VOLKSWAGEN TIGUAN 2017 Owner´s Manual
Manufacturer: VOLKSWAGEN, Model Year: 2017, Model line: TIGUAN, Model: VOLKSWAGEN TIGUAN 2017Pages: 341, PDF Size: 9.14 MB
Page 41 of 341

Fig. 35 An unbelted driver is thrown forwards.
Fig. 36 The unbelted rear passenger is thrown forwards, hitting the belted driver.
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings⇒
Introduction
Many people believe that they can brace their weight with their hands in a minor collision. This is
not true.
Even at low speeds, the forces acting on the body in a collision are so great that it is not possible to
brace oneself with arms and hands. In a frontal collision, vehicle occupants who have not fastened
their seat belts will be thrown forward and will make unchecked contact with parts of the vehicle
interior, e.g. the steering wheel, dash panel, or windscreen ⇒ Fig. 35.
The airbag system is not a substitute for the seat belts. When triggered, the airbags only provide
additional protection. Airbags are not triggered in all kinds of accidents. Even if the vehicle is
equipped with an airbag system, all vehicle occupants, including the driver, must fasten their seat
belt and wear it correctly while the vehicle is in motion. This reduces the risk of severe or fatal
injuries in the event of an accident – regardless of whether an airbag is fitted for the seat.
Each airbag can only be triggered once. To achieve best possible protection, seat belts must
always be worn properly. This also ensures that protection is provided in accidents in which the
airbag is not triggered. Any vehicle occupants not wearing a seat belt can be thrown out of the
vehicle and sustain more severe or even fatal injuries as a result.
It is also important for the rear seat occupants to wear seat belts properly, as they could otherwise
be thrown forwards violently in an accident. Rear passengers who are not wearing seat belts
endanger not only themselves and the driver, but also other people in the vehicle ⇒ Fig. 36.
Seat belt protection
Fig. 37 Driver restrained by a properly positioned seat belt during a sudden braking manoeuvre.
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings⇒
Introduction
Correctly fastened seat belts can make a major difference. When fastened properly, seat belts hold
the vehicle occupants in the correct sitting positions and considerably reduce the kinetic energy in
the event of an accident. Seat belts also help to prevent uncontrolled movements that could lead to
severe injuries. In addition, wearing seat belts properly reduces the risk of being thrown from the
vehicle ⇒ Fig. 37.
Passengers wearing seat belts correctly benefit greatly from the ability of the belts to reduce the
kinetic energy. The front crumple zones and other passive safety features (such as the airbag
system) are also designed to reduce kinetic energy. The amount of energy generated will thus
decrease, thereby reducing the risk of injury.
The examples describe frontal collisions. Of course, properly worn seat belts substantially reduce
the risk of injury in all other types of accidents. This is why seat belts must be fastened before every
Page 42 of 341
Check the condition of all seat belts regularly.
Keep the seat belts clean.
Avoid allowing any foreign substances or liquids to get on to the seat belt or latch plate or
into the slot in the seat belt buckle.
Do not trap or damage the seat belt and latch plate, for example when closing the door.
Never remove, modify or repair the seat belt or any part of the belt fixture system.
Always fasten the seat belt correctly before every journey and keep it fastened while the
vehicle is in motion.
trip – even if you are only planning to drive a very short distance. Ensure that all passengers also
wear their seat belts properly.
Accident statistics have shown properly worn seat belts to be an effective means of substantially
reducing the risk of injury and improving the chances of survival in a serious accident. Furthermore,
properly worn seat belts improve the protection provided by airbags in the event of an accident.
This is why wearing a seat belt is a legal requirement in most countries.
Although the vehicle is equipped with airbags, the seat belts must be fastened and worn. For
example, the front airbags will be triggered only in certain types of frontal collision. The front airbags
will not be triggered during minor frontal collisions, minor side collisions, rear collisions, rolls or
accidents in which the airbag trigger threshold in the control unit is not exceeded.
Therefore, always wear your seat belt and ensure that your passengers have fastened their seat
belts properly before you drive off.
