SKODA ROOMSTER 2006 1.G Owner's Manual
Manufacturer: SKODA, Model Year: 2006, Model line: ROOMSTER, Model: SKODA ROOMSTER 2006 1.GPages: 274, PDF Size: 48.64 MB
Page 171 of 274
Transporting children safely
170
•Do not place any objects within the deployment area of the side
airbag - risk of injury!
Child seat
Classification of child seats into groups
Only child safety seats which have an official approval and
are suitable for the child, may be used.
ECE-R 44 standard applies to child safety seats. ECE-R means:
Economic Commission of Europe - Regulation.
Child safety seats which have been tested for conformity with ECE-R 44
have a non-detachable test seal (a large E within a circle and below this
the test number) attached to the seat.
Child safety seats are classified in 5 groups:
Children of more than 150 cm in height may use the seat belts fitted to the
vehicle without a seat bolster.
Use of child seats
An overview of the usefulness of child seats on each of the seats
according to the EG guidelines 77/541 and ECE 44 standard:
Universal category - seat is suitable for all approved types of child
safety seats.
The seat can be fitted with fixing eyes for the “ ISOFIX*”system.
The seat is equipped as standard with the fixing system “ Top
Te t h e r ”.
GroupWeight
00 - 10 kg⇒page 171
0+up to 13 kg⇒page 171
19 - 18 kg⇒page 171
215 - 25 kg⇒page 172
322 - 36 kg⇒page 173
WARNING (continued)
Child seat
according to
groupFront passenger seatRear seatoutsideRear seat middle
0
0+
1
2 and 3
AUAUA+ATAU
AUAUA+ATAU
AUAUA+ATAU
AUAUAU
AU
A+
AT
NKO 20 A05.book Page 170 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 172 of 274
Transporting children safely 171
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
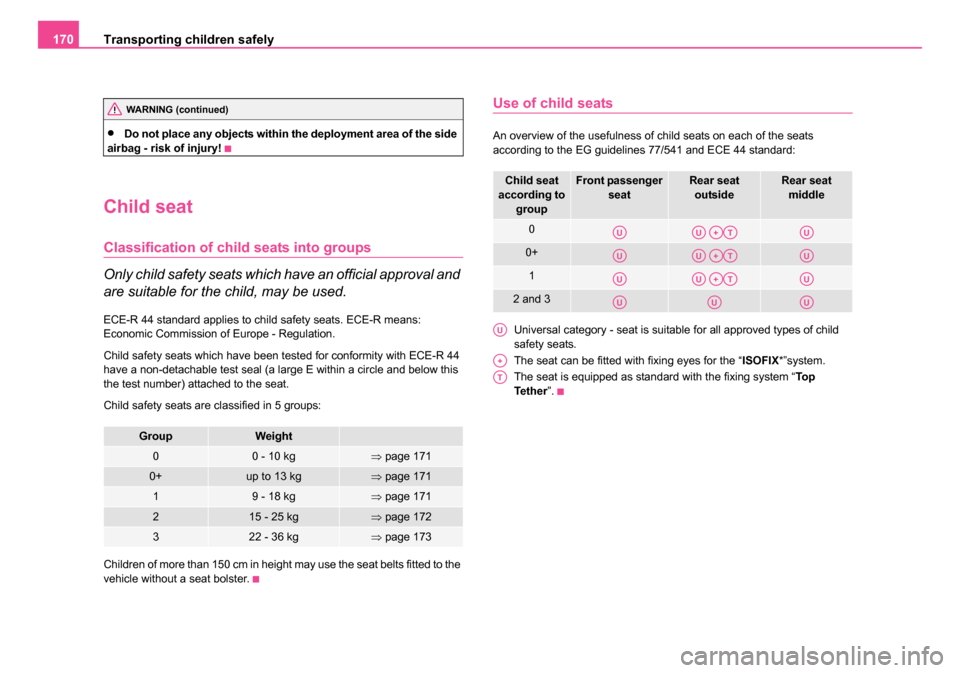
Child seats of group 0/0+
The optimal solution for babies of up to about 9 months old weighing up
to 10 kg or babies up to about 18 months old weighing up to 13 kg is a
child safety seat which is fastened in the opposite direction of travel
⇒fig. 138 .
Child seats in which the child is facing with its back towards the
direction of travel should not be used on the front passenger seat
when the vehicle is fitted with a front passenger airbag ⇒ page 168,
“Use of child safety seats on the front passenger seat”.
