oil OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 795 of 6000
4D2–28
TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
Tension of Lock-up Fork Spring
If the measurement exceeds the limit, replace the
spring. (When compressed to 41.4 mm)
Standard : 27.1-33.8 N {2.76-3.45 kg/6.08-7.61 Ib}
Allowable limit : 24.5 N {2.5 kg/5.5 Ib}
014RW048
Tension of Detent Spring Assembly
If the measurement exceeds the limit, replace the
spring. N {kg} (When compressed by 3 mm from the
free length)
Standard : 139 N -203 {14.2-20.7 kg/31.3-45.6 Ib}
Allowable limit : 130 N {13.3 kg/29.3 Ib}
261RW041
Oil Pump
Remove foreign materials from the strainer. If the
strainer is damaged, replace it.
If the area into which the shaft is inserted is
excessively worn or damaged, replace the pump.
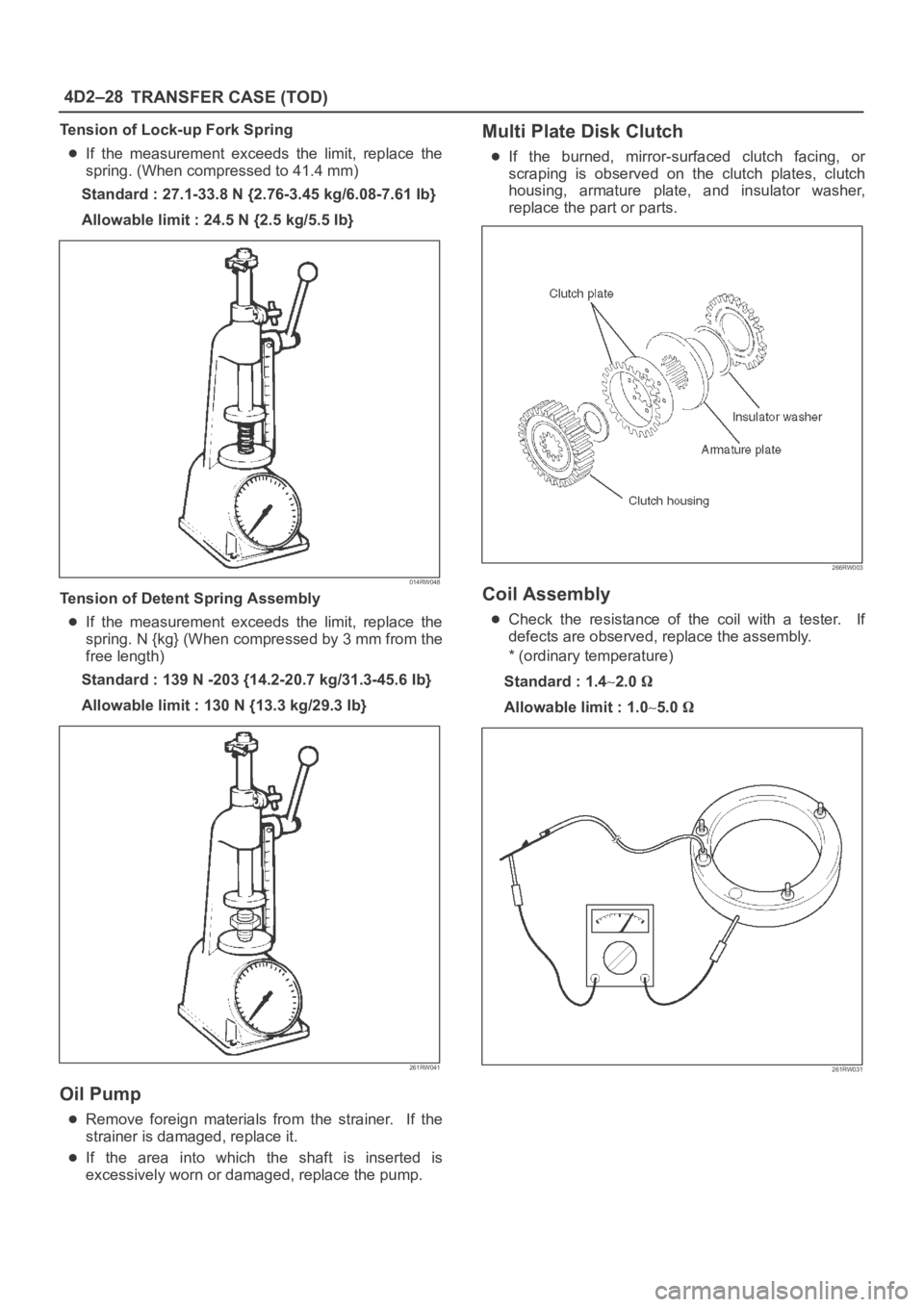
Multi Plate Disk Clutch
If the burned, mirror-surfaced clutch facing, or
scraping is observed on the clutch plates, clutch
housing, armature plate, and insulator washer,
replace the part or parts.
