battery location OPEL FRONTERA 1998 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1998, Model line: FRONTERA, Model: OPEL FRONTERA 1998Pages: 6000, PDF Size: 97 MB
Page 1981 of 6000

6E–88
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1194 (Flash DTC 61)
Rail Pressure System Low Voltage
060RW134
Circuit Description
The rail pressure (RP) sensor responds to changes in oil
rail pressure.
The ECM monitors the RP signals for voltages outside the
normal range of the RP sensor. If the ECM detects a RP
signal voltage that is excessively low, DTC P1194 will be
set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P1194 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Check for intermittent codes.
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change
in the display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P1194 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently,
performing the DTC P1194 Diagnostic Chart may isolate
the cause of the fault.
Page 1983 of 6000
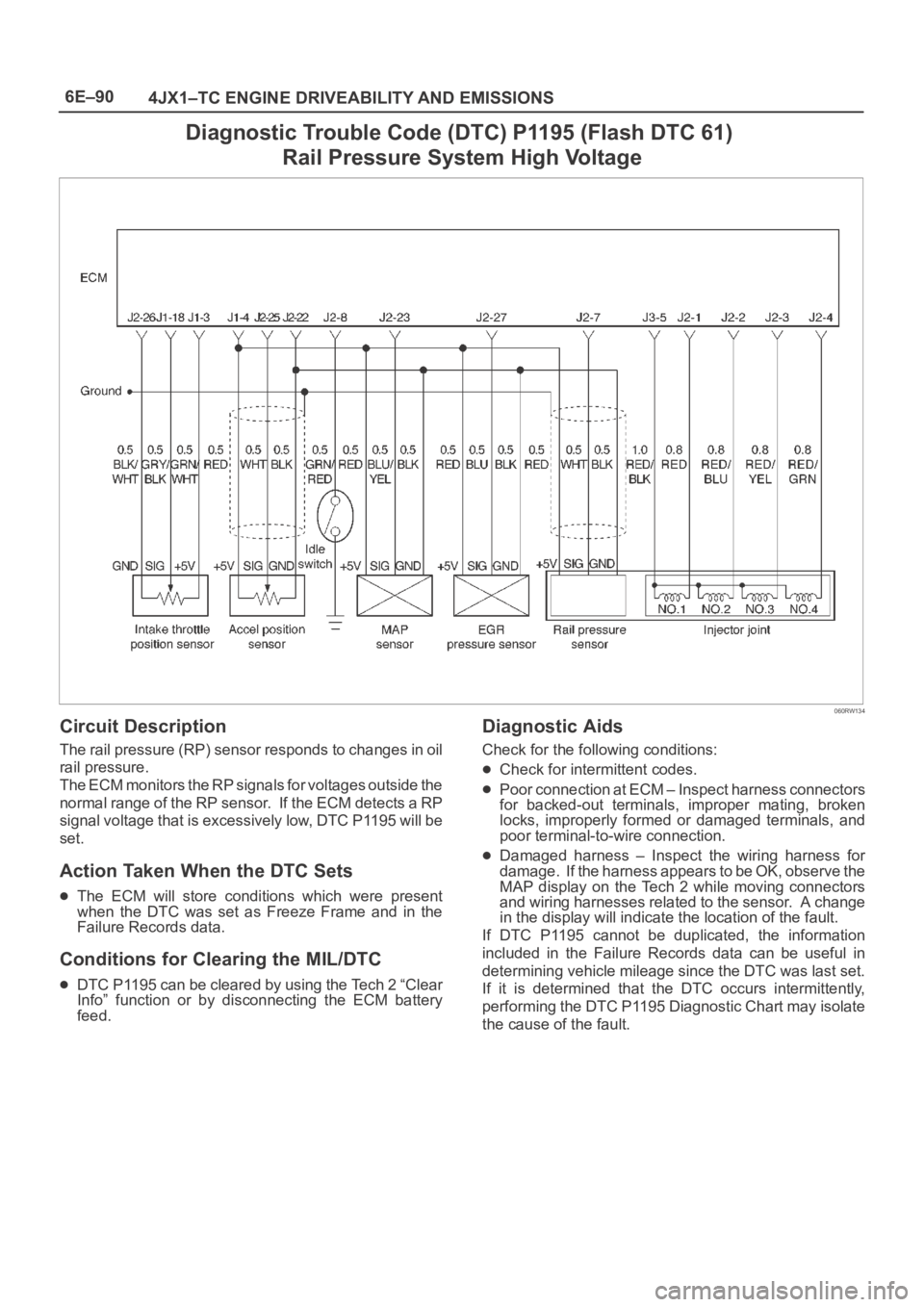
6E–90
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P1195 (Flash DTC 61)
Rail Pressure System High Voltage
060RW134
Circuit Description
The rail pressure (RP) sensor responds to changes in oil
rail pressure.
The ECM monitors the RP signals for voltages outside the
normal range of the RP sensor. If the ECM detects a RP
signal voltage that is excessively low, DTC P1195 will be
set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P1195 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Check for intermittent codes.
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
MAP display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the sensor. A change
in the display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P1195 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently,
performing the DTC P1195 Diagnostic Chart may isolate
the cause of the fault.
Page 1986 of 6000

