throttle body TOYOTA SIENNA 2007 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: TOYOTA, Model Year: 2007, Model line: SIENNA, Model: TOYOTA SIENNA 2007Pages: 3000, PDF Size: 52.26 MB
Page 1132 of 3000

FU–202GR-FE FUEL – FUEL INJECTOR
FU
(e) Connect the union to check valve hose. (*1)
(f) Connect the No. 1 ventilation hose. (*2)
(g) Install the clamp and connect the throttle with motor
body assembly connector. (*3)
(h) Connect the vapor feed hose assembly. (*4)
(i) Connect the 2 water by-pass hoses to the throttle
with motor body assembly. (*5)
4. INSTALL AIR CLEANER CAP SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Install the 2 bolts and air cleaner cap sub-assembly.
(b) Connect the No. 2 ventilation hose and air cleaner
hose band.
(c) Connect the vacuum hose (EVAP) to the air cleaner
hose.
(d) Connect the 3 vacuum hoses.
5. ADD ENGINE COOLANT (See page CO-7)
6. CONNECT CABLE TO NEGATIVE BATTERY
TERMINAL
7. INSPECT FOR ENGINE COOLANT LEAK (See page
CO-1)
8. INSTALL NO. 1 ENGINE UNDER COVER
9. INSPECT FOR FUEL LEAK (See page FU-7)
A162431E01
A129464E10
A163204
A135113E01
A135112E01
Page 1135 of 3000
FU–142GR-FE FUEL – FUEL INJECTOR
FU
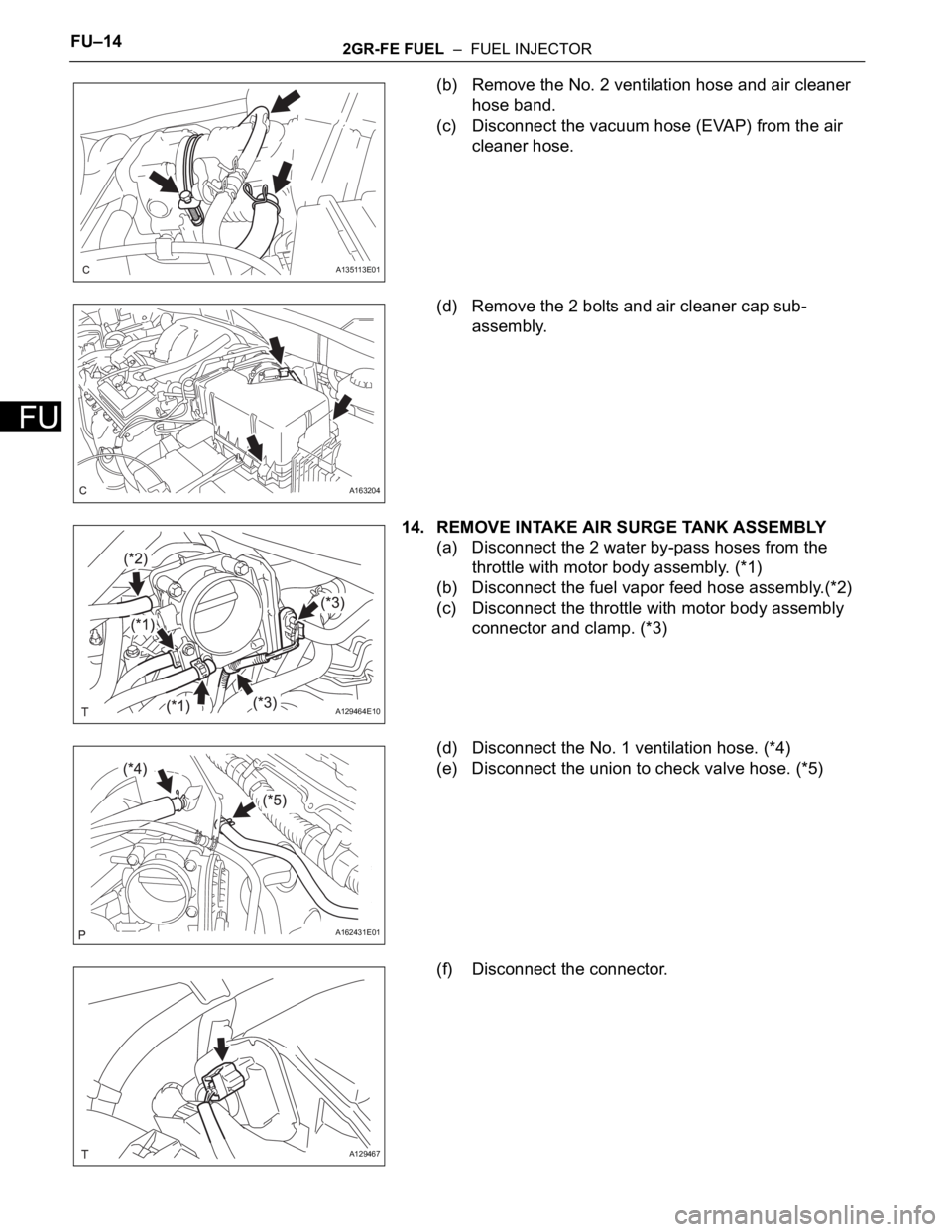
