sensor RENAULT SCENIC 2011 J95 / 3.G Engine And Peripherals EDC16C36 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: RENAULT, Model Year: 2011, Model line: SCENIC, Model: RENAULT SCENIC 2011 J95 / 3.GPages: 431, PDF Size: 2.03 MB
Page 21 of 431

13B-21V9 MR-372-J84-13B450$050.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Features13B
EDC16 C36
Program No.: 91
Vdiag No.: 44, 4C, 48,
50, 54, 58
Catalysed particle filter management (for F9Q816 engine only):
The particle filter prevents the escape of carbon particles emitted by the engine but not yet removed from the
exhaust gases.
The particle filter is a microporous structure containing channels arranged so as to force-filter the exhaust gases.
The exhaust pipe consists of several components:
– an oxidation catalytic converter mounted after the turbocharger. This catalytic converter ensures that HC/CO levels
meet current standards by generating the heat (rise in exhaust temperature caused by catalysis) required for
particle filter regeneration.
– a particle filter located under the body,
– a differential pressure sensor to inform the computer of the pressure difference upstream and downstream of the
particle filter
– a particle filter upstream temperature sensor,
– a particle filter downstream temperature sensor (only on certain F9Q816 engines in VDiag 48),
– a temperature sensor upstream of the turbine (TAVT).
During driving, the particle filter becomes loaded with particles of soot. When a given weight of soot determined by
computer mapping is reached, regeneration mode can be triggered if the maximum weight of soot in the particle filter
has not been reached and the engine operating conditions are met (coolant temperature, etc.)
Particle filter regeneration consists of burning the particles of soot that have accumulated in the filter.
The differential pressure sensor measures the particle filter inlet/outlet pressure differential; this measurement is
used to estimate the weight of soot present in the particle filter by mapping in the computer:
(soot weight = pressure differential as a function of exhaust volume flow rate).
Page 24 of 431

13B-24V9 MR-372-J84-13B450$050.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Features13B
EDC16 C36
Program No.: 91
Vdiag No.: 44, 4C, 48,
50, 54, 58
ORANGE particle filter specific warning light (F9Q816 engine only):
F9Q816 Vdiag 48 engines:
This warning light is used to warn the driver that the particle filter is loaded with particles (weight of soot greater than
36 g or more than 6 regeneration failures while driving due to driving conditions not being favourable for
regeneration). As soon as possible the driver must then drive at an average speed of 48 mph (80 km/h) subject to
the road conditions and authorised speed limits.
F9Q816 Vdiag 50 engines:
This warning light is used to warn the driver that the particle filter is loaded with particles.
European On Board Diagnostic management:
The OBD (On Board Diagnostic) system permits detection of any faults relating to the vehicle emission control
system (OBD EURO IV emission control standards being exceeded).
This system should be active for the entire life of the vehicle.
1. Conditions of an OBD fault appearing
An OBD fault will be detected after 3 trip cycles.
It allows the driver to know whether the vehicle has a fault directly linked to the emission control system.
2. System faults displayed by the OBD
List of the faults recorded by the OBD system:
– DF002 Air temperature sensor circuit.
– DF004 Turbocharging pressure sensor circuit.
– DF011 Sensor supply voltage no. 1.
– DF012 Sensor supply voltage no. 2.
– DF013 Sensor supply voltage no. 3.
– DF026 Cylinder 1 injector control circuit.
– DF027 Cylinder 2 injector control circuit.
– DF028 Cylinder 3 injector control circuit.
– DF029 Cylinder 4 injector control circuit.
– DF054 Turbocharging solenoid valve control circuit.
– DF055 Turbocharging pressure regulation circuit.
Page 25 of 431

13B-25V9 MR-372-J84-13B450$050.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Features13B
EDC16 C36
Program No.: 91
Vdiag No.: 44, 4C, 48,
50, 54, 58
– DF056 Air flowmeter circuit.
– DF107 Computer memory.
– DF200 Atmospheric pressure sensor.
– DF209 EGR valve position sensor circuit.
– DF272 EGR valve control circuit.
– DF310 Particle filter upstream temp.* sensor
– DF315 Particle filter diff.* pressure sensor
– DF316 Particle filter diff* pressure
– DF647 EGR valve position regulation.
Some repair operations require programming to ensure that certain engine components function correctly.
Follow the programming procedures (see Replacement of components), if replacing the exhaust gas
recirculation valve or an injector.
*temp: temperature
* diff: differential
3. Conditions for deleting an OBD fault
An OBD fault is deleted in several phases.
The fault present on the diagnostic tool will only become stored (after a repair operation) after the vehicle has
been driven 3 times.
