check engine light NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2005, Model line: NAVARA, Model: NISSAN NAVARA 2005Pages: 3171, PDF Size: 49.59 MB
Page 1647 of 3171
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-25
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
lHeat sensitive
lFreezing
lWater intrusion
lElectrical load
lCold or hot start up
Get a thorough description of the incident from the customer. It is important for simulating the conditions of the
problem.
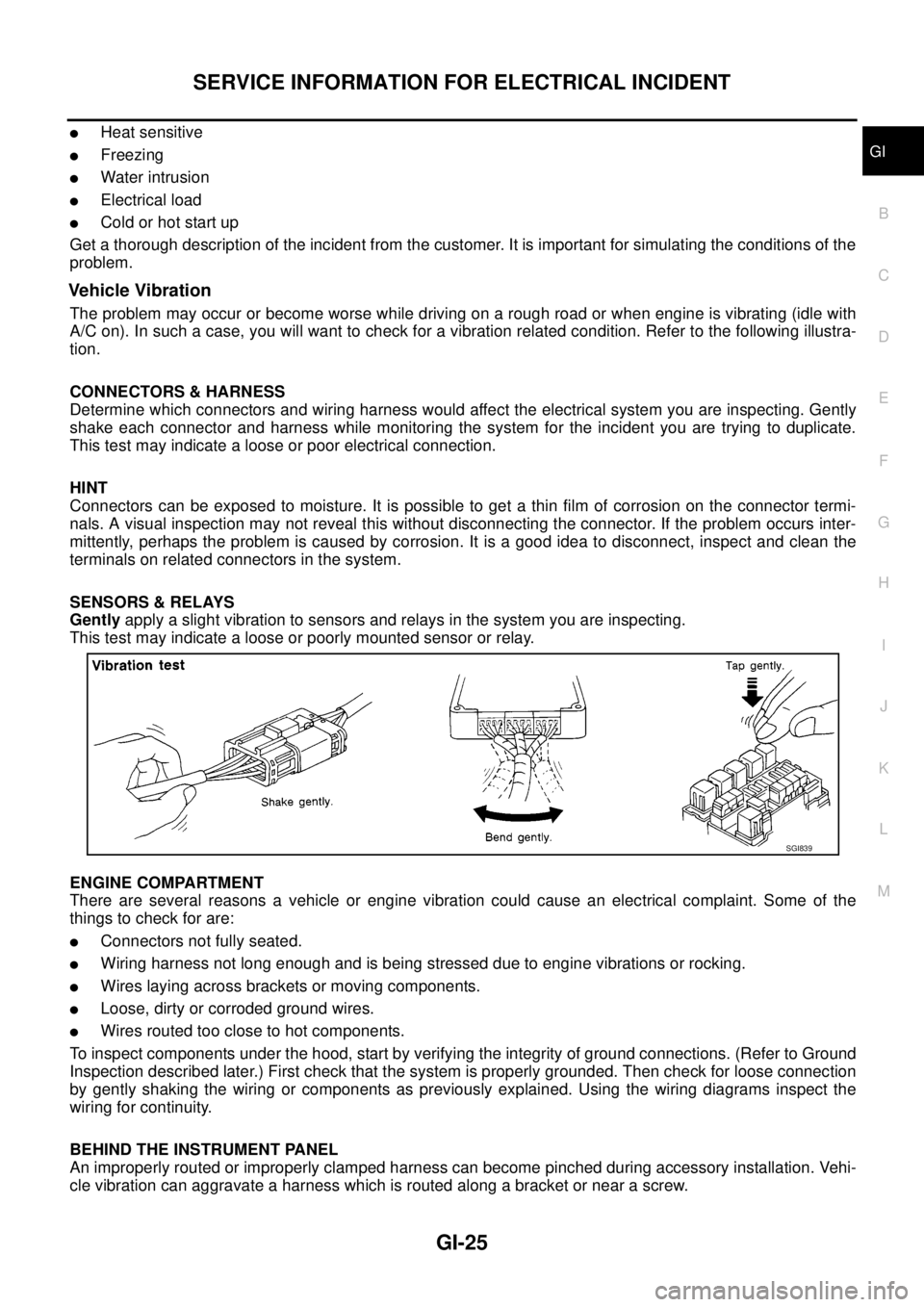
Vehicle Vibration
The problem may occur or become worse while driving on a rough road or when engine is vibrating (idle with
A/C on). In such a case, you will want to check for a vibration related condition. Refer to the following illustra-
tion.
CONNECTORS & HARNESS
Determine which connectors and wiring harness would affect the electrical system you are inspecting. Gently
shake each connector and harness while monitoring the system for the incident you are trying to duplicate.
This test may indicate a loose or poor electrical connection.
HINT
Connectors can be exposed to moisture. It is possible to get a thin film of corrosion on the connector termi-
nals. A visual inspection may not reveal this without disconnecting the connector. If the problem occurs inter-
mittently, perhaps the problem is caused by corrosion. It is a good idea to disconnect, inspect and clean the
terminals on related connectors in the system.
SENSORS & RELAYS
Gentlyapply a slight vibration to sensors and relays in the system you are inspecting.
This test may indicate a loose or poorly mounted sensor or relay.
ENGINE COMPARTMENT
There are several reasons a vehicle or engine vibration could cause an electrical complaint. Some of the
things to check for are:
lConnectors not fully seated.
lWiring harness not long enough and is being stressed due to engine vibrations or rocking.
lWires laying across brackets or moving components.
lLoose, dirty or corroded ground wires.
lWires routed too close to hot components.
To inspect components under the hood, start by verifying the integrity of ground connections. (Refer to Ground
Inspection described later.) First check that the system is properly grounded. Then check for loose connection
by gently shaking the wiring or components as previously explained. Using the wiring diagrams inspect the
wiring for continuity.
BEHIND THE INSTRUMENT PANEL
An improperly routed or improperly clamped harness can become pinched during accessory installation. Vehi-
cle vibration can aggravate a harness which is routed along a bracket or near a screw.
