relay PONTIAC FIERO 1988 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: PONTIAC, Model Year: 1988, Model line: FIERO, Model: PONTIAC FIERO 1988Pages: 1825, PDF Size: 99.44 MB
Page 44 of 1825

AIR CONDITIONING 1B-1
SECTION 1B
R COND
When performing air conditioning diagnosis on vehicles equipped with a catalytic converter, it will be necessary to
WARM the engine to a NORMAL operating temperature BEFORE attempting to idle the engine for periods greater
than five
(5) minutes. Once the engine attains normal idle, diagnosis and adjustments can be made.
CONTENTS
.................. General Description .................................. 1B-1 Accumulator Assembly Service .1B-19
.......................... C.C.O.T. A!C System ................................ 1B-1 On-Vehicle Sewice ..... 1B-20
....................................... System Components - Functional ................. 1B-2 Blower Motor .1B-20
..................................... System Components - Control ..................... 1B-3 Hi-Blower Relay 1B-20
...................................... Relays and Switches ................................... 1B-3 Blower Resistor 1B-20
Diagnosis ................................................. 1B-5 Controller, Blower Switch or Vacuum
................................................ Testing the Refrigerant System ...................... 1B-5 Valve .lB-20
Insufficient Cooling "Quick-Check Temperature Control Cable ....................... .1B-20
.................................... Procedure.. ............................................. 1B-5 Vacuum
Harness .lB-20
C.C.O.T. A/C System Diagnostic Control Wiring Harness ........................... .1B-20
..... ................................. Procedure.. ............................................. 1B-8 Heater
Core .. .lB-21
................................ Leak Testing ........................................... 1B-12 Lower Heater Outlet 1B-21
............................... Service Procedures ................................. .1B-12 Heater Module Case .lB-21
.......................... O-Ring Replacement ................................ .1B- 12 Pressure Cycling Switch .1B-21
....................................... Handling Refrigerant- 12 ............................ .1B- 13 Vacuum Tank .lB-21
Discharging, Adding Oil, Evacuating Liquid Line .......................................... .1B-23
and
Charging Procedures - AIC Accumulator ......................................... .1B-23
.................................... Systems .............................................. .1B-14 Evaporator Core .1B-24
In-Line Air Conditioning Evaporator Case .................................... .1B-24
.......................................... Filter
Installation.. .................................. .1B- 18 Compressor .lB-24
.............................................
................ Expansion Tube (Orifice) Service .1 B- 19 Condenser IB-24
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
All engines are equipped with a fixed displace- evaporator temperature. The pressure cycling switch
ment (R-4) air conditioning compressor. This
com- is the freeze protection device in the system and
pressor may cycle on and off under normal air
senses refrigerant pressure on the suction side of the
conditioning demand. system. This switch is located on a standard
Schrader- -
All air conditioning systems that use the fixed
displacement R-4 compressor are referred to as
C. C.O.T. (Cycling Clutch, Orifice Tube) type sys-
tems. This is the same system that has been used on
all General Motors vehicles in the past several years.
The C.C.O.T. NG System
The Cycling Clutch Orifice Tube (C.C.O.T.)
refrigeration system is designed to cycle a compressor
on and off to maintain desired cooling and to prevent
evaporator freeze. Passenger compartment comfort is
maintained by the temperature lever on the controller.
Control of the refrigeration cycle (on and off
operation of the compressor) is done with a switch
which senses low-side pressure as an indicator of type
valve low-side fitting. During air temperatures
over 10°C
(50°F), the equalized pressures within the
charged
A/C system will close the contacts of the
pressure switch. When an air conditioning mode
(max, norm, bi-level, defrost) is selected, electrical
energy is supplied to the compressor clutch coil. AS
the compressor reduces the evaporator pressure
to
approximately 175 kPa (25 psi), the pressure switch
will open, de-energizing the compressor clutch.
As
the system equalizes and the pressure reaches approxl-
mately 315 kPa (46 psi), the pressure switch contacts
close, re-energizing the clutch coil. This cycling
coy
tinues and maintains average evaporator discharge air
temperature at approximately 1°C (33°F). Because of
this cycling, some slight increases and decreases of
engine speedlpower may be noticed under certain con-
ditions. This is normal as the system is designed
to
cycle to maintain desired cooling, thus preventing
evaporator freeze-up.
Page 46 of 1825

AIR CONDITIONING 1 B-3
A low-side pressure Schrader valve service fit-
ting is located near the top of the accumulator. A
similar Schrader fitting may be provided for mounting
the pressure cycling switch. It is not necessary to dis-
charge the system to replace the switch. The accumu-
lator is serviced only as a replacement assembly.
Heater Core
The heater core heats the air before it enters the
car. Engine coolant is circulated through the core to
heat the outside air passing over the fins of the core.
The core is functional at all times (no water valve) and
may be used to temper conditioned air in
A/C mode,
as well as heat or vent mode.
SYSTEM COMPONENTS --- CON"FOL
Controller
The operation of the A/C system is controlled by
the switches and the lever on the control head. The
compressor clutch and blower are connected electri-
cally to the control head by a wiring harness. The
blower circuit is open in the off mode and air flow is
provided by the four blower speeds available in the
remaining modes. Cooled and dehumidified air is
available in the max, normal, bi-level and defrost
modes.