The OBD warning light will only go out after these 3 trips.
The instrument panel warning light coming on does not automatically mean that the system has a fault.
In order for the OBD fault and display parameters to be cleared from the computer, the system requires
40 engine heating cycles.
An engine heating cycle is a driving cycle during which:
– the engine coolant temperature reaches at least 71.1°C,
– the engine coolant temperature varies by 22.2°C in relation to the engine starting temperature.
If one of these conditions is not fulfilled, the OBD fault will still be present or stored on the injection
computer.
Page 26 of 431
13B-26V9 MR-372-J84-13B450$060.mif
13B
EDC16 C36
Program No.: 91
Vdiag No.: 44, 4C, 48,
50, 54, 58
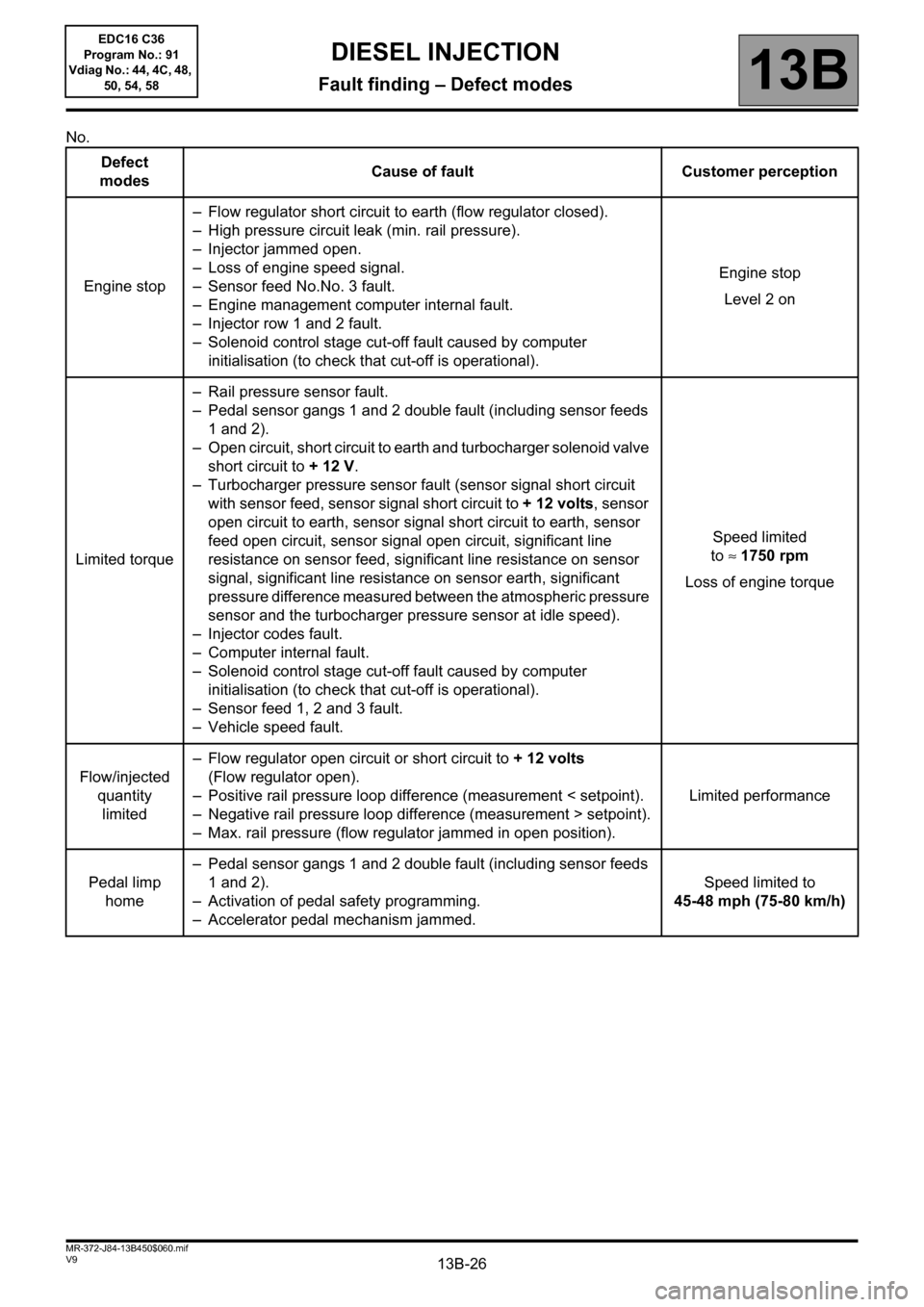
No.
