air condition NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2005, Model line: NAVARA, Model: NISSAN NAVARA 2005Pages: 3171, PDF Size: 49.59 MB
Page 2479 of 3171
MTC-92
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS
Low-pressure Side Sometimes Becomes Negative
Low-pressure Side Becomes Negative
Gauge indication Refrigerant cycle Probable cause Corrective action
Low-pressure side sometimes
becomes negative.
lAir conditioning system
does not function and does
not cyclically cool the com-
partment air.
lThe system constantly func-
tions for a certain period of
time after compressor is
stopped and restarted.Refrigerant does not dis-
charge cyclically.
¯
Moisture is frozen at expan-
sion valve outlet and inlet.
¯
Water is mixed with refriger-
ant.
lDrain water from refrigerant
or replace refrigerant.
lReplace liquid tank.
AC354A
Gauge indication Refrigerant cycle Probable cause Corrective action
Low-pressure side becomes nega-
tive.
Liquid tank or front/rear side of
expansion valve¢spipeis
frosted or dewed.High-pressure side is closed
and refrigerant does not flow.
¯
Expansion valve or liquid tank
is frosted.Leave the system at rest until
no frost is present. Start it
again to check whether or not
the malfunction is caused by
waterorforeignparticles.
lIf water is the cause, initially
cooling is okay. Then the
water freezes causing a
blockage. Drain water from
refrigerant or replace refrig-
erant.
lIf due to foreign particles,
remove expansion valve
and remove the particles
with dry and compressed air
(not shop air).
lIf either of the above meth-
ods cannot correct the mal-
function, replace expansion
valve.
lReplace liquid tank.
lCheck lubricant for contami-
nation.
AC362A
Page 2488 of 3171
AIR CONDITIONER FILTER
MTC-101
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
AIR CONDITIONER FILTERPFP:27277
Removal and InstallationEJS005GW
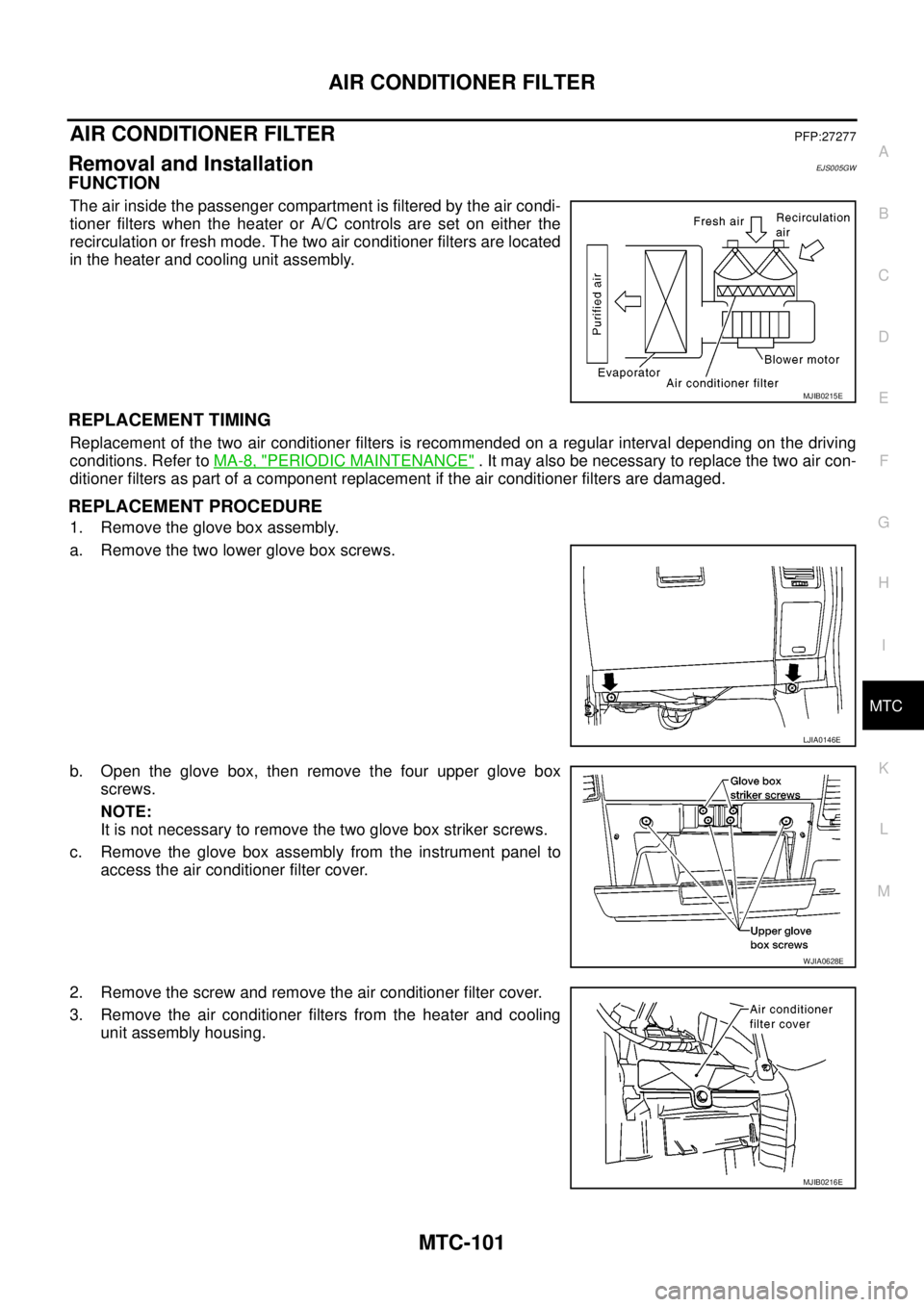
FUNCTION
The air inside the passenger compartment is filtered by the air condi-
tioner filters when the heater or A/C controls are set on either the
recirculation or fresh mode. The two air conditioner filters are located
in the heater and cooling unit assembly.
