fuel injector SUZUKI SX4 2006 1.G Service Owner's Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: SUZUKI, Model Year: 2006, Model line: SX4, Model: SUZUKI SX4 2006 1.GPages: 1556, PDF Size: 37.31 MB
Page 247 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-197
Troubleshooting
NOTE
• Before performed trouble shooting, be sure to read the “Precautions of ECM Circuit Inspection”.
• When measuring circuit voltage, resistance and/or pulse signal at ECM connector, connect the
special tool to ECM and/or the ECM connectors referring to “Inspection of ECM and Its Circuits”.
Step Action Yes No
1Fuel injector check for operating sound
1) Using sound scope, check each injector for operating
sound at engine cranking.
Do all 4 injector make operating sound?Fuel injectors circuit is
in good condition.Go to Step 2.
2Fuel injector resistance check
1) Disconnect connectors from fuel injectors with ignition
switch turned OFF.
2) Check for proper connection to fuel injector at each
terminals.
3) If OK, check all 4 fuel injectors for resistance referring to
“Fuel Injector On-Vehicle Inspection in Section 1G”.
Are all injectors in good condition?Go to Step 3. Faulty fuel injector.
3Fuel injector insulation resistance check
1) Check that there is insulation between each fuel injector
terminal and engine ground.
Is there insulation?Go to Step 4. Faulty fuel injector.
4Fuel injector power supply check
1) Measure voltage between each “BLK/RED” wire terminal
of fuel injector connector and engine ground with ignition
switch turned ON.
Is voltage 10 – 14 V?Go to Step 5. “BLK/RED” wire is open
or shorted to ground
circuit.
If it is in good condition,
go to “ECM Power and
Ground Circuit Check”.
5Wire circuit check
1) Turn OFF ignition switch.
2) Disconnect connectors from ECM.
3) Measure resistance between each “BLU/YEL”, “BLU/
WHT”, “BLU/RED”, “BLU/ORN” wire terminal of fuel
injector connector and vehicle body ground.
Is resistance infinity?Go to Step 6. “BLU/YEL”, “BLU/WHT”,
“BLU/RED” and/or
“BLU/ORN” wire(s) are
shorted to ground.
6Wire circuit check
1) Measure voltage between each “BLU/YEL”, “BLU/WHT”,
“BLU/RED”, “BLU/ORN” wire terminal of fuel injector