(b) Remove the No. 2 ventilation hose and air cleaner
hose band.
(c) Disconnect the vacuum hose (EVAP) from the air
cleaner hose.
(d) Remove the 2 bolts and air cleaner cap sub-
assembly.
14. REMOVE INTAKE AIR SURGE TANK ASSEMBLY
(a) Disconnect the 2 water by-pass hoses from the
throttle with motor body assembly. (*1)
(b) Disconnect the fuel vapor feed hose assembly.(*2)
(c) Disconnect the throttle with motor body assembly
connector and clamp. (*3)
(d) Disconnect the No. 1 ventilation hose. (*4)
(e) Disconnect the union to check valve hose. (*5)
(f) Disconnect the connector.
A135113E01
A163204
A129464E10
A162431E01
A129467
Page 1140 of 3000
2GR-FE FUEL – FUEL INJECTORFU–19
FU
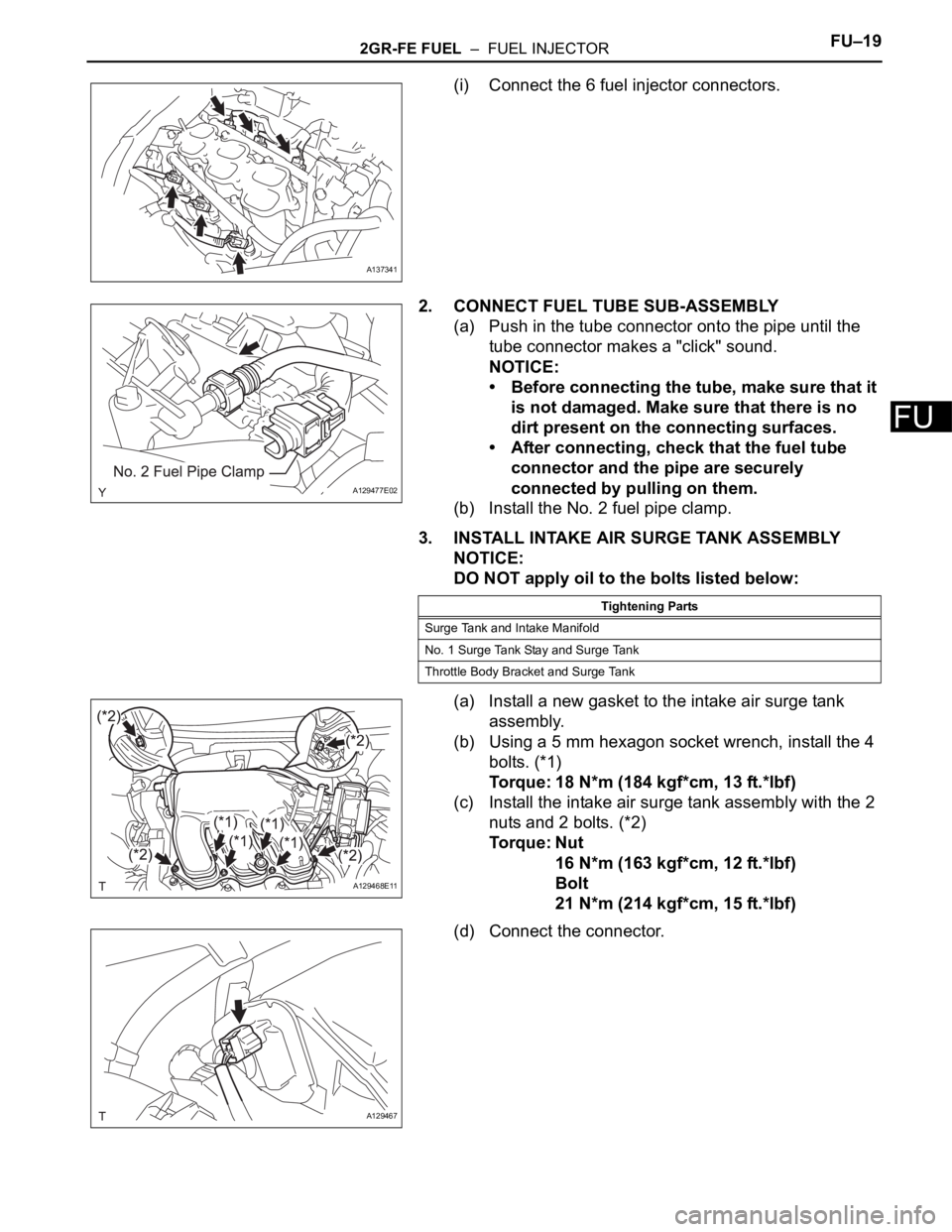
(i) Connect the 6 fuel injector connectors.
2. CONNECT FUEL TUBE SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Push in the tube connector onto the pipe until the
tube connector makes a "click" sound.
NOTICE:
• Before connecting the tube, make sure that it
is not damaged. Make sure that there is no
dirt present on the connecting surfaces.
• After connecting, check that the fuel tube
connector and the pipe are securely
connected by pulling on them.
(b) Install the No. 2 fuel pipe clamp.
