relay NISSAN NAVARA 2005 Repair Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2005, Model line: NAVARA, Model: NISSAN NAVARA 2005Pages: 3171, PDF Size: 49.59 MB
Page 1639 of 3171
HOW TO USE THIS MANUAL
GI-17
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
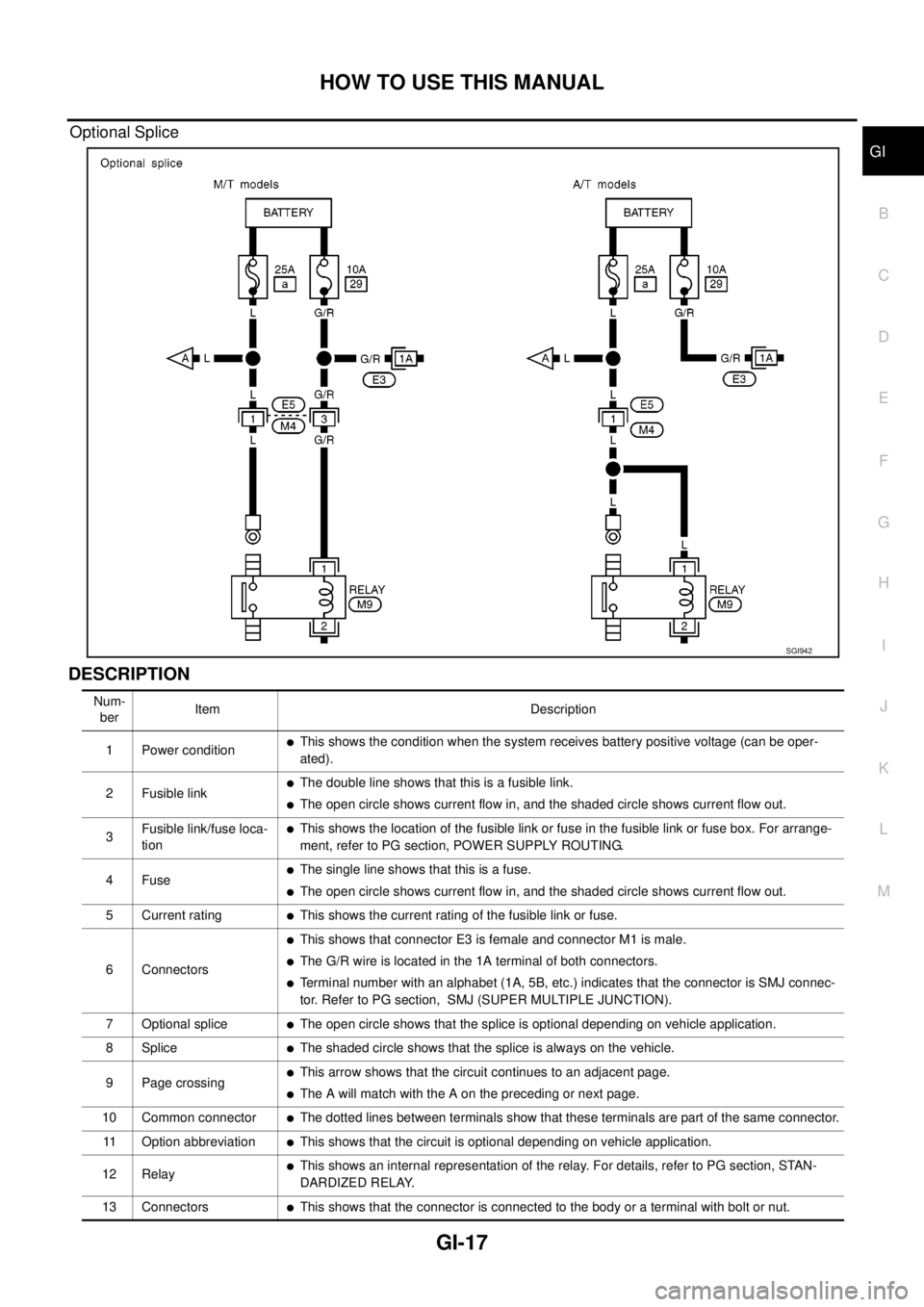
Optional Splice
DESCRIPTION
SGI942
Num-
berItem Description
1 Power condition
lThis shows the condition when the system receives battery positive voltage (can be oper-
ated).
2 Fusible link
lThe double line shows that this is a fusible link.
lThe open circle shows current flow in, and the shaded circle shows current flow out.
3Fusible link/fuse loca-
tion
lThis shows the location of the fusible link or fuse in the fusible link or fuse box. For arrange-
ment, refer to PG section, POWER SUPPLY ROUTING.
4Fuse
lThe single line shows that this is a fuse.
lThe open circle shows current flow in, and the shaded circle shows current flow out.
5 Current rating
lThis shows the current rating of the fusible link or fuse.
6 Connectors
lThis shows that connector E3 is female and connector M1 is male.
lThe G/R wire is located in the 1A terminal of both connectors.
lTerminal number with an alphabet (1A, 5B, etc.) indicates that the connector is SMJ connec-
tor. Refer to PG section, SMJ (SUPER MULTIPLE JUNCTION).
7 Optional splice
lThe open circle shows that the splice is optional depending on vehicle application.
8Splice
lThe shaded circle shows that the splice is always on the vehicle.
9 Page crossing
lThis arrow shows that the circuit continues to an adjacent page.
lThe A will match with the A on the preceding or next page.
10 Common connector
lThe dotted lines between terminals show that these terminals are part of the same connector.
11 Option abbreviation
lThis shows that the circuit is optional depending on vehicle application.
12 Relay
lThis shows an internal representation of the relay. For details, refer to PG section, STAN-
DARDIZED RELAY.
13 Connectors
lThis shows that the connector is connected to the body or a terminal with bolt or nut.
Page 1647 of 3171
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-25
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
lHeat sensitive
lFreezing
lWater intrusion
lElectrical load
lCold or hot start up
Get a thorough description of the incident from the customer. It is important for simulating the conditions of the
problem.
