check engine TOYOTA SIENNA 2007 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SIENNA, Model: TOYOTA SIENNA 2007Pages: 3000, PDF Size: 52.26 MB
Page 547 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–241
ES
HINT:
• These DTCs indicate malfunctions relating to the primary circuit.
• If DTC P0351 is set, check the No. 1 ignition coil with igniter circuit.
• If DTC P0352 is set, check the No. 2 ignition coil with igniter circuit.
• If DTC P0353 is set, check the No. 3 ignition coil with igniter circuit.
• If DTC P0354 is set, check the No. 4 ignition coil with igniter circuit.
• If DTC P0355 is set, check the No. 5 ignition coil with igniter circuit.
• If DTC P0356 is set, check the No. 6 ignition coil with igniter circuit.
DESCRIPTION
A Direct Ignition System (DIS) is used on this vehicle.
The DIS is a 1-cylinder ignition system in which each cylinder is ignited by one ignition coil and one spark
plug is connected to the end of each secondary wiring. High-voltage is generated in the secondary wiring
and then applied directly to each spark plug. The sparks of the spark plugs pass from the center
electrodes to the ground electrodes.
The ECM determines the ignition timing and transmits the ignition (IGT) signals to each cylinder. Using the
IGT signal, the ECM turns the power transistor inside the igniter on and off. The power transistor, in turn,
switches on and off the current to the primary coil. When the current to the primary coil is cut off, high-
voltage is generated in the secondary coil. This voltage is applied to the spark plugs, causing them to
spark inside the cylinders. As the ECM cuts the current to the primary coil off, the igniter sends back an
