valve SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2000, Model line: SWIFT, Model: SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.GPages: 698, PDF Size: 16.01 MB
Page 409 of 698
6-40 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
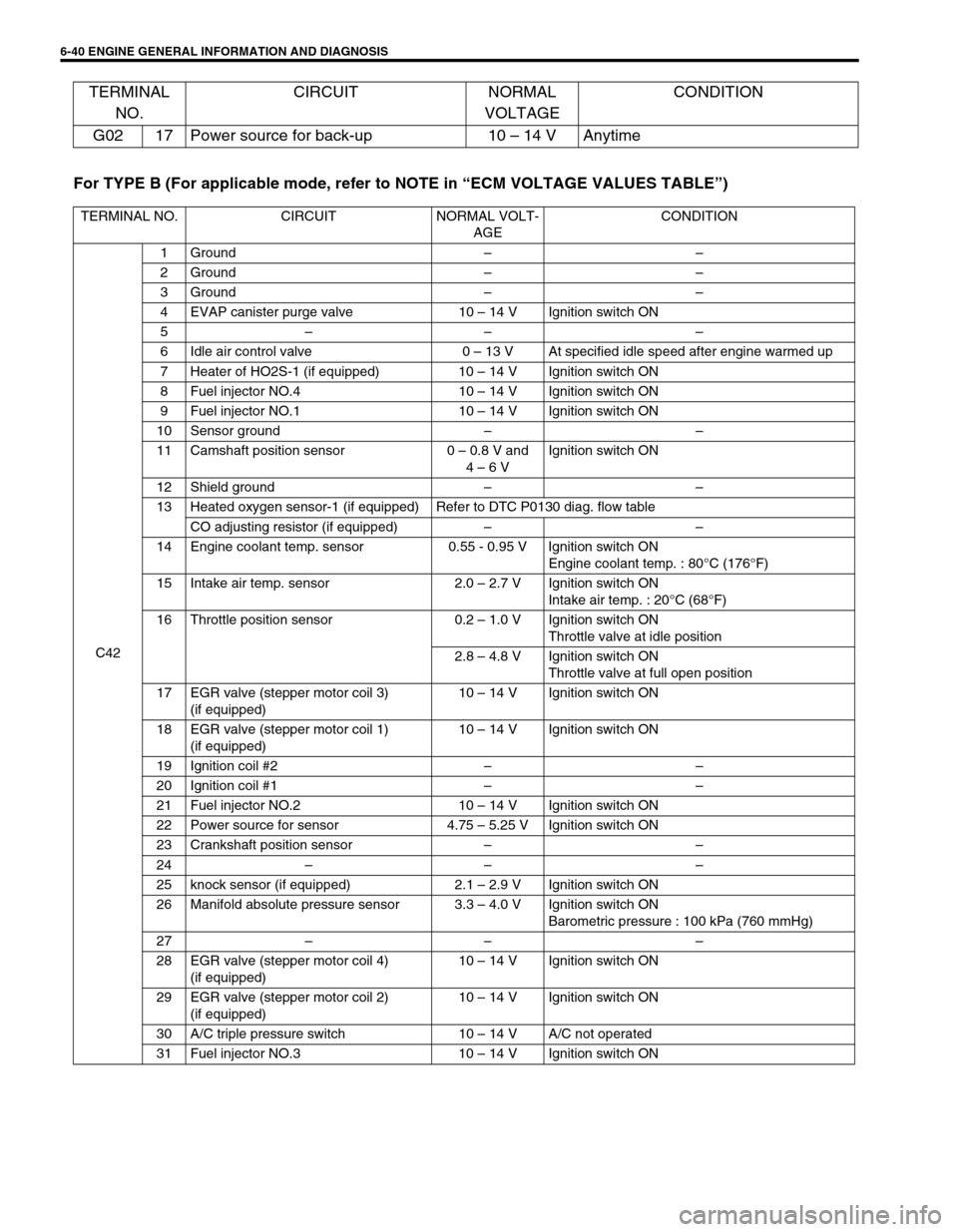
For TYPE B (For applicable mode, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE”) G02 17 Power source for back-up 10 – 14 V Anytime
TERMINAL NO. CIRCUIT NORMAL VOLT-
AGECONDITION
C421Ground––
2Ground––
3Ground––
4 EVAP canister purge valve 10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
5–– –
6 Idle air control valve 0 – 13 V At specified idle speed after engine warmed up
7 Heater of HO2S-1 (if equipped) 10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
8 Fuel injector NO.4 10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
9 Fuel injector NO.1 10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
10 Sensor ground––
11 Camshaft position sensor 0 – 0.8 V and
4 – 6 VIgnition switch ON
12 Shield ground––
13 Heated oxygen sensor-1 (if equipped) Refer to DTC P0130 diag. flow table
CO adjusting resistor (if equipped)––
14 Engine coolant temp. sensor 0.55 - 0.95 V Ignition switch ON
Engine coolant temp. : 80°C (176°F)
15 Intake air temp. sensor 2.0 – 2.7 V Ignition switch ON
Intake air temp. : 20°C (68°F)
16 Throttle position sensor 0.2 – 1.0 V Ignition switch ON
Throttle valve at idle position
2.8 – 4.8 V Ignition switch ON
Throttle valve at full open position
17 EGR valve (stepper motor coil 3)
