engine coolant MITSUBISHI LANCER 2005 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2005, Model line: LANCER, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER 2005Pages: 788, PDF Size: 45.98 MB
Page 46 of 788
Page 47 of 788
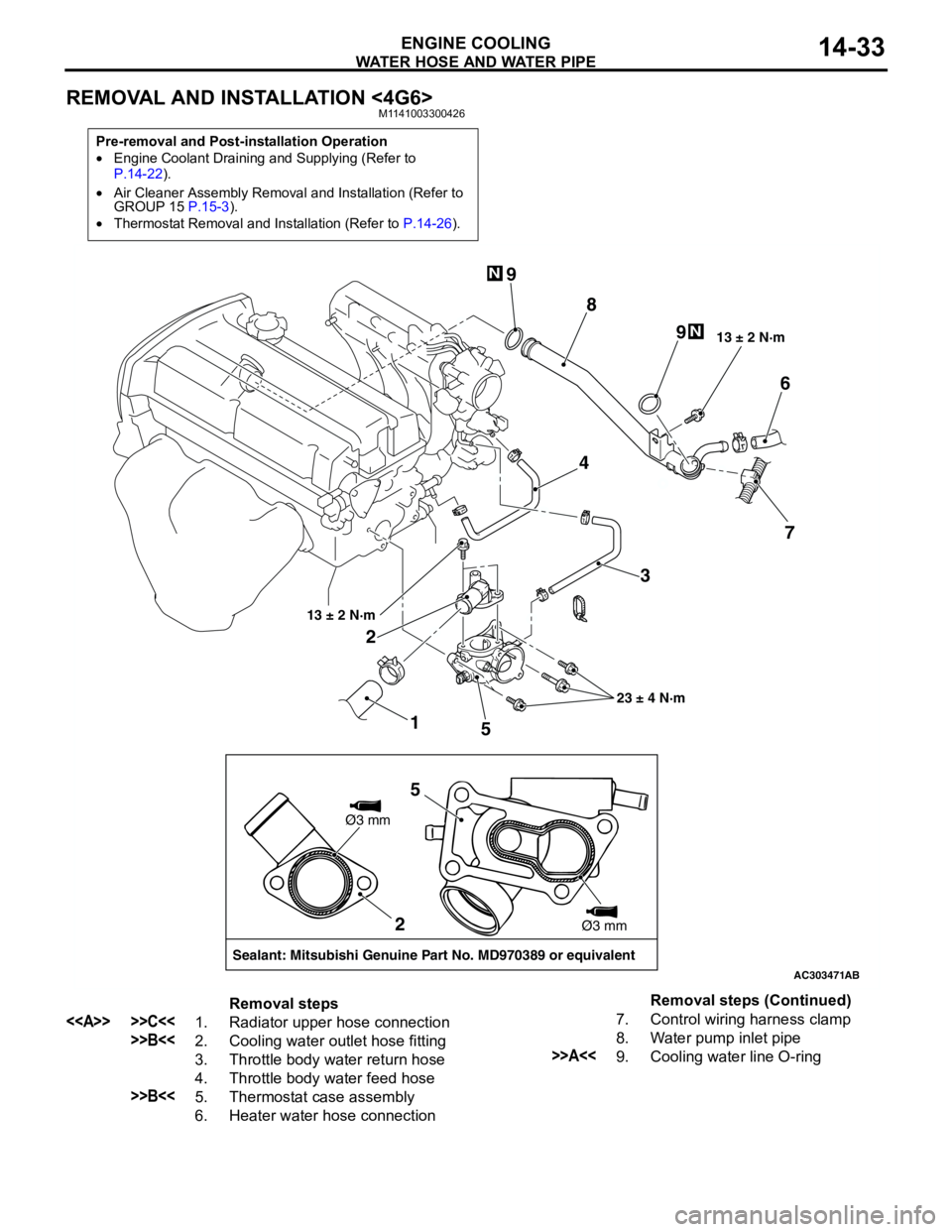
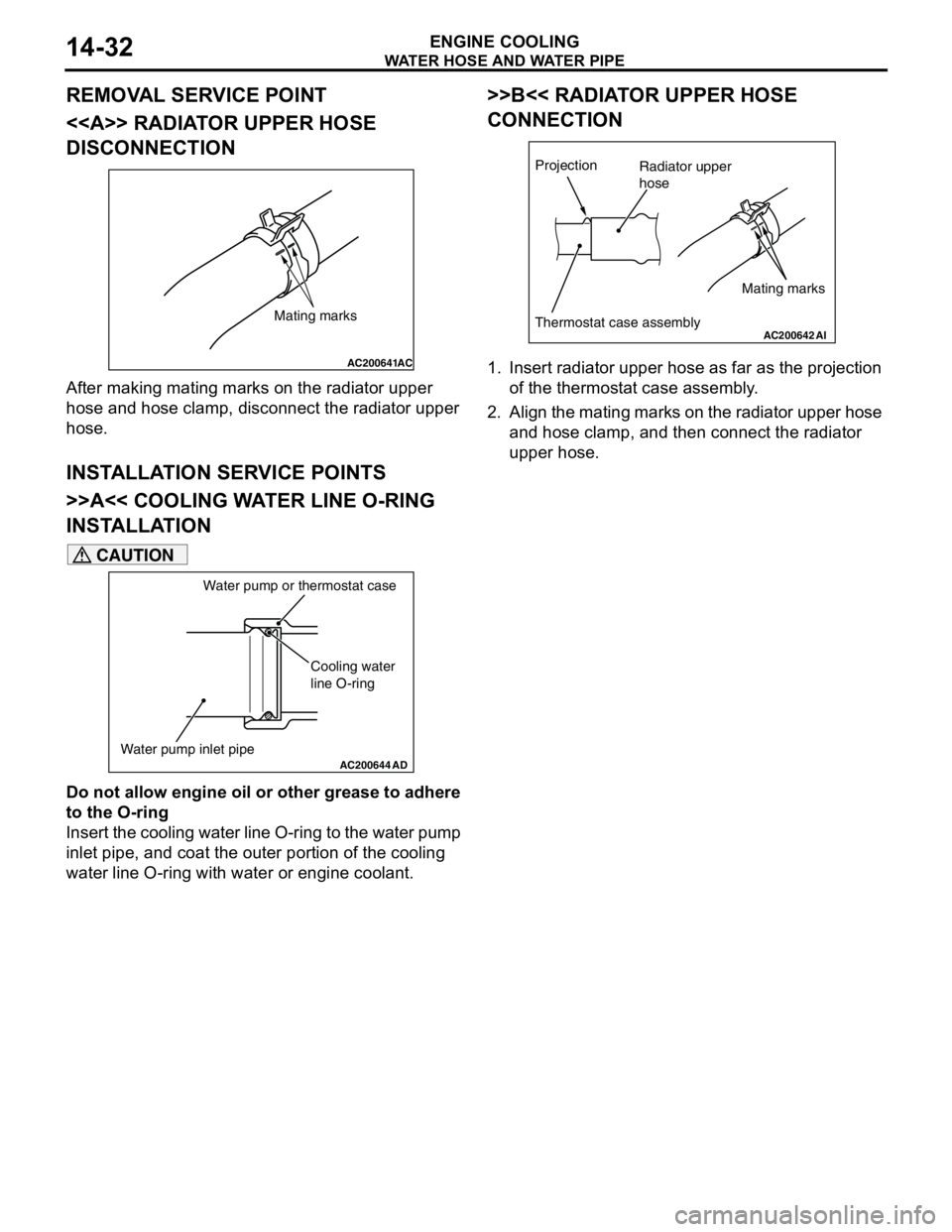
WATER HOSE AND WATER PIPE
ENGINE COOLING14-33
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION <4G6>M1141003300426
Pre-removal and Post-installation Operation
•Engine Coolant Draining and Supplying (Refer to
P.14-22).
•Air Cleaner Assembly Removal and Installation (Refer to
GROUP 15 P.15-3).
•Thermostat Removal and Installation (Refer to P.14-26).
AC303471
1 23 4
56
7 8 9
9
13 ± 2 N·m
