wiring OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 3478 of 6000
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM9J–41
Installation
1. Install the combination switch assembly with SRS
coil.
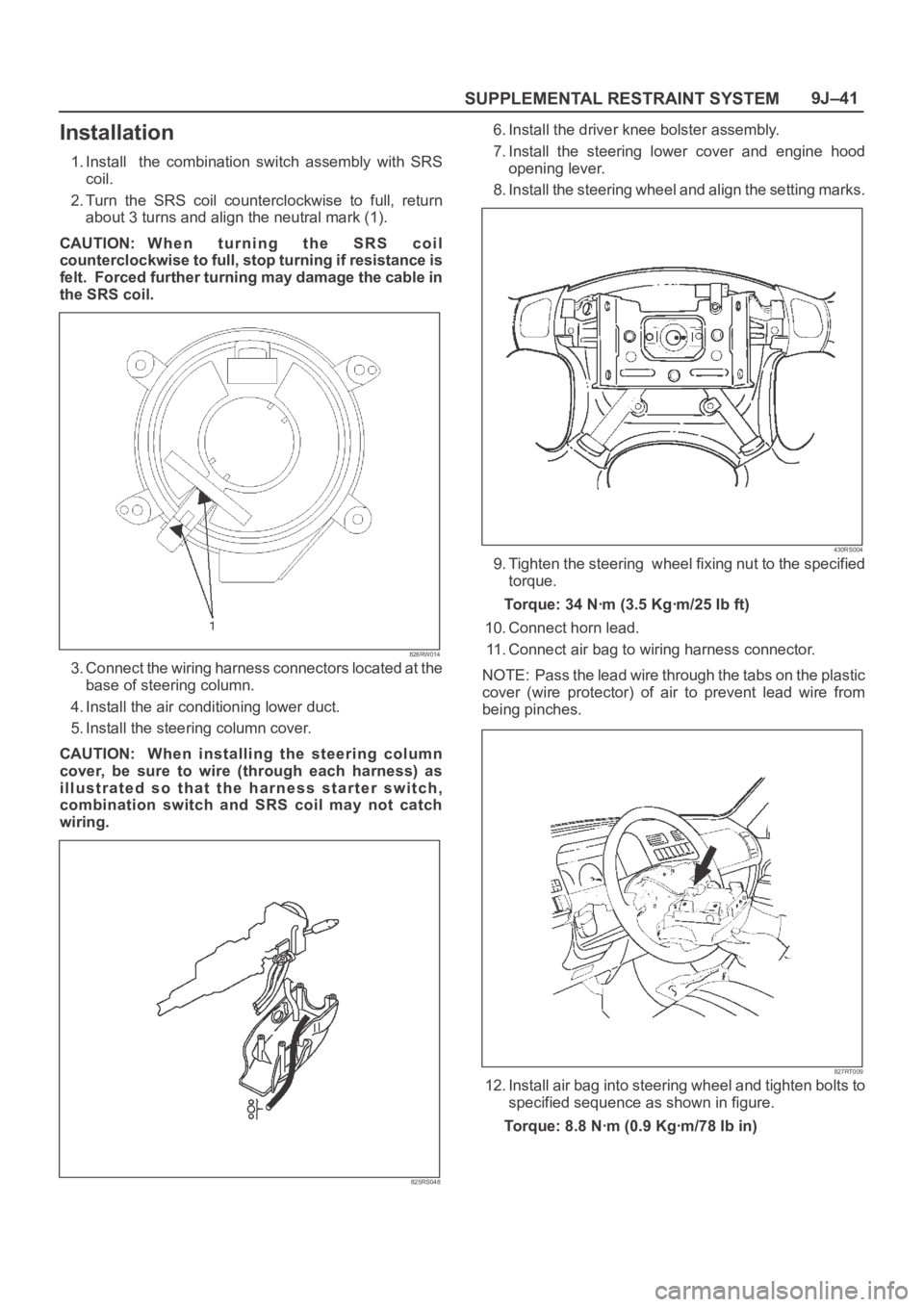
2. Turn the SRS coil counterclockwise to full, return
about 3 turns and align the neutral mark (1).
CAUTION: W h e n t u r n i n g t h e S R S c o i l
counterclockwise to full, stop turning if resistance is
felt. Forced further turning may damage the cable in
the SRS coil.
826RW014
3. Connect the wiring harness connectors located at the
base of steering column.
4. Install the air conditioning lower duct.
5. Install the steering column cover.
CAUTION: When installing the steering column
cover, be sure to wire (through each harness) as
illustrated so that the harness starter switch,
combination switch and SRS coil may not catch
wiring.
825RS048
6. Install the driver knee bolster assembly.
7. Install the steering lower cover and engine hood
opening lever.