connector and vehicle body ground with ignition switch
turned ON.
Is voltage 0 V?Go to Step 7. “BLU/YEL”, “BLU/WHT”,
“BLU/RED” and/or
“BLU/ORN” wire(s) are
shorted to power supply
circuit.
7Fuel injector drive signal check
1) Connect connectors to each fuel injector and ECM with
ignition switch turned OFF.
2) Turn ON ignition switch.
3) Measure voltage between each “C01-1”, “C01-2”, “C01-
16”, “C01-17” terminal of ECM connector and vehicle
body ground.
Is voltage 10 – 14 V?Check fuel injector
referring to “Fuel
Injector Inspection in
Section 1G”.
If check result is
satisfactory, substitute a
known-good ECM and
recheck.“BLU/YEL”, “BLU/WHT”,
“BLU/RED” and/or
“BLU/ORN” wire(s) are
open circuit.
Page 251 of 1556
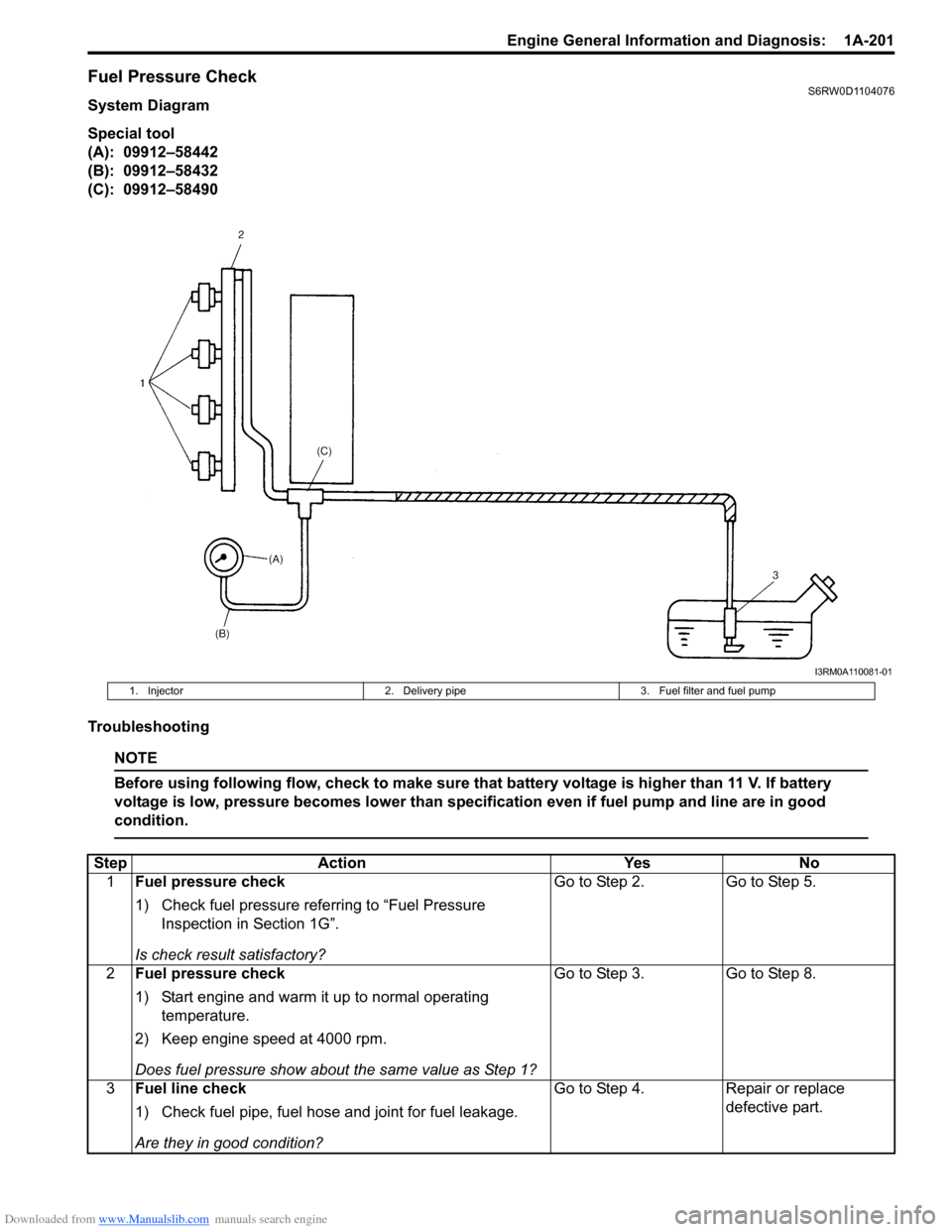
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine General Information and Diagnosis: 1A-201
Fuel Pressure CheckS6RW0D1104076
System Diagram
Special tool
(A): 09912–58442
(B): 09912–58432
(C): 09912–58490
Troubleshooting
NOTE
Before using following flow, check to make sure that battery voltage is higher than 11 V. If battery
voltage is low, pressure becomes lower than specification even if fuel pump and line are in good
condition.
I3RM0A110081-01
1. Injector 2. Delivery pipe 3. Fuel filter and fuel pump
Step Action Yes No
1Fuel pressure check
1) Check fuel pressure referring to “Fuel Pressure
Inspection in Section 1G”.
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 2. Go to Step 5.
2Fuel pressure check
1) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating
temperature.
2) Keep engine speed at 4000 rpm.
Does fuel pressure show about the same value as Step 1?Go to Step 3. Go to Step 8.
3Fuel line check
1) Check fuel pipe, fuel hose and joint for fuel leakage.
Are they in good condition?Go to Step 4. Repair or replace
defective part.
Page 287 of 1556
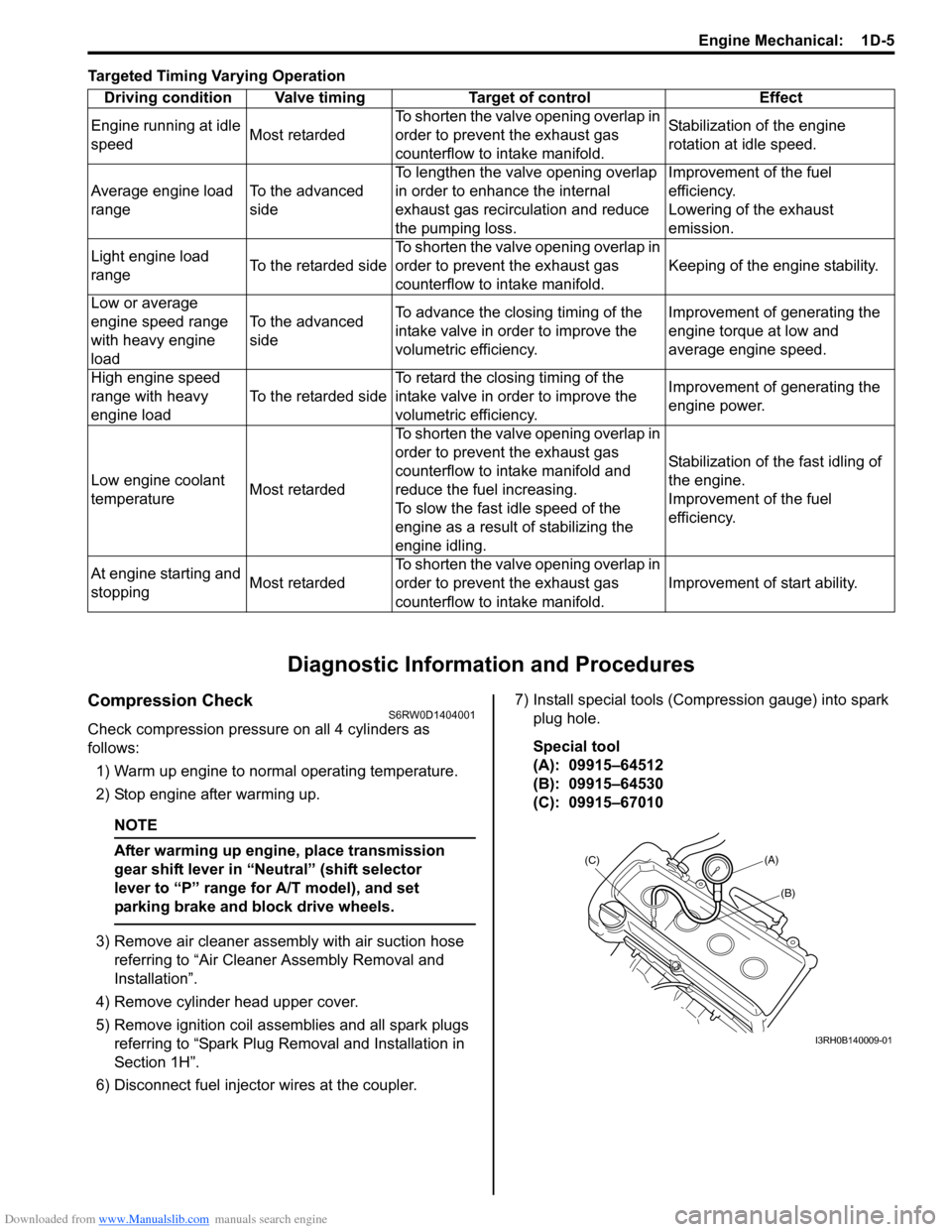
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-5
Targeted Timing Varying Operation
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Compression CheckS6RW0D1404001
Check compression pressure on all 4 cylinders as
follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
2) Stop engine after warming up.
