Pressure fuel regulator OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1434 of 6000

6E–317 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Installation Procedure
1. Install the fuel pressure regulator attaching screw.
Tighten
Tighten the fuel pressure regulator attaching screw
to 3 Nꞏm (26 lb in.).
F06RW043
2. Install the fuel pressure regulator on the fuel rail.
3. Install the two bolts to the protector that secures the
common chamber.
014RW109
4. Install the pressure regulator hose to the fuel
pressure regulator.
014RW110
5. Install the fuel pump relay. Refer to Fuel Pump Relay.
6. Connect the negative battery cable.
7. Crank the engine until it starts. Cranking the engine
may take longer than usual due to trapped air in the
fuel lines.
Fuel Metering System
Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of fire and personal
injury, it is necessary to relieve the fuel system
pressure before servicing the fuel system
components.
CAUTION: After relieving the system pressure, a
small amount of fuel may be released when servicing
fuel lines or connections. Reduce the chance of
personal injury by covering the fuel line fittings with
a shop towel before you disconnect the fittings. The
towels will absorb any fuel that may leak out. When
the disconnect is completed, place the towel in an
approved container.
1. Remove the fuel cap.
Page 1437 of 6000

6E–320
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
IMPORTANT:An eight-digit identification number is
stamped on the side of the fuel rail. Refer to this number
when you service the fuel rail or when a replacement part
is required.
TS24022
Before removal, the fuel rail assembly may be cleaned
with a spray type engine cleaner. Follow the spray
package instructions. Do not immerse the fuel rails in
liquid cleaning solvent.
1. Depressurize the fuel system. Refer to Fuel Pressure
Relief Procedure in this Section.
2. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
3. Remove the engine cover.
4. Disconnect the accelerator pedal cable from throttle
body and cable bracket.
5. Disconnect the connectors from manifold absolute
pressure sensor, solenoid valve, electric vacuum
sensing valve.
6. Disconnect the vacuum hose on canister VSV and
positive crankcase ventilation hose.
7. Remove the common chamber. Refer to the common
chamber in Engine Mechanical.
1. Lift up carefully on the fuel injectors. Do not
separate the fuel injectors from the fuel rail.
2. If an injector becomes separated from the fuel
rail, the infector O-ring seals and the retainer clip
must be replaced.
3. Drain residual fuel into an approved container.
014RW164
8. If removal of the fuel pressure regulator is necessary,
refer to
Fuel Pressure Regulator.
9. If removal of the fuel injectors is necessary, refer to
Fuel Injectors.
Installation Procedure
1. If the fuel injectors were removed, install them. Refer
to
Fuel Injectors.
2. If the fuel pressure regulator was removed, install it.
Refer to
Fuel Pressure Regulator.
3. Install the common chamber. Refer to common
chamber in engine Mechanical.
014RW164
Page 1459 of 6000

6E–342
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
PCM to calculate true sequential multiport fuel injection
(SFI). Loss of this signal will set a DTC P0341. If the CMP
signal is lost while the engine is running, the fuel injection
system will shift to a calculated sequential fuel injection
based on the last fuel injection pulse, and the engine will
continue to run. The engine can be restarted and will run
in the calculated sequential mode as long as the fault is
present, with a 1-in-6 chance of being correct.
Clear Flood Mode
Clear a flooded engine by pushing the accelerator pedal
down all the way. The PCM then de-energizes the fuel
injectors. The PCM holds the fuel injectors de-energized
as long as the throttle remains above 80% and the engine
speed is below 800 RPM. If the throttle position becomes
less than 80%, the PCM again begins to pulse the
injectors “ON” and “OFF,” allowing fuel into the cylinders.
Deceleration Mode
The PCM reduces the amount of fuel injected when it
detects a decrease in the throttle position and the air flow.
When deceleration is very fast, the PCM may cut off fuel
completely for short periods.
Engine Speed/Vehicle Speed/Fuel Disable
Mode
The PCM monitors engine speed. It turns off the fuel
injectors when the engine speed increase above 6400
RPM. The fuel injectors are turned back on when engine
speed decreases below 6150 RPM.
