relay PONTIAC FIERO 1988 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: PONTIAC, Model Year: 1988, Model line: FIERO, Model: PONTIAC FIERO 1988Pages: 1825, PDF Size: 99.44 MB
Page 191 of 1825
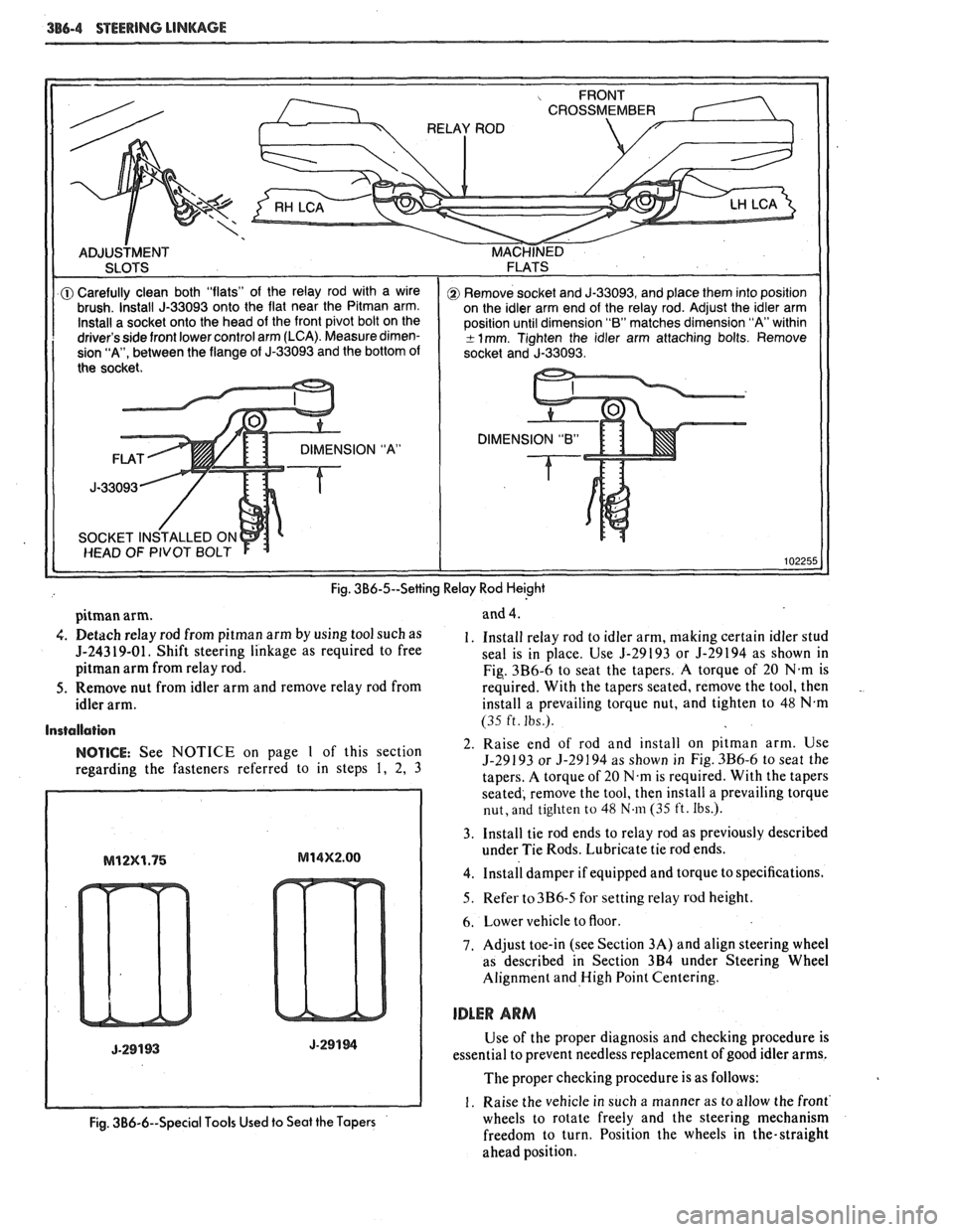
386-4 STEERING LINKAGE
DIMENSION "B"
Fig. 3B6-5--Setting Relay Rod Heighi
pitman arm.
4. Detach relay rod from pitman arm by using tool such as
5-24319-01. Shift steering linkage as required to free
pitman arm from relay rod.
5. Remove nut from idler arm and remove relay rod from
idler arm.
Installation
NOTICE: See NOTICE on page 1 of this section
regarding the fasteners referred to in steps
1, 2, 3 and
4.
1. Install relay
rod to idler arm, making certain idler stud
seal is in place. Use
5-29193 or 5-29194 as shown in
Fig. 3B6-6 to seat the tapers. A torque of
20 N.m is
required. With the tapers seated, remove the tool, then
.
install a prevailing torque nut, and tighten to 48 N.m
(35 ft. Ibs.).
2. Raise end of rod and install on pitman arm. Use
5-29193 or 3-29194 as shown in Fig. 3B6-6 to seat the
tapers. A torque of
20 N.m is required. With the tapers
seated, remove the tool, then install a prevailing torque
nut, and tighten to 48 N.111 (35 ft. Ibs.).
3. Install tie rod ends to relay rod as previously described
under Tie Rods. Lubricate tie rod ends.
4. ~nstall damper if equipped and torque to specifications.
5. Refer to3B6-5 for setting relay rod height.
6. Lower vehicle to floor
7. Adjust toe-in (see Section 3A) and align steering wheel
as described in Section
3B4 under Steering Wheel
Alignment and High Point Centering.
IDLER ARM
Use of the proper diagnosis and checking procedure is
essential to prevent needless replacement of good idler arms.