REPLACEMENT TIMING
Replacement of the two air conditioner filters is recommended on a regular interval depending on the driving
conditions. Refer toMA-8, "
PERIODIC MAINTENANCE". It may also be necessary to replace the two air con-
ditioner filters as part of a component replacement if the air conditioner filters are damaged.
REPLACEMENT PROCEDURE
1. Remove the glove box assembly.
a. Remove the two lower glove box screws.
b. Open the glove box, then remove the four upper glove box
screws.
NOTE:
It is not necessary to remove the two glove box striker screws.
c. Remove the glove box assembly from the instrument panel to
access the air conditioner filter cover.
2. Remove the screw and remove the air conditioner filter cover.
3. Remove the air conditioner filters from the heater and cooling
unit assembly housing.
MJIB0215E
LJIA0146E
WJIA0628E
MJIB0216E
Page 2489 of 3171
MTC-102
AIR CONDITIONER FILTER
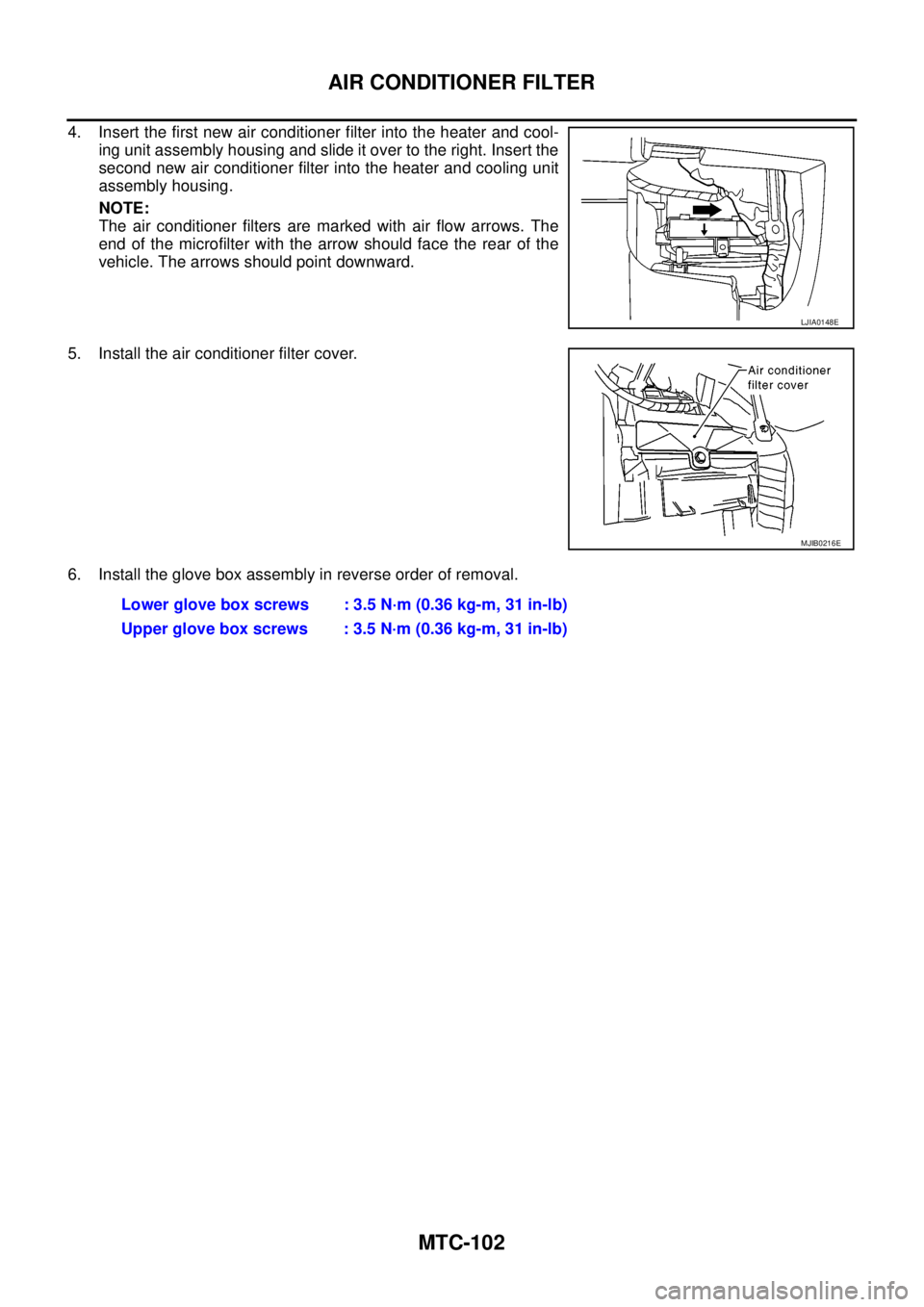
4. Insert the first new air conditioner filter into the heater and cool-
ing unit assembly housing and slide it over to the right. Insert the
second new air conditioner filter into the heater and cooling unit
assembly housing.