3. INSTALL INTAKE AIR SURGE TANK ASSEMBLY
NOTICE:
DO NOT apply oil to the bolts listed below:
(a) Install a new gasket to the intake air surge tank
assembly.
(b) Using a 5 mm hexagon socket wrench, install the 4
bolts. (*1)
Torque: 18 N*m (184 kgf*cm, 13 ft.*lbf)
(c) Install the intake air surge tank assembly with the 2
nuts and 2 bolts. (*2)
Torque: Nut
16 N*m (163 kgf*cm, 12 ft.*lbf)
Bolt
21 N*m (214 kgf*cm, 15 ft.*lbf)
(d) Connect the connector.
A137341
A129477E02
Tightening Parts
Surge Tank and Intake Manifold
No. 1 Surge Tank Stay and Surge Tank
Throttle Body Bracket and Surge Tank
A129468E11
A129467
Page 1141 of 3000

FU–202GR-FE FUEL – FUEL INJECTOR
FU
(e) Connect the union to check valve hose. (*1)
(f) Connect the No. 1 ventilation hose. (*2)
(g) Install the clamp and connect the throttle with motor
body assembly connector. (*3)
(h) Connect the vapor feed hose assembly. (*4)
(i) Connect the 2 water by-pass hoses to the throttle
with motor body assembly. (*5)
4. INSTALL AIR CLEANER CAP SUB-ASSEMBLY
(a) Install the 2 bolts and air cleaner cap sub-assembly.
(b) Connect the No. 2 ventilation hose and air cleaner
hose band.
(c) Connect the vacuum hose (EVAP) to the air cleaner
hose.
(d) Connect the 3 vacuum hoses.
