SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.GPages: 698, PDF Size: 16.01 MB
Page 471 of 698
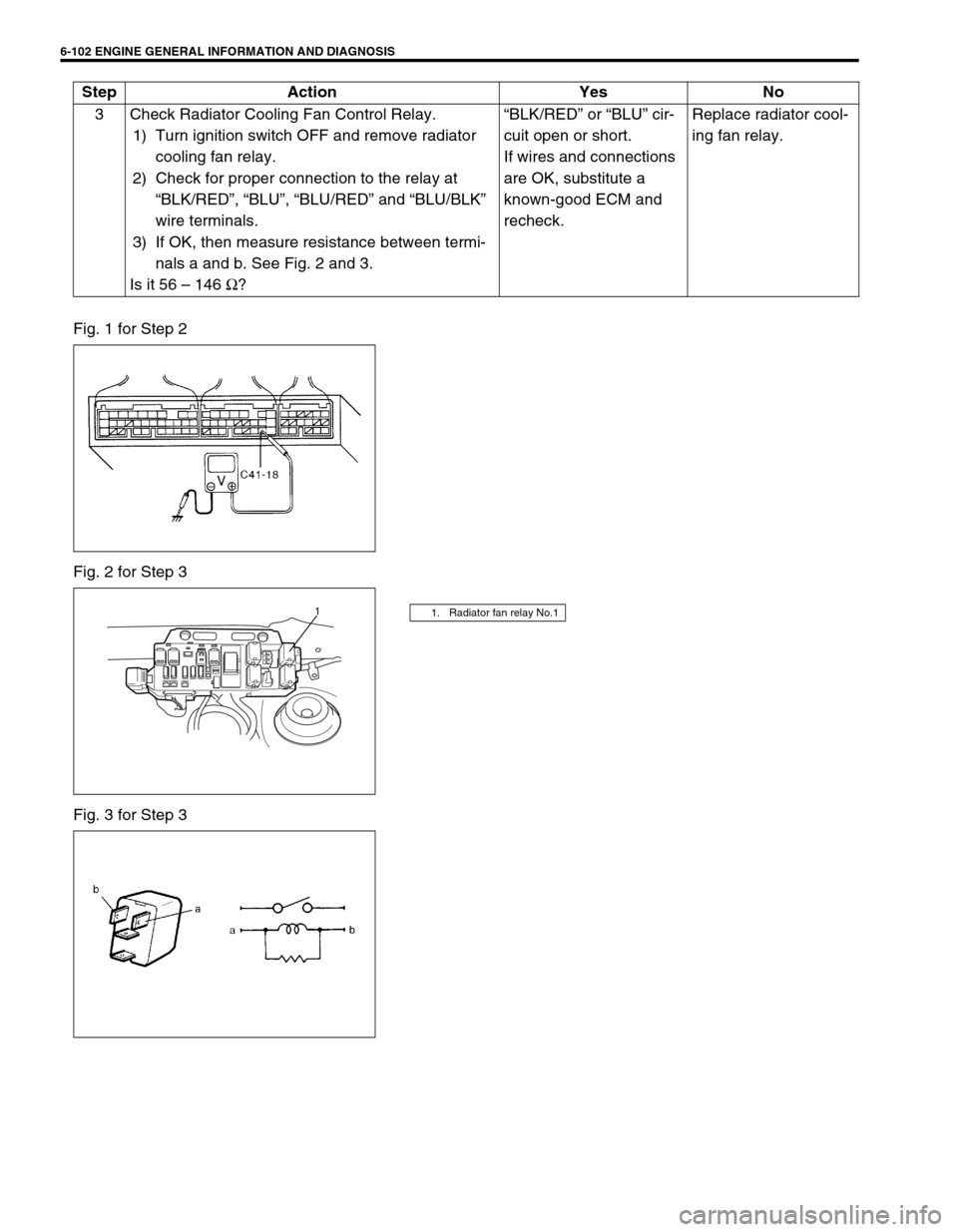
6-102 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Fig. 1 for Step 2
Fig. 2 for Step 3
Fig. 3 for Step 33 Check Radiator Cooling Fan Control Relay.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF and remove radiator
cooling fan relay.
2) Check for proper connection to the relay at
“BLK/RED”, “BLU”, “BLU/RED” and “BLU/BLK”
wire terminals.
3) If OK, then measure resistance between termi-
nals a and b. See Fig. 2 and 3.
Is it 56 – 146 Ω?“BLK/RED” or “BLU” cir-
cuit open or short.