266RW003
Coil Assembly
Check the resistance of the coil with a tester. If
defects are observed, replace the assembly.
* (ordinary temperature)
Standard : 1.4
2.0
Allowable limit : 1.05.0
261RW031
Page 796 of 6000
4D2–29 TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
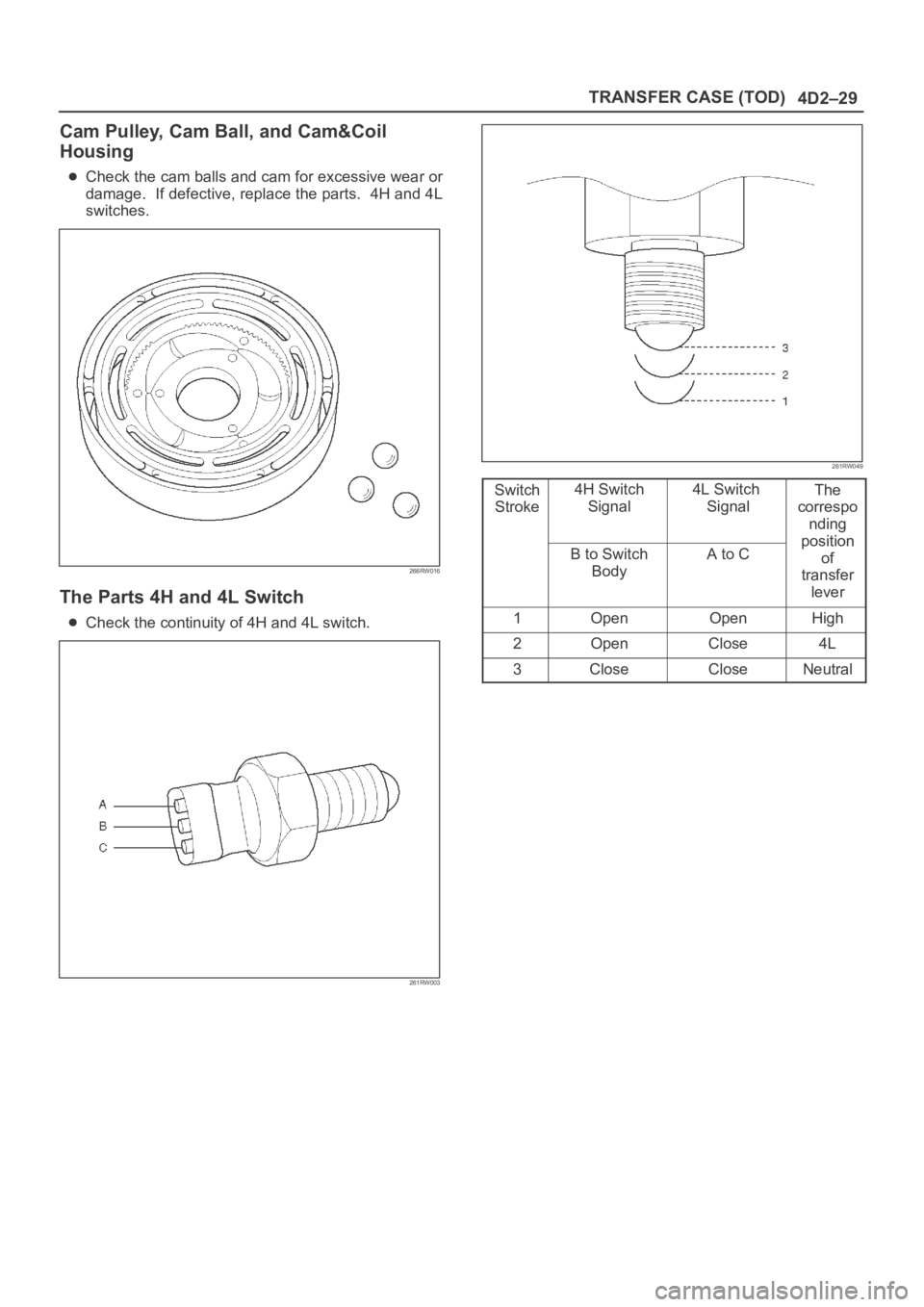
Cam Pulley, Cam Ball, and Cam&Coil
Housing
Check the cam balls and cam for excessive wear or
damage. If defective, replace the parts. 4H and 4L
switches.