5. ADD ENGINE COOLANT (See page CO-7)
6. CONNECT CABLE TO NEGATIVE BATTERY
TERMINAL
7. INSPECT FOR ENGINE COOLANT LEAK (See page
CO-1)
8. INSTALL NO. 1 ENGINE UNDER COVER
9. INSPECT FOR FUEL LEAK (See page FU-7)
A162431E01
A129464E10
A163204
A135113E01
A135112E01
Page 1176 of 3000
EC–62GR-FE EMISSION CONTROL – EMISSION CONTROL SYSTEM
EC
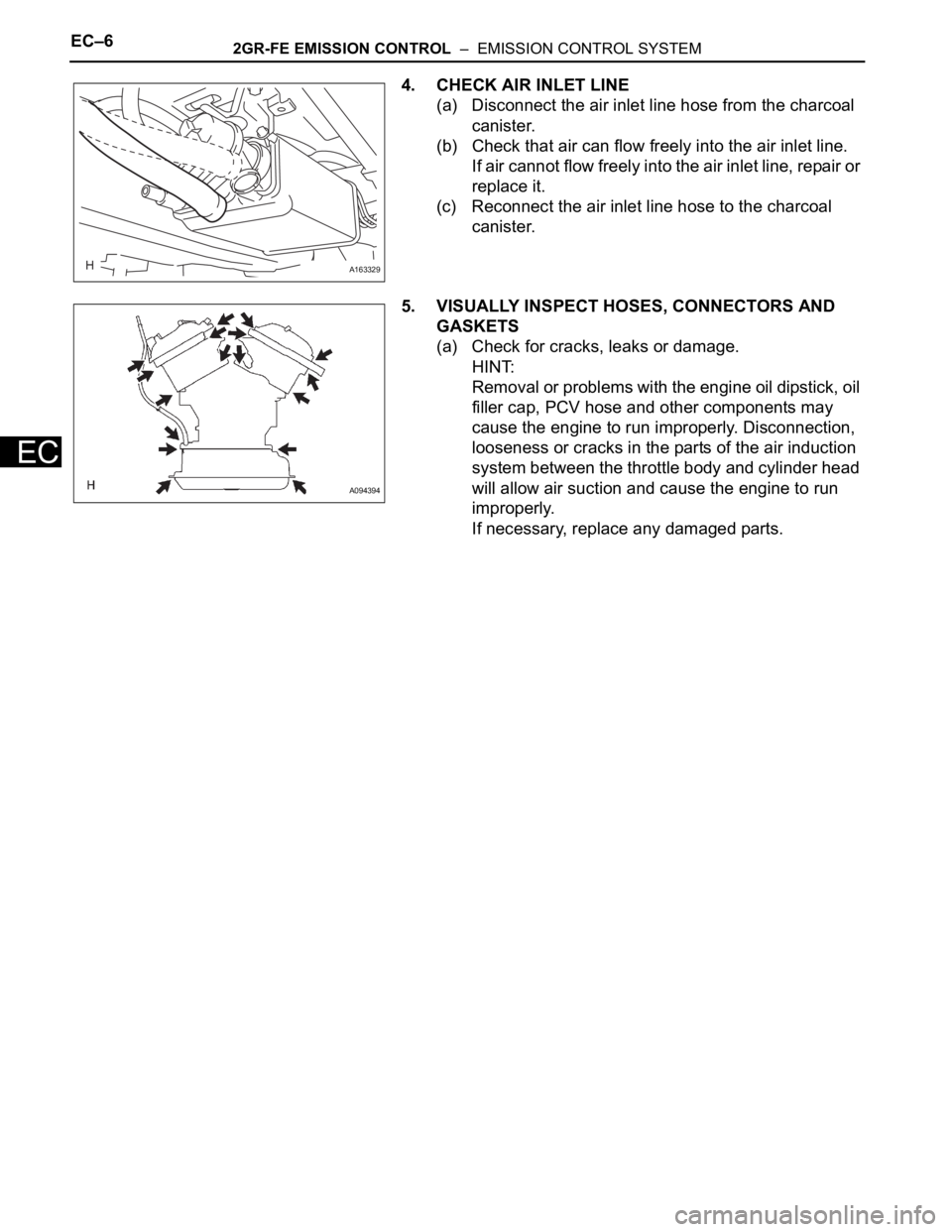
4. CHECK AIR INLET LINE
(a) Disconnect the air inlet line hose from the charcoal
canister.