8. Install the steering wheel and align the setting marks.
430RS004
9. Tighten the steering wheel fixing nut to the specified
torque.
Torque: 34 Nꞏm (3.5 Kgꞏm/25 Ib ft)
10. Connect horn lead.
11. Connect air bag to wiring harness connector.
NOTE: Pass the lead wire through the tabs on the plastic
cover (wire protector) of air to prevent lead wire from
being pinches.
827RT009
12. Install air bag into steering wheel and tighten bolts to
specified sequence as shown in figure.
Torque: 8.8 Nꞏm (0.9 Kgꞏm/78 Ib in)
Page 3482 of 6000
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM9J–45
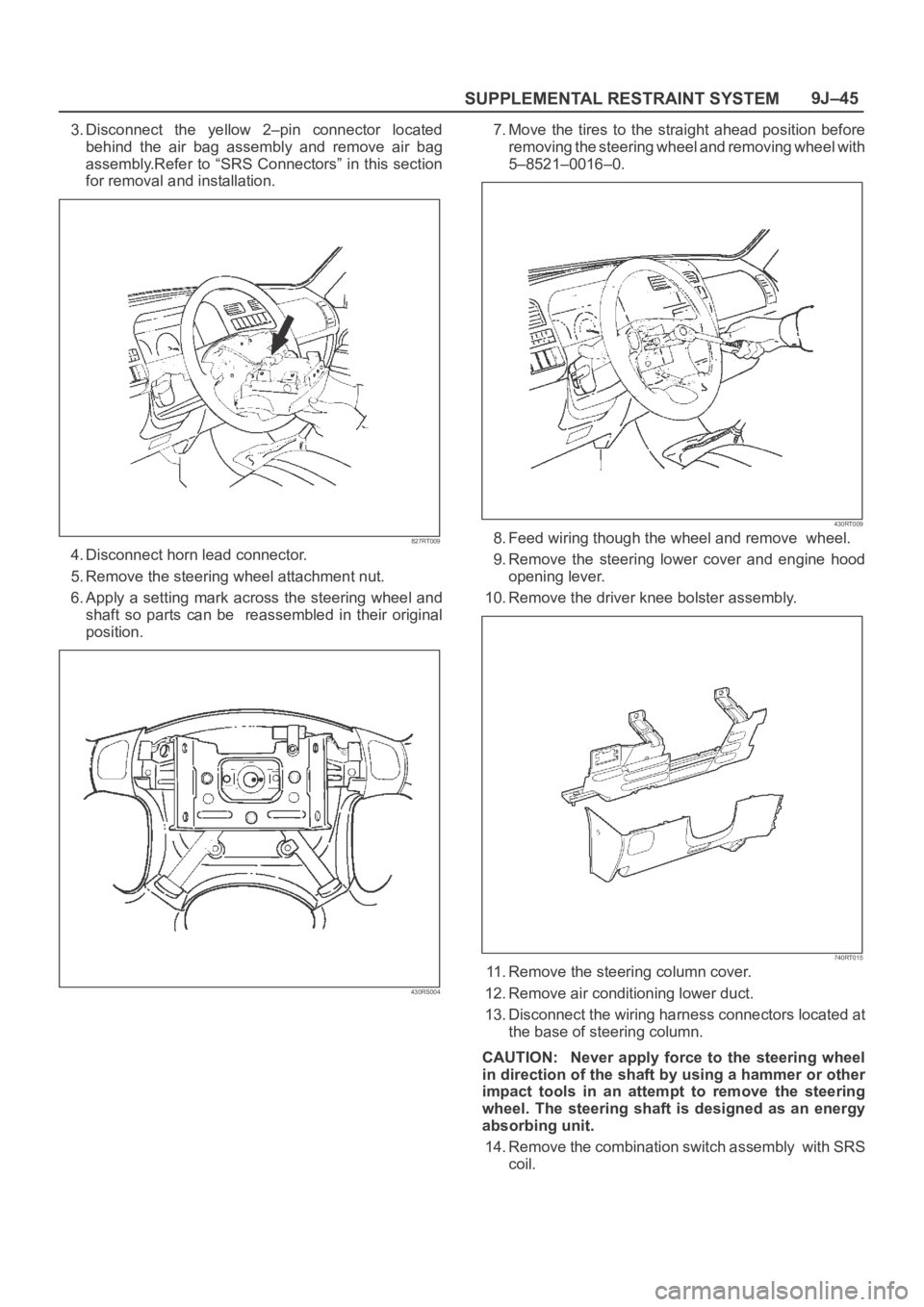
3. Disconnect the yellow 2–pin connector located
behind the air bag assembly and remove air bag
assembly.Refer to “SRS Connectors” in this section
for removal and installation.
