ESP NISSAN X-TRAIL 2003 Electronic Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: NISSAN, Model Year: 2003, Model line: X-TRAIL, Model: NISSAN X-TRAIL 2003Pages: 3066, PDF Size: 51.47 MB
Page 2 of 3066

FOREWORD
This manual contains maintenance and repair procedures for the NISSAN
X-TRAIL , model T30 series.
In order to assure your safety and the efficient functioning of the vehicle,
this manual should be read thoroughly. It is especially important that the
PRECAUTIONS in the GI section be completely understood before starting
any repair task.
All information in this manual is based on the latest product information
at the time of publication. The right is reserved to make changes in speci-
fications and methods at any time without notice.
IMPORTANT SAFETY NOTICE
The proper performance of service is essential for both the safety of the
technician and the efficient functioning of the vehicle.
The service methods in this Service Manual are described in such a man-
ner that the service may be performed safely and accurately.
Service varies with the procedures used, the skills of the technician and the
tools and parts available. Accordingly, anyone using service procedures,
tools or parts which are not specifically recommended by NISSAN must
first be completely satisfied that neither personal safety nor the vehicle's
safety will be jeopardized by the service method selected.
NISSAN EUROPE N.V.
Service Operations Section
Paris, France
Page 7 of 3066

AT-1
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
C TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE
CONTENTS
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
M
SECTION
A
B
AT
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
PRECAUTIONS .......................................................... 5
Precautions for Supplemental Restraint System
(SRS) “AIR BAG” and “SEAT BELT PRE-TEN-
SIONER” .................................................................. 5
Precautions for On Board Diagnostic (EURO-OBD)
System of A/T and Engine — Euro-OBD — ............. 5
Precautions For Trouble Diagnosis .......................... 5
Precautions For Harness Repair .............................. 5
Precautions .............................................................. 6
Service Notice or Precautions .................................. 7
Wiring Diagrams and Trouble Diagnosis .................. 8
PREPARATION ........................................................... 9
Special Service Tools ............................................... 9
Commercial Service Tools .......................................11
A/T FLUID ................................................................. 13
Checking A/T Fluid ................................................. 13
Changing A/T Fluid ................................................ 13
OVERALL SYSTEM ................................................. 14
A/T Electrical Parts Location .................................. 14
Circuit Diagram ...................................................... 16
Cross-sectional View .............................................. 17
Hydraulic Control Circuit ........................................ 18
Shift Mechanism ..................................................... 19
Control System ....................................................... 27
Control Mechanism ................................................ 29
Control Valve .......................................................... 33
EURO-OBD
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INDEX ........................... 35
Alphabetical & P No. Index for DTC ....................... 35
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIP-
TION .......................................................................... 37
Introduction ............................................................ 37
EURO-OBD Function for A/T System .................... 37
One or Two Trip Detection Logic of EURO-OBD ... 37
EURO-OBD Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) ......... 37
Malfunction Indicator lamp (MIL) ............................ 41
CONSULT-II ........................................................... 41
Diagnostic Procedure Without CONSULT-II ........... 50TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INTRODUCTION ........... 56
Introduction ............................................................. 56
Work Flow ............................................................... 61
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — BASIC INSPECTION .... 64
A/T Fluid Check ...................................................... 64
Stall Test ................................................................. 65
Line Pressure Test .................................................. 68
Road Test ............................................................... 69
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — GENERAL DESCRIP-
TION .......................................................................... 86
Symptom Chart ....................................................... 86
TCM Terminals and Reference Value ...................125
CAN COMMUNICATION .........................................129
System Description ...............................................129
DTC P0705 PARK/NEUTRAL POSITION (PNP)
SWITCH ..................................................................130
Description ............................................................130
Wiring Diagram — AT — PNP/SW .......................132
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................133
Component Inspection ..........................................135
DTC P0710 A/T FLUID TEMPERATURE SENSOR
CIRCUIT ..................................................................136
Description ............................................................136
Wiring Diagram — AT — FTS ..............................138
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................139
Component Inspection ..........................................141
DTC P0720 VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR·A/T (REV-
OLUTION SENSOR) ...............................................142
Description ............................................................142
Wiring Diagram — AT — VSSA/T ........................144
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................145
DTC P0725 ENGINESPEED SIGNAL ...................147
Description ............................................................147
Wiring Diagram — AT — ENGSS .........................148
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................149
DTC P0731 A/T 1ST GEAR FUNCTION ................151
Description ............................................................151
Wiring Diagram — AT — 1ST ...............................154
Diagnostic Procedure ...........................................155
Component Inspection ..........................................156
Page 14 of 3066

AT-8
PRECAUTIONS
lVehicle has TCC shudder and/or no TCC apply. Replace only after all hydraulic and electrical diagnoses
have been made. (Converter clutch material may be glazed.)
lConverter is contaminated with engine coolant containing antifreeze.
lInternal failure of stator roller clutch.
lHeavy clutch debris due to overheating (blue converter).
lSteel particles or clutch lining material found in fluid filter or on magnet when no internal parts in unit are
worn or damaged — indicates that lining material came from converter.
