drain TOYOTA RAV4 2006 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2006, Model line: RAV4, Model: TOYOTA RAV4 2006Pages: 2000, PDF Size: 45.84 MB
Page 47 of 2000
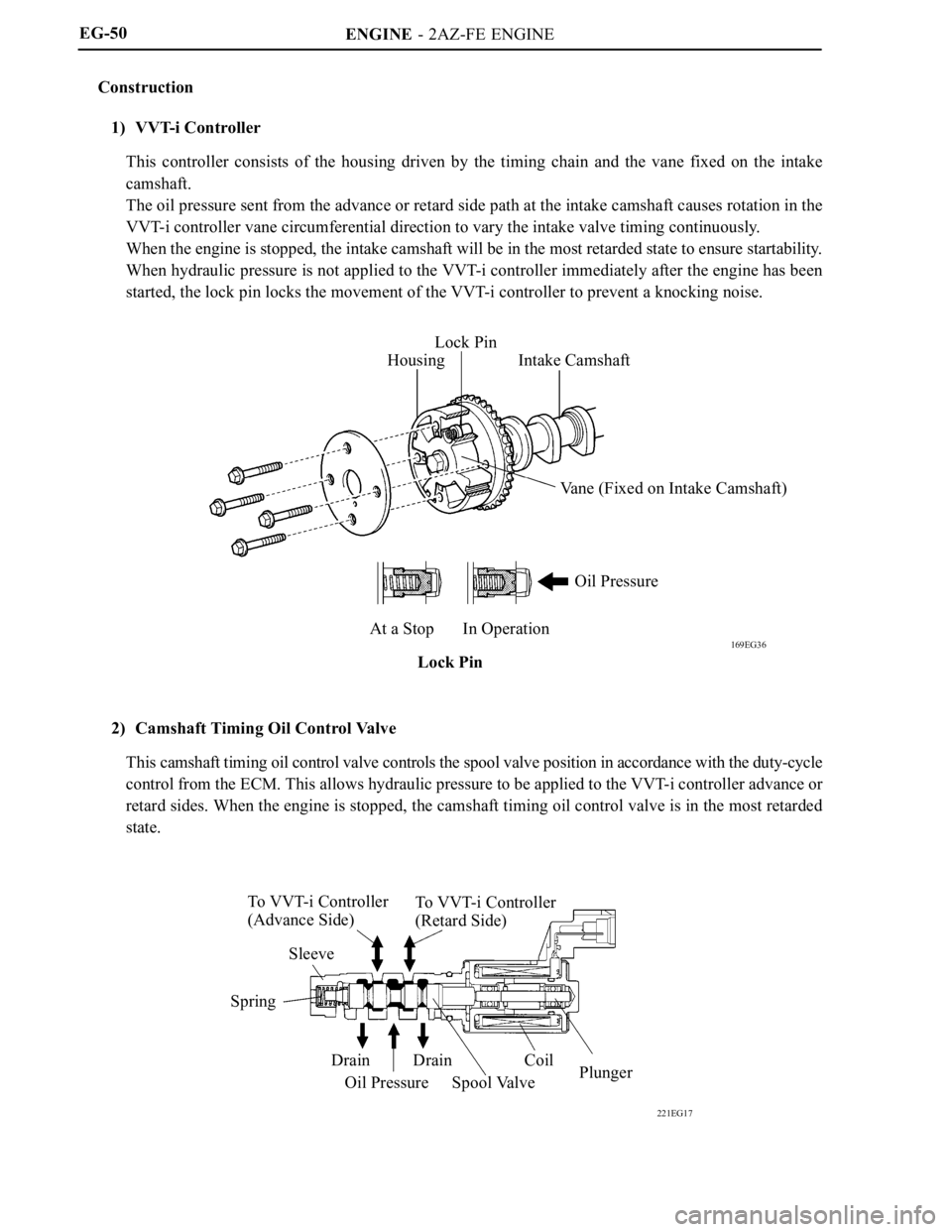
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
169EG36
HousingLock Pin
Intake Camshaft
Vane (Fixed on Intake Camshaft)
Oil Pressure
At a Stop In Operation
Lock Pin
221EG17
To VVT-i Controller
(Advance Side)To V V T- i C o n t r o l l e r
(Retard Side)
Sleeve
Spring
Drain
Oil PressureDrain
Spool ValveCoil
Plunger EG-50
Construction
1) VVT-i Controller
This controller consists of the housing driven by the timing chain and the vane fixed on the intake
camshaft.
The oil pressure sent from the advance or retard side path at the intake camshaft causes rotation in the
VVT-i controller vane circumferential direction to vary the intake valve timing continuously.
When the engine is stopped, the intake camshaft will be in the most retarded state to ensure startability.
When hydraulic pressure is not applied to the VVT-i controller immediately after the engine has been
started, the lock pin locks the movement of the VVT-i controller to prevent a knocking noise.
2) Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve
This camshaft timing oil control valve controls the spool valve position in accordance with the duty-cycle
control from the ECM. This allows hydraulic pressure to be applied to the VVT-i controller advance or
retard sides. When the engine is stopped, the camshaft timing oil control valve is in the most retarded
state.
Page 48 of 2000
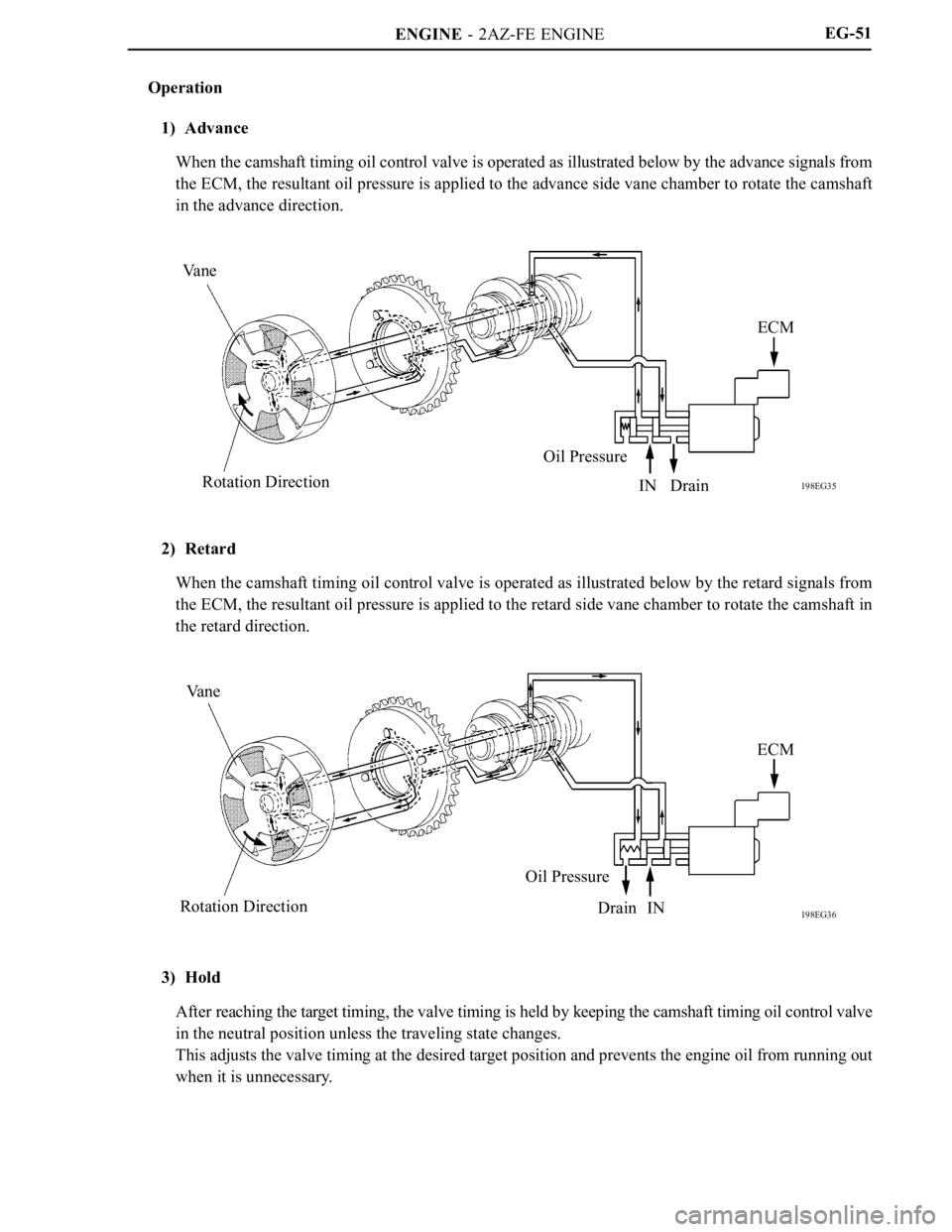
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
198EG35
Va n e
Rotation DirectionOil PressureECM
IN Drain
198EG36
Va n e
Rotation DirectionOil Pressure
Drain INECMEG-51
Operation
1) Advance
When the camshaft timing oil control valve is operated as illustrated below by the advance signals from
the ECM, the resultant oil pressure is applied to the advance side vane chamber to rotate the camshaft
in the advance direction.
2) Retard
When the camshaft timing oil control valve is operated as illustrated below by the retard signals from
the ECM, the resultant oil pressure is applied to the retard side vane chamber to rotate the camshaft in
the retard direction.
3) Hold
After reaching the target timing, the valve timing is held by keeping the camshaft timing oil control valve
in the neutral position unless the traveling state changes.