NOTE:
The air conditioner filters are marked with air flow arrows. The
end of the microfilter with the arrow should face the rear of the
vehicle. The arrows should point downward.
5. Install the air conditioner filter cover.
6. Install the glove box assembly in reverse order of removal.
LJIA0148E
MJIB0216E
Lower glove box screws : 3.5 N·m (0.36 kg-m, 31 in-lb)
Upper glove box screws : 3.5 N·m (0.36 kg-m, 31 in-lb)
Page 2494 of 3171

HEATER CORE
MTC-107
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
Removal and InstallationEJS005H0
REMOVAL
1. Remove the heater and cooling unit assembly. Refer toMTC-103, "HEATER&COOLING UNIT ASSEM-
BLY".
2. Remove the four screws and remove the upper bracket.
3. Remove the four screws and remove the heater core cover.
4. Remove the heater core pipe bracket.
5. Remove the heater core.
NOTE:
If the air conditioner filters are contaminated from coolant leak-
ing from the heater core, replace the air conditioner filters with
new ones before installing the new heater core.
INSTALLATION
Installation is in the reverse order of removal.
MJIB0216E
Page 2518 of 3171

REFRIGERANT LINES
MTC-131
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
K
L
MA
B
MTC
Checking for Refrigerant LeaksEJS0062F
Perform a visual inspection of all refrigeration parts, fittings, hoses and components for signs of A/C lubricant
leakage, damage and corrosion. A/C lubricant leakage may indicate an area of refrigerant leakage. Allow
extra inspection time in these areas when using either an electronic refrigerant leak detector or fluorescent
dye leak detector.
If dye is observed, confirm the leak with an electronic refrigerant leak detector. It is possible a prior leak was
repaired and not properly cleaned.
When searching for leaks, do not stop when one leak is found but continue to check for additional leaks at all
system components and connections.
When searching for refrigerant leaks using an electronic leak detector, move the probe along the suspected
leak area at 1 to 2 inches per second and no further than 1/4 inch from the component.
CAUTION:
Moving the electronic leak detector probe slower and closer to the suspected leak area will improve
the chances of finding a leak.
Checking System for Leaks Using the Fluorescent Leak DetectorEJS0062G
1. Check A/C system for leaks using the UV lamp and safety goggles [SST: J-42220] in a low sunlight area
(area without windows preferable). Illuminate all components, fittings and lines. The dye will appear as a
bright green/yellow area at the point of leakage. Fluorescent dye observed at the evaporator drain open-
ing indicates an evaporator core assembly (tubes, core or expansion valve) leak.
2. If the suspected area is difficult to see, use an adjustable mirror or wipe the area with a clean shop rag or
cloth, with the UV lamp for dye residue.
3. After the leak is repaired, remove any residual dye using dye cleaner [SST: J-43872] to prevent future mis-
diagnosis.
4. Perform a system performance check and verify the leak repair with an approved electronic refrigerant
leak detector.
NOTE:
Other gases in the work area or substances on the A/C components, for example, anti-freeze, windshield
washer fluid, solvents and lubricants, may falsely trigger the leak detector. Make sure the surfaces to be
checked are clean.
Clean with a dry cloth or blow off with shop air.
Do not allow the sensor tip of the detector to contact with any substance. This can also cause false readings
and may damage the detector.
Dye InjectionEJS0062H
(This procedure is only necessary when recharging the system or when the compressor has seized and was
replaced.)