The torque converter should not be replaced if:
lThe fluid has an odor, is discolored, and there is no evidence of metal or clutch facing particles.
lThe threads in one or more of the converter bolt holes are damaged.
lTransaxle failure did not display evidence of damaged or worn internal parts, steel particles or clutch plate
lining material in unit and inside the fluid filter.
lVehicle has been exposed to high mileage (only). The exception may be where the torque converter
clutch dampener plate lining has seen excess wear by vehicles operated in heavy and/or constant traffic,
such as taxi, delivery or police use.
EURO-OBD SELF-DIAGNOSIS — EURO-OBD —
lA/T self-diagnosis is performed by the TCM in combination with the ECM. The results can be read through
the blinking pattern of the O/D OFF indicator lamp or the malfunction indicator lamp (MIL). Refer to the
table onAT-42, "
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULT TEST MODE"for the indicator used to display each self-
diagnostic result.
lThe self-diagnostic results indicated by the MIL are automatically stored in both the ECM and TCM mem-
ories.
Always perform the procedure “HOW TO ERASE DTC” onAT-39, "
HOW TO ERASE DTC"to com-
plete the repair and avoid unnecessary blinking of the MIL.
lThe following self-diagnostic items can be detected using ECM self-diagnostic results mode* only when
the O/D OFF indicator lamp does not indicate any malfunctions.
–PNP switch
–A/T 1st, 2nd, 3rd, or 4th gear function
*: For details of EURO-OBD, refer toAT - 3 7 , "
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION".
lCertain systems and components, especially those related to EURO-OBD, may use a new style