If wires and connections
are OK, substitute a
known-good ECM and
recheck.Replace radiator cool-
ing fan relay. Step Action Yes No
1. Radiator fan relay No.11
Page 472 of 698
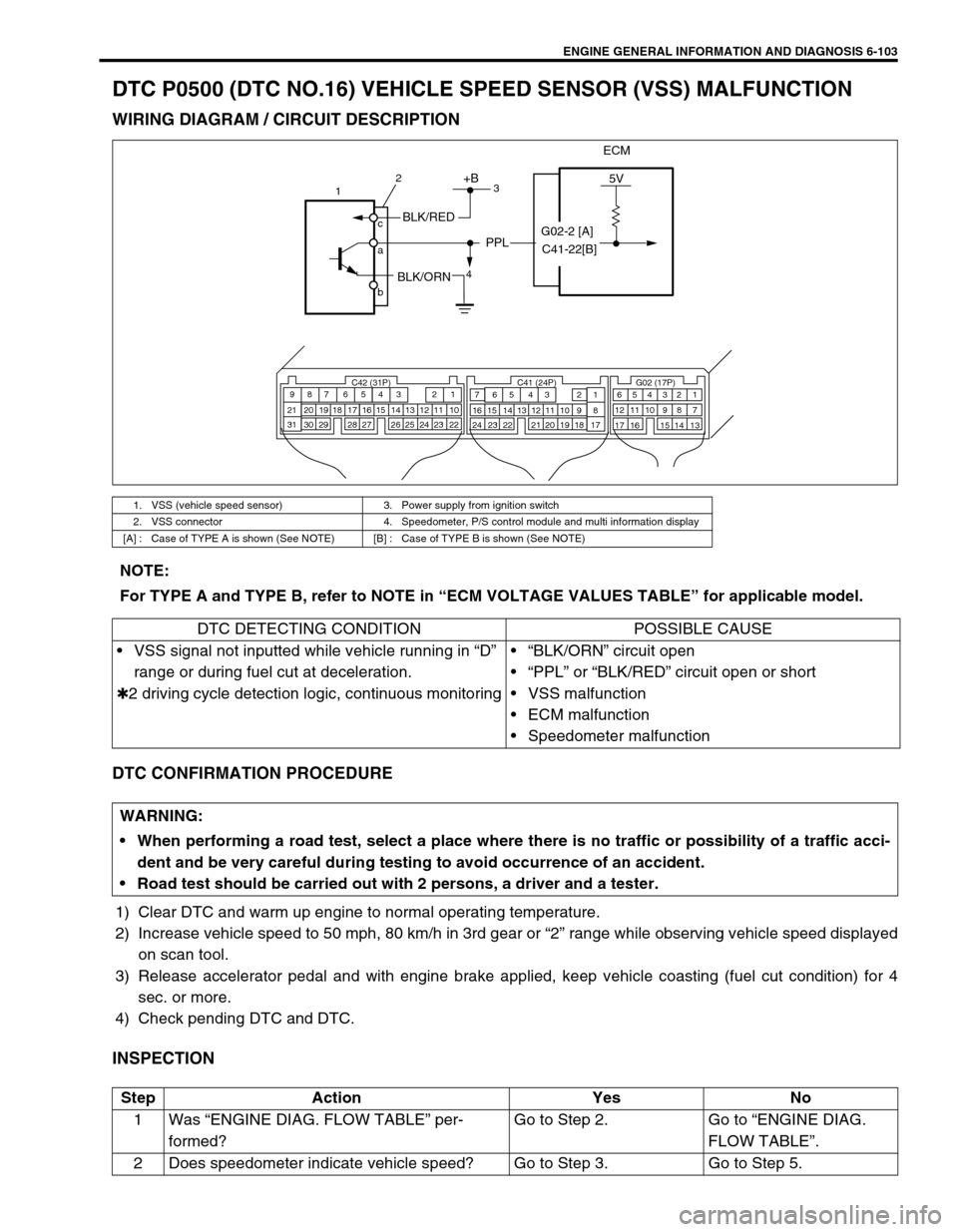
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-103
DTC P0500 (DTC NO.16) VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR (VSS) MALFUNCTION
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Clear DTC and warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
2) Increase vehicle speed to 50 mph, 80 km/h in 3rd gear or “2” range while observing vehicle speed displayed
on scan tool.
3) Release accelerator pedal and with engine brake applied, keep vehicle coasting (fuel cut condition) for 4
sec. or more.
4) Check pending DTC and DTC.
INSPECTION
1. VSS (vehicle speed sensor) 3. Power supply from ignition switch
2. VSS connector 4. Speedometer, P/S control module and multi information display
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
ECM
5V+B
BLK/RED
BLK/ORN
PPL
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
1
4 c
a
b2
3
G02-2 [A]
C41-22[B]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
VSS signal not inputted while vehicle running in “D”
range or during fuel cut at deceleration.
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitoring“BLK/ORN” circuit open
“PPL” or “BLK/RED” circuit open or short
VSS malfunction
ECM malfunction
Speedometer malfunction
WARNING:
When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic acci-
dent and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester.
