air conditioning OPEL GT-R 1973 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: OPEL, Model Year: 1973, Model line: GT-R, Model: OPEL GT-R 1973Pages: 625, PDF Size: 17.22 MB
Page 542 of 625

REFRIGERANT COMPONENTS ALL MODELS99- 33
That the attraction of the drying material for mois-
ture is so powerful that if the receiver is left open,
moisture will be drawn in from the outside air.
That just one drop of water added to the refrigerantwill start chemical changes that can result in corro-
sion and eventual breakdown of the chemicals in the
system. Hydrochloric acid is the result of an R-12
mixture with water.
That the smallest amount of air in the refrigeration
system may start reactions that can cause malfunc-
tions.
That the drying agent in the receiver-dehydrator is
Activated Silica Alumina (silica-gel).
That
the inert gas in the expansion valve capillary
line is carbon dioxide.
DESCRIPTION OF AIR CONDITIONING
COMPONENTS
Compressor
The compressor is located in the engine compart-
ment. The purpose of the unit is to draw the low
pressure,gas from the evaporator and compress this
gas into a high temperature, high pressure gas. This
action will result in the refrigerant having a higher
temperature than the surrounding air.
The
cortipressor is of basic double action piston de-
sign. Three horizontal double acting pistons make up
a six cylinder compressor (See Figure
9B-162). The
pistons operate in
l-1/2 inch bore and have a l-1/8
inch stroke. A
wash plate keyed to the shaft drives
the pistons. The shaft is belt driven through a mag-
netic clutch and pulley arrangement. An oil pump
mounted at the rear of the compressor picks up oil
from the
botto’m of the compressor and lubricates the
bearings’and other internal parts of the compressor.
Reed type valves at each end of the compressor open
or close to control the flow of incoming and outgoing refrigerant. Two gas tight passages interconnect
chambers of the front and rear heads so that there is
one common suction port, and one common dis-
charge port. The internal parts of the compressor
function, as follows:
1. Suction Valve Reed Discs and Discharge Valve
Plates
_ The two suction valve reed discs and two
discharge valve plates (see Figure
9B-25) operate in
a similar but opposite manner. The discs are com-
posed of three reeds and function to open when the
pistons are on the intake portion of their stroke
(downstroke), and close on the compression stroke.
The reeds allow low pressure gas to enter the cylin- ders. The discharge valve plates also have three
reeds, however, they function to open when the pis- tons are on the compression portion of their stroke
(upstroke), and close on the intake stroke. High pres-
sure gas exits from discharge ports in the discharge
valve plate. Three retainers riveted directly above the
reeds on the valve plate serve to limit the opening of
the reeds on the compression stroke.
SUCTION VALVE
DISCHARGE-VALVE PLATES
Figure
98-25 - Compressor Suction Valve Reed Discs
and Discharge Valve Plates
2. Front and Rear Heads - The front and rear heads
(Figure
9B-26) serve to channel the refrigerant into
and out of the cylinders. The front head is divided
into two separate passages and the rear head is di-
vided into three separate passages. The outer passage
on both the front and rear heads channels high pres-
sure gas from the discharge valve reeds. The middle
passage of the rear head also contains the port open-
ing to the superheat switch cavity. This opening in
the rear head permits the superheat switch to be
affected by suction gas pressure and suction gas tem-
perature for the operating protection of the compres-
sor. The inner passage on the rear head houses the
oil pump inner and outer rotors. A Teflon sealing
material is bonded to the sealing surfaces separating
the passages in the rear head.
“0” rings are used to
affect a seal between the mating surfaces of the heads
and the shell. The front head suction and discharge
passages are connected to the suction and discharge
passages of the rear head by a discharge tube and
suction passage in the
body of the cylinder assembly.
A screen located in the suction port of the rear head
prevents foreign material from entering the circuit.
3. Oil Pump
- An internal tooth outer rotor and
external tooth inner rotor comprise the oil pump.
