Negative SUBARU TRIBECA 2009 1.G Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUBARU, Model Year: 2009, Model line: TRIBECA, Model: SUBARU TRIBECA 2009 1.GPages: 2453, PDF Size: 46.32 MB
Page 1043 of 2453
VDC(diag)-51
Diagnostic Procedure with Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC)
VEHICLE DYNAMICS CONTROL (VDC) (DIAGNOSTICS)
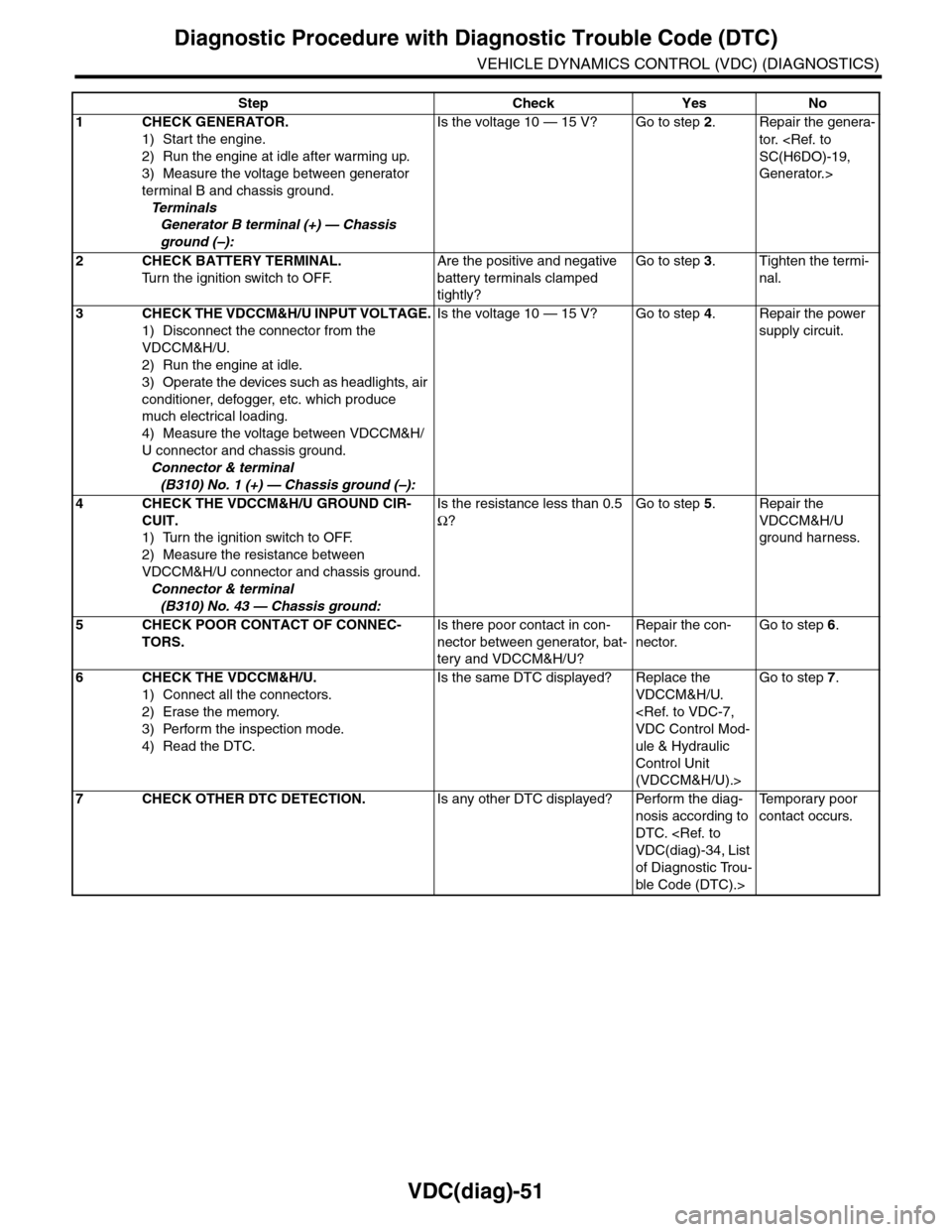
Step Check Yes No
1CHECK GENERATOR.
1) Start the engine.
2) Run the engine at idle after warming up.
3) Measure the voltage between generator
terminal B and chassis ground.
Te r m i n a l s
Generator B terminal (+) — Chassis
ground (–):
Is the voltage 10 — 15 V? Go to step 2.Repair the genera-
tor.
Generator.>
2CHECK BATTERY TERMINAL.
Tu r n t h e i g n i t i o n s w i t c h t o O F F.
Are the positive and negative
battery terminals clamped
tightly?
Go to step 3.Tighten the termi-
nal.
3CHECK THE VDCCM&H/U INPUT VOLTAGE.
1) Disconnect the connector from the
VDCCM&H/U.
2) Run the engine at idle.
3) Operate the devices such as headlights, air
conditioner, defogger, etc. which produce
much electrical loading.
4) Measure the voltage between VDCCM&H/
U connector and chassis ground.
Connector & terminal
(B310) No. 1 (+) — Chassis ground (–):
Is the voltage 10 — 15 V? Go to step 4.Repair the power
supply circuit.
4CHECK THE VDCCM&H/U GROUND CIR-
CUIT.
1) Turn the ignition switch to OFF.
2) Measure the resistance between
VDCCM&H/U connector and chassis ground.
Connector & terminal
(B310) No. 43 — Chassis ground:
Is the resistance less than 0.5
Ω?
Go to step 5.Repair the
VDCCM&H/U
ground harness.
5CHECK POOR CONTACT OF CONNEC-
TORS.
Is there poor contact in con-
nector between generator, bat-
tery and VDCCM&H/U?
Repair the con-
nector.
Go to step 6.
6CHECK THE VDCCM&H/U.
1) Connect all the connectors.
2) Erase the memory.
3) Perform the inspection mode.
4) Read the DTC.
Is the same DTC displayed? Replace the
VDCCM&H/U.
ule & Hydraulic
Control Unit
(VDCCM&H/U).>
Go to step 7.
7CHECK OTHER DTC DETECTION.Is any other DTC displayed? Perform the diag-
nosis according to
DTC.
of Diagnostic Trou-
ble Code (DTC).>
Te m p o r a r y p o o r
contact occurs.