slide-locking type harness connector.
For description and how to disconnect, refer toPG-70, "
HARNESS CONNECTOR".
Wiring Diagrams and Trouble DiagnosisECS004Q4
When you read wiring diagrams, refer to the following:
lGI-14, "How to Read Wiring Diagrams".
lPG-2, "POWER SUPPLY ROUTING".
When you perform trouble diagnosis, refer to the following:
lGI-11, "HOW TO FOLLOW TEST GROUPS IN TROUBLE DIAGNOSES".
l"", “HOW TO PERFORM EFFICIENT DIAGNOSIS FOR AN ELECTRICAL INCIDENT”
Page 34 of 3066
AT-28
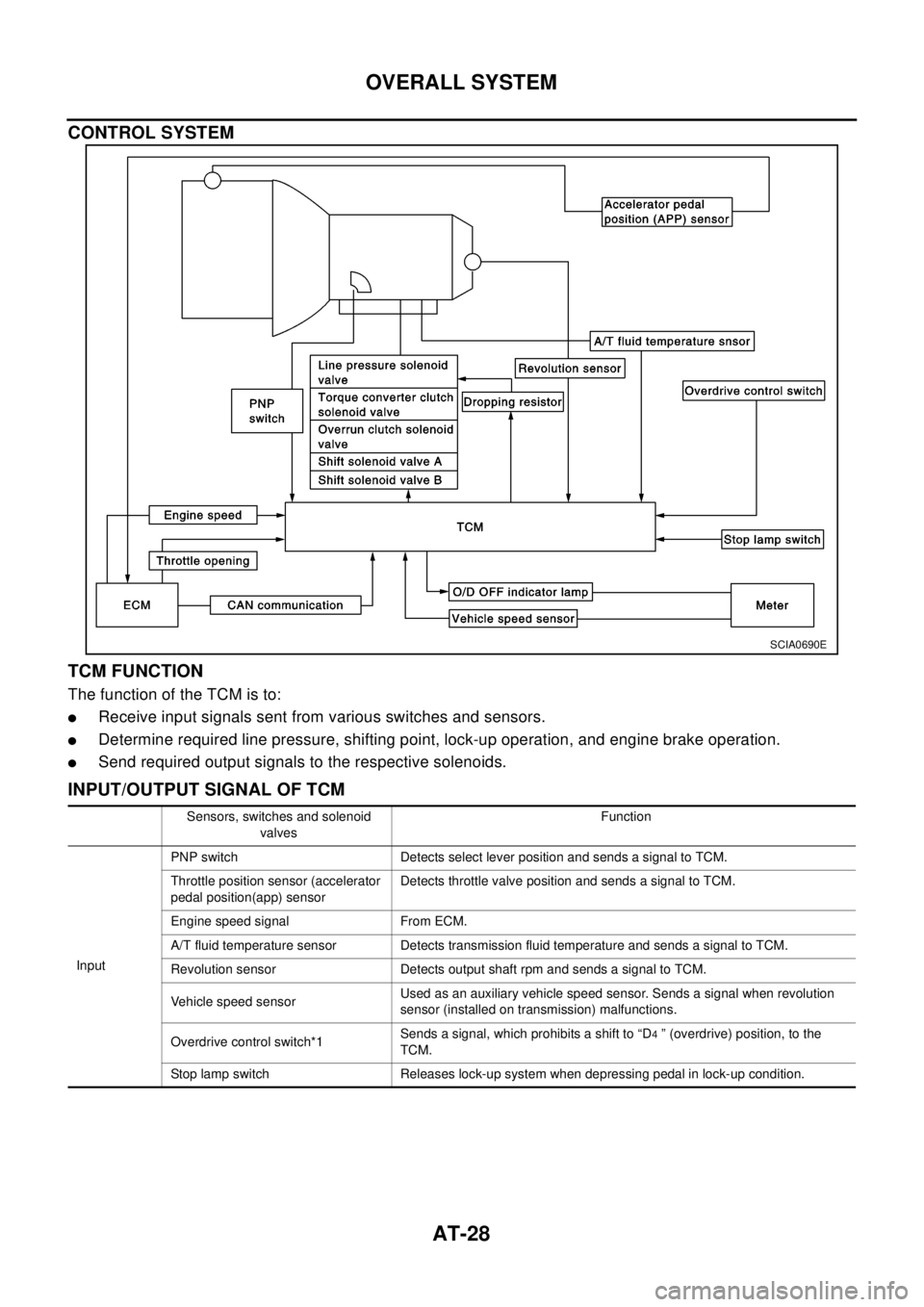
OVERALL SYSTEM
CONTROL SYSTEM
TCM FUNCTION
ThefunctionoftheTCMisto:
lReceive input signals sent from various switches and sensors.
lDetermine required line pressure, shifting point, lock-up operation, and engine brake operation.
lSend required output signals to the respective solenoids.
INPUT/OUTPUT SIGNAL OF TCM
SCIA0690E
Sensors, switches and solenoid
valvesFunction
InputPNP switch Detects select lever position and sends a signal to TCM.
Throttle position sensor (accelerator
pedal position(app) sensorDetects throttle valve position and sends a signal to TCM.
Engine speed signal From ECM.
A/T fluid temperature sensor Detects transmission fluid temperature and sends a signal to TCM.
Revolution sensor Detects output shaft rpm and sends a signal to TCM.
Vehicle speed sensorUsed as an auxiliary vehicle speed sensor. Sends a signal when revolution
sensor (installed on transmission) malfunctions.
Overdrive control switch*1Sends a signal, which prohibits a shift to “D
4” (overdrive) position, to the
TCM.
Stop lamp switch Releases lock-up system when depressing pedal in lock-up condition.
Page 35 of 3066