Defect
modesCause of fault Customer perception
Engine stop– Flow regulator short circuit to earth (flow regulator closed).
– High pressure circuit leak (min. rail pressure).
– Injector jammed open.
– Loss of engine speed signal.
– Sensor feed No.No. 3 fault.
– Engine management computer internal fault.
– Injector row 1 and 2 fault.
– Solenoid control stage cut-off fault caused by computer
initialisation (to check that cut-off is operational).Engine stop
Level 2 on
Limited torque– Rail pressure sensor fault.
– Pedal sensor gangs 1 and 2 double fault (including sensor feeds
1 and 2).
– Open circuit, short circuit to earth and turbocharger solenoid valve
short circuit to + 12 V.
– Turbocharger pressure sensor fault (sensor signal short circuit
with sensor feed, sensor signal short circuit to +12volts, sensor
open circuit to earth, sensor signal short circuit to earth, sensor
feed open circuit, sensor signal open circuit, significant line
resistance on sensor feed, significant line resistance on sensor
signal, significant line resistance on sensor earth, significant
pressure difference measured between the atmospheric pressure
sensor and the turbocharger pressure sensor at idle speed).
– Injector codes fault.
– Computer internal fault.
– Solenoid control stage cut-off fault caused by computer
initialisation (to check that cut-off is operational).
– Sensor feed 1, 2 and 3 fault.
– Vehicle speed fault.Speed limited
to≈1750 rpm
Loss of engine torque
Flow/injected
quantity
limited– Flow regulator open circuit or short circuit to + 12 volts
(Flow regulator open).
– Positive rail pressure loop difference (measurement < setpoint).
– Negative rail pressure loop difference (measurement > setpoint).
– Max. rail pressure (flow regulator jammed in open position).Limited performance
Pedal limp
home– Pedal sensor gangs 1 and 2 double fault (including sensor feeds
1 and 2).
– Activation of pedal safety programming.
– Accelerator pedal mechanism jammed.Speed limited to
45-48 mph (75-80 km/h)
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Defect modes
Page 27 of 431

13B-27V9 MR-372-J84-13B450$060.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Defect modes13B
EDC16 C36
Program No.: 91
Vdiag No.: 44, 4C, 48,
50, 54, 58
* normally aspirated: naturally aspiratedDefect
modesCause of fault Customer perception
Turbocharger
cut-off– Turbocharging pressure loop difference (vanes jammed,
compressor/turbine fault, turbocharging pressure sensor fault,
sensor connection fault, functional solenoid valve fault
(disconnected, hose kinked, solenoid valve mechanism jammed),
high pressure circuit leak (high pressure hose, major distributor
leak).
– Flowmeter failure (plausibility of the reading):
– significant line resistance on earth sensor,
– significant line resistance on sensor feed, significant line resistance
on sensor signal,
– flowmeter sensing element damaged,
– wiring/connection fault,
– flowmeter voltage or 5 V reference voltage deviation.
– Flowmeter failure (plausibility of sensitivity variation):
– flowmeter clogged/flow underestimated,
– flow overestimated,
– air circuit leak between flowmeter and compressor,
– air circuit leak after compressor.
– Electrical faults:
– signal short circuit to + 12 V,
– signal short circuit to earth,
– signal open circuit,
– sensor feed open circuit,
– open circuit, short circuit to earth and turbocharger solenoid valve
short circuit to + 12 V.
– Turbocharger pressure sensor fault (sensor signal short circuit with
sensor feed, sensor signal short circuit to + 12 V, sensor open
circuit to earth, sensor signal short circuit to earth, sensor feed open
circuit, sensor signal open circuit, significant line resistance on
sensor feed, significant line resistance on sensor signal, significant
line resistance on sensor earth, significant pressure difference
measured between the atmospheric pressure sensor and the
turbocharger pressure sensor at idle speed).
– EGR valve fault (valve clogged, valve jammed open).
– Camshaft sensor fault.
– Engine speed sensor fault.
– Sensor feed No. 1 fault.25-50% loss of engine
performance (normally
aspirated engine)
Rail pressure
limited– Rail pressure sensor fault.
– Sensor feed No. 3 fault.Poor performance
Rail pressure
reduction
– Positive rail pressure loop difference (measurement < setpoint).
Poor performance
Page 28 of 431

13B-28V9 MR-372-J84-13B450$070.mif
13B
EDC16 C36
Program No.: 91
Vdiag No.: 44, 4C, 48,
50, 54, 58
Summary of available configuration readings
NOTESConfiguration readings are used to check the state of configurations performed.
The configuration readings cannot be changed.