Page 1622 of 2453

GD(H6DO)-10
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
4. GENERAL DRIVING CYCLE
1. Crankshaft Timing Diagnosis
Perform the diagnosis continuously after starting engine and while AVCS is not operating.
2. Slow Response Diagnosis
Perform the diagnosis continuously after warm-up, while AVCS is operating and the target timing advance is
small.
5. DIAGNOSTIC METHOD
1. Crankshaft Timing Diagnosis
Judge as NG when the timing advance is large. Judge as OK when it is small.
Judge as NG when all the following conditions are established and the continuous time is more than 20 sec-
onds. Judge as OK and clear the NG when the following conditions are not established and the continuous
time is more than one second.
Time Needed for Diagnosis: 20 seconds
Malfunction Indicator Light Illumination: Illuminates when malfunctions occur in 2 continuous driving cycles.
2. Slow Response Diagnosis
Calculates (integrate by positive and negative separately) the AVCS deviation amount when the timing ad-
vance is large. Judges NG if the integrated value is large after 30 seconds has passed, and judges OK if it
is small.
Abnormality Judgment
When all of the following conditions are established, judged as OK.
Time Needed for Diagnosis: 30 seconds
Malfunction Indicator Light Illumination: Illuminates when malfunctions occur in 2 continuous driving cy-
cles.
Normality Judgment
Judges OK when all of the following conditions are established, and clears the NG.
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value
Basic timing advance < –18°CA
or
> 18°CA
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value
AV C S t a r g e t p o s i t i o n≥ 0°CA
Ta r g e t t i m i n g a d v a n c e l a r g e i n t e g r a t e d
counter
30 seconds or more
AV C S p o s i t i v e d ev i a t i o n i n t e g r a t e d va l u e
or
AV C S n e g a t i v e d ev i a t i o n i n t e g r a t e d
value
> 8000 (R Bank)°CA
8000 (L Bank)
< –2500 (R Bank)°CA
–2500 (L Bank)
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value
AV C S t a r g e t p o s i t i o n≥ 0°CA
Ta r g e t t i m i n g a d v a n c e l a r g e i n t e g r a t e d
counter
30 seconds or more
AV C S p o s i t i v e d ev i a t i o n i n t e g r a t e d va l u e
or
AV C S n e g a t i v e d ev i a t i o n i n t e g r a t e d
value
≤ 8000 (R Bank)°CA
8000 (L Bank)
≥ –2500 (R Bank)°CA
–2500 (L Bank)
Page 1718 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-106
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
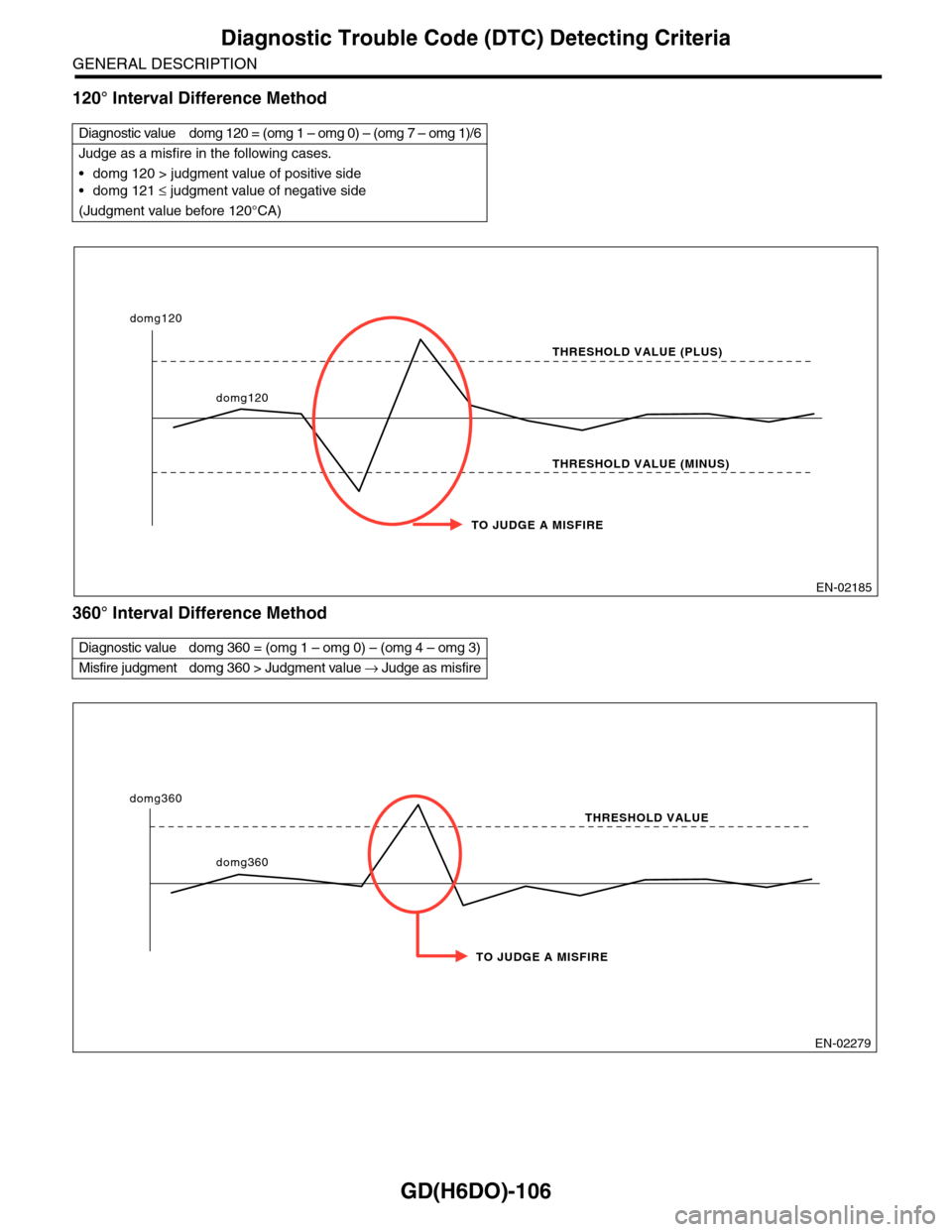
120° Interval Difference Method
360° Interval Difference Method
Diagnostic value domg 120 = (omg 1 – omg 0) – (omg 7 – omg 1)/6
Judge as a misfire in the following cases.