266RW016
The Parts 4H and 4L Switch
Check the continuity of 4H and 4L switch.
261RW003
261RW049
Switch
Stroke4H Switch
Signal4L Switch
SignalThe
correspo
nding
p
ositionB to Switch
BodyA to Cosition
of
transfer
lever
1OpenOpenHigh
2OpenClose4L
3CloseCloseNeutral
Page 797 of 6000
4D2–30
TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
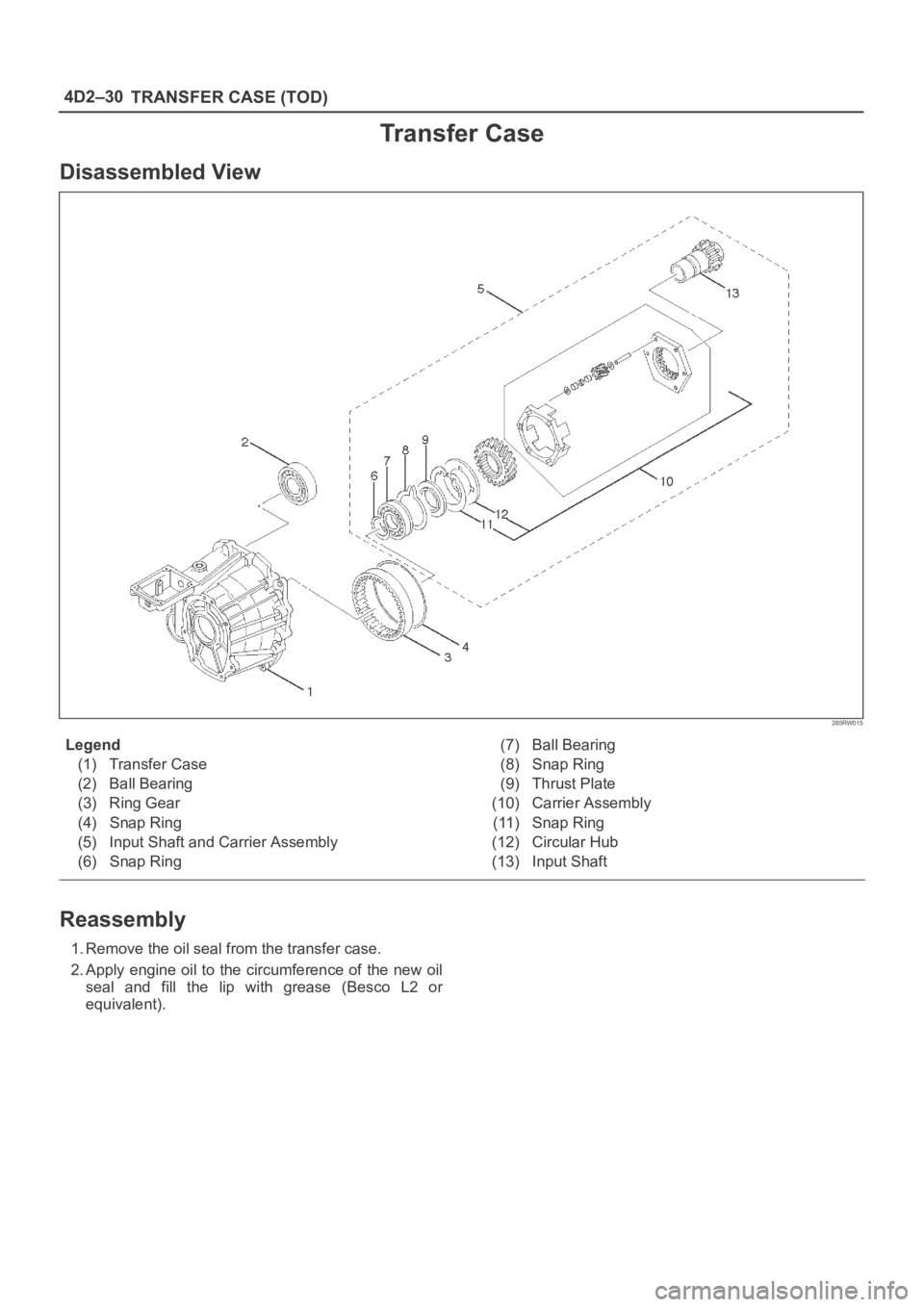
Transfer Case
Disassembled View
265RW015
Legend
(1) Transfer Case
(2) Ball Bearing
(3) Ring Gear
(4) Snap Ring
(5) Input Shaft and Carrier Assembly
(6) Snap Ring(7) Ball Bearing
(8) Snap Ring
(9) Thrust Plate
(10) Carrier Assembly
(11) Snap Ring
(12) Circular Hub
(13) Input Shaft
Reassembly
1. Remove the oil seal from the transfer case.
2. Apply engine oil to the circumference of the new oil
seal and fill the lip with grease (Besco L2 or
equivalent).
Page 798 of 6000

4D2–31 TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
3. Using the front output shaft oil seal installer
5-8840-2410-0 (J-42807), install the oil seal to the
transfer case.
261RW053
Front Output Shaft Oil Seal
Distance between the transfer case end and oil seal.
NOTE: When installing the oil seal to the specified
dimension, be careful not to damage it.
Distance : 0.93 — 1.43mm (0.037 — 0.056 in)
A04RW003
4. Using the input shaft (main) oil seal installer
5-8840-2411-0 (J-42808), install the oil seal to the
transfer case.
261RW055
Input Shaft Oil Seal
Distance between the transfer case end and oil seal.
NOTE: When installing the oil seal to the specified
dimension, be careful not to damage it.
Distance : 3.25 — 3.75mm (0.13 — 0.15 in)
A04RW002
Page 804 of 6000

4D2–37 TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
Sprocket and Mechanical Lock
Disassembled View
266RW008
Legend
(1) Strainer
(2) Hose
(3) Oil Pump Assembly
(4) Thrust Washer
(5) Mechanical Lock Hub