The computer is configured as soon as the one of the vehicle's optional system
components is operated.
In the event of a fault, consult the interpretation of command RZ005 Programming.
LC009Air conditioning
WITH OR WITHOUT
LC056Heating elements
WITH OR WITHOUT
LC065Water in diesel fuel sensor
WITH OR WITHOUT
LC120Cruise control
WITH OR WITHOUT
LC121Speed limiter
WITH OR WITHOUT
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Configuration and programming
Page 34 of 431
13B-34V9 MR-372-J84-13B450$090.mif
13B
EDC16 C36
Program No.: 91
Vdiag No.: 44, 4C, 48,
50, 54, 58
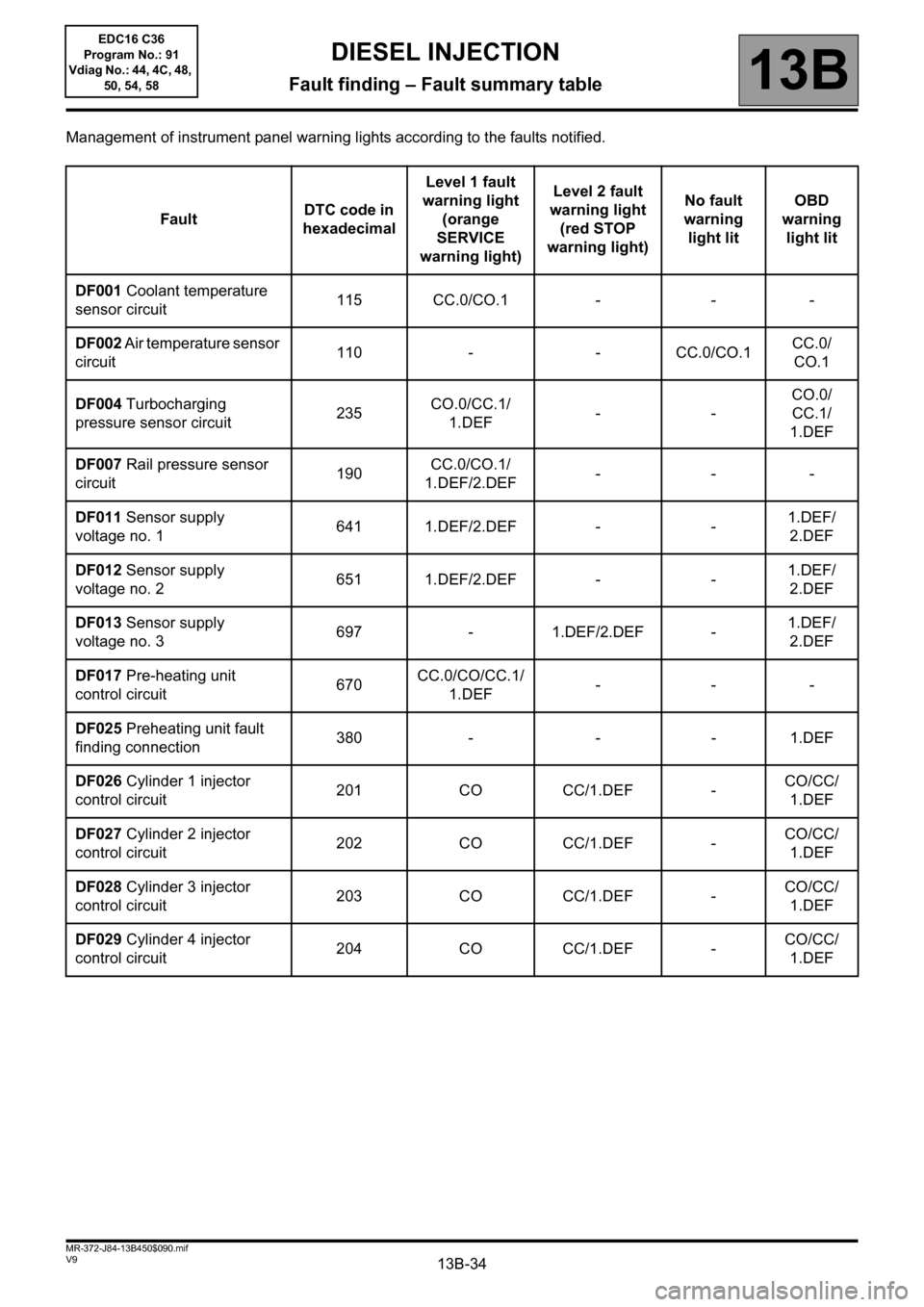
Management of instrument panel warning lights according to the faults notified.