•domg 120 > judgment value of positive side
•domg 121 ≤ judgment value of negative side
(Judgment value before 120°CA)
Diagnostic value domg 360 = (omg 1 – omg 0) – (omg 4 – omg 3)
Misfire judgment domg 360 > Judgment value → Judge as misfire
EN-02185
TO JUDGE A MISFIRE
THRESHOLD VALUE (PLUS)
THRESHOLD VALUE (MINUS)
domg120
domg120
EN-02279
TO JUDGE A MISFIRE
THRESHOLD VALUE
domg360
domg360
Page 1737 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-125
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
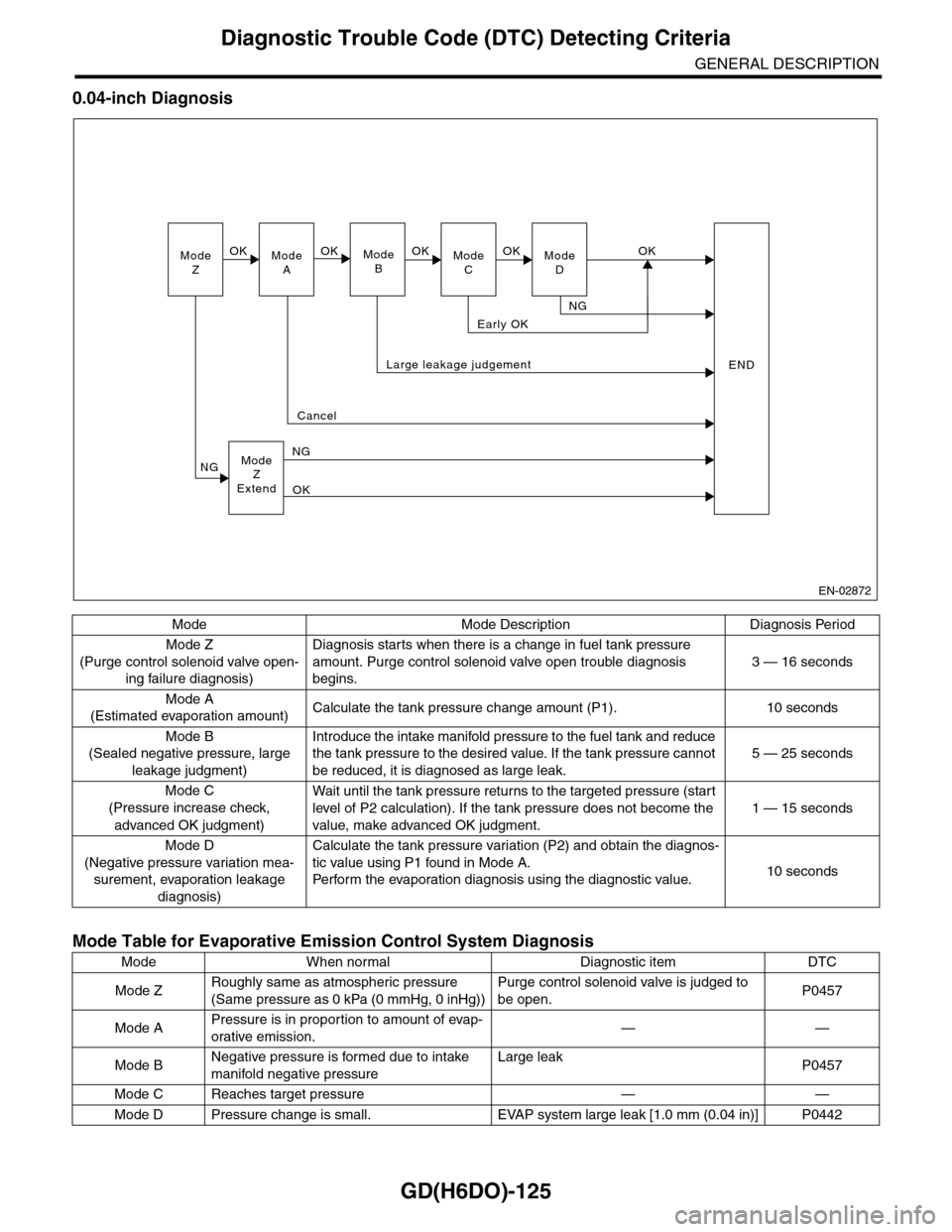
0.04-inch Diagnosis
Mode Mode Description Diagnosis Period
Mode Z
(Purge control solenoid valve open-
ing failure diagnosis)
Diagnosis starts when there is a change in fuel tank pressure
amount. Purge control solenoid valve open trouble diagnosis
begins.
3 — 16 seconds
Mode A
(Estimated evaporation amount)Calculate the tank pressure change amount (P1). 10 seconds
Mode B
(Sealed negative pressure, large
leakage judgment)
Introduce the intake manifold pressure to the fuel tank and reduce
the tank pressure to the desired value. If the tank pressure cannot
be reduced, it is diagnosed as large leak.
5 — 25 seconds
Mode C
(Pressure increase check,
advanced OK judgment)
Wait until the tank pressure retur ns to the targeted pressure (star t
level of P2 calculation). If the tank pressure does not become the
value, make advanced OK judgment.
1 — 15 seconds
Mode D
(Negative pressure variation mea-
surement, evaporation leakage
diagnosis)
Calculate the tank pressure variation (P2) and obtain the diagnos-
tic value using P1 found in Mode A.