23 ± 4 N·m 13 ± 2 N·m
N
N
AB
2
Sealant: Mitsubishi Genuine Part No. MD970389 or equivalentØ3 mm
Ø3 mm
5
Removal steps
<> >>C<<1. Radiator upper hose connection
>>B<<2. Cooling water outlet hose fitting
3. Throttle body water return hose
4. Throttle body water feed hose
>>B<<5. Thermostat case assembly
6. Heater water hose connection7. Control wiring harness clamp
8. Water pump inlet pipe
>>A<<9. Cooling water line O-ringRemoval steps (Continued)
Page 48 of 788
Page 49 of 788
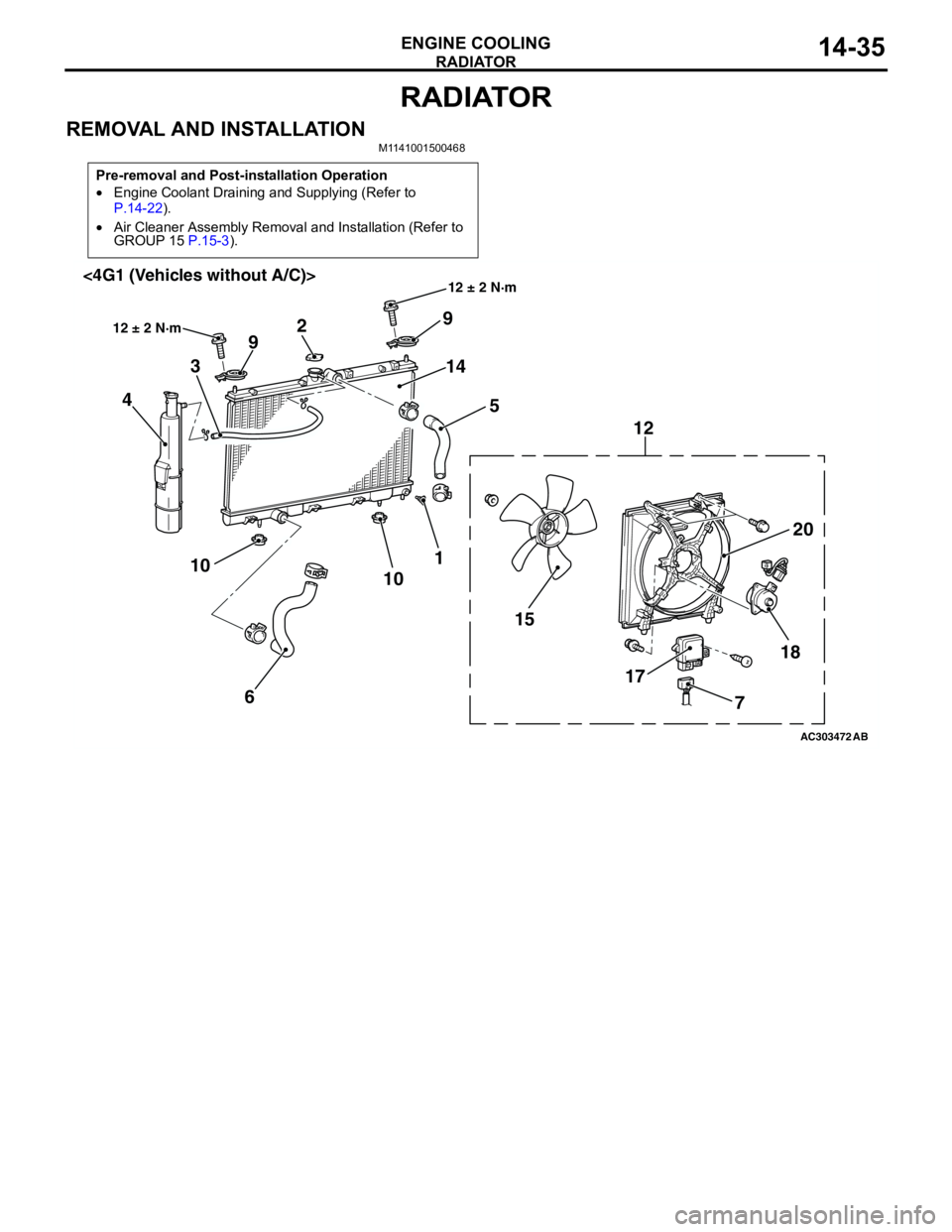
RADIATOR
ENGINE COOLING14-35
RADIATOR
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATIONM1141001500468
Pre-removal and Post-installation Operation
•Engine Coolant Draining and Supplying (Refer to
P.14-22).