This adjusts the valve timing at the desired target position and prevents the engine oil from running out
when it is unnecessary.
Page 52 of 2000
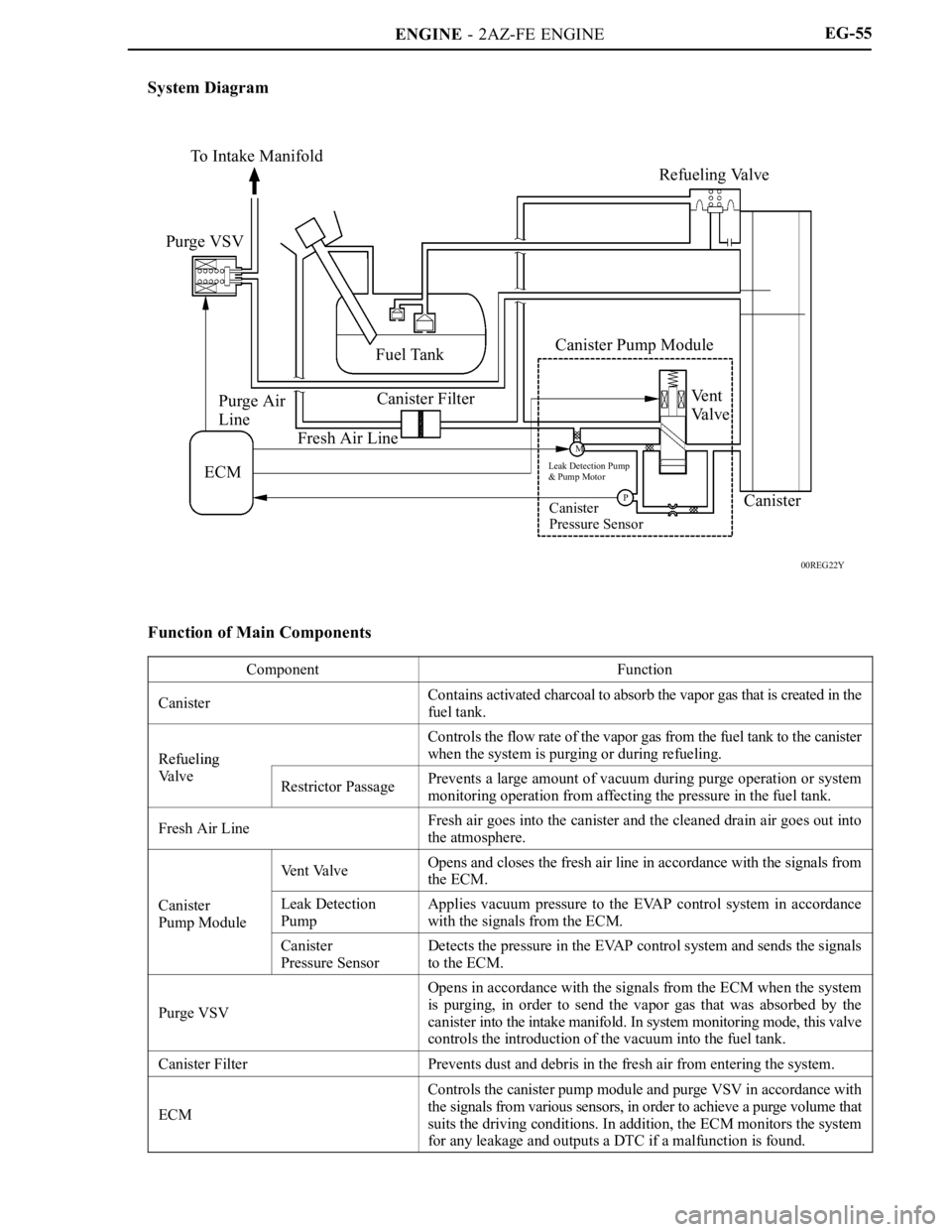
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
00REG22Y
To Intake Manifold
Purge VSV
Purge Air
Line
ECMFuel Tank
Canister Filter
Fresh Air LineRefueling Valve
Canister Pump Module
Ve n t
Va l v e
Leak Detection Pump
& Pump Motor
Canister
Pressure SensorCanisterP M
EG-55
System Diagram
Function of Main Components
ComponentFunction
CanisterContains activated charcoal to absorb the vapor gas that is created in the
fuel tank.
Refueling
Controls the flow rate of the vapor gas from the fuel tank to the canister
when the system is purging or during refueling.
Refueling
Va l v eRestrictor PassagePrevents a large amount of vacuum during purge operation or system
monitoring operation from affecting the pressure in the fuel tank.
Fresh Air LineFresh air goes into the canister and the cleaned drain air goes out into
the atmosphere.
Vent ValveOpens and closes the fresh air line in accordance with the signals from
the ECM.