Pe r fo r m t he eva po ra ti o n d ia g no si s u si n g t h e d ia g no st i c val u e.10 seconds
Mode Table for Evaporative Emission Control System Diagnosis
Mode When normal Diagnostic item DTC
Mode ZRoughly same as atmospheric pressure
(Same pressure as 0 kPa (0 mmHg, 0 inHg))
Purge control solenoid valve is judged to
be open.P0457
Mode APressure is in proportion to amount of evap-
orative emission.——
Mode BNegative pressure is formed due to intake
manifold negative pressure
Large leakP0457
Mode C Reaches target pressure — —
Mode D Pressure change is small. EVAP system large leak [1.0 mm (0.04 in)] P0442
ModeZModeAModeBModeCModeD
OKOKOKOKOK
NG
Early OK
Large leakage judgement
Cancel
ModeZExtend
NG
NG
OK
END
EN-02872
Page 1738 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-126
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
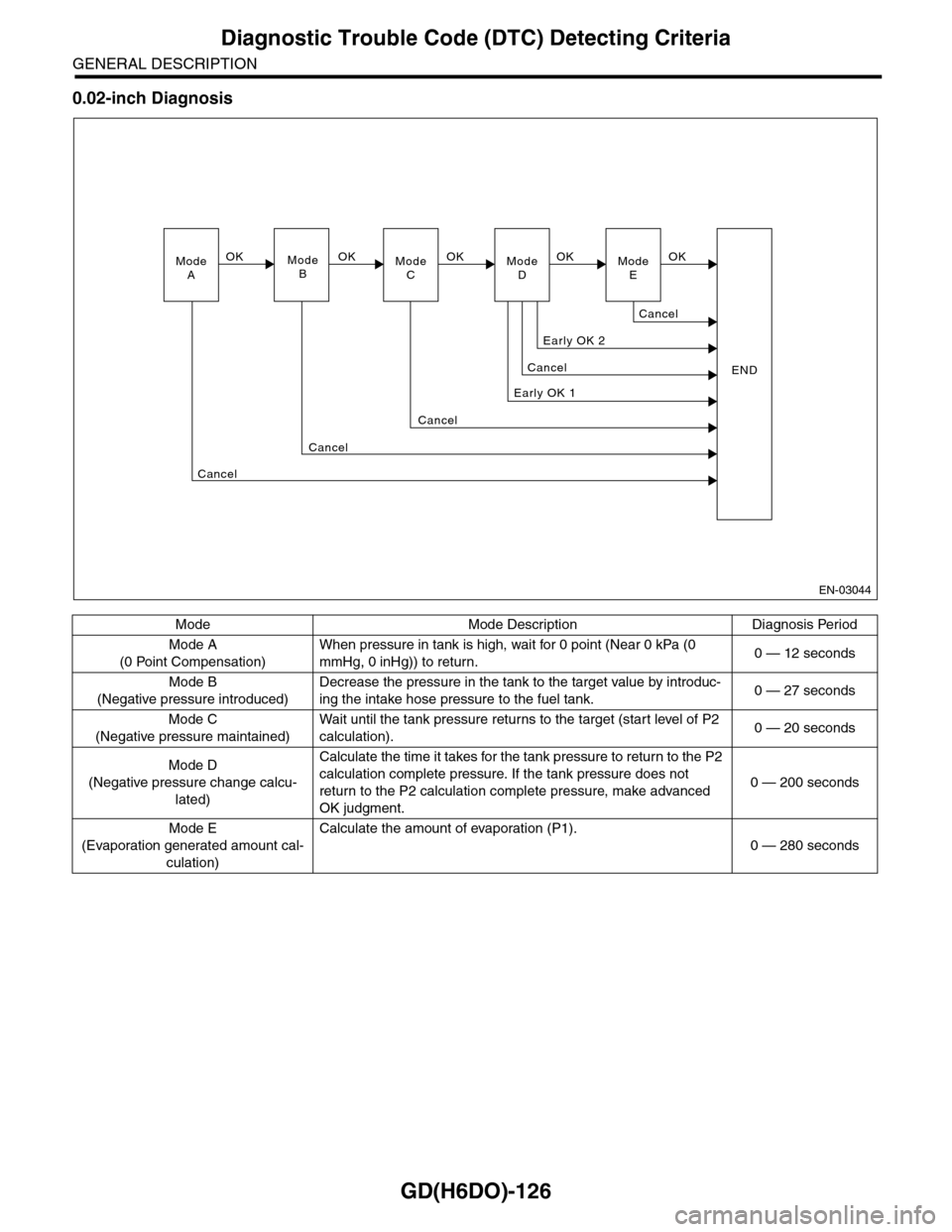
0.02-inch Diagnosis
Mode Mode Description Diagnosis Period
Mode A
(0 Point Compensation)
When pressure in tank is high, wait for 0 point (Near 0 kPa (0
mmHg, 0 inHg)) to return.0 — 12 seconds
Mode B
(Negative pressure introduced)
Decrease the pressure in the tank to the target value by introduc-
ing the intake hose pressure to the fuel tank.0 — 27 seconds
Mode C
(Negative pressure maintained)
Wa i t u nt i l t h e t a nk pr e ss ur e r et u r ns to t he t ar g e t ( s ta r t leve l o f P 2
calculation).0 — 20 seconds
Mode D
(Negative pressure change calcu-
lated)
Calculate the time it takes for the tank pressure to return to the P2
calculation complete pressure. If the tank pressure does not
return to the P2 calculation complete pressure, make advanced
OK judgment.
0 — 200 seconds
Mode E
(Evaporation generated amount cal-
culation)
Calculate the amount of evaporation (P1).
0 — 280 seconds
EN-03044
ModeAModeBModeCModeD
OKOKOK
Early OK 1
Cancel
Cancel
END
Cancel
Cancel
Early OK 2
OKModeE
Cancel
OK
Page 1744 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-132
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Leak Diagnosis
DTC
P0442 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Small Leak)
P0457 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (Fuel Cap Loose/Off)
Diagnostic method
The diagnostic method consists of creating a sealed vacuum in the fuel tank and then determining the pres-
ence of leakage from the speed at which the tank internal pressure returns to atmospheric pressure.
Mode A: (Estimated evaporation gas amount)
Calculate the tank pressure change amount (P1) when using mode A. After calculating P1, switch to mode B.
Mode B: (Negative pressure sealed)
Introduce negative pressure in the intake manifold to the tank.
Approx. 0 → –1.4 (0 → –10.5, 0 → –0.41) kPa (mmHg, inHg)
When the pressure above (desired negative pressure) is reached, enters Mode C.
In this case, if the tank pressure does not become the desired negative pressure, judge that there is a large
leakage (10 seconds or 25 seconds) in the system.
Abnormality Judgment
Judge as NG (large leak) when the criteria below are met.
Mode C: (Check pressure rise)
Stop the introduction of negative pressure. (Wait until the tank pressure returns to the start level of P2 cal-
culation.)
Change to Mode D when the tank pressure returns to the start level of P2 calculation.
Judge immediate OK and change to Mode E when it does not return in spite of spending the specified time.
Mode D: (Measure amount of negative pressure change)
Monitor the tank pressure change amount when using mode D. In this case, the tank pressure increases,
(nears atmospheric pressure) because evaporation occurs. However, if any leakage exists, the pressure in-
creases additionally in proportion to this leakage. The pressure variation of this tank is P2.
After calculating P2, perform a small leak diagnosis according to the items below.