OVERALL SYSTEM
AT-29
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
AT
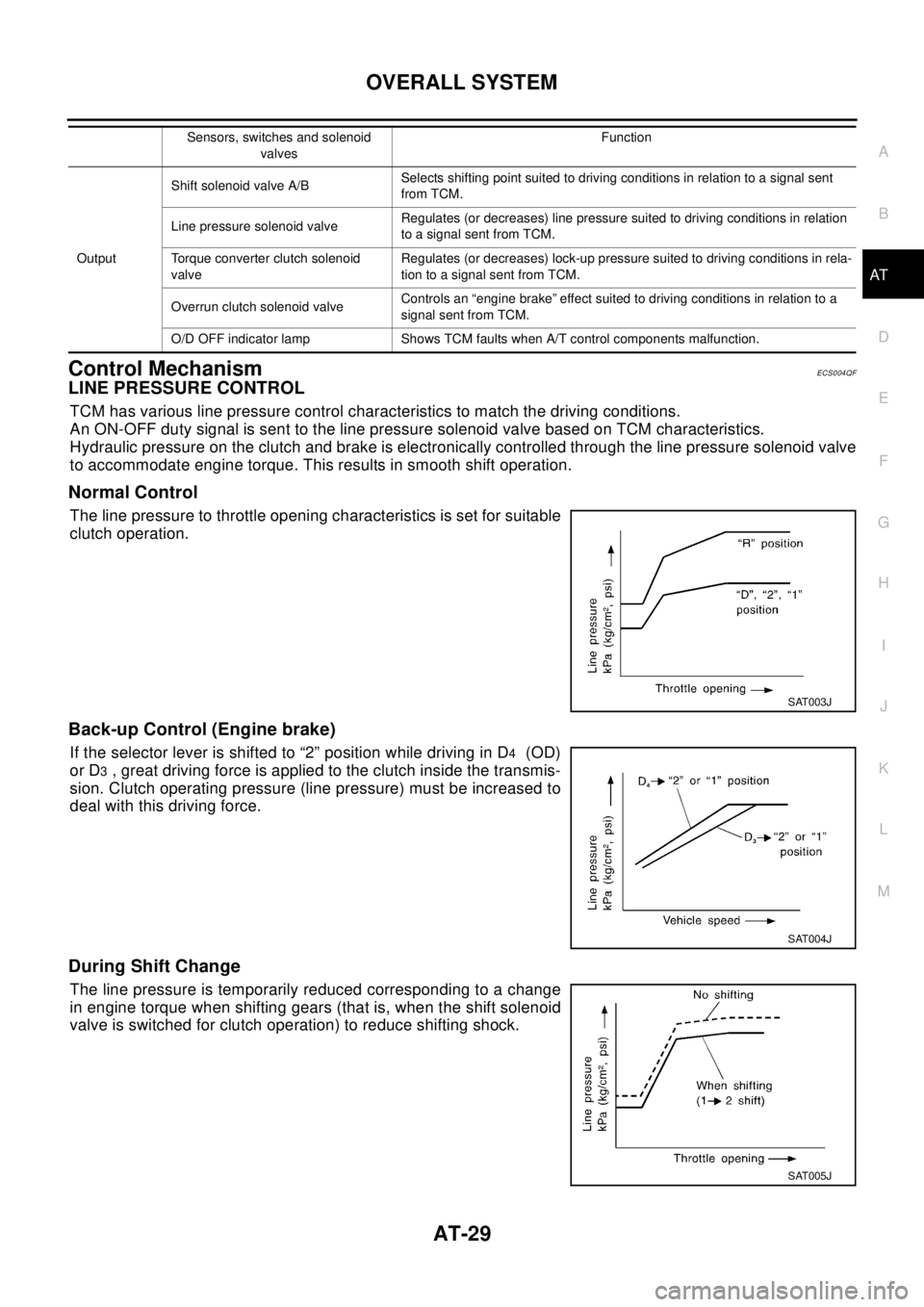
Control MechanismECS004QF
LINE PRESSURE CONTROL
TCM has various line pressure control characteristics to match the driving conditions.
An ON-OFF duty signal is sent to the line pressure solenoid valve based on TCM characteristics.
Hydraulic pressure on the clutch and brake is electronically controlled through the line pressure solenoid valve
to accommodate engine torque. This results in smooth shift operation.
Normal Control
The line pressure to throttle opening characteristics is set for suitable
clutch operation.
Back-up Control (Engine brake)
If the selector lever is shifted to “2” position while driving in D4(OD)
or D
3, great driving force is applied to the clutch inside the transmis-
sion. Clutch operating pressure (line pressure) must be increased to
deal with this driving force.
During Shift Change
The line pressure is temporarily reduced corresponding to a change
in engine torque when shifting gears (that is, when the shift solenoid
valve is switched for clutch operation) to reduce shifting shock.
OutputShift solenoid valve A/BSelects shifting point suited to driving conditions in relation to a signal sent
from TCM.
Line pressure solenoid valveRegulates (or decreases) line pressure suited to driving conditions in relation
to a signal sent from TCM.
Torque converter clutch solenoid
valveRegulates (or decreases) lock-up pressure suited to driving conditions in rela-
tion to a signal sent from TCM.
Overrun clutch solenoid valveControls an “engine brake” effect suited to driving conditions in relation to a
signal sent from TCM.