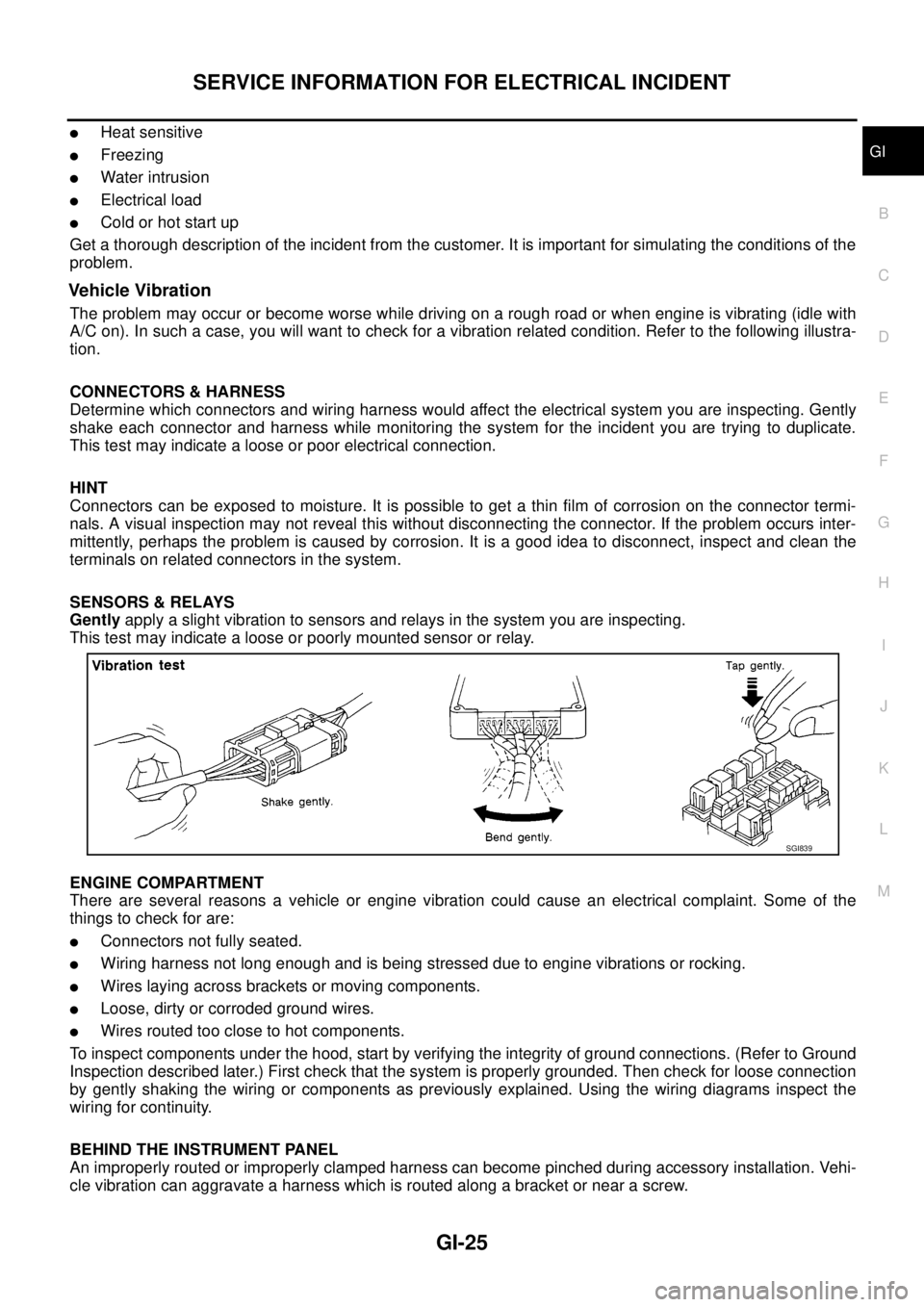
Vehicle Vibration
The problem may occur or become worse while driving on a rough road or when engine is vibrating (idle with
A/C on). In such a case, you will want to check for a vibration related condition. Refer to the following illustra-
tion.
CONNECTORS & HARNESS
Determine which connectors and wiring harness would affect the electrical system you are inspecting. Gently
shake each connector and harness while monitoring the system for the incident you are trying to duplicate.
This test may indicate a loose or poor electrical connection.
HINT
Connectors can be exposed to moisture. It is possible to get a thin film of corrosion on the connector termi-
nals. A visual inspection may not reveal this without disconnecting the connector. If the problem occurs inter-
mittently, perhaps the problem is caused by corrosion. It is a good idea to disconnect, inspect and clean the
terminals on related connectors in the system.
SENSORS & RELAYS
Gentlyapply a slight vibration to sensors and relays in the system you are inspecting.
This test may indicate a loose or poorly mounted sensor or relay.
ENGINE COMPARTMENT
There are several reasons a vehicle or engine vibration could cause an electrical complaint. Some of the
things to check for are:
lConnectors not fully seated.
lWiring harness not long enough and is being stressed due to engine vibrations or rocking.
lWires laying across brackets or moving components.
lLoose, dirty or corroded ground wires.
lWires routed too close to hot components.
To inspect components under the hood, start by verifying the integrity of ground connections. (Refer to Ground
Inspection described later.) First check that the system is properly grounded. Then check for loose connection
by gently shaking the wiring or components as previously explained. Using the wiring diagrams inspect the
wiring for continuity.
BEHIND THE INSTRUMENT PANEL
An improperly routed or improperly clamped harness can become pinched during accessory installation. Vehi-
cle vibration can aggravate a harness which is routed along a bracket or near a screw.
SGI839
Page 1649 of 3171
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-27
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
Cold or Hot Start Up
On some occasions an electrical incident may occur only when the car is started cold, or it may occur when
the car is restarted hot shortly after being turned off. In these cases you may have to keep the car overnight to
make a proper diagnosis.
CIRCUIT INSPECTION
Introduction
In general, testing electrical circuits is an easy task if it is approached in a logical and organized method.
Before beginning it is important to have all available information on the system to be tested. Also, get a thor-
ough understanding of system operation. Then you will be able to use the appropriate equipment and follow
the correct test procedure.
You may have to simulate vehicle vibrations while testing electrical components. Gently shake the wiring har-
ness or electrical component to do this.
NOTE:
Refer to “How to Check Terminal” to probe or check terminal.