(6) Lock-up Sleeve(7) Lock-up Fork
(8) Chain
(9) Lower Drive Sprocket
(10) Front Tone Wheel
(11) Drive Sprocket
(12) Sprocket Spacer
Reassembly
1. Connect the hose and strainer to the oil pump
assembly.
2. Install the oil pump assembly to the output shaft and
set the magnet to the strainer position.
3. Install the thrust washer.
4. Install the spring to the lock-up fork.
Page 806 of 6000

4D2–39 TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
Clutch Pack and Clutch Cam
Disassembled View
266RW006
Legend
(1) Clutch Pack Assembly
(2) Insulator Washer
(3) Armature Plate
(4) Snap Ring(5) Wave Spring
(6) Cam Pulley
(7) Cam Ball
(8) Cam and Coil Housing
(9) Thrust Bearing
Reassembly
1. Mount the clutch pack assembly to which the multi
plate disk clutch is already installed to the output
shaft.
NOTE: Mount the clutch pack assembly while adjusting
the phase of both the clutch housing and drive sprocket.
2. Install the insulator washer.
3. Install the armature plate.
Page 807 of 6000

4D2–40
TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
4. Using snap ring pliers, install the snap ring.
266RW009
5. Install the wave spring.
6. Install the cam pulley.
7. Place a ball on each groove of the cam pulley.
266RW013
8. Install the cam and coil housing.
9. Install the thrust bearing.
Page 808 of 6000

4D2–41 TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
Main Data and Specifications
Leading Particulars
Ty p eTransfer case with low range reduction mechanism
2H Rear wheel drive
TOD Electronically controlled torque split four wheel drive
4L Low-speed mechanical lock-up four wheel drive
Control systemFloor direct control
Gear ratioH1.000
L2.480
Oil quantity, Lit1.9
OilAT F D E X R O N-IIE or ATF DEXRON-III
Torque Specifications
E04RW012
Page 810 of 6000

4D2–43 TRANSFER CASE (TOD)
Special Tools
ILLUSTRATIONTOOL NO.