1. Check A/C system static (at rest) pressure. Pressure must be at least 345 kPa (3.45 bar, 3.52 kg/cm
2,50
psi).
2. Pour one bottle (1/4 ounce / 7.4 cc) of the A/C refrigerant dye into the injector tool [SST: J-41459].
3. Connect the injector tool to the A/C Low-pressure side service fitting.
4. Start engine and switch A/C ON.
5. When the A/C operating (compressor running), inject one bottle (1/4 ounce / 7.4 cc) of fluorescent dye
through the low-pressure service valve using dye injector tool J-41459 (refer to the manufacture’s operat-
ing instructions).
6. With the engine still running, disconnect the injector tool from the service fitting.
CAUTION:
Be careful the A/C system or replacing a component, pour the dye directly into the open system
connection and proceed with the service procedures.
7. Operate the A/C system for a minimum of 20 minutes to mix the dye with the system oil. Depending on the
leak size, operating conditions and location of the leak, it may take from minutes to days for the dye to
penetrate a leak and become visible.
Page 2597 of 3171
PG-68
HARNESS
Wiring Diagram Codes (Cell Codes)
EKS00LJ9
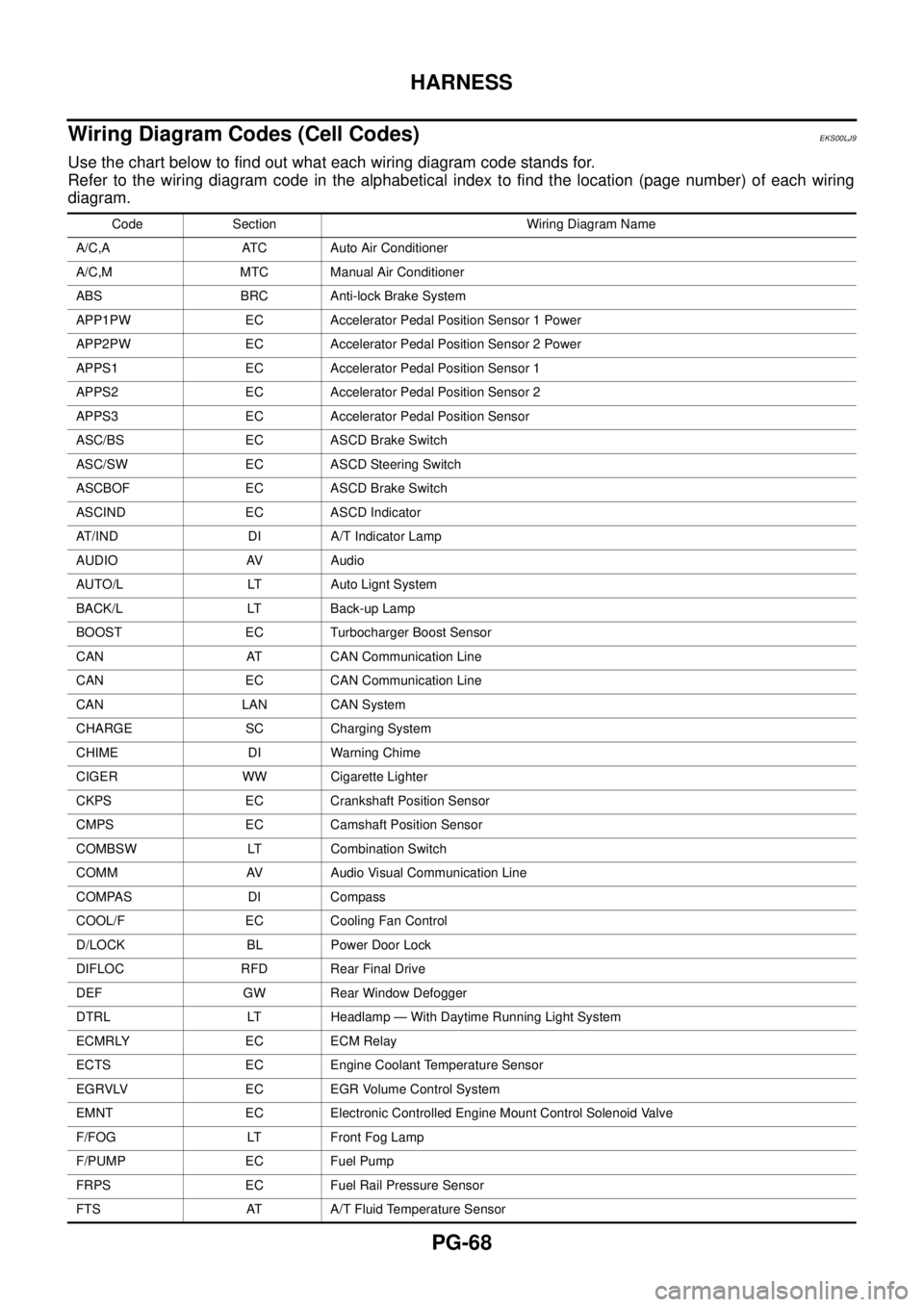
Use the chart below to find out what each wiring diagram code stands for.
