is canceled.Although a small current (voltage 5 V) flows through
the starter, it is not activated.
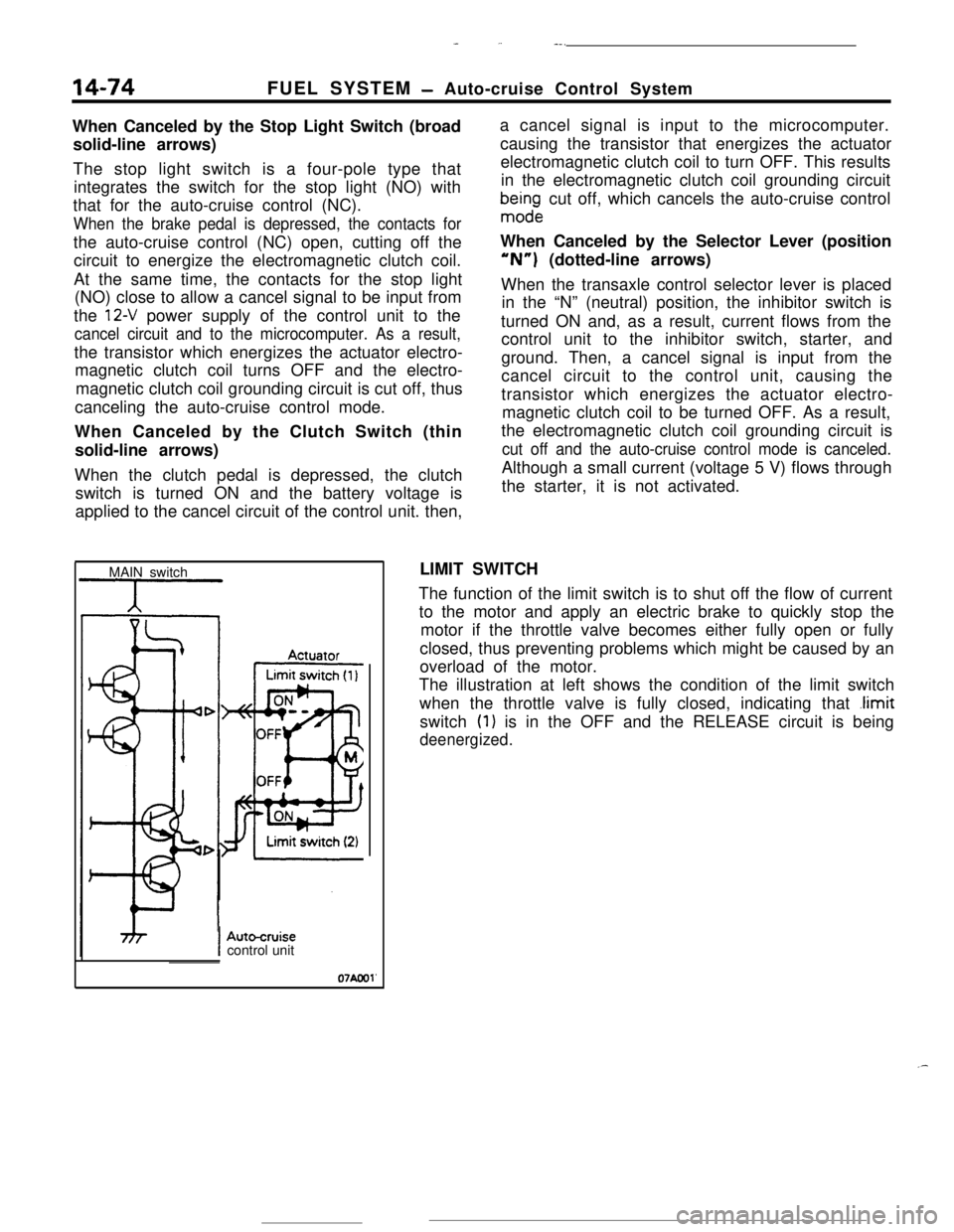
MAIN switchLIMIT SWITCH
The function of the limit switch is to shut off the flow of current
to the motor and apply an electric brake to quickly stop the
motor if the throttle valve becomes either fully open or fully
closed, thus preventing problems which might be caused by an
overload of the motor.
