Changes MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007 Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: MITSUBISHI, Model Year: 2007, Model line: LANCER EVOLUTION, Model: MITSUBISHI LANCER EVOLUTION 2007Pages: 1449, PDF Size: 56.82 MB
Page 1055 of 1449

BASIC BRAKE SYSTEM -On-vehicle Service35A-13
(5) Apply repair kit grease to the portions of the pads
indicated on the left. At this time, make sure that
the grease will not be applied to any other surfaces.
(6) Mount the pads to the caliper so that its side with
the wear indicator is on the outside of the vehicle.
With the rear pads, ensure that the arrow on the
pad faces in the same direction as the brake disc
turns when the vehicle moves forward.
(7) Holding the cross spring with one hand, fit pins in
the caliper.
(8) Using a spring balance, measure the turning sliding
resistance of the hub in the forward direction.
(9) Find the brake disc drag force [the difference in
measurements taken in step(3) and in step(8)].
Standard value: 69 N or less
DISC BRAKE ROTOR CHECK
Caution
When servicing disc brakes, it is necessary to exercise caution to keep the disc brakes within
the allowable service values in order to maintain normal brake operation.
Before re-finishing or re-processing the brake disc surface, the following conditions should be checked.
Inspection itemsRemarks
Scratches, rust, saturated lining materials
and wearDIf the vehicle is not driven for a certain period, the sections of
the discs that are not in contact with lining will become rusty, causing
noise and shuddering.
DIf grooves resulting from excessive disc wear and scratches are
not removed prior to installing a new pad assembly, there will
momentarily be inappropriate contact between the disc and the
lining (pad).
Run-out or driftExcessive run-out or drift of the discs will increase the pedal depression
resistance due to piston knock-back.
Change in thickness (parallelism)If the thickness of the disc changes, this will cause pedal pulsation,
shuddering and surging.
Inset or warping (flatness)Overheating and improper handling while servicing will cause inset or
warping.
Front Rear
Cross
spring
Pins
Page 1085 of 1449
ABS <4WD> -Troubleshooting35B-15
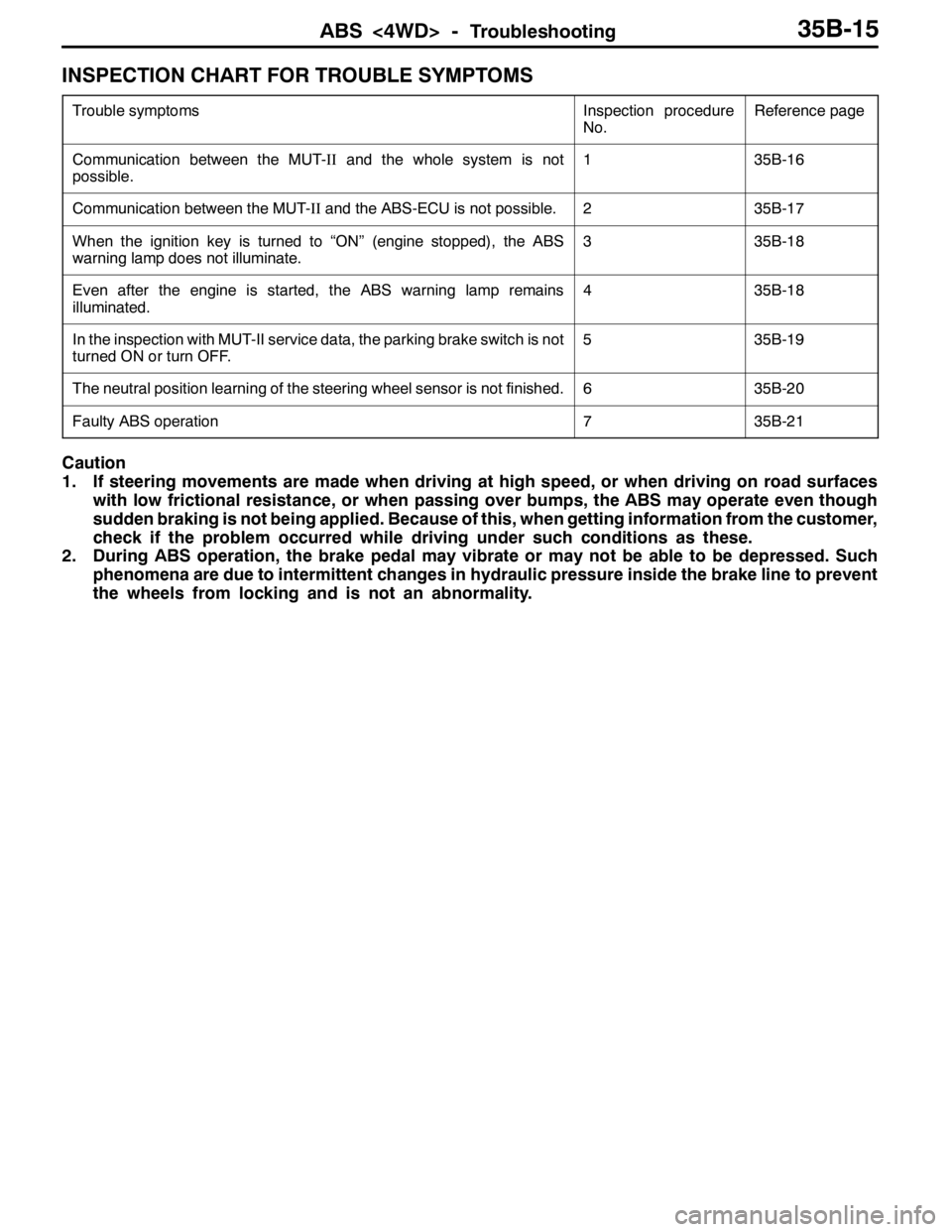
INSPECTION CHART FOR TROUBLE SYMPTOMS
Trouble symptomsInspection procedure
No.Reference page
Communication between the MUT-IIand the whole system is not
possible.135B-16
Communication between the MUT-IIand the ABS-ECU is not possible.235B-17
When the ignition key is turned to “ON” (engine stopped), the ABS
warning lamp does not illuminate.335B-18