The pump works on the principle of a rotary type pump. Oil is drawn up from oil reservoir in underside
of shell through the oil inlet tube (see Figure
9B-27)
Page 545 of 625
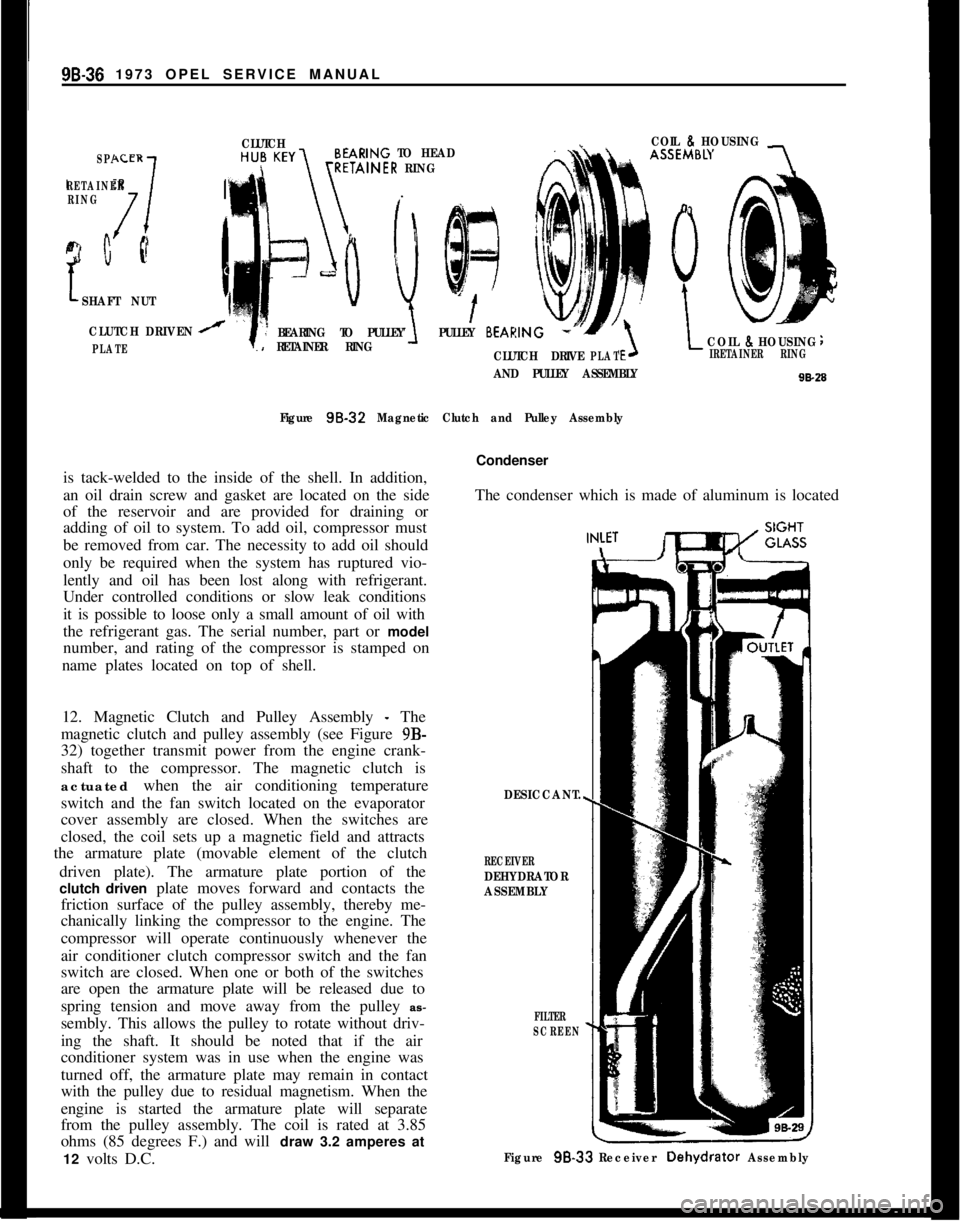
98-36 1973 OPEL SERVICE MANUALSPACER
17
RETAINER
RING
c Q
CLUTCHCOIL 8HOUSINGARING TO HEADTAINER RING
SHAFT NUT
CLUTCH DRIVEN
PLATE
BEARING TO PULLEYPULLEY BEARIN
RETAINER RINGCOIL 8HOUSING
CLUTCH DRIVEPLATIRETAINER RING
AND PULLEY ASSEMBLY
Figure 98-32
Magnetic Clutch and Pulley Assemblyis tack-welded to the inside of the shell. In addition,
an oil drain screw and gasket are located on the side
of the reservoir and are provided for draining or
adding of oil to system. To add oil, compressor must
be removed from car. The necessity to add oil should
only be required when the system has ruptured vio-
lently and oil has been lost along with refrigerant.
Under controlled conditions or slow leak conditions
it is possible to loose only a small amount of oil with
the refrigerant gas. The serial number, part or model
number, and rating of the compressor is stamped on
name plates located on top of shell.