ignition confirmation (IGF) signal to the ECM, for each cylinder ignition.
DTC P0351 Ignition Coil "A" Primary / Secondary Circuit
DTC P0352 Ignition Coil "B" Primary / Secondary Circuit
DTC P0353 Ignition Coil "C" Primary / Secondary Circuit
DTC P0354 Ignition Coil "D" Primary / Secondary Circuit
DTC P0355 Ignition Coil "E" Primary / Secondary Circuit
DTC P0356 Ignition Coil "F" Primary / Secondary Circuit
Page 549 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–243
ES
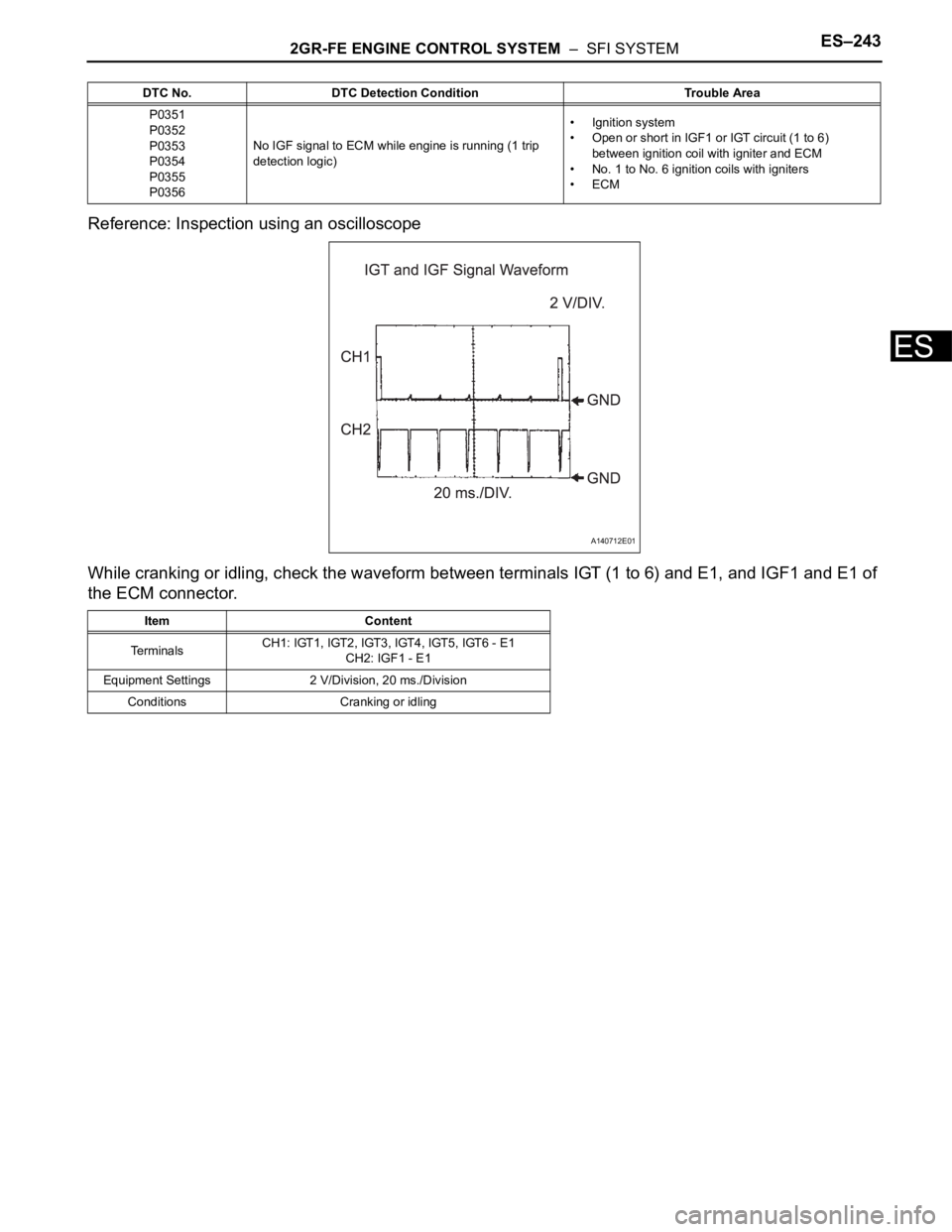
Reference: Inspection using an oscilloscope
While cranking or idling, check the waveform between terminals IGT (1 to 6) and E1, and IGF1 and E1 of
the ECM connector.
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0351
P0352
P0353
P0354
P0355
P0356No IGF signal to ECM while engine is running (1 trip
detection logic)• Ignition system
• Open or short in IGF1 or IGT circuit (1 to 6)
between ignition coil with igniter and ECM
• No. 1 to No. 6 ignition coils with igniters
•ECM
Item Content
TerminalsCH1: IGT1, IGT2, IGT3, IGT4, IGT5, IGT6 - E1
CH2: IGF1 - E1
Equipment Settings 2 V/Division, 20 ms./Division
Conditions Cranking or idling
A140712E01
Page 553 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–247
ES
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Read freeze frame data using the intelligent tester. The ECM records vehicle and driving condition
information as freeze frame data the moment a DTC is stored. When troubleshooting, freeze frame data
can be helpful in determining whether the vehicle was running or stopped, whether the engine was
warmed up or not, whether the air-fuel ratio was lean or rich, as well as other data recorded at the time of
a malfunction.