When Mode D is ended
Assign tank variations measured in Mode A and Mode B; P1 and P2, to the formula below, judge small leaks
in the system. If the measured judgment value exceeds the threshold value, it is judged to be a malfunction.
Judge as NG when the criteria below are completed and Judge as OK when not completed.
* 1.5: Evaporation amount compensation value when below negative pressure (Amount of evaporation occurrence increases as
a vacuum condition increases.)
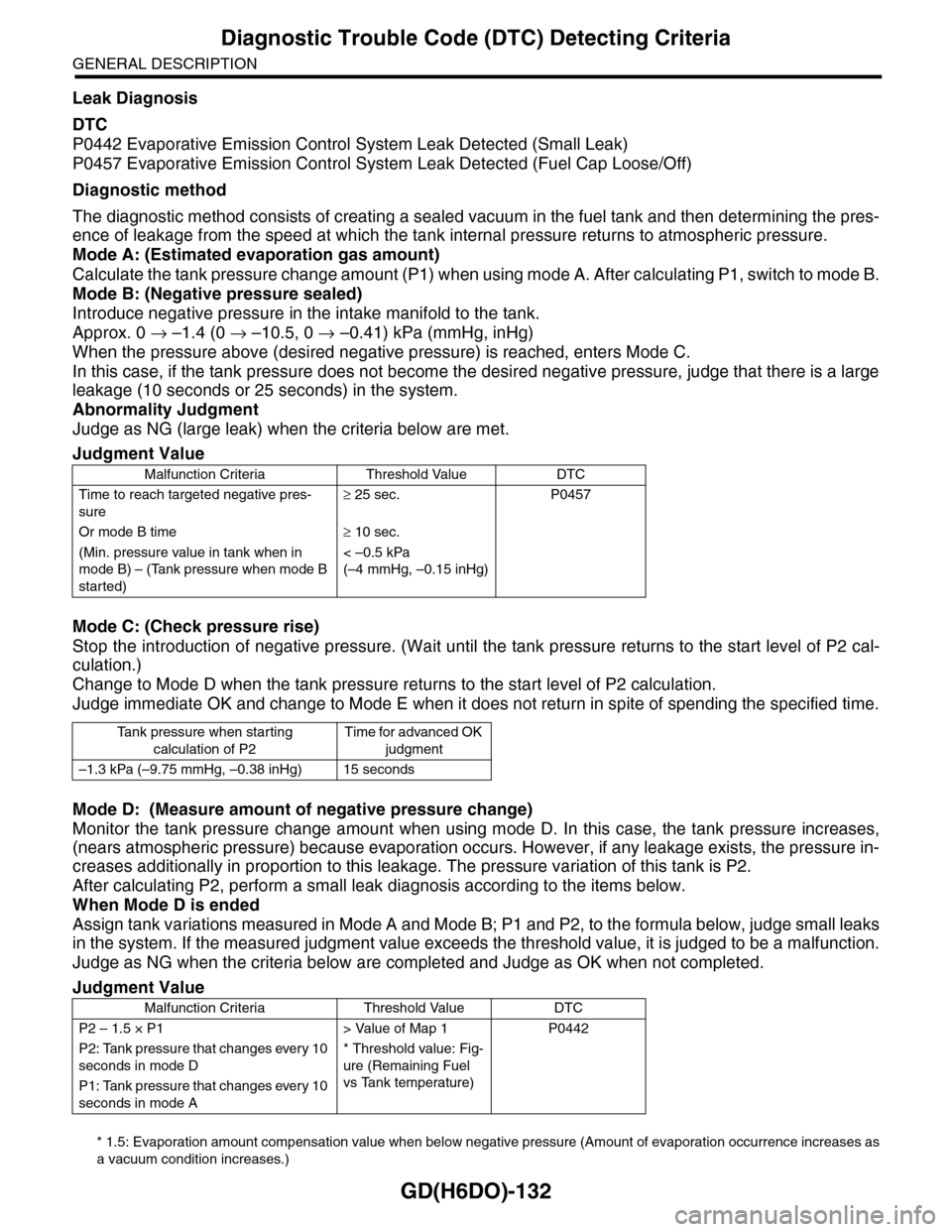
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value DTC
Time to reach targeted negative pres-
sure
≥ 25 sec. P0457
Or mode B time≥ 10 sec.
(Min. pressure value in tank when in
mode B) – (Tank pressure when mode B
started)
< –0.5 kPa
(–4 mmHg, –0.15 inHg)
Ta n k p r e s s u r e w h e n s t a r t i n g
calculation of P2
Time for advanced OK
judgment
–1.3 kPa (–9.75 mmHg, –0.38 inHg) 15 seconds
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value DTC
P2 – 1.5 × P1 > Value of Map 1 P0442
P2: Tank pressure that changes every 10
seconds in mode D
* Threshold value: Fig-
ure (Remaining Fuel
vs Tank temperature)
P1: Tank pressure that changes every 10
seconds in mode A
Page 1745 of 2453
GD(H6DO)-133
Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Detecting Criteria
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
Time Needed for Diagnosis: 30 to 100 seconds
0.02-inch Diagnosis
DTC
P0456 Evaporative Emission Control System Leak Detected (very small leak)
Diagnostic method
The diagnostic method consists of creating a sealed vacuum in the fuel tank and then determining the pres-
ence of leakage from the speed at which the tank internal pressure returns to atmospheric pressure.
Mode A: (0 Point Compensation)
When pressure in tank is high, wait for 0 point 0 kPa (Near 0 mmHg, 0 inHg) to return.Shift to mode B when
0 point returns.
Cancel the diagnosis when 0 point does not return in the specified time.
Mode B: (Negative pressure introduced)
Introduce negative pressure in the intake manifold to the tank.
Approx. 0 → –2.0 kPa (0 mmHg → –15 mmHg, 0 → –0.59 inHg)
When the pressure above (desired negative pressure) is reached, Mode C is entered.
Cancel the diagnosis when the targeted pressure in the tank is not reached.
Mode C: (Negative pressure maintained)
Stop the introduction of negative pressure and wait until the tank pressure returns to the start level of P2 cal-
culation.
Change to Mode D either when the tank pressure returns to the start level of P2 calculation, or when the pre-
determined amount of time has passed.
Mode D: (Calculate the amount of negative pressure change)
Monitor the tank pressure in mode D, calculate (P2) the pressure change in the tank, and measure the time
(evpdset) for the tank pressure to return when calculation of P2 is completed. Shift to mode E when pressure
returns. Make an advance OK judgment using the value of P2, or cancel, when the pressure in the tank does
not return after calculation of P2 is completed even when the predetermined amount of time has passed.