Canister
Pump ModuleLeak Detection
PumpApplies vacuum pressure to the EVAP control system in accordance
with the signals from the ECM.
p
Canister
Pressure SensorDetects the pressure in the EVAP control system and sends the signals
to the ECM.
Purge VSV
Opens in accordance with the signals from the ECM when the system
is purging, in order to send the vapor gas that was absorbed by the
canister into the intake manifold. In system monitoring mode, this valve
controls the introduction of the vacuum into the fuel tank.
Canister FilterPrevents dust and debris in the fresh air from entering the system.
ECM
Controls the canister pump module and purge VSV in accordance with
the signals from various sensors, in order to achieve a purge volume that
suits the driving conditions. In addition, the ECM monitors the system
for any leakage and outputs a DTC if a malfunction is found.
Page 53 of 2000
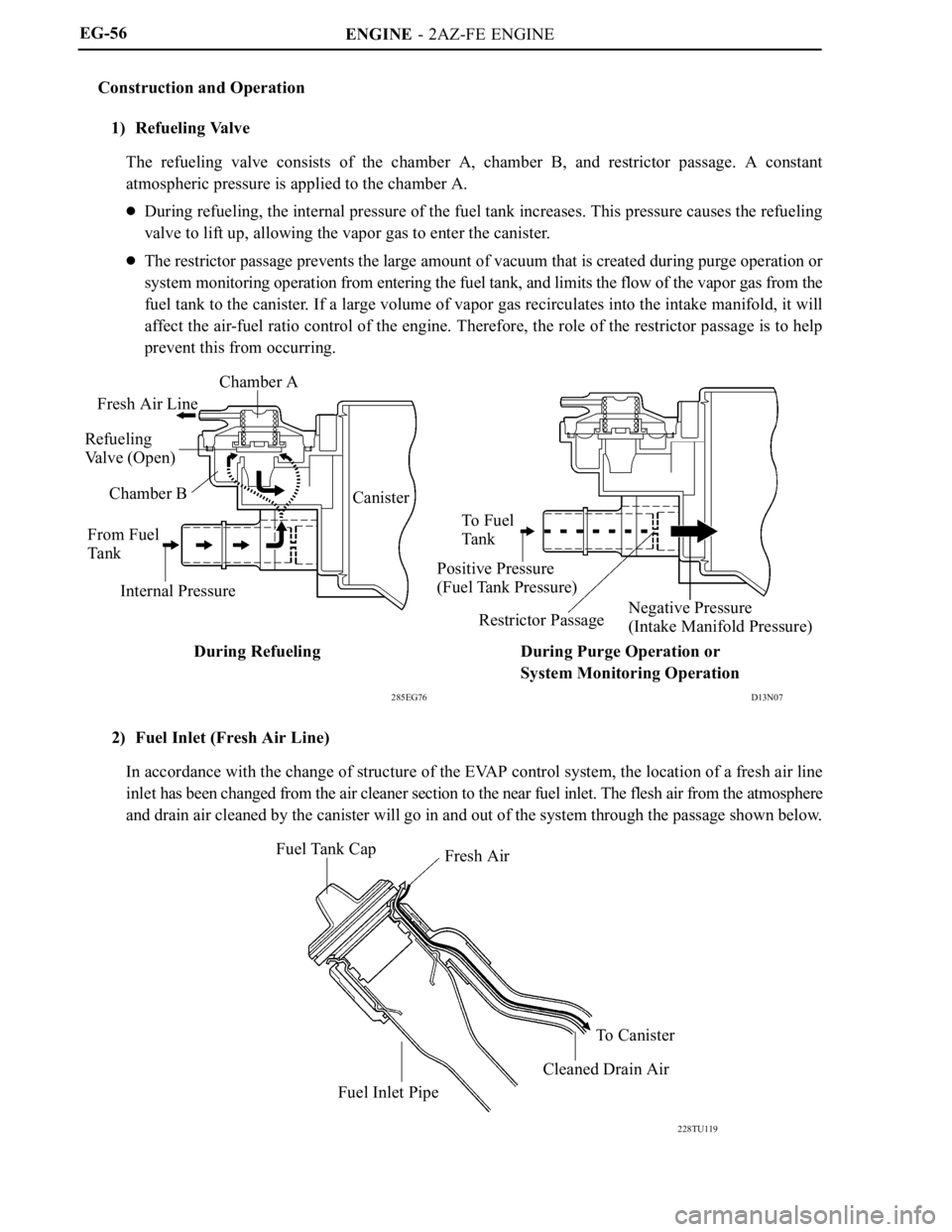
ENGINE - 2AZ-FE ENGINE
D13N07 285EG76
Chamber A
Fresh Air Line
Refueling
Valve (Open)
Chamber B
From Fuel
Ta n k
Internal PressureCanister
To F u e l
Ta n k
Positive Pressure
(Fuel Tank Pressure)
Restrictor PassageNegative Pressure
(Intake Manifold Pressure)
During Refueling During Purge Operation or
System Monitoring Operation
228TU119
Fuel Tank Cap
Fresh Air
Fuel Inlet PipeTo Canister
Cleaned Drain Air EG-56
Construction and Operation
1) Refueling Valve
The refueling valve consists of the chamber A, chamber B, and restrictor passage. A constant
atmospheric pressure is applied to the chamber A.