NOTE
After warming up engine, place transmission
gear shift lever in “Neutral” (shift selector
lever to “P” range for A/T model), and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
3) Remove air cleaner assembly with air suction hose
referring to “Air Cleaner Assembly Removal and
Installation”.
4) Remove cylinder head upper cover.
5) Remove ignition coil assemblies and all spark plugs
referring to “Spark Plug Removal and Installation in
Section 1H”.
6) Disconnect fuel injector wires at the coupler.7) Install special tools (Compression gauge) into spark
plug hole.
Special tool
(A): 09915–64512
(B): 09915–64530
(C): 09915–67010 Driving condition Valve timing Target of control Effect
Engine running at idle
speedMost retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to intake manifold.Stabilization of the engine
rotation at idle speed.
Average engine load
rangeTo the advanced
sideTo lengthen the valve opening overlap
in order to enhance the internal
exhaust gas recirculation and reduce
the pumping loss.Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
Lowering of the exhaust
emission.
Light engine load
rangeTo the retarded sideTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to intake manifold.Keeping of the engine stability.
Low or average
engine speed range
with heavy engine
loadTo the advanced
sideTo advance the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency.Improvement of generating the
engine torque at low and
average engine speed.
High engine speed
range with heavy
engine loadTo the retarded sideTo retard the closing timing of the
intake valve in order to improve the
volumetric efficiency.Improvement of generating the
engine power.
Low engine coolant
temperatureMost retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to intake manifold and
reduce the fuel increasing.
To slow the fast idle speed of the
engine as a result of stabilizing the
engine idling.Stabilization of the fast idling of
the engine.
Improvement of the fuel
efficiency.
At engine starting and
stoppingMost retardedTo shorten the valve opening overlap in
order to prevent the exhaust gas
counterflow to intake manifold.Improvement of start ability.
(A)
(C)
(B)
I3RH0B140009-01
Page 288 of 1556
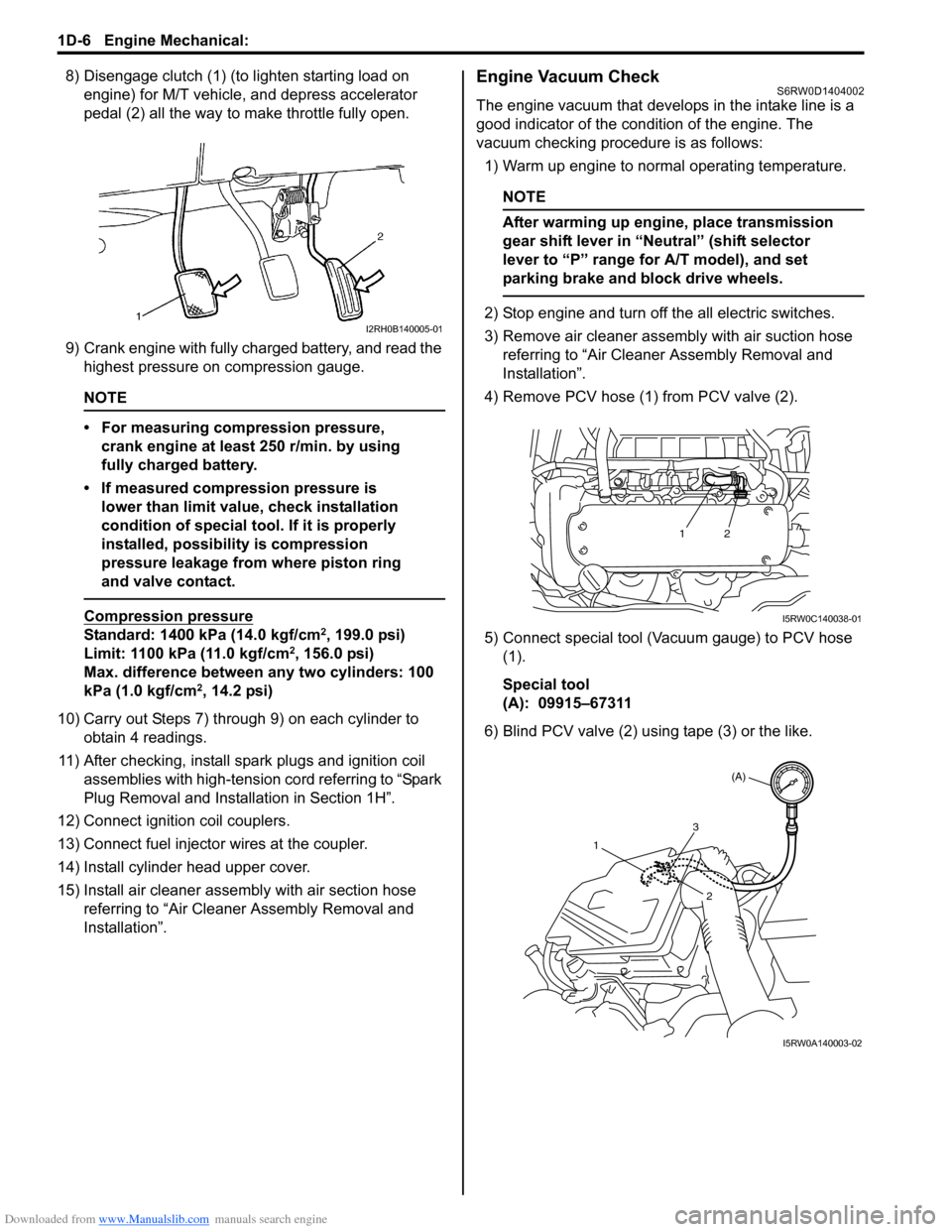
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-6 Engine Mechanical:
8) Disengage clutch (1) (to lighten starting load on
engine) for M/T vehicle, and depress accelerator
pedal (2) all the way to make throttle fully open.
9) Crank engine with fully charged battery, and read the
highest pressure on compression gauge.
NOTE
• For measuring compression pressure,
crank engine at least 250 r/min. by using
fully charged battery.
• If measured compression pressure is
lower than limit value, check installation
condition of special tool. If it is properly
installed, possibility is compression
pressure leakage from where piston ring
and valve contact.