(b) Check that air can flow freely into the air inlet line.
If air cannot flow freely into the air inlet line, repair or
replace it.
(c) Reconnect the air inlet line hose to the charcoal
canister.
5. VISUALLY INSPECT HOSES, CONNECTORS AND
GASKETS
(a) Check for cracks, leaks or damage.
HINT:
Removal or problems with the engine oil dipstick, oil
filler cap, PCV hose and other components may
cause the engine to run improperly. Disconnection,
looseness or cracks in the parts of the air induction
system between the throttle body and cylinder head
will allow air suction and cause the engine to run
improperly.
If necessary, replace any damaged parts.
A163329
A094394
Page 1433 of 3000

U151E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE – AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYSTEMAX–67
AX
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The ECM uses the signals from the throttle position sensor, air-flow meter, turbine (input) speed sensor,
intermediate (counter) shaft speed sensor and crankshaft position sensor to monitor the engagement
condition of the lock-up clutch.
Then the ECM compares the engagement condition of the lock-up clutch with the lock-up schedule in the
ECM memory to detect a mechanical problems of the shift solenoid valve DSL, valve body and torque
converter clutch.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
Torque converter lock-up is controlled by the ECM based on the speed sensor (NT), speed sensor (NC),
engine rpm, engine load, engine temperature, vehicle speed, transmission temperature, and gear
selection. The ECM determines the lock-up status of the torque converter by comparing the engine rpm
(NE) to the input turbine rpm (NT). The ECM calculates the actual transmission gear by comparing input
turbine rpm (NT) to counter gear rpm (NC). When conditions are appropriate, the ECM requests "lock-up"
by applying control voltage to the shift solenoid DSL. When the DSL is turned on, it applies pressure to the
lock-up relay valve and locks the torque converter clutch.
If the ECM detects no lock-up after lock-up has been requested or if it detects lock-up when it is not
requested, the ECM interprets this as a fault in the shift solenoid valve DSL or lock-up system
performance. The ECM will turn on the MIL and store the DTC.
HINT:
Example:
When any of the following is met, the system judges it as a malfunction.
• There is a difference in rotation between the input side (engine speed) and output side (input turbine
speed) of the torque converter when the ECM commands lock-up.
(Engine speed is at least 100 rpm greater than input turbine speed.)
• There is no difference in rotation between the input side (engine speed) and output side (input turbine
speed) of the torque converter when the ECM commands lock-up off.
(The difference between engine speed and input turbine speed is less than 35 rpm.)
MONITOR STRATEGY
DTC P0741Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Performance
(Shift Solenoid Valve DSL)
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0741Lock-up does not occur when driving in the lock-up
range (normal driving at 80 km/h [50 mph]), or lock up
remains ON in the lock-up OFF range.
(2-trip detection logic)• Shift solenoid valve DSL remains open or closed
• Valve body is blocked
• Torque converter clutch
• Automatic transaxle (clutch, brake or gear etc.)
• Line pressure is too low
Related DTCsP0741:
Shift solenoid valve DSL/OFF malfunction
Shift solenoid valve DSL/ON malfunction
Required sensors/ComponentsShift solenoid valve DSL, Speed sensor (NT), Speed sensor (NC),
Crankshaft position sensor (NE), Throttle position sensor (VPA1),
Mass air flow sensor (MAF), Transmission temperature sensor
(THO1), Engine coolant temperature sensor (ECT)
Frequency of operation Continuous
DurationOFF malfunction (A)
Continuous.
OFF malfunction (B)
1 sec.
OFF malfunction (C)
3.5 sec.
ON malfunction
1.8 sec.