12. Magnetic Clutch and Pulley Assembly
- The
magnetic clutch and pulley assembly (see Figure 9B-
32) together transmit power from the engine crank-
shaft to the compressor. The magnetic clutch is
actuated when the air conditioning temperature
switch and the fan switch located on the evaporator
cover assembly are closed. When the switches are
closed, the coil sets up a magnetic field and attracts
the armature plate (movable element of the clutch
driven plate). The armature plate portion of the
clutch driven plate moves forward and contacts the
friction surface of the pulley assembly, thereby me-
chanically linking the compressor to the engine. The
compressor will operate continuously whenever the
air conditioner clutch compressor switch and the fan
switch are closed. When one or both of the switches
are open the armature plate will be released due to
spring tension and move away from the pulley as-
sembly. This allows the pulley to rotate without driv-
ing the shaft. It should be noted that if the air
conditioner system was in use when the engine was
turned off, the armature plate may remain in contact
with the pulley due to residual magnetism. When the
engine is started the armature plate will separate
from the pulley assembly. The coil is rated at 3.85
ohms (85 degrees F.) and will draw 3.2 amperes at
12 volts D.C.Condenser
The condenser which is made of aluminum is locatedIN:ET
DESICCANT.
RECEIVERDEHYDRATOR
ASSEMBLY
FILTER
SCREEN
Figure 98-33 Receiver Dehydrator Assembly
Page 549 of 625

98.40 1973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
2. Interconnect manifold and gage set (J-5725-01),
gage charging lines (J-5418) and gage adapters
(J-5420) to air conditioning system as shown in Figure
9B-40.3. Place transmission in “Park” for automatics and
in neutral for manuals. Apply hand brake.
4. Turn blower switch to the “Hi” position.
5. Turn temperature switch to “Max” position.
6. Run engine at 2000 RPM for ten (10) minutes with
car doors and windows closed and the hood up. Place
a high volume industrial type fan in front of radiator
if head pressure should exceed 250 psi and also at
high ambients to bring the pressures to within the
limits specified in the Functional Charts in Division
V.In the case of the Opel 1900 and the Manta, a ther-
mometer should be placed in a position to read the
temperature of the air discharging from the right-
hand A/C outlet. In case of the GT, a thermometer
should be placed in a position to read the tempera-
ture of the air discharging from the left-rear A/C
outlet.
HEATER-AIR CONDITIONER REFRIGERANT
CIRCUIT TROUBLE DIAGNOSIS GUIDE
Insufficient Cooling (Check Air Flow)
Normal Air Flow (Inspect system for visual defects.
Run functional tests.)
Discharge Air
- Normal Temp Check for air leaks
through dash, car body, windows, or from heater or
ventilators.
Discharge Air
- High Temp Check sight glass for
foaming and compressor clutch for engagement.
No Compressor Clutch Engagement Check connec-
tions at clutch switch, harness connectors, and check
clutch switch.
No Foaming Compare evaporator pressure to that
on functional test table.
Foaming System is probably low on refrigerant.
Check for leaks, repair, evacuate, and charge. If
foaming still occurs, check for restriction in refriger-
ant lines between condenser and receiver dehydrator.
Evaporator Pressure Normal Compare head pres-
sure to pressure on functional test table.
Evaporator Pressure Low Ice may be forming on
evaporator. Low volume of air discharging at A/C
outlet after system has been running above idle con-dition
,for approximately 15-30 min.utes. Discharging
air gradually elevating in temperature. Check expan-
sion valve. If valve isn’t permitting flow of liquid,
this will be indicated by a warm pipe out of the
evaporator. This may be caused by: 1) Clogged or
Plugged inlet screen in the expansion valve; 2)
Broken capillary line; or 3) Discharged temperature
bulb. If the valve is okay, the pipe out of the evapora-
tor will be cold.
Evaporator Pressure High Check the expansion
valve to determine if themobulb is making good con-
tact and is properly insulated. Operate engine at 2000
RPM with maximum air conditioning setting. If
evaporator pressure remains high, feel suction line.
If line feels frosty or extremely
(cold with relative
high ambient conditions, then partially cover the
condenser to obtain head pressures from 265 psi to
280 psi maximum. If evaporator pressure rises above
30 psi, change the expansion valve.
Also, check if compressor may be the cause due to
some internal or external mechanical trouble which
prevents reduction of pressure. Check for external
troubles, slipping belt, bad clutch and/or pulley, or
improper clutch engagement, before investigating
the compressor internally.
Head Pressure High Check for the following: Con-
denser air flow low, air in system, excessive refriger-
ant in system, restriction in condenser.Head.PressureLowRestriction in flow of refrigerant
to evaporator, or expansion valve plugged or defec-
tive.
Low Air Flow (Check blower operation and
evaporator. Check operation of controls.)
Ice BIocking Evaporator Run functional test. If
evaporator pressure is low, ice may form on evapora-
tor and reduce air flow.