(if equipped)10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
18 EGR valve (stepper motor coil 1)
(if equipped)10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
19 Ignition coil #2––
20 Ignition coil #1––
21 Fuel injector NO.2 10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
22 Power source for sensor 4.75 – 5.25 V Ignition switch ON
23 Crankshaft position sensor––
24–– –
25 knock sensor (if equipped) 2.1 – 2.9 V Ignition switch ON
26 Manifold absolute pressure sensor 3.3 – 4.0 V Ignition switch ON
Barometric pressure : 100 kPa (760 mmHg)
27–– –
28 EGR valve (stepper motor coil 4)
(if equipped)10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
29 EGR valve (stepper motor coil 2)
(if equipped)10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
30 A/C triple pressure switch 10 – 14 V A/C not operated
31 Fuel injector NO.3 10 – 14 V Ignition switch ON
TERMINAL
NO.CIRCUIT NORMAL
VOLTAGECONDITION
Page 412 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-43
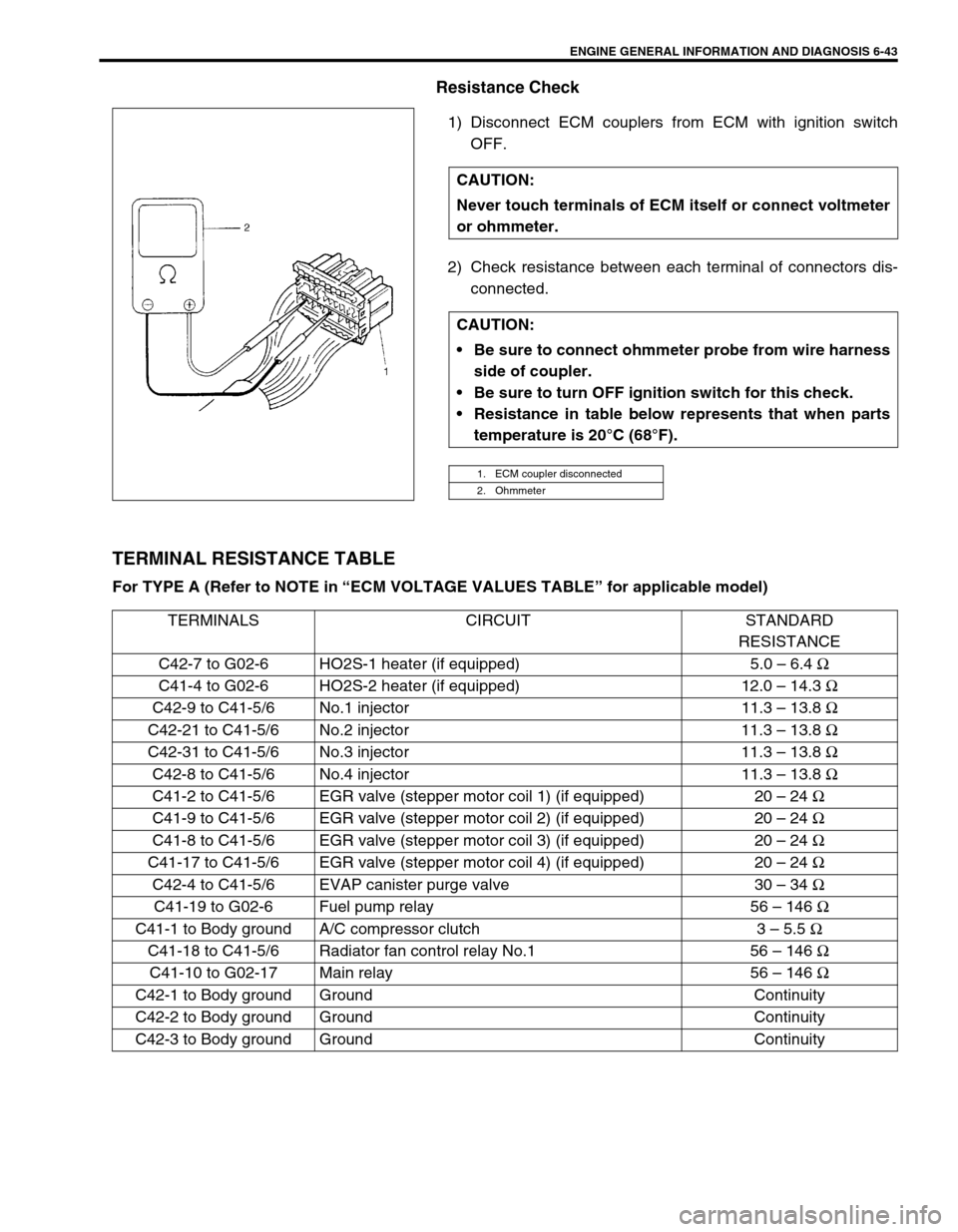
Resistance Check
1) Disconnect ECM couplers from ECM with ignition switch
OFF.
2) Check resistance between each terminal of connectors dis-
connected.
TERMINAL RESISTANCE TABLE
For TYPE A (Refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model) CAUTION:
Never touch terminals of ECM itself or connect voltmeter
or ohmmeter.
CAUTION:
Be sure to connect ohmmeter probe from wire harness
side of coupler.
Be sure to turn OFF ignition switch for this check.
Resistance in table below represents that when parts
temperature is 20°C (68°F).