827RT009
4. Disconnect horn lead connector.
5. Remove the steering wheel attachment nut.
6. Apply a setting mark across the steering wheel and
shaft so parts can be reassembled in their original
position.
430RS004
7. Move the tires to the straight ahead position before
removing the steering wheel and removing wheel with
5–8521–0016–0.
430RT009
8. Feed wiring though the wheel and remove wheel.
9. Remove the steering lower cover and engine hood
opening lever.
10. Remove the driver knee bolster assembly.
740RT015
11. Remove the steering column cover.
12. Remove air conditioning lower duct.
13. Disconnect the wiring harness connectors located at
the base of steering column.
CAUTION: Never apply force to the steering wheel
in direction of the shaft by using a hammer or other
impact tools in an attempt to remove the steering
wheel. The steering shaft is designed as an energy
absorbing unit.
14. Remove the combination switch assembly with SRS
coil.
Page 3483 of 6000
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM 9J–46
NOTE: SRS coil is a part of combination switch
assembly, which cannot be replaced separately.
Therefore, be sure not to remove the SRS coil from the
combination switch assembly.
15. Remove the snap ring.
16. Remove the cushion rubber.
17. Disconnect shift lock cable (A/T only).
18. Disconnect the starter switch harness connector
located base of steering column.
19. Remove steering lock cylinder assembly.
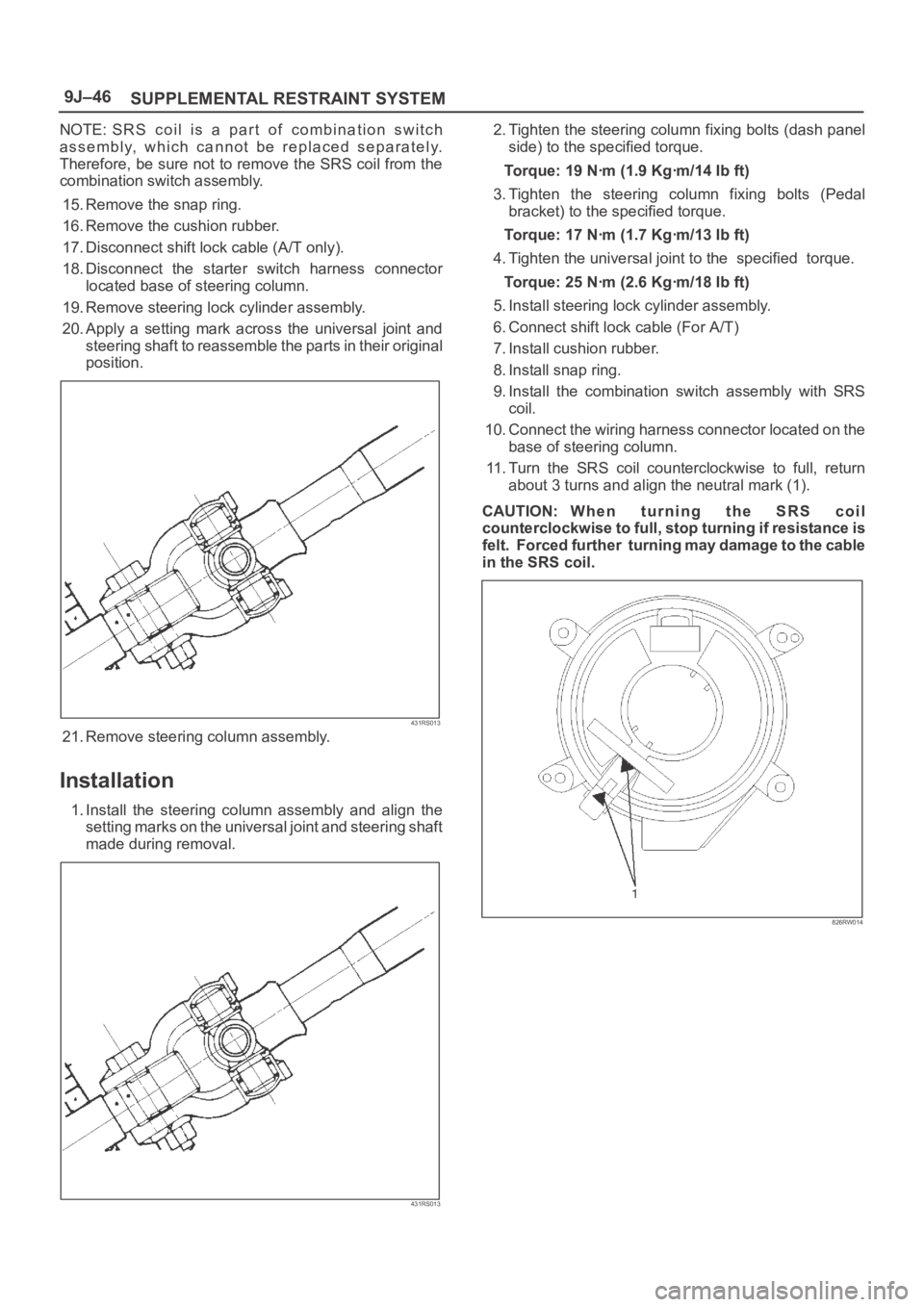
20. Apply a setting mark across the universal joint and
steering shaft to reassemble the parts in their original
position.