Compression pressure
Standard: 1400 kPa (14.0 kgf/cm2, 199.0 psi)
Limit: 1100 kPa (11.0 kgf/cm2, 156.0 psi)
Max. difference between any two cylinders: 100
kPa (1.0 kgf/cm
2, 14.2 psi)
10) Carry out Steps 7) through 9) on each cylinder to
obtain 4 readings.
11) After checking, install spark plugs and ignition coil
assemblies with high-tension cord referring to “Spark
Plug Removal and Installation in Section 1H”.
12) Connect ignition coil couplers.
13) Connect fuel injector wires at the coupler.
14) Install cylinder head upper cover.
15) Install air cleaner assembly with air section hose
referring to “Air Cleaner Assembly Removal and
Installation”.
Engine Vacuum CheckS6RW0D1404002
The engine vacuum that develops in the intake line is a
good indicator of the condition of the engine. The
vacuum checking procedure is as follows:
1) Warm up engine to normal operating temperature.
NOTE
After warming up engine, place transmission
gear shift lever in “Neutral” (shift selector
lever to “P” range for A/T model), and set
parking brake and block drive wheels.
2) Stop engine and turn off the all electric switches.
3) Remove air cleaner assembly with air suction hose
referring to “Air Cleaner Assembly Removal and
Installation”.
4) Remove PCV hose (1) from PCV valve (2).
5) Connect special tool (Vacuum gauge) to PCV hose
(1).
Special tool
(A): 09915–67311
6) Blind PCV valve (2) using tape (3) or the like.I2RH0B140005-01
12
I5RW0C140038-01
(A)
1
2
3
I5RW0A140003-02
Page 299 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Engine Mechanical: 1D-17
Engine Assembly Removal and InstallationS6RW0D1406013
Removal
1) Relieve fuel pressure according to “Fuel Pressure
Relief Procedure in Section 1G”.
2) Disconnect negative and positive cable at battery.
3) Disconnect ECM connectors.
4) Remove battery and battery tray with ECM.
5) Remove right and left side engine under covers.
6) Remove A/C compressor belt by referring to
“Compressor Drive Belt Removal and Installation in
Section 7B” or “Compressor Drive Belt Removal and
Installation in Section 7B”.
7) Drain engine oil referring to “Engine Oil and Filter
Change in Section 0B”.
8) Drain transaxle oil referring to “Manual Transaxle Oil
Change in Section 5B” or “A/T Fluid Change in
Section 5A”.
9) Drain transfer oil referring to “Transfer Oil Change in
Section 3C”.
10) Drain coolant referring to “Cooling System Draining
in Section 1F”
11) Remove air cleaner assembly referring to “Air
Cleaner Assembly Removal and Installation”.
12) With hose connected, detach A/C compressor from
its bracket referring to “Compressor Assembly
Removal and Installation in Section 7B” or
“Compressor Assembly Removal and Installation in
Section 7B”.
CAUTION!
Suspend removed A/C compressor at a place
where no damage will be caused during
removal and installation of engine assembly.
13) Remove cylinder upper cover (1).14) Disconnect the following electric wires/connectors
and each clamps.