1. ECM coupler disconnected
2. Ohmmeter
TERMINALS CIRCUIT STANDARD
RESISTANCE
C42-7 to G02-6 HO2S-1 heater (if equipped) 5.0 – 6.4 Ω
C41-4 to G02-6 HO2S-2 heater (if equipped) 12.0 – 14.3 Ω
C42-9 to C41-5/6 No.1 injector 11.3 – 13.8 Ω
C42-21 to C41-5/6 No.2 injector 11.3 – 13.8 Ω
C42-31 to C41-5/6 No.3 injector 11.3 – 13.8 Ω
C42-8 to C41-5/6 No.4 injector 11.3 – 13.8 Ω
C41-2 to C41-5/6 EGR valve (stepper motor coil 1) (if equipped) 20 – 24 Ω
C41-9 to C41-5/6 EGR valve (stepper motor coil 2) (if equipped) 20 – 24 Ω
C41-8 to C41-5/6 EGR valve (stepper motor coil 3) (if equipped) 20 – 24 Ω
C41-17 to C41-5/6 EGR valve (stepper motor coil 4) (if equipped) 20 – 24 Ω
C42-4 to C41-5/6 EVAP canister purge valve 30 – 34 Ω
C41-19 to G02-6 Fuel pump relay 56 – 146 Ω
C41-1 to Body ground A/C compressor clutch 3 – 5.5 Ω
C41-18 to C41-5/6 Radiator fan control relay No.1 56 – 146 Ω
C41-10 to G02-17 Main relay 56 – 146 Ω
C42-1 to Body ground Ground Continuity
C42-2 to Body ground Ground Continuity
C42-3 to Body ground Ground Continuity
Page 413 of 698
6-44 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
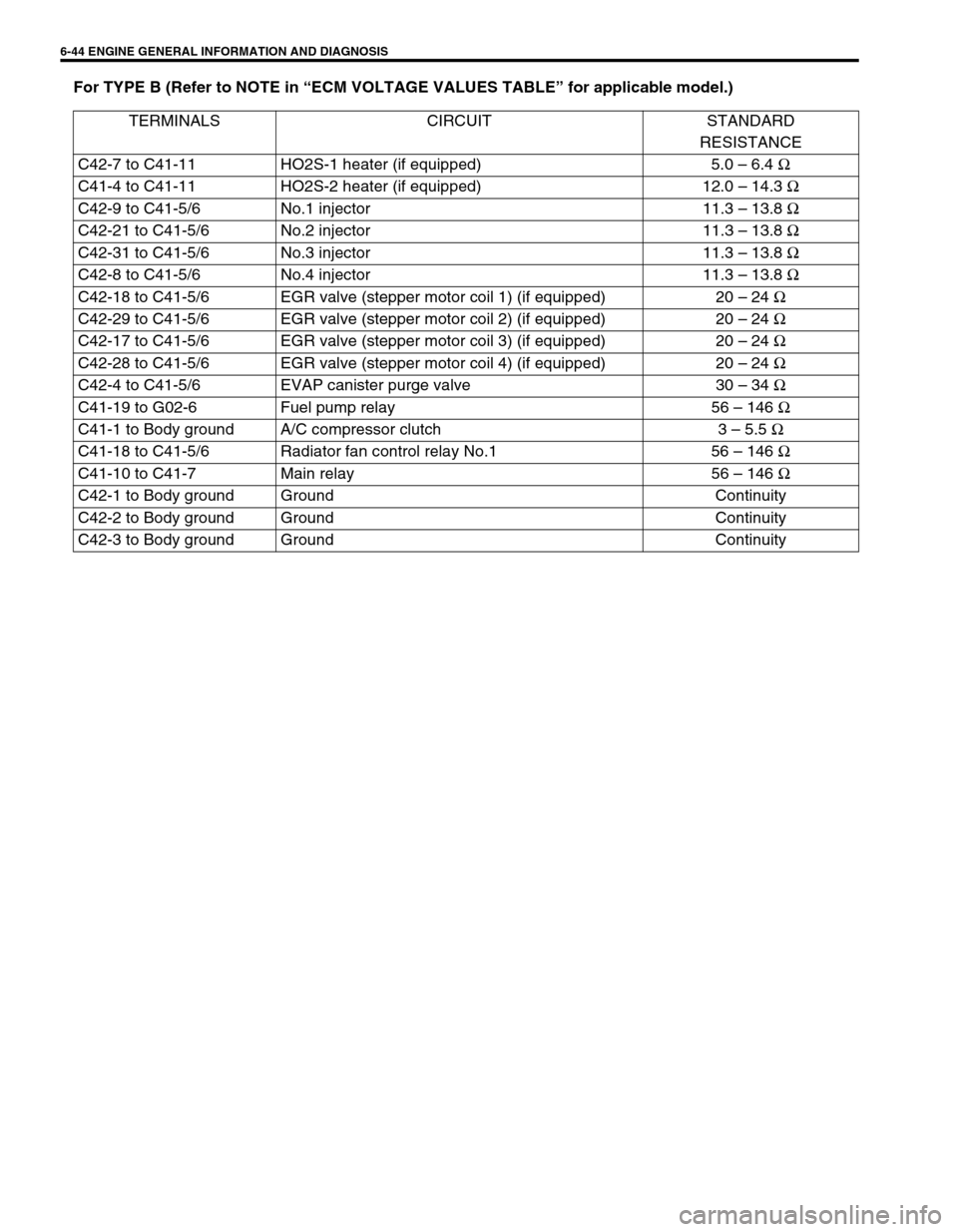
For TYPE B (Refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.)