WARNING
•It is essential to always switch off the front passenger airbag
(airbags) at a specialist garage or with the switch for front
passenger airbag(s)* when attaching in exceptional circumstances
a child safety seat on the front passenger seat where the child is
seated with its back facing in direction of travel (in some countries
also when the child is facing the direction of travel) ⇒page 164.
•In certain countries national legal provisions require that
besides the front passenger airbag also the side or head passenger
airbags are deactivated. Please comply with any differing national
legal regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
•If this is not done, a child seated on the front passenger seat
may suffer severe or even fatal injuries if the front passenger airbag
or airbags are deployed.
•You should have the front passenger airbag (or airbags) reacti-
vated just as soon as you no longer use a child safety seat on the
front passenger seat.
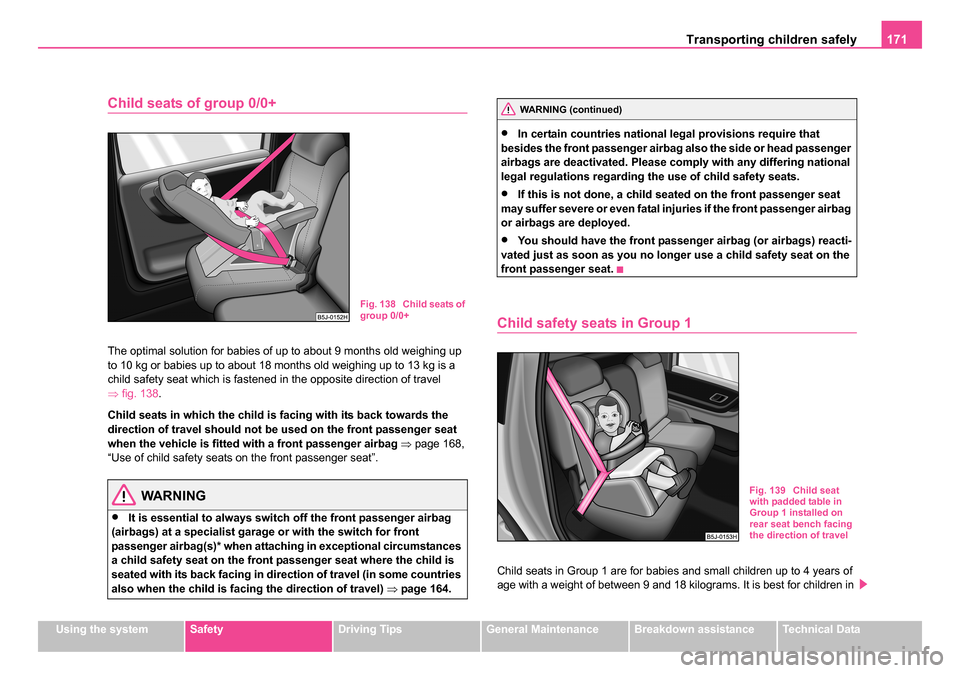
Child safety seats in Group 1
Child seats in Group 1 are for babies and small children up to 4 years of
age with a weight of between 9 and 18 kilograms. It is best for children in
Fig. 138 Child seats of
group 0/0+
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 139 Child seat
with padded table in
Group 1 installed on
rear seat bench facing
the direction of travel
NKO 20 A05.book Page 171 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 173 of 274

Transporting children safely
172
the lower range of this group, to use a child seat which allows the child to
sit with its back to the direction of travel. It is best for children in the upper
range of the Group 0+, to use a child seat which allows the child to sit
⇒ fig. 139 in the direction of travel.
Child seats in which th e child is facing with its back towards the
direction of travel should not be used on the front passenger seat
when the vehicle is fitted with a front passenger airbag ⇒ page 168,
“Use of child safety seats on the front passenger seat”.
WARNING
•It is essential to always switch off the front passenger airbag
(airbags) at a specialist garage or with the switch for front
passenger airbag(s)* when attaching in exceptional circumstances
a child safety seat on the front passenger seat where the child is
seated with its back facing in direction of travel (in some countries
also when the child is facing the direction of travel) ⇒page 164.
•In certain countries national legal provisions require that
besides the front passenger airbag also the side or head passenger
airbags are deactivated. Please comply with any differing national
legal regulations regarding the use of child safety seats.