431RS013
21. Remove steering column assembly.
Installation
1. Install the steering column assembly and align the
setting marks on the universal joint and steering shaft
made during removal.
431RS013
2. Tighten the steering column fixing bolts (dash panel
side) to the specified torque.
Torque: 19 Nꞏm (1.9 Kgꞏm/14 Ib ft)
3. Tighten the steering column fixing bolts (Pedal
bracket) to the specified torque.
Torque: 17 Nꞏm (1.7 Kgꞏm/13 Ib ft)
4. Tighten the universal joint to the specified torque.
Torque: 25 Nꞏm (2.6 Kgꞏm/18 Ib ft)
5. Install steering lock cylinder assembly.
6. Connect shift lock cable (For A/T)
7. Install cushion rubber.
8. Install snap ring.
9. Install the combination switch assembly with SRS
coil.
10. Connect the wiring harness connector located on the
base of steering column.
11. Turn the SRS coil counterclockwise to full, return
about 3 turns and align the neutral mark (1).
CAUTION: W h e n t u r n i n g t h e S R S c o i l
counterclockwise to full, stop turning if resistance is
felt. Forced further turning may damage to the cable
in the SRS coil.
826RW014
Page 3484 of 6000

SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM9J–47
12. Install steering column cover.
CAUTION: When installing the steering column
cover, be sure to wire (through each harness) as
illustrated so that the harness starter switch,
combination switch and SRS coil may not catch
wiring.
825RS048
13. Install the steering wheel and align the setting marks.
430RS004
14. Tighten the steering wheel fixing nut to the specified
torque.
Torque: 34 Nꞏm (3.5 Kgꞏm/25 Ib ft)15. Connect horn lead.
16. Connect air bag wiring harness connector.
NOTE: Pass the lead wire through the tabs on the plastic
cover (wire protector) of air bag to prevent lead wire from
being pinched.
827RT009
17. Install air bag into steering wheel and tighten bolts to
specified sequence as shown in figure.
Torque: 8 Nꞏm (0.8 Kgꞏm/69 Ib in)
CAUTION: Never use the air bag assembly from
another vehicle. Use only the air bag assembly
proper to the Trooper which is being repaired.
827RT008
18. Enable the SRS (Refer to “Enabling the SRS” in this
section).
Page 3486 of 6000

SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM9J–49
10. Install glove box cover.
11. Install glove box assembly with lid.
12. Install ECM and SDM cover.
13. Install rear console assembly and connect harness
connector.14. Install front console assembly.
15. Install gear control knob.
16. Enable the SRS (Refer to “Enabling the SRS” in this
section).
Pretensioner Seat Belt (If so equipped)
Service Precaution
WARNING: WHEN PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR
AROUND THE PRETENSIONER SEAT BELT OR THE
PRETENSIONER SEAT BELT WIRING, FOLLOW THE
PROCEDURES LISTED BELOW TO TEMPORARILY
DISABLE THE PRETENSIONER SEAT BELT.
FAILURE TO FOLLOW PROCEDURES COULD
RESULT IN POSSIBLE THE PRETENSIONER SEAT
BELT DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY OR
OTHERWISE UNNEEDED THE PRETENSIONER
SEAT BELT REPAIR.
AS A PRECAUTION, WEAR GLOVES AND SAFETY
GLASSES WHEN PERFORMING THE
PRETENSIONER SEAT BELT. WHEN DEPLOY A LIVE
PRETENSIONER SEAT BELT AT OUTSIDE THE
VEHICLE, DEPLOYMENT HARNESS SHALL REMAIN
SHORTED AND NOT BE CONNECTED TO A POWER
SOURCE UNTIL THE PRETENSIONER SEAT BELT IS
TO BE DEPLOYED. THE PRETENSIONER SEAT
BELT WILL IMMEDIATELY DEPLOY WHEN A POWER
SOURCE IS CONNECTED TO IT. CONNECTING THE
DEPLOYMENT HARNESS SHOULED ALWAYS BE
THE FINAL STEP IN THE PRETENSIONER SEAT
BELT DEPLOYMENT PROCEDURE. FAILURE TO
FOLLOW PROCEDURES IN THE ORDER LISTED
COULD RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY.