Temperature is controlled by the position of the
temperature lever on the control head. A cable con-
nects this lever to the temperature door which controls
air flow through the heater core. As the temperature
lever is moved through its range of travel, a sliding
clip on the cable at the temperature valve connection
should assume a position assuring that the temperature
door will seat in both extreme positions. Temperature
door position is independent of mode selection. The
temperature cable attaches to the right side of the air
conditioning module. The temperature door on some
models is controlled electrically, thereby eliminating
the need for the temperature cable.
The electric engine cooling fan on some cars is
not part of the
A/C system; however, the fan is
operational any time the
A/C control is in Max.,
Norm, or Bi-Level modes. Some models provide for
engine cooling fan operation when the controller is in
the defrost mode. This added feature is part of the
A/C
controller function and is aimed at preventing exces-
sive compressor head temperatures. It also allows the
A/C system to function more efficiently. On some
models during road speed (above
35 mph) conditions
when air flow through the condenser coil is adequate
for efficient cooling, the engine cooling fan will be
turned off. The operation of the cooling fan is con-
trolled by the ECM through the cooling fan relay.
Complete wiring diagrams and diagnosis for the
AIC Electrical System are in Section 8A. Section 8A
also contains additional diagnostic information
regarding air flows and vacuum logic.
Vacuum Lines
Vacuum lines are molded to a connector which
is attached to a vacuum control switch on the control
head assembly.
In case of leakage or hose collapse, it will not be
necessary to replace the entire harness assembly.
Replacement can be made by cutting the hose and
inserting a plastic connector. If an entire hose must be
replaced, cut all hoses off at the connector and then
attach hoses directly to the control head vacuum
switch. (NOTE: The Fiero uses an electric motor to
control mode selection. Therefore, it will not have a
vacuum harness.
)
Vacuum Tank
During heavy acceleration, the vacuum supply
from the carburetor drops. A check valve in the vac-
uum tank maintains vacuum so that, under load condi-
tions, vacuum will be available for continuous use.
REWVS AND SWITCHES
High-Pressure Compresssr Gut-OFF Switch
The high-side, high-pressure cut-off switch in
the rear head of the compressor is a protective device
intended to prevent excessive compressor head pres-
sures and reduce the chance of refrigerant escape
through a safety relief valve. Normally closed, this
switch will open the circuit at a high-side pressure of
approximately 2700
kPa (430 psi 9 20 psi) and
reclose the circuit at approximately 1379 kPa (200 psi
9 50 psi).
Lsw-Pressure Cut-On Switch
Compressor protection is provided on some cars
by a low-pressure cut-off switch which will open in
the event of a low-charge condition. This switch can
be located in the liquid line or in the rear head of the
compressor. This switch will also keep the compres-
sor from running during cold weather.
Pressure eyesing Switch
The refrigeration cycle (on and off operation of
the compressor) is controlled by a switch which
senses the low-side pressure as an indicator of evapo-
rator temperature. The pressure cycling switch is the
freeze protection device in the system and senses
refrigerant pressure on the suction side of the system.
This switch is located on a standard Schrader-type
valve low-side fitting. This switch also provides com-
pressor cut-off during cold weather.
Additional compressor protection results from
the operating characteristics of the low-side pressure
cycling system. If a massive discharge occurs or the
orifice tube becomes plugged, low-side pressures
could be insufficient to close the contacts of the pres-