The illustration at left shows the condition of the limit switch
when the throttle valve is fully closed, indicating that
.limitswitch
(1) is in the OFF and the RELEASE circuit is being
deenergized.
IAutocruisecontrol unit
07Aool'
.-
Page 192 of 391
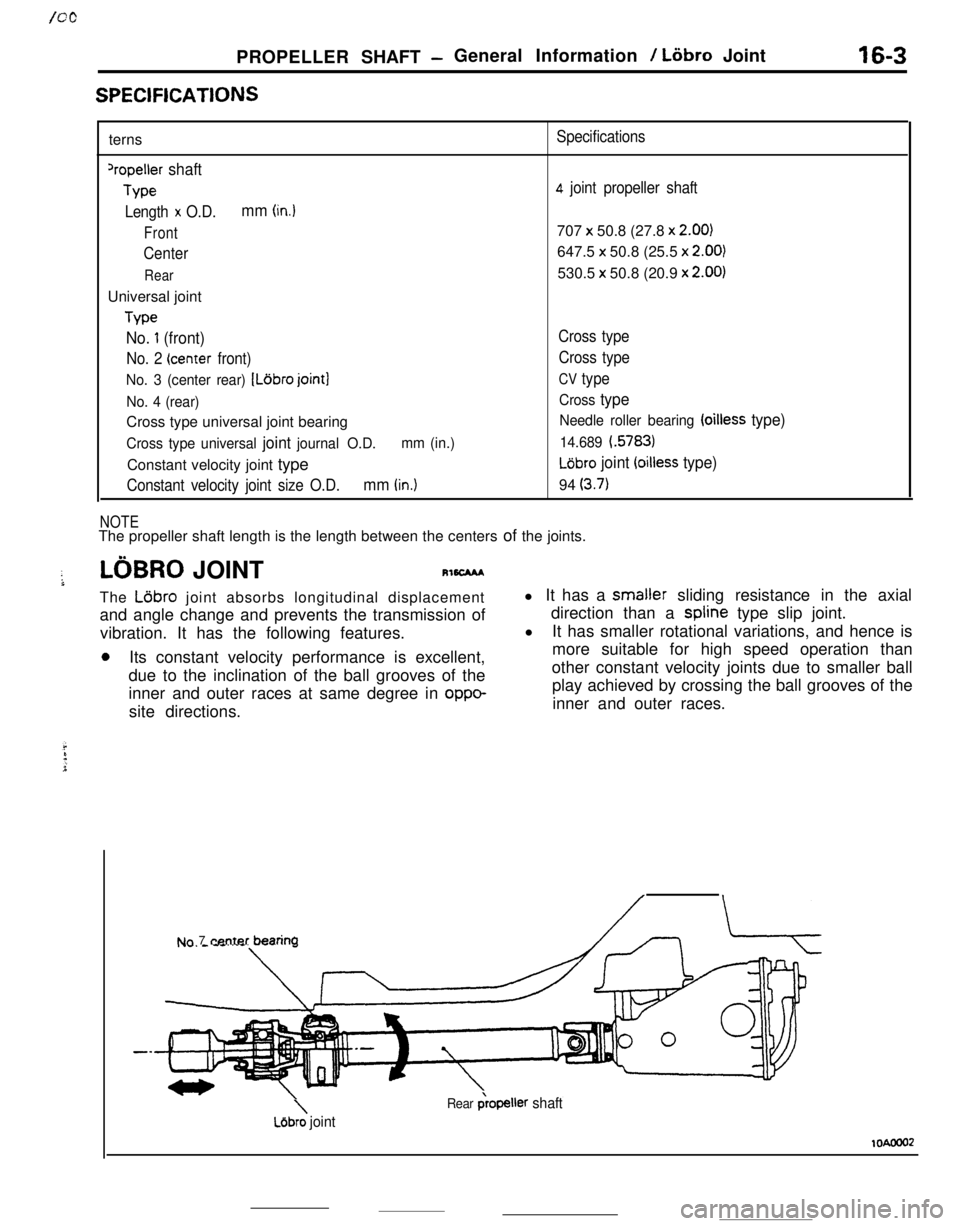
PROPELLER SHAFT -General Information / Liibro Joint16-3
SPEClFlCATlONSterns
‘repeller shaft
Type
Length
x O.D.mm (in.)