TOOL NAME
5–8840–0133–0
(J–8614–11)
Flange Holder
5–8840–2412–0
(J–42804)
Rear Oil Seal Installer
5–8840–2293–0
(J–39209)
Punch
5–8840–2409–0
(J–42805)
Bearing Remover
5–8840–0084–0
(J–2619–01)
Slide Hammer
5–8840–0015–0
(J–22912–01)
Bearing Remover
ILLUSTRATIONTOOL NO.
TOOL NAME
5–8840–2413–0
(J–42806)
Ring Gear Replacer
5–8840–2410–0
(J–42807)
Front Out Oil Seal
Installer
5–8840–2411–0
(J–42808)
Input Shaft Oil Seal
Installer
5–8840–2416–0
(J–42809)
Ring Gear Installer
Page 814 of 6000

5A–4
BRAKE CONTROL SYSTEM
normal braking when a malfunction has occurred in the
ABS.
The EHCU has a self-diagnosing function which can
indicate faulty circuits during diagnosis.
The EHCU is mounted on the engine compartment front
right side. It consists of a Motor, Plunger Pump, Solenoid
Valves and Check Valve.
On the outside, the relay box containing a motor relay and
a valve relay is installed.
Solenoid Valves: Reduces or holds the caliper fluid
pressure for each front disc brake or both rear disc brakes
according to the signal sent from the EHCU.
Reservoir: Temporarily holds the brake fluid that returns
from the front and rear disc brake caliper so that pressure
of front disc brake caliper can be reduced smoothly.
Plunger Pump: Feeds the brake fluid held in the reservoir
to the master cylinder.
Motor: Drives the pump according to the signal from
EHCU.
Check Valve: Controls the brake fluid flow.
ABS Warning Light
821RW033Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System have
an amber “ABS” warning light in the instrument panel.
The “ABS” warning light will illuminate if a malfunction in
the Anti-lock Brake System is detected by the Electronic
Hydraulic Control Unit (EHCU). In case of an electronic
malfunction, the EHCU will turn “ON” the “ABS” warning
light and disable the Anti-lock braking function.
The “ABS” light will turn “ON” for approximately three
seconds after the ignition switch is to the “ON” position.
If the “ABS” light stays “ON” after the ignition switch is the
“ON” position, or comes “ON” and stays “ON” while
driving, the Anti-lock Brake System should be inspected
for a malfunction according to the diagnosis procedure.
Wheel Speed Sensor
It consists of a sensor and a rotor. The sensor is attached
to the knuckle on the front wheels and to the axle shaft
bearing holder on the rear wheels.
The rotor is press-fit in the axle shaft.The flux generated from electrodes magnetized by a
magnet in the sensor varies due to rotation of the rotor,
and the electromagnetic induction generates alternating
voltage in the coil. This voltage draws a “sine curve” with
the frequency proportional to rotor speed and it allows
detection of wheel speed.
G-Sensor
The G-sensor installed inside the center console detects
the vehicle deceleration speed and sends a signal to the
EHCU. In 4WD operation, all four wheels may be
decelerated in almost the same phase, since all wheels
are connected mechanically.
This tendency is noticeable particularly on roads with low
friction coefficient, and the ABS control is adversely
affected.
The G-sensor judges whether the friction coefficient of
road surface is low or high, and changes the EHCU’s
operating system to ensure ABS control.
Normal and Anti-lock Braking
Under normal driving conditions, the Anti-lock Brake
System functions the same as a standard power assisted
brake system. However, with the detection of wheel
lock-up, a slight bump or kick-back will be felt in the brake
pedal. This pedal “bump” will be followed by a series of
short pedal pulsations which occurs in rapid succession.
The brake pedal pulsation will continue until there is no
longer a need for the anti-lock function or until the vehicle
is stopped. A slight ticking or popping noise may be heard
during brake applications when the Anti-lock features is
being used.
When the Anti-lock feature is being used, the brake pedal
may rise even as the brakes are being applied. This is
also normal. Maintaining a constant force on the pedal
will provide the shortest stopping distance.
Brake Pedal Travel
Vehicles equipped with the Anti-lock Brake System may
be stopped by applying normal force to the brake pedal.
Although there is no need to push the pedal beyond the
point where it stops or holds the vehicle, by applying more
force the pedal will continue to travel toward the floor.
This extra brake pedal travel is normal.
Acronyms and Abbreviations
Several acronyms and abbreviations are commonly used
throughout this section:
ABS
Anti-lock Brake System
CKT
Circuit
DLC
Data Link Connector
EHCU
Electronic Hydraulic Control Unit
FL
Front Left