sure switch. In the event of a low charge, insufficient
cooling accompanied by rapid compressor clutch
cycling will be noticed at high air temperatures.
Page 47 of 1825
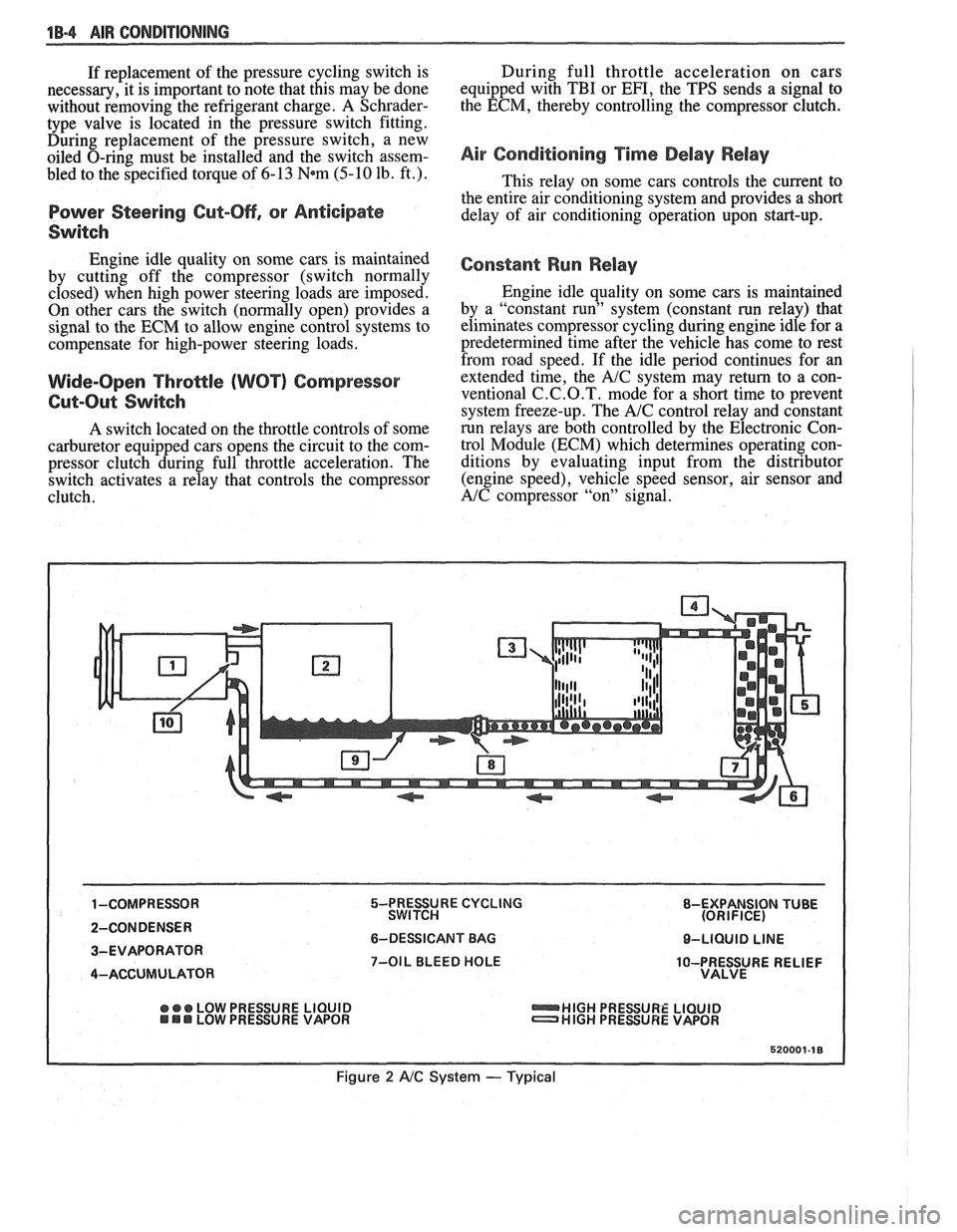
18-4 AIR CONDITIONING
If replacement of the pressure cycling switch is
necessary, it is important to note that this may be done
without removing the refrigerant charge.
A Schrader-
type valve is located in the pressure switch fitting.
During replacement of the pressure switch, a new
oiled O-ring must be installed and the switch assem-
bled to the specified torque of
6- 13 N*m (5- 10 lb. ft.).
Power Steering Gut-OH, or Anticipate
Switch
Engine idle quality on some cars is maintained
by cutting off the compressor (switch normally
closed) when high power steering loads are imposed.
On other cars the switch (normally open) provides a
signal to the ECM to allow engine control systems to
compensate for high-power steering loads.
Wide-Open Tkroale (WOT) Compressor
Cut-Out
Switch
A switch located on the throttle corltrols of some
carburetor equipped cars opens the circuit to the com-
pressor clutch during full throttle acceleration. The
switch activates a relay that controls the compressor
clutch. During full throttle acceleration
on cars
equipped with TBI or
Em, the TPS sends a signal to
the ECM, thereby controlling the compressor clutch.
Air Conditioning Time Delay Relay
This relay on some cars controls the current to
the entire air conditioning system and provides a short
delay of air conditioning operation upon start-up.
Constant Run Relay
Engine idle quality on some cars is maintained
by a "constant run" system (constant run relay) that
eliminates compressor cycling during engine idle for a
predetermined time after the vehicle has come to rest
from road speed.
If the idle period continues for an
extended time, the
A/C system may return to a con-
ventional C.C.O.T. mode for a short time to prevent
system freeze-up. The
A/C control relay and constant
run relays are both controlled by the Electronic Con-
trol Module (ECM) which determines operating con-
ditions by evaluating input from the distributor
(engine speed), vehicle speed sensor, air sensor and
A/C compressor "on" signal.
5-PRESSURE CYCLING 8-EXPANSION TUBE
SWITCH (ORIFICE)
6-DESSICANT BAG O-LIQUID LINE
7-OIL BLEED HOLE
10-PRESSURE RELIEF
VALVE
@ ee LOW PRESSURE LIQUID HIGH PRESSURE LIQUID LOW PRESURE VAPOR HIGH PRESSURE VAPOR
Figure 2 A/C System - Typical
Page 63 of 1825

18-28 AIR CONDITIONING
DO NOT REPLACE the accumulator assembly
when:
1. Merely a dent is found in the outer shell of the
accumulator.
2. A
vehicle is involved in a collision and no phys-
ical perforation to the accumulator is found.
OM-VEHICLE SERVICE
R-"1 CHARGING CAPACITIES
The 420ml (14 fl. oz.) disposable can of R-12
refrigerant is equivalent to .399 kg (. 88 lb.).
BLOWER MOTOR
a Remove or Disconnect
1. Disconnect negative battery cable.
2. Remove motor cooling tube.
3. Disconnect electrical connections.
4. Remove blower motor attaching screws, remove
motor and case assembly.
5. Loosen retaining nut and remove blower cage
from motor shaft.
6. Inspect blower cage for broken vanes, etc.
Replace if necessary.
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall. Replace
seals or sealant as required.
HI-BLOWER RELAY
Relay is a plug-in type with connector mounted
on top of the evaporator case.
BLOWER RESISTOR
Remove or Disconnect
1. Disconnect negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect electrical connections.
3. Remove two (2) screws, remove resistor.
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall.
CONTROLLER, BLOWER SWITCH OR
WCUUM VALVE
Remove or Disconnect
1. Disconnect negative battery cable.
2. Remove NC control-radio console trim plate.
3. Remove three (3) NC control retaining screws.
4. Pull A/C control out and disconnect electrical
and vacuum connections and remove tempera-
ture cable.