FaultDTC code in
hexadecimalLevel 1 fault
warning light
(orange
SERVICE
warning light)Level 2 fault
warning light
(red STOP
warning light)No fault
warning
light litOBD
warning
light lit
DF001 Coolant temperature
sensor circuit115 CC.0/CO.1 - - -
DF002 Air temperature sensor
circuit110 - - CC.0/CO.1CC.0/
CO.1
DF004 Turbocharging
pressure sensor circuit235CO.0/CC.1/
1.DEF--CO.0/
CC.1/
1.DEF
DF007 Rail pressure sensor
circuit190CC.0/CO.1/
1.DEF/2.DEF---
DF011 Sensor supply
voltage no. 1641 1.DEF/2.DEF - -1.DEF/
2.DEF
DF012 Sensor supply
voltage no. 2651 1.DEF/2.DEF - -1.DEF/
2.DEF
DF013 Sensor supply
voltage no. 3697 - 1.DEF/2.DEF -1.DEF/
2.DEF
DF017 Pre-heating unit
control circuit670CC.0/CO/CC.1/
1.DEF---
DF025 Preheating unit fault
finding connection380 - - - 1.DEF
DF026 Cylinder 1 injector
control circuit201 CO CC/1.DEF -CO/CC/
1.DEF
DF027 Cylinder 2 injector
control circuit202 CO CC/1.DEF -CO/CC/
1.DEF
DF028 Cylinder 3 injector
control circuit203 CO CC/1.DEF -CO/CC/
1.DEF
DF029 Cylinder 4 injector
control circuit204 CO CC/1.DEF -CO/CC/
1.DEF
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Fault summary table
Page 35 of 431
13B-35V9 MR-372-J84-13B450$090.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Fault summary table13B
EDC16 C36
Program No.: 91
Vdiag No.: 44, 4C, 48,
50, 54, 58
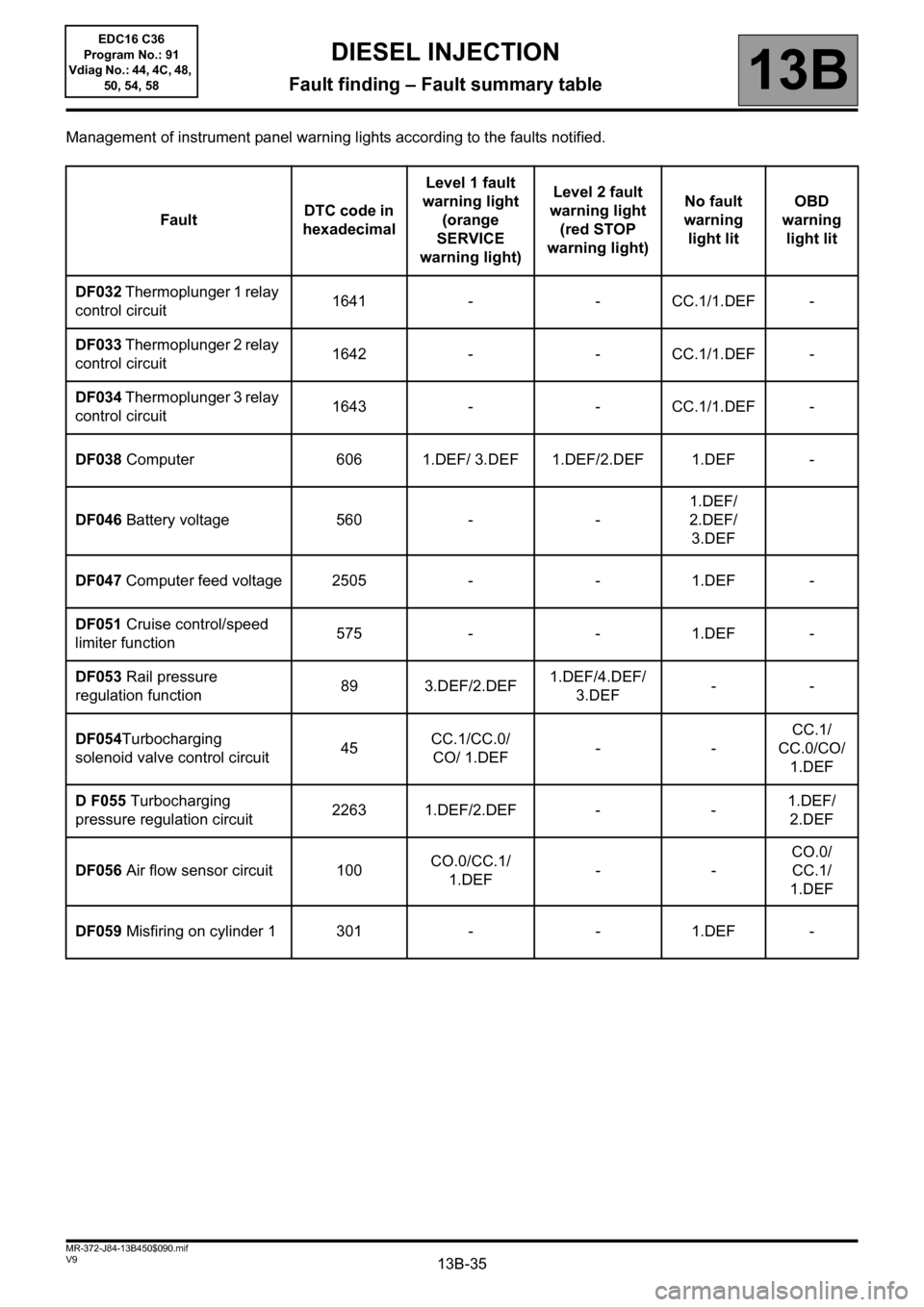
Management of instrument panel warning lights according to the faults notified.