Using seat belts
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings⇒
Introduction
Checklist
Using seat belts ⇒:
Twisted seat belt
If it is difficult to remove the seat belt from the belt guide, the seat belt may have become twisted if
it was returned too quickly into the side trim:
•Take hold of the latch plate then slowly and carefully pull out the seat belt.
•Untwist the seat belt and guide it back slowly by hand.
Fasten the seat belt even if you are unable to undo the twist. However, the twist should not be in
part of the seat belt that comes into direct contact with the body. The twist should be corrected
immediately by a qualified workshop.
Fastening and unfastening seat belts
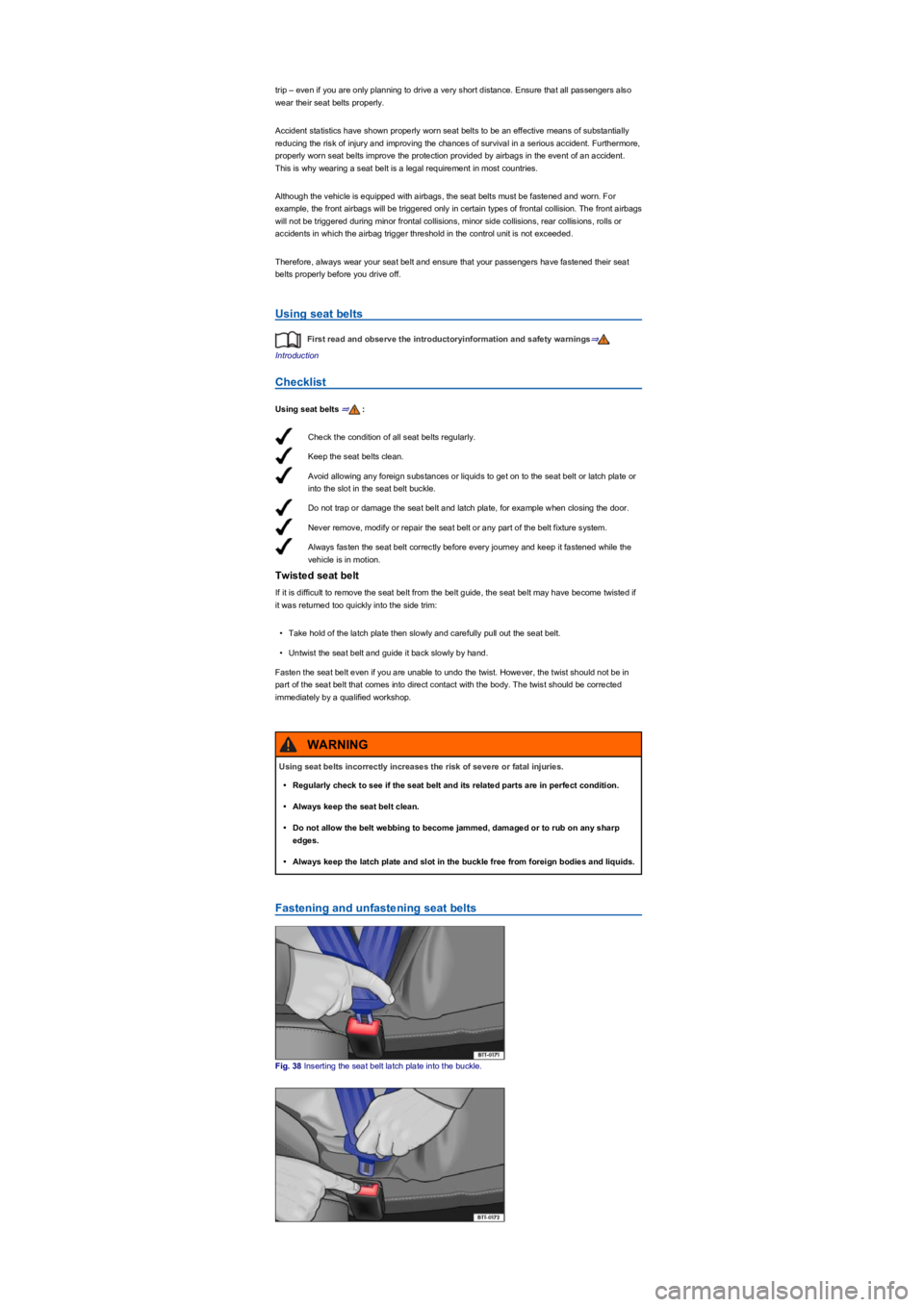
Fig. 38 Inserting the seat belt latch plate into the buckle.