The proper checking procedure is as follows:
1. Raise the vehicle in such a manner as to allow the front'
Fig. 3B6-6--Special Tools Used to Seat the Tapers wheels to rotate freely and the steering mechanism
freedom to turn. Position the wheels in the-straight
ahead position.
Page 192 of 1825
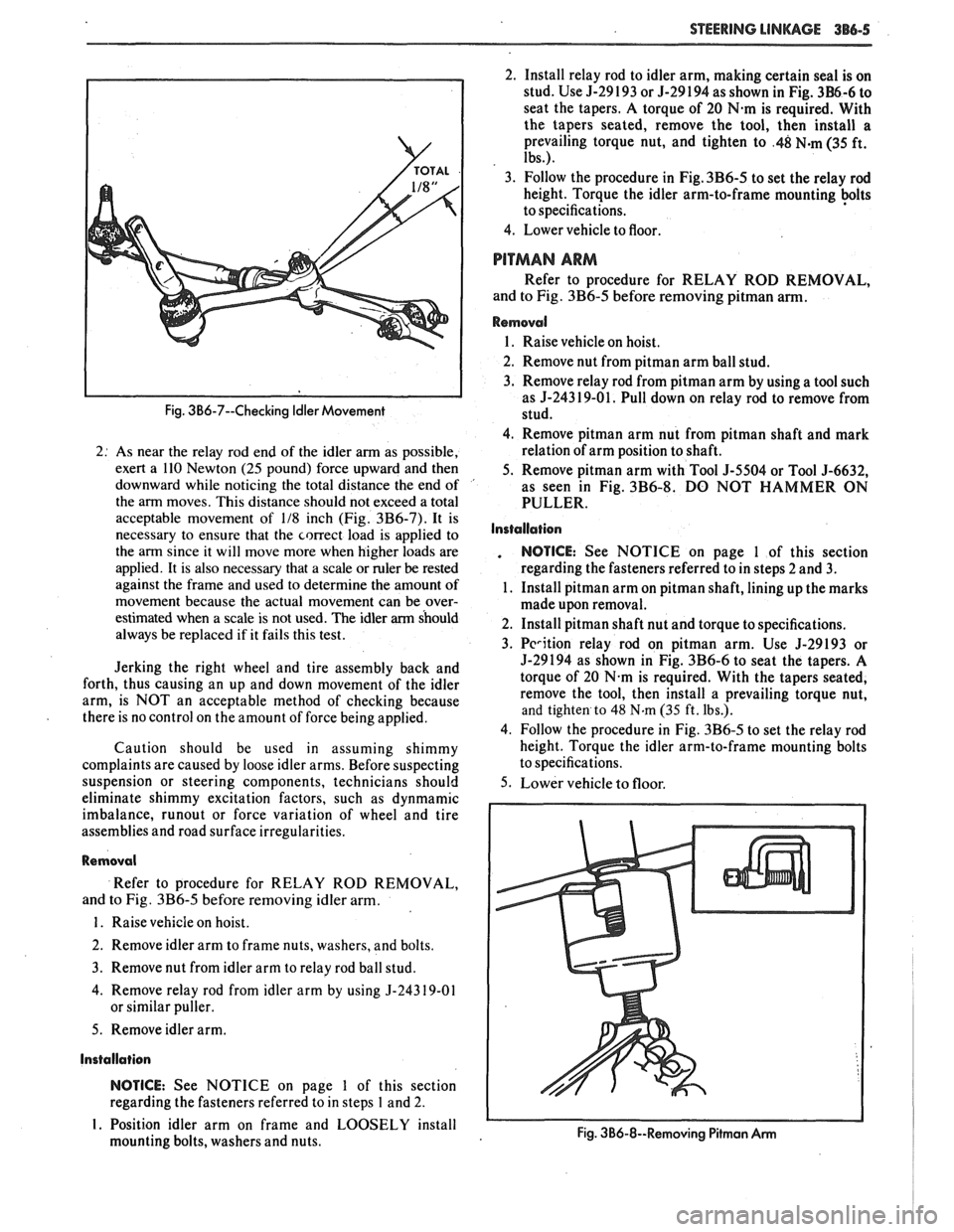
STEERING LINKAGE 386-5
Fig. 3B6-7--Checking Idler Movement
2: As near the relay rod end of the idler arm as possible,
exert a 110 Newton
(25 pound) force upward and then
downward while noticing the total distance the end of '
the arm moves. This distance should not exceed a total
acceptable movement of
118 inch (Fig. 3B6-7). It is
necessary to ensure that the correct load is applied to
the arm since it will move more when higher loads are
applied. It is also necessary that a scale or ruler
be rested
against the frame and used to determine the amount of
movement because the actual movement can be over-
estimated when a scale is not used. The idler
arm should
always be replaced if it fails this test.
Jerking the right wheel and tire assembly back and
forth, thus causing an up and down movement of the idler
arm, is NOT an acceptable method of checking because
there is no control on the amount of force being applied.
Caution should be used in assuming shimmy
complaints are caused by loose idler arms. Before suspecting
suspension or steering components, technicians should
eliminate shimmy excitation factors, such as dynmamic
imbalance,
runout or force variation of wheel and tire
assemblies and road surface irregularities.
Removal
Refer to procedure for RELAY ROD REMOVAL,
and to Fig.
3B6-5 before removing idler arm.
1. Raise vehicle on hoist.
2. Remove idler arm to frame nuts, washers, and bolts.
3. Remove nut from idler arm to relay rod ball stud.
4. Remove relay rod from idler arm by using
5-24319-01
or similar puller.
5. Remove idler arm.
Installation
NOTICE: See NOTICE on page 1 of this section
regarding the fasteners referred to in steps
1 and 2.
I. Position idler arm on frame and LOOSELY install
mounting bolts, washers and nuts. 2.