HINT:
(See page ES-211)
NG
OK
1CHECK FOR SPARKS AND CHECK SPARK PLUG OF MISFIRING CYLINDER
A140714E02
Go to step 4
Page 554 of 3000
ES–2482GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
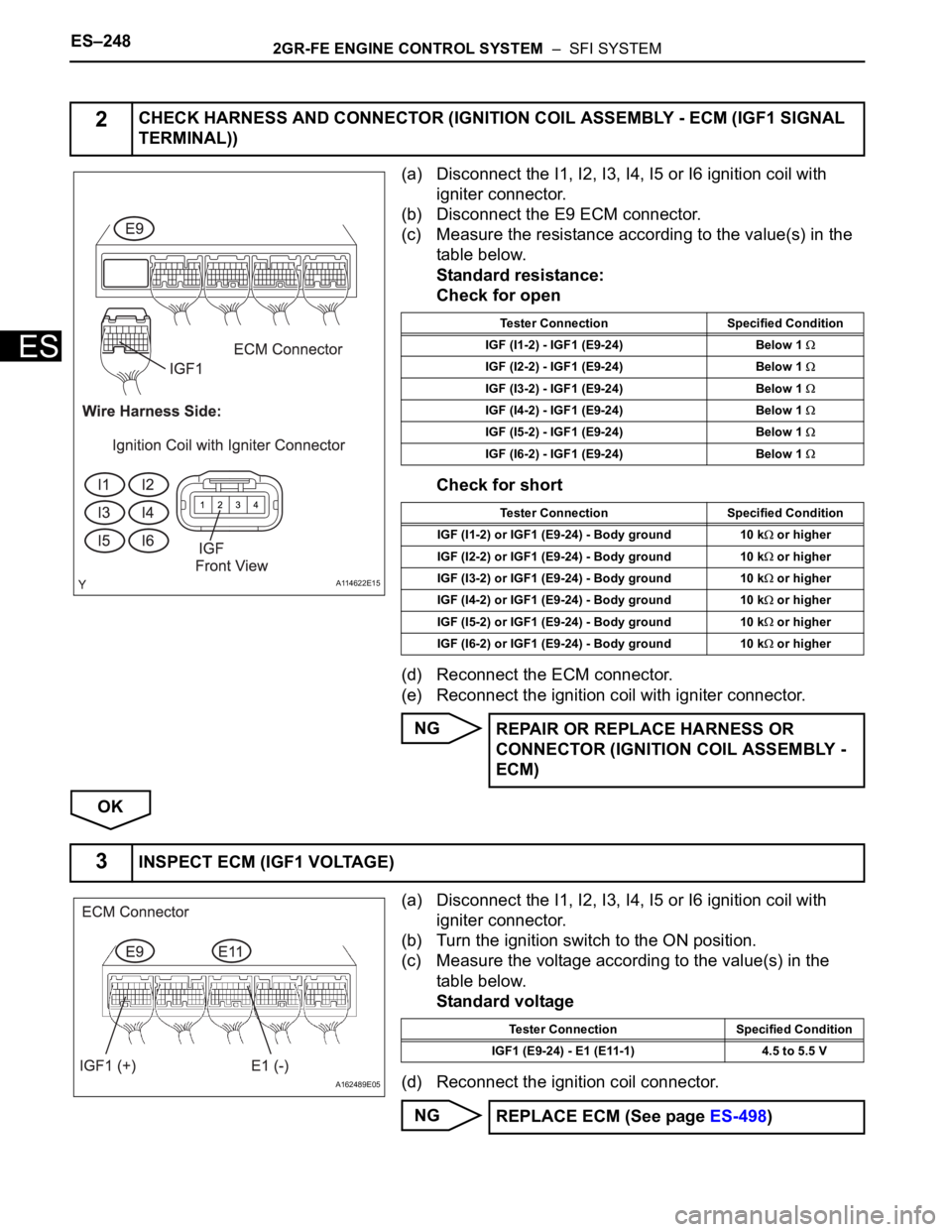
(a) Disconnect the I1, I2, I3, I4, I5 or I6 ignition coil with
igniter connector.
(b) Disconnect the E9 ECM connector.
(c) Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the
table below.
Standard resistance:
Check for open
Check for short
(d) Reconnect the ECM connector.
(e) Reconnect the ignition coil with igniter connector.
NG
OK
(a) Disconnect the I1, I2, I3, I4, I5 or I6 ignition coil with
igniter connector.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the
table below.
Standard voltage
(d) Reconnect the ignition coil connector.