• TP sensor (1)
• MAP sensor (2)
• ECT sensor (3)
•EGR valve (4)
• CMP sensor (5)
• Ignition coil assembly (6)
• Injector (7)
•HO2S (8)
• Oil control valve (9) (for engine with VVT system)
• Engine oil pressure switch (10)
• CKP sensor (12)
• Knock sensor (13)
• Generator (14)
• Starting motor (15)
• Ground terminal (16) from cylinder block
• Battery ground cable (17) from transaxle
• Back-up light switch (18) (for M/T model)
• Torque sensor (19)
• P/S motor (20)
• Output shaft speed sensor (VSS) (29) (for A/T
model)
• Solenoid valve (30) (for A/T model)
• Transmission range sensor (31) (for A/T model)
• Input shaft speed sensor (32) (for A/T model)
15) Disconnect the following cables, and remove control
cable bracket (23)
• Gear select control cable (21) (for M/T model)
• Gear shift control cable (22) (for M/T model)
• A/T select cable (33) (for A/T model)
16) Disconnect the following hoses.
• Brake booster hose (24) from intake manifold
• Radiator inlet and outlet hoses (25) from radiator
• Heater inlet and outlet hoses (26) from heater
core
• Fuel feed hose (27) from fuel feed pipe
• Fuel vapor hose (11) from fuel vapor pipe
• Clutch hose (28) from transaxle (for M/T model)
• A/T fluid cooler hoses (for A/T model)
F: Vehicle forward 8. Engine front mounting bracket : 55 N⋅m (5.5 kgf-m, 40.0 lb-ft)
1. Engine right mounting bracket 9. Engine front mounting
: Be sure to direct yellow mark to forward.: 95 N⋅m (9.5 kgf-m, 69.0 lb-ft)
2. Engine right mounting 10. Transfer : 65 N⋅m (6.5 kgf-m, 47.0 lb-ft)
3. Engine left mounting bracket 11. Suspension frame : 25 N⋅m (2.5 kgf-m, 18.0 lb-ft)
1
I5RW0A140009-01
Page 326 of 1556
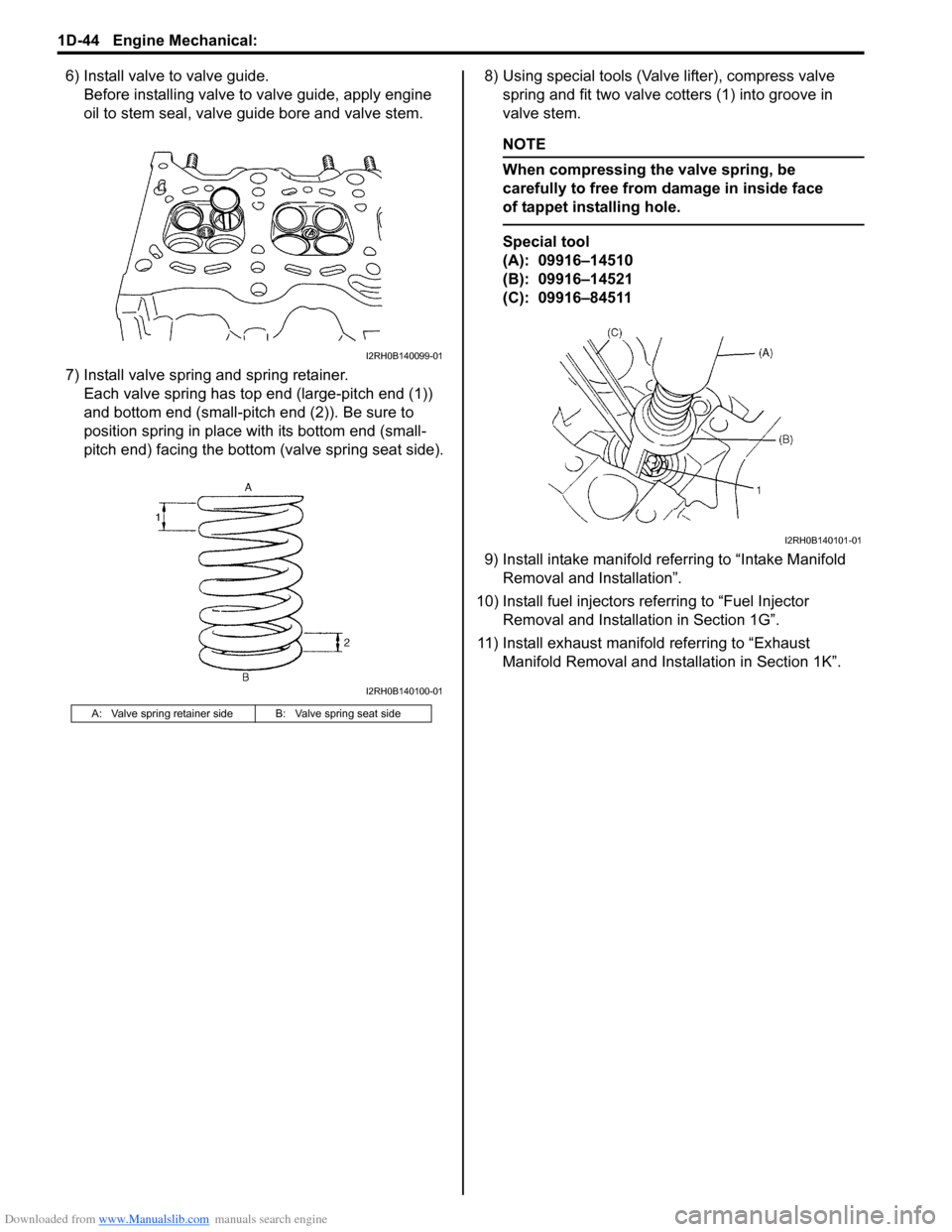
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1D-44 Engine Mechanical:
6) Install valve to valve guide.