Install relay rod to idler arm, making certain seal is on
stud. Use 5-29 193 or 5-29 194 as shown in Fig.
3B6-6 to
seat the tapers. A torque of 20
N.m is required. With
the tapers seated, remove the tool, then install a
prevailing torque nut, and tighten to
.48 N-m (35 ft.
Ibs.).
3. Follow the procedure in Fig. 3B6-5 to set the relay rod
height. Torque the idler arm-to-frame mounting
+Its
to specifications.
4. Lower vehicle to floor.
PITMAN ARM
Refer to procedure for RELAY ROD REMOVAL,
and to Fig.
3B6-5 before removing pitman arm.
Removal
1. Raise vehicle on hoist.
2. Remove nut from
pitman arm ball stud.
3. Remove relay rod from pitman arm by using a tool such
as
5-243 19-01. Pull down on relay rod to remove from
stud.
4. Remove pitman arm nut from pitman shaft and mark
relation of arm position to shaft.
5. Remove
pitman arm with Tool 5-5504 or Tool 5-6632,
as seen in Fig.
3B6-8. DO NOT HAMMER ON
PULLER.
Installation
. NOTICE: See NOTICE on page 1 of this section
regarding the fasteners referred to in steps 2 and
3.
1. Install pitman arm on pitman shaft, lining up the marks
made upon removal.
2. Install pitman shaft nut and torque to specifications.
3.
Pcrition relay rod on pitman arm. Use 5-29193 or
5-29194 as shown in Fig. 3B6-6 to seat the tapers. A
torque of 20
N.m is required. With the tapers seated,
remove the tool, then install a prevailing torque nut,
and tighten to 48 N.m (35 ft. Ibs.).
4. Follow the procedure in Fig.
3B6-5 to set the relay rod
height. Torque the idler arm-to-frame mounting bolts
to specifications.
5. Lower vehicle to floor.
Fig. 3B6-8--Removing Pitmon Arm I I
Page 212 of 1825

FRONT SUSPENSION 3C-1
SEC"T0RI 3C
FRONT SUSPENS
NOTICE: All front suspension fasteners are an important attaching part in that it could affect the
performance of vital parts and systems, and/or could result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with
one of the same part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do not use a
replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque values must be used as specified during reassembly
to assure proper retention of this part.
NOTICE: Never attempt to heat, quench or straighten any front suspension part. Replace it with a new part
or
damage to the part may result.
CONTENTS
General lnformation ....................................................................................................... 3C-I
On-Car Service ................................................................................................................... 3C- I
Specifications ..................................................................................................................... 3C- 10
GENERAL INFORMATION
The front suspension is designed to allow each
wheel to compensate for changes in the road surface ON-CAR SERVICE
level without appreciably affecting the opposite wheel. WHEEL BEARINGS
Each wheel is independently connected to the frame by
The proper functioning of the front suspension
a steering
kunckle, strut assembly, ball joint, and lower cannot be maintained unless the front wheel tapered arm. The steering in a roller bearings are correctly adjusted. The bearings
prescribed three dimensional arc. The front wheels are
must be a slip fit on the spindle and the inside diameter held in proper relationship to each other by two tie rods of the bearings should be lubricated to insure proper which are connected to steering arms on the knuckles ~h~ spindle nut must be a free-running fit and to the relay rod assembly.
on the threads.
Coil chassis springs are mounted between the
spring housings on the front crossmember and the
lower control arms. Ride control is provided by double,
direct acting strut assemblies. The upper portion of
each strut assembly extends through the fender well
and attaches to the upper mount assembly with a nut.
Side roll of the front suspension is controlled by
a spring steel stabilizer shaft. It is mounted in rubber
bushings which are held to the frame side rails by
brackets. The ends of the stabilizer are connected to the
lower control arms by link bolts and are isolated by
rubber grommets.
The inner ends of the lower control arms have
pressed in bushings. Bolts (passing through the
bushings) attach the arm to the suspension
crossmember. The lower ball joint assembly is a press
fit in the arm and attaches to the steering knuckle with
a torque prevailing nut.
Rubber grease seals are provided at ball socket
assemblies to keep dirt and moisture from entering the
joint and damaging bearing surfaces.
Adjustment
Figure 602
NOTICE: See NOTICE on Page 3C-1
of this
section.
1. Remove dust cap from hub.
2. Remove cotter pin from spindle and spindle nut.
3. Tighten the spindle nut to 16 Nsm (12 lb. ft.)
while turning the wheel assembly forward by
hand to fully seat the bearings. This will remove
any grease or burrs which could cause excessive
wheel bearing play later.
4. Back off the nut to the "just loose" position.
5. Hand tighten the spindle nut. Loosen spindle nut
until either hole in the spindle lines up with a slot
in the nut. Not
nlore than 1/2 flat.
6. Install
new cotter pin. Bend the ends of the cotter
pin against nut, cut off extra length to ensure ends
will not interfere with the dust cap.
7. Measure the looseness in the hub assembly. There
will be
from .03 to . l3mm (.001 to .005 inches)
end play when properly adjusted.
8. Install dust cap on hub.
FRONT SUSPENSION
Refer to Fig. 610 for illustration of attachment
provisions for the bolted-on front suspension
suspension
crossmember.
Page 414 of 1825

ENGINE COOLING 88.3
since a small oil pump driven by the separator plate
forces the silicone oil into a reservoir between the
separator plate and the front cover assembly. In this
position, the passage from this cavity to the clutch area
is closed by a slide valve. As operating conditions
produce a high radiator air temperature discharge,
above approximately 66°C
(150"F), the temperature
sensitive bi-metal coil tightens to move the slide valve
(attached to the coil) which opens a port in the
separator plate. This allows a flow of silicone oil into
the clutch chamber to engage the clutch, providing a
maximum fan speed of approximately 2200 rpm. The
clutch coil is calibrated so that, with a road load at an
ambient temperature of approximately 32°C
(90T), the
clutch is just at a point of shift between high and low
fan speed. No attempt should be made to disturb the
calibration of the engine clutch fan assembly as each
assembly is individually calibrated at the time of
manufacture. Under certain temperature conditions
there is a lateral movement at the fan tip which should
not be considered as a hub or bearing failure. This
condition is a design feature of the clutch assembly
which allows up to approximately
1/4" lateral
movement measured at the fan tip.