Evaporator Pressure Low Ice may be forming on
evaporator. Low volume of air discharging at A/C
outlet after system has been running above idle con-
dition for approximately 15-30 minutes. Discharging
air gradually elevating in temperature. Check expan-
sion valve. If valve isn’t permitting flow of liquid,
this will be indicated by a warm pipe out of the
evaporator. This may be caused by: 1) Clogged or
plugged inlet screen in the expansion valve; 2)
Broken capillary line, or 3) Discharged temperature
bulb. If the valve is okay, the pipe out of the evapora-
tor will be cold.BlowerNot OperatingCheck for the following: Fuse
blown, blower switch defective, wire broken or loose
connection, poor ground connection, or blower mo-
tor defective.
Page 550 of 625

REFRIGERANT COMPONENTS ALL MODELS9s. 41
BIower Operating Normal Check for the following:Restriction or leakage in air ducts, A/C outlets not
opening.2. Do not carry cylinder in passenger compartment
of car.3. Do not subject cylinder to high temperatures.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS4. Do not weld or steam clean on or near cylinder.
5. Do not fill cylinder completely.
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION AND SAFETY
PRECAUTIONS6. Do not discharge vapor into area where flame is
exposed or directly into engine air intake.
General InformationAll subassemblies are shipped sealed and dehy-
drated. They are to remain sealed until just prior to
making connections, and should be at room tempera-
ture before uncapping. This prevents condensation of
moisture from air that enters the system.
All precautions should be taken to prevent damage
to fittings or connections. Even minute damage to a
connection could cause it to leak. Any fittings with
grease or dirt on them should be wiped clean with a
cloth dipped in alcohol.
Do not clean fitting or hoses with solvents because
they are contaminants. If dirt, grease or moisture
gets inside the pipes or hoses and cannot be removed,the pipe or hose is to be replaced. Use a small amount
of clean refrigeration oil on all tube and hose con-
necting joints, and lubricate the
“0” ring gasket with
this oil before assembling the joint. The oil will help
in effectitig a leak-proofjoint and assist the
“0” ring
to slip into the proper location without being cut or
damaged. Always use new
“0” rings.
When tightening joints, use a second wrench to hold
the stationary part of the connection to prevent
twisting and to prevent hose kinking. Kinked hoses
are apt to transmit noise and vibration. Tighten all
connections in accordance with recommended
torques (see Division VI, Specifications).7. Do not expose eyes to liquid
- WEAR SAFETY
GOGGLES whenever discharging, charging or leak
testing system.
CHARGING AND DISCHARGING SYSTEMRemoval of any part in the refrigerant circuit will
require discharging of the entire system.
Discharging the System1. Remove caps from gauge fittings on the compres-
sor adapter fitting on the compressor.
2. With both valves on manifold gauge set (J-5725-
04) closed (clockwise), attach manifold to the com-
pressor adapter fitting on the compressor, using
J-5420 valve adapter at suction gauge fitting and
J-9459 valve adapter at discharge gauge fitting. See
Figure
9B-41.3. Fully open high pressure valve on manifold gauge
set to allow escape of refrigerant from system
through the manifold gauge set and out the center
fitting and hose. (Place end of hose in clean container
to collect oil loss due to rapid discharge of system).
4. When hissing ceases, indicating all refrigerant
has escaped, close high pressure valve on manifold
gauge set by turning valve clockwise.
Do not connect receiver-dehydrator assembly until
all other connections have been made. This is neces-
sary to itisure maximum moisture removal from sys-
tem.It is important that air conditioning hoses do not rest
on or contact body sheet metal except where neces-
sary. Because of the high frequency at which the
compressor operates, the passenger compartment is
susceptible to transfer of noise.
Evacuating the SystemWhen the refrigeration system is depressurized and
opened for service, some air will enter the lines, re-
gardless of how quickly openings are capped. In
or-der to remove this air and as much as possible of the
moisture it contains, the complete system must be
evacuated. Evacuating is merely the process of
removing all air from the system, thereby creating a
vacuum in the system.
Safety PiecautionsThe following safety precautions should always be
followed~,when servicing refrigerant charged compo-nents:Under no circumstances should alcohol be used in
the system in an attempt to remove moisture,
regard-less of the successful use of alcohol in other refrigera-
tion systems.
Preparations for Evacuating Complete System
1. Do not leave Refrigerant-12 cylinder uncapped.
1. Check the low pressure gauge for proper calibra-
Page 553 of 625

9B-44 1973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
Do not turn refrigerant drum upside down, as this
would allow liquid refrigerant to enter compressor
which may cause damage.
4. If line at center gauge fitting has not been purged
of air, loosen line at center fitting on gauge set and
crack valve on refrigerant drum to blow air from
line. Retighten line at center fitting and record exact
weight of refrigerant tank in water on the scales.