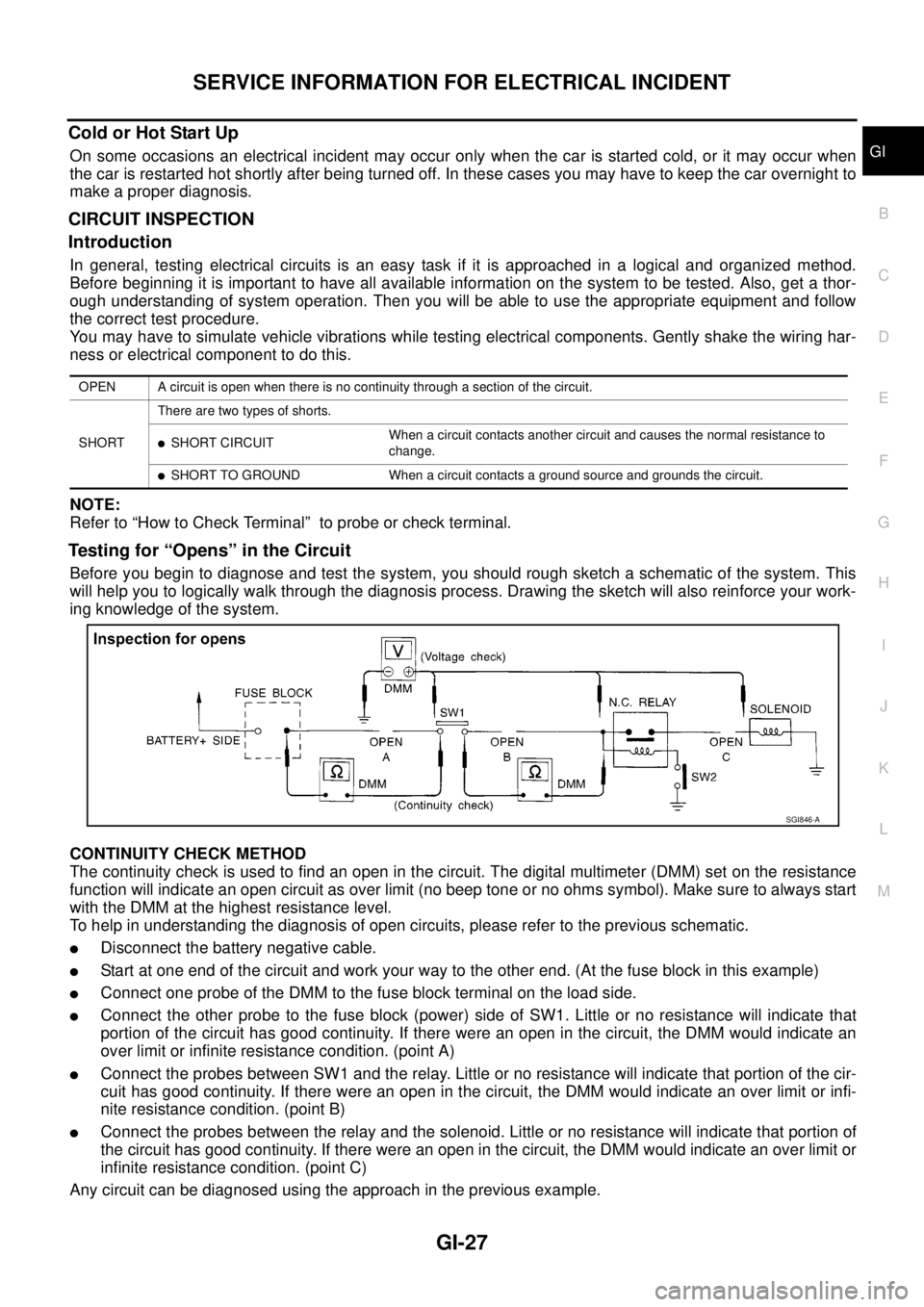
Testing for “Opens” in the Circuit
Before you begin to diagnose and test the system, you should rough sketch a schematic of the system. This
will help you to logically walk through the diagnosis process. Drawing the sketch will also reinforce your work-
ing knowledge of the system.
CONTINUITY CHECK METHOD
The continuity check is used to find an open in the circuit. The digital multimeter (DMM) set on the resistance
function will indicate an open circuit as over limit (no beep tone or no ohms symbol). Make sure to always start
with the DMM at the highest resistance level.
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits, please refer to the previous schematic.
lDisconnect the battery negative cable.
lStart at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end. (At the fuse block in this example)
lConnect one probe of the DMM to the fuse block terminal on the load side.
lConnect the other probe to the fuse block (power) side of SW1. Little or no resistance will indicate that
portion of the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an
over limit or infinite resistance condition. (point A)
lConnect the probes between SW1 and the relay. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of the cir-
cuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or infi-
nite resistance condition. (point B)
lConnect the probes between the relay and the solenoid. Little or no resistance will indicate that portion of
the circuit has good continuity. If there were an open in the circuit, the DMM would indicate an over limit or
infinite resistance condition. (point C)
Any circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
OPEN A circuit is open when there is no continuity through a section of the circuit.
SHORTThere are two types of shorts.
lSHORT CIRCUITWhen a circuit contacts another circuit and causes the normal resistance to
change.
lSHORT TO GROUND When a circuit contacts a ground source and grounds the circuit.
SGI846-A
Page 1650 of 3171
GI-28
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
To help in understanding the diagnosis of open circuits please refer to the previous schematic.
In any powered circuit, an open can be found by methodically checking the system for the presence of voltage.
This is done by switching the DMM to the voltage function.
lConnect one probe of the DMM to a known good ground.
lBegin probing at one end of the circuit and work your way to the other end.
lWith SW1 open, probe at SW1 to check for voltage.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than SW1.
no voltage; open is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
lClose SW1 and probe at relay.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the relay.
no voltage; open is between SW1 and relay (point B).
lClose the relay and probe at the solenoid.
voltage; open is further down the circuit than the solenoid.
no voltage; open is between relay and solenoid (point C).
Any powered circuit can be diagnosed using the approach in the previous example.