Page 1483 of 3000
U151E AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE – AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYSTEMAX–117
AX
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
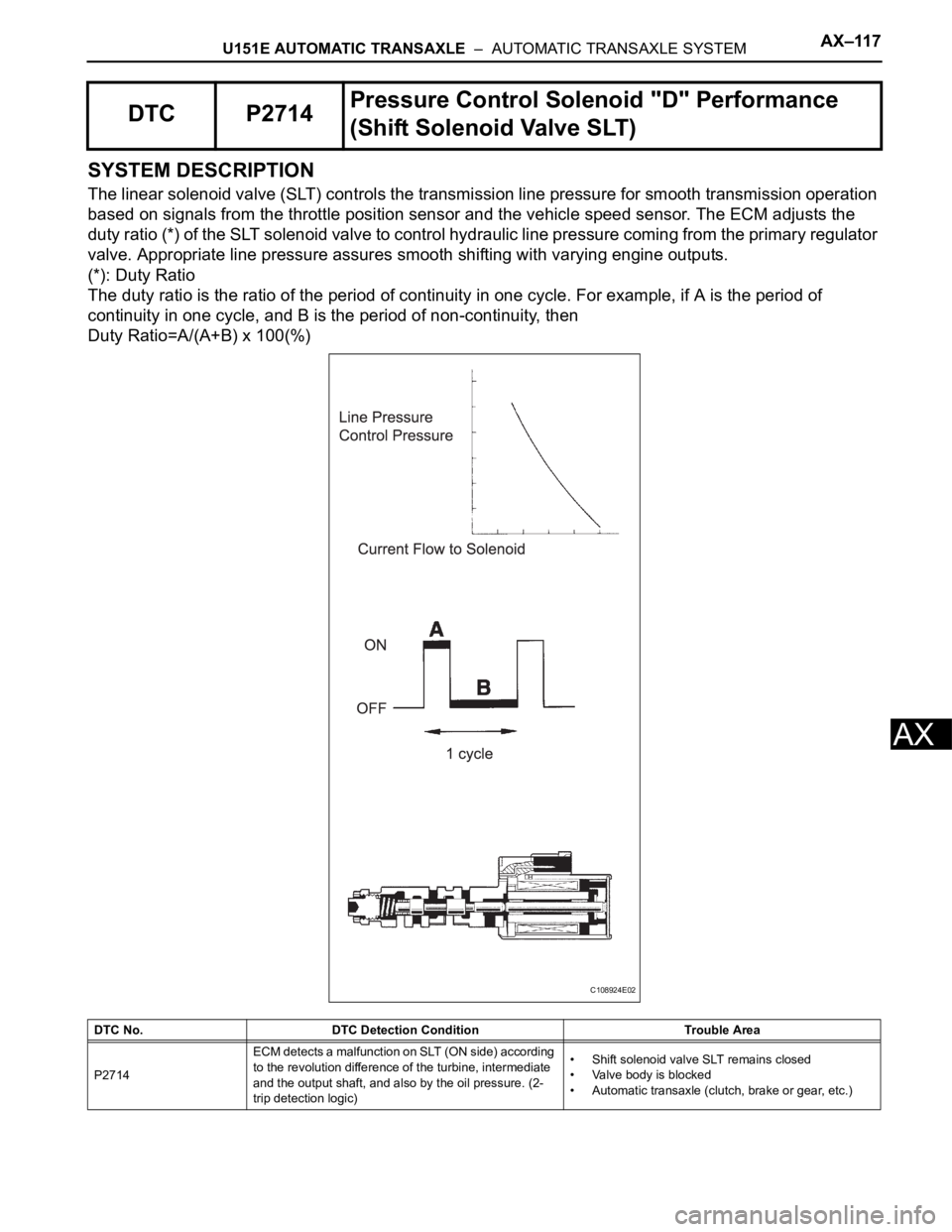
The linear solenoid valve (SLT) controls the transmission line pressure for smooth transmission operation
based on signals from the throttle position sensor and the vehicle speed sensor. The ECM adjusts the
duty ratio (*) of the SLT solenoid valve to control hydraulic line pressure coming from the primary regulator
valve. Appropriate line pressure assures smooth shifting with varying engine outputs.
(*): Duty Ratio
The duty ratio is the ratio of the period of continuity in one cycle. For example, if A is the period of
continuity in one cycle, and B is the period of non-continuity, then
Duty Ratio=A/(A+B) x 100(%)
DTC P2714Pressure Control Solenoid "D" Performance
(Shift Solenoid Valve SLT)
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P2714ECM detects a malfunction on SLT (ON side) according
to the revolution difference of the turbine, intermediate
and the output shaft, and also by the oil pressure. (2-
trip detection logic)• Shift solenoid valve SLT remains closed
• Valve body is blocked
• Automatic transaxle (clutch, brake or gear, etc.)