Fuel Cutoff Mode
No fuel is delivered by the fuel injectors when the ignition
is “OFF.” This prevents engine run-on. In addition, the
PCM suspends fuel delivery if no reference pulses are
detected (engine not running) to prevent engine flooding.
Fuel Injector
The sequential multiport fuel injection (SFI) fuel injector is
a solenoid-operated device controlled by the PCM. The
PCM energizes the solenoid, which opens a valve to allow
fuel delivery.
The fuel is injected under pressure in a conical spray
pattern at the opening of the intake valve. Excess fuel not
used by the injectors passes through the fuel pressure
regulator before being returned to the fuel tank.
A fuel injector which is stuck partly open will cause a loss
of fuel pressure after engine shut down, causing long
crank times.
0003
Fuel Metering System Components
The fuel metering system is made up of the following
parts:
The fuel injectors.
The throttle body.
The fuel rail.
The fuel pressure regulator.
The PCM.
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor.
The camshaft position (CMP) sensor.
The idle air control (IAC) valve.
The fuel pump.
The fuel pump relay.
Basic System Operation
The fuel metering system starts with the fuel in the fuel
tank. An electric fuel pump, located in the fuel tank,
pumps fuel to the fuel rail through an in-line fuel filter. The
pump is designed to provide fuel at a pressure above the
pressure needed by the injectors. A fuel pressure
regulator in the fuel rail keeps fuel available to the fuel
injectors at a constant pressure. A return line delivers
unused fuel back to the fuel tank. Refer to
Section 6C f o r
further information on the fuel tank, line filter, and fuel
pipes.
Fuel Metering System Purpose
The basic function of the air/fuel metering system is to
control the air/fuel delivery to the engine. Fuel is delivered
to the engine by individual fuel injectors mounted in the
intake manifold near each intake valve.
The main control sensor is the heated oxygen sensor
(HO2S) located in the exhaust system. The HO2S tells
the PCM how much oxygen is in the exhaust gas. The
PCM changes the air/fuel ratio to the engine by controlling
the amount of time that fuel injector is “ON.” The best
mixture to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7 parts of air
to 1 part of gasoline by weight, which allows the catalytic
converter to operate most efficiently. Because of the
Page 1460 of 6000

6E–343 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
constant measuring and adjusting of the air/fuel ratio, the
fuel injection system is called a “closed loop” system.
The PCM monitors signals from several sensors in order
to determine the fuel needs of the engine. Fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions called “modes.”
All modes are controlled by the PCM.
Fuel Pressure Regulator
The fuel pressure regulator is a diaphragm-operated
relief valve mounted on the fuel rail with fuel pump
pressure on one side and manifold pressure on the other
side. The fuel pressure regulator maintains the fuel
pressure available to the injector at three times
barometric pressure adjusted for engine load. It may be
serviced separate.
If the pressure is too low, poor performance and a DTC
P0131, DTC P0151,DTC P0171 or DTC P1171 will be the
result. If the pressure is too high, excessive odor and/or a
DTC P0132, DTC P0152,DTC P0172 or DTC P0175 will
be the result. Refer to
Fuel System Diagnosis for
information on diagnosing fuel pressure conditions.
0011
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit
When the key is first turned “ON,” the PCM energizes the
fuel pump relay for two seconds to build up the fuel
pressure quickly. If the engine is not started within two
seconds, the PCM shuts the fuel pump off and waits until
the engine is cranked. When the engine is cranked and
the 58 X crankshaft position signal has been detected by
the PCM, the PCM supplies 12 volts to the fuel pump relay
to energize the electric in-tank fuel pump.
An inoperative fuel pump will cause a “no-start” condition.
A fuel pump which does not provide enough pressure will
result in poor performance.
Fuel Rail
The fuel rail is mounted to the top of the engine and
distributes fuel to the individual injectors. Fuel is
delivered to the fuel inlet tube of the fuel rail by the fuel
lines. The fuel goes through the fuel rail to the fuel
pressure regulator. The fuel pressure regulator maintainsa constant fuel pressure at the injectors. Remaining fuel
is then returned to the fuel tank.