Front
Center
RearUniversal joint
Type
No. 1 (front)
No. 2 (center front)
No. 3 (center rear) [Ldbro joint]
No. 4 (rear)Cross type universal joint bearing
Cross type universal joint journal O.D.mm (in.)Constant velocity joint type
Constant velocity joint size O.D.mm (in.)
NOTE
Specifications
4 joint propeller shaft707
x 50.8 (27.8 x 2.00)647.5 x 50.8 (25.5 x
2.00)530.5 x 50.8 (20.9 x
2.00)
Cross type
Cross type
CV type
Cross type
Needle roller bearing (oilless type)
14.689 i.5783)
LGbro joint (oilless type)94
(3.7)The propeller shaft length is the length between the centers of the joints.
LOBRO JOINTRl6CMAThe
L6bro joint absorbs longitudinal displacement
and angle change and prevents the transmission of
vibration. It has the following features.
0Its constant velocity performance is excellent,
due to the inclination of the ball grooves of the
inner and outer races at same degree in
oppo-site directions.l It has a smaller sliding resistance in the axial
direction than a spline type slip joint.
l
It has smaller rotational variations, and hence is
more suitable for high speed operation than
other constant velocity joints due to smaller ball
play achieved by crossing the ball grooves of the
inner and outer races.
Nn 7 center bearina
\Lejbro joint
Rear &opeller shaft
lOAooo2
Page 202 of 391
_ -. ..__ .-
REAR SUSPENSION
<4WD> - Geneal (nformation
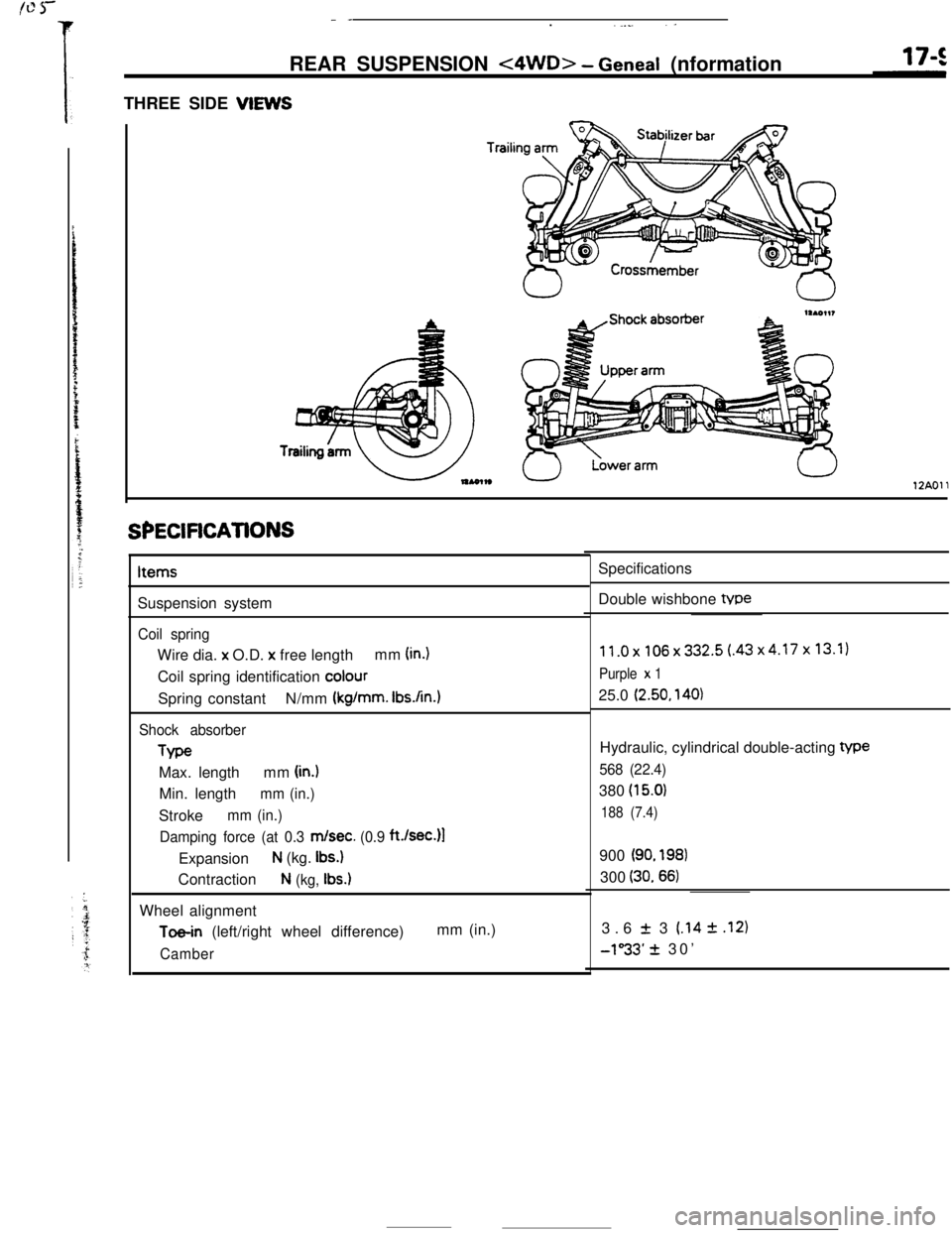
THREE SIDE VIEWS
Trailil
12AOll
SPECiFiCATiONSItems
Suspension system
Coil springWire dia. x O.D.
x free lengthmm (in.)Coil spring identification
colourSpring constantN/mm
(kg/mm. Ibs.An.1
Shock absorberType