5. Open valve on refrigerant drum and both valves
on gauge set to allow refrigerant to flow into system.
Continue charging until the scales show that 2
Ibs.Opel 1900
- Manta and 2 l/4 lbs. GT, of refrigerant
have been transferred from refrigerant drum to sys-
tem.If full charge cannot be obtained, close both valves
on gauge set, start engine, and set temperature con-
trol knob to full cold position with blower in Max Hi.
Open low pressure valve on gauge set slowly and
leave open until full charge is added.
WARNING: Observe high pressure gauge while charg-
ing with compressor running. Shut
offengine ifpres-
sure exceeds 250 psi. A large fan placed in front
ol
the car wi// help reduce excessively high head pres-6. Close both valves on gauge set (high pressure valve
will already be closed if charging was completed by
running compressor) and close valve on refrigerant
drum.
If the engine was used to complete the charge into
the system, close valve on refrigerant drum to permit
compressor to draw any refrigerant left in the line
from the drum to the center fitting of the gauge set,
then close the low pressure valve on the gauge set.
7. Operate engine at 2000 RPM with temperature
control knob at full cold, blower speed in Max Hi.
After ten minutes of operation, observe appearance
of refrigerant in receiver-dehydrator. If bubbles are
observed, open low pressure gauge valve and valve
on refrigerant drum to allow more refrigerant to en-
ter system. Close valve when receiver-dehydrator
clears
up.If an air inlet temperature is below 70 degrees F.
when this check is made, bubbles may appear, even
though the proper amount of refrigerant is in the
system. Air inlet temperature must be 70 degrees F.
or above to make an accurate check.
8. When refrigerant has been installed, continue to
operate system and test for proper operation as ou-
tlined under “Operational Test”.
9. When satisfied that air conditioning system is op-
erating properly, stop engine, remove gauge set and
replace protective caps on compressor fittings.10. Using leak detector, check complete system for
leaks.Disposable Can Method
After having
depress&ed, repaired (if necessary)
and evacuated the refrigerant system, the system
may be charged as follows using refrigerant in dis-
posable cans:
1. Obtain three (3) 1
lb. cans or one 12 lb. can of
refrigerant.
2. If using 1 lb. cans, mount two (2) cans in J-6272-
02 (Multi-opener) or attach J-6271 (single-can
opener valve) on one can. If using the 12
lb. disposa-
ble can, attach J-23390 (disposable can control valve)
on can.WARNING: Make sure outlet valve on opener is
closed (clockwise) before installing opener.A. If the J-6272-02 multi-opener is used, raise lock-
ing lever, position three (3) cans of refrigerant and
force locking lever down to secure cans and at same
time puncture top of can to make it ready for charg-
ing.
B. If the J-6271 valve is used, back off the valve from
the can top retainer, slip the valve onto the can and
turn the valve into retainer until tight. DO NOT
open outlet valve during this operation, as turning
the valve into the retainer punctures top of can to
make it ready for charging.
3. Connect center flexible line of gauge set to fitting
on a can opener valve. If the line at center gauge
fitting has not been purged of air, loosen line at
center fitting on gauge set and “crack” valve at can
opener (for a second or two) to force air from the
line. Retighten line at center fitting.
4. Open valve at refrigerant source and at low and
high pressure valves on manifold gauge set. Leave
valve open at refrigerant source until all refrigerant
(when using 1 lb. can) has ‘entered the refrigeration
system or system is fully charged. Close valve on can.
A. If the system is charged using
1 lb. cans and the
J- 627 1 valve, disconnect valve from can. Leave valve
closed to flexible line to the center fitting of the
manifold gauge set. Install valve on a new and full
disposable can of refrigerant.
Page 554 of 625

REFRIGERANT COMPONENTS ALL MODELS9t3- 45
B. If system is charged using J-6272-02, close the
valve of opener after all cans are empty. Release the locking lever and discard the three (3) empty cans.
If this tool will be used to complete the charge with
additional cans to provide the required refrigerant
charge, leave the empty cans in position, locate one
full can and lock the lever into place. These empty
cans balance the assembly and prevent the loss of
refrigerant through the open “series” passage. Align
the pierced hole in the empty can with the punch in
the cover of the tool.
If the J-6271 valve for single cans is available, com-
plete charging as explained in 4a above.
5. Close high side valve on manifold gauge set,
WARNING: Prior to starting up engine, the high side
valve on the charging manifold must be closed due
to excessive pressure
bui/d-up which can result in
bursting of the container(s) causing serious injury. If
you are inexperienced in the use of this procedure, seek professional assistance.