SGI839
Page 1671 of 3171
CONSULT-II CHECKING SYSTEM
GI-49
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Checking EquipmentEAS001H5
When ordering the following equipment, contact your NISSAN/INFINITI distributor.
CAUTION:
lPrevious CONSULT-II “I” and “Y” DLC-I and DLC-II cables should NOT be used anymore because
their DDL connector pins can be damaged during cable swapping.
lIf CONSULT-ll is used with no connection of CONSULT-ll CONVERTER, malfunctions might be
detected in self-diagnosis depending on control unit which carries out CAN communication.
lIf CONVERTER is not connected with CONSULT-ll, vehicle occur the "FAIL-SAFE MODE" which is
"LIGHT UP the HEADLIGHT" and/or "Cooling FAN ROTATING" when CONSULT-ll is started.
NOTE:
lThe CONSULT-II must be used in conjunction with a program card.
CONSULT-II does not require loading (Initialization) procedure.
lBe sure the CONSULT-II is turned off before installing or removing a program card.
CONSULT-II Start ProcedureEAS001H6
Turning ignition switch off when performing CAN diagnosis could cause CAN memory to be erased.
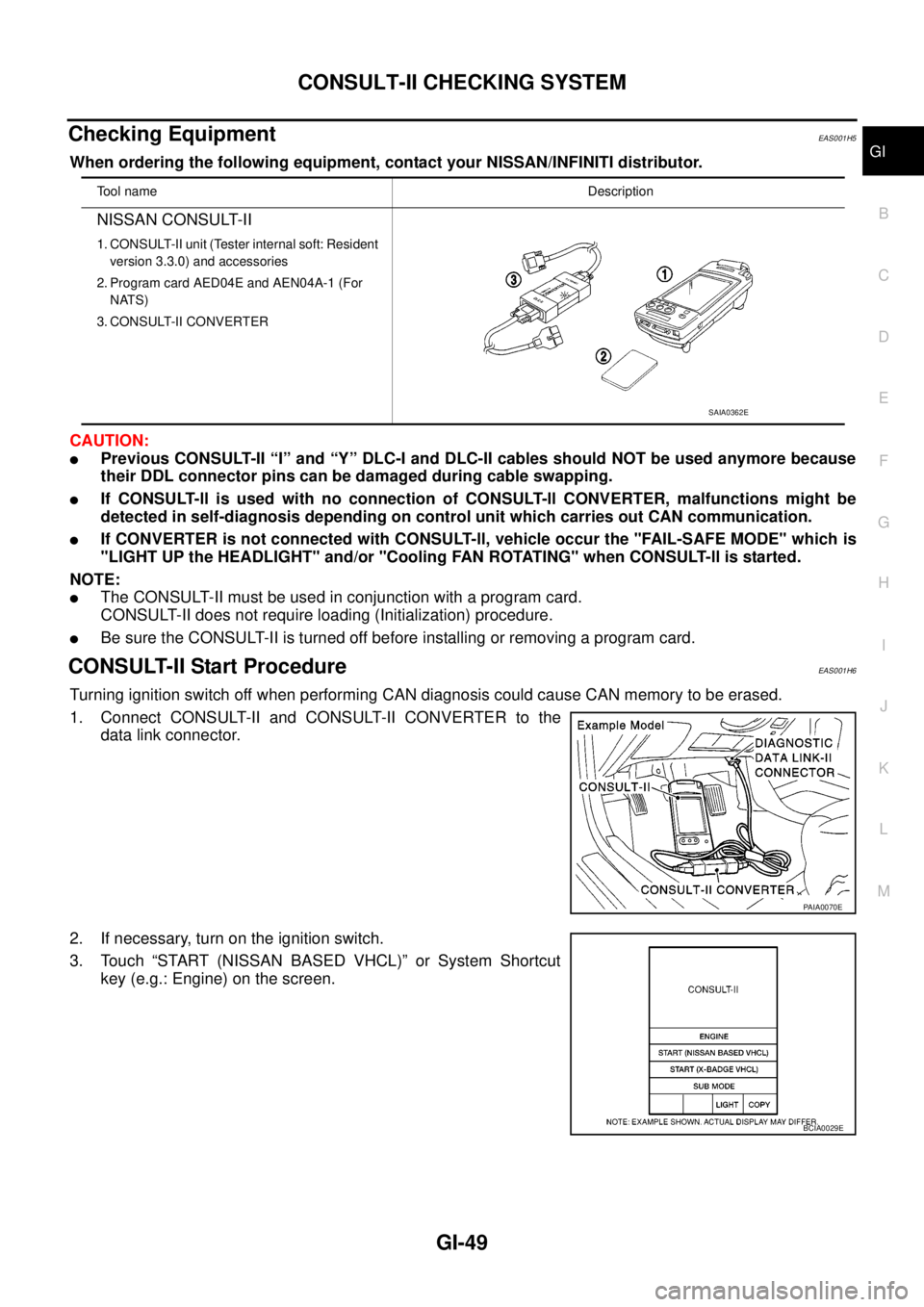
1. Connect CONSULT-II and CONSULT-II CONVERTER to the
data link connector.
2. If necessary, turn on the ignition switch.
3. Touch “START (NISSAN BASED VHCL)” or System Shortcut
key (e.g.: Engine) on the screen.