Before installing valve to valve guide, apply engine
oil to stem seal, valve guide bore and valve stem.
7) Install valve spring and spring retainer.
Each valve spring has top end (large-pitch end (1))
and bottom end (small-pitch end (2)). Be sure to
position spring in place with its bottom end (small-
pitch end) facing the bottom (valve spring seat side).8) Using special tools (Valve lifter), compress valve
spring and fit two valve cotters (1) into groove in
valve stem.
NOTE
When compressing the valve spring, be
carefully to free from damage in inside face
of tappet installing hole.
Special tool
(A): 09916–14510
(B): 09916–14521
(C): 09916–84511
9) Install intake manifold referring to “Intake Manifold
Removal and Installation”.
10) Install fuel injectors referring to “Fuel Injector
Removal and Installation in Section 1G”.
11) Install exhaust manifold referring to “Exhaust
Manifold Removal and Installation in Section 1K”.
A: Valve spring retainer side B: Valve spring seat side
I2RH0B140099-01
I2RH0B140100-01
I2RH0B140101-01
Page 378 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1G-1 Fuel System:
Engine
Fuel System
Precautions
Precautions on Fuel System ServiceS6RW0D1700001
WARNING!
Before attempting service of any type on fuel system, the following should be always observed in
order to reduce the risk of fire and personal injury.
• Disconnect negative cable at battery.
• Do not smoke, and place no smoking signs near work area.
• Be sure to have CO
2 fire extinguisher handy.
• Be sure to perform work in a well-ventilated area and away from any open flames (such as gas hot
heater).
• Wear safety glasses.
• To relieve fuel vapor pressure in fuel tank, remove fuel filler cap from fuel filler neck and then
reinstall it.
• As fuel feed line is still under high fuel pressure even after stopping engine, loosening or
disconnecting fuel feed line directly may cause dangerous spout of fuel. Before loosening or
disconnecting fuel feed line, make sure to relieve fuel pressure referring to “Fuel Pressure Relief
Procedure”.
• A small amount of fuel may be released when the fuel line is disconnected. In order to reduce the
risk of personal injury, cover a shop cloth to the fitting to be disconnected. Be sure to put that cloth
in an approved container after disconnecting.
• Never run engine with fuel pump relay disconnected when engine and exhaust system are hot.
• Note that fuel hose connection varies with each type of pipe. Be sure to connect and clamp each
hose correctly referring to “Fuel Hose Disconnecting and Reconnecting”.
After connecting, make sure that it has no twist or kink.
• When installing injector or fuel feed pipe, lubricate its O-ring with gasoline.
• When servicing the fuel tank, it should be treated with respect, with no contact with sharp edges or
hot surfaces. In addition, the fuel tank should not be dropped since fuel tank, fuel pump and other
components can be damaged by the impact. If dropped, all components should be replaced because
there is a risk of damage.
• The fuel tank is made of resin.
Be sure not to allow solvent (chemical article such as grease and sealant) to attach to the fuel tank
as some chemical reaction may occur, causing the fuel tank to be swollen, hardened or distorted
leakage and resulting in fuel leakage from the fuel tank.
Page 379 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Fuel System: 1G-2
General Description
Fuel System DescriptionS6RW0D1701001
CAUTION!
This engine requires the unleaded fuel only.
The leaded and/or low lead fuel can result in
engine damage and reduce the effectiveness
of the emission control system.
The main components of the fuel system are fuel tank,
fuel pump assembly (with fuel filter, fuel level gauge, fuel
pressure regulator), fuel feed line and fuel vapor line.
For the details of fuel flow, refer to “Fuel Delivery System
Diagram”.
Fuel Delivery System DescriptionS6RW0D1701002
The fuel delivery system consists of the fuel tank, fuel
pump assembly (with built-in fuel filter and fuel pressure
regulator), delivery pipe, injectors and fuel feed line.
The fuel in the fuel tank is pumped up by the fuel pump,
sent into delivery pipe and injected by the injectors.
As the fuel pump assembly is equipped with built-in fuel
filter and fuel pressure regulator, the fuel is filtered and
its pressure is regulated before being sent to the feed
pipe.
The excess fuel at fuel pressure regulation process is
returned back into the fuel tank.
Also, fuel vapor generated in fuel tank is led through the
fuel vapor line into the EVAP canister.
For system diagram, refer to “Fuel Delivery System
Diagram”.