Max. lengthmm
(in.)Min. length
mm (in.)Stroke
mm (in.)
Damping force (at 0.3
m/set. (0.9 ft./sec.)l
Expansion
N (kg. Ibs.)Contraction
N (kg, Ibs.)Wheel alignment
Toe-in (left/right wheel difference)mm (in.)
CamberSpecifications
Double wishbone tvpe
11.0x106x332.5(.43x4.17x13.1)
Purple x 125.0
(2.50, 140)Hydraulic, cylindrical double-acting
We
568 (22.4)380
(15.0)
188 (7.4)900
(90. 198)300
(30.66)3.6
f 3 (.14 2 .I21
-1”33’ + 30’
Page 207 of 391
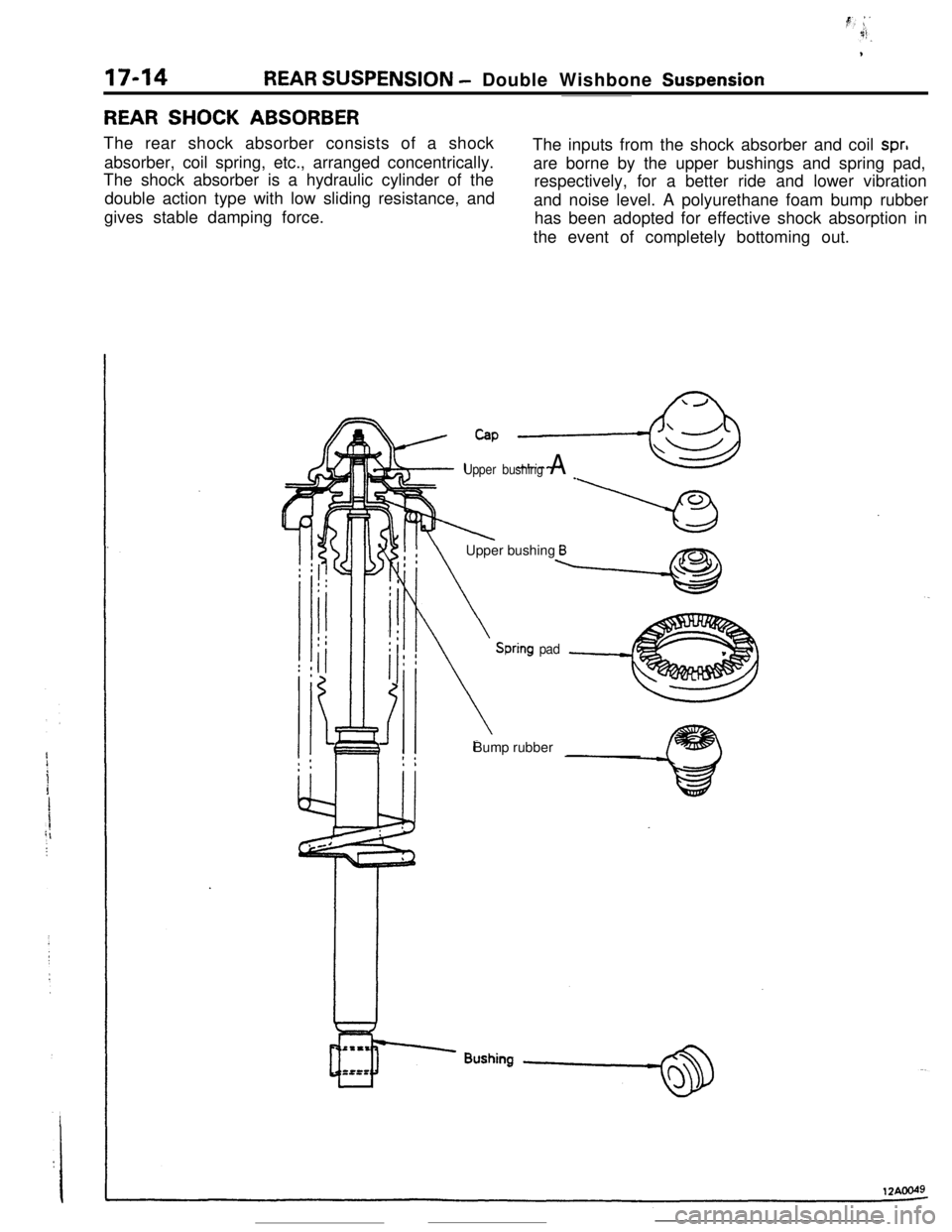
17-14REAR SUSPENSION - Double Wishbone Suwension
REAR SHOCK ABSORBERThe rear shock absorber consists of a shock
absorber, coil spring, etc., arranged concentrically.
The shock absorber is a hydraulic cylinder of the
double action type with low sliding resistance, and
gives stable damping force.The inputs from the shock absorber and coil