5. Remove A/C control and replace vacuum valve
or blower switch as required.
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall. Install
lower right screw in controller first to align con-
troller in console.
TEMPERATURE CONTROL CABLE,
VACUUM HARNESS
Remove or Disconnect
1. Remove the following hush panel(s):
a. Vacuum Harness - R.H. and L.H. hush
panel.
b. Temperature Cable
- R.H. hush panels.
Remove
controller/radio console trim plate.
Remove three (3) controller screws and pull
controller partially out of console.
Disconnect controller
end(s) of temperature
cable
andlor vacuum harness.
Disconnect component
end(s) of temperature
cable
andlor vacuum harness.
Install or Conned
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall. When
installing controller, install lower right screw
first to align controller location. Replace any
retaining straps, etc. removed.
2. Perform functional check of controller.
CONTROL WlRlNG HARNESS
a Remove or Disconnect
1. Disconnect negative battery cable.
2. Remove
control/radio console trim plate and
hush panels (see Section
8C).
3. Remove three (3) screws holding control in con-
sole and pull control out far enough to discon-
nect electrical and vacuum connector. Remove
controller.
4. Remove instrument panel carrier (see Section
8C).
5. Remove heater case covers (core and mode door
sides).
6. Remove two (2) interior screws and one (1)
exterior nut holding case to cowl. Pull left side
of case back to gain access to harness at cowl.
Case will still be retained by one (I) screw
behind the evaporator core
- do not attempt
complete removal of case. -
7. Loosen cowl grommet and disconnect purple
vacuum line.
Page 64 of 1825

AIR CONDITIONING 18-21
8. Disconnect blower motor
and blower resistor
electrical connection.
9. Remove hi-blower relay connector from evapo-
rator case.
10. Carefully pull
cowl grommet from cowl and pull
wiring
hmess into engine compartment.
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal procedure to
reinstall. When
reinstalling controller, install lower right screw
first to align controller.
ACNENTILATIONIDEFROSVER DUCTS
See section 8C for removal.
HEATER CORE
Remove or Disconnect
1. Negative battery cable.
2. Drain cooling system.
3. Remove heater inlet and outlet hoses
from
heater core.
4. Remove right lower hush panel (see Section
8C).
5. Remove right
lower I.P. trim panel (see Section
8C) .
6. Remove lower right I.P. carrier to cowl screw.
7. Remove ECM attaching screws and move to the
side.
8. Remove four
(4) heater case cover screws.
Upper left screw may be reached with a long
318 ' socket extension through the I.P. openings
exposed by removal of the lower right I.P. trim
panel. Carefully lift the lower right corner of the
I.P. to align socket extension.
9. Remove heater case cover.
10. Remove core support plate
and baffle screws.
- -
11. Remove
heater core, support plate and baffle
from case.
Install or Conned
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall. Restore
all seals
and/or sealant disturbed during removal
procedure.
2. Refill cooling system and check for leaks.
LOWER (FLOOR) )-IEA"FEB$OU"fET
Remove or Disconnect
1. Console. (See Section 8C.)
2. L.H. and R.H. hush panels.
3. Two (2) floor outlet retaining screws.
4. Floor outlet from core case.
lnstall or Connect
1. Floor outlet to core case.
2. Two (2) floor outlet retaining screws.
3. L.H. and R.H. hush panels.
4. Console.
HEATER MODULE (CASE)
Remove or Disconnect
1. Disconnect negative battery cable.
2. Drain cooling system.
3. Remove hush panels and instrument panel car-
rier (see Section
8C).
4. Remove lower heater outlets.
5. Disconnect control cables and vacuum hoses at
module and controller.
6. Remove heater core.
7. Remove two (2) interior screws and one (I)
exterior nut holding case to cowl.
8. Remove evaporator core.
9. Remove screw holding case to cowl from engine
compartment side.
10. Remove case (module).
11. Transfer usable parts to new case (module).
lnstall or Conned
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall.
2. Refill coolant system.
3. Recharge
A/C system.
4. Inspect A/C and cooling system for leaks.
NC PRESSURE CYCLING SWITCH
Do not discharge A/C system. Pressure cycling
switch is mounted on
a Schrader-type valve.
Remove or Disconnect
1. Disconnect switch electrical connection.
2. Remove switch.
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall. Tighten
switch to
4-5.5 N*m (35-49 in. lb.).
Ale CONTROL VACUUM TANK
Remove or Disconnect
1 . Disconnect vacuum hoses.
2. Remove vacuum
tank attaching screws, remove
tank.
lndall or Connect
1. Reverse removal procedure to
reinstall.