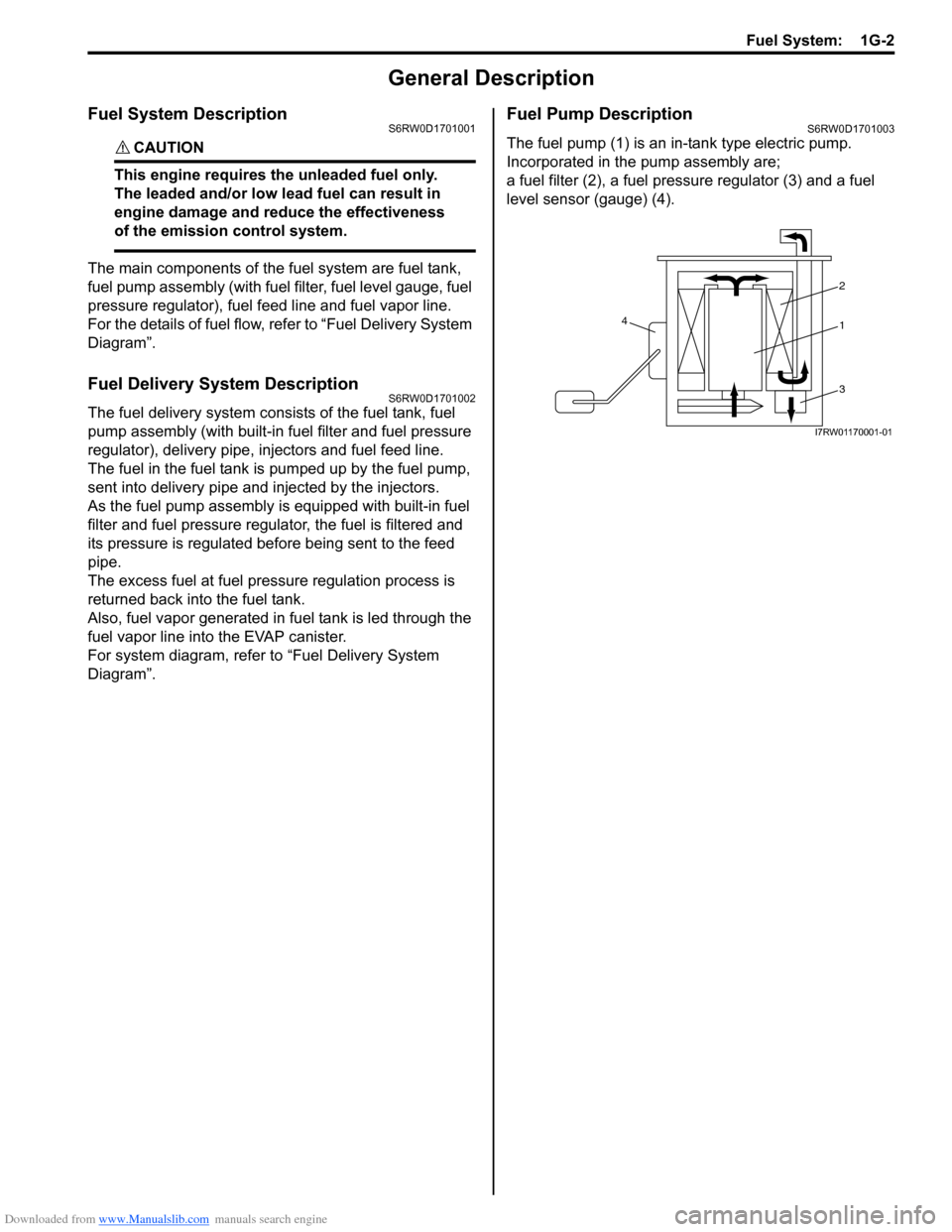
Fuel Pump DescriptionS6RW0D1701003
The fuel pump (1) is an in-tank type electric pump.
Incorporated in the pump assembly are;
a fuel filter (2), a fuel pressure regulator (3) and a fuel
level sensor (gauge) (4).
2
41
3
I7RW01170001-01
Page 380 of 1556
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 1G-3 Fuel System:
Schematic and Routing Diagram
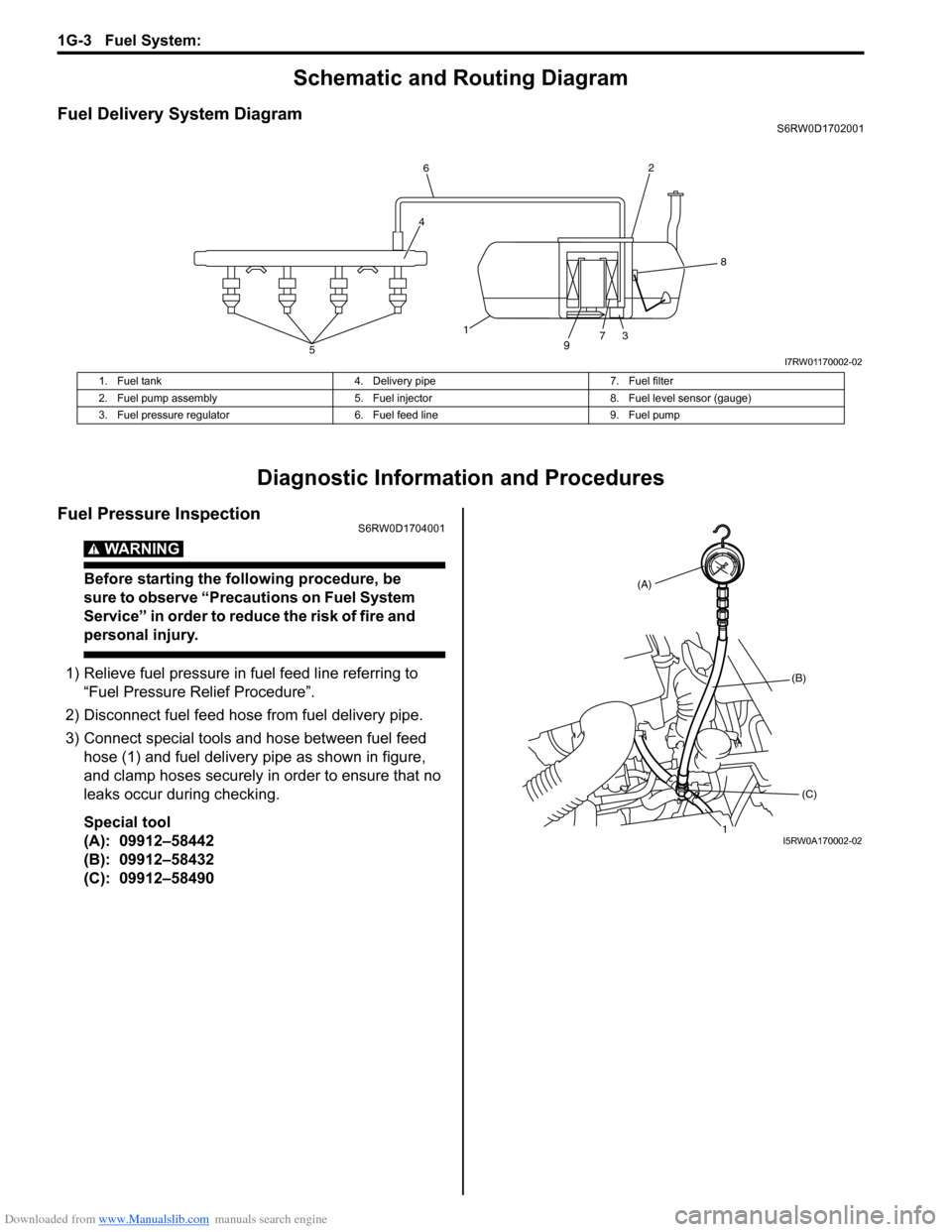
Fuel Delivery System DiagramS6RW0D1702001
Diagnostic Information and Procedures
Fuel Pressure InspectionS6RW0D1704001
WARNING!
Before starting the following procedure, be
sure to observe “Precautions on Fuel System
Service” in order to reduce the risk of fire and
personal injury.
1) Relieve fuel pressure in fuel feed line referring to
“Fuel Pressure Relief Procedure”.
2) Disconnect fuel feed hose from fuel delivery pipe.
3) Connect special tools and hose between fuel feed
hose (1) and fuel delivery pipe as shown in figure,
and clamp hoses securely in order to ensure that no
leaks occur during checking.
Special tool
(A): 09912–58442
(B): 09912–58432
(C): 09912–58490
73 6
1 4
5
8
9
2
I7RW01170002-02
1. Fuel tank 4. Delivery pipe 7. Fuel filter
2. Fuel pump assembly 5. Fuel injector 8. Fuel level sensor (gauge)
3. Fuel pressure regulator 6. Fuel feed line 9. Fuel pump
(C) (B)
(A)
1I5RW0A170002-02
Page 381 of 1556

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine Fuel System: 1G-4
4) Check that battery voltage is 11 V or more.
5) Measure fuel pressure at each condition.
If measured pressure is out of specification, refer to
“Fuel Pressure Check in Section 1A” and check each
possibly defective part. Replace if found defective.
a) Turn ignition switch ON to operate fuel pump and
after 2 seconds turn it OFF. Repeat this 3 or 4