TERMINALS CIRCUIT STANDARD
RESISTANCE
C42-7 to C41-11 HO2S-1 heater (if equipped) 5.0 – 6.4 Ω
C41-4 to C41-11 HO2S-2 heater (if equipped) 12.0 – 14.3 Ω
C42-9 to C41-5/6 No.1 injector 11.3 – 13.8 Ω
C42-21 to C41-5/6 No.2 injector 11.3 – 13.8 Ω
C42-31 to C41-5/6 No.3 injector 11.3 – 13.8 Ω
C42-8 to C41-5/6 No.4 injector 11.3 – 13.8 Ω
C42-18 to C41-5/6 EGR valve (stepper motor coil 1) (if equipped) 20 – 24 Ω
C42-29 to C41-5/6 EGR valve (stepper motor coil 2) (if equipped) 20 – 24 Ω
C42-17 to C41-5/6 EGR valve (stepper motor coil 3) (if equipped) 20 – 24 Ω
C42-28 to C41-5/6 EGR valve (stepper motor coil 4) (if equipped) 20 – 24 Ω
C42-4 to C41-5/6 EVAP canister purge valve 30 – 34 Ω
C41-19 to G02-6 Fuel pump relay 56 – 146 Ω
C41-1 to Body ground A/C compressor clutch 3 – 5.5 Ω
C41-18 to C41-5/6 Radiator fan control relay No.1 56 – 146 Ω
C41-10 to C41-7 Main relay 56 – 146 Ω
C42-1 to Body ground Ground Continuity
C42-2 to Body ground Ground Continuity
C42-3 to Body ground Ground Continuity
Page 414 of 698
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-45
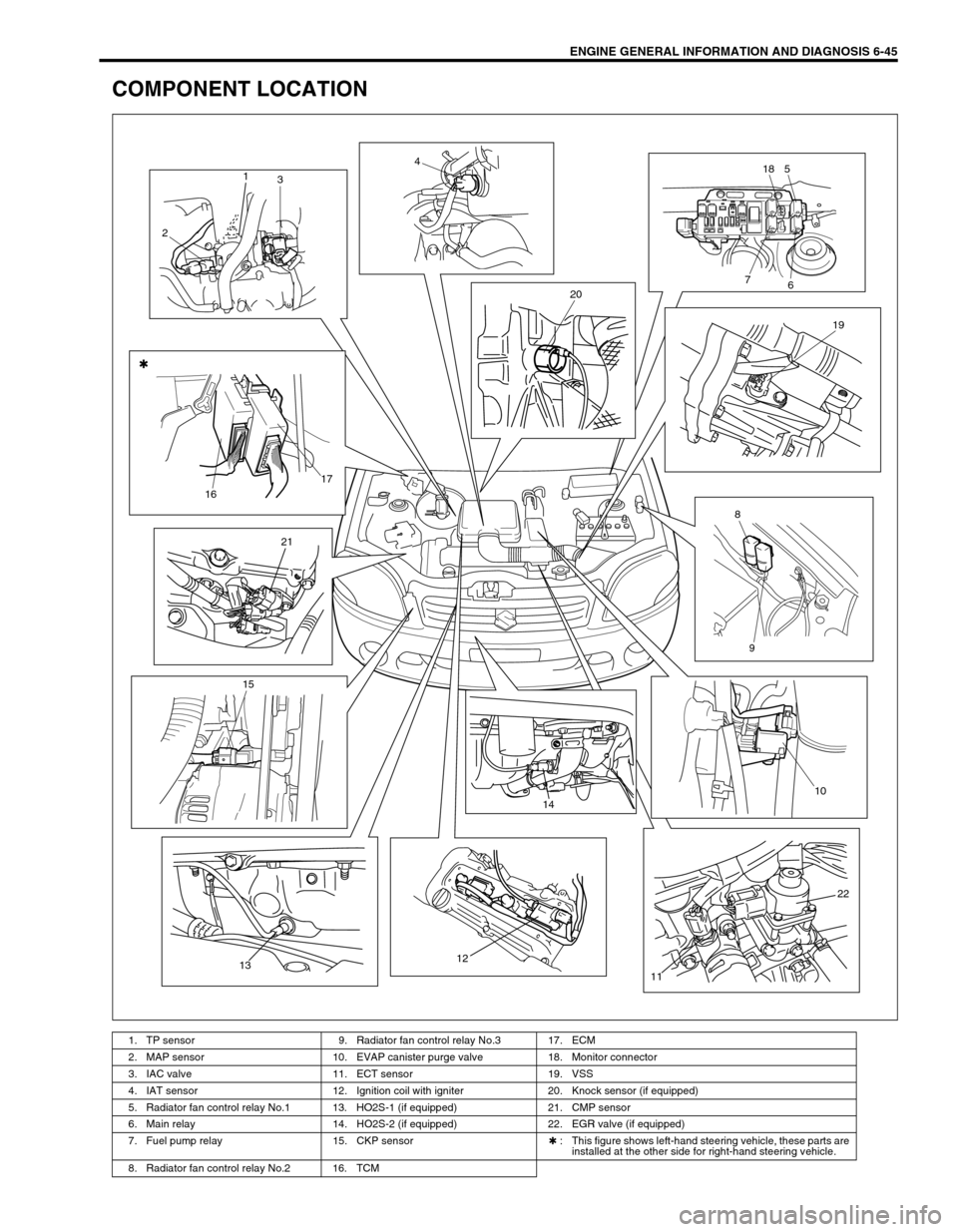
COMPONENT LOCATION
1. TP sensor 9. Radiator fan control relay No.3 17. ECM
2. MAP sensor 10. EVAP canister purge valve 18. Monitor connector
3. IAC valve 11. ECT sensor 19. VSS
4. IAT sensor 12. Ignition coil with igniter 20. Knock sensor (if equipped)
5. Radiator fan control relay No.1 13. HO2S-1 (if equipped) 21. CMP sensor
6. Main relay 14. HO2S-2 (if equipped) 22. EGR valve (if equipped)
7. Fuel pump relay 15. CKP sensor✱ : This figure shows left-hand steering vehicle, these parts are
installed at the other side for right-hand steering vehicle.