•If this is not done, a child seated on the front passenger seat
may suffer severe or even fatal injuries if the front passenger airbag
or airbags are deployed.
•You should have the front passenger airbag (or airbags) reacti-
vated just as soon as you no longer use a child safety seat on the
front passenger seat.
Child safety seats in Group 2
For children up to about 7 years of age weighing between 15 and 25 kg
the optimal solution is a child safety seat in combination with the three-
point seat belt ⇒fig. 140 .
WARNING
•When transporting a child on the front passenger seat, please
comply with the appropriate national regulations regarding the use
of child safety seats. Switch off the front passenger airbag if
necessary at a specialist garage or switch it off with the switch for
front passenger airbag* ⇒page 164.
•The shoulder part of the seat belt must run approximately
across the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly against the chest.
It must on no account run across the neck. The lap part of the seat
belt must run across the pelvis and fits snugly; it must not run over
the belly. Tighten the belt webbing over your hip if necessary.
Fig. 140 Child seat in
Group 2 installed on
the rear seat facing the
direction of travel
NKO 20 A05.book Page 172 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 174 of 274
Transporting children safely 173
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
•Please comply with any differin g national legal regulations
regarding the use of child safety seats.
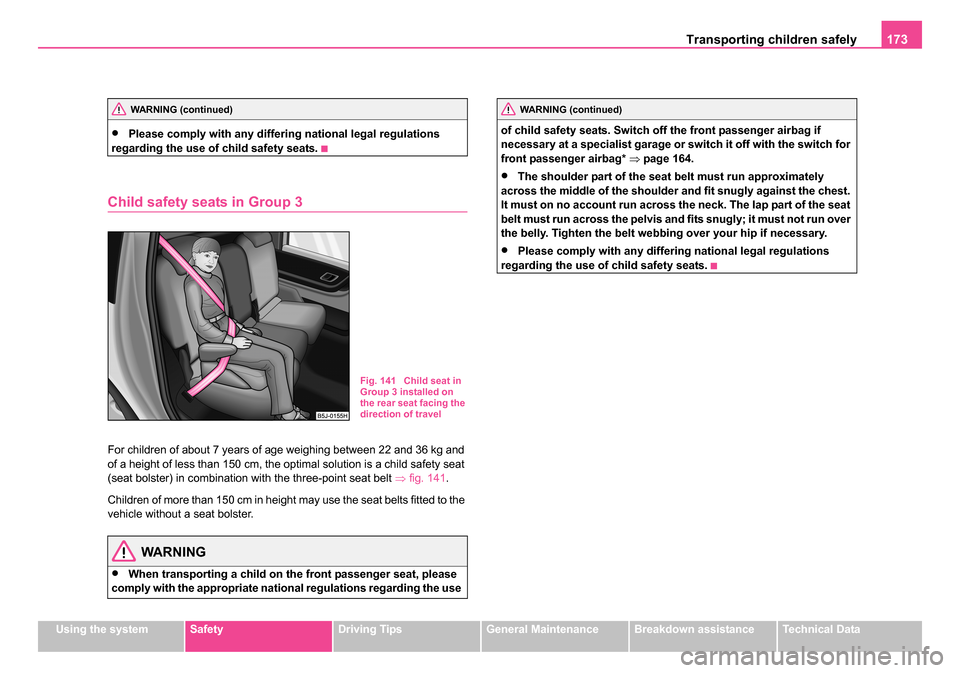
Child safety seats in Group 3
For children of about 7 years of age weighing between 22 and 36 kg and
of a height of less than 150 cm, the optimal solution is a child safety seat
(seat bolster) in combination with the three-point seat belt ⇒fig. 141 .
Children of more than 150 cm in height may use the seat belts fitted to the
vehicle without a seat bolster.
WARNING
•When transporting a child on the front passenger seat, please
comply with the appropriate nation al regulations regarding the use of child safety seats. Switch off the front passenger airbag if
necessary at a specialist garage or switch it off with the switch for
front passenger airbag*
⇒page 164.
•The shoulder part of the seat belt must run approximately
across the middle of the shoulder and fit snugly against the chest.
It must on no account run across the neck. The lap part of the seat
belt must run across the pelvis and fits snugly; it must not run over
the belly. Tighten the belt webbing over your hip if necessary.
•Please comply with any differ ing national legal regulations
regarding the use of child safety seats.