Refer to the wiring diagram code in the alphabetical index to find the location (page number) of each wiring
diagram.
Code Section Wiring Diagram Name
A/C,A ATC Auto Air Conditioner
A/C,M MTC Manual Air Conditioner
ABS BRC Anti-lock Brake System
APP1PW EC Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 1 Power
APP2PW EC Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 2 Power
APPS1 EC Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 1
APPS2 EC Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor 2
APPS3 EC Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
ASC/BS EC ASCD Brake Switch
ASC/SW EC ASCD Steering Switch
ASCBOF EC ASCD Brake Switch
ASCIND EC ASCD Indicator
AT/IND DI A/T Indicator Lamp
AUDIO AV Audio
AUTO/L LT Auto Lignt System
BACK/L LT Back-up Lamp
BOOST EC Turbocharger Boost Sensor
CAN AT CAN Communication Line
CAN EC CAN Communication Line
CAN LAN CAN System
CHARGE SC Charging System
CHIME DI Warning Chime
CIGER WW Cigarette Lighter
CKPS EC Crankshaft Position Sensor
CMPS EC Camshaft Position Sensor
COMBSW LT Combination Switch
COMM AV Audio Visual Communication Line
COMPAS DI Compass
COOL/F EC Cooling Fan Control
D/LOCK BL Power Door Lock
DIFLOC RFD Rear Final Drive
DEF GW Rear Window Defogger
DTRL LT Headlamp — With Daytime Running Light System
ECMRLY EC ECM Relay
ECTS EC Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
EGRVLV EC EGR Volume Control System
EMNT EC Electronic Controlled Engine Mount Control Solenoid Valve
F/FOG LT Front Fog Lamp
F/PUMP EC Fuel Pump
FRPS EC Fuel Rail Pressure Sensor
FTS AT A/T Fluid Temperature Sensor
Page 2628 of 3171

PS-1
POWER STEERING SYSTEM
G STEERING
CONTENTS
C
D
E
F
H
I
J
K
L
M
SECTIONPS
A
B
PS
POWER STEERING SYSTEM
PRECAUTIONS .......................................................... 2
Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS)“AIRBAG”and“SEATBELTPRE-TEN-
SIONER” .................................................................. 2
Precautions for Steering System .............................. 2
PREPARATION ........................................................... 3
Special Service Tools [SST] ..................................... 3
Commercial Service Tools ........................................ 4
NOISE, VIBRATION, AND HARSHNESS (NVH)
TROUBLESHOOTING ................................................ 5
NVH Troubleshooting Chart ..................................... 5
POWER STEERING FLUID ........................................ 6
Checking Fluid Level ................................................ 6
Checking Fluid Leakage ........................................... 6
Air Bleeding Hydraulic System ................................. 6
STEERING WHEEL .................................................... 8
On-Vehicle Inspection and Service .......................... 8
CHECKING CONDITION OF INSTALLATION ...... 8
CHECKING STEERING WHEEL PLAY ................ 8
CHECKING NEUTRAL POSITION STEERING
WHEEL ................................................................. 8
CHECKING STEERING WHEEL TURNING
FORCE .................................................................. 8
CHECKING FRONT WHEEL TURNING ANGLE..... 9
Removal and Installation ........................................ 10
REMOVAL ........................................................... 10
INSTALLATION ................................................... 10
STEERING COLUMN ................................................11
Removal and Installation ......................................... 11
COMPONENT ...................................................... 11
REMOVAL ............................................................ 11
INSPECTION AFTER REMOVAL ....................... 12
INSTALLATION ................................................... 12
INSPECTION AFTER INSTALLATION ............... 13
POWER STEERING GEAR AND LINKAGE ............ 14Removal and Installation ........................................ 14
COMPONENT ..................................................... 14
REMOVAL ........................................................... 14
INSTALLATION ................................................... 15
INSPECTION AFTER INSTALLATION ................ 15
Disassembly and Assembly .................................... 16
COMPONENT ..................................................... 16
DISASSEMBLY ................................................... 17
INSPECTION AFTER DISASSEMBLY ................ 18
ASSEMBLY ......................................................... 20
POWER STEERING OIL PUMP ............................... 25
On-Vehicle Inspection and Service ......................... 25
CHECKING RELIEF OIL PRESSURE ................ 25
Removal and Installation ........................................ 25
REMOVAL ........................................................... 25
INSTALLATION ................................................... 26
Disassembly and Assembly .................................... 26
COMPONENT ..................................................... 26
INSPECTION BEFORE DISASSEMBLY ............. 26
DISASSEMBLY ................................................... 27
INSPECTION AFTER DISASSEMBLY ................ 27
ASSEMBLY ......................................................... 28
HYDRAULIC LINE .................................................... 30
Component (RHD Models) ..................................... 30
Component (LHD Models) ...................................... 32
Removal and Installation ........................................ 33
SERVICE DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS (SDS) ...... 34
Steering Wheel ....................................................... 34
Steering Angle ........................................................ 34
Steering Column ..................................................... 34
Steering Outer Socket and Inner Socket ................ 34
Steering Gear ......................................................... 35
Oil Pump ................................................................. 35
Steering Fluid .......................................................... 35
Page 2629 of 3171

PS-2
PRECAUTIONS
PRECAUTIONS
PFP:00001
Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System (SRS) “AIR BAG” and “SEAT
BELT PRE-TENSIONER”
EGS001M0
The Supplemental Restraint System such as “AIR BAG” and “SEAT BELT PRE-TENSIONER”, used along
with a front seat belt, helps to reduce the risk or severity of injury to the driver and front passenger for certain
types of collision. Information necessary to service the system safely is included in the SRS and SB section of
this Service Manual.