Tool nameDescription
NISSAN CONSULT-II
1. CONSULT-II unit (Tester internal soft: Resident
version 3.3.0) and accessories
2. Program card AED04E and AEN04A-1 (For
NATS)
3. CONSULT-II CONVERTER
SAIA0362E
PAIA0070E
BCIA0029E
Page 1684 of 3171
GI-62
TERMINOLOGY
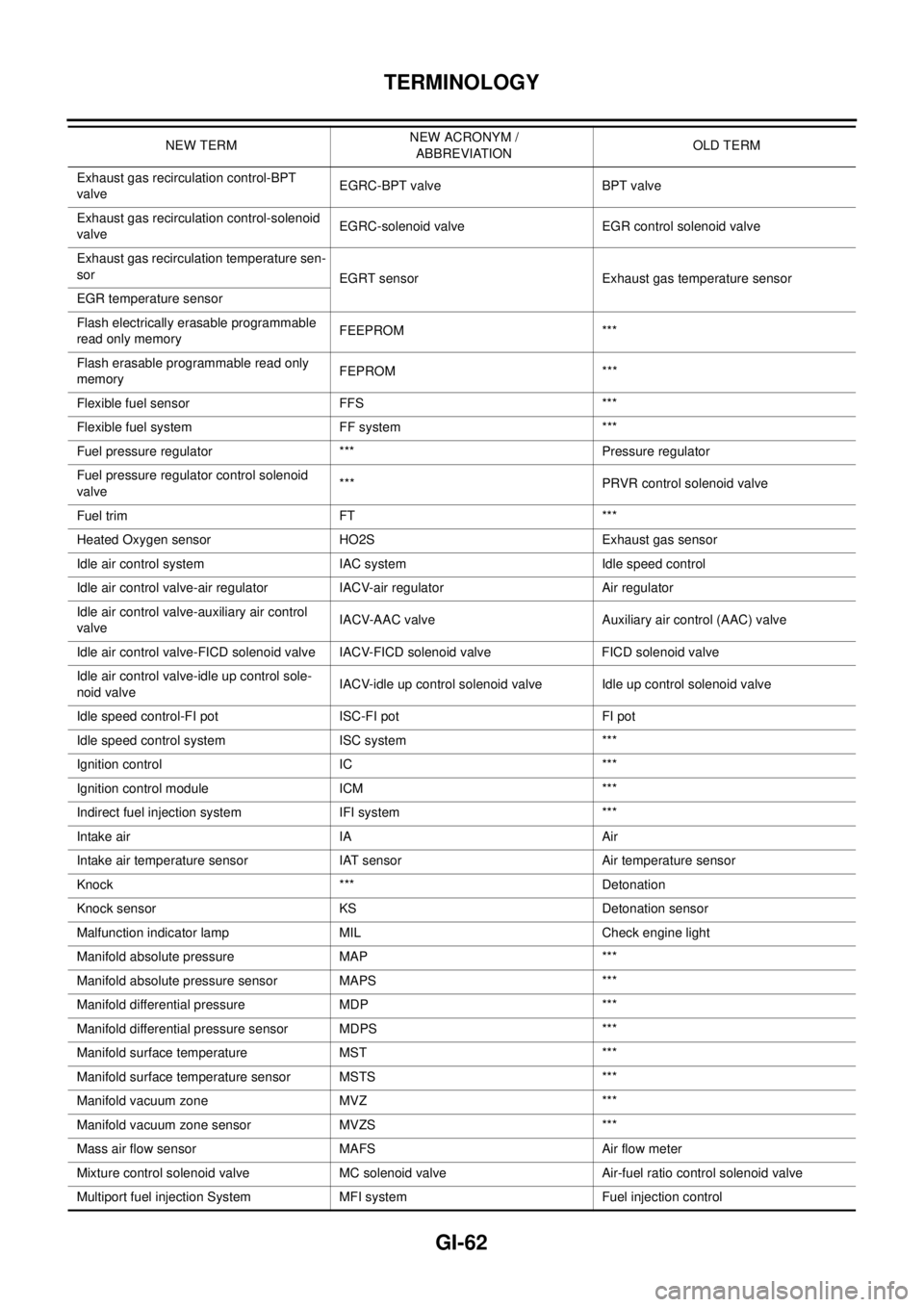
Exhaust gas recirculation control-BPT
valveEGRC-BPT valve BPT valve
Exhaust gas recirculation control-solenoid
valveEGRC-solenoid valve EGR control solenoid valve
Exhaust gas recirculation temperature sen-
sor
EGRT sensor Exhaust gas temperature sensor
EGR temperature sensor
Flash electrically erasable programmable
read only memoryFEEPROM ***
Flash erasable programmable read only
memoryFEPROM ***
Flexible fuel sensor FFS ***
Flexible fuel system FF system ***
Fuel pressure regulator *** Pressure regulator
Fuel pressure regulator control solenoid
valve*** PRVR control solenoid valve
Fuel trim FT ***
Heated Oxygen sensor HO2S Exhaust gas sensor
Idle air control system IAC system Idle speed control
Idle air control valve-air regulator IACV-air regulator Air regulator
Idle air control valve-auxiliary air control
valveIACV-AAC valve Auxiliary air control (AAC) valve
Idle air control valve-FICD solenoid valve IACV-FICD solenoid valve FICD solenoid valve
Idle air control valve-idle up control sole-
noid valveIACV-idle up control solenoid valve Idle up control solenoid valve
Idle speed control-FI pot ISC-FI pot FI pot
Idle speed control system ISC system ***
Ignition control IC ***
Ignition control module ICM ***
Indirect fuel injection system IFI system ***
Intake air IA Air
Intake air temperature sensor IAT sensor Air temperature sensor
Knock *** Detonation
Knock sensor KS Detonation sensor
Malfunction indicator lamp MIL Check engine light
Manifold absolute pressure MAP ***
Manifold absolute pressure sensor MAPS ***
Manifold differential pressure MDP ***
Manifold differential pressure sensor MDPS ***
Manifold surface temperature MST ***
Manifold surface temperature sensor MSTS ***
Manifold vacuum zone MVZ ***
Manifold vacuum zone sensor MVZS ***
Mass air flow sensor MAFS Air flow meter
Mixture control solenoid valve MC solenoid valve Air-fuel ratio control solenoid valve
Multiport fuel injection System MFI system Fuel injection controlNEW TERMNEW ACRONYM /
ABBREVIATIONOLD TERM
Page 1692 of 3171
GW-6
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
If possible, drive the vehicle with the customer until the noise is duplicated. Note any additional information on
the Diagnostic Worksheet regarding the conditions or location of the noise. This information can be used to
duplicate the same conditions when you confirm the repair.