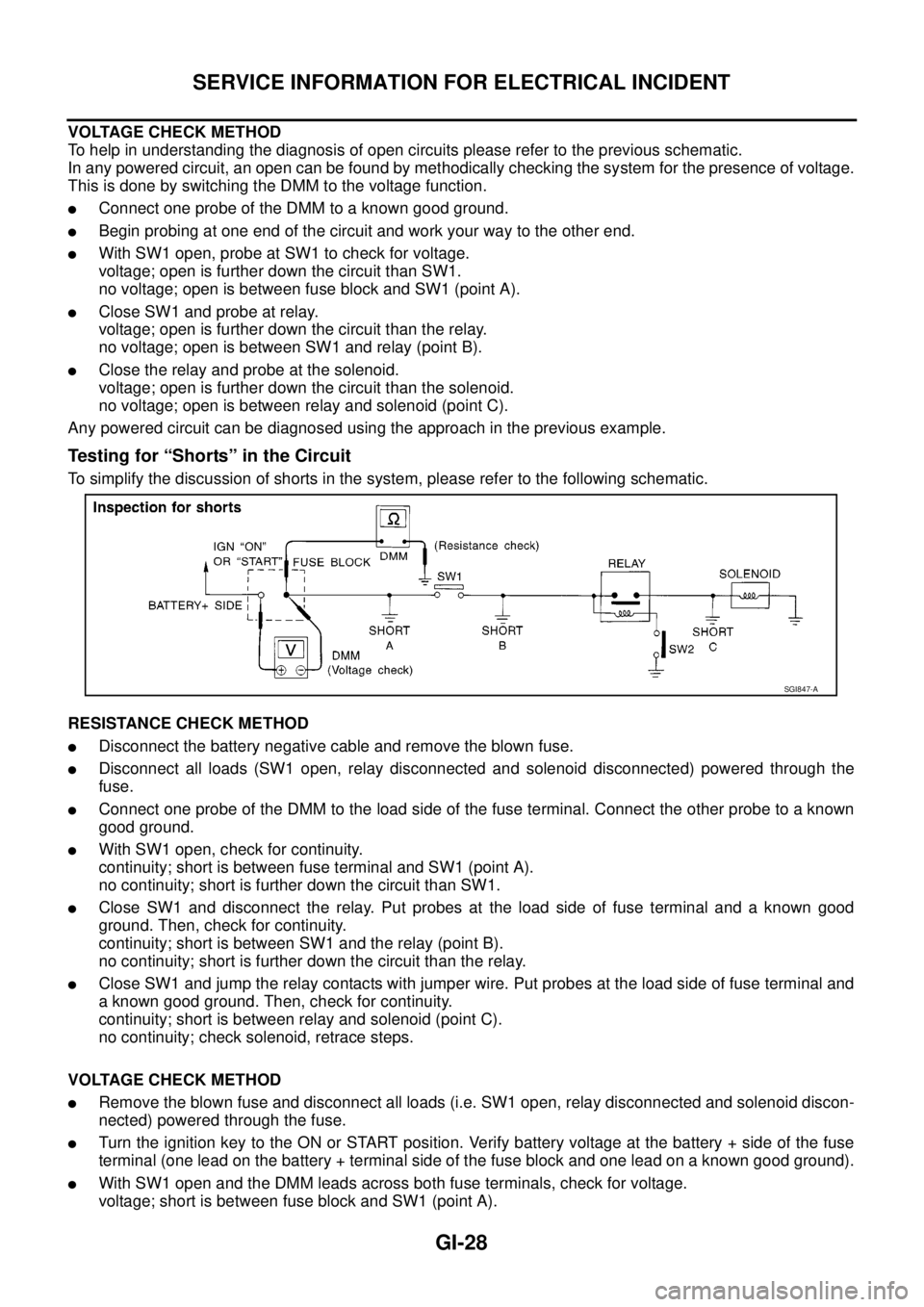
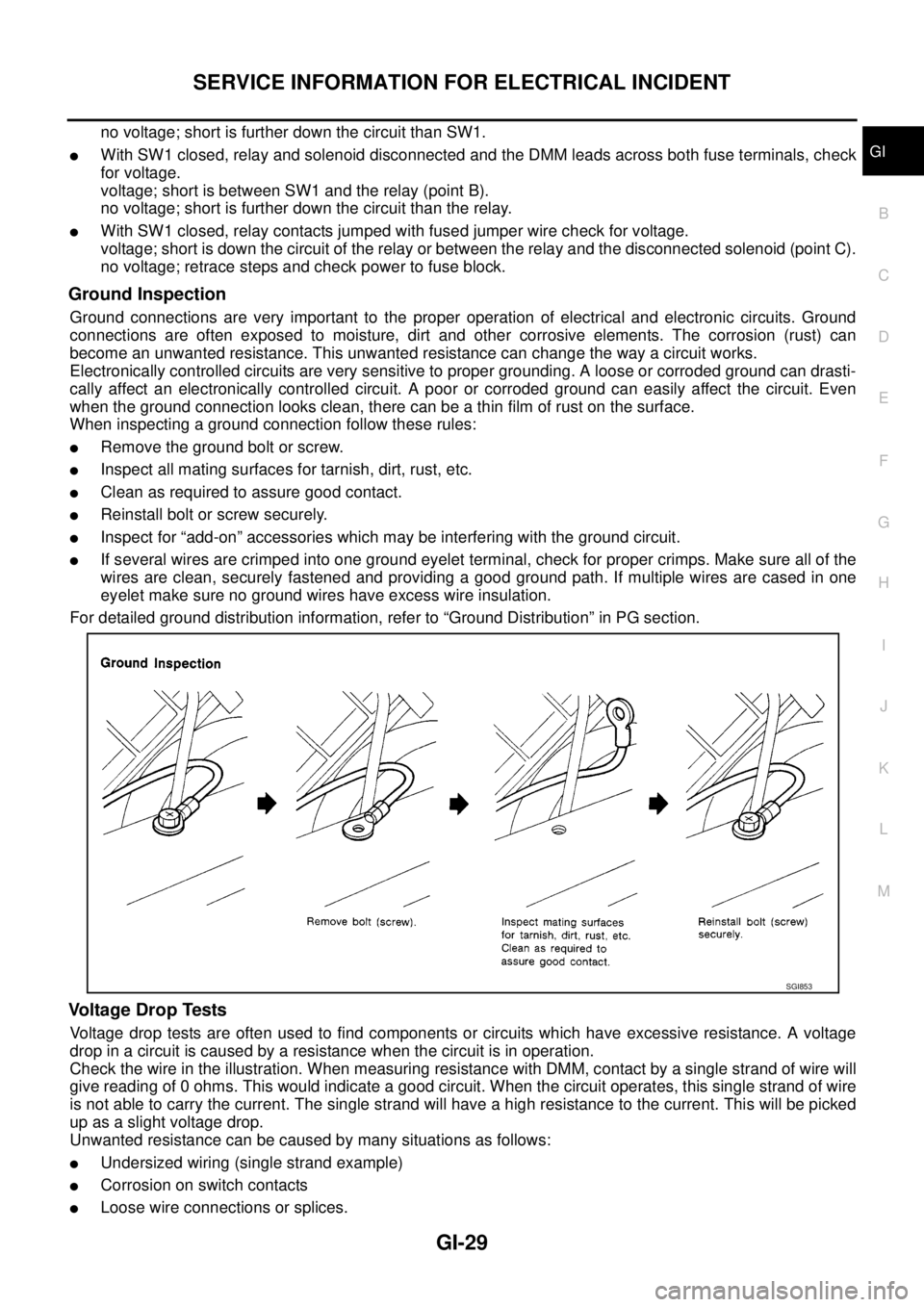
Testing for “Shorts” in the Circuit
To simplify the discussion of shorts in the system, please refer to the following schematic.