Using seat belts incorrectly increases the risk of severe or fatal injuries.
•Regularly check to see if the seat belt and its related parts are in perfect condition.
•Always keep the seat belt clean.
•Do not allow the belt webbing to become jammed, damaged or to rub on any sharp
edges.
•Always keep the latch plate and slot in the buckle free from foreign bodies and liquids.
WARNING
Page 43 of 341
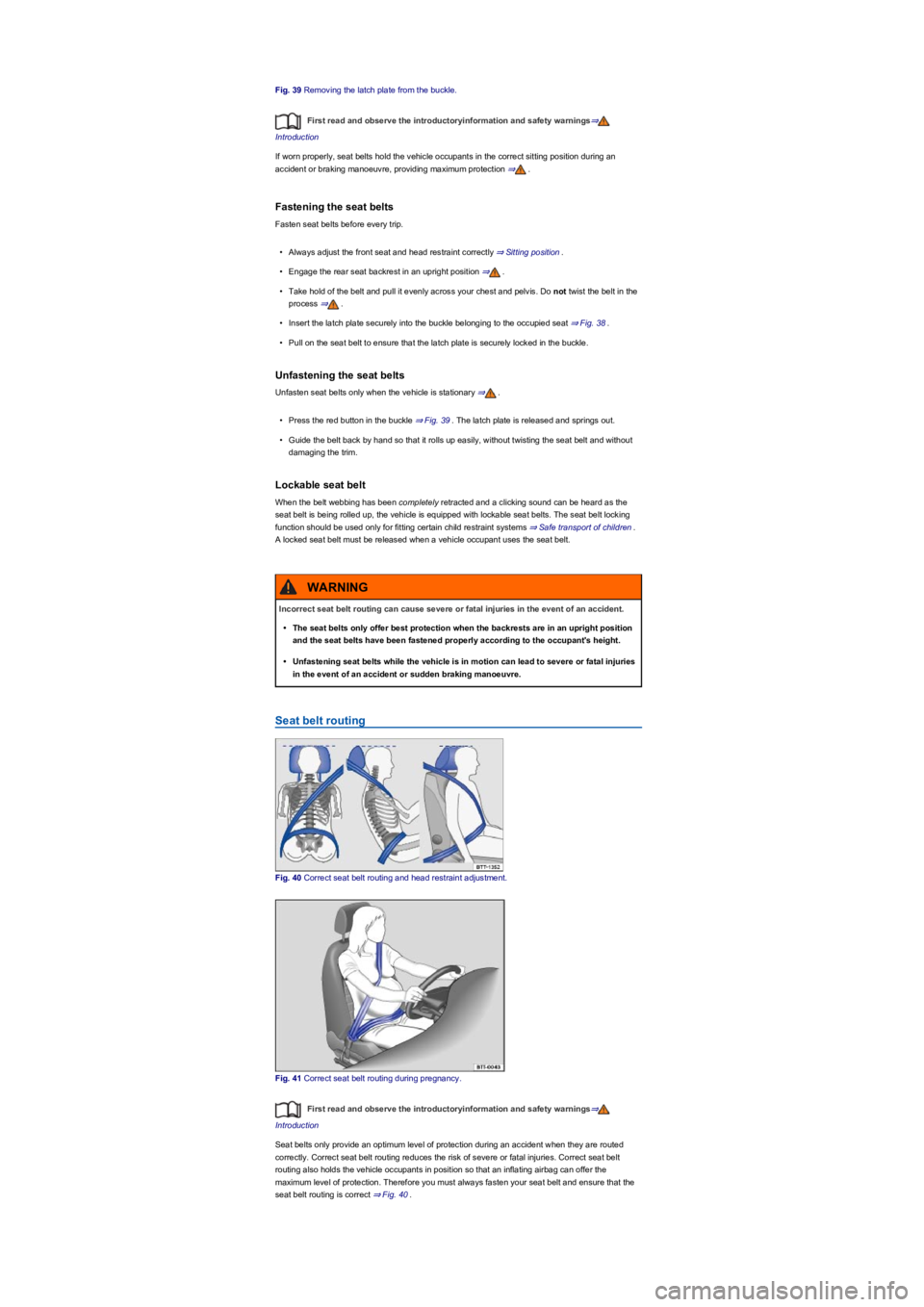
Fig. 39 Removing the latch plate from the buckle.