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Does speedometer indicate vehicle speed? Go to Step 3. Go to Step 5.
Page 473 of 698
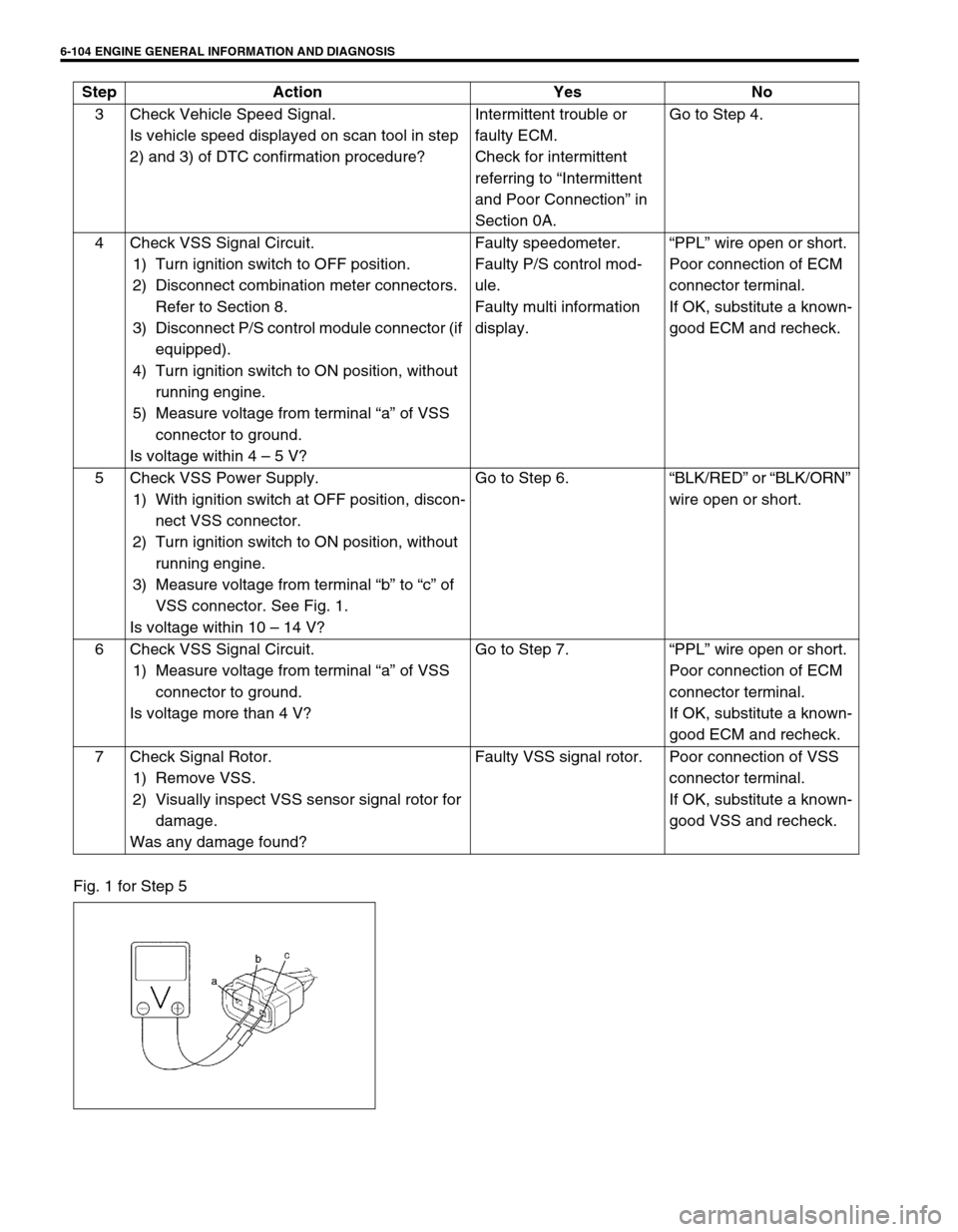
6-104 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
Fig. 1 for Step 53 Check Vehicle Speed Signal.
Is vehicle speed displayed on scan tool in step
2) and 3) of DTC confirmation procedure?Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0A.Go to Step 4.
4 Check VSS Signal Circuit.
1) Turn ignition switch to OFF position.
2) Disconnect combination meter connectors.
Refer to Section 8.
3) Disconnect P/S control module connector (if
equipped).
4) Turn ignition switch to ON position, without
running engine.
5) Measure voltage from terminal “a” of VSS
connector to ground.
Is voltage within 4 – 5 V?Faulty speedometer.
Faulty P/S control mod-
ule.
Faulty multi information
display.“PPL” wire open or short.
Poor connection of ECM
connector terminal.
If OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
5 Check VSS Power Supply.
1) With ignition switch at OFF position, discon-
nect VSS connector.