6. Operate engine at 2000 RPM with temperature
control knob at full cold position and blower speed
on Max Hi. If air inlet temperature at the condenser
is below 70 degrees F. when this check is made,
bubbles may appear, even though the proper amount
of refrigerant is in the system. Air inlet temperature
must be 70 degrees F. or above to make an accurate
check.
7. When refrigerant has been installed, continue to
operate system and test for proper operation as ou-
tlined
under “Operational Test”.
8. When satisfied that the air conditioning system
is operating properly, stop engine, remove gauge set
and replace protective caps on suction and discharge
fittings.
from thegauge fitting to prevent damage-or injury to
personnel.
9. Using a leak detector, check complete system for
leaks.
Charging Station Method
INSTALLING J-8393-02
-
1. Be ceitain compressor hand shut-off valves to
gauge fittings are closed (counterclockwise).
2. Be certain all valves on charging station are
closed.
3. Connect high pressure gauge line to compressor
high pressure gauge fitting.
4. Turn high pressure hand shut-off valve one turn
clockwise, and high pressure control one turn coun-
terclockwise (open). Crack open low pressure con-
trol and allow refrigerant gas to hiss from low
pressure gauge line for three seconds, then connect
low pressure gauge line to low pressure gauge fitting
on compressor adapter fitting. (Place J-9459 adapter
on hose, then attach adapter to gauge fitting.)
FILLING CHARGING CYLINDER
1. Open Control valve on refrigerant container.
2. Open valve on bottom of charging cylinder, al-
lowing refrigerant to enter cylinder.
3. Bleed charging cylinder to valve (behind control
panel) only as required to allow refrigerant to enter
cylinder. When refrigerant reaches desired charge
level, close valve at bottom of charging cylinder and
be certain cylinder bleed valve is closed securely.
While filling the cylinder, it will be necessary to close
the bleed valve periodically to allow boiling to sub-
side so that refrigerant level in the charging cylinder
can be accurately read.
CHARGING THE SYSTEM USING J-8393-02
1. With charging station connected, as previously
described, remove low pressure gauge line at com-
pressor adapter fitting.
2. Crack open high and low pressure control valves
on station and allow refrigerant gas to purge from
system. Purge slowly enough so, that oil does not
escape from system along with refrigerant.
3. When refrigerant flow nearly stops, connect low
pressure gauge line to
compress& adapter fitting.
4. Turn on vacuum pump and open vacuum control
valve.
5. With system purged as
abovk, run pump until
26-28 inches of vacuum is obtained Continue to run
pump for 15 minutes after the system reaches 26-28
inches vacuum.
In all evacuating procedures, the specification of
26.
28 inches of mercury vacuum is used. These figures
are only attainable at or near sea level. For each 1000
feet above sea level where this operation is being
performed, the specifications should be lowered by 1
inch. For example, at 5000 feet elevation, only 21 to
23 inches vacuum can normally be obtained.
6. If 26-28 inches vacuum (corrected to sea level)
cannot be obtained, close vacuum: control valve and
Page 555 of 625

98-46 1973 OPEL SERVICE MANUAL
shut off vacuum pump. Open refrigerant control
valve and allow some refrigerant to enter system.
Locate and repair all leaks.
7. After evacuating for 15 minutes, add l/2 lb. of
refrigerant to system. Purge this
l/2 lb. and reevacu-
ate for 15 minutes. This second evacuation is to be
certain that as much contamination is removed from
the system as possible.
8. Only after evacuating as above, system is ready
for charging. Note reading on sight glass of charging
cylinder. If it does not contain a sufficient amount
for a full charge, till to proper level.
9. Close low pressure valve on charging station.
Fully open station refrigerant control valve and al-
low all liquid refrigerant to enter system. When full
charge of refrigerant has entered system, turn off
refrigerant control valve and close both hand shut-
off valves.
10. If full charge of refrigerant will not enter system,
close high pressure control and refrigerant control
valves. Start engine and run at low idle with com-
pressor operating. Crack refrigerant control valve
and low pressure control on station. Watch low side
gauge and keep gauge below 50 psi by regulating
refrigerant control valve. Closing valve will lower
pressure. This is to prevent liquid refrigerant from
reaching the compressor while the compressor is op-
erating. When required charge has entered system,
close refrigerant control valve and close low pressure
control.
11. System is now charged and should be perform-
ance- tested before removing gauges.
Adding Refrigerant
The following procedure should be used in adding
small amounts of refrigerant that may have been lost
by leaks or while opening system for servicing the
compressor. Before adding refrigerent to replace that
lost by leaks, check for evidence of oil loss and add
oil if necessary.
This procedure will only apply if the air inlet temper-
ature is above 70 degrees F. at the condenser.