FaultDTC code in
hexadecimalLevel 1 fault
warning light
(orange
SERVICE
warning light)Level 2 fault
warning light
(red STOP
warning light)No fault
warning
light litOBD
warning
light lit
DF032 Thermoplunger 1 relay
control circuit1641 - - CC.1/1.DEF -
DF033 Thermoplunger 2 relay
control circuit1642 - - CC.1/1.DEF -
DF034 Thermoplunger 3 relay
control circuit1643 - - CC.1/1.DEF -
DF038 Computer 606 1.DEF/ 3.DEF 1.DEF/2.DEF 1.DEF -
DF046 Battery voltage 560 - -1.DEF/
2.DEF/
3.DEF
DF047 Computer feed voltage 2505 - - 1.DEF -
DF051 Cruise control/speed
limiter function575 - - 1.DEF -
DF053 Rail pressure
regulation function89 3.DEF/2.DEF1.DEF/4.DEF/
3.DEF--
DF054Turbocharging
solenoid valve control circuit45CC.1/CC.0/
CO/ 1.DEF--CC.1/
CC.0/CO/
1.DEF
D F055 Turbocharging
pressure regulation circuit2263 1.DEF/2.DEF - -1.DEF/
2.DEF
DF056 Air flow sensor circuit 100CO.0/CC.1/
1.DEF--CO.0/
CC.1/
1.DEF
DF059 Misfiring on cylinder 1 301 - - 1.DEF -
Page 36 of 431
13B-36V9 MR-372-J84-13B450$090.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Fault summary table13B
EDC16 C36
Program No.: 91
Vdiag No.: 44, 4C, 48,
50, 54, 58
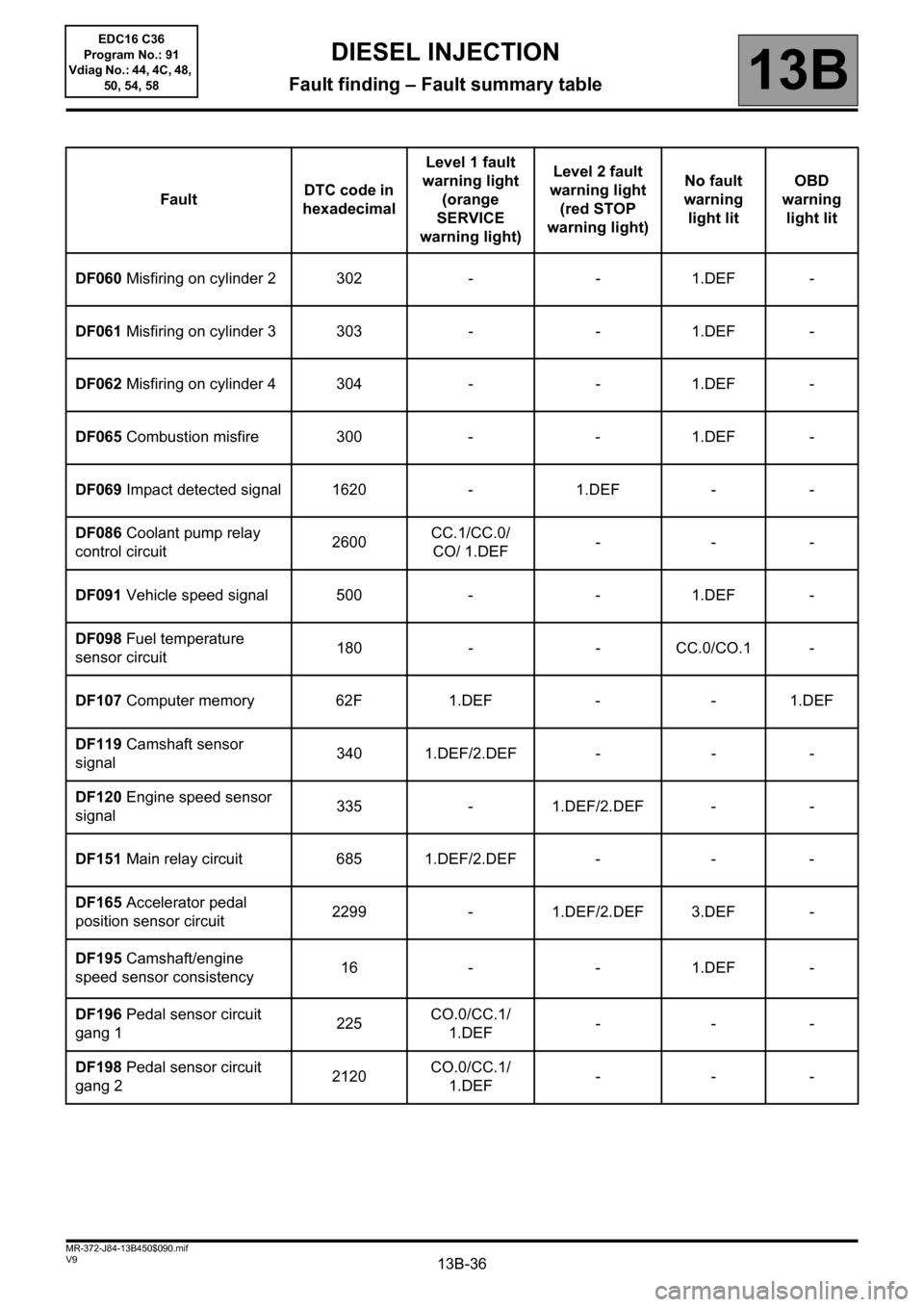