If the noise can be duplicated easily during the test drive, to help identify the source of the noise, try to dupli-
cate the noise with the vehicle stopped by doing one or all of the following:
1) Close a door.
2) Tap or push/pull around the area where the noise appears to be coming from.
3) Rev the engine.
4) Use a floor jack to recreate vehicle “twist”.
5) At idle, apply engine load (electrical load, half-clutch on M/T model, drive position on A/T model).
6) Raise the vehicle on a hoist and hit a tire with a rubber hammer.
lDrive the vehicle and attempt to duplicate the conditions the customer states exist when the noise occurs.
lIf it is difficult to duplicate the noise, drive the vehicle slowly on an undulating or rough road to stress the
vehicle body.
CHECK RELATED SERVICE BULLETINS
After verifying the customer concern or symptom, check ASIST for Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) related
to that concern or symptom.
If a TSB relates to the symptom, follow the procedure to repair the noise.
LOCATE THE NOISE AND IDENTIFY THE ROOT CAUSE
1. Narrow down the noise to a general area. To help pinpoint the source of the noise, use a listening tool
(Engine Ear or mechanics stethoscope).
2. Narrowdownthenoisetoamorespecificareaandidentifythecauseofthenoiseby:
lremoving the components in the area that you suspect the noise is coming from.
Do not use too much force when removing clips and fasteners, otherwise clips and fastener can be broken
or lost during the repair, resulting in the creation of new noise.
ltapping or pushing/pulling the component that you suspect is causing the noise.
Do not tap or push/pull the component with excessive force, otherwise the noise will be eliminated only
temporarily.
lfeeling for a vibration with your hand by touching the component(s) that you suspect is (are) causing the
noise.
lplacing a piece of paper between components that you suspect are causing the noise.
llooking for loose components and contact marks.
Refer toGW-7, "
Generic Squeak and Rattle Troubleshooting".
REPAIR THE CAUSE
lIf the cause is a loose component, tighten the component securely.
lIf the cause is insufficient clearance between components:
–separate components by repositioning or loosening and retightening the component, if possible.
–insulate components with a suitable insulator such as urethane pads, foam blocks, felt cloth tape or ure-
thane tape are available through your authorized Nissan Parts Department.
CAUTION:
Do not use excessive force as many components are constructed of plastic and may be damaged.
NOTE:
Always check with the Parts Department for the latest parts information.
Each item can be ordered separately as needed.
URETHANE PADS [1.5 mm (0.059 in) thick]
Insulates connectors, harness, etc.
76268-9E005: 100´135 mm (3.94´5.31 in)/76884-71L01: 60´85 mm (2.36´3.35 in)/76884-71L02: 15´
25 mm (0.59´0.98 in)
INSULATOR (Foam blocks)
Insulates components from contact. Can be used to fill space behind a panel.
73982-9E000: 45 mm (1.77 in) thick, 50´50 mm (1.97´1.97 in)/73982-50Y00: 10 mm (0.39 in) think, 50
´50 mm (1.97´1.97 in)
INSULATOR (Light foam block)
80845-71L00: 30 mm (1.18 in) thick, 30´50 mm (1.18´1.97 in)
Page 2130 of 3171
HEADLAMP - DAYTIME LIGHT SYSTEM -
LT-47
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
L
MA
B
LT
Daytime Light Control Does Not Operate Properly (Normal Headlamps Operate
Properly)
EKS00Q7Q
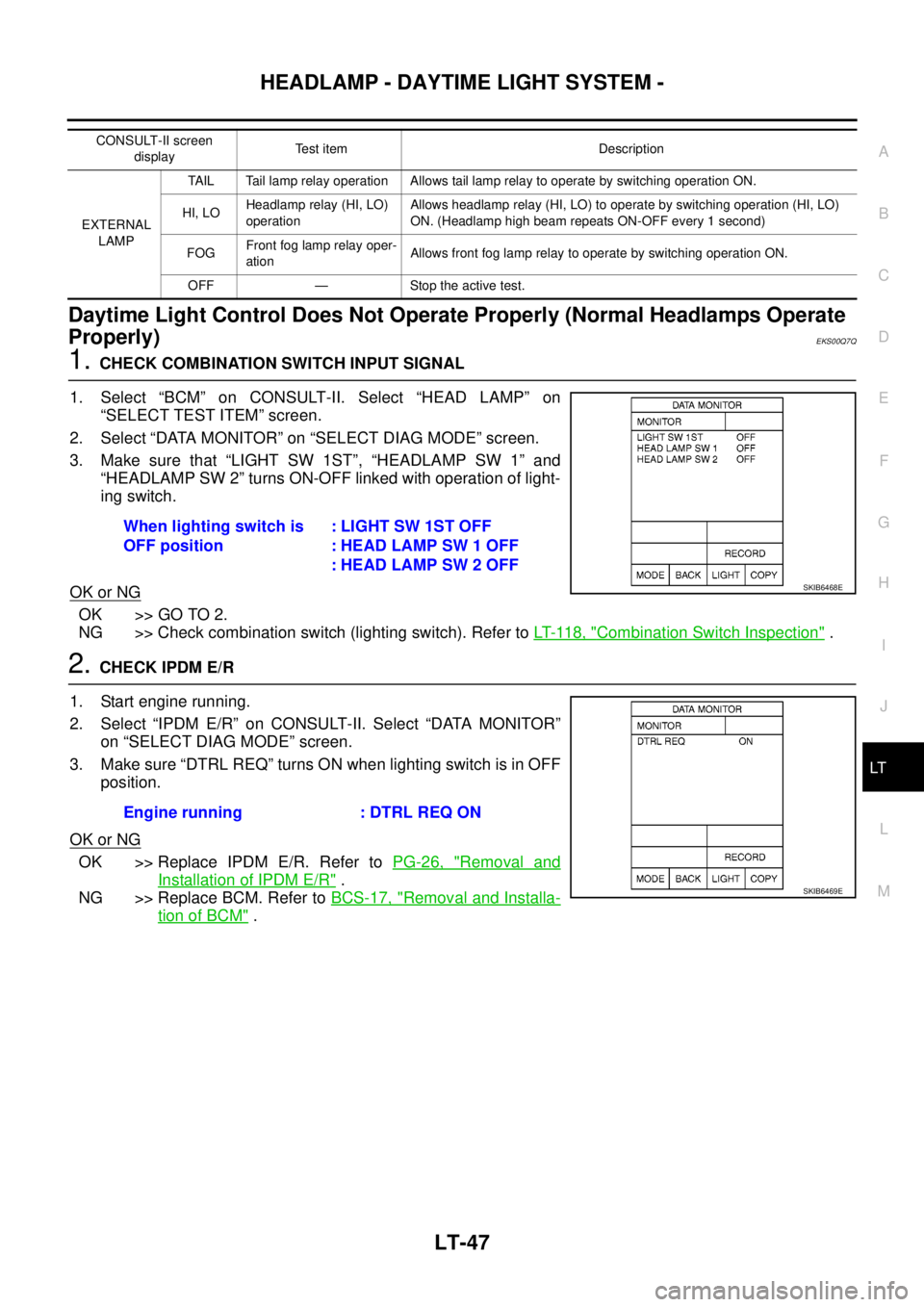
1.CHECK COMBINATION SWITCH INPUT SIGNAL
1. Select “BCM” on CONSULT-II. Select “HEAD LAMP” on
“SELECT TEST ITEM” screen.