2) Turn ignition switch to ON position, without
running engine.
3) Measure voltage from terminal “b” to “c” of
VSS connector. See Fig. 1.
Is voltage within 10 – 14 V?Go to Step 6.“BLK/RED” or “BLK/ORN”
wire open or short.
6 Check VSS Signal Circuit.
1) Measure voltage from terminal “a” of VSS
connector to ground.
Is voltage more than 4 V?Go to Step 7.“PPL” wire open or short.
Poor connection of ECM
connector terminal.
If OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
7 Check Signal Rotor.
1) Remove VSS.
2) Visually inspect VSS sensor signal rotor for
damage.
Was any damage found?Faulty VSS signal rotor. Poor connection of VSS
connector terminal.
If OK, substitute a known-
good VSS and recheck. Step Action Yes No
Page 474 of 698
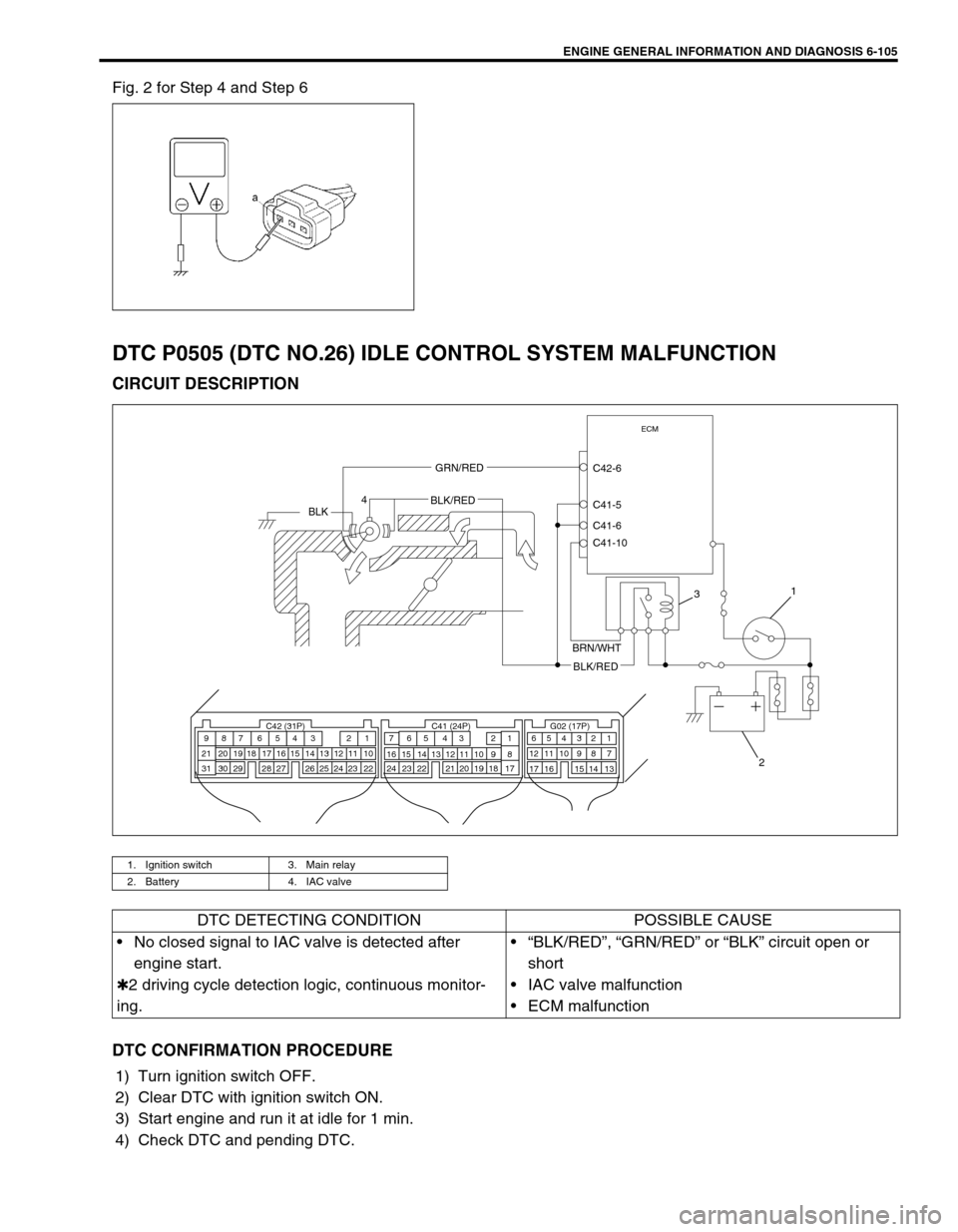
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-105
Fig. 2 for Step 4 and Step 6
DTC P0505 (DTC NO.26) IDLE CONTROL SYSTEM MALFUNCTION
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON.