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 141 Child seat in
Group 3 installed on
the rear seat facing the
direction of travel
WARNING (continued)
NKO 20 A05.book Page 173 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 175 of 274
Transporting children safely
174
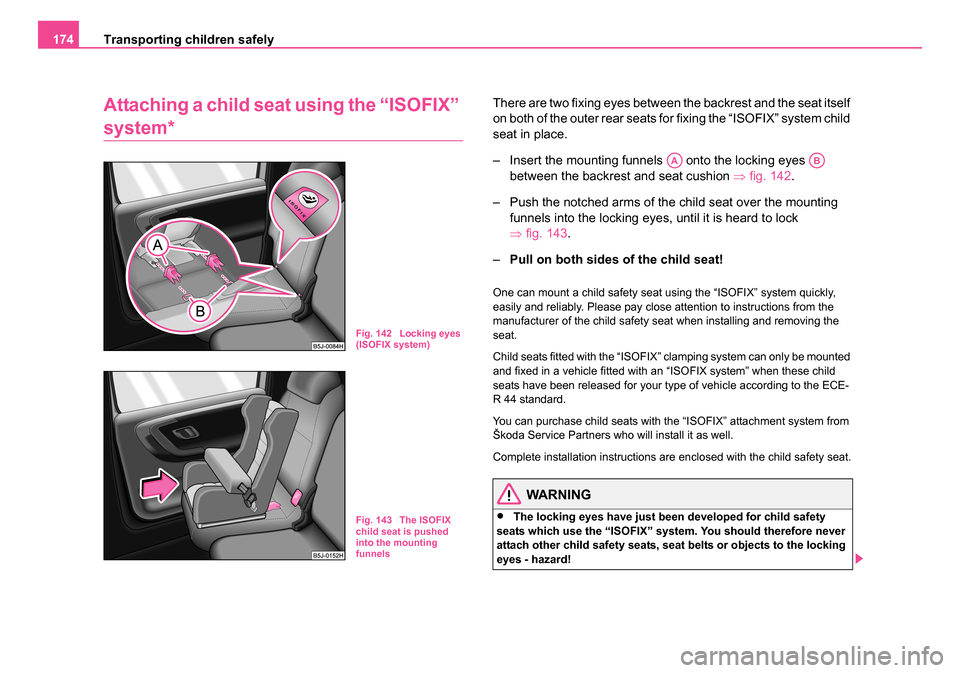
Attaching a child seat using the “ISOFIX”
system*
There are two fixing eyes between the backrest and the seat itself
on both of the outer rear seats for fixing the “ISOFIX” system child
seat in place.
– Insert the mounting funnels onto the locking eyes
between the backrest and seat cushion ⇒fig. 142 .
– Push the notched arms of the child seat over the mounting funnels into the locking eyes, until it is heard to lock
⇒fig. 143 .
– Pull on both sides of the child seat!
One can mount a child safety seat using the “ISOFIX” system quickly,
easily and reliably. Please pay close attention to instructions from the
manufacturer of the child safety seat when installing and removing the
seat.
Child seats fitted with the “ISOFIX” clamping system can only be mounted
and fixed in a vehicle fitted with an “ISOFIX system” when these child
seats have been released for your type of vehicle according to the ECE-
R 44 standard.
You can purchase child seats with the “ISOFIX” attachment system from
Škoda Service Partners who will install it as well.
Complete installation instructions are enclosed with the child safety seat.
WARNING
•The locking eyes have just been developed for child safety
seats which use the “ISOFIX” system. You should therefore never
attach other child safety seats, seat belts or objects to the locking
eyes - hazard!
Fig. 142 Locking eyes
(ISOFIX system)
Fig. 143 The ISOFIX
child seat is pushed
into the mounting
funnels
AAAB
NKO 20 A05.book Page 174 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 176 of 274
Transporting children safely 175
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
•Ask a Škoda Service Partner whether a child seat which you
bought for another vehicle is recommended for use in a Škoda
before using an “ISOFIX” system.
•Certain child seats which use the “ISOFIX” system can be
attached with standard three-point seat belts. Please pay close
attention to instructions from the manufacturer of the child safety
seat when installing and removing the seat.
Note
•Child seats which use the “ISOFIX” system are currently available for
children weighing up to about 18 kg. This corresponds to an age range up
to 4 years.
•The child seats can also be fitted with the “Top Tether” system
⇒ page 175.