Testing a clutch fan by holding the small hub
with one hand and rotating the aluminum housing in
a
clockwise/counter-clockwise motion will cause the
clutch to freewheel, which is a normal condition when
operated in this manner. This should not be considered
a test by which replacement is determined.
Temperature Switch
This switch activates a warning lamp in the
instrument cluster if the engine overheats. With
optional instrumentation, a temperature gage replaces
the warning lamp and the temperature switch is
replaced with a transducer. See Section
8A for
Temperature Switch location and diagnosis.
Coolant Temperature Fan Switch
This switch regulates voltage to the coolant fan
relay, which operates the fan whenever the engine
coolant temperature exceeds 230"
F (110" C). For
location and diagnosis see Section 8A for Coolant
Temperature Fan Switch.
Thermostat
A pellet-type thermostat is used in the coolant
outlet passage to control the flow of engine coolant, to
provide fast engine warm-up and to regulate coolant
temperatures.
A wax pellet element in the thermostat
expands when heated and contracts when cooled. The
pellet element is connected through a piston to a valve.
When the pellet element is heated, pressure is exerted
against a rubber diaphragm which forces the valve to
open. As the pellet element is cooled, the contraction
allows a spring to close the valve. Thus, the valve
remains closed while the coolant is cold, preventing
circulation of coolant through the radiator. At this
point, coolant is allowed to circulate only throughout
the engine to warm it quickly and evenly.
As the engine warms, the pellet element expands
and the thermostat valve opens, permitting coolant to flow
through the radiator, where heat is dissipated
through the radiator walls. This opening and closing of
the thermostat permits enough coolant to enter the
radiator to keep the engine within operating limits.
Fig. 3 Pellet Type Thermostat
Coolant Recovery System
A recovery-type cooling system is standard on all
cars and is designed to maintain the engine at proper
operating temperatures. The recovery tank collects
coolant that expands with rising temperature and
would otherwise overflow from the system. When the
system temperature drops, the coolant is drawn from
the recovery tank back into the radiator by the suction
created by coolant contraction. The cooling system has
been filled at the factory with a high-quality, inhibited,
year-around coolant that meets the standards of
General Motors Specification 1825-M. This coolant
solution provides freezing protection to at least -37°C
(-34°F). It has been formulated to be used for two full
calendar years or
30,OO miles, whichever first occurs,
of normal operation without replacement, provided the
proper concentration of coolant is maintained.
DIAGNOSIS
The following diagnostic information covers
common problems and possible causes. When the
proper diagnosis is made the problem should be
corrected by part replacement, adjustment, or repair as
required. Refer to the appropriate section of the service
manual for these procedures.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
Cooling System Care
The radiator cap should not be removed to check
coolant level. Check the coolant level visually in the
"see-through" coolant recovery tank every time hood
is up. Level should be near "ADD" mark when the
system is cold. At normal operating temperature the
coolant level should increase to the "FULL" mark on
the recovery tank. Coolant should be added only to the
reservoir to raise level to the "FULL" mark. Use a
50/50 mixture of high-quality ethylene glycol
antifreeze and water for coolant additions.
Page 432 of 1825

ENGINE FUEL BC-1
SECTION 6C
NE FUEL
CONTENTS
General Description ..................................... 6C-1 Fuel
Cap ........................................................... 6C-3
.................................................. ............................................. Alcohol-In-Fuel 6C- 1 Fuel Filter Neck 6C-3
................... ............ Fuel Metering .................................................. 6C-2 Fuel Gage Sending Unit .. 6C-4
....................... ............................... Throttle Body Injection (TBI) .... 6C-2 Diagnosis ,. 6C-4 ................... Service
Procedures ............................................. 6C-4
Port Fuel Injection ...................................... 6C-2
Pressure Relief ........................................... 6C-4
Fuel Feed and Return Pipe
............................... 6C-2
Flow Test .................................................... 6C-4
Fuel Pipes (MPFI)
.......................................... 6C-3
Pressure Test - TBI ................................... 6C-4
Fuel and Vapor Hoses
....................................... 6C-3
Pressure Test - MPFI .................................... 6C-4
Fuel Pump ........................................................ 6C-3 ...................................................... Fuel Pump Relay .............................................. 6C-3 Fuel Tank 6C-4
Fuel Filter
......................................................... 6C-3 Accelerator Controls ...................................... 6C-5
Fuel Tank
....................................................... 6C-3
All new General Motors vehicles are certified by
the United States Environmental Protection Agency as
conforming to the requirements of the regulations for
the control of air pollution from new motor vehicles.
This certification is contingent on certain adjustments
being set to factory standards. In most cases, these
adjustment points either have been permanently
sealed and/or made inaccessible to prevent
indiscriminate or routine adjustment in the field. For
this reason, the factory procedure for temporarily
removing plugs, caps, etc., for purposes of servicing the
product must be strictly followed and, wherever
practicable, returned to the original intent of the
design.
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
All gasoline engines are designed to use only
unleaded gasoline. Unleaded gasoline must be used for
proper emission control system operation. Its use will
also minimize spark plug fouling and extend engine oil
life. Using leaded gasoline can damage the emission
control system and could result in loss of emission
warranty coverage.
All cars are equipped with an Evaporative
Emission System. The purpose of the system is to
minimize the escape of fuel vapors to the atmosphere.