3) Start engine and run it at idle for 1 min.
4) Check DTC and pending DTC.
1. Ignition switch 3. Main relay
2. Battery 4. IAC valve
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
2
13 4
ECM
C42-6
C41-5
C41-6
C41-10GRN/RED
BLKBLK/RED
BRN/WHT
BLK/RED
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
No closed signal to IAC valve is detected after
engine start.
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitor-
ing.“BLK/RED”, “GRN/RED” or “BLK” circuit open or
short
IAC valve malfunction
ECM malfunction
Page 475 of 698
6-106 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
INSPECTION
Fig. 1 for Step 3Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Is SUZUKI scan tool available? Go to Step 3. Go to Step 4.
3 Check Idle Air Control System.
1) Connect SUZUKI scan tool to DLC with igni-
tion switch OFF, set parking brake and
block drive wheels.
2) Warm up engine to normal operating tem-
perature.
3) Clear DTC and select “MISC TEST” mode
on SUZUKI scan tool. See Fig. 1.
Is it possible to control (increase and reduce)
engine idle speed by using SUZUKI scan tool? Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0A.Go to Step 5.
4 Check Idle Air Control System.
1) Remove IAC valve from throttle body refer-
ring to “IAC Valve Removal” in Section 6E1.
2) Check IAC valve for operation referring to
“IAC Valve Inspection” in Section 6E1. See
Fig. 2.
Is check result satisfactory?Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0A.Go to Step 5.
5 Check Wire Harness for open and short.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Disconnect IAC valve connector.
3) Check for proper connection to IAC valve at
each terminals.
4) If OK, disconnect ECM connector.
5) Check for proper connection to ECM at
C42-6 terminal.
6) If OK, check “BLK/RED”, “GRN/RED” and
“BLK” circuit for open and short.
Are they in good condition?Replace IAC valve and
recheck.Repair or replace.
[A] : When using SUZUKI scan tool:[ A]
Page 476 of 698
![SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Workshop Manual ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-107
Fig. 2 for Step 4
[A] : Without using SUZUKI scan tool: SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Workshop Manual ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-107
Fig. 2 for Step 4
[A] : Without using SUZUKI scan tool:](/img/20/7606/w960_7606-475.png)
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-107
Fig. 2 for Step 4
[A] : Without using SUZUKI scan tool:
Page 477 of 698
6-108 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P1450 BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR LOW/HIGH INPUT
DTC P1451 BAROMETRIC PRESSURE SENSOR PERFORMANCE PROBLEM
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Barometric pressure sensor is installed in ECM.
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON.
3) Turn ignition switch ON for 2 sec., crank engine for 2 sec. and run it at idle for 1 min.
4) Check pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode and DTC in “DTC” mode.
INSPECTION
DTC P1450 :
Substitute a known-good ECM and recheck.
DTC P1451 :
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
DTC P1450 :
Barometric pressure : Sensor voltage is 4.7 V or higher, or
1.6 V or lowerECM (barometric pressure sensor) malfunc-
tion
DTC P1451 :
Vehicle stopped
Engine cranking
Difference between barometric pressure and intake mani-
fold absolute pressure is 26 kPa, 200 mmHg or more
Difference between intake manifold absolute pressure at
engine start and the pressure after engine start is 1.3 kPa,
10 mmHg or less.
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, monitoring once/1 driving.Manifold absolute pressure sensor and its
circuit malfunction
ECM (barometric pressure sensor) malfunc-
tion
NOTE:
Note that atmospheric pressure varies depending on weather conditions as well as altitude.
Take that into consideration when performing these check.
Step Action Yes No
1 Check Barometric Pressure Valve.
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition
switch OFF.
2) Turn ignition switch ON and select “DATA
LIST” mode on scan tool.
3) Check manifold absolute pressure. See Fig.
1.
Is it barometric pressure (approx. 100 kPa, 760
mmHg) at sea level?Substitute a known-good
ECM and recheck.Go to Step 2.