RESISTANCE CHECK METHOD
lDisconnect the battery negative cable and remove the blown fuse.
lDisconnect all loads (SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid disconnected) powered through the
fuse.
lConnect one probe of the DMM to the load side of the fuse terminal. Connect the other probe to a known
good ground.
lWith SW1 open, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between fuse terminal and SW1 (point A).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
lClose SW1 and disconnect the relay. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and a known good
ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no continuity; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
lClose SW1 and jump the relay contacts with jumper wire. Put probes at the load side of fuse terminal and
a known good ground. Then, check for continuity.
continuity; short is between relay and solenoid (point C).
no continuity; check solenoid, retrace steps.
VOLTAGE CHECK METHOD
lRemove the blown fuse and disconnect all loads (i.e. SW1 open, relay disconnected and solenoid discon-
nected) powered through the fuse.
lTurn the ignition key to the ON or START position. Verify battery voltage at the battery + side of the fuse
terminal (one lead on the battery + terminal side of the fuse block and one lead on a known good ground).
lWith SW1 open and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check for voltage.
voltage; short is between fuse block and SW1 (point A).
SGI847-A
Page 1651 of 3171
SERVICE INFORMATION FOR ELECTRICAL INCIDENT
GI-29
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MB
GI
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than SW1.
lWith SW1 closed, relay and solenoid disconnected and the DMM leads across both fuse terminals, check
for voltage.
voltage; short is between SW1 and the relay (point B).
no voltage; short is further down the circuit than the relay.
lWith SW1 closed, relay contacts jumped with fused jumper wire check for voltage.
voltage; short is down the circuit of the relay or between the relay and the disconnected solenoid (point C).
no voltage; retrace steps and check power to fuse block.
Ground Inspection
Ground connections are very important to the proper operation of electrical and electronic circuits. Ground
connections are often exposed to moisture, dirt and other corrosive elements. The corrosion (rust) can
become an unwanted resistance. This unwanted resistance can change the way a circuit works.
Electronically controlled circuits are very sensitive to proper grounding. A loose or corroded ground can drasti-
cally affect an electronically controlled circuit. A poor or corroded ground can easily affect the circuit. Even
when the ground connection looks clean, there can be a thin film of rust on the surface.
When inspecting a ground connection follow these rules:
lRemove the ground bolt or screw.
lInspect all mating surfaces for tarnish, dirt, rust, etc.
lClean as required to assure good contact.
lReinstall bolt or screw securely.
lInspect for “add-on” accessories which may be interfering with the ground circuit.
lIf several wires are crimped into one ground eyelet terminal, check for proper crimps. Make sure all of the
wires are clean, securely fastened and providing a good ground path. If multiple wires are cased in one
eyelet make sure no ground wires have excess wire insulation.
For detailed ground distribution information, refer to “Ground Distribution” in PG section.
Voltage Drop Tests
Voltage drop tests are often used to find components or circuits which have excessive resistance. A voltage
drop in a circuit is caused by a resistance when the circuit is in operation.
Check the wire in the illustration. When measuring resistance with DMM, contact by a single strand of wire will
give reading of 0 ohms. This would indicate a good circuit. When the circuit operates, this single strand of wire
is not able to carry the current. The single strand will have a high resistance to the current. This will be picked
up as a slight voltage drop.
Unwanted resistance can be caused by many situations as follows:
lUndersized wiring (single strand example)
lCorrosion on switch contacts
lLoose wire connections or splices.
SGI853
Page 1733 of 3171
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
GW-47
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGERPFP:25350
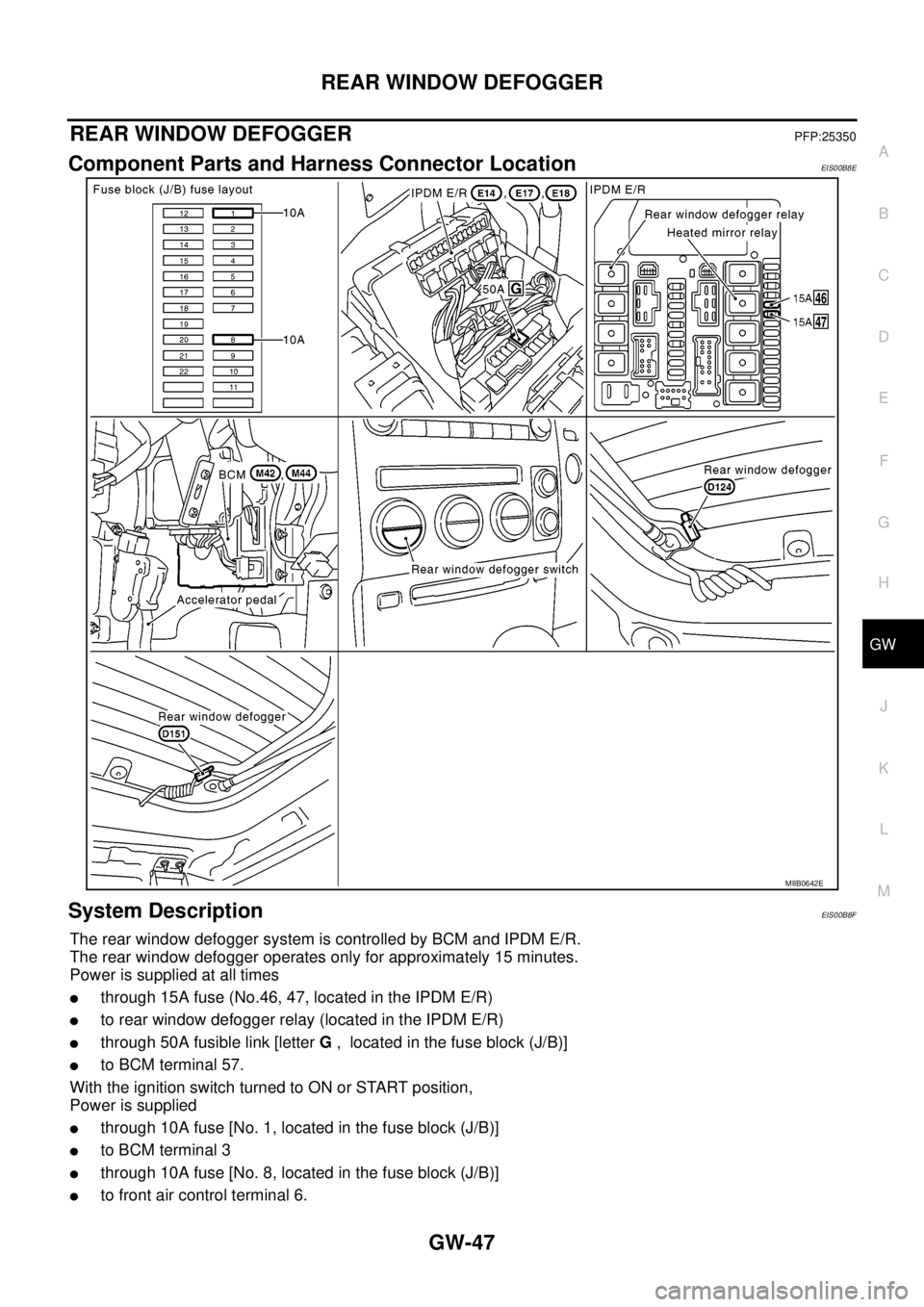
Component Parts and Harness Connector LocationEIS00B8E
System DescriptionEIS00B8F
The rear window defogger system is controlled by BCM and IPDM E/R.