spr,are borne by the upper bushings and spring pad,
respectively, for a better ride and lower vibration
and noise level. A polyurethane foam bump rubber
has been adopted for effective shock absorption in
the event of completely bottoming out.
Cap ,-&
Upper bushing A _
IlXk!! \Upper bushing Bx?nb
Spring padBump rubber
Page 211 of 391
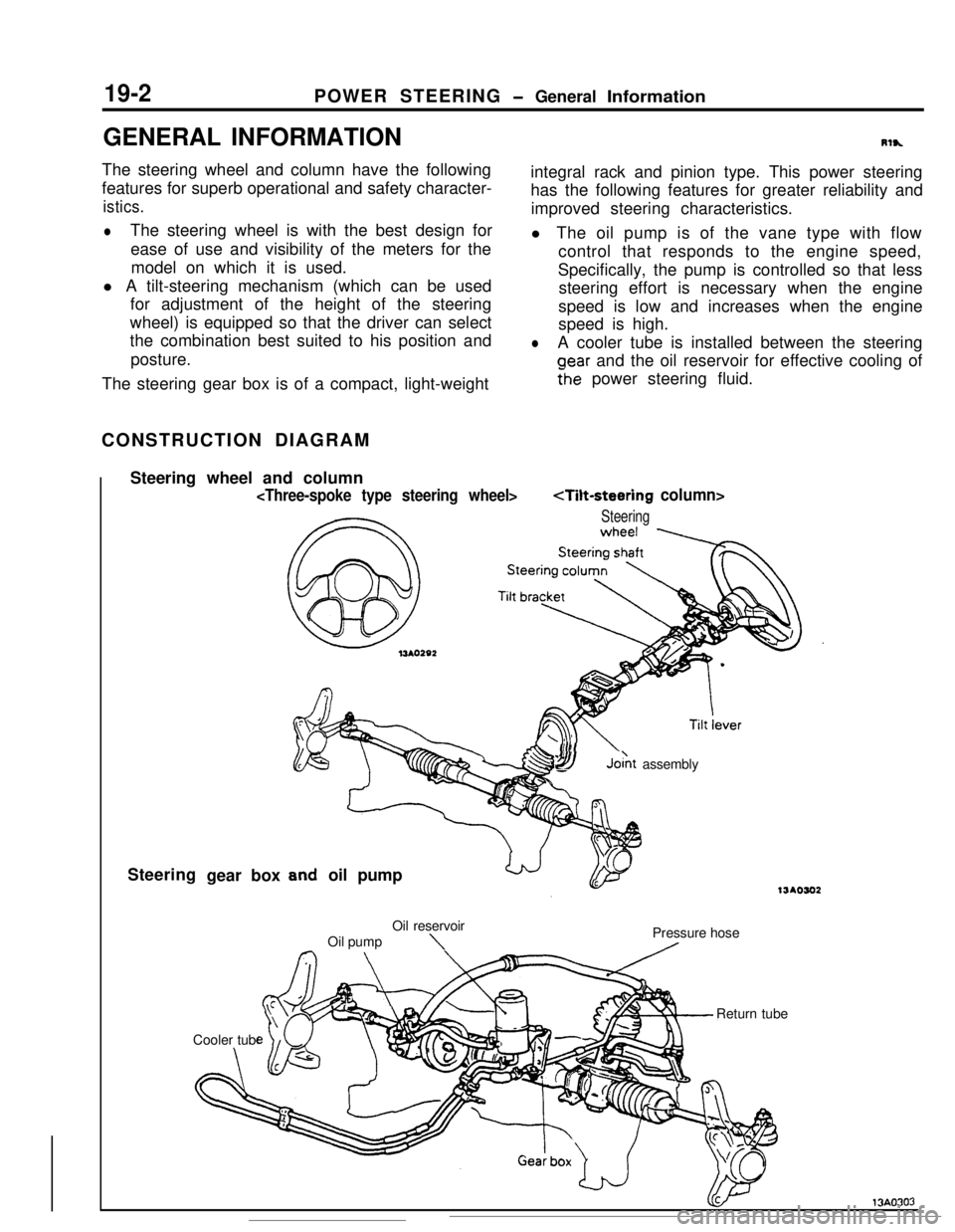
19-2 POWER STEERING
Rlh
integral rack and pinion type. This power steering
oear and the oil reservoir for effective cooling of
Fhe power steering fluid.The steering gear box is of a compact, light-weight
Steering
SYJo& assembly
oil pump
\Pressure hose
A
Page 212 of 391

POWER STEERING- General Information19-3
SPEClFlCATlONSItems
Steering wheel O.D.
mm (in.)Steering wheel maximum turns