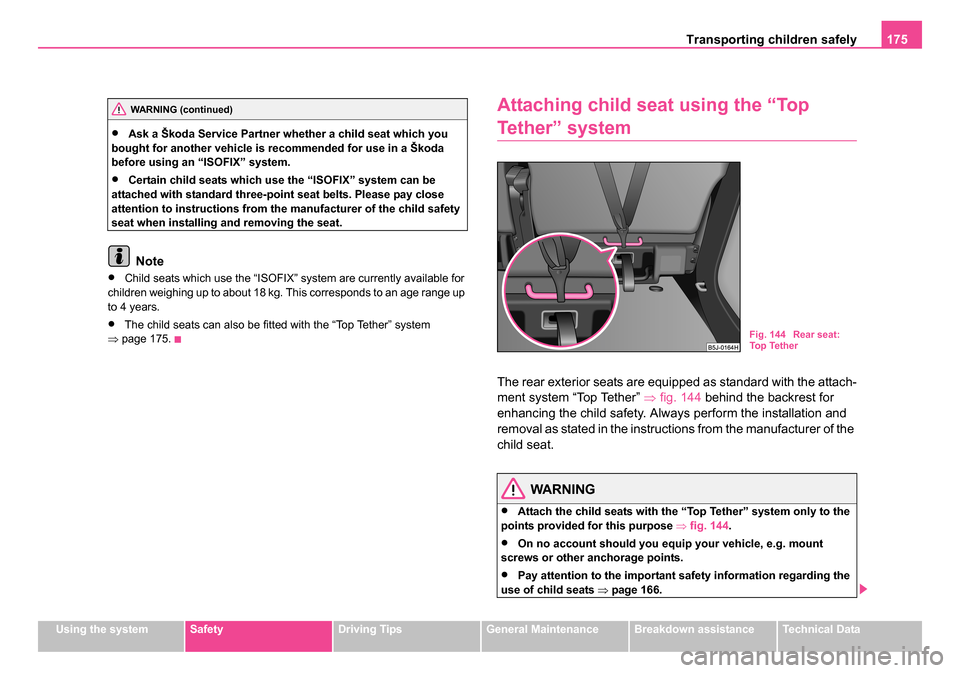
Attaching child seat using the “Top
Tether” system
The rear exterior seats are equipped as standard with the attach-
ment system “Top Tether” ⇒fig. 144 behind the backrest for
enhancing the child safety. Always perform the installation and
removal as stated in the instructions from the manufacturer of the
child seat.
WARNING
•Attach the child seats with the “Top Tether” system only to the
points provided for this purpose ⇒fig. 144 .
•On no account should you equi p your vehicle, e.g. mount
screws or other anchorage points.
•Pay attention to the important safety information regarding the
use of child seats ⇒page 166.
WARNING (continued)
Fig. 144 Rear seat:
To p Te t h e r
NKO 20 A05.book Page 175 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 177 of 274

Transporting children safely
176
Note
Store the remaining part of the belt for the “Top Tether” system in a textile
pocket, which is located at the child seat.
NKO 20 A05.book Page 176 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 178 of 274

Intelligent Technology177
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
Driving Tips
Intelligent Technology
Electronic stability programme (ESP)*
General
General
The ESP aids you maintain control of your vehicle in situations in border-
line driving situations such as when negotiating a curve too fast. The risk
of skidding is reduced and your car thus offers greater driving stability
depending on the conditions of the road surface. This occurs at all speeds.
The following systems are integrated into the electronic stability
programme:
•Electronic Differential Lock (EDL),
•Traction control system (TCS),
•Antilock brake system (ABS),
•Brake Assist.
Operating principle
The ESP switches on automatically when the engine is started and then
conducts a self-test. The ESP control unit processes data from the indi-
vidual systems. It also processes additional measurement data which are
supplied by highly sensitive sensors: the rotational velocity of the vehicle
about its vertical axis, the lateral acceleration of the vehicle, the braking
pressure and the steering angle.
The direction which the driver wishes to take is determined based on the
steering angle and the speed of the vehicle and is constantly compared
with the actual behaviour of the vehicle. If differences exist, such as the
car beginning to skid, the ESP will automatically brake the appropriate
wheel.
The car is stabilised again by the forces which take effect when the wheel
is braked. Intervention into the brake system takes place primarily on the
outer front wheel of a vehicle which tends to oversteer (tendency for the
rear of the vehicle to break away) while occurs this is on the inner rear
wheel of a vehicle which tends to understeer (tendency to shift out of the
curve). This braking control cycle is accompanied by noises.