The rear window defogger operates only for approximately 15 minutes.
Power is supplied at all times
lthrough 15A fuse (No.46, 47, located in the IPDM E/R)
lto rear window defogger relay (located in the IPDM E/R)
lthrough 50A fusible link [letterG, located in the fuse block (J/B)]
lto BCM terminal 57.
WiththeignitionswitchturnedtoONorSTARTposition,
Power is supplied
lthrough 10A fuse [No. 1, located in the fuse block (J/B)]
lto BCM terminal 3
lthrough 10A fuse [No. 8, located in the fuse block (J/B)]
lto front air control terminal 6.
MIIB0642E
Page 1734 of 3171

GW-48
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
Ground is supplied
lto BCM terminal 55
lto front air control terminal 20
lthrough body grounds M21, M80 and M83
lto IPDM E/R terminals 38 and 59
lthrough body grounds E21, E41 and E61.
When front air control (rear window defogger switch) is turned to ON,
Ground is supplied
lto BCM terminal 20
lthrough front air control terminal 11
lthrough front air control terminal 20
lthrough body grounds M21, M80 and M83.
Then rear window defogger switch is illuminated.
Then BCM recognizes that rear window defogger switch is turned to ON.
Then it sends rear window defogger switch signals to IPDM E/R via DATA LINE (CAN H, CAN L).
When display panel receives rear window defogger switch signals it illuminates on the screen.
When IPDM E/R receives rear window defogger switch signals,
Ground is supplied
lto rear window defogger relay (located in the IPDM E/R)
lthrough IPDM E/R terminals 38 and 59
lthrough body grounds E21, E41 and E61
and then rear window defogger relay and heated mirror is energized.
Power is supplied
lthrough IPDM E/R terminal 60
lto rear window defogger terminal 1.
Ground is supplied
lto rear window window defogger terminal 2
lthrough body ground D152.
With power and ground supplied, rear window defogger filaments heat and defog the rear window.
CAN Communication System DescriptionEIS00B8G
Refer toLAN-23, "CAN COMMUNICATION".
Page 1745 of 3171
REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER
GW-59
C
D
E
F
G
H
J
K
L
MA
B
GW
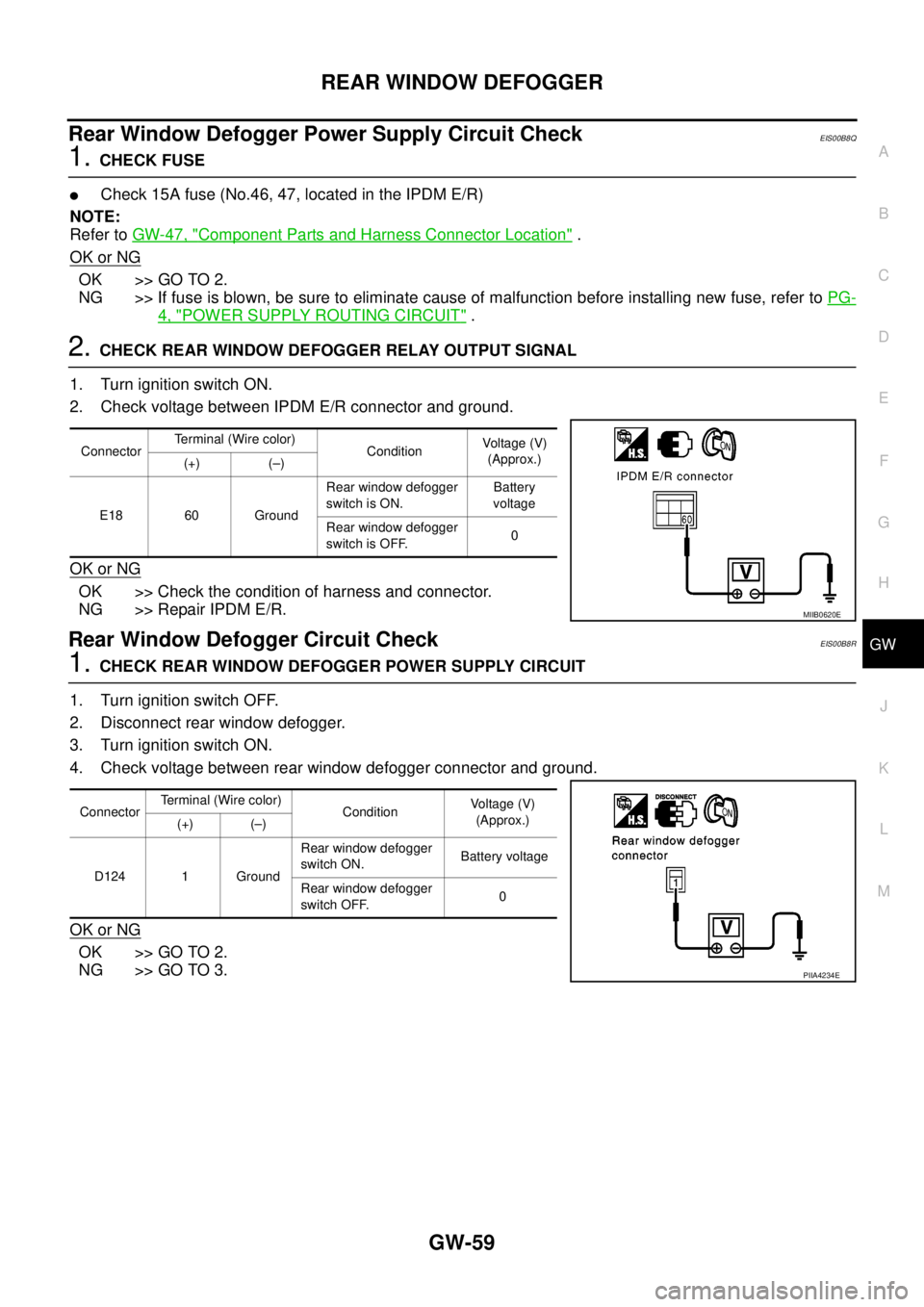
Rear Window Defogger Power Supply Circuit CheckEIS00B8Q
1.CHECK FUSE
lCheck 15A fuse (No.46, 47, located in the IPDM E/R)
NOTE:
Refer toGW-47, "
Component Parts and Harness Connector Location".