C108924E02
Page 1739 of 3000

U151F AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE – AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYSTEMAX–67
AX
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The ECM uses the signals from the throttle position sensor, air-flow meter, turbine (input) speed sensor,
intermediate (counter) shaft speed sensor and crankshaft position sensor to monitor the engagement
condition of the lock-up clutch.
Then the ECM compares the engagement condition of the lock-up clutch with the lock-up schedule in the
ECM memory to detect a mechanical problems of the shift solenoid valve DSL, valve body and torque
converter clutch.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
Torque converter lock-up is controlled by the ECM based on the speed sensor (NT), speed sensor (NC),
engine rpm, engine load, engine temperature, vehicle speed, transmission temperature, and gear
selection. The ECM determines the lock-up status of the torque converter by comparing the engine rpm
(NE) to the input turbine rpm (NT). The ECM calculates the actual transmission gear by comparing input
turbine rpm (NT) to counter gear rpm (NC). When conditions are appropriate, the ECM requests "lock-up"
by applying control voltage to the shift solenoid DSL. When the DSL is turned on, it applies pressure to the
lock-up relay valve and locks the torque converter clutch.
If the ECM detects no lock-up after lock-up has been requested or if it detects lock-up when it is not
requested, the ECM interprets this as a fault in the shift solenoid valve DSL or lock-up system
performance. The ECM will turn on the MIL and store the DTC.
HINT:
Example:
When any of the following is met, the system judges it as a malfunction.
• There is a difference in rotation between the input side (engine speed) and output side (input turbine
speed) of the torque converter when the ECM commands lock-up.
(Engine speed is at least 100 rpm greater than input turbine speed.)
• There is no difference in rotation between the input side (engine speed) and output side (input turbine
speed) of the torque converter when the ECM commands lock-up off.
(The difference between engine speed and input turbine speed is less than 35 rpm.)
MONITOR STRATEGY
DTC P0741Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Performance
(Shift Solenoid Valve DSL)
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P0741Lock-up does not occur when driving in the lock-up
range (normal driving at 80 km/h [50 mph]), or lock up
remains ON in the lock-up OFF range.
(2-trip detection logic)• Shift solenoid valve DSL remains open or closed
• Valve body is blocked
• Torque converter clutch
• Automatic transaxle (clutch, brake or gear etc.)
• Line pressure is too low
Related DTCsP0741:
Shift solenoid valve DSL/OFF malfunction
Shift solenoid valve DSL/ON malfunction
Required sensors/ComponentsShift solenoid valve DSL, Speed sensor (NT), Speed sensor (NC),
Crankshaft position sensor (NE), Throttle position sensor (VPA1),
Mass air flow sensor (MAF), Transmission temperature sensor
(THO1), Engine coolant temperature sensor (ECT)
Frequency of operation Continuous
DurationOFF malfunction (A)
Continuous.
OFF malfunction (B)
1 sec.
OFF malfunction (C)
3.5 sec.
ON malfunction
1.8 sec.