times and then check fuel pressure.
Fuel pressure specification
With fuel pump operating and engine
stopped: 360 – 400 kPa (3.6 – 4.0 kgf/cm2,
51.2 – 56.9 psi)
b) Start engine and warm it up to normal operating
temperature, and measure fuel pressure at
idling.
Fuel pressure specification
At specified idle speed: 360 – 400 kPa (3.6 –
4.0 kgf/cm2, 51.2 – 56.9 psi)
c) Stop engine, and measure fuel pressure at one
minute after stopping.
Fuel pressure specification
With 1 min. after engine (fuel pump) stop
(Pressure reduces as time passes): Over 250
kPa (2.5 kgf/cm
2, 35.6 psi)
6) After checking fuel pressure, remove fuel pressure
gauge.
WARNING!
As fuel feed line is still under high fuel
pressure, make sure to release fuel pressure
according to the following procedures.
• Place fuel container under joint.
• Cover joint with rag (1) and loosen joint nut
slowly in order to release fuel pressure
gradually.
7) Remove special tools from fuel delivery pipe and fuel
feed hose.
8) Connect fuel feed hose to fuel delivery pipe and
clamp it securely.
9) With engine OFF and ignition switch ON, check for
fuel leaks.
Fuel Cut Operation InspectionS6RW0D1704002
NOTE
Before inspection, make sure that gear shift
lever is in neutral position (shift select lever
is “P” range for A/T vehicle), A/C is OFF and
parking brake lever is pulled all the way up.
1) Warm engine up to normal operating temperature.
2) While listening to sound of injector (2) by using
sound scope (1) or such, increase engine speed to
higher than 3,000 r/min.
3) Check to make sure that injector operation sound is
stop when throttle valve is closed instantly and it is
heard again when engine speed is reduced to
approx. 2,000 r/min or less.
I5RW0A170003-01
I2RH0B170004-01