•Air Cleaner Assembly Removal and Installation (Refer to
GROUP 15 P.15-3).
AC303472
18
17 1520 12 9
14
5 2
9
3
4
1
10
6 10
AB
12 ± 2 N·m
12 ± 2 N·m<4G1 (Vehicles without A/C)>
7
Page 57 of 788
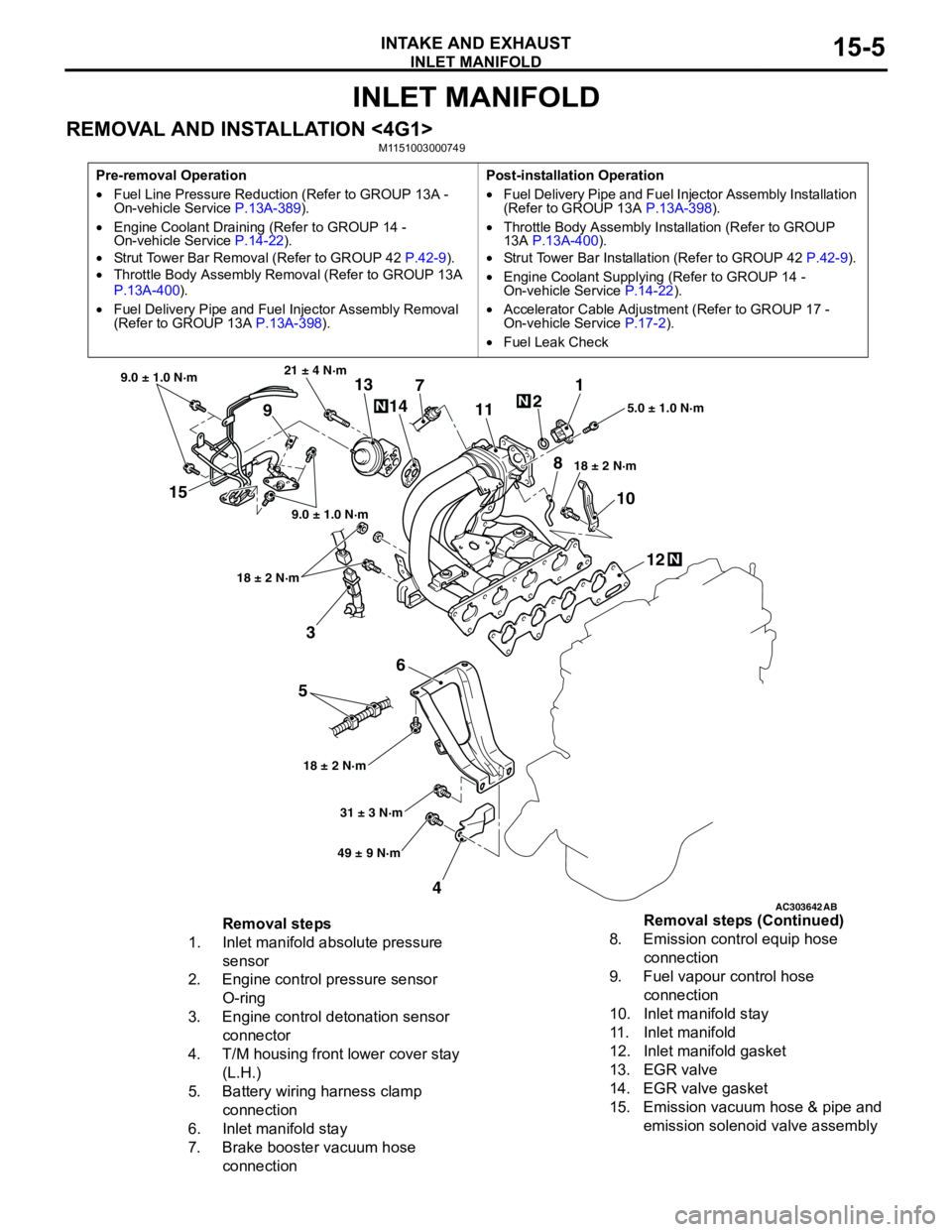
INLET MANIFOLD
INTAKE AND EXHAUST15-5
INLET MANIFOLD
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION <4G1>M1151003000749
Pre-removal Operation
•Fuel Line Pressure Reduction (Refer to GROUP 13A -
On-vehicle Service P.13A-389).
•Engine Coolant Draining (Refer to GROUP 14 -
On-vehicle Service P.14-22).
•Strut Tower Bar Removal (Refer to GROUP 42 P.42-9).
•Throttle Body Assembly Removal (Refer to GROUP 13A
P.13A-400).