WARNING:
lTo avoid rendering the SRS inoperative, which could increase the risk of personal injury or death
in the event of a collision which would result in air bag inflation, all maintenance must be per-
formed by an authorized NISSAN/INFINITI dealer.
lImproper maintenance, including incorrect removal and installation of the SRS, can lead to per-
sonal injury caused by unintentional activation of the system. For removal of Spiral Cable and Air
Bag Module, see the SRS section.
lDo not use electrical test equipment on any circuit related to the SRS unless instructed to in this
Service Manual. SRS wiring harnesses can be identified by yellow and/or orange harnesses or
harness connectors.
Precautions for Steering SystemEGS001L9
lIn case of removing steering gear assembly, make the final tightening with grounded and unloaded vehi-
cle condition, and then check wheel alignment.
lObserve the following precautions when disassembling.
–Before disassembly, thoroughly clean the outside of the unit.
–Disassembly should be done in a clean work area. It is important to prevent the internal parts from becom-
ing contaminated by dirt or other foreign matter.
–For easier and proper assembly, place disassembled parts in order on a parts rack.
–Use nylon cloth or paper towels to clean the parts; common shop rags can leave lint that might interfere
with their operation.
–Do not reuse non-reusable parts.
–Before assembling, apply the specified grease to the directed parts.
Page 2642 of 3171
POWER STEERING GEAR AND LINKAGE
PS-15
C
D
E
F
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
PS
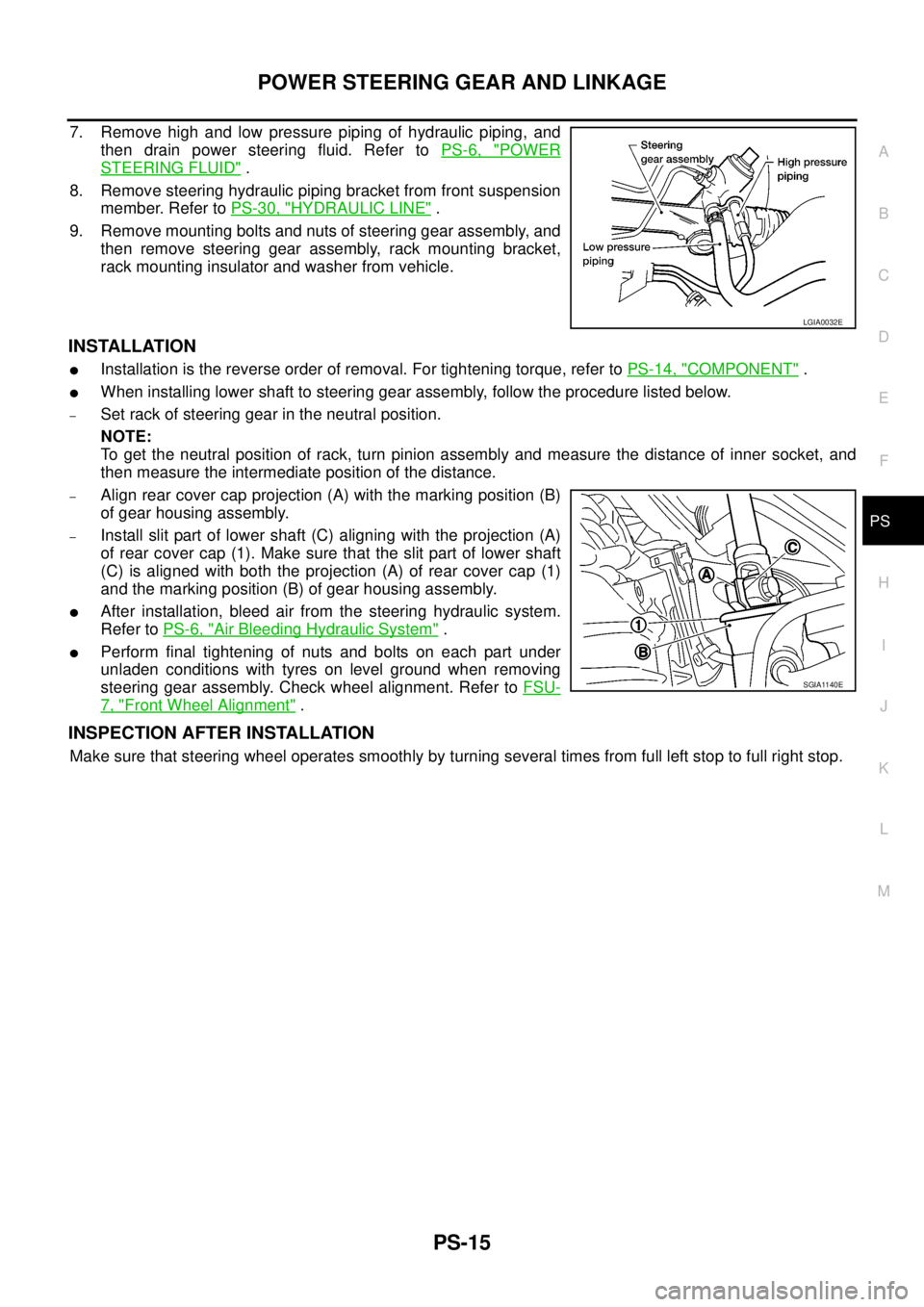