During refueling, the internal pressure of the fuel tank increases. This pressure causes the refueling
valve to lift up, allowing the vapor gas to enter the canister.
The restrictor passage prevents the large amount of vacuum that is created during purge operation or
system monitoring operation from entering the fuel tank, and limits the flow of the vapor gas from the
fuel tank to the canister. If a large volume of vapor gas recirculates into the intake manifold, it will
affect the air-fuel ratio control of the engine. Therefore, the role of the restrictor passage is to help
prevent this from occurring.
2) Fuel Inlet (Fresh Air Line)
In accordance with the change of structure of the EVAP control system, the location of a fresh air line
inlet has been changed from the air cleaner section to the near fuel inlet. The flesh air from the atmosphere
and drain air cleaned by the canister will go in and out of the system through the passage shown below.
Page 83 of 2000

ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
01MEG12Y
Oil Filter Case
Element
Filter Cap
Drain PlugElement
Filter Cap
Drain Plug
Drain Pipe
Hose
(Inside Diameter: 15 mm (0.59 in.))
When draining engine oil
Service Tip
The engine oil in the oil filter can be drained by removing the drain plug and inserting the drain
pipe supplied with the element into the oil filter. For details, refer to the 2006 RAV4 Repair Manual
(Pub. No. RM01M1U).
The engine oil maintenance interval for a model that has an oil filter with a replaceable element
is the same as that for the conventional model.
EG-87
4. Oil Filter
An oil filter with a replaceable element is used. The element uses a high-performance filter paper to