•Fuel Delivery Pipe and Fuel Injector Assembly Removal
(Refer to GROUP 13A P.13A-398).Post-installation Operation
•Fuel Delivery Pipe and Fuel Injector Assembly Installation
(Refer to GROUP 13A P.13A-398).
•Throttle Body Assembly Installation (Refer to GROUP
13A P.13A-400).
•Strut Tower Bar Installation (Refer to GROUP 42 P.42-9).
•Engine Coolant Supplying (Refer to GROUP 14 -
On-vehicle Service P.14-22).
•Accelerator Cable Adjustment (Refer to GROUP 17 -
On-vehicle Service P.17-2).
•Fuel Leak Check
AC303642AB
15
3
6
5
412 10 71
2
11
913
14
21 ± 4 N·m
9.0 ± 1.0 N·m
9.0 ± 1.0 N·m
18 ± 2 N·m
18 ± 2 N·m18 ± 2 N·m5.0 ± 1.0 N·m
31 ± 3 N·m
49 ± 9 N·m
N
N
N
8
Removal steps
1. Inlet manifold absolute pressure
sensor
2. Engine control pressure sensor
O-ring
3. Engine control detonation sensor
connector
4. T/M housing front lower cover stay
(L.H.)
5. Battery wiring harness clamp
connection
6. Inlet manifold stay
7. Brake booster vacuum hose
connection8. Emission control equip hose
connection
9. Fuel vapour control hose
connection
10. Inlet manifold stay
11. Inlet manifold
12. Inlet manifold gasket
13. EGR valve
14. EGR valve gasket
15. Emission vacuum hose & pipe and
emission solenoid valve assembly Removal steps (Continued)
Page 58 of 788
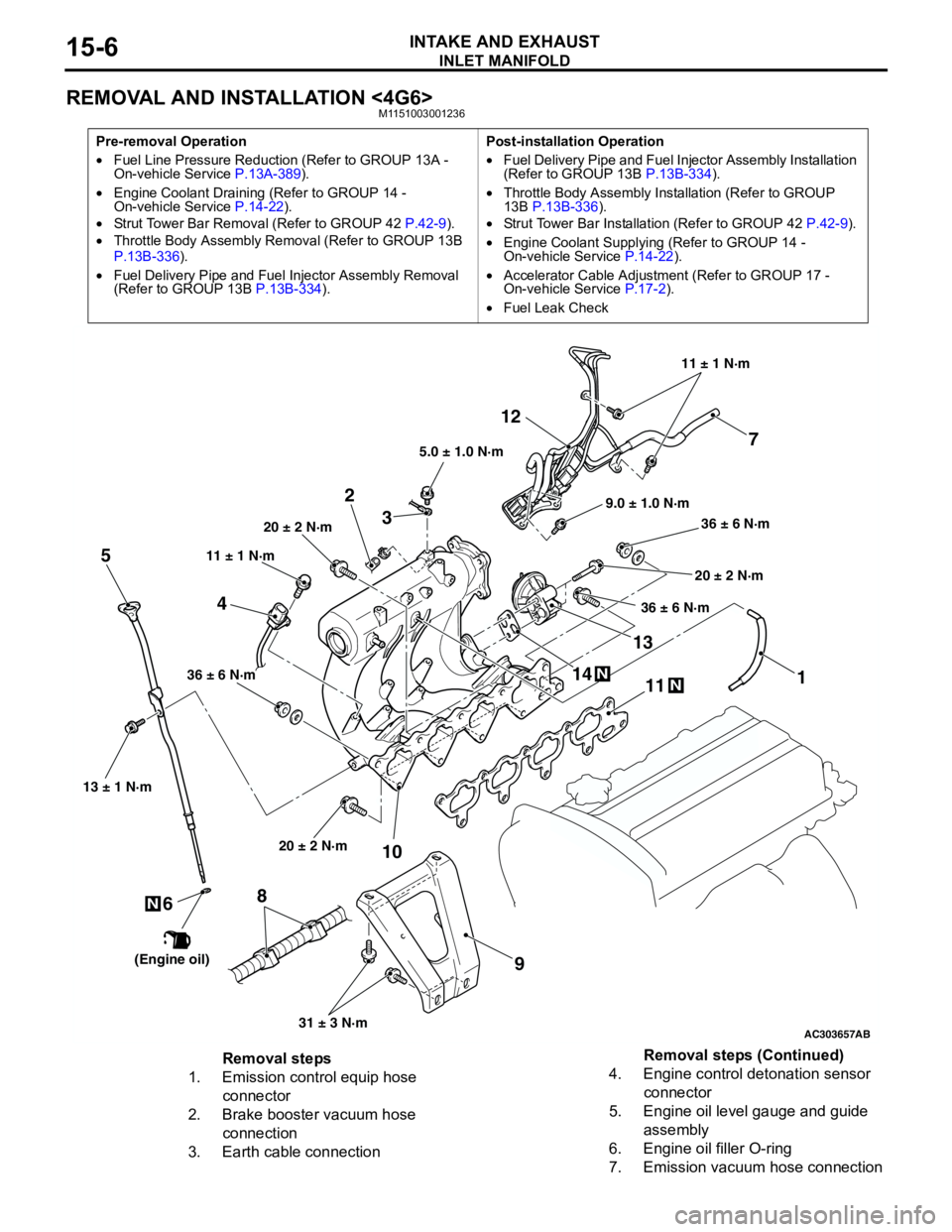
INLET MANIFOLD
INTAKE AND EXHAUST15-6
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION <4G6>M1151003001236
Pre-removal Operation
•Fuel Line Pressure Reduction (Refer to GROUP 13A -
On-vehicle Service P.13A-389).
•Engine Coolant Draining (Refer to GROUP 14 -
On-vehicle Service P.14-22).
•Strut Tower Bar Removal (Refer to GROUP 42 P.42-9).