Even after the engine is started, the ABS warning lamp remains
illuminated.435B-18
In the inspection with MUT-II service data, the parking brake switch is not
turned ON or turn OFF.535B-19
The neutral position learning of the steering wheel sensor is not finished.635B-20
Faulty ABS operation735B-21
Caution
1. If steering movements are made when driving at high speed, or when driving on road surfaces
with low frictional resistance, or when passing over bumps, the ABS may operate even though
sudden braking is not being applied. Because of this, when getting information from the customer,
check if the problem occurred while driving under such conditions as these.
2. During ABS operation, the brake pedal may vibrate or may not be able to be depressed. Such
phenomena are due to intermittent changes in hydraulic pressure inside the brake line to prevent
the wheels from locking and is not an abnormality.
Page 1123 of 1449

STEERING -On-vehicle Service37A-9
POWER STEERING FLUID LEVEL CHECK
1. Park the vehicle on a flat, level surface, start the engine,
and then turn the steering wheel several times to raise
the temperature of the fluid to approximately 50 - 60_C.
2. With the engine running, turn the wheel all the way to
the left and right several times.
3. Check the fluid in the oil reservoir for foaming or milkiness.
Check the difference of the fluid level when the engine
is stopped, and while it is running. If the change of the
fluid level is 5 mm or more, air bleeding should be done.
POWER STEERING FLUID REPLACEMENT
1. Raise the front wheels on a jack, and then support them
with rigid racks.
2. Disconnect the return hose connection.
3. Connect a vinyl hose to the return hose, and drain the
oil into a container.
4. Disconnect the ignition coil connectors. (Refer to
GROUP16 - Ignition System.)
5. While operating the starting motor intermittently, turn the
steering wheel all the way to the left and right several
times to drain all of the fluid.
6. Connect the return hoses securely, and then secure it
with the clip.
7. Fill the oil reservoir with specified fluid up to the lower
position of the filter, and then bleed air.
Specified fluid:
Automatic transmission fluid DEXRONII
Caution
Do not use ATF-SPIIM and ATF-SPIII.
POWER STEERING SYSTEM BLEEDING
1. Jack up the vehicle and support the front wheels with
rigid racks.
2. Disconnect the ignition coil connectors. (Refer to
GROUP16 - Ignition System.)
3. Cranking the engine with the starter several times
intermittently (during 15 to 20 seconds), turn the steering
wheel left and right fully five or six times.