2. Select “DATA MONITOR” on “SELECT DIAG MODE” screen.
3. Make sure that “LIGHT SW 1ST”, “HEADLAMP SW 1” and
“HEADLAMP SW 2” turns ON-OFF linked with operation of light-
ing switch.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 2.
NG >> Check combination switch (lighting switch). Refer toLT- 11 8 , "
Combination Switch Inspection".
2.CHECK IPDM E/R
1. Start engine running.
2. Select “IPDM E/R” on CONSULT-II. Select “DATA MONITOR”
on “SELECT DIAG MODE” screen.
3. Make sure “DTRL REQ” turns ON when lighting switch is in OFF
position.
OK or NG
OK >> Replace IPDM E/R. Refer toPG-26, "Removal and
Installation of IPDM E/R".
NG >> Replace BCM. Refer toBCS-17, "
Removal and Installa-
tion of BCM".
CONSULT-II screen
displayTest item Description
EXTERNAL
LAMPTAIL Tail lamp relay operation Allows tail lamp relay to operate by switching operation ON.
HI, LOHeadlamp relay (HI, LO)
operationAllows headlamp relay (HI, LO) to operate by switching operation (HI, LO)
ON. (Headlamp high beam repeats ON-OFF every 1 second)
FOGFront fog lamp relay oper-
ationAllows front fog lamp relay to operate by switching operation ON.
OFF — Stoptheactivetest.