improve filtration performance. It is also combustible for environmental protection.
An aluminum alloy filter cap is used to extend its life.
This oil filter has a structure which can drain the engine oil remaining in the oil filter. This prevents engine
oil from spattering when replacing the element and allows the technician to work without touching hot
engine oil.
Page 119 of 2000
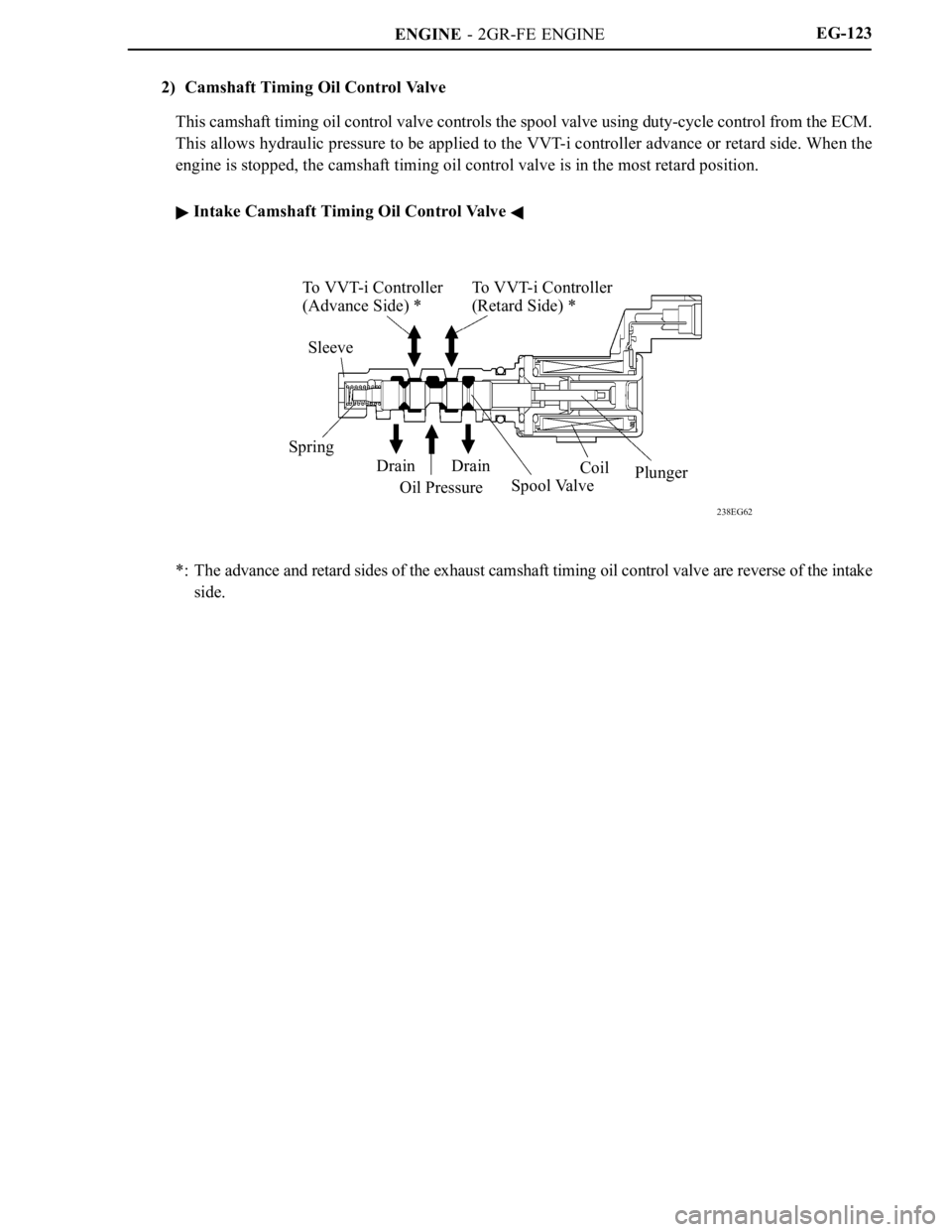
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
238EG62
To VVT-i Controller
(Advance Side) *To VVT-i Controller
(Retard Side) *
Sleeve
Spring
Drain
Oil PressureDrain
Spool ValveCoil
PlungerEG-123
2) Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve
This camshaft timing oil control valve controls the spool valve using duty-cycle control from the ECM.
This allows hydraulic pressure to be applied to the VVT-i controller advance or retard side. When the
engine is stopped, the camshaft timing oil control valve is in the most retard position.
Intake Camshaft Timing Oil Control Valve
*: The advance and retard sides of the exhaust camshaft timing oil control valve are reverse of the intake
side.
Page 120 of 2000
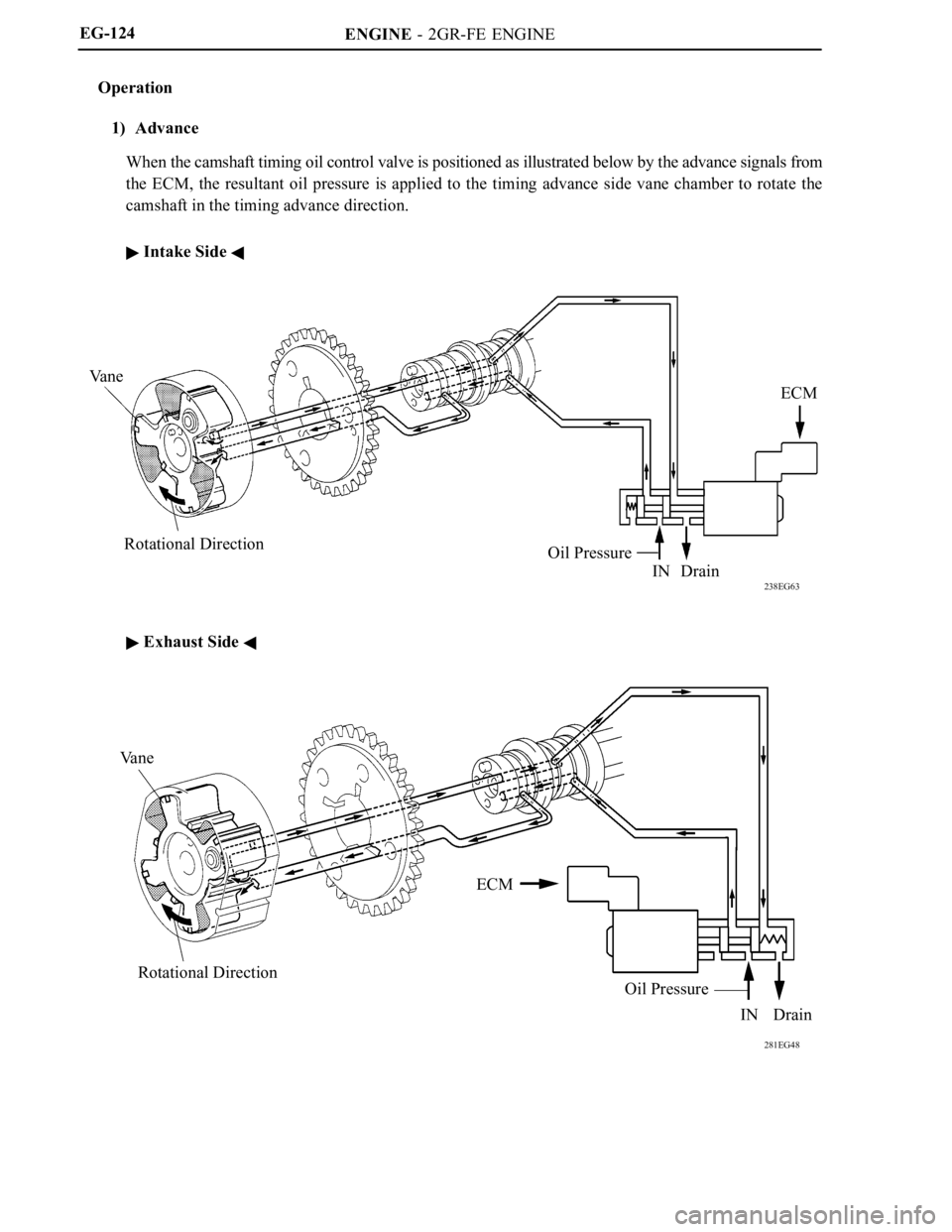
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
238EG63
Va n e
Rotational Direction
Oil Pressure
IN DrainECM
281EG48
Va n e
Rotational DirectionECM
Oil Pressure
IN Drain EG-124
Operation
1) Advance
When the camshaft timing oil control valve is positioned as illustrated below by the advance signals from
the ECM, the resultant oil pressure is applied to the timing advance side vane chamber to rotate the
camshaft in the timing advance direction.