8. Radiator fan control relay No.2 16. TCM
1
3
24
518
6 7
20
19
8
9 1617
21
15
131214
10
22
11
Page 430 of 698
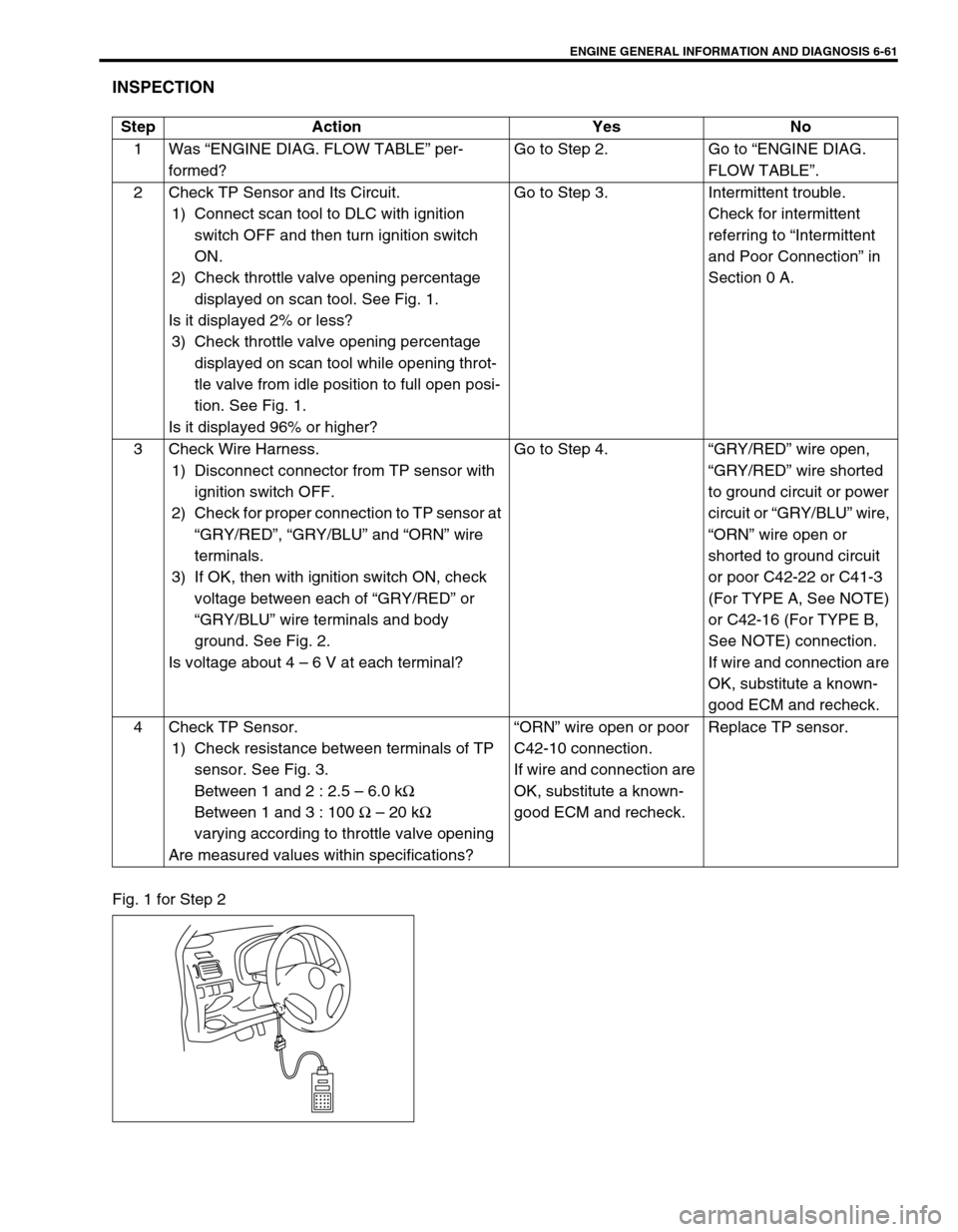
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-61
INSPECTION
Fig. 1 for Step 2Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Check TP Sensor and Its Circuit.
1) Connect scan tool to DLC with ignition
switch OFF and then turn ignition switch
ON.