Page 67 of 1825
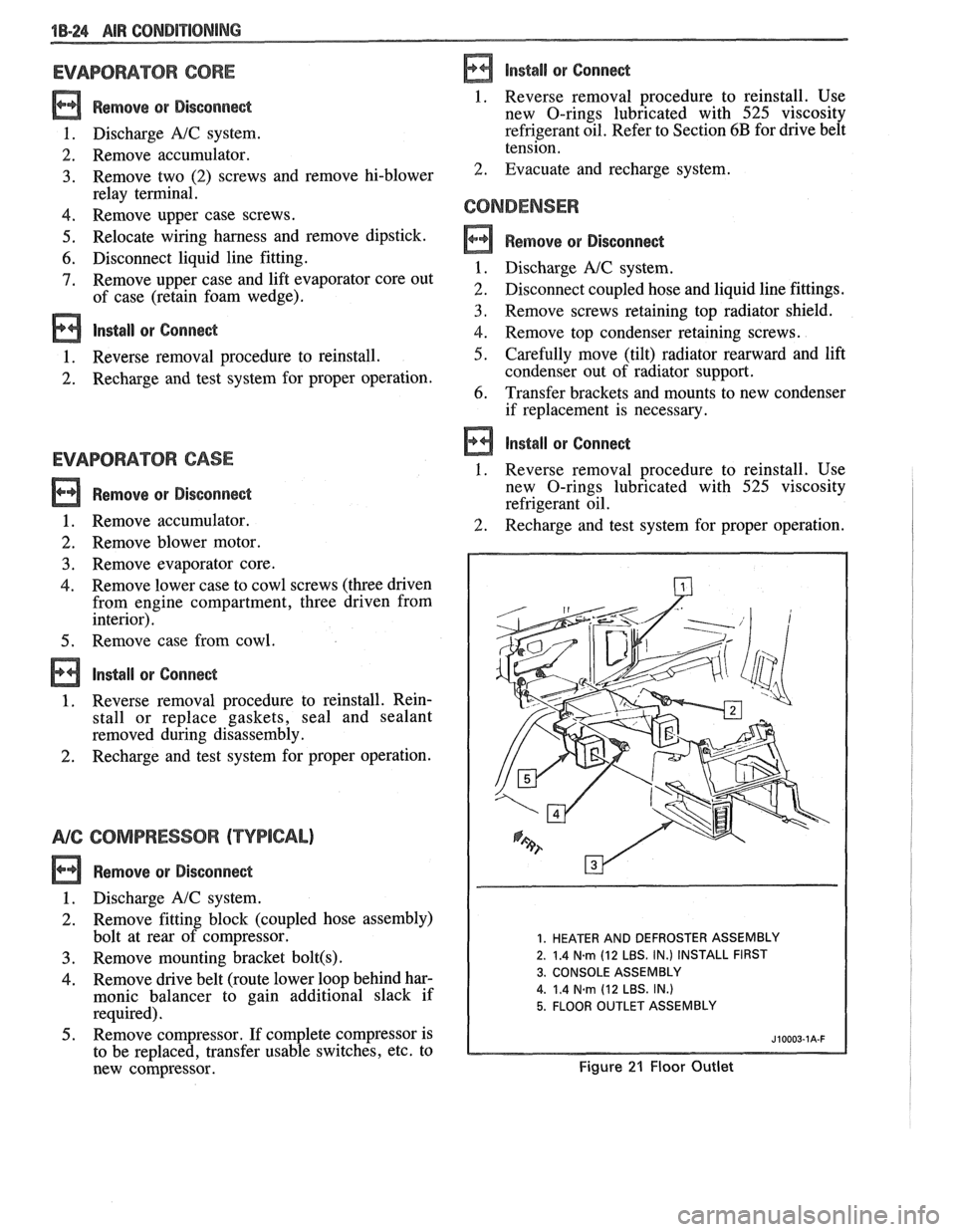
1B-24 AIR CONDPTIBNING
EVAPORATOR CORE
Remove QP Disconnect
1. Discharge A/C system.
2. Remove accumulator.
3. Remove two (2) screws and remove hi-blower
relay terminal.
4. Remove upper case screws.
5. Relocate wiring harness and remove dipstick.
6. Disconnect liquid line fitting.
7. Remove upper case and lift evaporator core out
of case (retain foam wedge).
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall.
2. Recharge and test system for proper operation.
EVAPBRAWORCASE
Remove or Disconnect
1. Remove accumulator.
2. Remove blower motor.
3. Remove evaporator core.
Remove lower case to cowl screws (three driven from engine compartment, three driven from
interior).
Remove case from cowl.
Install or Connect
Reverse removal procedure to reinstall. Rein-
stall or replace gaskets, seal and sealant
removed during disassembly.
Recharge and test system for proper operation.
NG COMPRESSOR (TYPICAL)
Remove or Disconnect
1. Discharge A/C system.
2. Remove fitting block (coupled hose assembly)
bolt at rear of compressor.
3. Remove mounting bracket bolt(s) .
4. Remove drive belt (route lower loop behind har-
monic balancer to gain additional slack if
required).
5. Remove compressor. If complete compressor is
to be replaced, transfer usable switches, etc. to
new compressor.
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal
procedure to reinstall. Use
new O-rings lubricated with
525 viscosity
refrigerant oil. Refer to Section
6B for drive belt
tension.
2. Evacuate and recharge system.
CONDENSER
a Remove or Disconnect
1. Discharge A/C system.
2. Disconnect coupled hose and liquid line fittings.
3, Remove screws retaining top radiator shield.
4. Remove top condenser retaining screws.
5. Carefully move (tilt) radiator rearward and lift
condenser out of radiator support.
6. Transfer brackets and mounts to new condenser
if replacement is necessary.
Install or Connect
1. Reverse removal procedure to reinstall. Use
new O-rings lubricated with
525 viscosity
refrigerant oil.
2. Recharge and test system for proper operation.
1. HEATER AND DEFROSTER ASSEMBLY
2. 1.4
N.m (12 LBS. IN.) INSTALL FIRST
3. CONSOLE ASSEMBLY
4.