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings⇒
Introduction
If worn properly, seat belts hold the vehicle occupants in the correct sitting position during an
accident or braking manoeuvre, providing maximum protection ⇒.
Fastening the seat belts
Fasten seat belts before every trip.
•Always adjust the front seat and head restraint correctly ⇒ Sitting position.
•Engage the rear seat backrest in an upright position ⇒.
•Take hold of the belt and pull it evenly across your chest and pelvis. Do not twist the belt in the
process ⇒.
•Insert the latch plate securely into the buckle belonging to the occupied seat ⇒ Fig. 38.
•Pull on the seat belt to ensure that the latch plate is securely locked in the buckle.
Unfastening the seat belts
Unfasten seat belts only when the vehicle is stationary ⇒.
•Press the red button in the buckle ⇒ Fig. 39. The latch plate is released and springs out.
•Guide the belt back by hand so that it rolls up easily, without twisting the seat belt and without
damaging the trim.
Lockable seat belt
When the belt webbing has been completely retracted and a clicking sound can be heard as the
seat belt is being rolled up, the vehicle is equipped with lockable seat belts. The seat belt locking
function should be used only for fitting certain child restraint systems ⇒ Safe transport of children.
A locked seat belt must be released when a vehicle occupant uses the seat belt.
Seat belt routing
Fig. 40 Correct seat belt routing and head restraint adjustment.
Fig. 41 Correct seat belt routing during pregnancy.
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings⇒
Introduction
Seat belts only provide an optimum level of protection during an accident when they are routed
correctly. Correct seat belt routing reduces the risk of severe or fatal injuries. Correct seat belt
routing also holds the vehicle occupants in position so that an inflating airbag can offer the
maximum level of protection. Therefore you must always fasten your seat belt and ensure that the
seat belt routing is correct ⇒ Fig. 40.
Incorrect seat belt routing can cause severe or fatal injuries in the event of an accident.
•The seat belts only offer best protection when the backrests are in an upright position
and the seat belts have been fastened properly according to the occupant's height.
•Unfastening seat belts while the vehicle is in motion can lead to severe or fatal injuries
in the event of an accident or sudden braking manoeuvre.
WARNING
Page 44 of 341
Assuming an incorrect sitting position can cause severe or fatal injuries ⇒ Sitting position.
Correct seat belt routing
•The shoulder part of the seat belt must always lie on the centre of the shoulder, never across
the neck, over or under the arm or behind the back.
•The lap part of the seat belt must always lie across the pelvis, never across the stomach.
•The seat belt must always lie flat and snugly on the body. Tighten the belt if necessary.
For pregnant women the seat belt must be positioned evenly over the chest and as low as
possible over the pelvis. It must lie flat so that no pressure is exerted on the lower body – this
applies in every stage of pregnancy ⇒ Fig. 41.
Correct seat belt routing according to height
The following equipment can be used to adjust the seat belt routing:
•Seat belt height adjuster for the front seats ⇒ Seat belt height adjuster.
•Height-adjustable front seats ⇒ Sitting position.
If a person's physical build prevents them from routing the seat belt properly, contact a
qualified workshop to find out about any special modifications so that the seat belts and airbags can
provide the optimum level of protection. Volkswagen recommends using a Volkswagen dealership
for this purpose.