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 2.
NG >> If fuse is blown, be sure to eliminate cause of malfunction before installing new fuse, refer toPG-
4, "POWER SUPPLY ROUTING CIRCUIT".
2.CHECK REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER RELAY OUTPUT SIGNAL
1. Turn ignition switch ON.
2. Check voltage between IPDM E/R connector and ground.
OK or NG
OK >> Check the condition of harness and connector.
NG >> Repair IPDM E/R.
Rear Window Defogger Circuit CheckEIS00B8R
1.CHECK REAR WINDOW DEFOGGER POWER SUPPLY CIRCUIT
1. Turn ignition switch OFF.
2. Disconnect rear window defogger.
3. Turn ignition switch ON.
4. Check voltage between rear window defogger connector and ground.
OK or NG
OK >> GO TO 2.
NG >> GO TO 3.
ConnectorTerminal (Wire color)
ConditionVoltag e (V)
(Approx.)
(+) (–)
E18 60 GroundRear window defogger
switch is ON.Battery
voltage
Rear window defogger
switch is OFF.0
MIIB0620E
ConnectorTerminal (Wire color)
ConditionVo l ta g e (V )
(Approx.)
(+) (–)
D124 1 GroundRear window defogger
switch ON.Battery voltage
Rear window defogger
switch OFF.0
PIIA4234E
Page 1755 of 3171

IDX-3
A
C
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L B
IDX
ALPHABETICAL INDEX
C
Camshaft ...........................................................EM-59
Camshaft inspection ..........................................EM-60
Camshaft position sensor (CMPS) .....EC-82,EC-171,
EC-177
CAN ....................................................................DI-65
CAN - Wiring diagram ...........EC-80,LAN-26,LAN-44,
LAN-56
,LAN-68,LAN-82,LAN-96,LAN-112,LAN-125,
LAN-139
,LAN-152,LAN-166,LAN-181,LAN-198,
LAN-213
,LAN-230,LAN-248,LAN-267,LAN-279
CAN (Controller Area Network) ..BL-25,BL-59,RF-13
CAN communication .....EC-22,EC-79,AT-91,TF-19,
TF-82
,RFD-43,RFD-69,BRC-28,BL-25,BL-59,RF-13,
LT-88
CHARGE - Wiring diagram ................................SC-15
Charging system ................................................SC-14
Chassis and body maintenance ........................MA-28
CHIME - Wiring diagram .....................................DI-53
CIGAR - Wiring diagram ..................................WW-55
Cigarette lighter ...............................................WW-55
Circuit breaker ...................................................PG-74
CKPS - Wiring diagram .....................EC-161,EC-167
Clutch cover .......................................................CL-17
Clutch disc .........................................................CL-17
Clutch master cylinder .........................................CL-9
Clutch operating cylinder ...................................CL-11
Clutch pedal .........................................................CL-6
CMPS - Wiring diagram .....................EC-173,EC-179
Coil spring (front) .............................................FSU-10
Collision diagnosis ...........................................SRS-56
Combination lamp, front, removal and installation ........
LT-30
Combination lamp, rear, removal and installation ........
LT-144
Combination meter ...............................................DI-4
Combination switch ..........................................LT-114
COMBSW - Wiring diagram ..............................LT-114
COMPAS - Wiring diagram .................................DI-68
Compass ............................................................DI-66
Component Location (auto A/C) .......ATC-36,MTC-36
Compression pressure ......................................EM-92
Compressor clutch removal and installation .ATC-143,
MTC-123
Compressor mounting ..................ATC-142,MTC-122
Compressor special service tool .......ATC-16,MTC-16
Condenser ....................................ATC-147,MTC-127
Connecting rod ................................................EM-127
Connecting rod bearing clearance ...................EM-131
Connecting rod bushing clearance ..................EM-127
Console box - See Instrument panel ...................IP-10
CONSULT for all-mode 4WD .............................TF-44
CONSULT-II for engine .....................................EC-59
Control units (terminal arrangement) .................PG-78
Control valve (A/T) .............................................AT-33
Controller Area Network (CAN) ..BL-25,BL-59,RF-13
Converter housing installation .........................AT-250
COOL/F - Wiring diagram ................................EC-135
Cooling circuit (engine) ........................................CO-6
Cooling fan ........................................................CO-19
Cooling fan motor ............................................EC-141
Cooling unit (A/C evaporator) ......ATC-124,ATC-149,
MTC-103
,MTC-129
Counter gear (M/T) ............................................MT-21
Coupling sleeve (M/T) ........................................MT-21
Crankcase ventilation system ............................EC-21
Crankshaft position sensor (TDC) ......EC-82,EC-159,
EC-165
Cylinder block .................................................EM-110
Cylinder block boring ......................................EM-129
Cylinder head ....................................................EM-92
Cylinder head bolt tightening ............................EM-96
Cylinder head gasket selection .........................EM-96
D
Data link connector for Consult ..........................EC-59
Daytime light system ...........................................LT-31
Daytime running light - See Daytime light systemLT-31
Diagnosis sensor unit .....................................SRS-48
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) ..........................EC-27
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) for OBD system ..EC-6
Diagnostic trouble code (DTC) inspection priority chart
EC-37
Differential gear oil replacement ...........MA-33,MA-34
DIFLOC - Wiring diagram ...............................RFD-46
Dimensions .........................................................GI-60
Direct clutch solenoid valve ...............AT-142,AT-144
Display and amp.assembly ...............ATC-60,MTC-55
Dome light - See Interior lamp ..........................LT-145
Door glass ...........................................GW-35,GW-38
Door lock ..........................................................BL-126
Door mirror lamp ...............................................LT-145
Door trim .............................................................EI-30
Door, front .............................BL-118,BL-120,GW-35
Door, rear ............................................BL-118,GW-38
Drive belt ...........................................................EM-12
Drive chain (Transfer) .........................TF-114,TF-120
Driver air bag ..................................................SRS-36
DTRL - Wiring diagram .......................................LT-35
Duct and grilles .............................ATC-134,MTC-113
E
ECM input/output signal .....................................EC-52
ECM power supply .............................................EC-71
ECM relay ........................................................EC-232
ECTS - Wiring diagram ....................................EC-105
EGR function ...................................................EC-302