•Throttle Body Assembly Removal (Refer to GROUP 13B
P.13B-336).
•Fuel Delivery Pipe and Fuel Injector Assembly Removal
(Refer to GROUP 13B P.13B-334).Post-installation Operation
•Fuel Delivery Pipe and Fuel Injector Assembly Installation
(Refer to GROUP 13B P.13B-334).
•Throttle Body Assembly Installation (Refer to GROUP
13B P.13B-336).
•Strut Tower Bar Installation (Refer to GROUP 42 P.42-9).
•Engine Coolant Supplying (Refer to GROUP 14 -
On-vehicle Service P.14-22).
•Accelerator Cable Adjustment (Refer to GROUP 17 -
On-vehicle Service P.17-2).
•Fuel Leak Check
AC303657
9.0 ± 1.0 N·m11 ± 1 N·m
20 ± 2 N·m
31 ± 3 N·m 36 ± 6 N·m
20 ± 2 N·m
20 ± 2 N·m
36 ± 6 N·m
36 ± 6 N·m
11
9 10 212
N1413N
AB
5.0 ± 1.0 N·m
3
1
11 ± 1 N·m
4
N
13 ± 1 N·m
5
6
(Engine oil)
7
8
Removal steps
1. Emission control equip hose
connector
2. Brake booster vacuum hose
connection
3. Earth cable connection4. Engine control detonation sensor
connector
5. Engine oil level gauge and guide
assembly
6. Engine oil filler O-ring
7. Emission vacuum hose connectionRemoval steps (Continued)
Page 94 of 788
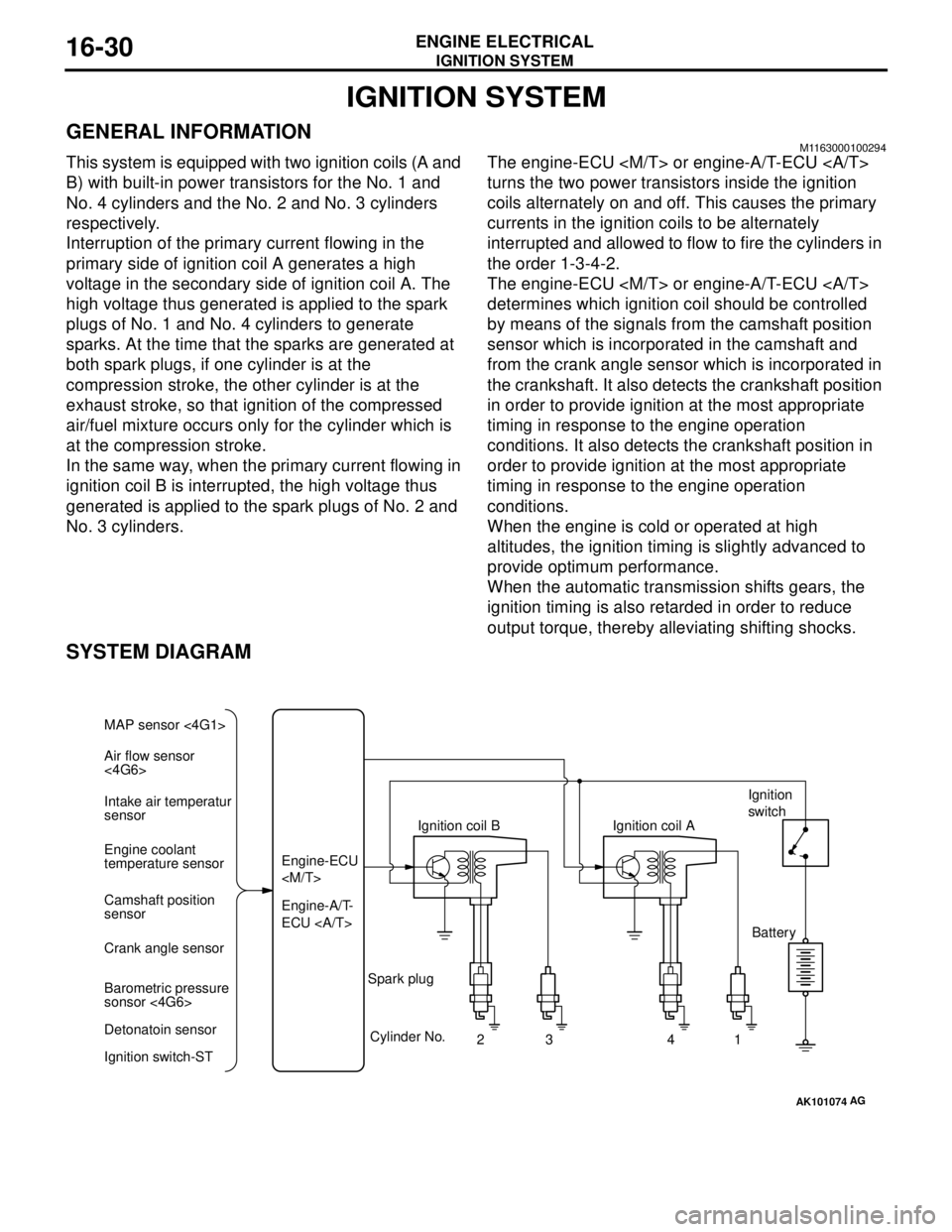
IGNITION SYSTEM
ENGINE ELECTRICAL16-30
IGNITION SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATIONM1163000100294
This system is equipped with two ignition coils (A and
B) with built-in power transistors for the No. 1 and
No. 4 cylinders and the No. 2 and No. 3 cylinders
respectively.
Interruption of the primary current flowing in the
primary side of ignition coil A generates a high
voltage in the secondary side of ignition coil A. The
high voltage thus generated is applied to the spark
plugs of No. 1 and No. 4 cylinders to generate
sparks. At the time that the sparks are generated at
both spark plugs, if one cylinder is at the
compression stroke, the other cylinder is at the
exhaust stroke, so that ignition of the compressed
air/fuel mixture occurs only for the cylinder which is
at the compression stroke.