1. Remove caps from compressor gauge fittings.
Attach gauge set to gauge fittings, making sure
adapter (J- 5420) is between low pressure gauge hose
and suction gauge fitting, and J-9459 is between high
pressure gauge hose and discharge gauge fitting.
2. Start engine, turn air conditioning temperature
control knob to full cold position, blower switch to
Max Hi. Operate for ten
(IO) minutes at 2000 RPM
to stabilize system.
3. Observe the refrigerant through the sight glasscover of receiver-dehydrator with the system operat-
ing,
IO see if there are any bubbles evident.
a. If no bubbles are evident, then bleed system slowly
through the discharge valve until bubbles appear in
the receiver-dehydrator. Add 1 lb. of refrigerant as
explained under “Charging the
ISystem”.b. If bubbles are visible in the receiver-dehydrator
with the temperature control krlob in the full cold
position and the blower at MAX speed, it indicates
a partial or complete plug in a line, a shortage of
refrigerant, or both. Correct condition. Add refriger-
ant
u~ntil the sight glass clears, then add another 1 lb.
of refrigerant.
4. Attach flexible hose from center fitting of gauge
set loosely to refrigerant drum or on disposable can
valvxs. Open high and low pressure valves on the
gauge set slightly to purge pressure gauge lines of air.
Tighten fitting of refrigerant drum or can when satis-
fied ihat all air has been removed from gauge lines.
Close (clockwise) both hand shut-off valves or gauge
set.5. Partially charge system.
REFRIGERANT DRUM METHOD:
A. Place pail containing hot water that does not have
a temperature exceeding 125 degrees F. on scales,
place refrigerant drum in pa” containing water, note
weig,ht and only open low pressure valve on gauge
set.B. Start engine, turn temperature control knob to full
cold position and place blower switch in Max Hi.
Operate engine for 10 minutes at 2000 RPM to sta-
bilize system.
C. With compressor operating, slowly open valve on
refrigerant drum and allow refrigerant to flow into
system (through manifold gauge set) until liquid in-
dicator clears up and immediately shut off valve ai
gauge set or on refrigerant drum. Check weight of
refrigerant drum and pail of water. Then slowly open
valve on gauge set (or refrigerant drum) and add one
more lb. of refrigerant. Note total amount of refriger-
ant added.
DISPOSABLE CAN METHOD:
A. Make sure the outlet valve on the J-6271 valve is
fully clockwise and attach the J-6271 to a 1 lb. can
of refrigerant by backing off the valve from the top
of the retainer, slipping the valve onto the can and
turning the valve into the retainer until tight. DO
NOT accidentally open outlet valve during this oper-
ation, as turning the valve into the retainer punctures
the top of the can to make it ready for charging.
.
Page 556 of 625

REFRIGERANT COMPONENTS ALL MODELS9a- 47
B. Connect center flexible line of gauge set to the
fitting on the valve.
C. Start engine, turn temperature control knob to full
cold position, set blower switch to Max Hi. Operate
engine for 10 minutes at 2000 RPM to stabilize sys-tem.D. With compressor operating, slowly open valve on
refrigerant can and allow refrigerant to flow into
system (through manifold gauge set) until liquid in-
dicator clears up and immediately shut off valve at
gauge set and on refrigerant can. Check weight of
can and valve assembly and record.
E. Add an additional 1 lb. of refrigerant by adding
refrigerant from the can just weighed until can is
empty. Attach another can and add refrigerant until
can and valve assembly weigh the same as recorded.
6. Close valves at refrigerant drum or
can,7. Test for leaks and make operational check of
system.
ADDING OIL TO THE SYSTEM (MAJOR
OVERHAUL)The oil in the refrigeration system does not remain
in the compressor during system operation, but cir-culates throughout the system. The compressor is
initially charged with 10 oz. of 525 viscosity oil.
After system has been in operation the oil content in
the compressor will vary depending on the engine
RPM and air conditioning load. At higher engine
RPM’s a lesser amount of oil will be retained in the
compressor reservoir. It is important that the total
system oil content does not vary from a total of10-l/2 oz. Excessive oil content will reduce cooling
capacity. Inadequate oil content may result in dam-
age to compressor moving parts.
The refrigeration system will not require adding of
oil unless there is an oil loss because of a ruptured
line, badly leaking compressor seal, replacement of
evaporator, compressor, receiver-dehydrator, or loss
due to a collision. Oil is generally added to the sys-
tem via the oil drain hole in the lower side of the
compressor for this condition. To add oil to the sys-
tem via the compressor, the compressor must be
removed. If no major loss of oil has occurred and a
component (condenser,receiver-dehydrator or
evaporator) is removed for servicing, the oil may be
added directly to the component. To add oil to a
component removed for servicing and when no ma-
jor loss has occurred, drain and measure oil in com-
ponent, then replace with a like amount. To add oil
to the system when a major loss of oil is evidenced,
or when the compressor is being serviced, remove
compressor, drain and measure oil, and replace oil
amount specified in the Oil Replacement Table.