Parts Location
760RW028
Legend
(1) Seat
(2) Pretensioner Cover
(3) Bolt
(4) Pretensioner Harness
(5) Pretensioner
Removal
1. Turn ignition switch to “LOCK”, remove key.
2. Remove the foot rest located behind the seat.
3. Remove the cover on seat slide.
4. Disconnect the 2-pin connector at the base of the
seat.
5. Remove four fixing bolts the seat slide and remove
seat.
6. Remove the pretensioner seat belt cover.
7. Remove the pretensioner seat belt assembly.
Installation
1. Install the pretensioner seat belt assembly.
2. Install the pretensioner seat belt cover.
3. Install the seat on seat slide and four fixing bolts.
4. Connect the yellow 2-pin connector at the base of the
seat.
5. Install the cover on seat slide.
6. Install the foot rest located behind the seat.
Page 3488 of 6000

9J1–1
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
Service Precaution 9J1–1. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Diagnostic Information 9J1–2. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
System Schematic 9J1–4. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
SRS Diagnostic System Check 9J1–4. . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart A SDM Integrity Check 9J1–6. . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart B “AIR BAG” Warning Lamp
Comes “ON” Steady 9J1–8. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Chart C “AIR BAG” Warning Lamp
Does Not Come “ON” Steady 9J1–10. . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 15 Passenger Deployment Loop
Resistance High 9J1–13. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 16 Passenger Deployment loop
Resistance Low 9J1–15. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 17 Passenger Deployment Loop
Open 9J1–17. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 18 Passenger Deployment Loop
Short To Ground 9J1–19. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 19 Passenger Deployment Loop
Short To B+ 9J1–21. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 21 Driver Deployment Loop
Resistance High 9J1–23. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 22 Driver Deployment Loop
Resistance Low 9J1–26. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 24 Driver Deployment Loop
Short To Ground 9J1–29. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 25 Driver Deployment Loop
Short To B+ 9J1–31. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 26 Driver Deployment Loop Open 9J1–33. . . . DTC 51 Air Bag Deployment Event
Commanded 9J1–35. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 53 Deployment Commanded With
Deployment Loop Fault Or Energy
Reserves Out Of Range 9J1–37. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 61 Warning Lamp Circuit Failure 9J1–39. . . . .
DTC 71 Internal SDM Fault 9J1–41. . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 29 Passenger Pretensioner Loop
Short To Ground 9J1–43. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 31 Passenger Pretensioner Loop
Resistance High 9J1–45. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 32 Passenger Pretensioner loop
Resistance Low 9J1–47. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 33 Passenger Pretensioner Loop
Short To Voltage 9J1–49. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 34 Passenger Pretensioner Loop
Open 9J1–51. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 41 Driver Pretensioner Loop
Resistance High 9J1–53. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 42 Driver Pretensioner Loop
Resistance Low 9J1–55. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 44 Driver Pretensioner Loop
Open 9J1–57. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 45 Driver Pretensioner Loop
Short To Ground 9J1–59. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 46 Driver Pretensioner Loop
Short To Voltage 9J1–61. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
DTC 52 Pretensioner Deployment
Event Commanded 9J1–63. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Service Precaution
WARNING: IF SO EQUIPPED WITH A
SUPPLEMENTAL RESTRAINT SYSTEM (SRS),
REFER TO THE SRS COMPONENT AND WIRING
LOCATION VIEW IN ORDER TO DETERMINE
WHETHER YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE ON OR
NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS
WIRING. WHEN YOU ARE PERFORMING SERVICE
ON OR NEAR THE SRS COMPONENTS OR THE SRS
WIRING, REFER TO THE SRS SERVICE
INFORMATION. FAILURE TO FOLLOW WARNINGS
COULD RESULT IN POSSIBLE AIR BAG
DEPLOYMENT, PERSONAL INJURY, OR
OTHERWISE UNNEEDED SRS SYSTEM REPAIRS.CAUTION: Always use the correct fastener in the
proper location. When you replace a fastener, use
ONLY the exact part number for that application.
ISUZU will call out those fasteners that require a
replacement after removal. ISUZU will also call out
the fasteners that require thread lockers or thread
sealant. UNLESS OTHERWISE SPECIFIED, do not
use supplemental coatings (Paints, greases, or other
corrosion inhibitors) on threaded fasteners or
fastener joint interfaces. Generally, such coatings
adversely affect the fastener torque and the joint
clamping force, and may damage the fastener. When
you install fasteners, use the correct tightening
sequence and specifications. Following these
instructions can help you avoid damage to parts and
systems.