6E–93 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Circuit Description
The rail pressure control valve (RPCV) is built in the high
pressure oil circuit.
RPCV is an important device which is used to control oil
pressure in the HEUI system.
The circuit receives current through Engine 15A fuse from
the battery, current flowing in the order of RPCV.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P1196 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
Rail Pressure Control display on the Tech 2 while
moving connectors and wiring harnesses related to the
Rail Pressure Control. A change in the Rail Pressure
Control display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P1196 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. Verifies that the fault is present.
DTC P1196 – RP System High Warning
StepActionVa l u e ( s )Ye sNo
1Was the “On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check”
performed?
—Go to Step 2
Go to OBD
System
Check
21. Engine is running.
2. Observe the “Rail Pressure Control” display on the
Te c h 2 .
Is the action correct?
—Go to Step 4Go to Step 3
3Replace the RPCV.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repairGo to Step 4
41. Engine is running.
2. Review and record Tech 2 Failure Records data.
3. Operate the vehicle within Failure Records
conditions as noted.
4. Using a Tech 2, monitor “ DTC” info for DTC P1196.
Does the Tech 2 indicate DTC P1196 failed this
ignition?
—Go to Step 5—
51. Check the 2 way valve.
2. Observe the “RP Control” display on the Tech 2.
Is the action correct?
—Go to Step 4Go to Step 6
6Replace the 2 way valve.
Is the action complete?
—Verify repair—
Page 1987 of 6000

6E–94
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0197 (Flash DTC 16)
Oil Temp Sensor Low Voltage
060RW129
Circuit Description
The engine oil temperature (OT) sensor is a thermistor
mounted in the oil rail. The Engine Control Module ECM
applies a voltage (about 5 volts) through a pull-up resistor
to the ECT signal circuit. When the engine oil is cold, the
sensor (thermistor) resistance is high, therefore the ECM
will measure a high signal voltage. As the engine oil
warms, the sensor resistance becomes lower, and the OT
signal voltage measured at the ECM drops.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0197 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
OT display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the OT sensor. A change
in the OT display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0197 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently.
Page 1989 of 6000

6E–96
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0198 (Flash DTC 16)
Oil Temp Sensor High Voltage
060RW129
Circuit Description
The engine oil temperature (OT) sensor is a thermistor
mounted in the oil rail. The Engine Control Module ECM
applies a voltage (about 5 volts) through a pull-up resistor
to the ECT signal circuit. When the engine oil is cold, the
sensor (thermistor) resistance is high, therefore the ECM
will measure a high signal voltage. As the engine oil
warms, the sensor resistance becomes lower, and the OT
signal voltage measured at the ECM drops.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0198 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, broken
locks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
OT display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the OT sensor. A change
in the OT display will indicate the location of the fault.
If DTC P0198 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently.
Page 2000 of 6000

6E–107 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0217 (Flash DTC 22)
High Coolant Temp Waring
060RW129
Circuit Description
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor mounted on a coolant crossover pipe at the
rear of the engine. The Engine Control Module ECM
applies a voltage (about 5 volts) through a pull-up resistor
to the ECT signal circuit. When the engine coolant is cold,
the sensor (thermistor) resistance is high, therefore the
ECM will measure a high signal voltage. As the engine
coolant warms, the sensor resistance becomes lower,
and the ECT signal voltage measured at the ECM drops.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0217 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
Check for the following conditions:
Poor connection at ECM – Inspect harness connectors
for backed-out terminals, improper mating, brokenlocks, improperly formed or damaged terminals, and
poor terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, observe the
ECT display on the Tech 2 while moving connectors
and wiring harnesses related to the ECT sensor. A
change in the ECT display will indicate the location of
the fault.
If DTC P0217 cannot be duplicated, the information
included in the Failure Records data can be useful in
determining vehicle mileage since the DTC was last set.
If it is determined that the DTC occurs intermittently.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. Verifies that the fault is present.
3. If DTC P0117 can be repeated only by duplicating
the Failure Records conditions, refer to the
“Temperature vs. Resistance Values” table. The
table may be used to test the ECT sensor at various
temperatures to evaluate the possibility of a
“shifted” sensor that may be shorted above or below
a certain temperature. If this is the case, replace
the ECT sensor. If the ECT sensor appears to be
OK, the fault is intermittent; refer to
Diagnostic Aids.
Page 2007 of 6000