O/D OFF indicator lamp Shows TCM faults when A/T control components malfunction.Sensors, switches and solenoid
valvesFunction
SAT003J
SAT004J
SAT005J
Page 36 of 3066
AT-30
OVERALL SYSTEM
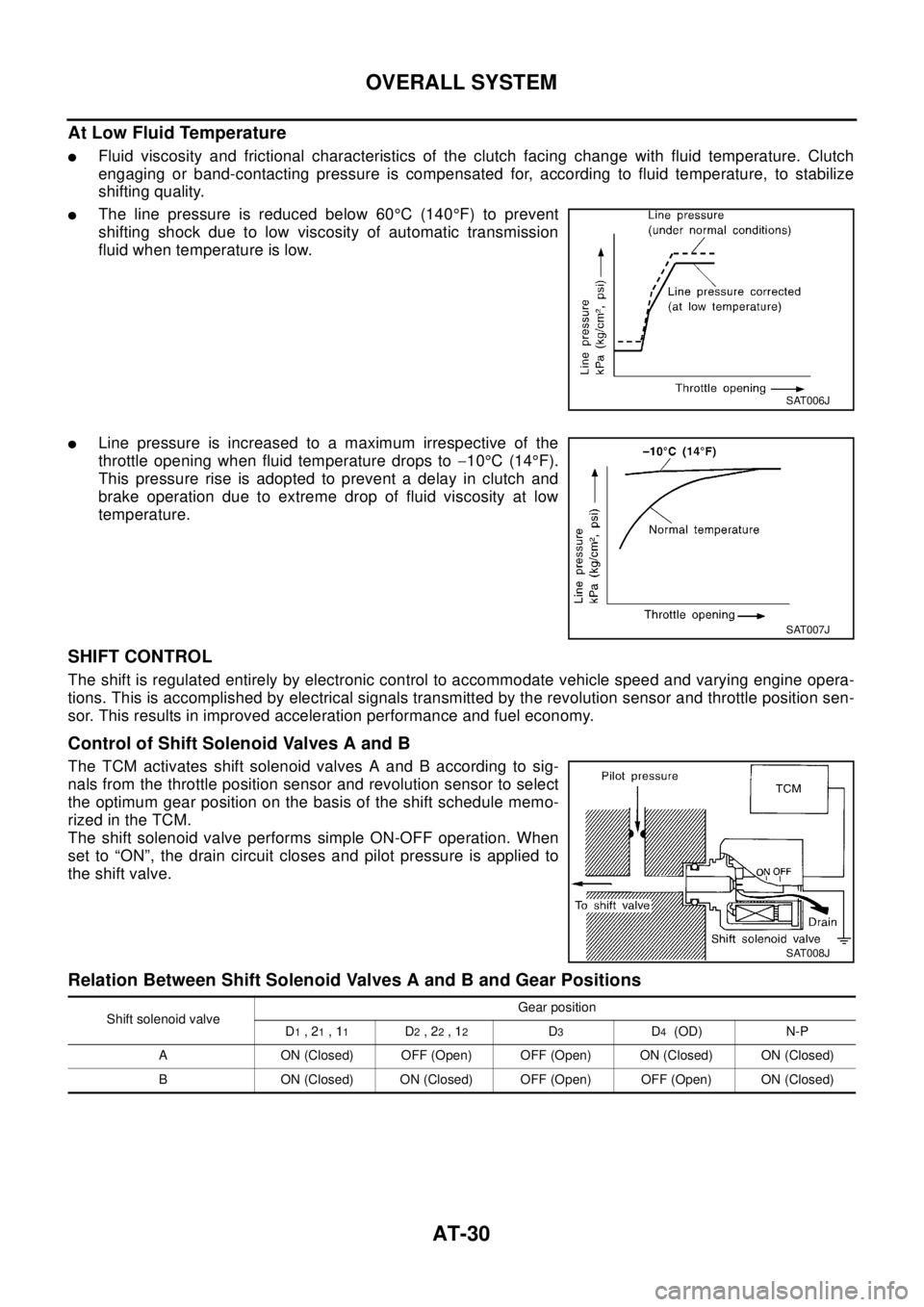
At Low Fluid Temperature
lFluid viscosity and frictional characteristics of the clutch facing change with fluid temperature. Clutch
engaging or band-contacting pressure is compensated for, according to fluid temperature, to stabilize
shifting quality.
lThe line pressure is reduced below 60°C(140°F) to prevent
shifting shock due to low viscosity of automatic transmission
fluid when temperature is low.
lLine pressure is increased to a maximum irrespective of the
throttle opening when fluid temperature drops to-10°C(14°F).
This pressure rise is adopted to prevent a delay in clutch and
brake operation due to extreme drop of fluid viscosity at low
temperature.
SHIFT CONTROL
The shift is regulated entirely by electronic control to accommodate vehicle speed and varying engine opera-
tions. This is accomplished by electrical signals transmitted by the revolution sensor and throttle position sen-
sor. This results in improved acceleration performance and fuel economy.
Control of Shift Solenoid Valves A and B
The TCM activates shift solenoid valves A and B according to sig-
nals from the throttle position sensor and revolution sensor to select
the optimum gear position on the basis of the shift schedule memo-
rizedintheTCM.
The shift solenoid valve performs simple ON-OFF operation. When
set to “ON”, the drain circuit closes and pilot pressure is applied to
the shift valve.