When the following conditions are established, it is OK.
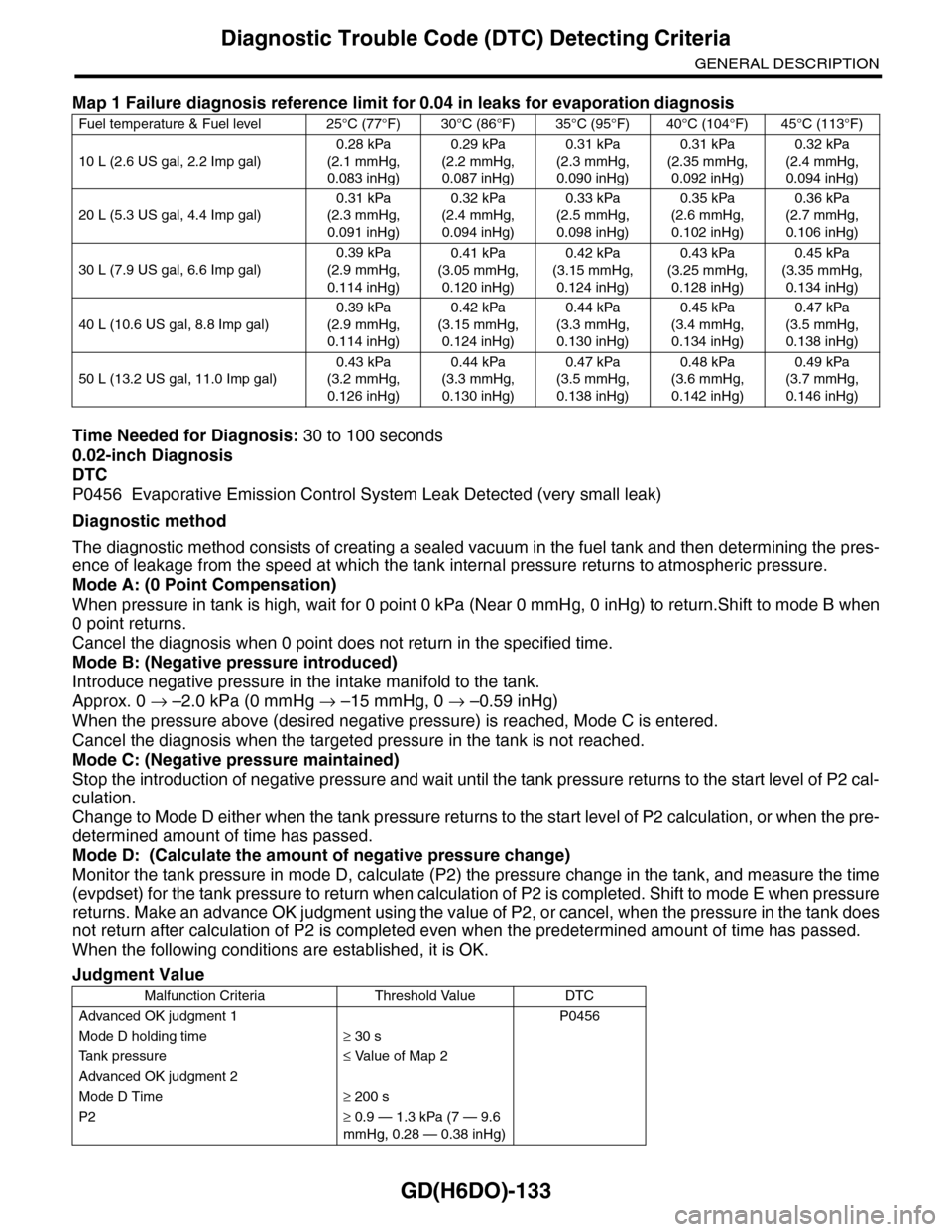
Map 1 Failure diagnosis reference limit for 0.04 in leaks for evaporation diagnosis
Fuel temperature & Fuel level 25°C (77°F) 30°C (86°F) 35°C (95°F) 40°C (104°F) 45°C (113°F)
10 L (2.6 US gal, 2.2 Imp gal)
0.28 kPa
(2.1 mmHg,
0.083 inHg)
0.29 kPa
(2.2 mmHg,
0.087 inHg)
0.31 kPa
(2.3 mmHg,
0.090 inHg)
0.31 kPa
(2.35 mmHg,
0.092 inHg)
0.32 kPa
(2.4 mmHg,
0.094 inHg)
20 L (5.3 US gal, 4.4 Imp gal)
0.31 kPa
(2.3 mmHg,
0.091 inHg)
0.32 kPa
(2.4 mmHg,
0.094 inHg)
0.33 kPa
(2.5 mmHg,
0.098 inHg)
0.35 kPa
(2.6 mmHg,
0.102 inHg)
0.36 kPa
(2.7 mmHg,
0.106 inHg)
30 L (7.9 US gal, 6.6 Imp gal)
0.39 kPa
(2.9 mmHg,
0.114 inHg)
0.41 kPa
(3.05 mmHg,
0.120 inHg)
0.42 kPa
(3.15 mmHg,
0.124 inHg)
0.43 kPa
(3.25 mmHg,
0.128 inHg)
0.45 kPa
(3.35 mmHg,
0.134 inHg)
40 L (10.6 US gal, 8.8 Imp gal)
0.39 kPa
(2.9 mmHg,
0.114 inHg)
0.42 kPa
(3.15 mmHg,
0.124 inHg)
0.44 kPa
(3.3 mmHg,
0.130 inHg)
0.45 kPa
(3.4 mmHg,
0.134 inHg)
0.47 kPa
(3.5 mmHg,
0.138 inHg)
50 L (13.2 US gal, 11.0 Imp gal)
0.43 kPa
(3.2 mmHg,
0.126 inHg)
0.44 kPa
(3.3 mmHg,
0.130 inHg)
0.47 kPa
(3.5 mmHg,
0.138 inHg)
0.48 kPa
(3.6 mmHg,
0.142 inHg)
0.49 kPa
(3.7 mmHg,
0.146 inHg)
Judgment Value
Malfunction Criteria Threshold Value DTC