1.4 Narn (12 LBS. IN.)
5. FLOOR OUTLET ASSEMBLY
Figure 21 Floor Outlet
Page 72 of 1825
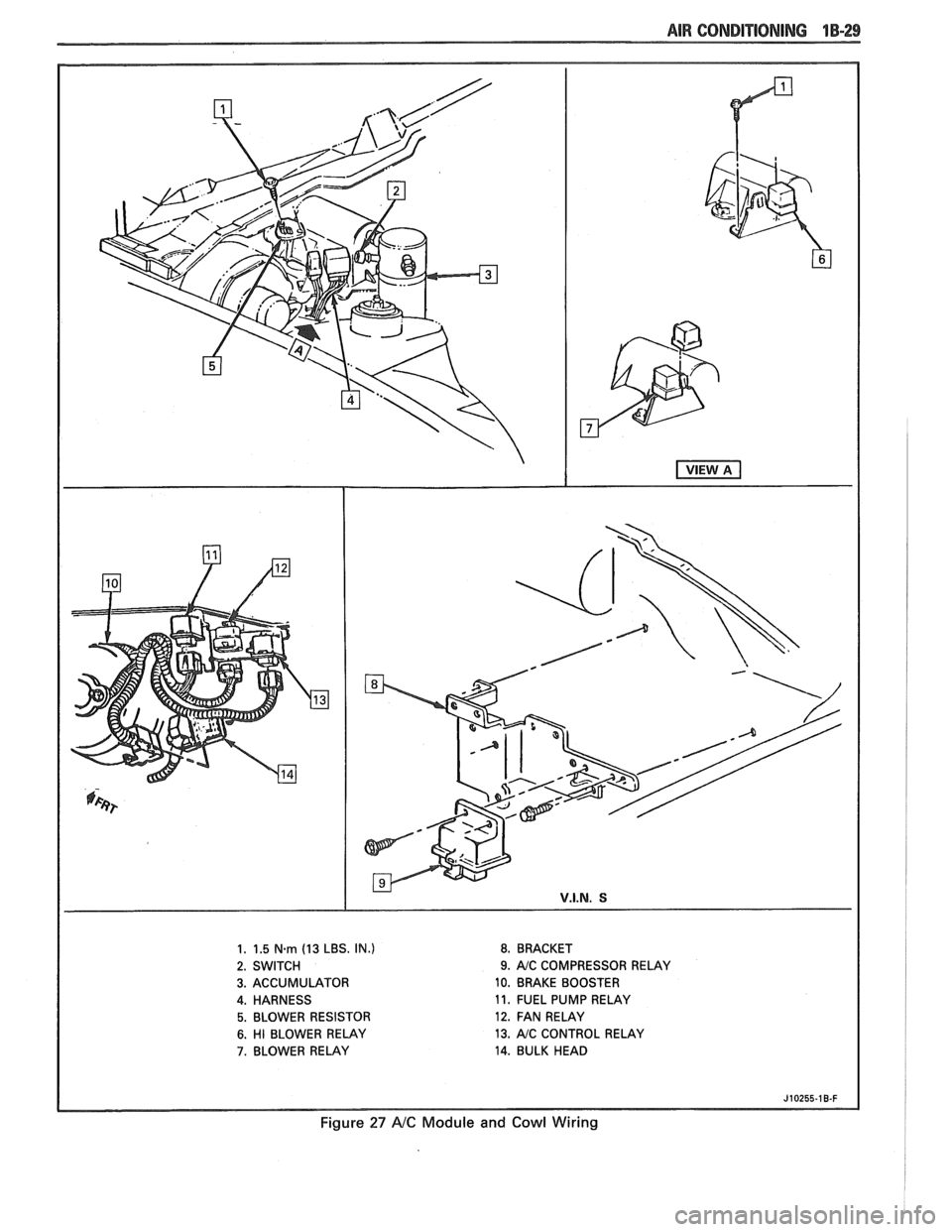
AIR CONDITIONING 1B-29
1. 1.5 N.m (13 LBS. IN.) 8. BRACKET
2. SWITCH
9. AJC COMPRESSOR RELAY
3. ACCUMULATOR 10. BRAKE BOOSTER
4. HARNESS 11.
FUEL PUMP RELAY
5. BLOWER RESISTOR 12. FAN RELAY
6. HI BLOWER RELAY 13. AJC CONTROL
RELAY
7. BLOWER RELAY 14. BULK HEAD
J10255-18-F
Figure 27 A/C Module and Cowl Wiring
Page 188 of 1825

STEERING LINKAGE 3B6-1
SECTION 3B6
STEERING LINKAGE
The following notice applies to one or more steps in the assembly
procedure of components in this portion of the manual as Notice indicated at
appropriate locations by the terminology "See Caution on Page
1 of this
Section
" .
NOTICE: These fasteners are important attaching parts in that they
could affect the performance of vital components and systems,
andlor could
result in major repair expense. They must be replaced with one of the same
part number or with an equivalent part if replacement becomes necessary. Do
not use a replacement part of lesser quality or substitute design. Torque
values must be used as specified during reassembly to assure proper retention
of these parts. For prevailing torque
nut(s) and bolt(s), refer to the "Reuse of
Prevailing Torque
Nut(s) and Bolt(s)" chart in Section 10.