Relation Between Shift Solenoid Valves A and B and Gear Positions
SAT006J
SAT007J
SAT008J
Shift solenoid valveGear position
D1,21,11D2,22,12D3D4(OD) N-P
A ON (Closed) OFF (Open) OFF (Open) ON (Closed) ON (Closed)
B ON (Closed) ON (Closed) OFF (Open) OFF (Open) ON (Closed)
Page 39 of 3066
OVERALL SYSTEM
AT-33
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
AT
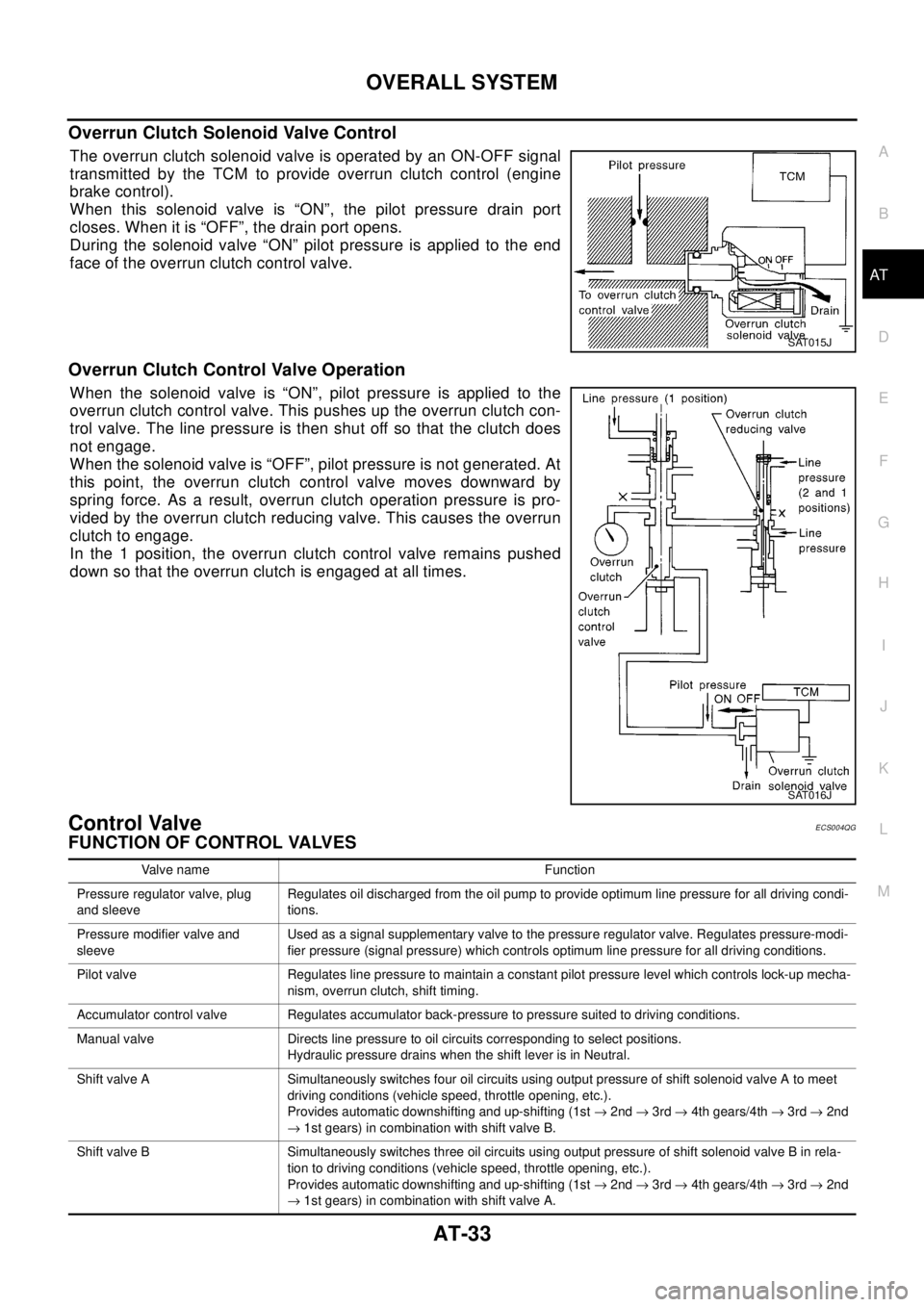
Overrun Clutch Solenoid Valve Control
TheoverrunclutchsolenoidvalveisoperatedbyanON-OFFsignal
transmitted by the TCM to provide overrun clutch control (engine
brake control).
When this solenoid valve is “ON”, the pilot pressure drain port
closes. When it is “OFF”, the drain port opens.
During the solenoid valve “ON” pilot pressure is applied to the end
face of the overrun clutch control valve.
Overrun Clutch Control Valve Operation
When the solenoid valve is “ON”, pilot pressure is applied to the
overrun clutch control valve. This pushes up the overrun clutch con-
trol valve. The line pressure is then shut off so that the clutch does
not engage.