Information on this system will be found in Section
6E2, or 6E3.
When working on the fuel system, there are
several things to keep in mind.
@ Any time fuel system is being worked on,
disconnect the negative battery cable
except for those tests where battery
Adhere to all Notices and Cautions.
Always keep a dry chemical (Class B) fire
extinguisher near the work area.
-
Always use a backup wrench when loosening or
tightening a screw couple fitting.
The torque on a screw fitting is
30 N-m (22 lb.
ft.).
Pipe is used on all MPFI, TPI, SFI, and TBI
applications. Fittings require the use of an
"0"
Ring. Replace all pipe with the same type of pipe
and fittings that were removed.
All fuel pipes must meet GM Specification
124-M, or its equivalent.
All fuel hoses must meet GM Specification
6163-M, or its equivalent.
Do not replace fuel pipe with fuel hose.
voltage is required.
@ On MPFI, TPI, SF1 and TBI systems, always A1cohol-ln-Fuel
relieve the line pressure before servicing any fuel Certain driveability complaints such as
system components. hesitation, lack of power, stall, no start, etc., may be
@ Do not repair the fuel system until you have read caused
by an excessive amount of alcohol-in-fuel. The
the copy and checked the illustrations relating to complaints
may be due to fuel system corrosion and
that repair. subsequent
fuel filter plugging, deterioration of rubber
Page 434 of 1825

ENGINE FUEL 6C.3
a Fuel feed and return pipes are secured to the
underbody with clamps and screw assemblies.
The pipes should be inspected occasionally for
leaks, kinks or dents.
e Follow the same routing as the original pipe.
e Pipes must be properly secured to the frame to
prevent chafing. A minimum of 6 mm
(1/4")
clearance must be maintained around a pipe to
prevent contact and chafing.
MPFl Fuel Pipes
Due to the fact that fuel pipes are under high
pressure, these systems require special consideration for service.
Many feed and return pipes use screw couplings
with
"0" Rings. Any time these fittings are loosened
to service or replace components, ensure that:
a A backup wrench is used while loosening and
tightening the fitting.
e Check all "0" rings at fitting locations (if
applicable) for cuts or any damage and replace
any that appear worn or damaged.
e Use correct torque when tightening fittings.
If pipes are replaced always use original
equipment parts, or parts that meet GM
specifications.
Fuel and Vapor Hoses
NOTICE: Fuel and vapor hoses are specially
manufactured. If replacement becomes necessary,
it is important to use only replacement hoses
meeting GM Specification 6163-M. These hoses
are identified with the words "Fluoroelastomer"
on them. Hoses not so marked could cause early
failure, or fail to meet emission standards.
e Do not use rubber hose within 4" of any part of
the exhaust system, or within
10" of the catalytic
converter.
FUEL PUMP
The electric fuel pump is in the fuel tank. The
tank has an outlet for a vapor return system. Any vapor
which forms is returned to the fuel tank along with hot
fuel through a separate line. This greatly reduces any
possibility of vapor lock by keeping cool fuel from the
tank constantly circulating through the fuel pump.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
To control fuel pump operation, a fuel pump
relay is used.
When the ignition switch is turned to "RUN"
position, the fuel pump relay activates the electric fuel
pump for
1.5 to 2.0 seconds to prime the injector(s). If
the ECM does not receive reference pulses from the
distributor after this time, the ECM signals the relay
to turn off the fuel pump. The relay will once again
activate the fuel pump when the
ECM receives
distributor reference pulses.
Fuel Filter
CAUTION: To reduce the risk of fire
and personal injury, it is necessary
to
relieve the fuel system pressure
before servicing fuel system
components. (See Fuel System
Pressure Relief.)
The inline filters can be found on the rear
crossmember of the vehicle. Always use a backup
wrench any time that the fuel filter is removed or
installed. Also make sure that a good
"0" Ring is used
at all screw couple locations. Torque on fittings is
30
N-m (22 lb. ft.).
FUEL TANK
The fuel tank is usually located under the rear of
the vehicle and a number of shapes and sizes are used
depending on the application.
The tank is held in place by two metal straps,
hinged (with a bolt through the hinge) and secured at
the opposite end with a nut and bolt assembly.
Anti-squeak pieces are used on top of the tank to
reduce rattles and other annoying noises.
The fuel tank, cap and lines should be inspected
for road damage, whch could cause leakage. Inspect
fuel cap for correct sealing and indications of physical
damage. Replace any damaged or malfunctioning
parts.
Before attempting service of any type on the fuel
tank, always
(1) remove negative battery cable from
battery, (2) place "no smoking" signs near work areas,
(3) be sure to have C02 fire extinguisher handy, (4)
wear safety glasses and
(5) siphon or pump fuel into an
explosion proof container.
Fuel Filler Gap
The fuel tank filler neck is equipped with a
screw-type cap. The threaded part of the cap requires
several turns counterclockwise to remove. The long
threaded area is designed to allow any remaining fuel
tank pressure to escape while the cap is being removed.
A built-in torque-limiting device prevents
overtightening. To install, turn the cap clockwise until
a clicking noise is heard. This signals that the correct
torque has been reached and the cap is fully seated.
N OTI G E: If a fuel filler cap requires replacement,
use only a cap with the same features. Failure to
use the correct cap can result in a serious
malfunction of the system.
Available on some models is an electric locking
fuel filler cap. Information on this option will be found
in Section
9E.
FUEL TANK FILLER NECK
To help prevent refueling with leaded gasoline,
the fuel filler neck on gasoline engine cars has a built-in
restrictor and deflector. The opening in the restrictor
will only admit the smaller unleaded gas nozzle spout,
which must be fully inserted to bypass the deflector.