Page 478 of 698
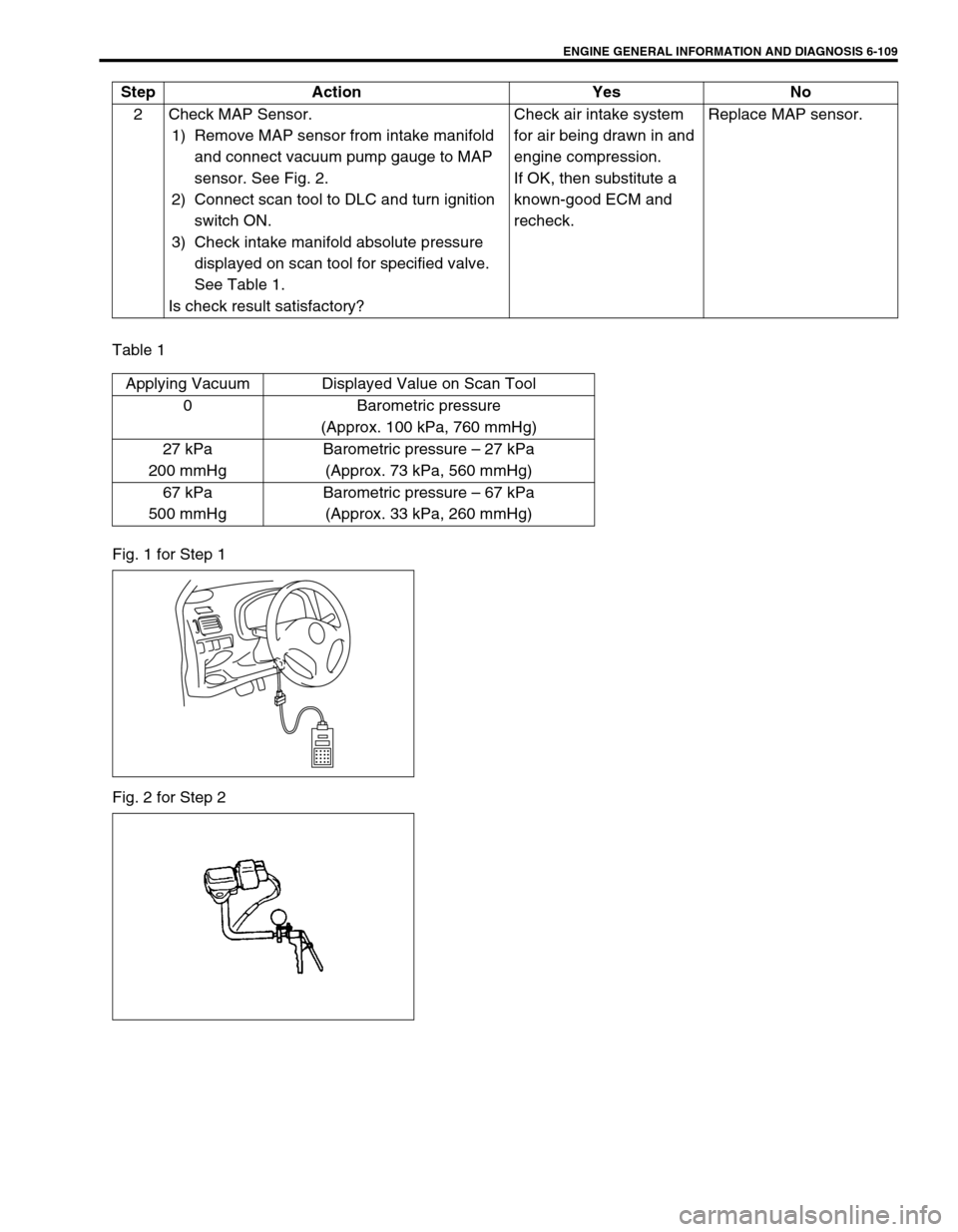
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-109
Table 1
Fig. 1 for Step 1
Fig. 2 for Step 22 Check MAP Sensor.
1) Remove MAP sensor from intake manifold
and connect vacuum pump gauge to MAP
sensor. See Fig. 2.
2) Connect scan tool to DLC and turn ignition
switch ON.
3) Check intake manifold absolute pressure
displayed on scan tool for specified valve.
See Table 1.
Is check result satisfactory?Check air intake system
for air being drawn in and
engine compression.