When the solenoid valve is “OFF”, pilot pressure is not generated. At
this point, the overrun clutch control valve moves downward by
spring force. As a result, overrun clutch operation pressure is pro-
vided by the overrun clutch reducing valve. This causes the overrun
clutch to engage.
In the 1 position, the overrun clutch control valve remains pushed
down so that the overrun clutch is engaged at all times.
Control ValveECS004QG
FUNCTION OF CONTROL VALVES
SAT015J
SAT016J
Valve name Function
Pressure regulator valve, plug
and sleeveRegulates oil discharged from the oil pump to provide optimum line pressure for all driving condi-
tions.
Pressure modifier valve and
sleeveUsed as a signal supplementary valve to the pressure regulator valve. Regulates pressure-modi-
fier pressure (signal pressure) which controls optimum line pressure for all driving conditions.
Pilot valve Regulates line pressure to maintain a constant pilot pressure level which controls lock-up mecha-
nism, overrun clutch, shift timing.
Accumulator control valve Regulates accumulator back-pressure to pressure suited to driving conditions.
Manual valve Directs line pressure to oil circuits corresponding to select positions.
Hydraulic pressure drains when the shift lever is in Neutral.
Shift valve A Simultaneously switches four oil circuits using output pressure of shift solenoid valve A to meet
driving conditions (vehicle speed, throttle opening, etc.).
Provides automatic downshifting and up-shifting (1st®2nd®3rd®4th gears/4th®3rd®2nd
®1st gears) in combination with shift valve B.
Shift valve B Simultaneously switches three oil circuits using output pressure of shift solenoid valve B in rela-
tion to driving conditions (vehicle speed, throttle opening, etc.).
Provides automatic downshifting and up-shifting (1st®2nd®3rd®4th gears/4th®3rd®2nd
®1st gears) in combination with shift valve A.
Page 43 of 3066
![NISSAN X-TRAIL 2003 Electronic Repair Manual ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
AT-37
[EURO-OBD]
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
AT
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONPFP:00000
IntroductionECS004QH
The A/T system has two self-diagnostic systems.
T NISSAN X-TRAIL 2003 Electronic Repair Manual ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
AT-37
[EURO-OBD]
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
AT
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONPFP:00000
IntroductionECS004QH
The A/T system has two self-diagnostic systems.
T](/img/5/57402/w960_57402-42.png)
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
AT-37
[EURO-OBD]
D
E
F
G
H
I
J
K
L
MA
B
AT
ON BOARD DIAGNOSTIC SYSTEM DESCRIPTIONPFP:00000
IntroductionECS004QH
The A/T system has two self-diagnostic systems.
The first is the emission-related on board diagnostic system (EURO-OBD) performed by the TCM in combina-
tion with the ECM. The malfunction is indicated by the MIL (malfunction indicator lamp) and is stored as a DTC
in the ECM memory but not the TCM memory.
The second is the TCM original self-diagnosis indicated by the O/D OFF indicator lamp. The malfunction is
stored in the TCM memory. The detected items are overlapped with EURO-OBD self-diagnostic items. For
detail, refer toAT - 4 2 , "
SELF-DIAGNOSTIC RESULT TEST MODE".
EURO-OBD Function for A/T SystemECS004QI
The ECM provides emission-related on board diagnostic (EURO-OBD) functions for the A/T system. One
function is to receive a signal from the TCM used with EURO-OBD-related parts of the A/T system. The signal
is sent to the ECM when a malfunction occurs in the corresponding EURO-OBD-related part. The other func-
tion is to indicate a diagnostic result by means of the MIL (malfunction indicator lamp) on the instrument panel.
Sensors, switches and solenoid valves are used as sensing elements.
The MIL automatically illuminates in One or Two Trip Detection Logic when a malfunction is sensed in relation
to A/T system parts.
One or Two Trip Detection Logic of EURO-OBDECS0 04 QJ
ONETRIPDETECTIONLOGIC
If a malfunction is sensed during the first test drive, the MIL will illuminate and the malfunction will be stored in
the ECM memory as a DTC. The TCM is not provided with such a memory function.
TWO TRIP DETECTION LOGIC
When a malfunction is sensed during the first test drive, it is stored in the ECM memory as a 1st trip DTC
(diagnostic trouble code) or 1st trip freeze frame data. At this point, the MIL will not illuminate. — First Trip
If the same malfunction as that experienced during the first test drive is sensed during the second test drive,
the MIL will illuminate. — Second Trip
A/T-related parts for which the MIL illuminates during the first or second test drive are listed below.
The “trip” in the “One or Two Trip Detection Logic” means a driving mode in which self-diagnosis is performed
during vehicle operation.
EURO-OBD Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)ECS004QK
HOW TO READ DTC AND 1ST TRIP DTC
DTC and 1st trip DTC can be read by the following methods.