Caution
(1) During the bleeding, refill the fluid so that the
level never falls below the lower position of the
filter.
(2) Be sure to bleed air only while cranking. If the
bleeding is done with the engine running, the air
will be broken up and absorbed into the fluid.
4. Connect the ignition coil connectors and idle the engine.
5. Turn the steering wheel left and right fully until no bubbles
comes out in the oil reservoir.
6. See that the fluid is not milky and that the fluid level
is up to the specified position on the level gauge.
7. See that the fluid level changes little when the steering
wheel is turned left and right.
8. Check difference in fluid levels between the engine
stopped and running.
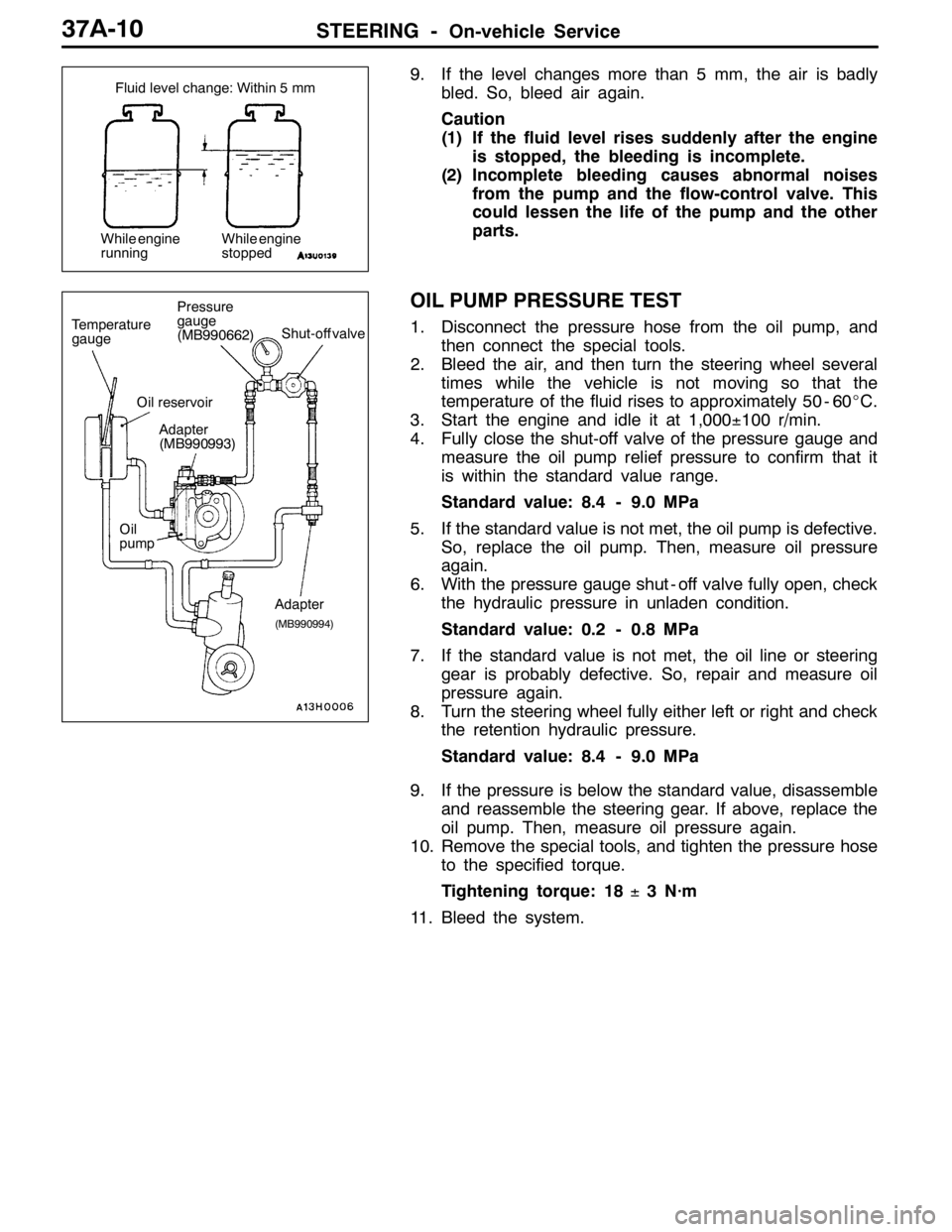
Fluid level change: Within 5 mm
While engine
runningWhile engine
stopped
Return hose
Vinyl hose
Page 1124 of 1449
STEERING -On-vehicle Service37A-10
9. If the level changes more than 5 mm, the air is badly
bled. So, bleed air again.