2) Check throttle valve opening percentage
displayed on scan tool. See Fig. 1.
Is it displayed 2% or less?
3) Check throttle valve opening percentage
displayed on scan tool while opening throt-
tle valve from idle position to full open posi-
tion. See Fig. 1.
Is it displayed 96% or higher?Go to Step 3. Intermittent trouble.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0 A.
3 Check Wire Harness.
1) Disconnect connector from TP sensor with
ignition switch OFF.
2) Check for proper connection to TP sensor at
“GRY/RED”, “GRY/BLU” and “ORN” wire
terminals.
3) If OK, then with ignition switch ON, check
voltage between each of “GRY/RED” or
“GRY/BLU” wire terminals and body
ground. See Fig. 2.
Is voltage about 4 – 6 V at each terminal?Go to Step 4.“GRY/RED” wire open,
“GRY/RED” wire shorted
to ground circuit or power
circuit or “GRY/BLU” wire,
“ORN” wire open or
shorted to ground circuit
or poor C42-22 or C41-3
(For TYPE A, See NOTE)
or C42-16 (For TYPE B,
See NOTE) connection.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
4 Check TP Sensor.
1) Check resistance between terminals of TP
sensor. See Fig. 3.
Between 1 and 2 : 2.5 – 6.0 kΩ
Between 1 and 3 : 100 Ω – 20 kΩ
varying according to throttle valve opening
Are measured values within specifications?“ORN” wire open or poor
C42-10 connection.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.Replace TP sensor.
Page 432 of 698
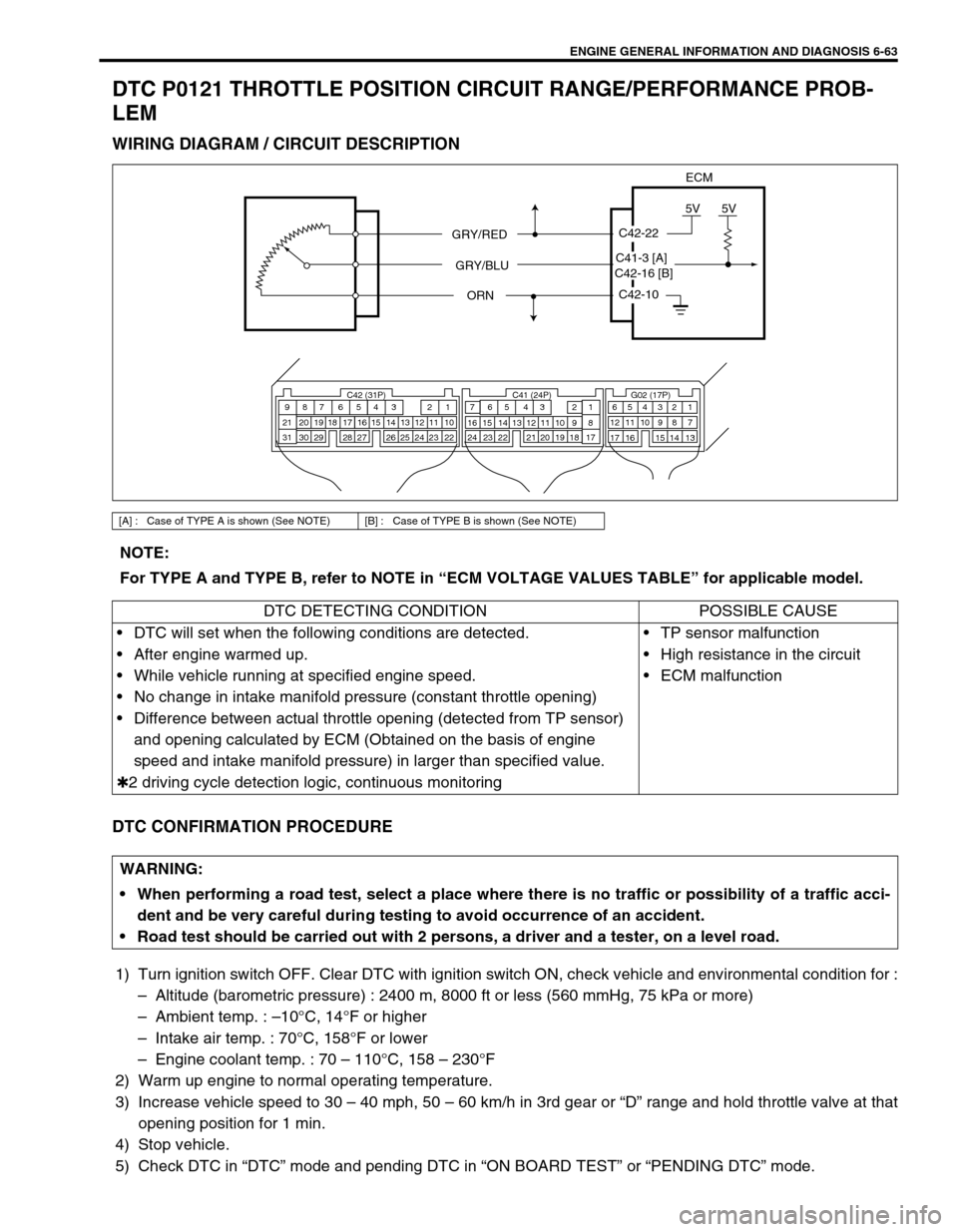
ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-63
DTC P0121 THROTTLE POSITION CIRCUIT RANGE/PERFORMANCE PROB-
LEM
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF. Clear DTC with ignition switch ON, check vehicle and environmental condition for :
–Altitude (barometric pressure) : 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
–Ambient temp. : –10°C, 14°F or higher
–Intake air temp. : 70°C, 158°F or lower
–Engine coolant temp. : 70 – 110°C, 158 – 230°F
2) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
3) Increase vehicle speed to 30 – 40 mph, 50 – 60 km/h in 3rd gear or “D” range and hold throttle valve at that
opening position for 1 min.