7. Remove high and low pressure piping of hydraulic piping, and
then drain power steering fluid. Refer toPS-6, "
POWER
STEERING FLUID".
8. Remove steering hydraulic piping bracket from front suspension
member. Refer toPS-30, "
HYDRAULIC LINE".
9. Remove mounting bolts and nuts of steering gear assembly, and
then remove steering gear assembly, rack mounting bracket,
rack mounting insulator and washer from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
lInstallation is the reverse order of removal. For tightening torque, refer toPS-14, "COMPONENT".
lWhen installing lower shaft to steering gear assembly, follow the procedure listed below.
–Set rack of steering gear in the neutral position.
NOTE:
To get the neutral position of rack, turn pinion assembly and measure the distance of inner socket, and
then measure the intermediate position of the distance.
–Align rear cover cap projection (A) with the marking position (B)
of gear housing assembly.
–Install slit part of lower shaft (C) aligning with the projection (A)
of rear cover cap (1). Make sure that the slit part of lower shaft
(C) is aligned with both the projection (A) of rear cover cap (1)
and the marking position (B) of gear housing assembly.
lAfter installation, bleed air from the steering hydraulic system.
Refer toPS-6, "
Air Bleeding Hydraulic System".
lPerform final tightening of nuts and bolts on each part under
unladen conditions with tyres on level ground when removing
steering gear assembly. Check wheel alignment. Refer toFSU-
7, "Front Wheel Alignment".
INSPECTION AFTER INSTALLATION
Make sure that steering wheel operates smoothly by turning several times from full left stop to full right stop.