FaultDTC code in
hexadecimalLevel 1 fault
warning light
(orange
SERVICE
warning light)Level 2 fault
warning light
(red STOP
warning light)No fault
warning
light litOBD
warning
light lit
DF060 Misfiring on cylinder 2 302 - - 1.DEF -
DF061 Misfiring on cylinder 3 303 - - 1.DEF -
DF062 Misfiring on cylinder 4 304 - - 1.DEF -
DF065 Combustion misfire 300 - - 1.DEF -
DF069 Impact detected signal 1620 - 1.DEF - -
DF086 Coolant pump relay
control circuit2600CC.1/CC.0/
CO/ 1.DEF---
DF091 Vehicle speed signal 500 - - 1.DEF -
DF098 Fuel temperature
sensor circuit180 - - CC.0/CO.1 -
DF107 Computer memory 62F 1.DEF - - 1.DEF
DF119 Camshaft sensor
signal340 1.DEF/2.DEF - - -
DF120 Engine speed sensor
signal335 - 1.DEF/2.DEF - -
DF151 Main relay circuit 685 1.DEF/2.DEF - - -
DF165 Accelerator pedal
position sensor circuit2299 - 1.DEF/2.DEF 3.DEF -
DF195 Camshaft/engine
speed sensor consistency16 - - 1.DEF -
DF196 Pedal sensor circuit
gang 1225CO.0/CC.1/
1.DEF---
DF198 Pedal sensor circuit
gang 22120CO.0/CC.1/
1.DEF---
Page 37 of 431
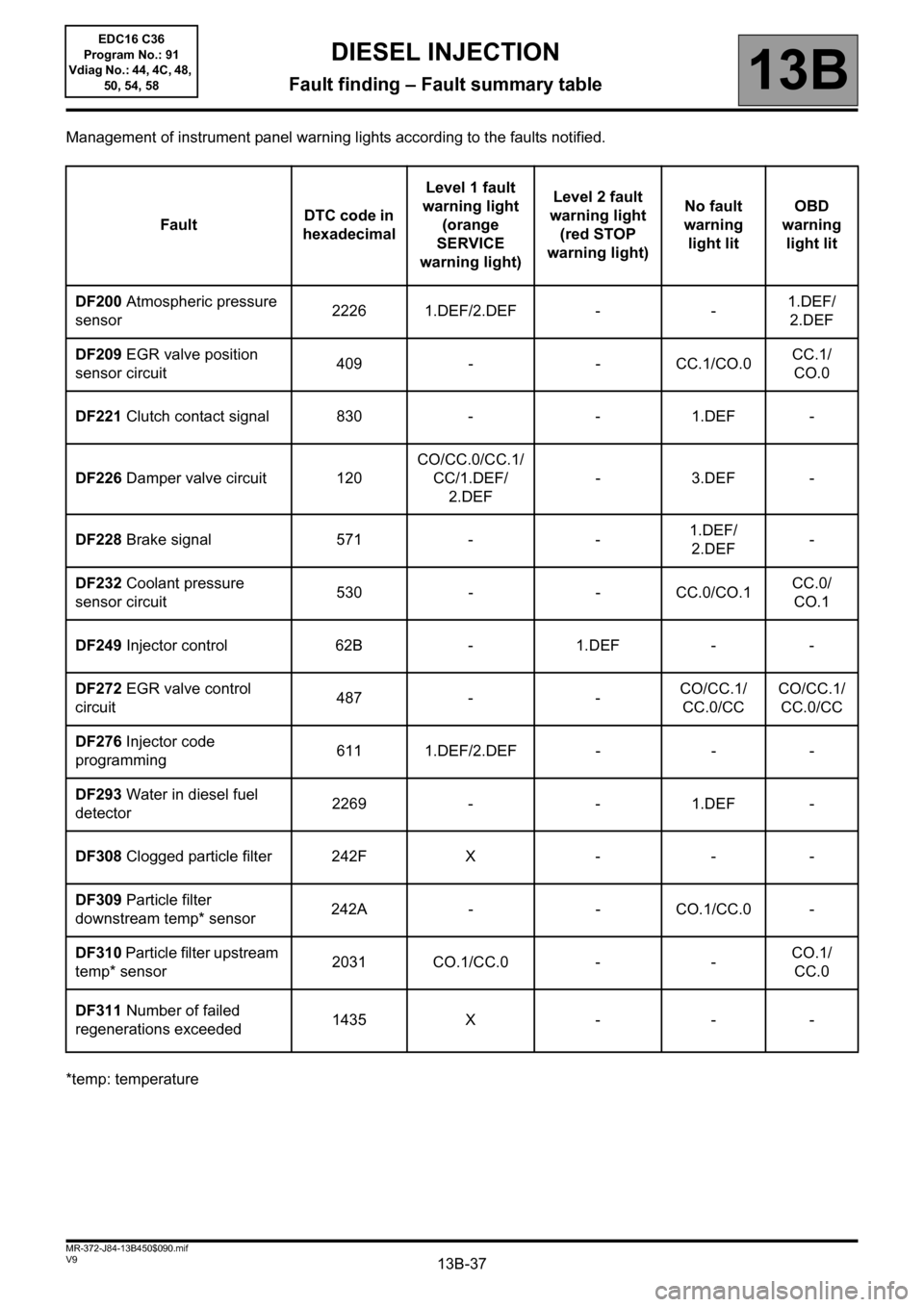
13B-37V9 MR-372-J84-13B450$090.mif
DIESEL INJECTION
Fault finding – Fault summary table13B