NG
2CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (IGNITION COIL ASSEMBLY - ECM (IGF1 SIGNAL
TERMINAL))
A114622E15
Tester Connection Specified Condition
IGF (I1-2) - IGF1 (E9-24) Below 1
IGF (I2-2) - IGF1 (E9-24) Below 1
IGF (I3-2) - IGF1 (E9-24) Below 1
IGF (I4-2) - IGF1 (E9-24) Below 1
IGF (I5-2) - IGF1 (E9-24) Below 1
IGF (I6-2) - IGF1 (E9-24) Below 1
Tester Connection Specified Condition
IGF (I1-2) or IGF1 (E9-24) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
IGF (I2-2) or IGF1 (E9-24) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
IGF (I3-2) or IGF1 (E9-24) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
IGF (I4-2) or IGF1 (E9-24) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
IGF (I5-2) or IGF1 (E9-24) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
IGF (I6-2) or IGF1 (E9-24) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR
CONNECTOR (IGNITION COIL ASSEMBLY -
ECM)
3INSPECT ECM (IGF1 VOLTAGE)
A162489E05
Tester Connection Specified Condition
IGF1 (E9-24) - E1 (E11-1) 4.5 to 5.5 V
REPLACE ECM (See page ES-498)
Page 555 of 3000
2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–249
ES
OK
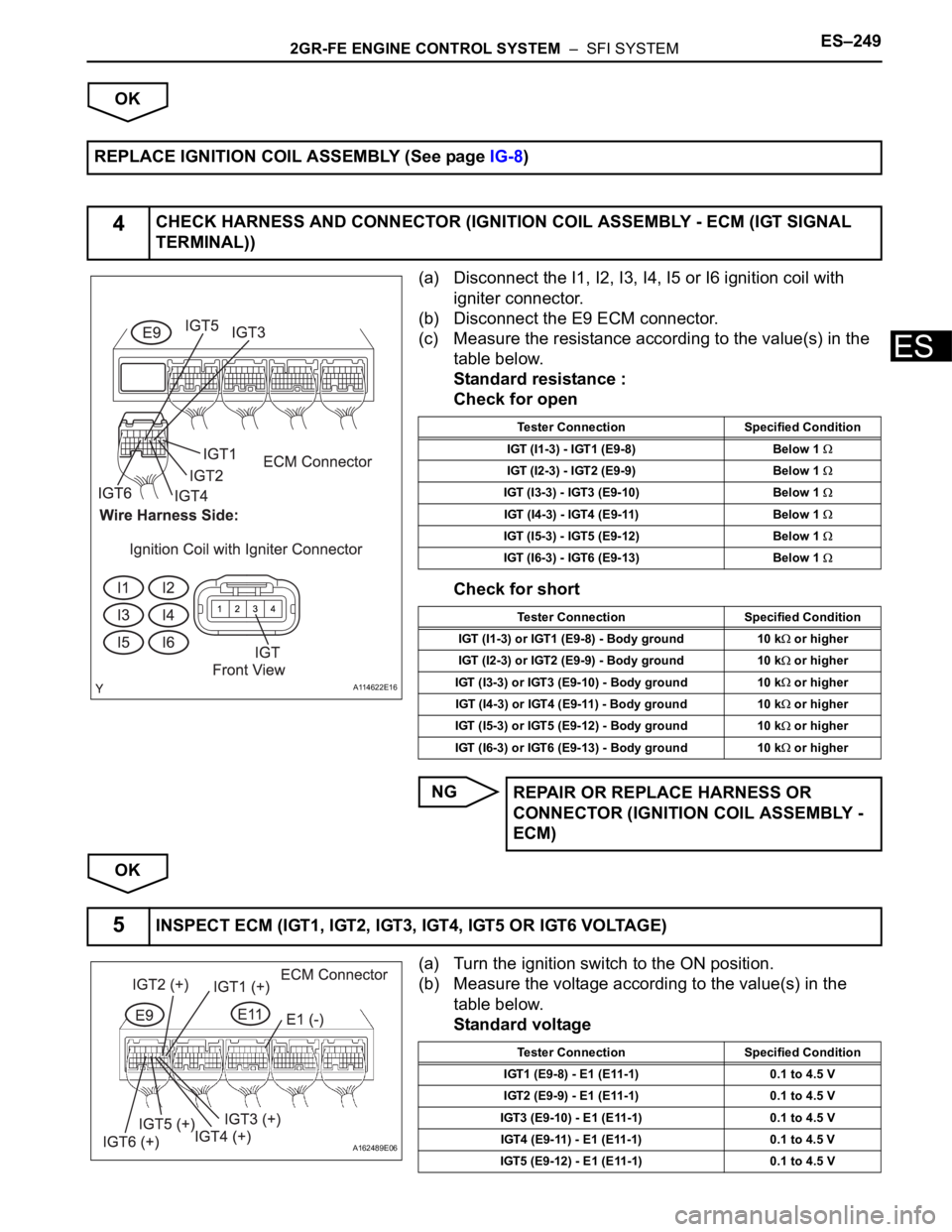
(a) Disconnect the I1, I2, I3, I4, I5 or I6 ignition coil with
igniter connector.
(b) Disconnect the E9 ECM connector.
(c) Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the
table below.
Standard resistance :
Check for open
Check for short
NG
OK
(a) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(b) Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the
table below.
Standard voltage REPLACE IGNITION COIL ASSEMBLY (See page IG-8)
4CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR (IGNITION COIL ASSEMBLY - ECM (IGT SIGNAL
TERMINAL))
A114622E16
Tester Connection Specified Condition