LGIA0032E
SGIA1140E
Page 2681 of 3171
RF-4
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
SQUEAK AND RATTLE TROUBLE DIAGNOSES
PFP:00000
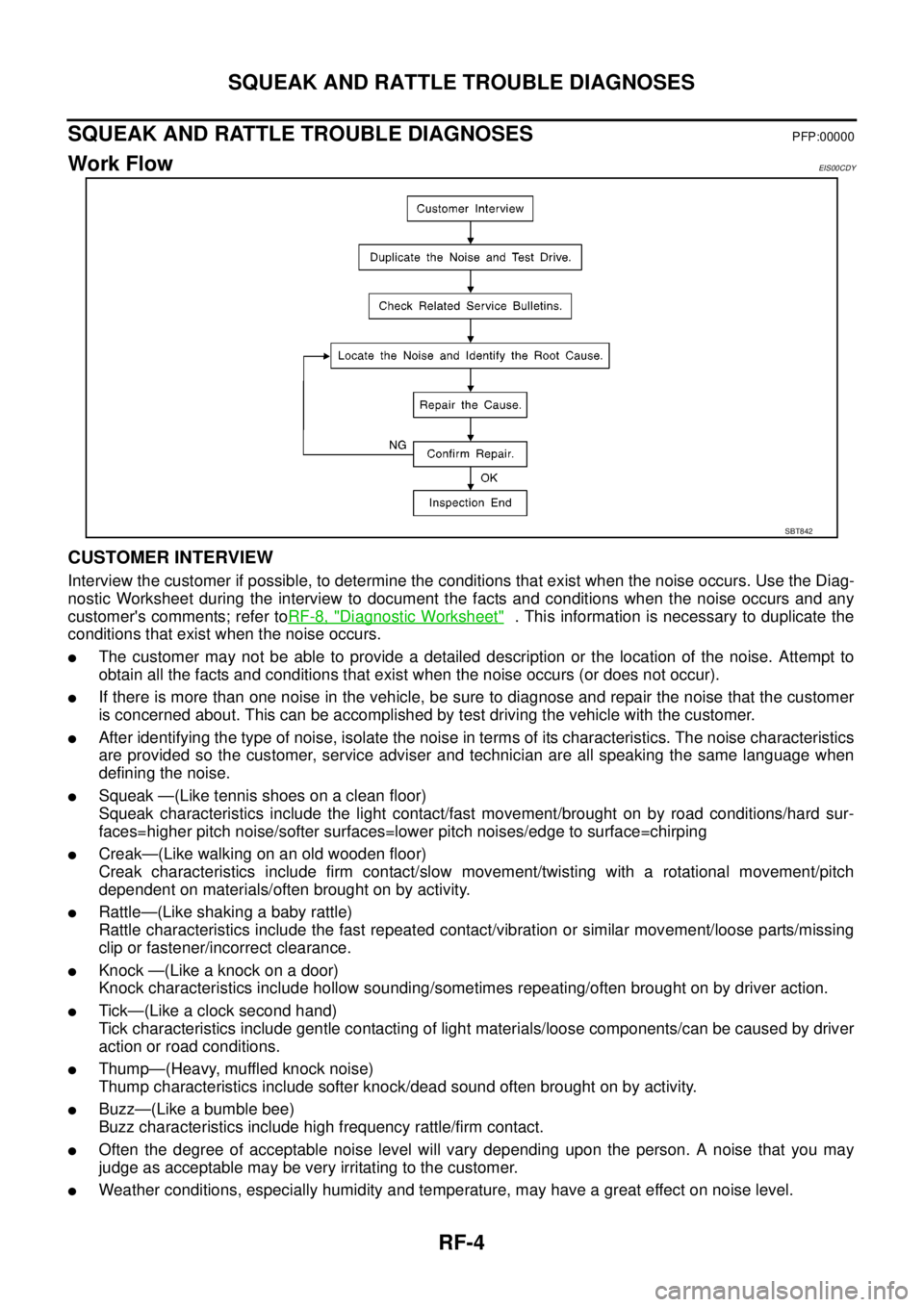
Work FlowEIS00CDY
CUSTOMER INTERVIEW
Interview the customer if possible, to determine the conditions that exist when the noise occurs. Use the Diag-
nostic Worksheet during the interview to document the facts and conditions when the noise occurs and any
customer's comments; refer toRF-8, "
Diagnostic Worksheet". This information is necessary to duplicate the
conditions that exist when the noise occurs.
lThe customer may not be able to provide a detailed description or the location of the noise. Attempt to
obtain all the facts and conditions that exist when the noise occurs (or does not occur).
lIf there is more than one noise in the vehicle, be sure to diagnose and repair the noise that the customer
is concerned about. This can be accomplished by test driving the vehicle with the customer.
lAfter identifying the type of noise, isolate the noise in terms of its characteristics. The noise characteristics
are provided so the customer, service adviser and technician are all speaking the same language when
defining the noise.
lSqueak —(Like tennis shoes on a clean floor)
Squeak characteristics include the light contact/fast movement/brought on by road conditions/hard sur-
faces=higher pitch noise/softer surfaces=lower pitch noises/edge to surface=chirping
lCreak—(Like walking on an old wooden floor)
Creak characteristics include firm contact/slow movement/twisting with a rotational movement/pitch
dependent on materials/often brought on by activity.
lRattle—(Like shaking a baby rattle)
Rattle characteristics include the fast repeated contact/vibration or similar movement/loose parts/missing
clip or fastener/incorrect clearance.
lKnock —(Like a knock on a door)
Knock characteristics include hollow sounding/sometimes repeating/often brought on by driver action.
lTick—(Like a clock second hand)
Tick characteristics include gentle contacting of light materials/loose components/can be caused by driver
action or road conditions.
lThump—(Heavy, muffled knock noise)
Thump characteristics include softer knock/dead sound often brought on by activity.
lBuzz—(Like a bumble bee)
Buzz characteristics include high frequency rattle/firm contact.
lOften the degree of acceptable noise level will vary depending upon the person. A noise that you may
judge as acceptable may be very irritating to the customer.
lWeather conditions, especially humidity and temperature, may have a great effect on noise level.
SBT842