6E–114
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0336 (Flash DTC 43)
CKP (Crank Position) Sensor Out of Synchro
060RW133
Circuit Description
The CKP reference signal is produced by the crankshaft
position (CKP) sensor. During one crankshaft revolution,
crankshaft pulses will be produced. The Engine Control
Module ECM uses the CKP reference signal to calculate
engine RPM and crankshaft position. If the ECM receives
an incorrect number of pulses on the CKP reference
circuit, DTC P0336 will set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0336 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
Poor connection – Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect
the ECM, turn the ignition on and observe a voltmeter
connected to the CKP reference circuit at the ECM
harness connector while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the ECM. A change in
voltage will indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Page 2009 of 6000

6E–116
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0337 (Flash DTC 43)
CKP (Crank Position) Sensor No Signal
060RW133
Circuit Description
The CKP reference signal is produced by the crankshaft
position (CKP) sensor. During one crankshaft revolution,
CKP crankshaft reference pulses will be produced. The
Engine Control Module ECM uses the CKP reference
signal to calculate engine RPM and crankshaft position. If
the ECM does not receive pulses on the CKP reference
circuit, DTC P0337 will set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0337 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
Poor connection – Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect
the ECM, turn the ignition on and observe a voltmeter
connected to the CKP reference circuit at the ECM
harness connector while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the ICM. A change in
voltage will indicate the location of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Page 2012 of 6000

6E–119 4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0341 (Flash DTC 41)
CMP (Cam Position) Sensor Out of Synchro
060RW133
Circuit Description
The CMP signal is produced by the camshaft position
(CMP) sensor pulses when the engine is running and
crankshaft position (CKP) sync pulses are also being
received. The Engine Control Module ECM uses the
CMP signal pulses to initiate sequential fuel injection. If
the ECM receives an incorrect number of pulses on the
CMP reference circuit, DTC P0341 will set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0341 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed–through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
Poor connection — Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks,improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal-to-wire connection.
Damaged harness — Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect
the ECM, turn the ignition on and observe a voltmeter
connected to the CMP signal circuit at the ECM
harness connector while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the ICM and the CMP
sensor. A change in voltage will indicate the location
of the fault.
Reviewing the Failure Records vehicle mileage since the
diagnostic test last failed may help determine how often
the condition that caused the DTC to be set occurs. This
may assist in diagnosing the condition.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. Ensures that the fault is present.
12.Determines whether the fault is being caused by a
missing camshaft magnet or a faulty sensor. The
voltage measured in this step should read around 4
volts, toggling to near 0 volts when the CMP sensor
interfaces with the camshaft magnet.
Page 2015 of 6000

6E–122
4JX1–TC ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) P0342 (Flash DTC 41)
CMP (Cam Position) Sensor No Signal
060RW133
Circuit Description
The CMP signal produced by the camshaft position
(CMP) sensor pulses when the engine is running and
crankshaft position (CKP) synchro pulses are also being
received. The hall type CMP sensor and the CKP sensor
share 5 V and ground connections at the Engine Control
Module ECM. The third wire at the sensor is a signal
c i r c u i t t o t h e E C M . T h e E C M u s e s t h e C M P s i g n a l p u l s e s
to initiate sequential fuel injection. If the ECM does not
receive pulses on the CMP reference circuit, DTC P0342
will set.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
The ECM will store conditions which were present
when the DTC was set as Freeze Frame and in the
Failure Records data.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
DTC P0342 can be cleared by using the Tech 2 “Clear
Info” function or by disconnecting the ECM battery
feed.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent may be caused by a poor connection,
rubbed-through wire insulation or a wire broken inside the
insulation. Check for:
Poor connection – Inspect the ECM harness and
connectors for improper mating, broken locks,
improperly formed or damaged terminals, and poor
terminal to wire connection.
Damaged harness – Inspect the wiring harness for
damage. If the harness appears to be OK, disconnect
the ECM, turn the ignition on and observe a voltmeter
connected to the CMP signal circuit at the ECM
harness connector while moving connectors and
wiring harnesses related to the ICM and the CMP
sensor. A change in voltage will indicate the location
of the fault.
Test Description
Number(s) below refer to the step number(s) on the
Diagnostic Chart.
2. Ensures that the fault is present.
14.Determines whether the fault is being caused by a
missing camshaft magnet or a faulty ECM. The
voltage measured in this step should read around 4
volts, toggling to near 0 volts when the CMP sensor
interfaces with the camshaft magnet.