055RW009
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve
The purpose of the idle air control (IAC) valve is to control
engine idle speed, while preventing stalls due to changes
in engine load. The IAC valve, mounted in the throttle
body, controls bypass air around the throttle plate. By
moving the conical valve (pintle) in (to decrease air flow)
or out (to increase air flow), a controlled amount of air can
move around the throttle plate. If the RPM is too low, the
PCM will retract the IAC pintle, resulting in more air
moving past the throttle plate to increase the RPM. If the
RPM is too high, the PCM will extend the IAC pintle,
allowing less air to move past the throttle plate,
decreasing the RPM.
The IAC pintle valve moves in small steps called counts.
During idle, the proper position of the IAC pintle is
calculated by the PCM based on battery voltage, coolant
temperature, engine load, and engine RPM. If the RPM
drops below a specified value, and the throttle plate is
closed, the PCM senses a near-stall condition. The PCM
will then calculate a new IAC pintle valve position to
prevent stalls.
If the IAC valve is disconnected and reconnected with the
engine running, the idle RPM will be wrong. In this case,
the IAC must be reset. The IAC resets when the key is
cycled “ON” then “OFF.” When servicing the IAC, it
should only be disconnected or connected with the
ignition “OFF.”
The position of the IAC pintle valve affects engine start-up
and the idle characteristics of the vehicle. If the IAC pintle
is fully open, too much air will be allowed into the manifold.
This results in high idle speed, along with possible hard
starting and a lean air/fuel ratio. DTC P0507 or DTC
P1509 may set. If the IAC pintle is stuck closed, too little
air will be allowed in the manifold. This results in a low idle
speed, along with possible hard starting and a rich air/fuel
ratio. DTC P0506 or DTC P1508 may set. If the IAC
pintle is stuck part-way open, the idle may be high or low
and will not respond to changes in the engine load.
Page 2134 of 6000
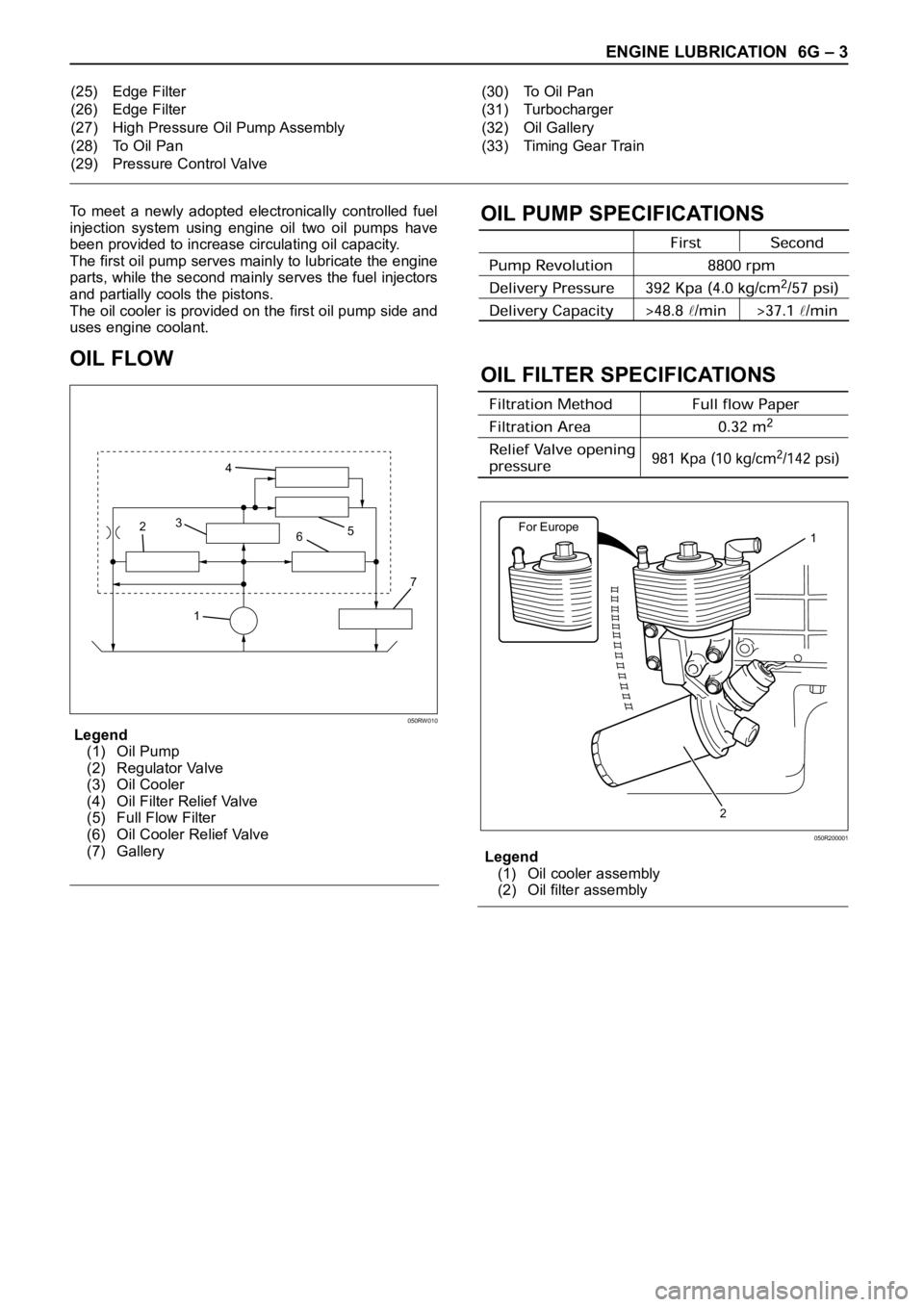
ENGINE LUBRICATION 6G – 3
To meet a newly adopted electronically controlled fuel
injection system using engine oil two oil pumps have
been provided to increase circulating oil capacity.
The first oil pump serves mainly to lubricate the engine
parts, while the second mainly serves the fuel injectors
and partially cools the pistons.
The oil cooler is provided on the first oil pump side and
uses engine coolant.
OIL FLOW
Legend
(1) Oil Pump
(2) Regulator Valve
(3) Oil Cooler
(4) Oil Filter Relief Valve
(5) Full Flow Filter
(6) Oil Cooler Relief Valve
(7) Gallery
OIL PUMP SPECIFICATIONS
OIL FILTER SPECIFICATIONS
Legend
(1) Oil cooler assembly
(2) Oil filter assembly (25) Edge Filter
(26) Edge Filter
(27) High Pressure Oil Pump Assembly
(28) To Oil Pan
(29) Pressure Control Valve(30) To Oil Pan