Page 3489 of 6000

RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM 9J1–2
Diagnostic Information
CAUTION: When fasteners are removed, always
reinstall them at the same location from which they
were removed. if a fastener needs to be replaced, use
the correct part number fastener for that application.
if the correct part number fastener is not available, a
fastener of equal size and strength (or stronger) may
be used. fasteners that are not reused, and those
requiring thread locking compound will be called
out. the correct torque value must be used when
installing fasteners that require it. if the above
conditions are not followed, parts or system damage
could result.
Diagnostic Procedures
WARNING: TO AVOID DEPLOYMENT WHEN
TROUBLESHOOTING THE SRS, DO NOT USE
ELECTRICAL TEST EQUIPMENT SUCH AS A
BATTERY–POWERED OR AC–POWERED
VOLTMETER, OHMMETER, ETC., OR ANY TYPE OF
ELECTRICAL EQUIPMENT OTHER THAN THAT
SPECIFIED IN THIS MANUAL. DO NOT USE A NON
POWERED, PROBE–TYPE TESTER.
INSTRUCTIONS IN THIS MANUAL MUST BE
FOLLOWED CAREFULLY, OTHERWISE PERSONAL
INJURY MAY RESULT.
The diagnostic procedures used in this section are
designed to aid in finding and repairing SRS problems.
Outlined below are the steps to find and repair SRS
problems quickly and effectively. Failure to carefully
follow these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis and incorrect parts
replacement.
1.Perform The “SRS Diagnostic System Check”.
The “SRS Diagnostic System Check” should always
be the starting point of any SRS diagnostics. The
“SRS Diagnostic System Check” checks for proper
“AIR BAG” warning lamp operation and checks for
SRS trouble codes using both “Flash Code” and
“Scan Tool” Methods.
2.Refer To The Proper Diagnostic Chart As Directed
By The “SRS Diagnostic System Check”.
The “SRS Diagnostic System Check” will lead you to
the correct chart to diagnose any SRS problems.
Bypassing these procedures may result in extended
diagnostic time, incorrect diagnosis and incorrect
parts replacement.
3.Repeat The “SRS Diagnostic System Check”
After Any Repair Or Diagnostic Procedures Have
Been Performed.
Preforming the “SRS Diagnostic System Check” after
all repair or diagnostic procedures will assure that the
repair has been made correctly and that no other
conditions exist.
Diagnostic Codes
The Sensing and Diagnostic Module (SDM) maintains a
history record of all diagnostic codes that have beendetected since the SRS codes were last cleared during
service.
1. Active Codes — Faults that are presently detected
this ignition cycle. Active codes are stored in RAM
(Random Access Memory).
2. History Codes — All faults detected since the last
time the history fault memory was cleared. History
codes are stored in EEPROM. (Electronically
Erasable Programmable Read only Memory)
How To Read Trouble Codes
All codes (Active and history) can be read (or cleared) by
using a scan tool or equivalent.
If a PDT is not available, have the vehicle serviced by
ISUZU dealer.
How To Clear Trouble Codes
Trouble codes can only be cleared by using a Scan Tool.
If a “scan tool” is not available then inform the owner of the
stored codes and suggest that the codes are cleared
upon the next visit to an Isuzu dealership.
Scan Tool Diagnostics
A scan tool can be used to read current and history codes
and to clear all history codes after a repair is complete.
The scan tool must be updated to communicate with the
SRS through a memory card or a manufacturer’s update
before it can be used for SRS diagnostics. To use the
scan tool, connect it to the DLC connector and turn the
ignition switch “ON”. Then follow the manufacturer’s
directions for communication with the SRS. The scan tool
reads serial data from the SDM “Serial Data” output
(terminal 24) to the DLC connector (terminal 9).
Basic Knowledge Required
Before using this section of the Service Manual, there is
some basic knowledge which will be required. Without
this knowledge, you will have trouble using the diagnostic
procedures in this section. Use care to prevent harm or
unwanted deployment. Read all cautions in the service
manual and on warning labels attached to SRS
components.
Basic Electrical Circuits
You should understand the basic theory of electricity
including series and parallel circuits, and understand the
voltage drops across series resistors. You should know
the meaning of voltage (volts), current (amps), and
resistance (ohms). You should understand what happens
in a circuit with an open or a shorted wire. You should be
able to read and understand a wiring diagram.
“Flash Code” Diagnostics
Flash code diagnostics can be used to read active codes
and to determine if history codes are present but cannot
be used to clear codes or read history codes. Flash code
diagnostics is enabled by grounding by terminal 4
shorting to terminal 13 of the DLC connector with the
ignition switch “ON”. Grounding terminal 4 of the DLC
connector pulls the “Diagnostics Request” input (Terminal
1) of the SDM low and signals the SDM to enter the flash
code diagnostic display mode.