(withCONSULT-IIor GST)CONSULT-II or GST (Generic Scan Tool) Examples: P0705, P0710,
P0720, P0725, etc.
These DTCs are prescribed by SAE J2012.
(CONSULT-II also displays the malfunctioning component or system.)
l1st trip DTC No. is the same as DTC No.
lOutput of the diagnostic trouble code indicates that the indicated circuit has a malfunction. How-
ever, in case of the Mode II and GST they do not indicate whether the malfunction is still occurring
or occurred in the past and returned to normal.
CONSULT-II can identify them as shown below. Therefore, using CONSULT-II (if available) is rec-
ommended.
ItemsMIL
One trip detection Two trip detection
Shift solenoid valve A — DTC: P0750 X
Shift solenoid valve B — DTC: P0755 X
Throttle position sensor — DTC: P1705 X
Except aboveX
Page 62 of 3066
![NISSAN X-TRAIL 2003 Electronic Repair Manual AT-56
[EURO-OBD]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INTRODUCTION
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INTRODUCTION
PFP:00000
IntroductionECS0 04 QO
The TCM receives a signal from the vehicle speed sensor, throttle
position senso NISSAN X-TRAIL 2003 Electronic Repair Manual AT-56
[EURO-OBD]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INTRODUCTION
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INTRODUCTION
PFP:00000
IntroductionECS0 04 QO
The TCM receives a signal from the vehicle speed sensor, throttle
position senso](/img/5/57402/w960_57402-61.png)
AT-56
[EURO-OBD]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INTRODUCTION
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — INTRODUCTION
PFP:00000
IntroductionECS0 04 QO
The TCM receives a signal from the vehicle speed sensor, throttle
position sensor or PNP switch and provides shift control or lock-up
control via A/T solenoid valves.
The TCM also communicates with the ECM by means of a signal
sent from sensing elements used with the EURO-OBD related parts
of the A/T system for malfunction-diagnostic purposes. The TCM is
capable of diagnosing malfunctioning parts while the ECM can store
malfunctions in its memory.
Input and output signals must always be correct and stable in the
operation of the A/T system. The A/T system must be in good oper-
ating condition and be free of valve seizure, solenoid valve malfunc-
tion, etc.
It is much more difficult to diagnose a problem that occurs intermit-
tently rather than continuously. Most intermittent problems are
caused by poor electric connections or improper wiring. In this case,
careful checking of suspected circuits may help prevent the replace-
ment of good parts.
A visual check only, may not find the cause of the problems. A road
test with CONSULT-II (or GST) or a circuit tester connected should
be performed. Follow the “Work Flow”. Refer toAT- 6 1 , "
Work Flow".
Before undertaking actual checks, take a few minutes to talk with a
customer who approaches with a driveability complaint. The cus-
tomer can supply good information about such problems, especially
intermittent ones. Find out what symptoms are present and under
what conditions they occur. A “Diagnostic Worksheet” like the exam-
ple (AT-57, "
DIAGNOSTIC WORKSHEET") should be used.
Start your diagnosis by looking for “conventional” problems first. This
will help troubleshoot driveability problems on an electronically con-
trolled engine vehicle.
Also check related Service bulletins for information.
SAT631IA
SAT632I
SEF234G
Page 74 of 3066
![NISSAN X-TRAIL 2003 Electronic Repair Manual AT-68
[EURO-OBD]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — BASIC INSPECTION
Line Pressure Test
ECS004QS
LINE PRESSURE TEST PORTS
Location of line pressure test ports are shown in the illustration.
lAlways replace pressur NISSAN X-TRAIL 2003 Electronic Repair Manual AT-68
[EURO-OBD]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — BASIC INSPECTION
Line Pressure Test
ECS004QS
LINE PRESSURE TEST PORTS
Location of line pressure test ports are shown in the illustration.
lAlways replace pressur](/img/5/57402/w960_57402-73.png)
AT-68
[EURO-OBD]
TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS — BASIC INSPECTION
Line Pressure Test
ECS004QS
LINE PRESSURE TEST PORTS
Location of line pressure test ports are shown in the illustration.
lAlways replace pressure plugs as they are self-sealing
bolts.
LINE PRESSURE TEST PROCEDURE
1. Check A/T fluid and engine oil levels. If necessary, add fluid or
oil.
2. Drive vehicle for approx. 10 minutes or until engine oil and ATF
reach operating temperature.
3. Install pressure gauge to corresponding line pressure port.
4. Set parking brake and block wheels.
lContinue to depress brake pedal fully while line pressure
test is being performed at stall speed.
SCIA0709E
ATF operating temperature: 50 - 80°C (122 -176°F)
SAT647B
UAT008
UAT008