Shaft and joint type
Steering angleInner wheel
Outer wheel
Tilt strokemm
(in.1Steering gear type
Rack strokemm (in.)Oil pump type
Oil pump displacement
cm3/rev. (cu.in./rev.)Specifications
372
(14.6)
2.7
Collapsible, cross joints (two joints used)
35”OO’ + 2”
29”20’
30
(1.2)
Rack and pinion
138
(5.41
Vane type9.6
l.59)
Page 214 of 391
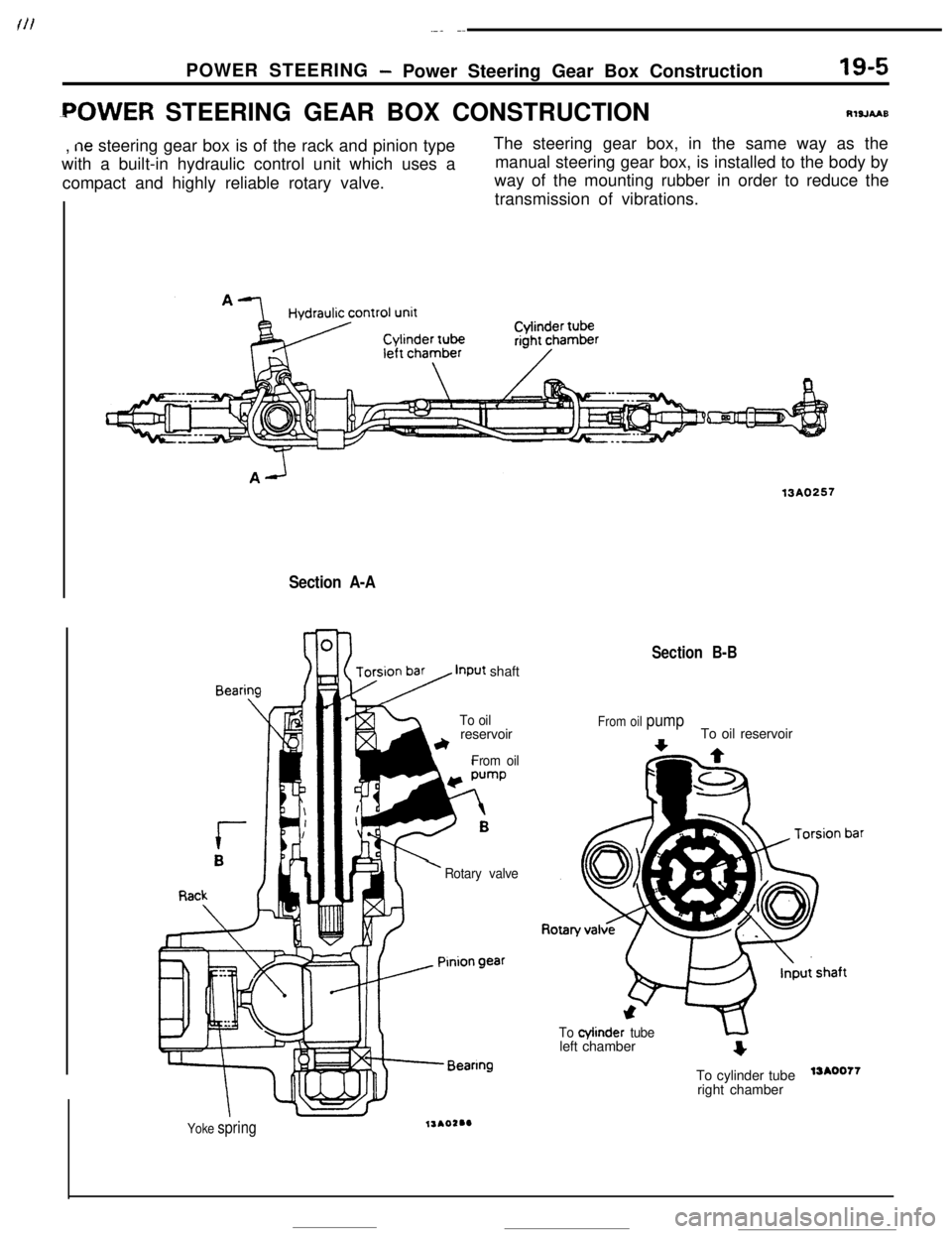
.-. --POWER STEERING
- Power Steering Gear Box Construction19-5
-POWER STEERING GEAR BOX CONSTRUCTIONRlsJLIIUB,
ne steering gear box is of the rack and pinion type
with a built-in hydraulic control unit which uses a
compact and highly reliable rotary valve.The steering gear box, in the same way as the
manual steering gear box, is installed to the body by
way of the mounting rubber in order to reduce the
transmission of vibrations.