When lighting switch is
OFF position:LIGHTSW1STOFF
: HEAD LAMP SW 1 OFF
: HEAD LAMP SW 2 OFF
SKIB6468E
Engine running : DTRL REQ ON
SKIB6469E
Page 2140 of 3171
AUTO LIGHT SYSTEM
LT-57
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
L
MA
B
LT
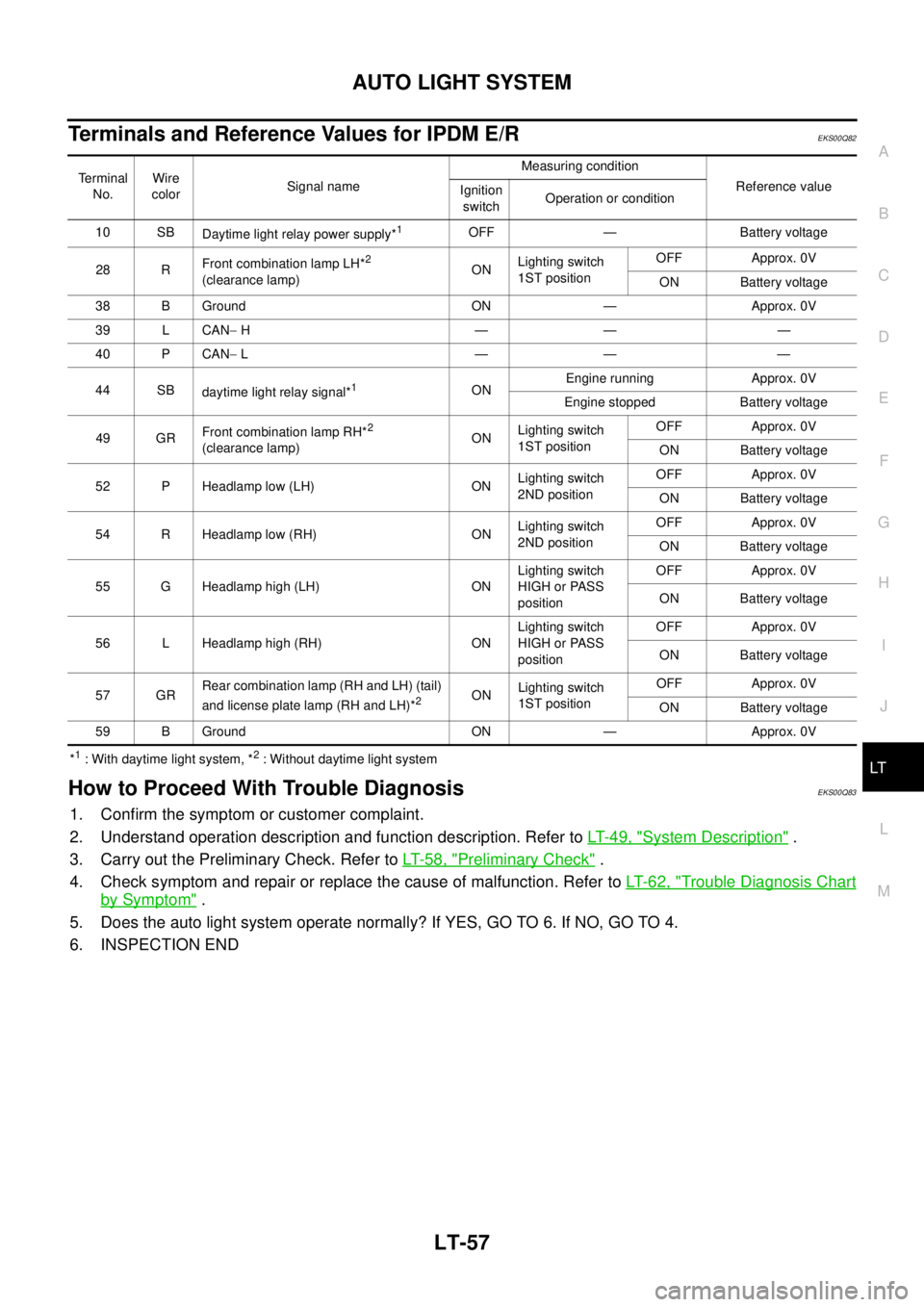
Terminals and Reference Values for IPDM E/REKS00Q82
*1: With daytime light system, *2: Without daytime light system
How to Proceed With Trouble DiagnosisEKS00Q83
1. Confirm the symptom or customer complaint.
2. Understand operation description and function description. Refer toLT-49, "
System Description".
3. Carry out the Preliminary Check. Refer toLT-58, "
Preliminary Check".
4. Check symptom and repair or replace the cause of malfunction. Refer toLT-62, "
Trouble Diagnosis Chart
by Symptom".
5. Does the auto light system operate normally? If YES, GO TO 6. If NO, GO TO 4.
6. INSPECTION END
Terminal
No.Wire
colorSignal nameMeasuring condition
Reference value
Ignition
switchOperation or condition
10 SB
Daytime light relay power supply*
1OFF — Battery voltage
28 RFront combination lamp LH*
2
(clearance lamp)ONLighting switch
1ST positionOFF Approx. 0V
ON Battery voltage
38 B Ground ON — Approx. 0V
39 L CAN-H———
40 P CAN-L———
44 SB
daytime light relay signal*
1ONEngine running Approx. 0V
Engine stopped Battery voltage
49 GRFront combination lamp RH*
2
(clearance lamp)ONLighting switch
1ST positionOFF Approx. 0V
ON Battery voltage
52 P Headlamp low (LH) ONLighting switch
2ND positionOFF Approx. 0V
ON Battery voltage
54 R Headlamp low (RH) ONLighting switch
2ND positionOFF Approx. 0V
ON Battery voltage
55 G Headlamp high (LH) ONLighting switch
HIGH or PASS
positionOFF Approx. 0V
ON Battery voltage
56 L Headlamp high (RH) ONLighting switch
HIGH or PASS
positionOFF Approx. 0V
ON Battery voltage
57 GRRear combination lamp (RH and LH) (tail)
and license plate lamp (RH and LH)*
2ONLighting switch
1ST positionOFF Approx. 0V
ON Battery voltage
59 B Ground ON — Approx. 0V
Page 2440 of 3171

TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
MTC-53
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
Operational CheckEJS005GB
The purpose of the operational check is to confirm that the system operates properly.
CHECKING BLOWER
1. Turn blower control switch clockwise. Blower should operate on
low speed. The blower symbol should have one blade lit (on dis-
play).
2. Turn the blower control switch again, and continue checking
blower speed and blower symbol until all speeds are checked.
3. Leave blower on MAX speed.
If NG, go to trouble diagnosis procedure for
If OK, continue with next check.
CHECKING DISCHARGE AIR
1. Turn the mode switch.
2. Each position indicator should change shape (on display, if
equipped).
3. Confirm that discharge air comes out according to the air distri-
bution table.
Mode door position is checked in the next step.
If NG, go to trouble diagnosis procedure forMTC-58, "
Mode Door
Motor Circuit".
If OK, continue with next check.
NOTE:
Confirm that the compressor clutch is engaged (sound or visual
inspection) and intake door position is at fresh when the DEF or D/F
is selected.
CHECKING RECIRCULATION
1. Press recirculation ( ) switch one time. Recirculation indica-
tor should illuminate.
2. Press recirculation ( ) switch one more time. Recirculation
indicator should go off.
3. Listen for intake door position change (blower sound should
change slightly).
If NG, go to trouble diagnosis procedure forMTC-68, "
Intake Door
Motor Circuit".
If OK, continue with next check.
NOTE:
Confirm that the compressor clutch is engaged (sound or visual
inspection) and intake door position is at fresh when the DEF or D/F is selected.Conditions : Engine running and at normal operating temperature
MJIB0223E
MJIB0224E
MJIB0284E
MJIB0225E
Page 2518 of 3171

REFRIGERANT LINES
MTC-131
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
Checking for Refrigerant LeaksEJS0062F
Perform a visual inspection of all refrigeration parts, fittings, hoses and components for signs of A/C lubricant
leakage, damage and corrosion. A/C lubricant leakage may indicate an area of refrigerant leakage. Allow
extra inspection time in these areas when using either an electronic refrigerant leak detector or fluorescent
dye leak detector.
If dye is observed, confirm the leak with an electronic refrigerant leak detector. It is possible a prior leak was
repaired and not properly cleaned.
When searching for leaks, do not stop when one leak is found but continue to check for additional leaks at all
system components and connections.
When searching for refrigerant leaks using an electronic leak detector, move the probe along the suspected
leak area at 1 to 2 inches per second and no further than 1/4 inch from the component.
CAUTION:
Moving the electronic leak detector probe slower and closer to the suspected leak area will improve
the chances of finding a leak.
Checking System for Leaks Using the Fluorescent Leak DetectorEJS0062G
1. Check A/C system for leaks using the UV lamp and safety goggles [SST: J-42220] in a low sunlight area
(area without windows preferable). Illuminate all components, fittings and lines. The dye will appear as a
bright green/yellow area at the point of leakage. Fluorescent dye observed at the evaporator drain open-
ing indicates an evaporator core assembly (tubes, core or expansion valve) leak.