Attempted refueling with a leaded gas nozzle or failure
Page 439 of 1825
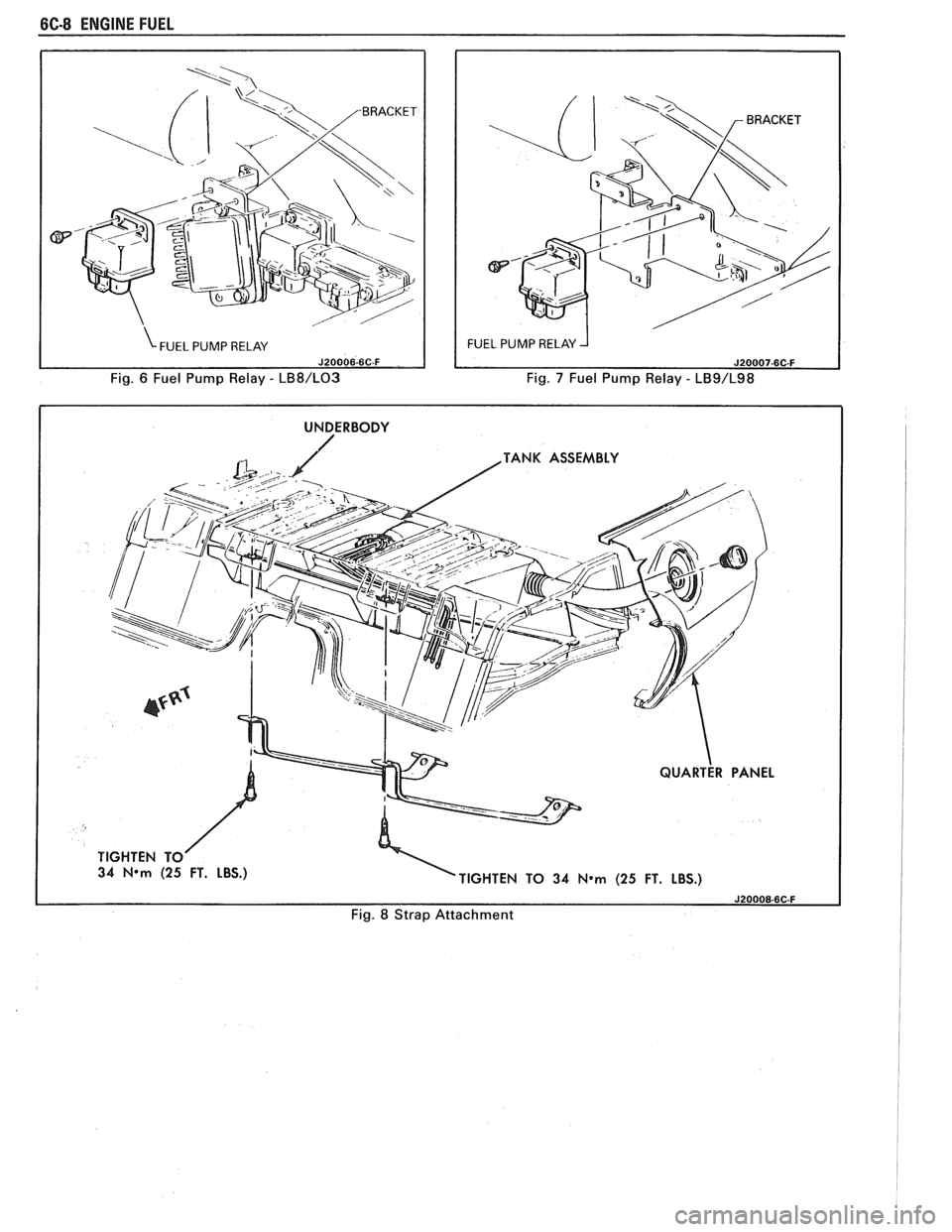
6C-8 ENGINE FUEL
Fig. 6 Fuel Pump Relay - LB8/L03 Fig. 7 Fuel Pump Relay - LB9/L98
I UNDERBODY I
TANK ASSEMBLY
34
N*m (25 FT. LBS.)
TIGHTEN TO 34 N*m (25 FT. LBS.)
Fig. 8 Strap Attachment
Page 480 of 1825
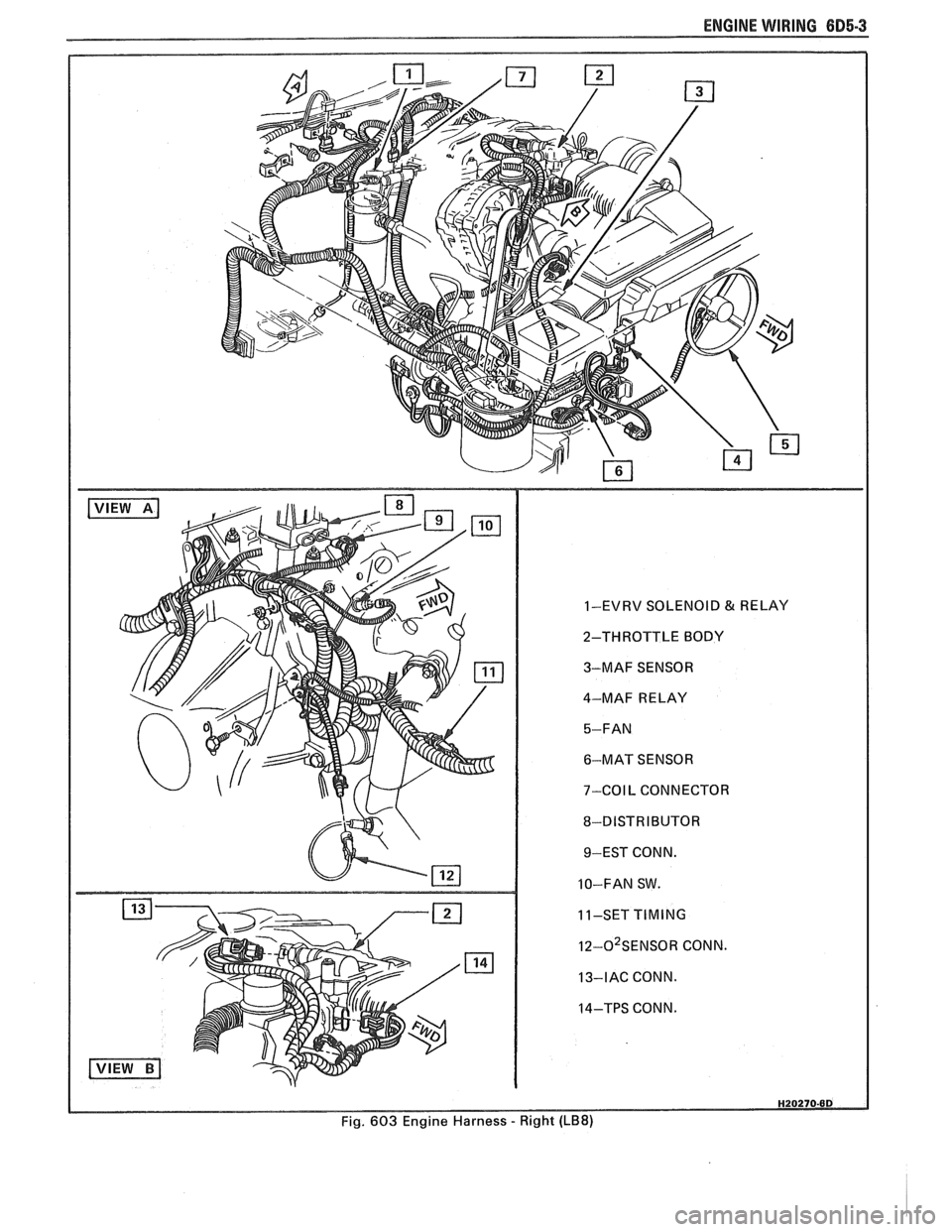
ENGINE WIRING 605.3