Page 3497 of 6000
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM 9J1–10
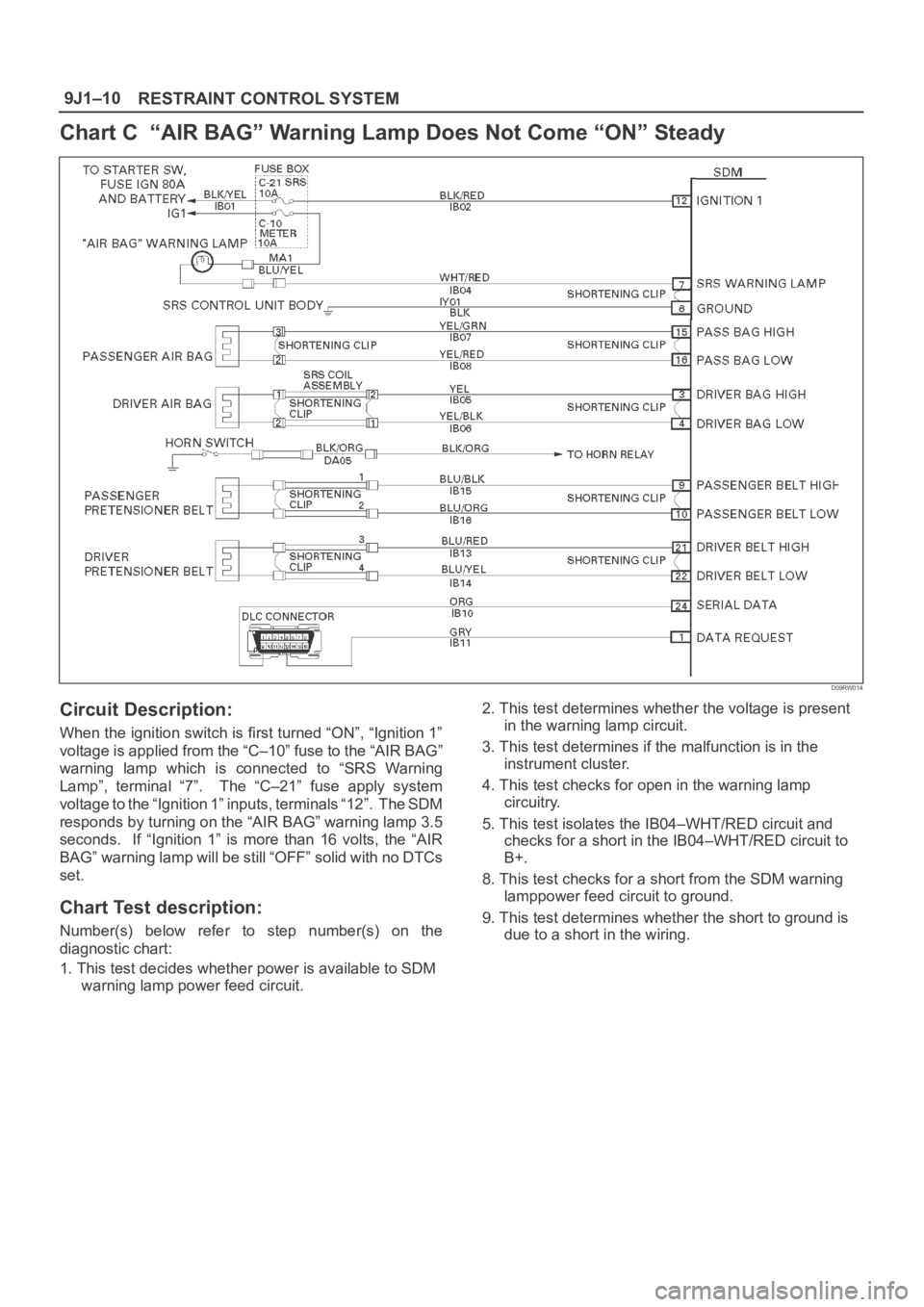
Chart C “AIR BAG” Warning Lamp Does Not Come “ON” Steady
D09RW014
Circuit Description:
When the ignition switch is first turned “ON”, “Ignition 1”
voltage is applied from the “C–10” fuse to the “AIR BAG”
warning lamp which is connected to “SRS Warning
Lamp”, terminal “7”. The “C–21” fuse apply system
voltage to the “Ignition 1” inputs, terminals “12”. The SDM
responds by turning on the “AIR BAG” warning lamp 3.5
seconds. If “Ignition 1” is more than 16 volts, the “AIR
BAG” warning lamp will be still “OFF” solid with no DTCs
set.
Chart Test description:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the
diagnostic chart:
1. This test decides whether power is available to SDM
warning lamp power feed circuit.2. This test determines whether the voltage is present
in the warning lamp circuit.