OIL REP,‘LACEMENT TABLE
Condition
1. Major loss of oil and
a component (conden-
ser, receiver-dehydra-
tor, or evaporator)
has to be replaced.
Amount of Oil Drained
From Compressora. More than 4 oz.Amount of 525 Oil to Install
In Compressora. Amount drained from compressor,
plus amount for component
being replaced.
Evaporator
- Add 2 oz.
Condenser
- Add I oz.
Receiver-Dehydrator
- Add 1 oz.
b. Less than 4 oz.b. Install 6 oz., plus amount for
component being replaced as
shown above.
2. Compressor being
replaced with a
ser-vice replacement
compressor
- no major
oil loss.a. More than 1
l/2 oz.a. Same amount as drained from
compressor being replaced.
b. Less than 1
l/2 oz.b. Install 6 oz
Page 621 of 625

SubjectPage Number
Subject Page Number
A
Air Conditioning Refrigerant Components .................
98.17
Opel 1900
& Manta-In Car Components .....9B-90
GT.ln Car Components..................98-97
Alignment Opel 1900
& Manta .....................3C-22
GT-Opel ..............................
3C-22
Alternator Description ...........................
lD-28
Specifications. .........................1 D-35
Overhaul K-l..........................lD-30
Removal & Installation ..................lD-30
Testing...............................lD-29
Wiring Diagrams
Manta .............................
1 J-105
Opel 1900
..........................lJ-103
GT ................................
lJ-107
AM
Radio-GT............................9C-105
AM Radio-Opel 1900 &Manta ...............
9C-109
Antenna, Installation .......................
9C-111
Antenna Trimmer .........................
9C-110
Assembly of Transmission from Major Units Manual ...............................
78-23
3 Speed Automatic .....................
7C-103
Axle,
R&r, Disassembly ....................48~11
Bolt Torque Specifications
Engine ...............................
6A-27
Transmission. Manual ....................
78-33
3 Speed Automatic .....................
7C-136
Clutch ...............................
7A-7
Body ................................
2A-4
Brakes
Brake Drum, Shoes & Linings .............5C-28
Hydraulic Wheel Cylinder ................
5C-30
Hydraulic Master Cylinder ................
5A-2
Parking Brake Cables .....................
5C-33
Standard Brakes ........................
X-22
Disc Brakes...........................5B-10
Brake Booster and Vacuum
Coritrol Valve ....5A-5
Bumpers, Front and Rear ...................
ZH-33
C
B
Balance,,Wheel and Tire....................3G-62
Ball
J&tUpper .........................3A-7
Lower ...............................
3A-7
Battery
Specifications ..........................
lA-9
Testing...............................lA-6
Charging ..............................lA-9
Trouble Diagnosis ......................lA-4
Battery Test 421.........................l A-6
Belt Tensions ............................
68.33
Blower and Air Inlet Assembly, Removal and Installation
Owl 1900&Manta.....................9A-15
GT
.: ................................9A-5
Body Name Plate ............................
OA-1
Style’Numbers ......................... OA-2
Windows and Weatherstrips ...............
ZC-9
Doors ................................
ZD-13
Interior Trim and Headlining ..............
26-33
Seatsi................................26-33
Roof&d Sunroof-Opel 1900
& Manta ......2F.24 Camshaft,
1.9L
Engine .....................6A-25
Car Model Identification .......
.,............OA-1
Carburetor..............................6E-44
Trouble Diagnosis ......................
6E-49
Description ...........................
6E-44
Overhaul .............................
6E-53
Adjust ...............................
6E-50
Removal
& Installation ......,............6E-52
Specifications ..........................
6E-58
Charging
System
Description ..............
:............ 1 D-28
Specifications. ............
.,............lD-35
Testing..................:............lD-29
Wiring Diagrams
Manta .............................
lJ-105
Opel 1900 ..........................
lJ.103
GT ................................
lJ-107
Chart Lubrication ........................ OC-5
Chassis Springs, Front. ........
!............3A-15
Clutch, Second-Automatic Transmission .......
7C-103
Clutch Adjustment .........................
7A-4
Control Arm Front Upper ...................
:............3A-10
Lower ...............................
3A-11
Converter Checking Procedure ................
7C-125
Coolant Flow ............................
68-32
4 Speed Manual Transmission ...
!,...........7B-12
Cranking System. See Starting
SyStem
Crankshaft..............................6A-16
Cylinder Head ...............
:............6A-12
D
Description
3.Speed Automatic.....................7C-37