Caution
(1) If the fluid level rises suddenly after the engine
is stopped, the bleeding is incomplete.
(2) Incomplete bleeding causes abnormal noises
from the pump and the flow-control valve. This
could lessen the life of the pump and the other
parts.
OIL PUMP PRESSURE TEST
1. Disconnect the pressure hose from the oil pump, and
then connect the special tools.
2. Bleed the air, and then turn the steering wheel several
times while the vehicle is not moving so that the
temperature of the fluid rises to approximately 50 - 60_C.
3. Start the engine and idle it at 1,000±100 r/min.
4. Fully close the shut-off valve of the pressure gauge and
measure the oil pump relief pressure to confirm that it
is within the standard value range.
Standard value: 8.4 - 9.0 MPa
5. If the standard value is not met, the oil pump is defective.
So, replace the oil pump. Then, measure oil pressure
again.
6. With the pressure gauge shut - off valve fully open, check
the hydraulic pressure in unladen condition.
Standard value: 0.2 - 0.8 MPa
7. If the standard value is not met, the oil line or steering
gear is probably defective. So, repair and measure oil
pressure again.
8. Turn the steering wheel fully either left or right and check
the retention hydraulic pressure.
Standard value: 8.4 - 9.0 MPa
9. If the pressure is below the standard value, disassemble
and reassemble the steering gear. If above, replace the
oil pump. Then, measure oil pressure again.
10. Remove the special tools, and tighten the pressure hose
to the specified torque.
Tightening torque: 18±3 N·m
11. Bleed the system.
Fluid level change: Within 5 mm
While engine
runningWhile engine
stopped
Temperature
gaugePressure
gauge
(MB990662)Shut-off valve
Oil
pumpOil reservoir
Adapter
(MB990994)
Adapter
(MB990993)
Page 1150 of 1449

BODY -Hood42-2
HOOD
ON - VEHICLE SERVICE
ADJUSTMENT OF CLEARANCE AROUND
HOOD
ADJUSTMENT OF ALIGNMENT OF HOOD
STEPPED PORTION AND HOOD STRIKER
ADJUSTMENT OF HOOD HEIGHT
With the marker as guide, turn the hood bumper to adjust
the hood height. The hood bumper height changes approx.
3mm (new hood bumper with one complete turn).
A
A
Section A-A
16.3 mmHood
Hood bumper
Page 1367 of 1449
SWS -Troubleshooting54B-3
INPUT SIGNAL CHECK
1. Check the inputs using MUT-II or a voltmeter. (Refer to GROUP 00 - How to Use
Troubleshooting/Inspection Service Points.)
2. The following input signals can be checked using MUT-II or a voltmeter connected to the diagnosis
connector.
NOTE
When fault is detected during input signal inspection, refer to Trouble Symptom Chart to perform
troubleshooting. (Refer to P.54B-7).