If OK, then substitute a
known-good ECM and
recheck.Replace MAP sensor. Step Action Yes No
Applying Vacuum Displayed Value on Scan Tool
0 Barometric pressure
(Approx. 100 kPa, 760 mmHg)
27 kPa
200 mmHgBarometric pressure – 27 kPa
(Approx. 73 kPa, 560 mmHg)
67 kPa
500 mmHgBarometric pressure – 67 kPa
(Approx. 33 kPa, 260 mmHg)
Page 479 of 698
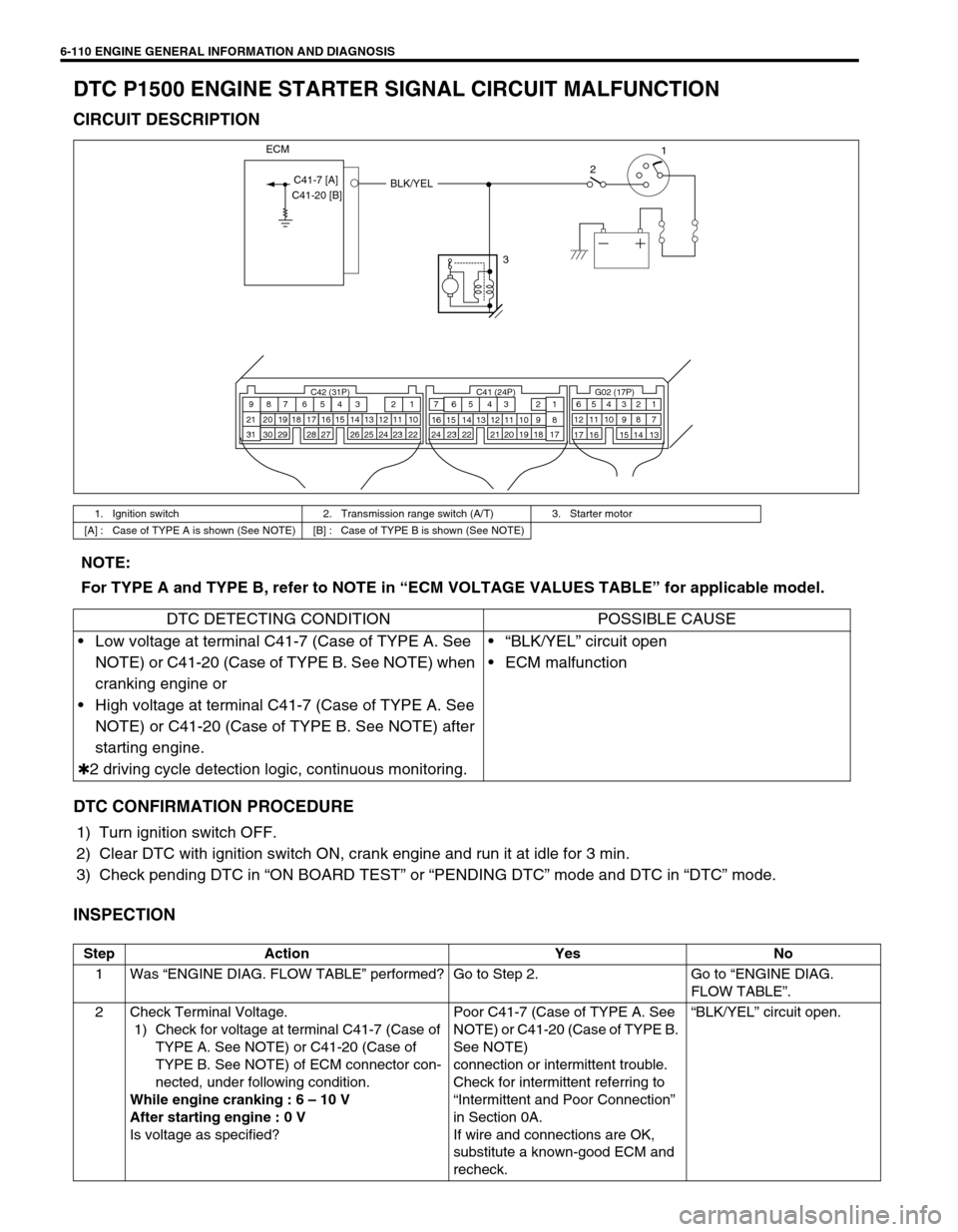
6-110 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P1500 ENGINE STARTER SIGNAL CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON, crank engine and run it at idle for 3 min.
3) Check pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode and DTC in “DTC” mode.
INSPECTION
1. Ignition switch 2. Transmission range switch (A/T) 3. Starter motor
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
321
BLK/YEL
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
ECM
C41-7 [A]
C41-20 [B]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
Low voltage at terminal C41-7 (Case of TYPE A. See
NOTE) or C41-20 (Case of TYPE B. See NOTE) when
cranking engine or
High voltage at terminal C41-7 (Case of TYPE A. See
NOTE) or C41-20 (Case of TYPE B. See NOTE) after
starting engine.
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitoring.“BLK/YEL” circuit open
ECM malfunction
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check Terminal Voltage.
1) Check for voltage at terminal C41-7 (Case of
TYPE A. See NOTE) or C41-20 (Case of
TYPE B. See NOTE) of ECM connector con-
nected, under following condition.
While engine cranking : 6 – 10 V
After starting engine : 0 V
Is voltage as specified?Poor C41-7 (Case of TYPE A. See
NOTE) or C41-20 (Case of TYPE B.
See NOTE)
connection or intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent referring to
“Intermittent and Poor Connection”
in Section 0A.
If wire and connections are OK,
substitute a known-good ECM and
recheck.“BLK/YEL” circuit open.