(31) Turbocharger
(32) Oil Gallery
(33) Timing Gear Train
17 65 4
3
2
050RW010
For Europe1
2
050R200001
Page 4660 of 6000

6E–3 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0351
Ignition 1 Control Circuit 6E–206. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0352
Ignition 2 Control Circuit 6E–209. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0353
Ignition 3 Control Circuit 6E–212. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0354
Ignition 4 Control Circuit 6E–215. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0355
Ignition 5 Control Circuit 6E–218. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0356
Ignition 6 Control Circuit 6E–221. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0402
EGR Pintle Crank Error 6E–224. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0404
EGR Open Stuck 6E–226. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0405
EGR Low Voltage 6E–228. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0406
EGR High Voltage 6E–231. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0502
VSS Circuit Low Input 6E–234. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0562
System Voltage Low 6E–237. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0563
System Voltage High 6E–239. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0601
PCM Memory 6E–240. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1154
HO2S Circuit Transition Time Ratio Bank 2
Sensor 1 6E–241. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1171
Fuel System Lean During Acceleration 6E–245. . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1380
ABS Rough Road ABS System Fault 6E–248. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1404
EGR Closed Stuck 6E–249. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1508
IAC System Low RPM 6E–251. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1509
IAC System High RPM 6E–254. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1618
Serial Peripheral Interface (SPI) PCM
Interprocessor Communication Error 6E–257. . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1625
PCM Unexpected Reset 6E–258. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1640
Driver-1-Input High Voltage 6E–259. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Symptom Diagnosis 6E–262. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Default Matrix Table 6E–288. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor 6E–291. . . . . . . . . .
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 6E–292. . . . . . . . .
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 6E–292.
Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S) 6E–293. . . . . . . . . . .
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor 6E–295. . . . . . .
Knock Sensor (KS) 6E–296. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor 6E–297. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor 6E–297.
Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) 6E–298. . . . . . . . . .
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) 6E–298. . . . . . . . .
EEPROM 6E–300. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Power Steering Pressure (PSP) Switch 6E–300
. . . .
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor 6E–301. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) 6E–302. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Air Cleaner/Air Filter 6E–303. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve 6E–304. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Common Chamber 6E–305. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accelerator Cable Assembly 6E–305. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accelerator Pedal Replacement 6E–308. . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filter Cap 6E–310. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Filter 6E–310. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Gauge Unit 6E–313. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Injectors 6E–314. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pressure Regulator 6E–315. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Metering System 6E–317. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pump Assembly 6E–318. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pump Relay 6E–319. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Rail Assembly 6E–319. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Tank 6E–321. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Throttle Body (TB) 6E–323. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electronic Ignition System 6E–324. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Catalytic Converter 6E–325. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Air Conditioning Relay 6E–325. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EVAP Canister Hoses 6E–326. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EVAP Canister 6E–326. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EVAP Canister Purge Solenoid 6E–327. . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Tank Vent Valve 6E–328. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) Valve 6E–328. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) Valve 6E–329.
Wiring and Connectors 6E–330. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Connectors and Terminals 6E–330. . . . . . . . . . .
Wire Harness Repair: Twisted Shielded
Cable 6E–330. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Twisted Leads 6E–331. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Weather-Pack Connector 6E–332. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Com-Pack III 6E–333. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Metri-Pack 6E–333. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description 6E–335. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (PCM and Sensors) 6E–335. . .
58X Reference PCM Input 6E–335. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A/C Request Signal 6E–335. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 6E–335. . . . . . .
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor and
Signal 6E–335. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Coolant Temperature (ECT) Sensor 6E–335
Electrically Erasable Programmable Read
Only Memory (EEPROM) 6E–336. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Control Heated Oxygen Sensors 6E–336. . . .
Intake Air Temperature (IAT) Sensor 6E–336. . . . .
Page 4661 of 6000

6E–4
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Knock Sensor 6E–337. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR)
Control 6E–337. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Mass Air Flow (MAF) Sensor 6E–337. . . . . . . . . . . .
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor 6E–338
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) 6E–338. . . . . . .
PCM Function 6E–338. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Components 6E–339. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Voltage Description 6E–339. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Input/Outputs 6E–339. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
PCM Service Precautions 6E–339. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Reprogramming The PCM 6E–339. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Throttle Position (TP) Sensor 6E–339. . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission Fluid Temperature (TFT)
Sensor 6E–340. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Transmission Range Switch 6E–340. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Vehicle Speed Sensor (VSS) 6E–340. . . . . . . . . . . .
Use of Circuit Testing Tools 6E–340. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum
Equipment 6E–340. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Electrostatic Discharge Damage 6E–341. . . . . . . . .
Upshift Lamp 6E–341. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (Air Induction) 6E–341. . . . . . . .
Air Induction System 6E–341. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (Fuel Metering) 6E–341. . . . . . .
Acceleration Mode 6E–341. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Accelerator Controls 6E–341. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Battery Voltage Correction Mode 6E–341. . . . . . . .
CMP Signal 6E–341. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Clear Flood Mode 6E–342. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Deceleration Mode 6E–342. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Engine Speed/Vehicle Speed/Fuel
Disable Mode 6E–342. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Cutoff Mode 6E–342. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Injector 6E–342. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Metering System Components 6E–342. . . . . . Fuel Metering System Purpose 6E–342. . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pressure Regulator 6E–343. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Pump Electrical Circuit 6E–343. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Fuel Rail 6E–343. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve 6E–343. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Run Mode 6E–344. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Starting Mode 6E–344. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Throttle Body Unit 6E–344. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (Electronic Ignition
System) 6E–344. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor 6E–344. . . . . . . .
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor 6E–345. . . . . . .
Electronic Ignition 6E–345. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ignition Coils 6E–345. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ignition Control 6E–345. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Ignition Control PCM Output 6E–347. . . . . . . . . . . .
Knock Sensor (KS) PCM Input 6E–347
. . . . . . . . . .
Powertrain Control Module (PCM) 6E–347. . . . . . .