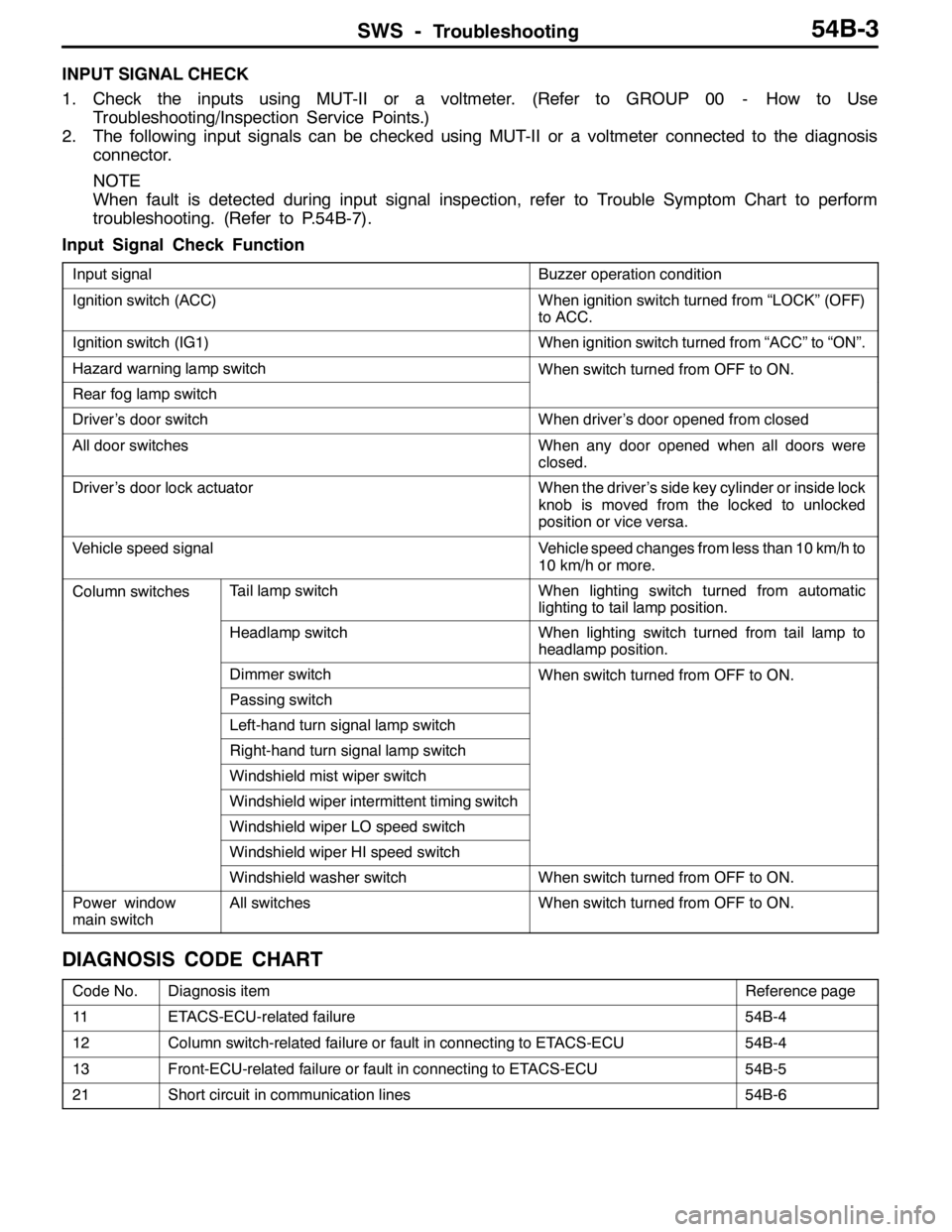
Input Signal Check Function
Input signalBuzzer operation condition
Ignition switch (ACC)When ignition switch turned from “LOCK” (OFF)
to ACC.
Ignition switch (IG1)When ignition switch turned from “ACC” to “ON”.
Hazard warning lamp switchWhen switch turned from OFF to ON.
Rear fog lamp switch
Driver’s door switchWhen driver’s door opened from closed
All door switchesWhen any door opened when all doors were
closed.
Driver’s door lock actuatorWhen the driver’s side key cylinder or inside lock
knob is moved from the locked to unlocked
position or vice versa.
Vehicle speed signalVehicle speed changes from less than 10 km/h to
10 km/h or more.
Column switchesTail lamp switchWhen lighting switch turned from automatic
lighting to tail lamp position.
Headlamp switchWhen lighting switch turned from tail lamp to
headlamp position.
Dimmer switchWhen switch turned from OFF to ON.
Passing switch
Left-hand turn signal lamp switch
Right-hand turn signal lamp switch
Windshield mist wiper switch
Windshield wiper intermittent timing switch
Windshield wiper LO speed switch
Windshield wiper HI speed switch
Windshield washer switchWhen switch turned from OFF to ON.
Power window
main switchAll switchesWhen switch turned from OFF to ON.
DIAGNOSIS CODE CHART
Code No.Diagnosis itemReference page
11ETACS-ECU-related failure54B-4
12Column switch-related failure or fault in connecting to ETACS-ECU54B-4
13Front-ECU-related failure or fault in connecting to ETACS-ECU54B-5
21Short circuit in communication lines54B-6