Seat belt height adjuster
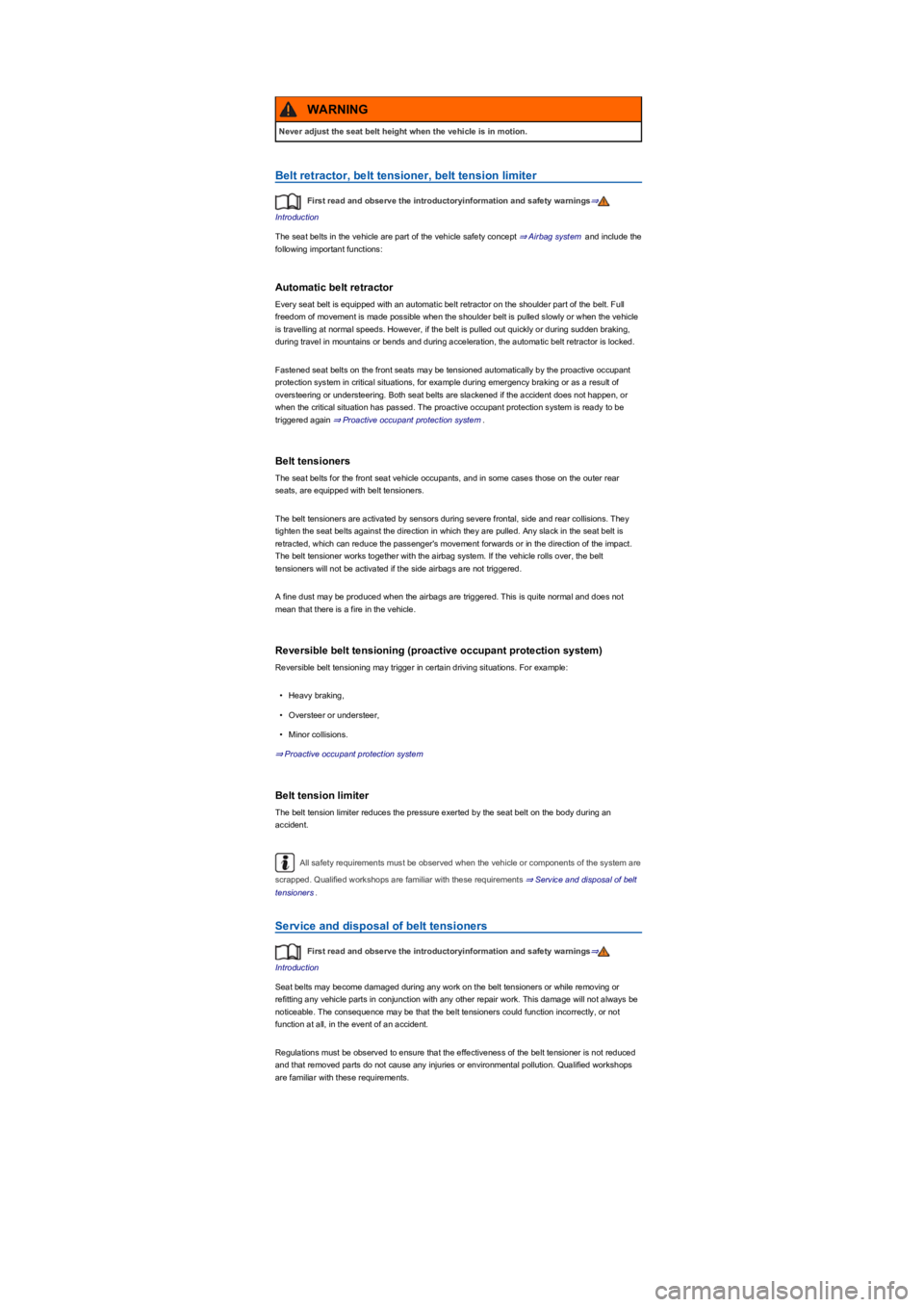
Fig. 42 Next to the front seats: belt height adjuster.