EDC16 C36
Program No.: 91
Vdiag No.: 44, 4C, 48,
50, 54, 58
Management of instrument panel warning lights according to the faults notified.
*temp: temperatureFaultDTC code in
hexadecimalLevel 1 fault
warning light
(orange
SERVICE
warning light)Level 2 fault
warning light
(red STOP
warning light)No fault
warning
light litOBD
warning
light lit
DF200 Atmospheric pressure
sensor2226 1.DEF/2.DEF - -1.DEF/
2.DEF
DF209 EGR valve position
sensor circuit409 - - CC.1/CO.0CC.1/
CO.0
DF221 Clutch contact signal 830 - - 1.DEF -
DF226 Damper valve circuit 120CO/CC.0/CC.1/
CC/1.DEF/
2.DEF-3.DEF-
DF228 Brake signal 571 - -1.DEF/
2.DEF-
DF232 Coolant pressure
sensor circuit530 - - CC.0/CO.1CC.0/
CO.1
DF249 Injector control 62B - 1.DEF - -
DF272 EGR valve control
circuit487 - -CO/CC.1/
CC.0/CCCO/CC.1/
CC.0/CC
DF276 Injector code
programming611 1.DEF/2.DEF - - -
DF293 Water in diesel fuel
detector2269 - - 1.DEF -
DF308 Clogged particle filter 242F X - - -
DF309 Particle filter
downstream temp* sensor242A - - CO.1/CC.0 -
DF310 Particle filter upstream
temp* sensor2031 CO.1/CC.0 - -CO.1/
CC.0
DF311 Number of failed
regenerations exceeded1435 X - - -