The ESP operates in combination with the ABS ⇒page 181, “Antilock
brake system (ABS)*”. If there is a fault in the ABS system, the ESP also
does not operate.
Fig. 145 ESP switch
NKO 20 A05.book Page 177 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 179 of 274
Intelligent Technology
178
The ESP warning light ⇒page 35 lights up in the instrument cluster when
there is a fault on the ESP.
Switching off
You can switch the ESP off and on again as you wish, by pressing the
button ⇒page 177, fig. 145 . The ESP warning light ⇒page 35 lights up
in the instrument cluster when the ESP is switched off.
The ESP should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice
in certain exceptional cases, such as when you wish to have wheel slip,
to switch off the system.
Examples:
•when driving with snow chains,
•when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface,
•when it is necessary to rock a car free when it has become stuck.
Then you should switch on the ESP again.
WARNING
It is also not possible for the E SP to overcome the physical limits
of the vehicle. Even if a vehicle fitted with ESP you should still
always adapt your style of driving to the condition of the road
surface and the traffic situation. This particularly applies when
driving on slippery and wet roads. The increased safety offered
must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise - risk of an
accident!
Note
•All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve
problem-free operation of the ESP. Differing rolling circumferences of the
tyres can lead to an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
•Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other
assignment of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the ESP
⇒ page 232, “Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Traction control system (TCS)*
The traction control system prevents the driven wheels
from spinning when accelerating.
General
The TCS makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off,
accelerate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface
are unfavourable.
Operating principle
The TCS switches on automatically when the engine is started and then
conducts a self-test. The system monitors the speeds of the driven wheels
with the aid of the ABS sensors. If the wheels are spinning, the force trans-
Fig. 146 TCS switch
NKO 20 A05.book Page 178 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM
Page 180 of 274
Intelligent Technology179
Using the systemSafetyDriving TipsGeneral MaintenanceBreakdown assistanceTechnical Data
mitted to the road surface is automatically adapted by reducing the engine
speed. This occurs at all speeds.
The TCS operates in combination with the ABS
⇒page 181, “Antilock
brake system (ABS)*”. The TCS will not f unction if a fault exists in the ABS
system.
The TCS warning light ⇒page 34 lights up in the instrument cluster when
there is a fault on the TCS.
Switching off
You can switch the TCS off and on again as you wish by pressing the
button ⇒page 178, fig. 146 . The TCS warning light ⇒page 34 lights up
in the instrument cluster when the TCS is switched off.
The TCS should normally always be switched on. It may be good practice
in certain exceptional cases, such as when you wish to have wheel slip,
to switch off the system.
Examples:
•when driving with snow chains,
•when driving in deep snow or on a loose surface,
•when it is necessary to rock a car free when it has become stuck.
then you should switch on the TCS again.
WARNING
You should always adjust your style of driving to the conditions of
the road surface and the traffic situation. The increased safety
offered must not tempt you to take greater risks than otherwise -
risk of an accident!
Note
•All four wheels must be fitted with the same tyres in order to achieve
problem-free operation of the TCS. Differing rolling circumferences of the
tyres can lead to an undesirable reduction in the engine output.
•Changes to vehicle (e.g. on engine, on the brakes, on chassis or other
assignment of tyres and wheels) can influence the function of the TCS
⇒ page 232, “Accessories, changes and replacement of parts”.
Electronic Differential Lock (EDL)*
The electronic differential lock prevents an individual
wheel from slipping.
Models fitted with ESP are equipped with electronic differential lock (EDL).
General
The EDL makes it much easier, and sometimes at all possible, to start off,
accelerate and climb a steep hill when the conditions of the road surface
are unfavourable.
Operating principle
The EDL is activated automatically, that is without any action on the part
of the driver. It monitors the speeds of the driven wheels with the aid of the
ABS sensors. Should only one drive wheel begin spinning on a slippery
surface there will be an appreciable difference in the speed of the driven
wheels. The EDL function brakes the slipping wheel and the differential
transmits a greater driving force to the other driven wheel. This control
process is also accompanied by noises.
Overheating of the brakes
The EDL switches off automatically if unusually severe stresses exist in
order to avoid excessive heat generation in the disc brake on the wheel
NKO 20 A05.book Page 179 Wednesday, June 21, 2006 1:42 PM