IGT (I1-3) - IGT1 (E9-8) Below 1
IGT (I2-3) - IGT2 (E9-9) Below 1
IGT (I3-3) - IGT3 (E9-10) Below 1
IGT (I4-3) - IGT4 (E9-11) Below 1
IGT (I5-3) - IGT5 (E9-12) Below 1
IGT (I6-3) - IGT6 (E9-13) Below 1
Tester Connection Specified Condition
IGT (I1-3) or IGT1 (E9-8) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
IGT (I2-3) or IGT2 (E9-9) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
IGT (I3-3) or IGT3 (E9-10) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
IGT (I4-3) or IGT4 (E9-11) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
IGT (I5-3) or IGT5 (E9-12) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
IGT (I6-3) or IGT6 (E9-13) - Body ground 10 k
or higher
REPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS OR
CONNECTOR (IGNITION COIL ASSEMBLY -
ECM)
5INSPECT ECM (IGT1, IGT2, IGT3, IGT4, IGT5 OR IGT6 VOLTAGE)
A162489E06
Tester Connection Specified Condition
IGT1 (E9-8) - E1 (E11-1) 0.1 to 4.5 V
IGT2 (E9-9) - E1 (E11-1) 0.1 to 4.5 V
IGT3 (E9-10) - E1 (E11-1) 0.1 to 4.5 V
IGT4 (E9-11) - E1 (E11-1) 0.1 to 4.5 V
IGT5 (E9-12) - E1 (E11-1) 0.1 to 4.5 V
Page 556 of 3000

ES–2502GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
NG
OK
(a) Disconnect the I1, I2, I3, I4, I5 or I6 ignition coil
connector.
(b) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(c) Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the
table below.
Standard voltage
(d) Reconnect the ignition coil connector.
NG
OK
(a) Disconnect the I1, I2, I3, I4, I5 or I6 ignition coil with
igniter connector.
(b) Measure the resistance according to the value(s) in the
table below.
Standard resistance:
Check for open
(c) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
(d) Measure the voltage according to the value(s) in the
table below.