1-EVRV SOLENOID & RELAY
2-THROTTLE BODY
3-MAF SENSOR
4-MAF RELAY
6-MAT SENSOR
7-COIL CONNECTOR
8-DISTRIBUTOR 9-EST CONN.
10-FAN SW.
11-SET
TIMING
I~-O~SENSOR CONN.
13-IAC CONN.
14-TPS CONN.
Fig. 603 Engine Harness
- Right (LB8)
Page 481 of 1825
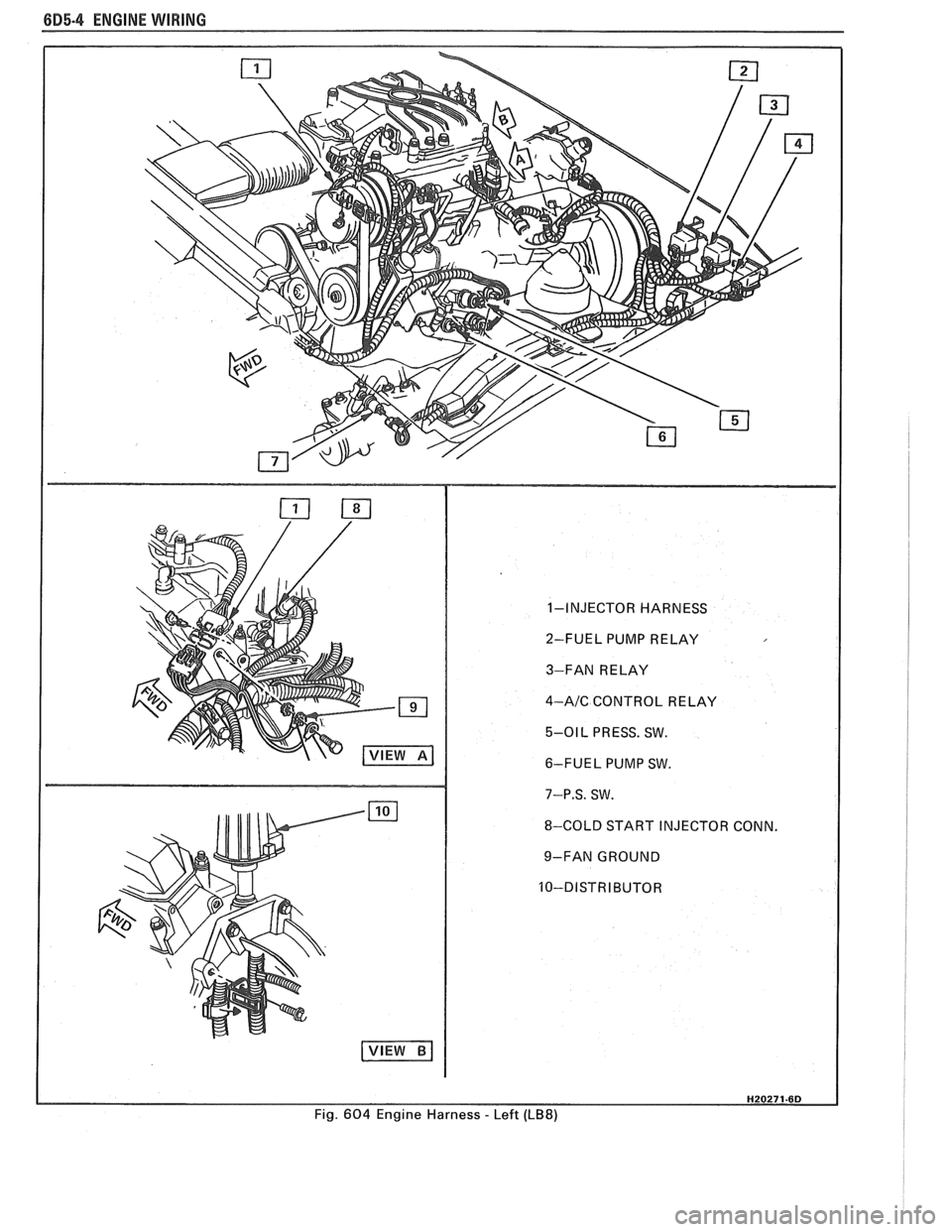
6D5-4 ENGINE WIRING
1-INJECTOR HARNESS
2-FUEL PUMP RELAY
3-FAN RELAY
4-AIC CONTROL RELAY
5-01 L PRESS. SW.