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings⇒
Introduction
The seat belt height adjusters for the front seats can be used to adjust the position of the seat belt
on the shoulder so that it can be fastened properly:
•Push the shoulder belt guide together in the direction of the arrows and hold ⇒ Fig. 42.
•Push the shoulder belt guide up or down so that the seat belt lies over the middle of the
shoulder ⇒ Seat belt routing.
•Let go of the shoulder belt guide.
•Pull sharply on the seat belt to check whether the shoulder belt guide is engaged securely.
Incorrect seat belt routing can cause severe injuries in the event of an accident or a
sudden braking or driving manoeuvre.
•The seat belts only offer best protection when the backrests are in an upright position
and the seat belts have been fastened properly.
•The seat belt itself or a loose seat belt can cause serious injuries if the seat belt shifts
from harder body parts in the direction of softer body parts (e.g. stomach).
•The shoulder part of the seat belt must lie on the centre of the shoulder and never
under the arm or across the neck.
•The seat belt must lie flat and snugly on the chest.
•The lap part of the seat belt must lie across the pelvis and never across the stomach.
The seat belt must lie flat and snugly on the pelvis. Tighten the belt if necessary.
•For pregnant women, the lap part of the seat belt must be as low as possible over the
pelvis and lie flat around the bulge of the belly.
•Do not twist the belt webbing while the seat belt is being worn.
•Never hold the seat belt away from the body by hand.
•The belt webbing should not lie over hard or fragile objects, such as glasses, pens or
keys.
•Never use seat belt clips, retaining rings or similar items to alter the seat belt routing.
WARNING
Page 45 of 341
Belt retractor, belt tensioner, belt tension limiter
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings⇒
Introduction
The seat belts in the vehicle are part of the vehicle safety concept ⇒ Airbag system and include the
following important functions:
Automatic belt retractor
Every seat belt is equipped with an automatic belt retractor on the shoulder part of the belt. Full
freedom of movement is made possible when the shoulder belt is pulled slowly or when the vehicle
is travelling at normal speeds. However, if the belt is pulled out quickly or during sudden braking,
during travel in mountains or bends and during acceleration, the automatic belt retractor is locked.
Fastened seat belts on the front seats may be tensioned automatically by the proactive occupant
protection system in critical situations, for example during emergency braking or as a result of
oversteering or understeering. Both seat belts are slackened if the accident does not happen, or
when the critical situation has passed. The proactive occupant protection system is ready to be
triggered again ⇒ Proactive occupant protection system.
Belt tensioners
The seat belts for the front seat vehicle occupants, and in some cases those on the outer rear
seats, are equipped with belt tensioners.
The belt tensioners are activated by sensors during severe frontal, side and rear collisions. They
tighten the seat belts against the direction in which they are pulled. Any slack in the seat belt is
retracted, which can reduce the passenger's movement forwards or in the direction of the impact.
The belt tensioner works together with the airbag system. If the vehicle rolls over, the belt
tensioners will not be activated if the side airbags are not triggered.
A fine dust may be produced when the airbags are triggered. This is quite normal and does not
mean that there is a fire in the vehicle.
Reversible belt tensioning (proactive occupant protection system)
Reversible belt tensioning may trigger in certain driving situations. For example:
•Heavy braking,
•Oversteer or understeer,
•Minor collisions.
⇒ Proactive occupant protection system
Belt tension limiter
The belt tension limiter reduces the pressure exerted by the seat belt on the body during an
accident.
All safety requirements must be observed when the vehicle or components of the system are
scrapped. Qualified workshops are familiar with these requirements ⇒ Service and disposal of belt
tensioners.
Service and disposal of belt tensioners
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings⇒
Introduction
Seat belts may become damaged during any work on the belt tensioners or while removing or
refitting any vehicle parts in conjunction with any other repair work. This damage will not always be
noticeable. The consequence may be that the belt tensioners could function incorrectly, or not
function at all, in the event of an accident.
Regulations must be observed to ensure that the effectiveness of the belt tensioner is not reduced
and that removed parts do not cause any injuries or environmental pollution. Qualified workshops
are familiar with these requirements.