IGT6 (E9-13) - E1 (E11-1) 0.1 to 4.5 V
REPLACE ECM (See page ES-498)
Tester Connection Specified Condition
6INSPECT ECM (IGT1, IGT2, IGT3, IGT4, IGT5 OR IGT6 VOLTAGE)
A114623E07
Tester Connection Specified Condition
IGT1 (E9-8) - E1 (E11-1) 4.5 V or more
IGT2 (E9-9) - E1 (E11-1) 4.5 V or more
IGT3 (E9-10) - E1 (E11-1) 4.5 V or more
IGT4 (E9-11) - E1 (E11-1) 4.5 V or more
IGT5 (E9-12) - E1 (E11-1) 4.5 V or more
IGT6 (E9-13) - E1 (E11-1) 4.5 V or more
REPLACE ECM (See page ES-498)
7INSPECT IGNITION COIL ASSEMBLY (POWER SOURCE)
A054393E92
Tester Connection Specified Condition
GND (I1-4) - Body ground Below 1
GND (I2-4) - Body ground Below 1
GND (I3-4) - Body ground Below 1
GND (I4-4) - Body ground Below 1
GND (I5-4) - Body ground Below 1
GND (I6-4) - Body ground Below 1
Page 558 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–265
ES
DTC SUMMARY
HINT:
The 0.02 inch orifice is located inside the pump module.
DESCRIPTION
The circuit description can be found in the EVAP (Evaporative Emission) System (See page ES-409).
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
Refer to the EVAP System (See page ES-412).
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
5 hours*1 after the ignition switch is turned off, the electric vacuum pump creates negative pressure
(vacuum) in the EVAP (Evaporative Emission) system. The ECM monitors for leaks and actuator
malfunctions based on the EVAP pressure.
HINT:
*1: If the engine coolant temperature is not below 35C (95F) 5 hours after the ignition switch is turned off,
the monitor check starts 2 hours later. If it is still not below 35
C (95F) 7 hours after the ignition switch is
turned off, the monitor check starts 2.5 hours later.
DTC P043EEvaporative Emission System Reference Ori-
fice Clog Up
DTC P043FEvaporative Emission System Reference Ori-
fice High Flow