CONTENTS
General Description ........................................... 3B6- 1 Relay Rod ............................................................ 3B6-3
Maintenance and Adjustments ............................... 3B6- I Idler Arm ............................................................. 3B6-4
On-Car Service ........................................................ 3B6-2 Pitman Arm ......................................................... 3B6-5
Tie Rods .............................................................. 3B6-2 Specifications ........................................................... 3B6-6
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
A parallelogram type steering linkage connects both
steering gear. The right end of the relay rod is supported by
front wheels to the steering gear through the
pitman arm,
the idler arm which pivots on a support attached to the
The right and left tie rods are attached to the steering arms
frame rail. The
pitman arm and idler arm remain parallel to
and to the relay rod by ball studs. The left end of the relay
each other while they move through symmetrical arcs. See
rod is supported by the
pitman arm, which is driven by the Fig. 3B6-2.
MAONTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
CHELKlNC STtLRING LINKAGE WEIR A? VltlItD FROhl ABOVL
POSITION DIAL INDICATOR
-TO CHECK MOVEMENT
AT THIS POINT
FRONT
OF
MOVE WHEEL IN AND OUT AT FRONT AND BACK
Fig. 3B6-1--Checking Linkage Wear
SUSPENSION AND STEERING LINKAGE CHECK
1. Raise car on one side at frame torque box located
directly behind the front wheel so that tire is
approximately one inch off the floor.
2. Position dial indicator as shown in Fig.
3B6- I .,
3. Position steering wheel so that it is in the locked
position.
4. Grasp front wheel as shown in Fig.
3B6- I. With wheels
in straight ahead position, move wheel back and forth
without moving steering wheel. Gage reading should
not exceed 2.74 mm
(. 108 ").
5. If gage reading is not within specifications, a check
should be made of all suspension and linkage gears.
RELAY ROD HEIGHT ADJUSTMENT
The relay rod position can be adjusted at the idler arm
attach men^. It is important for the height adjustment to be
equal from side-to-side. If not adjusted properly, right-hand
turns and left-hand turns could exhibit differell1
characteristics in handling. This is sometimes called
"orbital steer." Refer to Fig.3B6-5 for setting relay rod
height.
Page 189 of 1825

386-2 STEERING LINKAGE
LUBRICATION ADJUSTMENTS
The steering linkage should be lubricated with any
water resistant
EP type chassis lubricant at specified Toeein
intervals. Lubrication points and additional information on Adjust
the steering linkage for proper toe-in setting as
chassis lubrication can be found in Section
OB. outlined in Section 3A.
ON-CAR SERVICE 3. To remove outer ball stud, use a tool such as
RELAY ROD
Fig. 3B6-2--Series Linkage Components
TIE RODS
There are two tie rod assemblies. Each assembly is of
five piece construction, consisting of a sleeve, two clamps
and two tie rod ends. The ends are threaded into the sleeve
and locked with the clamps.
Right and left hand threads are
provided to facilitate toe-in adustment and steering gear
centering.
The tie rod ends are self-adjusting for wear and require
no attention in service other than periodic lubrication and
occasional inspection to see that ball studs are tight.
Tie rod adjuster components often become rusted
in
service. In such cases, it is recommended that if the torquc
required to remove the nut from thc bolt after break:iw:~>
exceeds 9 N.m (7 Ib, ft.), discard the nuts and bolth. Appl!
any penetrating oil betwoon thc clamp and tube ;~nd roliitc
the clamps until they movt. frcely. Install nc\4 bolts and nuts
having the same part number to assure proper clamping at
the specified nut torque.
Removal
I. qaise vehicle on hoiht.
2. Remove cotter pins and nuts from ball studs.
5-243 19-01, or 5-6627 as shown in Fig. 3B6-3
NOTICE: Do not attempt to disengage the joint by
driving a wedge between the joint and the knuckle,
because seal damage could result.
4. Remove inner ball stud from relay rod using same
procedure as described in Step 3.
5. To remove tie rod ends from tie rods, loosen clamp bolts
and unscrew end assemblies.
Installation
NOTICE: See NOTICE on page I of this section
regarding the fasteners referred to in step
4.
1. If the tie rod ends were removed, lubricate the tie rod
threads with any
EP type Chassis lube and install ends
on tie rod making sure both ends are threaded an equal
distance from the tie rod.
2. Make sure that the threads on the ball stud and in the
ball stud nuts are clean and smooth. If threads are not
clean and smooth, ball studs may turn in tie rod ends
when attempting to tighten nut. In addition tapered
surfaces should be clean and free from grease. Install
seals on ball studs.
3. Install ball studs in steering arms and relay rod.
4. Torque nuts to 48N.m (35 Ib. ft.). Then tighten nuts
enough to align the slot in the nut with the hole in the
stud. Install cotter pins. Lubricate tie rod
end\.