In the same way, when the primary current flowing in
ignition coil B is interrupted, the high voltage thus
generated is applied to the spark plugs of No. 2 and
No. 3 cylinders.The engine-ECU
turns the two power transistors inside the ignition
coils alternately on and off. This causes the primary
currents in the ignition coils to be alternately
interrupted and allowed to flow to fire the cylinders in
the order 1-3-4-2.
The engine-ECU
determines which ignition coil should be controlled
by means of the signals from the camshaft position
sensor which is incorporated in the camshaft and
from the crank angle sensor which is incorporated in
the crankshaft. It also detects the crankshaft position
in order to provide ignition at the most appropriate
timing in response to the engine operation
conditions. It also detects the crankshaft position in
order to provide ignition at the most appropriate
timing in response to the engine operation
conditions.
When the engine is cold or operated at high
altitudes, the ignition timing is slightly advanced to
provide optimum performance.
When the automatic transmission shifts gears, the
ignition timing is also retarded in order to reduce
output torque, thereby alleviating shifting shocks.
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
AK101074
Air flow sensor
<4G6> MAP sensor <4G1>
Intake air temperatur
sensor
Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Camshaft position
sensor
Crank angle sensor
Barometric pressure
sonsor <4G6>
Detonatoin sensor
Ignition switch-STEngine-A/T-
ECU Engine-ECU
Cylinder No.
23 4
AG
1 Spark plugIgnition coil AIgnition
switch
Battery
Page 117 of 788
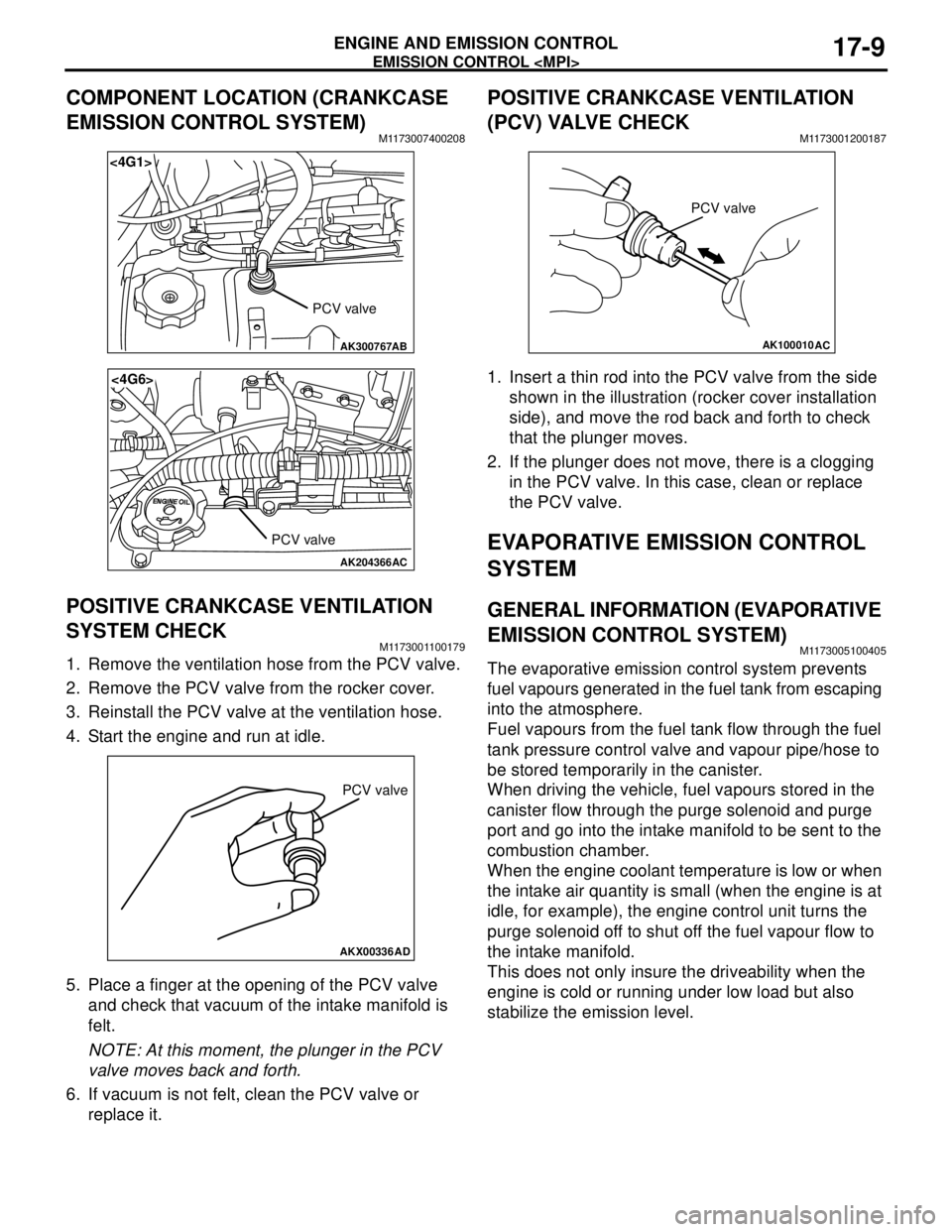
EMISSION CONTROL
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL17-9
COMPONENT LOCATION (CRANKCASE
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM)
M1173007400208
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION
SYSTEM CHECK
M1173001100179
1. Remove the ventilation hose from the PCV valve.
2. Remove the PCV valve from the rocker cover.
3. Reinstall the PCV valve at the ventilation hose.
4. Start the engine and run at idle.
5. Place a finger at the opening of the PCV valve
and check that vacuum of the intake manifold is
felt.