Section A-A
Beari
1-$ysy input shaft
To oilreservoir
LFrom oil
I’Rotary valve
Yoke spring
13A0257
Section B-B
From oil pumpTo oil reservoir
To cylinder tubeleft chamber
To cylinder tube
13A0077right chamber
Page 219 of 391
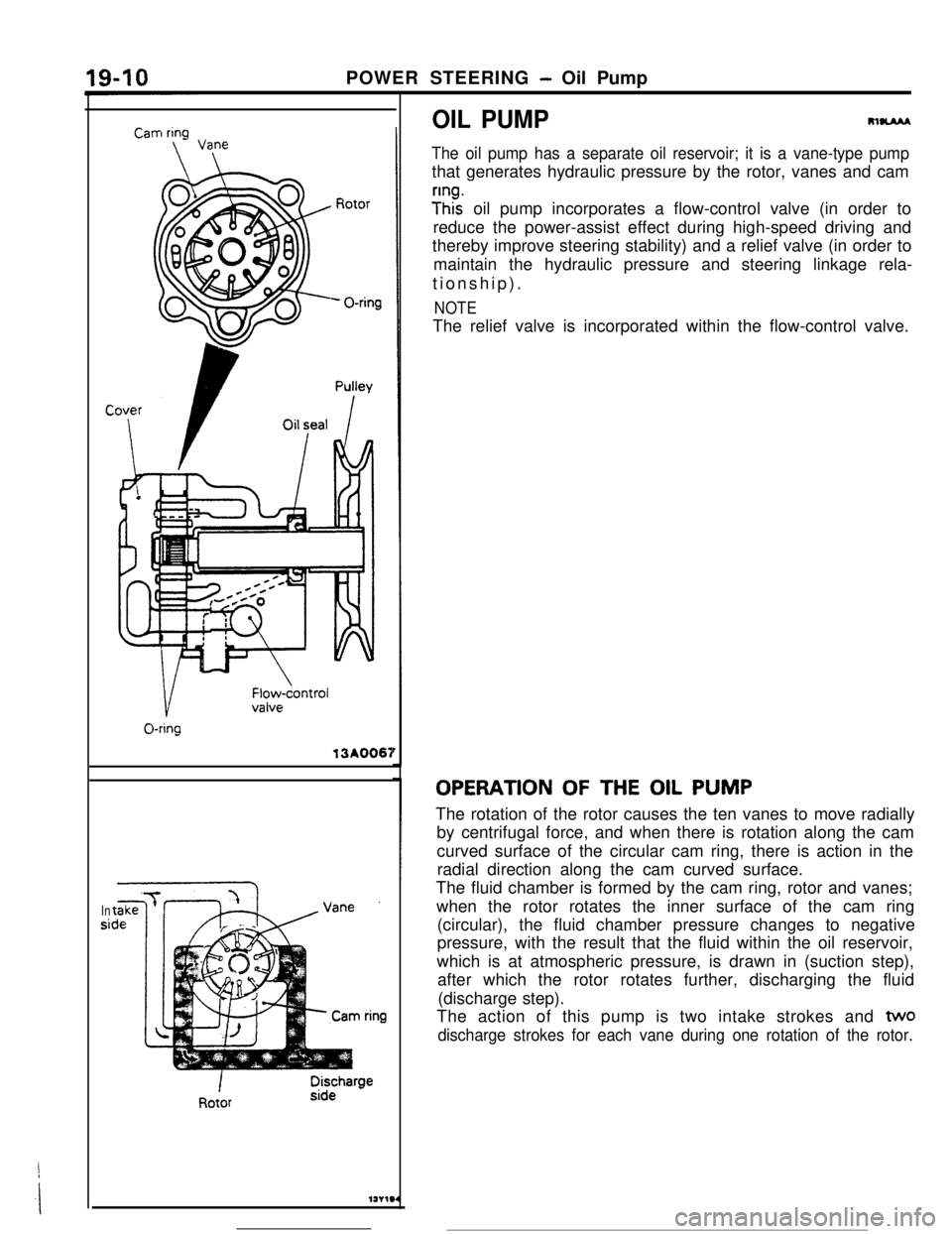
POWER STEERING - Oil Pump13A0067
Insi
OIL PUMPRlUAM
The oil pump has a separate oil reservoir; it is a vane-type pumpthat generates hydraulic pressure by the rotor, vanes and cam
y”ht oil pump incorporates a flow-control valve (in order to
reduce the power-assist effect during high-speed driving and
thereby improve steering stability) and a relief valve (in order to
maintain the hydraulic pressure and steering linkage rela-
tionship).
NOTEThe relief valve is incorporated within the flow-control valve.
OPERATION OF THE OIL PUMP
The rotation of the rotor causes the ten vanes to move radially
by centrifugal force, and when there is rotation along the cam
curved surface of the circular cam ring, there is action in the
radial direction along the cam curved surface.
The fluid chamber is formed by the cam ring, rotor and vanes;
when the rotor rotates the inner surface of the cam ring
(circular), the fluid chamber pressure changes to negative
pressure, with the result that the fluid within the oil reservoir,
which is at atmospheric pressure, is drawn in (suction step),
after which the rotor rotates further, discharging the fluid
(discharge step).
The action of this pump is two intake strokes and
two
discharge strokes for each vane during one rotation of the rotor.