4) Stop vehicle.
5) Check DTC in “DTC” mode and pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode.
[A] : Case of TYPE A is shown (See NOTE) [B] : Case of TYPE B is shown (See NOTE)
C42-10
C42-22
5V5V
ECM
GRY/RED
GRY/BLU
ORN
C42 (31P) C41 (24P) G02 (17P)1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21
22 23 24 25 26 28 27 29 30 315 6
1 2 3 4 5 6 7
11 12
9 10 11 13 12 14 15 16
16 171 2
7 8
13 14 3 4
9 10
15 17 188
19 20 21 22 23 24
C42-16 [B]C41-3 [A]
NOTE:
For TYPE A and TYPE B, refer to NOTE in “ECM VOLTAGE VALUES TABLE” for applicable model.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
DTC will set when the following conditions are detected.
After engine warmed up.
While vehicle running at specified engine speed.
No change in intake manifold pressure (constant throttle opening)
Difference between actual throttle opening (detected from TP sensor)
and opening calculated by ECM (Obtained on the basis of engine
speed and intake manifold pressure) in larger than specified value.
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitoringTP sensor malfunction
High resistance in the circuit
ECM malfunction
WARNING:
When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic acci-
dent and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester, on a level road.
Page 433 of 698
6-64 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
INSPECTION
Fig. 1 for Step 3Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” per-
formed?Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE DIAG.
FLOW TABLE”.
2 Is SUZUKI scan tool available? Go to Step 3. Go to Step 4.
3 Check TP Sensor and its Circuit.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF and connect
SUZUKI scan tool to DLC.
2) Turn ignition switch ON and check TP sen-
sor output voltage when throttle valve is at
idle position and fully opened. See Fig. 1
and 3.
Dose voltage vary within specified value linearly
as shown in figure?If voltmeter was used,
check terminal C41-3 (For
TYPE A, See NOTE) or
C42-16 (For TYPE B, See
NOTE) for poor connec-
tion.
If OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.Go to Step 5.
4 Check TP Sensor and Its Circuit.
1) Turn ignition switch ON.
2) Check voltage at terminal C41-3 (For TYPE
A, See NOTE) or C42-16 (For TYPE B, See
NOTE) of ECM connector connected, when
throttle valve is at idle position and fully
opened. See Fig. 2 and 3.
Dose voltage vary within specified value linearly
as shown in figure?If voltmeter was used,
check terminal C41-3 (For
TYPE A, See NOTE) or
C42-16 (For TYPE B, See
NOTE) for poor connec-
tion.
If OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.Go to Step 5.
5 Check TP Sensor.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Disconnect TP sensor connector.
3) Check for proper connection to TP sensor
at each terminal.
4) If OK, then measure resistance between
terminals and check if each measured value
is as specified below.
See Fig. 4.
Between 1 and 2 : 4.0 – 6.0 kΩ
Between 1 and 3 : 0.02 – 6.0 kΩ, varying
according to throttle valve opening.
Are measured values as specified?High resistance in “GRY/
RED”, “GRY/BLU” or
“ORN” circuit.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.Replace TP sensor.
[A] : When using SUZUKI scan tool:
[ A]
Page 445 of 698
![SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Repair Manual 6-76 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P0171 FUEL SYSTEM TOO LEAN
DTC P0172 FUEL SYSTEM TOO RICH
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
1. Injector [a] : Signal to decrease amount of fuel inj SUZUKI SWIFT 2000 1.G RG413 Service Repair Manual 6-76 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P0171 FUEL SYSTEM TOO LEAN
DTC P0172 FUEL SYSTEM TOO RICH
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
1. Injector [a] : Signal to decrease amount of fuel inj](/img/20/7606/w960_7606-444.png)
6-76 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P0171 FUEL SYSTEM TOO LEAN
DTC P0172 FUEL SYSTEM TOO RICH
WIRING DIAGRAM / CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
1. Injector [a] : Signal to decrease amount of fuel injection [f] : A/F mixture becomes leaner
2. HO2S-1 [b] : Signal to increase amount of fuel injection [g] : Oxygen concentration decreases
3. WU-TWC (Warm up-three way catalytic convec-
tor)[c] : High voltage [h] : Oxygen concentration increases
4. Sensed information [d] : Low voltage
5. ECM [e] : A/F mixture becomes richer
[a]
[b]
[f] [e] [g][d]
[h][c]
1
2 5
1
2
2
3
54
+BECM
C42-9
C42-21
C42-8 C42-31
C42-1
BLU/YEL
BLU/WHT
BLU/RED
BLK/ORN
C42-3
BLK/ORN BLU/ORN
WHT
ORNC42-10C42-13
E111
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
When one of the following conditions occurs while
engine running under closed loop condition.