NOTE: At this moment, the plunger in the PCV
valve moves back and forth.
6. If vacuum is not felt, clean the PCV valve or
replace it.
POSITIVE CRANKCASE VENTILATION
(PCV) VALVE CHECK
M1173001200187
1. Insert a thin rod into the PCV valve from the side
shown in the illustration (rocker cover installation
side), and move the rod back and forth to check
that the plunger moves.
2. If the plunger does not move, there is a clogging
in the PCV valve. In this case, clean or replace
the PCV valve.
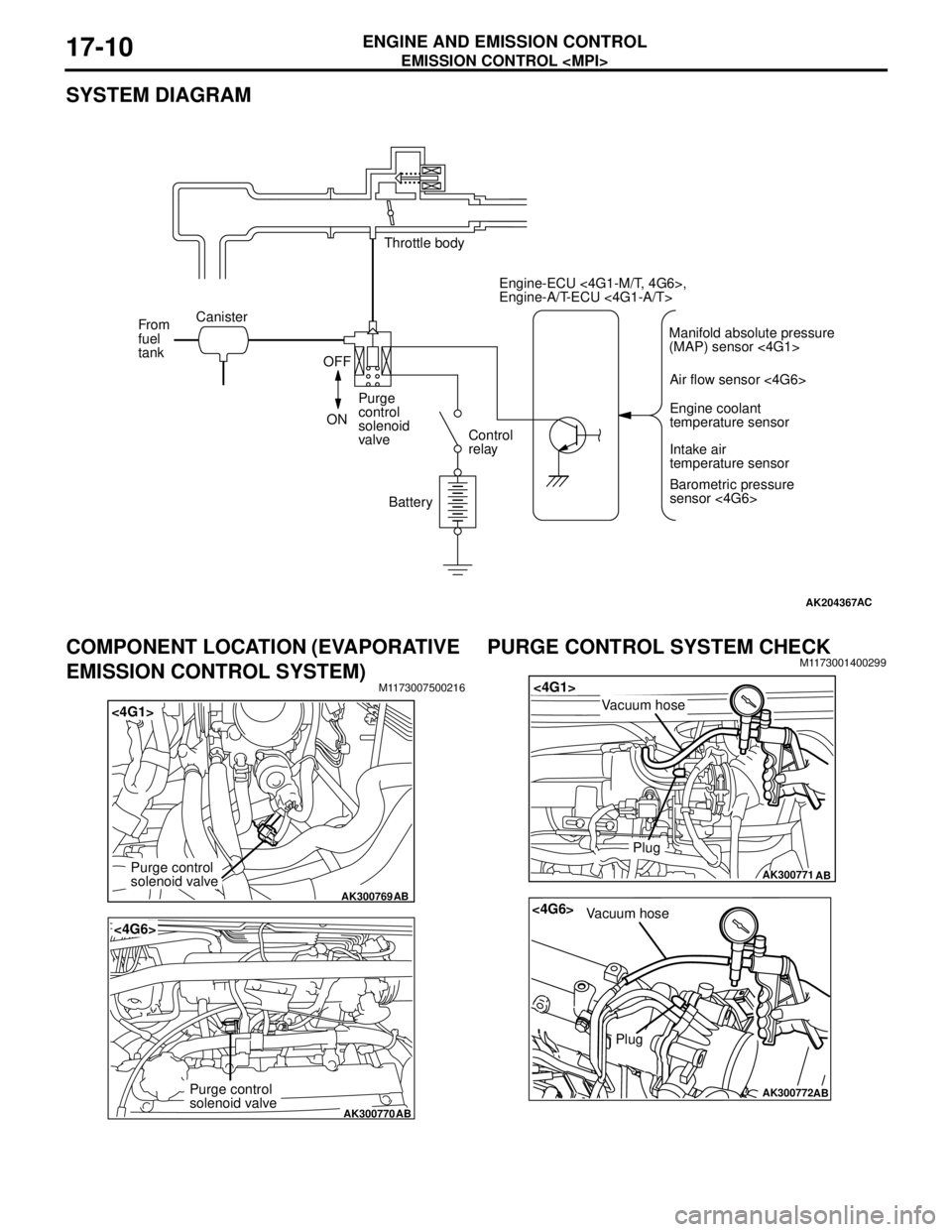
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM
GENERAL INFORMATION (EVAPORATIVE
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM)
M1173005100405
The evaporative emission control system prevents
fuel vapours generated in the fuel tank from escaping
into the atmosphere.
Fuel vapours from the fuel tank flow through the fuel
tank pressure control valve and vapour pipe/hose to
be stored temporarily in the canister.
When driving the vehicle, fuel vapours stored in the
canister flow through the purge solenoid and purge
port and go into the intake manifold to be sent to the
combustion chamber.
When the engine coolant temperature is low or when
the intake air quantity is small (when the engine is at
idle, for example), the engine control unit turns the
purge solenoid off to shut off the fuel vapour flow to
the intake manifold.
This does not only insure the driveability when the
engine is cold or running under low load but also
stabilize the emission level.