6-FUEL PUMP SW.
7-P.S. SW.
8-COLD START INJECTOR CONN.
9-FAN GROUND
Fig.
604 Engine Harness - Left (LB8)
Page 488 of 1825

DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.OL (VIN E) 6E2-3
........ FUEL METER COVER ASSEMBLY C2-7
FUEL INJECTOR ASSEMBLIES .......... C2-8
FUEL METER BODY ASSEMBLY ......... C2-9
..... THROTTLE POSITION SENSOR (TPS) C2-10
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) VALVE ........ 62-1 1
THROTTLE BODY ASSEMBLY
.......... C2-11
MINIMUM IDLE SPEED CHECK .......... C2-12
... THROTTLE BODY INJECTION (TBI) UNIT C2-13
FUEL
HOSEIPIPE ASSEMBLIES .......... C2-13
Materials ...................... C2-13
Fuel Line Repair .................. C2-13
FUEL PUMP RELAY .................. C2-13
............... OILPRESSURESWITCH C2-13
PARTS INFORMATION ................. C2-14
Idle Air Control (IAC) Valve Check
Chart C-2C
..................... C2-16
SECTION C3
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C3-1
........................ PURPOSE C3-1
VAPOR CANISTER
................... C3-1
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION SYSTEM
....... C3-1
IN-TANK PRESSURE CONTROL VALVE
. . C3-2
.... RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION C3-2
........................ DIAGNOSIS C3-2
VISUAL CHECK OF CANISTER
.......... C3-2
CANISTER PURGE SOLENOID
.......... C3-2
ON-CAR SERVICE ................. C3-2
FUEL VAPOR CANISTER
R/R ............ C3-2
CANISTER HOSES
.................... C3-2
PARTS INFORMATION ................ C3-2
Canister Purge Valve Check
Chart C-3
...................... C3-4
SECTION
C4
IGNITION SYSTEM I EST
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C4-1
PURPOSE ........................ C4-1
OPERATION ...................... C4-1
.. DIAGNOSIS ................... ... C4-1
RESULTS OF INCORRECT EST OPER ...... C4-1
HOW CODE 42 IS DETERMINED ....... C4-2
CODE12 ........................ C4-2
CHECKING EST PERFORMANCE ........ C4-2
ON-CAR SERVICE .................... C4-2
SETTINGTIMING .................. C4-2
PARTS INFORMATION ................ C4-2
Ignition System Check
Chart C-4
................... .. . C4-4
SECTION C5
ELECTRONIC SPARK CONTROL (ESC) SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
................ C5-1
PURPOSE ..*...................... C5-1
OPERATION
....................... C5-1
DIAGNOSIS
......................... C5-1
RESULTS OF INCORRECT ESC OPERATION
. C5-1
ON-CAR SERVICE
..................... C5-1 ESC
KNOCK SENSOR
................ C5-1
ESCMODULE
...................... C5-1
PARTS INFORMATION ................. C5-2
Electronic Spark Control (ESC) System Check
Chart C-5
...................... C5-4
SECTION C6
AIR INJECTION REACTION (A.I.R.) SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C6-1
PURPOSE
.*....................... C6-1
OPERATION
...................... C6-1
AIR CONTROL PEDES VALVE .......... C6-1
RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION
.... C6-2
DIAGNOSIS
........................ C6-2
OPERATIONAL CHECKS
.....*........ C6-2
AirPump ...................... C6-2
Hoses and Pipes
................. C6-3
Check Valve
.................... C6-3
ON-CAR SERVICE
.................... C6-3
DRIVEBELT ...................... C6-3
AIR INJECTION PUMP
............... C6-3
AIR INJECTION CONTROL
(PEDES) VALVE
.................. C6-3
AIR INJECTION CHECK VALVE ......... C6-4
PARTS INFORMATION
................ C6-4
AIR Management Check
. Pedes Valve
Chart C-6
..................... C6-6
SECTION C7
EXHAUST GAS RECIRCULATION (EGR) SYSTEM
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C7-1
PURPOSE
........................ C7-1
OPERATION
...................... C7-1
EGRCONTROL
..................... C7-1
NEGATIVE BACKPRESSURE VALVE
...... C7-1
EGR VALVE IDENTIFICATION
.......... C7-2
RESULTS OF INCORRECT OPERATION
.... C7-2
DIAGNOSIS
......................... C7-2
ON-CAR SERVICE
..................... C7-2
EGRVALVE
....................... C7-2
EGR Manifold Passage
............. C7-2
EGR CONTROL SOLENOID
............. C7-3
PARTS INFORMATION
................. C7-3
Exhaust Gas Recirculation (EGR) Check
Chart C-7
...................... C7-4
SECTION
C8
TRANSMISSION CONVERTER CLUTCH
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
............... C8-1
PURPOSE
........................ C8-1
OPERATION
...................... C8-1
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
............... C8-1
RESULTS OF INCORRECT TCC
OPERATION
..................... C8-2
DIAGNOSIS
......................... C8-2
ON-CAR SERVICE .................... C8-2
PARTS INFORMATION ................. C8-2