Spark Plug 6E–347. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A/C Clutch Diagnosis 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
A/C Clutch Circuit Operation 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . .
A/C Clutch Circuit Purpose 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . .
A/C Request Signal 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (Exhaust Gas
Recirculation (EGR) System) 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . .
EGR Purpose 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Linear EGR Valve 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Linear EGR Control 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Linear EGR Valve Operation and Results
of Incorrect Operation 6E–349. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
EGR Pintle Position Sensor 6E–350. . . . . . . . . . . . .
General Description (Positive Crankcase
Ventilation (PCV) System) 6E–350. . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Crankcase Ventilation System Purpose 6E–350. . .
Crankcase Ventilation System Operation 6E–350.
Page 4662 of 6000

6E–5 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Specifications
Tightening Specifications
ApplicationNꞏmLb Ft.Lb In.
Camshaft Position Sensor Retaining Screw9—78
Crankshaft Position Sensor Mounting Bolt10—87
EGR Bolt2821—
EGR Nut2821—
Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor207.7—
Fuel Drain Plug2922—
Fuel Pressure Regulator Attaching Screw6.5—60
Fuel Rail Bolts2518—
Fuel Tank Undercover Retaining Bolts3627—
Heated Oxygen Sensor4231—
Lower Intake Manifold to Engine Block Bolts2518—
Lower Intake Manifold to Engine Block Nuts2518—
Spark Plugs1813—
Throttle Body Mounting Bolts2518—
Upper Intake Manifold to Lower Intake Manifold Bolts2518—
VSS Retaining Bolt13—120
Vehicle Type Specifications
ECAUSTRALIA
THAILAND
SOUTH-EA
ST-ASIA
LATIN
AMERICAGULF
CONTRIES
SAUDI
CHINASOU
TH
AFRI
CA
EXPORTSpecifications
UBSUBSUBSUBSUBSUBS
OBD
O2
SENCATEGRMTATMTATMTATMTATMTMTATOBDSEN
SORAEGR
I21
I21
11
11
11
11
1
1
I
Page 4686 of 6000

6E–29 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Engine Component Locator Table
Number
NameLocation
1Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) ValveRear right side of the engine
2Throttle Position (TP) SensorOn the rear of the throttle body
3Intake Air Temperature (IAT) SensorOn the intake air duct near the throttle body
4Check Engine (MIL) LightOn the instrument panel beneath the
tachometer
5Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) ValveOn the left of the cylinder head cover
6Air CleanerLeft front of the engine bay
7Mass Air Flow (MAF) SensorAttached to the air filter box
8Camshaft Position (CMP) SensorOn the rear right side at the left of the cylinder
head cover
9Fuel Pressure RegulatorRear right side of the engine
10Idle Air Control (IAC) ValveOn the left of the throttle body
11Upper Intake ManifoldTop of the engine
12Fuse/Relay BoxAlong the inside of the right fender
13Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorBolted to the top of the upper intake manifold
14Throttle BodyBetween the intake air duct and the upper
intake manifold
15Engine Coolant Temperature SensorOn the coolant crossover pipe at the front of
the engine, near the throttle body
Page 4688 of 6000

6E–31 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Engine Component Locator Table
Number
NameLocation
1Linear Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) ValveRear right side of the engine
2Throttle Position (TP) SensorOn the rear of the throttle body
3Intake Air Temperature (IAT) SensorOn the intake air duct near the throttle body
4Check Engine (MIL) LightOn the instrument panel beneath the
tachometer
5Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) ValveOn the left of the cylinder head cover
6Air CleanerLeft front of the engine bay
7Mass Air Flow (MAF) SensorAttached to the air filter box
8Camshaft Position (CMP) SensorOn the rear right side at the left of the cylinder
head cover
9Fuel Pressure RegulatorRear right side of the engine
10Idle Air Control (IAC) ValveOn the left of the throttle body
11Upper Intake ManifoldTop of the engine
12Fuse/Relay BoxAlong the inside of the right fender
13Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) SensorBolted to the top of the upper intake manifold
14Throttle BodyBetween the intake air duct and the upper
intake manifold
15Engine Coolant Temperature SensorOn the coolant crossover pipe at the front of
the engine, near the throttle body