5. Lower vehicle to floor.
Fig. 3B6-3--Freeing Ball Stud
Page 190 of 1825
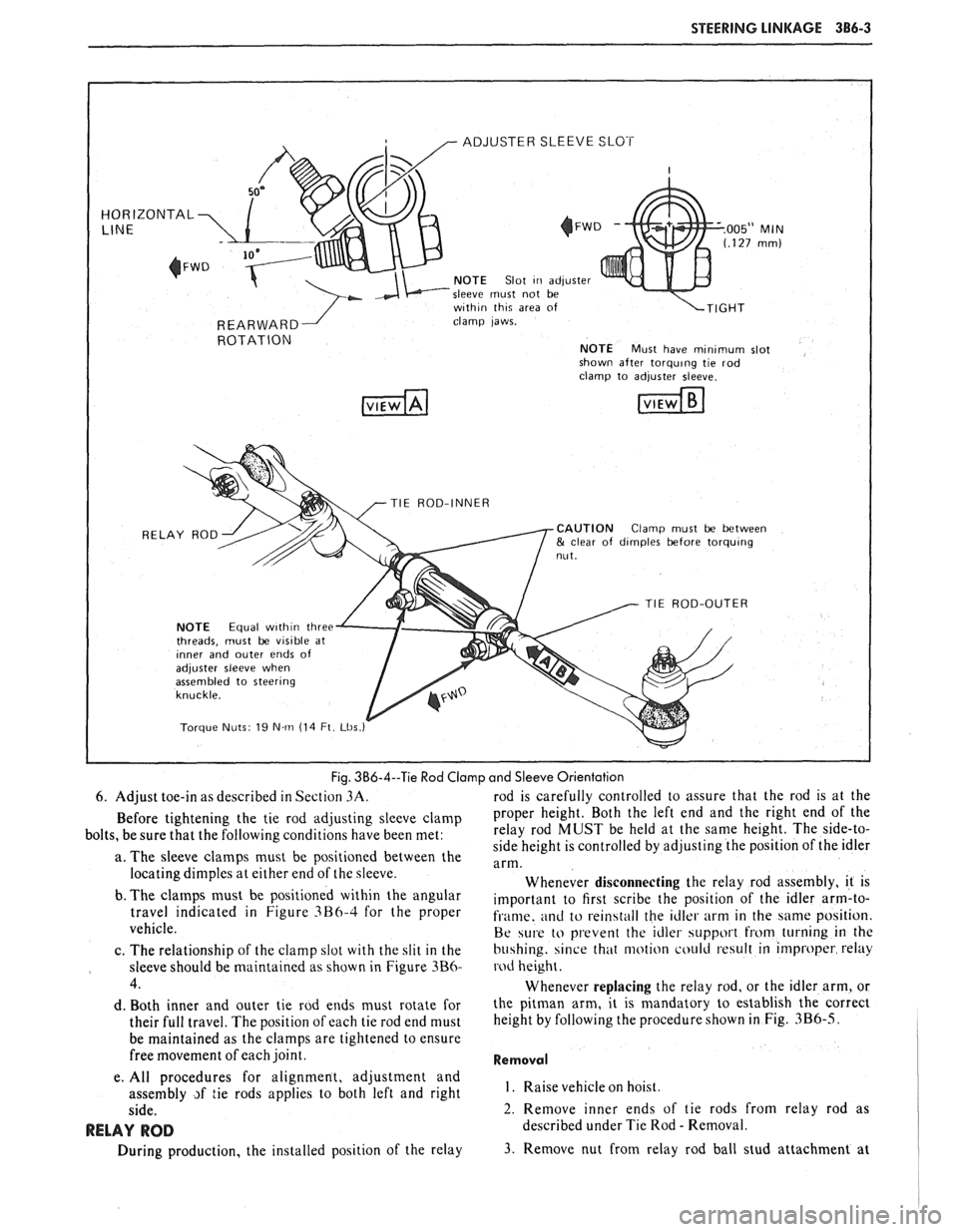
STEERING LINKAGE 386-3
ADJUSTER SLEEVE SLOT
HORIZONTAL
NOTE Slot Iri adjuster
sleeve must not be
w~th~n th~q area of
clamp laws.
ROTATION NOTE Must have mlnlmum slot
shown after torqulng tie rod
TIE ROD-INNER
RELAY ROD
CAUTION Clamp must be between & clear of d~mples before torqulng
TIE ROD-OUTER
NOTE Equal w~th~n three
threads, must be vis~ble at Inner and outer ends of adjuster sleeve when
assembled to steerlng
Torque Nuts 19 N m (14 Ft Lbs
Fig. 3B6-4--Tie Rod Clamp and Sleeve Orientation
6. Adjust toe-in as described in Section
3A. rod is carefully controlled to assure that the rod is at the
Before tightening the tie rod adjusting sleeve clamp Proper height. Both the left end and the right end of the
bolts, be sure that the following conditions have been met: relay
rod MUST be held at the same height. The side-to-
side height is controlled by adjusting the position of the idler
a. The sleeve clamps must be positioned between the
arm. locating dimples at either end of the sleeve.
Whenever disconnecting the relay rod assembly, it is
b. The
clalnps must be positioned within the angular important to first scribe the position of the idler arm-to- travel indicated in Figure 3B6-4 for the Proper fi.ame. and to rein4tall the idler arm in the same position.
vehicle.
Be w1.e to prevent the idler support hom turning in the
c. The relationship of the clamp slot with the slit in the
bu4hing. since that motion could result in improper relay
sleeve should be maintained as shown in Figure
3B6- rod height.
4. Whenever replacing the relay rod, or the idler arm, or
d. Both inner and outer tie rod ends must rotate for the pitman arm, it is mandatory to establish the correct
their full travel. The position of each tie rod end must height
by following the procedure shown
in Fig. 3B6-5.
be maintained as the clamps are tightened to ensure
free movement of each joint.
Removal
e. All procedures for alignment, adjustment and
assembly
~f tie rods applies to both left and right I. Raise vehicle hoist.
side. 2. Remove inner ends of tie rods from relay rod as
RELAY ROD described under Tie Rod - Removal.
During production, the installed position of the relay
3. Remove nut from relay rod ball stud attachment at