EGR volume control valve ...............................EC-302
EGRC/V - Wiring diagram ................................EC-304
Electric sunroof ..................................................RF-10
Electrical units location ......................................PG-71
Electronic fuel injection pump ...........................EM-49
Engine control circuit diagram ...........................EC-50
Engine control component parts location ...........EC-46
Engine control module (ECM) ...........EC-213,EC-215,
EC-269
Page 1756 of 3171

IDX-4
ALPHABETICAL INDEX
Engine control system diagram and chart .........EC-15
Engine coolant ....................................................CO-7
Engine coolant temperature sensor (ECTS) ....EC-103
Engine oil .............................................................LU-5
Engine oil filter replacement .............................MA-26
Engine oil precautions ..........................................GI-7
Engine removal ...............................................EM-106
Engine room cover ............................................EM-20
Engine serial number ..........................................GI-58
Evaporator ....................................ATC-149,MTC-129
Exhaust manifold ..............................................EM-34
Exhaust system ...................................................EX-2
Exhaust system inspection ..................................EX-2
Expansion valve ............................ATC-150,MTC-130
F
F/FOG - Wiring diagram .....................................LT-74
F/PUMP - Wiring diagram ..EC-248,EC-254,EC-260,
EC-266
Final drive pre-inspection .................................FFD-18
Final drive removal and installation ..RFD-14,RFD-81
Flow charts .........................................................GI-24
Fluid temperature sensor (A/T) ........................AT-118
Fluids ................................................................MA-14
Fluorescent leak detector .............ATC-150,MTC-131
Flywheel (clutch) ................................................CL-17
Flywheel runout ..............................................EM-134
Fog lamp, front ....................................................LT-71
Foot lamp ..........................................................LT-145
Fork rod (M/T) ....................................................MT-23
Freeze frame data .............................................EC-28
Front brake solenoid valve .................AT-137,AT-139
Front bumper ......................................................EI-15
Front case (Transfer) ..........................TF-114,TF-120
Front combination lamp removal and installationLT-30
Front door ................BL-118,BL-120,BL-126,GW-35
Front Door Trim ..................................................EI-30
Front drive shaft (Transfer) ...TF-114,TF-120,TF-133
Front final drive removal and installation (4WD) ...........
FFD-15
Front fog lamp .....................................................LT-71
Front passenger air bag ..................................SRS-40
Front seat ...........................................................SE-20
Front seat belt ............................................SB-3,SB-5
Front seat belt pre-tensioner ...............SRS-3,SRS-47
Front side air bag ............................................SRS-43
Front washer ......................................................WW-4
Front wiper .........................................................WW-4
FRPS - Wiring diagram ....................................EC-120
FTS - Wiring diagram .......................................EC-115
Fuel cut control (at no load high engine speed) .EC-20
Fuel filler lid ......................................................BL-136
Fuel filter ............................................................EC-23
Fuel filter replacement ..........................................FL-4
Fuel gauge ............................................................DI-4
Fuel injection control system .............................EC-18
Fuel injector ............EC-25,EC-123,EC-125,EC-237
Fuel injector and fuel tube ................................EM-44
Fuel leak ............................................................EC-88
Fuel line inspection ..............................................FL-3
Fuel pumpEC-86,EC-217,EC-245,EC-251,EC-258,
EC-263
Fuel pump(Learning Value Clearing) .................EC-24
Fuel rail pressure sensor .................................EC-118
Fuel system .........................................................FL-3
Fuel tank ..............................................................FL-9
Fuel temperature sensor ..................................EC-113
Fuse ......................................................PG-74,PG-84
Fuse and fusible link box ..................................PG-84
Fusible link ............................................PG-74,PG-84
G
Garage jack and safety stand .............................GI-52
Gauges .................................................................DI-4
Gear components (M/T) ....................................MT-21
Generator ...........................................................SC-14
Generator - See Alternator ................................SC-14
Glass ........................GW-11,GW-35,GW-38,GW-43
Glove box lamp ................................................LT-162
GLOW - Wiring diagram ..................................EC-296
Glow plug ............................................EM-41,EC-295
Glow relay ........................................................EC-295
Grease ..............................................................MA-14
Ground distribution ...........................................PG-27
H
H/AIM - Wiring diagram .....................................LT-66
Harness connector ............................................PG-75
Harness layout ..................................................PG-38
Hazard warning lamp .........................................LT-97
Headlamp aiming control ...................................LT-66
Headlamp leveler - See Headlamp aiming control ........
LT-66
Headlamp removal and installation ....................LT-30
Heat up switch .................................................EC-319
Heated seat .......................................................SE-12
Heater and cooling unit (Heater core) ..........ATC-124,
ATC-127
,MTC-103,MTC-106
Heater unit (heater core) ..............ATC-124,ATC-127,
MTC-103
,MTC-106
HEATUP - Wiring diagram ...............................EC-320
Height (Dimensions) ...........................................GI-60
HFC134a (R134a) system precaution .ATC-4,MTC-4
HFC134a (R134a) system service procedureATC-138,
MTC-118
HFC134a (R134a) system service tools ........ATC-16,
MTC-16
HFC134a system service equipment precaution ..........
ATC-12
,MTC-12
High and low reverse clutch solenoid valve ....AT-147,
AT-149
HLC - Wiring diagram ......................................WW-41
Horn .................................................................WW-59
HORN - Wiring diagram ...................................WW-59
How to erase DTC .............................................EC-27