2. If the suspected area is difficult to see, use an adjustable mirror or wipe the area with a clean shop rag or
cloth, with the UV lamp for dye residue.
3. After the leak is repaired, remove any residual dye using dye cleaner [SST: J-43872] to prevent future mis-
diagnosis.
4. Perform a system performance check and verify the leak repair with an approved electronic refrigerant
leak detector.
NOTE:
Other gases in the work area or substances on the A/C components, for example, anti-freeze, windshield
washer fluid, solvents and lubricants, may falsely trigger the leak detector. Make sure the surfaces to be
checked are clean.
Clean with a dry cloth or blow off with shop air.
Do not allow the sensor tip of the detector to contact with any substance. This can also cause false readings
and may damage the detector.
Dye InjectionEJS0062H
(This procedure is only necessary when recharging the system or when the compressor has seized and was
replaced.)
1. Check A/C system static (at rest) pressure. Pressure must be at least 345 kPa (3.45 bar, 3.52 kg/cm
2,50
psi).
2. Pour one bottle (1/4 ounce / 7.4 cc) of the A/C refrigerant dye into the injector tool [SST: J-41459].
3. Connect the injector tool to the A/C Low-pressure side service fitting.
4. Start engine and switch A/C ON.
5. When the A/C operating (compressor running), inject one bottle (1/4 ounce / 7.4 cc) of fluorescent dye
through the low-pressure service valve using dye injector tool J-41459 (refer to the manufacture’s operat-
ing instructions).
6. With the engine still running, disconnect the injector tool from the service fitting.
CAUTION:
Be careful the A/C system or replacing a component, pour the dye directly into the open system
connection and proceed with the service procedures.
7. Operate the A/C system for a minimum of 20 minutes to mix the dye with the system oil. Depending on the
leak size, operating conditions and location of the leak, it may take from minutes to days for the dye to
penetrate a leak and become visible.
Page 2635 of 3171
PS-8
STEERING WHEEL
STEERING WHEEL
PFP:48430
On-Vehicle Inspection and ServiceEGS001LG
CHECKING CONDITION OF INSTALLATION
lCheck installation conditions of steering gear assembly, front suspension assembly, axle and steering col-
umn assembly.
lCheck if movement exists when steering wheel is moved up and down, to the left and right and to the axial
direction.
lCheck steering gear assembly mounting bolts and nuts for looseness. Refer toPS-14, "COMPONENT".
CHECKING STEERING WHEEL PLAY
lTurn steering wheel so that front wheels come to the straight-ahead position. Start engine and lightly turn
steering wheel to the left and right until front wheels start to move. Measure steering wheel movement on
the outer circumference.
lWhen the measurement value is outside the standard value, check backlash for each joint of steering col-
umn assembly and installation condition of steering gear assembly.
CHECKING NEUTRAL POSITION STEERING WHEEL
lMake sure that steering gear assembly, steering column assembly and steering wheel are installed in the
correct position.
lPerform neutral position inspection after wheel alignment. Refer toFSU-7, "Front Wheel Alignment".
lSet vehicle to the straight-ahead position and confirm steering wheel is in the neutral position.
lLoosen outer socket lock nut and turn inner socket to left and right equally to make fine adjustment if
steering wheel is not in the neutral position.