Air/fuel ratio too lean
(Total fuel trim (short and long terms added) is more
than 30%)
Air/fuel ratio too rich
(Total fuel trim is less than – 30%)
✱2 driving cycle detection logic, continuous monitoring.Vacuum leaks (air drawn in).
Exhaust gas leakage.
Heated oxygen sensor-1 circuit malfunction.
Fuel pressure out of specification.
Fuel injector malfunction (clogged or leakage).
MAP sensor poor performance.
ECT sensor poor performance.
IAT sensor poor performance.
TP sensor poor performance.
EVAP control system malfunction.
PCV valve malfunction.
Page 447 of 698
6-78 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
5 Check Fuel Injectors and Circuit.
1) Using sound scope (1) or such, check oper-
ating sound of each injector (2) when
engine is running. Cycle of operating sound
should vary according to engine speed. See
Fig. 3. If no sound or an unusual sound is
heard, check injector circuit (wire or cou-
pler) or injector.
2) Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect a
fuel injector connector.
3) Check for proper connection to fuel injector
at each terminal. See Fig. 4.
4) If OK, then check injector resistance.
Injector Resistance : 11.3 – 13.8 ohm at
20°C (68°F)
5) Carry out steps 1) and 3) on each injector.
6) Check each injector for injected fuel volume
(1) referring to Section 6E1. See Fig. 5.
Injected Fuel Volume : 43 – 47 cc/15 sec
1.45/1.51 – 1.58/1.65 US/Imp.oz/15 sec)
7) Check each injector for fuel leakage after
injector closed. Fuel Leakage : Less than 1
drop/min.
Is check result in step 1) and 3) to 7) satisfac-
tory?Go to Step 6. Check injector circuit or
replace fuel injector(s).
6 Check EVAP Canister Purge Valve.
1) Disconnect purge hose from EVAP canister
purge valve.
2) Place finger against the end of EVAP canis-
ter purge valve.
3) Check that vacuum is not felt there when
engine is cool and running at idle. See Fig.
6.
Is vacuum felt?Check EVAP control sys-
tem (See Section 6E1).Go to Step 7.
7 Check Intake manifold absolute pressure sen-
sor for performance (See DTC P0105 (No.11)
Diag. Flow Table).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 8. Repair or replace.
8 Check Engine Coolant Temp. Sensor for perfor-
mance (See Section 6E1).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 9. Replace engine coolant
temp. sensor.
9 Check Intake Air Temp. Sensor for perfor-
mance (See Section 6E1).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 10. Replace intake air temp.
sensor.
10 Check Throttle Position Sensor for performance
(See Step 4 of DTC P0121 Diag. Flow Table).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 11. Replace throttle position
sensor.
11 Check PCV Valve for valve clogging (See Sec-
tion 6E1).
Is it good condition?Substitute a known-good
ECM and recheck.Replace PCV valve. Step Action Yes No
Page 451 of 698

6-82 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Clear DTC with ignition switch ON.
3) Check vehicle and environmental condition for :
–Altitude (barometric pressure) : 2400 m, 8000 ft or less (560 mmHg, 75 kPa or more)
–Ambient temp. : –10°C, 14°F or higher
–Intake air temp. : 70°C, 158°F or lower
–Engine coolant temp. : – 10 – 110°C, 14 – 230°F
4) Start engine and keep it at idle for 2 min. or more.
5) Check DTC in “DTC” mode and pending DTC in “ON BOARD TEST” or “PENDING DTC” mode.
6) If DTC is not detected at idle, consult usual driving based on information obtained in “Customer complaint
analysis” and “Freeze frame data check”.
INSPECTION
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
Engine under other than high revolution condition
Not on rough road
Engine speed changing rate (Below specified value)
Manifold absolute pressure changing rate (Below
specified value)
Throttle opening changing rate (Below specified
value)
Misfire rate per 200 or 1000 engine revolutions (how
much and how often crankshaft revolution speed
changes) is higher than specified valueEngine overheating
Vacuum leaks (air inhaling) from air intake system
Ignition system malfunction (spark plug(s), high-
tension cord(s), ignition coil assembly)
Fuel pressure out of specification
Fuel injector malfunction (clogged or leakage)
Engine compression out of specification
Valve lash (clearance) out of specification
Manifold absolute pressure sensor malfunction
Engine coolant temp. sensor malfunction
PCV valve malfunction
EVAP control system malfunction
EGR system malfunction
NOTE:
Among different types of random misfire, if misfire occurs at cylinders 1 and 4 or cylinders 3 and 2
simultaneously, it may not possible to reconfirm DTC by using the following DTC confirmation proce-
dure. When diagnosing the trouble of DTC P0300 (Random misfire detected) of the engine which is
apparently misfiring, even if DTC P0300 cannot be reconfirmed by using the following DTC confirma-
tion procedure, proceed to the following Diag. Flow Table.
WARNING:
When performing a road test, select a place where there is no traffic or possibility of a traffic acci-
dent and be very careful during testing to avoid occurrence of an accident.
Road test should be carried out with 2 persons, a driver and a tester.
CAUTION:
For iridium spark plugs, do not adjust air gap or clean.
Step Action Yes No
1Was “ENGINE DIAG. FLOW TABLE” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “ENGINE
DIAG. FLOW
TABLE”.