AK300767
<4G1>
AB
PCV valve
AK204366
<4G6>
AC
PCV valve
AKX00336
PCV valve
AD
AK100010
PCV valve
AC
Page 118 of 788
EMISSION CONTROL
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL17-10
SYSTEM DIAGRAM
COMPONENT LOCATION (EVAPORATIVE
EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM)
M1173007500216
PURGE CONTROL SYSTEM CHECKM1173001400299
AK204367AC
Throttle body
Canister
From
fuel
tank
OFF
ONPurge
control
solenoid
valveControl
relay
BatteryEngine-ECU <4G1-M/T, 4G6>,
Engine-A/T-ECU <4G1-A/T>
Air flow sensor <4G6>
Engine coolant
temperature sensor
Intake air
temperature sensor
Barometric pressure
sensor <4G6> Manifold absolute pressure
(MAP) sensor <4G1>
AK300769
<4G1>
AB
Purge control
solenoid valve
AK300770
<4G6>
AB
Purge control
solenoid valve
AK300771
<4G1>
AB
Plug
Vacuum hose
AK300772
<4G6>
AB
Plug
Vacuum hose
Page 119 of 788
EMISSION CONTROL
ENGINE AND EMISSION CONTROL17-11
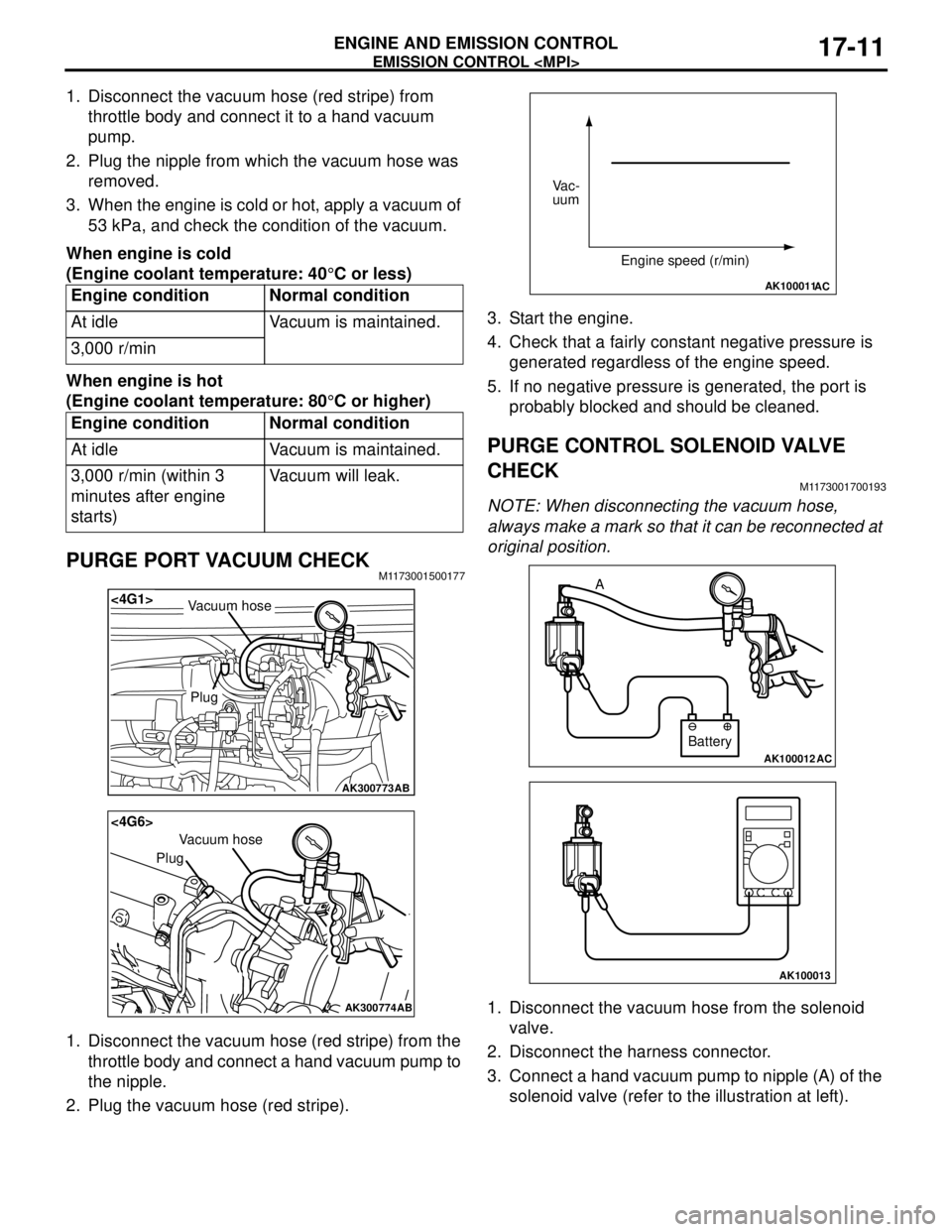
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (red stripe) from
throttle body and connect it to a hand vacuum
pump.
2. Plug the nipple from which the vacuum hose was
removed.
3. When the engine is cold or hot, apply a vacuum of
53 kPa, and check the condition of the vacuum.
When engine is cold
(Engine coolant temperature: 40°C or less)
When engine is hot
(Engine coolant temperature: 80°C or higher)
PURGE PORT VACUUM CHECKM1173001500177
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose (red stripe) from the
throttle body and connect a hand vacuum pump to
the nipple.
2. Plug the vacuum hose (red stripe).3. Start the engine.
4. Check that a fairly constant negative pressure is
generated regardless of the engine speed.
5. If no negative pressure is generated, the port is
probably blocked and should be cleaned.
PURGE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE
CHECK
M1173001700193
NOTE: When disconnecting the vacuum hose,
always make a mark so that it can be reconnected at
original position.
1. Disconnect the vacuum hose from the solenoid
valve.
2. Disconnect the harness connector.
3. Connect a hand vacuum pump to nipple (A) of the
solenoid valve (refer to the illustration at left). Engine condition Normal condition
At idle Vacuum is maintained.
3,000 r/min
Engine condition Normal condition
At idle Vacuum is maintained.
3,000 r/min (within 3
minutes after engine
starts)Vacuum will leak.
AK300773
<4G1>
AB
Plug
Vacuum hose
AK300774
<4G6>
AB
Plug
Vacuum hose
AK100011AC
Vac-
uum
Engine speed (r/min)
AK100012AC
Battery A
AK100013