Page 1789 of 3000
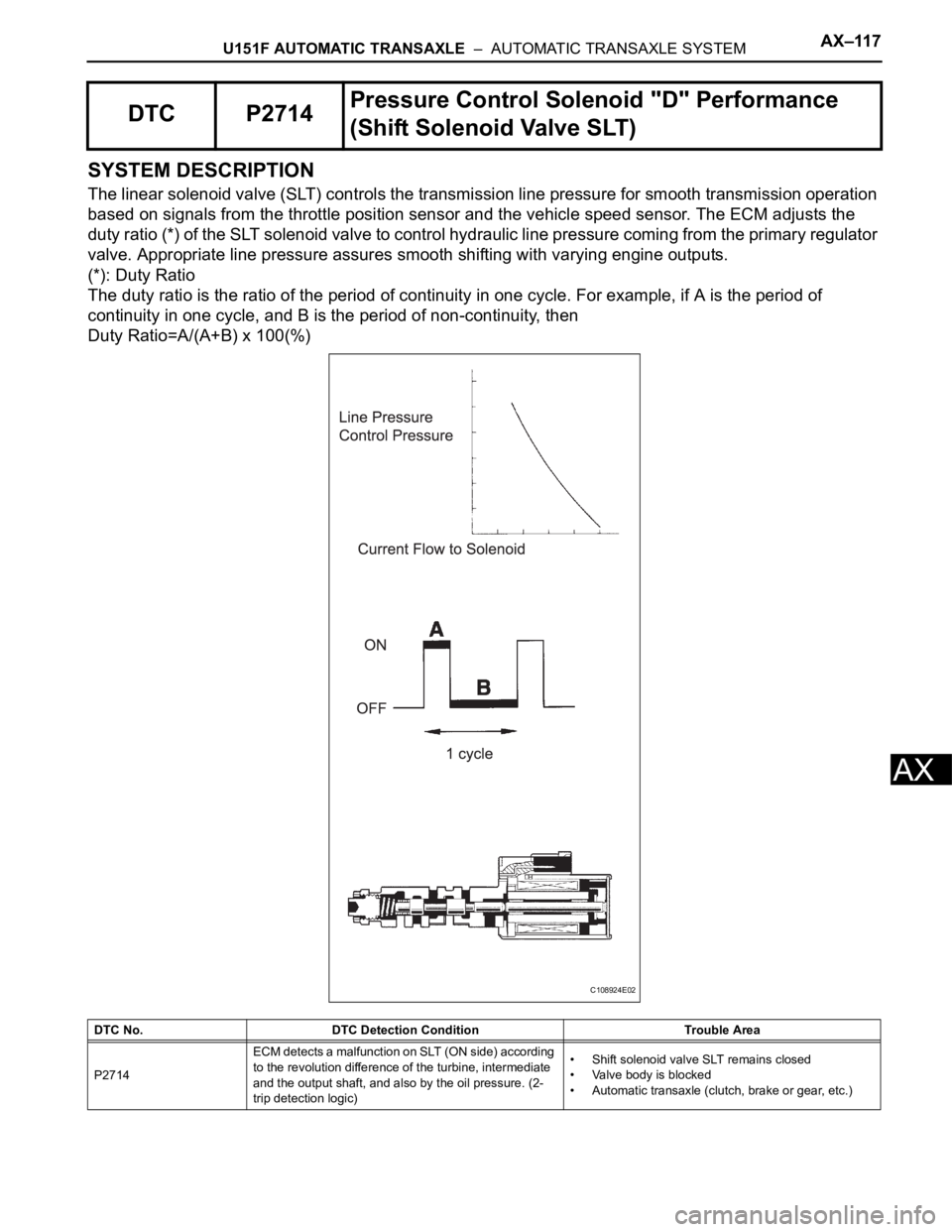
U151F AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE – AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE SYSTEMAX–117
AX
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The linear solenoid valve (SLT) controls the transmission line pressure for smooth transmission operation
based on signals from the throttle position sensor and the vehicle speed sensor. The ECM adjusts the
duty ratio (*) of the SLT solenoid valve to control hydraulic line pressure coming from the primary regulator
valve. Appropriate line pressure assures smooth shifting with varying engine outputs.
(*): Duty Ratio
The duty ratio is the ratio of the period of continuity in one cycle. For example, if A is the period of
continuity in one cycle, and B is the period of non-continuity, then
Duty Ratio=A/(A+B) x 100(%)
DTC P2714Pressure Control Solenoid "D" Performance
(Shift Solenoid Valve SLT)
DTC No. DTC Detection Condition Trouble Area
P2714ECM detects a malfunction on SLT (ON side) according
to the revolution difference of the turbine, intermediate
and the output shaft, and also by the oil pressure. (2-
trip detection logic)• Shift solenoid valve SLT remains closed
• Valve body is blocked
• Automatic transaxle (clutch, brake or gear, etc.)
C108924E02