Page 480 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-111
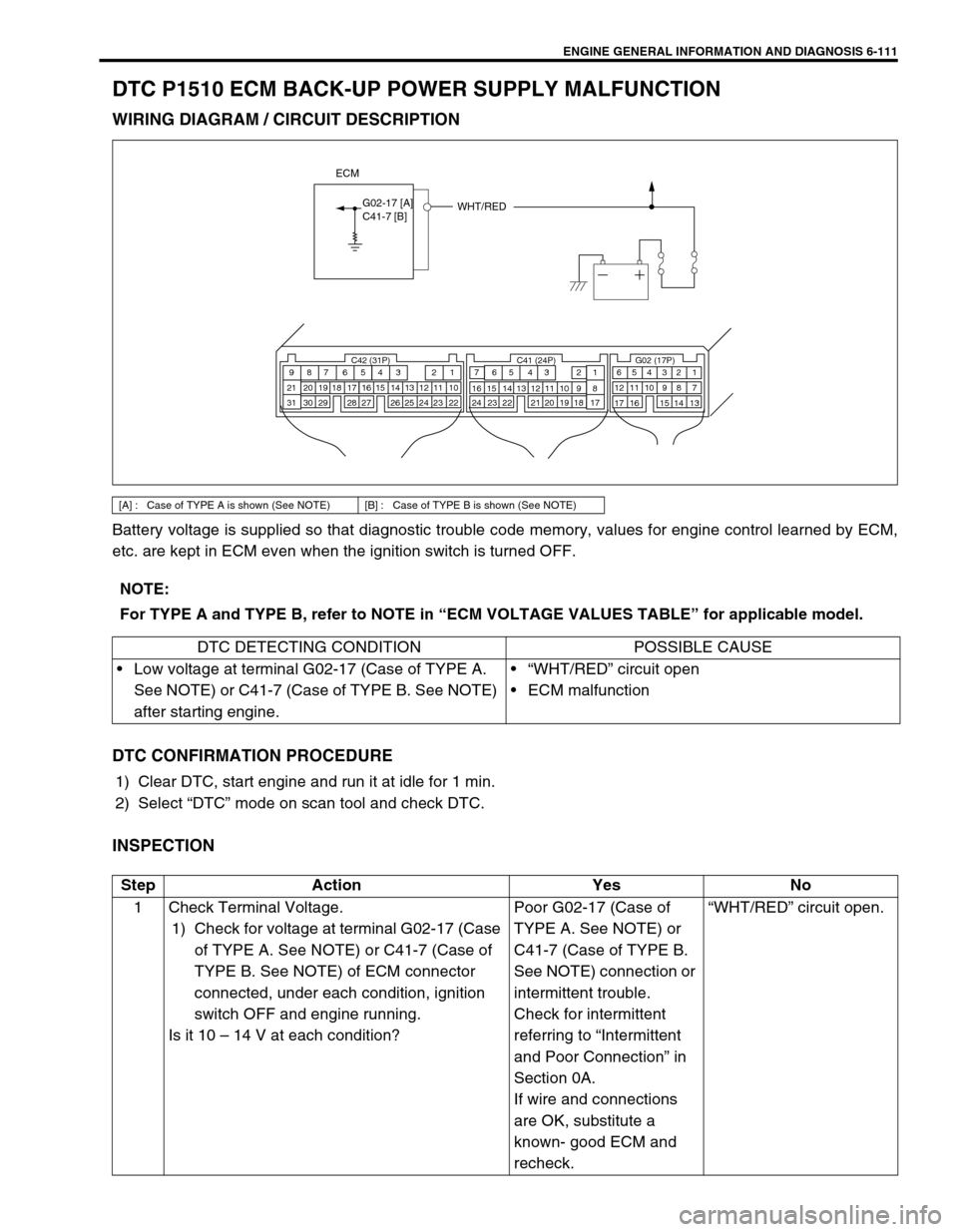
DTC P1510 ECM BACK-UP POWER SUPPLY MALFUNCTION
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Battery voltage is supplied so that diagnostic trouble code memory, values for engine control learned by ECM,
etc. are kept in ECM even when the ignition switch is turned OFF.
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Clear DTC, start engine and run it at idle for 1 min.
2) Select “DTC” mode on scan tool and check DTC.
INSPECTION
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
WHT/RED
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
ECM
G02-17 [A]C41-7 [B]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
Low voltage at terminal G02-17 (Case of TYPE A.
See NOTE) or C41-7 (Case of TYPE B. See NOTE)
after starting engine.“WHT/RED” circuit open
ECM malfunction
Step Action Yes No
1 Check Terminal Voltage.
1) Check for voltage at terminal G02-17 (Case
of TYPE A. See NOTE) or C41-7 (Case of
TYPE B. See NOTE) of ECM connector
connected, under each condition, ignition
switch OFF and engine running.
Is it 10 – 14 V at each condition?Poor G02-17 (Case of
TYPE A. See NOTE) or
C41-7 (Case of TYPE B.
See NOTE) connection or
intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0A.
If wire and connections
are OK, substitute a
known- good ECM and
recheck.“WHT/RED” circuit open.