Intake Side
Exhaust Side
Page 121 of 2000
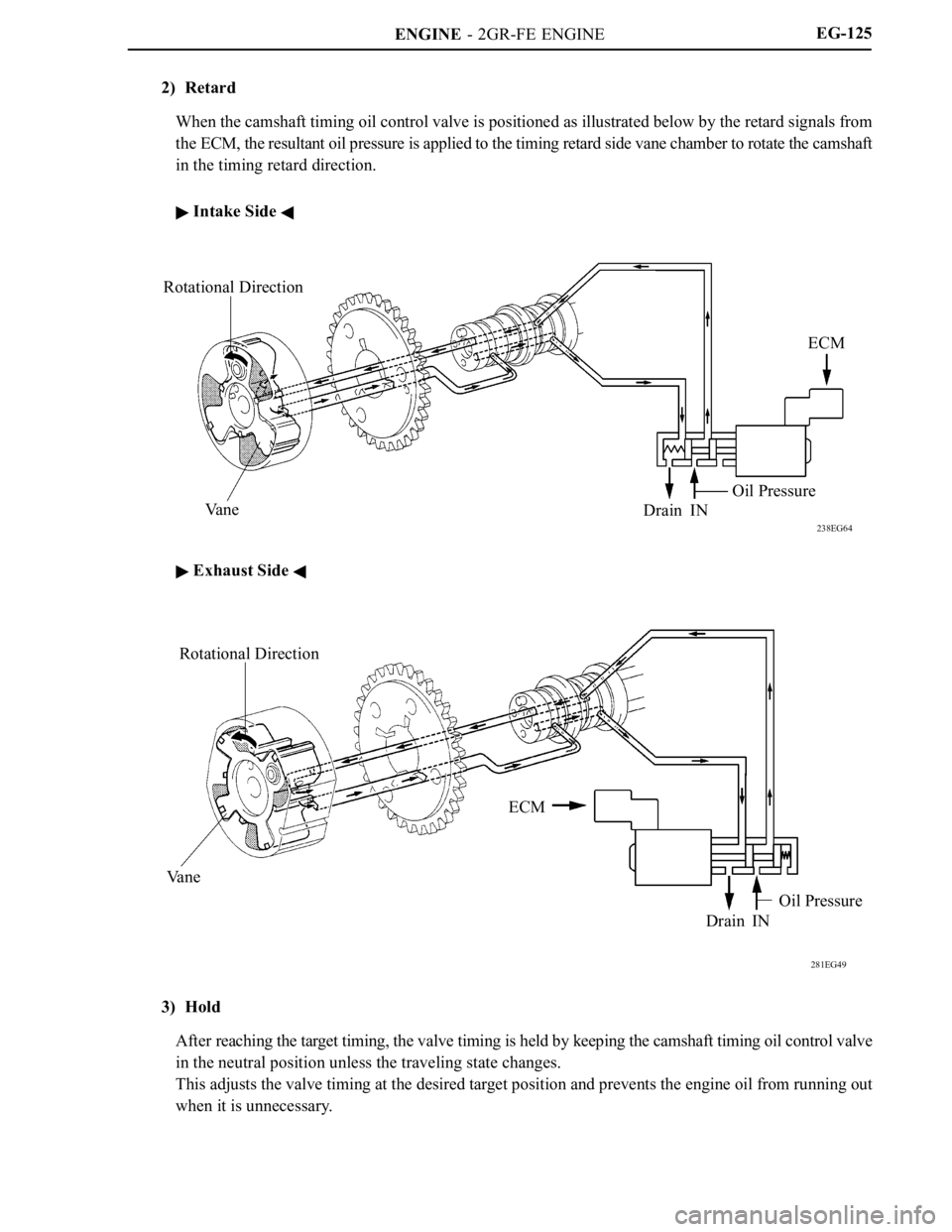
ENGINE - 2GR-FE ENGINE
238EG64
Rotational Direction
Va n e
Drain INOil PressureECM
281EG49
Rotational Direction
Va n eECM
Drain INOil Pressure
EG-125
2) Retard
When the camshaft timing oil control valve is positioned as illustrated below by the retard signals from
the ECM, the resultant oil pressure is applied to the timing retard side vane chamber to rotate the camshaft
in the timing retard direction.