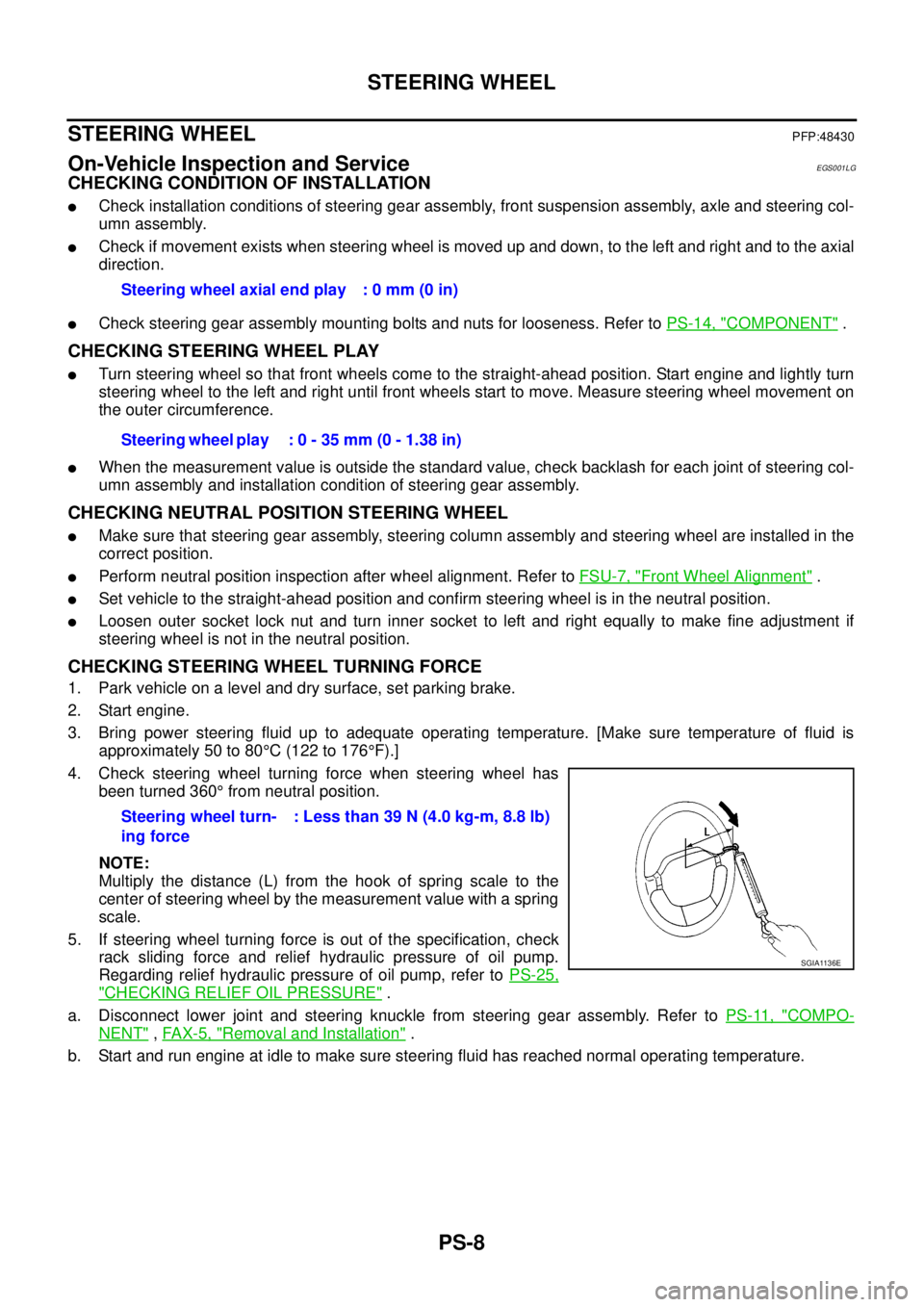
CHECKING STEERING WHEEL TURNING FORCE
1. Park vehicle on a level and dry surface, set parking brake.
2. Start engine.
3. Bring power steering fluid up to adequate operating temperature. [Make sure temperature of fluid is
approximately 50 to 80°C(122to176°F).]
4. Check steering wheel turning force when steering wheel has
been turned 360°from neutral position.
NOTE:
Multiply the distance (L) from the hook of spring scale to the
center of steering wheel by the measurement value with a spring
scale.
5. If steering wheel turning force is out of the specification, check
rack sliding force and relief hydraulic pressure of oil pump.
Regarding relief hydraulic pressure of oil pump, refer toPS-25,
"CHECKING RELIEF OIL PRESSURE".
a. Disconnect lower joint and steering knuckle from steering gear assembly. Refer toPS-11, "
COMPO-
NENT",FAX-5, "Removal and Installation".
b. Start and run engine at idle to make sure steering fluid has reached normal operating temperature.Steering wheel axial end play : 0 mm (0 in)
Steering wheel play : 0 - 35 mm (0 - 1.38 in)
Steering wheel turn-
ing force: Less than 39 N (4.0 kg-m, 8.8 lb)
SGIA1136E
Page 2682 of 3171
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
RF-5
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
RF
DUPLICATE THE NOISE AND TEST DRIVE
If possible, drive the vehicle with the customer until the noise is duplicated. Note any additional information on
the Diagnostic Worksheet regarding the conditions or location of the noise. This information can be used to
duplicate the same conditions when you confirm the repair.
If the noise can be duplicated easily during the test drive, to help identify the source of the noise, try to dupli-
cate the noise with the vehicle stopped by doing one or all of the following:
1) Close a door.
2) Tap or push/pull around the area where the noise appears to be coming from.
3) Rev the engine.
4) Use a floor jack to recreate vehicle “twist”.
5) At idle, apply engine load (electrical load, half-clutch on M/T models, drive position on A/T models).
6) Raisethevehicleonahoistandhitatirewitharubberhammer.
lDrive the vehicle and attempt to duplicate the conditions the customer states exist when the noise occurs.
lIf it is difficult to duplicate the noise, drive the vehicle slowly on an undulating or rough road to stress the
vehicle body.
CHECK RELATED SERVICE BULLETINS
After verifying the customer concern or symptom, check ASIST for Technical Service Bulletins (TSBs) related
to that concern or symptom.
If a TSB relates to the symptom, follow the procedure to repair the noise.
LOCATE THE NOISE AND IDENTIFY THE ROOT CAUSE
1. Narrow down the noise to a general area. To help pinpoint the source of the noise, use a listening tool
(Engine Ear or mechanics stethoscope).
2. Narrow down the noise to a more specific area and identify the cause of the noise by:
lremoving the components in the area that you suspect the noise is coming from.
Do not use too much force when removing clips and fasteners, otherwise clips and fastener can be broken
or lost during the repair, resulting in the creation of new noise.
ltapping or pushing/pulling the component that you suspect is causing the noise.
Do not tap or push/pull the component with excessive force, otherwise the noise will be eliminated only
temporarily.
lfeeling for a vibration with your hand by touching the component(s) that you suspect is (are) causing the
noise.
lplacing a piece of paper between components that you suspect are causing the noise.
llooking for loose components and contact marks.
Refer toRF-6, "
Generic Squeak and Rattle Troubleshooting".
REPAIR THE CAUSE
lIf the cause is a loose component, tighten the component securely.
lIf the cause is insufficient clearance between components:
–separate components by repositioning or loosening and retightening the component, if possible.
–insulate components with a suitable insulator such as urethane pads, foam blocks, felt cloth tape or ure-
thane tape are available through your authorized Nissan Parts Department.
CAUTION:
Do not use excessive force as many components are constructed of plastic and may be damaged.
NOTE:
Always check with the Parts Department for the latest parts information.
Each item can be ordered separately as needed.
URETHANE PADS [1.5 mm (0.059 in) thick]
Insulates connectors, harness, etc.
76268-9E005: 100´135 mm (3.94´5.31 in)/76884-71L01: 60´85 mm (2.36´3.35 in)/76884-71L02: 15´
25 mm (0.59´0.98 in)
INSULATOR (Foam blocks)
Insulates components from contact. Can be used to fill space behind a panel.
73982-9E000: 45 mm (1.77 in) thick, 50´50 mm (1.97´1.97 in)/73982-50Y00: 10 mm (0.39 in) thick, 50
´50 mm (1.97´1.97 in)
INSULATOR (Light foam block)
80845-71L00: 30 mm (1.18 in) thick, 30´50 mm (1.18´1.97 in)