Advanced OK judgment 1 P0456
Mode D holding time≥ 30 s
Ta n k p r e s s u r e≤ Value of Map 2
Advanced OK judgment 2
Mode D Time≥ 200 s
P2≥ 0.9 — 1.3 kPa (7 — 9.6
mmHg, 0.28 — 0.38 inHg)
Page 1974 of 2453
SC(H6DO)-16
Starter
STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS
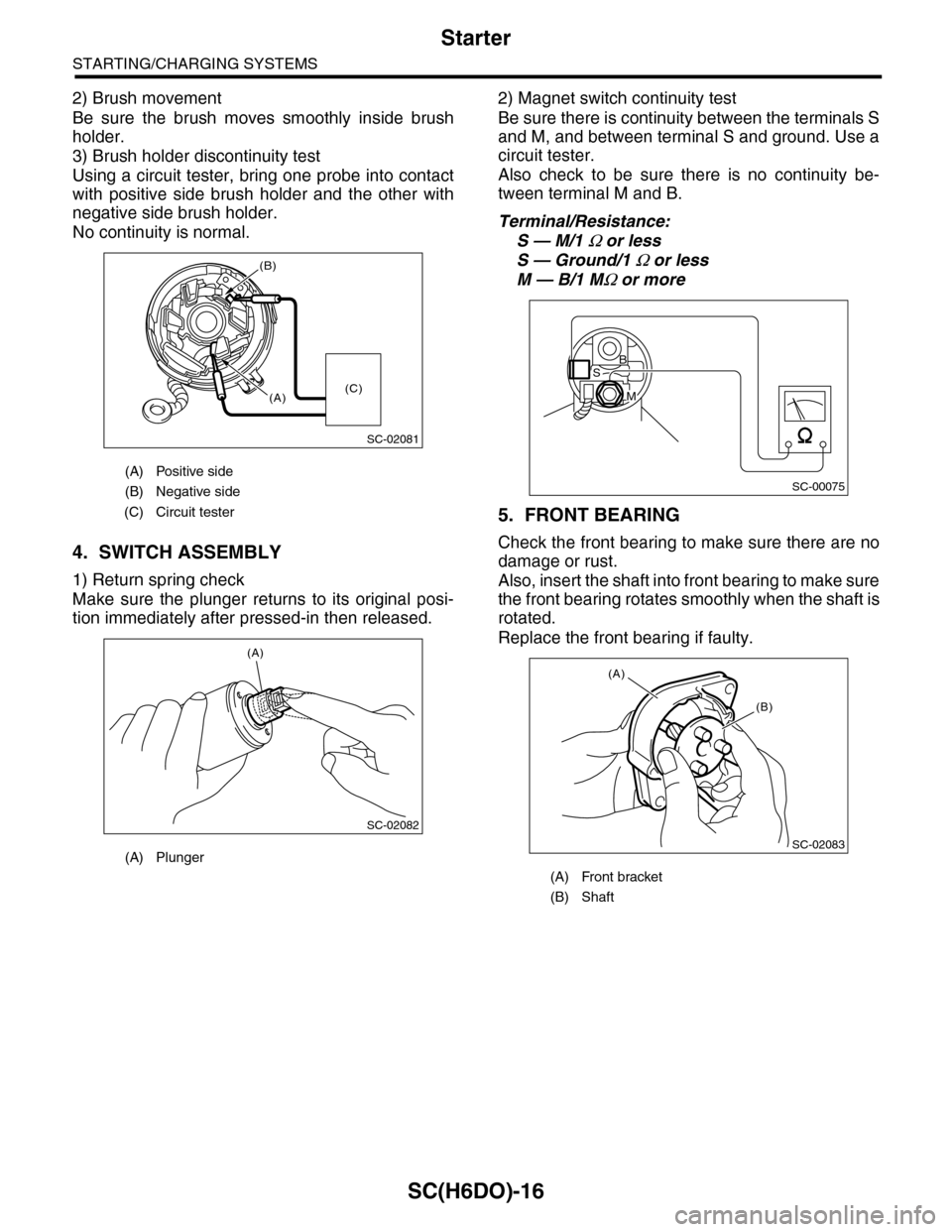
2) Brush movement
Be sure the brush moves smoothly inside brush
holder.
3) Brush holder discontinuity test
Using a circuit tester, bring one probe into contact
with positive side brush holder and the other with
negative side brush holder.
No continuity is normal.
4. SWITCH ASSEMBLY
1) Return spring check
Make sure the plunger returns to its original posi-
tion immediately after pressed-in then released.
2) Magnet switch continuity test
Be sure there is continuity between the terminals S
and M, and between terminal S and ground. Use a
circuit tester.
Also check to be sure there is no continuity be-
tween terminal M and B.
Terminal/Resistance:
S — M/1 Ω or less
S — Ground/1 Ω or less
M — B/1 MΩ or more
5. FRONT BEARING
Check the front bearing to make sure there are no
damage or rust.
Also, insert the shaft into front bearing to make sure
the front bearing rotates smoothly when the shaft is
rotated.
Replace the front bearing if faulty.