Intake Side
Exhaust Side
3) Hold
After reaching the target timing, the valve timing is held by keeping the camshaft timing oil control valve
in the neutral position unless the traveling state changes.
This adjusts the valve timing at the desired target position and prevents the engine oil from running out
when it is unnecessary.
Page 179 of 2000

SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS – U151E AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONSS–47
SS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
Automatic Transaxle Assembly
Part Tightened N*m kgf*cm ft*lbf
Park/neutral position switch Nut 6.9 70 61 in.*lbf
Bolt 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
Control shaft lever x Control shaft 13 133 10
Shift control cable x Control shaft lever 15 153 11
Transaxle housing x Engine block Upper side bolt 64 653 47
Lower side bolt
A37 377 27
Lower side bolt
B46 470 34
Torque converter clutch x Drive plate 41 418 30
Flywheel housing under cover x Automatic transaxle 7.8 80 69 in.*lbf
Front engine mounting bracket x Transaxle 64 653 47
Rear engine mounting bracket x Transaxle 45 459 33
Engine mounting bracket LH x Transaxle 64 653 47
Oil filler tube x Transaxle
Oil filler tube x Front engine mounting bracket5.5 56 49 in.*lbf
Control cable bracket No. 1 x Transaxle 12 122 9
Control cable bracket No. 2 x Transaxle 12 122 9
Oil cooler inlet elbow x Transaxle 27 276 20
Oil cooler outlet elbow x Transaxle 27 276 20
Starter x Transaxle37 377 27
Starter wire x Starter9.8 100 88 in.*lbf
Speed sensor (NC) x Transaxle 11 112 8
Speed sensor (NT) x Transaxle 11 112 8
Drain plug x Oil pan47 479 35
Transmission wire x Transaxle 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
ATF temperature sensor x Valve body 6.6 67 58 in.*lbf
Oil pan x Transaxle7.8 80 69 in.*lbf
Solenoid valve x Valve body SL2, DSL, S4 11 110 8
SL1, SL3 6.6 67 58 in.*lbf
Valve body x Transaxle11 11 2 8
Oil strainer x Valve body11 11 2 8
Floor shift assembly x Body12 122 9
Control cable clamp x Engine mounting insulator 12 122 9
Differential gear lube apply tube x Transaxle housing 9.8 100 87 in.*lbf
Front planetary gear lock nut 280 3,355 207
Brake apply tube clamp x Transaxle case 5.4 55 48 in.*lbf
Transaxle case No. 1 plug x Transaxle rear cover 7.4 75 65 in.*lbf
Transaxle rear cover x Transaxle case Bolt A 19 194 14
Other bolt 25 255 18
Parking lock pawl shaft x Transaxle case 9.8 100 87 in.*lbf
Oil pump assembly x Transaxle case 22 226 16
Transaxle housing x Transaxle case Bolt A 22 254 16
Bolt B 29 295 21
Bolt C 29 295 21
Bolt D 22 254 16
Automatic transmission case plug x Transaxle housing 7.4 75 65 in.*lbf
Automatic transmission case plug x Transaxle case 7.4 75 65 in.*lbf
Page 181 of 2000

SERVICE SPECIFICATIONS – DIFFERENTIALSS–75
SS
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
Differential
Part Tightened N*m kgf*cm ft.*lbf
Rear differential No. 2 support x
Rear suspension member86 877 63
Rear differential support x Rear
suspension member140 1,428 103
Rear differential No. 2 support x
Rear differential
Rear differential No. 1 support x
Rear differential55 561 41
Rear differential support x Rear
differential98 999 72
Drain plug x Differential carrier
Filler plug x Differential carrier39 398 29
Electromagnetic coupling x Stud
bolt8.0 82 71 in.*lbf
Electromagnetic coupling x
Differential carrier19.6 200 14
Yoke x Differential carrier 5.0 51 44 in.*lbf
Drive pinion nut x Differential
drive pinion245 or less 2,498 or less 181 or less
Differential side bearing retainer x
Differential carrier34.3 350 25
Differential carrier x Differential
breather plug oil deflector5.0 51 44 in.*lbf
Differential ring gear x Differential
case90 918 66