DTC P2401Evaporative Emission System Leak Detection
Pump Control Circuit Low
DTC P2402Evaporative Emission System Leak Detection
Pump Control Circuit High
DTC P2419Evaporative Emission System Switching Valve
Control Circuit Low
DTCs Monitoring Item Malfunction Detection Condition Trouble AreaDetection
TimingDetection
Logic
P043E 0.02 inch orifice clogged P043E, P043F, P2401, P2402, P2419
are present when one of the following
conditions is met during key-off EVAP
monitor
• Reference orifice clogged
• Reference orifice high-flow
• Leak detection pump OFF
malfunction
• Leak detection pump ON
malfunction
• Vent valve ON (close) malfunction• Pump module
• Connector/wire
harness (Pump
module - ECM)
•ECMWhile
ignition
switch OFF2 trip P043F 0.02 inch orifice high-flow
P2401 Vacuum pump stuck OFF
P2402 Vacuum pump stuck ON
P2419Vent valve stuck open
(vent)
Sequence Operation Description Duration
- ECM activationActivated by soak timer, 5 hours (7 or 9.5 hours) after ignition switch
turned off.-
Page 559 of 3000
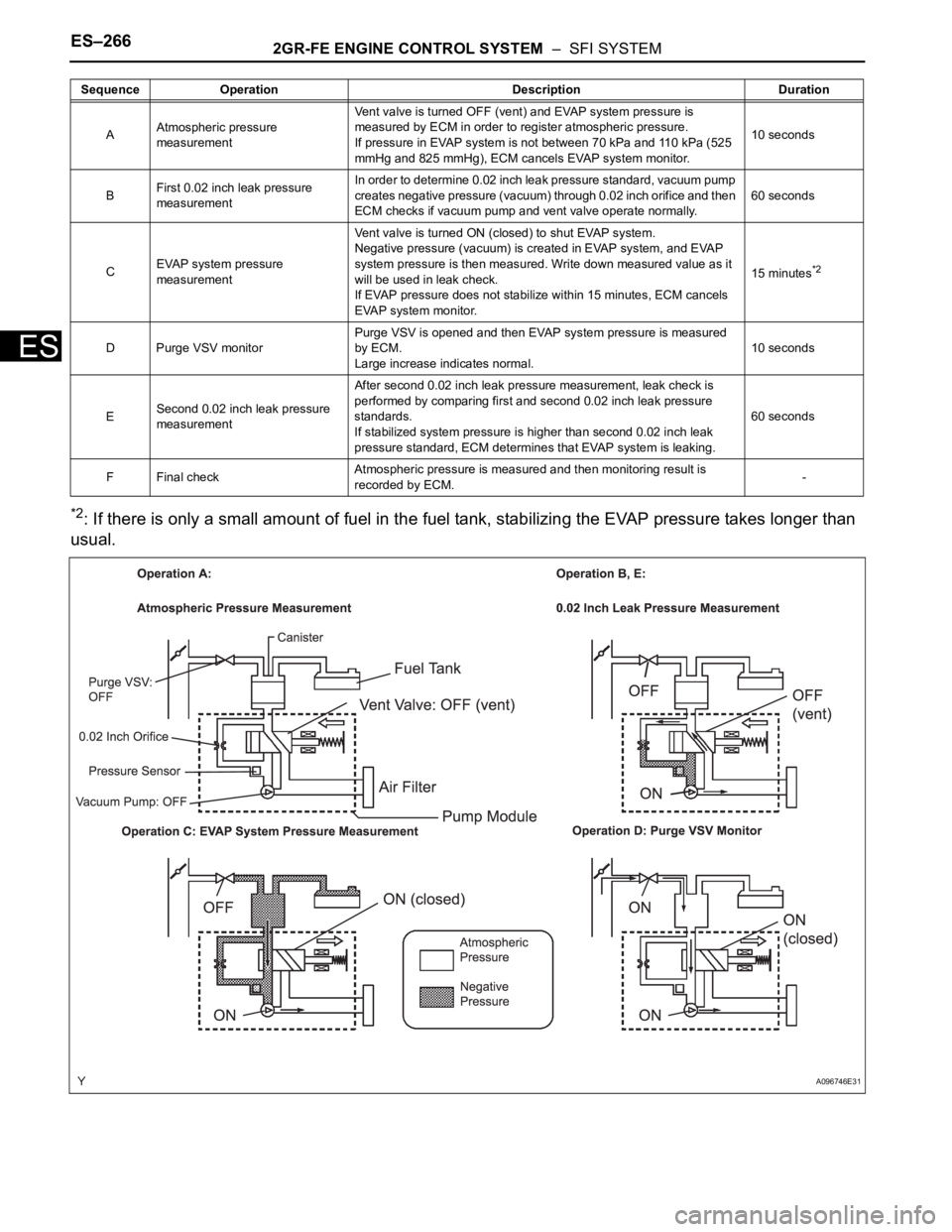
ES–2662GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ES
*2: If there is only a small amount of fuel in the fuel tank, stabilizing the EVAP pressure takes longer than
usual.
AAtmospheric pressure
measurementVent valve is turned OFF (vent) and EVAP system pressure is
measured by ECM in order to register atmospheric pressure.
If pressure in EVAP system is not between 70 kPa and 110 kPa (525
mmHg and 825 mmHg), ECM cancels EVAP system monitor.10 seconds
BFirst 0.02 inch leak pressure
measurementIn order to determine 0.02 inch leak pressure standard, vacuum pump
creates negative pressure (vacuum) through 0.02 inch orifice and then
ECM checks if vacuum pump and vent valve operate normally.60 seconds
CEVAP system pressure
measurementVent valve is turned ON (closed) to shut EVAP system.