3. This test determines if the malfunction is in the
instrument cluster.
4. This test checks for open in the warning lamp
circuitry.
5. This test isolates the IB04–WHT/RED circuit and
checks for a short in the IB04–WHT/RED circuit to
B+.
8. This test checks for a short from the SDM warning
lamppower feed circuit to ground.
9. This test determines whether the short to ground is
due to a short in the wiring.
Page 3500 of 6000

9J1–13
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
DTC 15 Passenger Deployment Loop Resistance High
D09RW014
Circuit Description:
When the ignition switch is turned “ON”, the SDM will
perform tests to diagnose critical malfunctions within
itself. Upon passing these tests “Ignition 1”, and
deployment loop voltages are measured to ensure they
are within their respective normal voltage ranges. The
SDM then proceeds with the “Resistance Measurement
Test”. “Passenger Bag Low” terminal “16” is grounded
through a resister and the passenger current source
connected to “Passenger Bag High” terminal “15” allows a
known amount of current to flow. By monitoring the
voltage difference between “Passenger Bag High” and
“Passenger Bag Low” the SDM calculates the combined
resistance of the passenger air bag assembly, harness
wiring IB07–YEL/GRN and IB08–YEL/RED connector
terminal contact.
DTC Will Set When:
The combined resistance of the passenger air bag
assembly, harness wiring IB07–YEL/GRN and
IB08–YEL/RED, and connector terminal contact is above
a specified value. This test is run once each ignition cycle
during the “Resistance Measurement Test” when:
1. No “higher priority faults” are detected during
“Turn–ON”,
2. “Ignition 1” voltage is in the specified value.
Action Taken:
SDM turns “ON” the “AIR BAG” warning lamp and sets a
diagnostic trouble code.
DTC Will Clear When:
The ignition switch is turned “OFF.”
DTC Chart Test Description:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This test determines whether the malfunction is in
the SDM.
3. This test verifies proper connection of the yellow
2–pin connector.
4. This test checks for proper contact and/or corrosion
of the yellow 2–pin connector terminals.
5. The test checks for a malfunctioning passenger air
bag assembly.
6. This test determines whether the malfunction is due
to high resistance in the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids:
An intermittent condition is likely to be caused by a poor
connection at the passenger air bag assembly harness
connector terminals “1” and “2”, SDM terminal “15” and
“16”, or a poor wire to terminal connection in
IB07–YEL/GRN and IB08–YEL/RED. This test for this
diagnostic trouble code is only run while the “AIR BAG”
Page 3502 of 6000

9J1–15
RESTRAINT CONTROL SYSTEM
DTC 16 Passenger Deployment loop Resistance Low
D09RW014
Circuit Description:
When the ignition switch is turned “ON”, the SDM will
perform tests to diagnose critical malfunctions within
itself. Upon passing these tests “Ignition 1”, and
deployment loop voltages are measured to ensure they
are within their respective normal voltage ranges. The
SDM then proceeds with the “Resistance Measurement
Test”. “Passenger Bag Low” terminal “16” is grounded
through a resistor and the passenger current source
connected to “Passenger Bag High” terminal “15” allows a
known amount of current to flow. By monitoring the
voltage difference between “Passenger Bag High” and
“Passenger Bag Low”, the SDM calculates the combined
resistance of the passenger air bag assembly, harness
wiring IB07–YEL/GRN and IB08–YEL/RED connector
terminal contact.
DTC Will Set When:
The combined resistance of the passenger air bag
assembly, harness wiring IB07–YEL/GRN and
IB08–YEL/RED, and connector terminal contact is above
a specified value. This test is run once each ignition cycle
during the “Resistance Measurement Test” when:
1. No “higher priority faults” are detected during
“Turn–ON”,
2. “Ignition 1” voltage is in the specified value.
Action Taken:
SDM turns “ON” the “AIR BAG” warning lamp and sets a
diagnostic trouble code.
DTC Will Clear When:
The ignition switch is turned “OFF.”
DTC Chart Test Description:
Number(s) below refer to step number(s) on the
diagnostic chart:
2. This test determines whether the malfunction is in
the SDM.
3. This test verifies connection of the yellow 2–pin
connector.
4. This test cheeks for proper operation of the shorting
clip in the yellow 2–pin connector.
5. The test checks for a malfunction passenger air bag
assembly.
6. This test determines whether the malfunctioning is
due to shortening in the wiring.
Diagnostic Aids:
An intermittent condition is likely to be caused by a short
between IB07–YEL/GRN and IB08–YEL/RED, or a
malfunctioning shorting clip on the passenger air bag
assembly which would require replacement of the air bag
assembly. The test for this diagnostic trouble code is only
run while “AIR BAG” warning lamp is performing the bulb