(A) Positive side
(B) Negative side
(C) Circuit tester
(A) Plunger
SC-02081
(B)
(A)(C)
SC-02082
(A)
(A) Front bracket
(B) Shaft
SC-00075
B
M
S
SC-02083
(A)
(B)
Page 1976 of 2453
SC(H6DO)-18
Starter
STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS
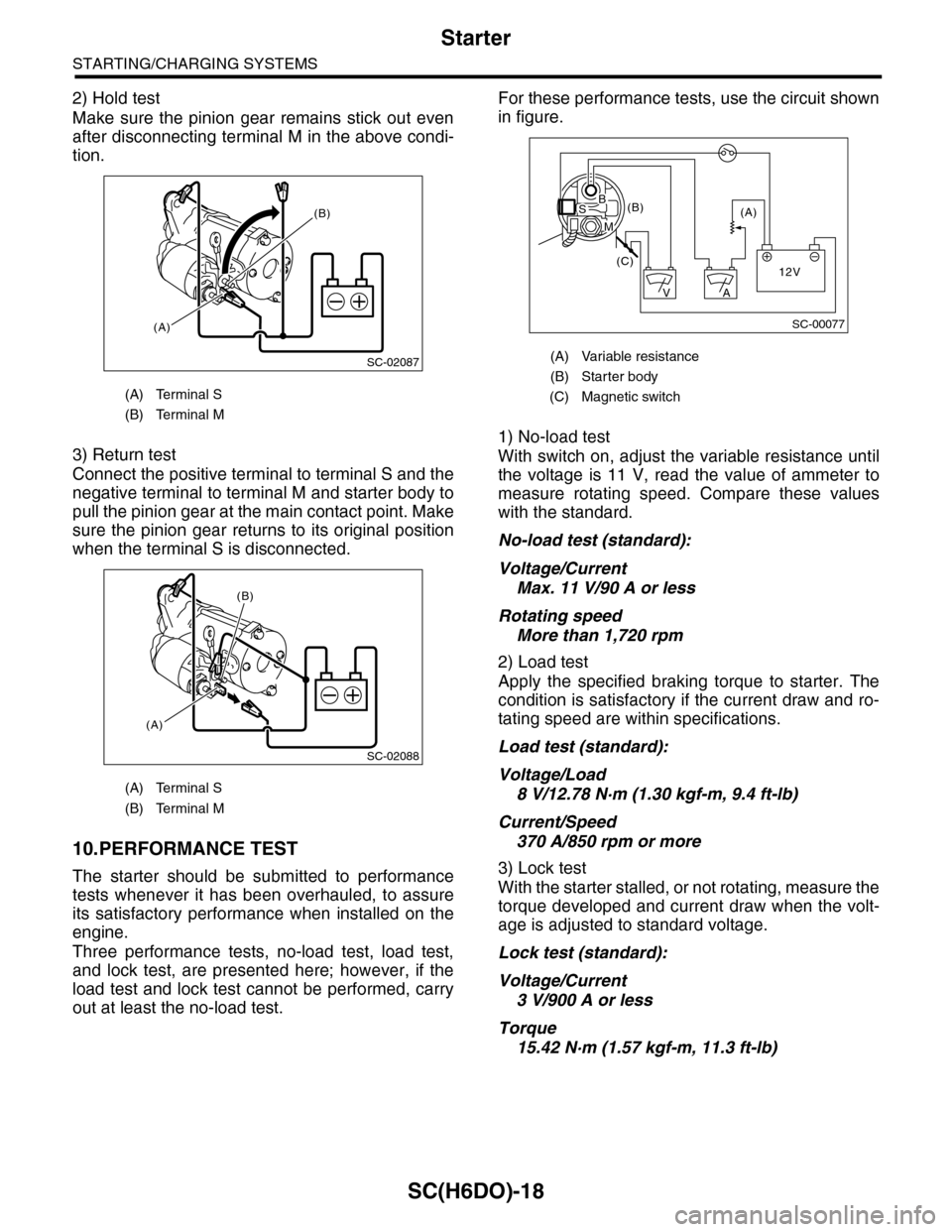
2) Hold test
Make sure the pinion gear remains stick out even
after disconnecting terminal M in the above condi-
tion.
3) Return test
Connect the positive terminal to terminal S and the
negative terminal to terminal M and starter body to
pull the pinion gear at the main contact point. Make
sure the pinion gear returns to its original position
when the terminal S is disconnected.
10.PERFORMANCE TEST
The starter should be submitted to performance
tests whenever it has been overhauled, to assure
its satisfactory performance when installed on the
engine.
Three performance tests, no-load test, load test,
and lock test, are presented here; however, if the
load test and lock test cannot be performed, carry
out at least the no-load test.
For these performance tests, use the circuit shown
in figure.
1) No-load test
With switch on, adjust the variable resistance until
the voltage is 11 V, read the value of ammeter to
measure rotating speed. Compare these values
with the standard.
No-load test (standard):
Voltage/Current
Max. 11 V/90 A or less
Rotating speed
More than 1,720 rpm
2) Load test
Apply the specified braking torque to starter. The
condition is satisfactory if the current draw and ro-
tating speed are within specifications.
Load test (standard):
Voltage/Load
8 V/12.78 N·m (1.30 kgf-m, 9.4 ft-lb)
Current/Speed
370 A/850 rpm or more
3) Lock test
With the starter stalled, or not rotating, measure the
torque developed and current draw when the volt-
age is adjusted to standard voltage.
Lock test (standard):
Voltage/Current
3 V/900 A or less
Torque
15.42 N·m (1.57 kgf-m, 11.3 ft-lb)
(A) Terminal S
(B) Terminal M
(A) Terminal S
(B) Terminal M
SC-02087
(B)
(A)
SC-02088
(A)
(B)
(A) Variable resistance
(B) Starter body
(C) Magnetic switch
SC-00077
(A)(B)
(C)12V
+
AV
BS
M
Page 1980 of 2453

SC(H6DO)-22
Generator
STARTING/CHARGING SYSTEMS
D: ASSEMBLY
Assemble in the reverse order of disassembly.
1) Pulling up brush
Before assembling, press the brush down into
brush holder, and then fix them in that position by
passing a [1 mm (0.08 in) dia. 40 to 50 mm (1.6 to
2.0 in) long] wire through the hole as shown in the
figure.
CAUTION:
Be sure to remove the wire after reassembly.
2) Install the ball bearing.
(1) Set the ball bearing on the front cover, and
then securely install an appropriate tool (such
as a fit socket wrench) to the bearing outer race.
(2) Press the ball bearing into the specified po-
sition using a press.
(3) Install the bearing retainer.
3) Press the bearing (rear side) into the rotor shaft
using a press to install.
4) Heat the bearing box in rear cover [50 to 60°C
(122 to 140°F)], and then press the rear bearing
into rear cover.
CAUTION:
Grease should not be applied to rear bearing.
Remove the oil completely if it is found on bear-
ing box.
5) After reassembly, turn the pulley by hand to
check that rotor turns smoothly.
E: INSPECTION
1. DIODE
CAUTION:
Never use a mega tester (designed for reading
high voltage) or any other similar instrument
for this test; otherwise, the diodes may be dam-
aged.
1) Checking positive diode
Check for continuity between the diode lead and
positive side heat sink. The positive diode is in
good condition if resistance is 1 Ω o r l e s s o n l y i n t h e
direction from the diode lead to heat sink.
2) Checking negative diode
Check for continuity between the negative side
heat sink and diode lead. The negative diode is in
good condition if resistance is 1 Ω o r l e s s o n l y i n t h e
direction from the heat sink to diode lead.
(A) Wire
SC-00092
(A)
(A) Diode lead
(B) Heat sink (positive side)
(A) Diode lead
(B) Heat sink (negative side)
SC-00042
(B)(A)
(A)
(B)
SC-00043