Negative pressure (vacuum) is created in EVAP system, and EVAP
system pressure is then measured. Write down measured value as it
will be used in leak check.
If EVAP pressure does not stabilize within 15 minutes, ECM cancels
EVAP system monitor.15 minutes
*2
D Purge VSV monitorPurge VSV is opened and then EVAP system pressure is measured
by ECM.
Large increase indicates normal.10 seconds
ESecond 0.02 inch leak pressure
measurementAfter second 0.02 inch leak pressure measurement, leak check is
performed by comparing first and second 0.02 inch leak pressure
standards.
If stabilized system pressure is higher than second 0.02 inch leak
pressure standard, ECM determines that EVAP system is leaking.60 seconds
F Final checkAtmospheric pressure is measured and then monitoring result is
recorded by ECM.- Sequence Operation Description Duration
A096746E31
Page 561 of 3000

ES–2682GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEM
ESKey-off monitor sequence 1 to 8
1. Atmospheric pressure measurement
2. First reference pressure measurement
3. EVAP canister vent valve close stuck check
4. Vacuum introduction
5. EVAP canister purge valve close stuck check
6. Second reference pressure measurement
7. Leak check
8. Atmospheric pressure measurement
Time after key-off 5 or 7 or 9.5 hours
EVAP pressure sensor malfunction (P0450, P0451,
P0452, P0453)Not detected
EVAP canister purge valve Not operated by scan tool
EVAP canister vent valve Not operated by scan tool
EVAP leak detection pump Not operated by scan tool
Both of the following conditions 1 and 2 are met before
key-off-
1. Duration that vehicle driven 5 minutes or more
2. EVAP purge operation Performed
ECT 4.4 to 35
C (40 to 95F)
IAT 4.4 to 35
C (40 to 95F)
Next sequence is run if the following condition is met: -
Atmospheric pressure change Less than 0.3 kPa (2.25 mmHg) in 1 second
Next sequence is run if all of the following conditions
are met:Conditions 1, 2 and 3
1. EVAP pressure just after reference pressure
measurement-1 kPa (-7.5 mmHg) or less
2. Reference pressure -4.85 to -1.057 kPa (-36.384 to -7.929 mmHg)
3. Reference pressure Saturated within 1 minute
Next sequence is run if the following condition is met: -
EVAP pressure change after vent valve is ON 0.3 kPa (2.25 mmHg) or more
Next sequence is run if the following condition is met: -
EVAP pressure Saturated within 15 minutes
Next sequence is run if the following condition is met: -
EVAP pressure change after purge valve is open 0.3 kPa (2.25 mmHg) or more
Next sequence is run if all of the following conditions
are met:Conditions 1, 2, 3 and 4
1. EVAP pressure just after reference pressure
measurement-1 kPa (-7.5 mmHg) or less
2. Reference pressure -4.85 to -1.057 kPa (-36.384 to -7.929 mmHg)
3. Reference pressure Saturated
4. Difference between first reference pressure and
second reference pressureLess than 0.7 kPa (5.25 mmHg)
Next sequence is run if the following condition is met -
EVAP pressure when vacuum introduction was
completeLower than second reference pressure
EVAP monitor is complete if the following condition is
met:-
Page 562 of 3000

2GR-FE ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM – SFI SYSTEMES–269
ES
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
MONITOR RESULT
Refer to CHECKING MONITOR STATUS (See page ES-19).
Atmospheric pressure difference between sequence 1
and 8Within 0.3 kPa (2.25 mmHg)
1. One of following conditions is met -
2. EVAP pressure just after reference pressure
measurement startMore than -1 kPa (-7.5 mmHg)
3. Reference pressure Less than -4.85 kPa (-36.384 mmHg)
4. Reference pressure -1.057 kPa (-7.929 mmHg) or more
5. Reference pressure Not saturated
6. Difference between first reference pressure and
second reference pressure0.7 kPa (5.25 mmHg) or more