Never adjust the seat belt height when the vehicle is in motion.
WARNING
Page 46 of 341
The airbag modules and belt tensioners may contain perchlorate. Please comply with
legislation regarding disposal.
Proactive occupant protection system
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings⇒
Introduction
The proactive occupant protection system is an assistance system that initiates action to protect
vehicle occupants in dangerous situations. However, the system cannot prevent a collision.
The full range of functions of the proactive occupant protection system will be available only if the
function has been activated in the Infotainment system, no special driving profile has been selected
and there are no malfunctions ⇒ Driving profile selection and 4MOTION Active Control, ⇒ Function
limitations.
Basic functions
Depending on country-specific legal requirements and also on the vehicle equipment, the following
functions may be initiated, either individually or jointly, in critical situations (e.g. emergency braking
or in the case of oversteering or understeering) as of a speed of approximately 30 km/h (19 mph):
•Temporary tensioning of the fastened front seat belts.
•Automatic closing of the glass roof and side windows down to a gap, depending on the vehicle
equipment.
The belts may be tensioned individually or together depending on the respective critical driving
situations.
Additional information for vehicles with an area monitoring system (Front
Assist)
In vehicles fitted with the area monitoring system (Front Assist) ⇒ Area monitoring system (Front
Assist), the probability of a collision with the vehicle ahead is also calculated within the system
limits. The system can trigger the proactive occupant protection system if it detects a probable
collision or initiates strong braking.
Settings in the Infotainment system
The full range of functions of the proactive occupant protection system can be activated and
deactivated in the Infotainment system ⇒ Operation and display in the Infotainment system.
The proactive occupant protection system will be reactivated every time the ignition is switched on.
It may not be possible to operate the setting function if the proactive occupant protection system
has already been adapted to the specific vehicle setup.
Setting in driving profile selection
In vehicles with driving profile selection, the proactive occupant protection system is adapted to the
special vehicle setup of the respective driving profile ⇒ Driving profile selection and 4MOTION
Active Control.
Function limitations
The proactive occupant protection system will not be available, or will only be available to a limited
extent, in the following situations:
•If there is a fault in the ESC, belt tensioner or in the airbag control unit ⇒ Seat belts or ⇒ Airbag
system.
•When the TCS or ESC are switched off, and when the vehicle is reversing ⇒ Brake support
systems.
•The temporary tensioning for the front passenger seat is switched off if the front passenger front
airbag is deactivated.
•If there is a system fault in the area monitoring system (Front Assist) ⇒ Area monitoring system
(Front Assist).
The risk of severe or fatal injuries may be increased if the seat belts, automatic belt
retractors and belt tensioners are not used correctly, or if they are repaired by a non-
professional. As a result, the belt tensioners may not be triggered when they should, or
they may be triggered unexpectedly.
•Any repairs, adjustments or removal and refitting of parts in the belt tensioners or seat
belts should always be carried out by a qualified workshop and never by yourself
⇒ Accessories, modifications, repairs and renewal of parts.
•Belt tensioners and automatic belt retractors cannot be repaired. They must be
replaced.
WARNING
Page 47 of 341

Troubleshooting
If there is a malfunction in the proactive occupant protection system, the message Proactive
occupant protection unavailable or Proactive occupant protection: function restricted is
shown permanently on the instrument cluster display.
Go to a qualified workshop and have the system checked.
Airbag system
Introduction
This chapter contains information on the followingsubjects:
⇒ Types of front passenger front airbag system
⇒ Indicator lamp
⇒ Description and function of the airbags
⇒ Front airbags
⇒ Switching the front passenger front airbag on and off
⇒ Side airbags
⇒ Curtain airbags
⇒ Knee airbags
The vehicle is equipped with a front airbag for the driver and front passenger. The front airbags can
provide front seat occupants with additional chest and head protection if the seat, seat belts, head
restraints and, in the case of the driver, steering wheel are adjusted and used correctly. Airbags are
meant only for additional protection. The airbags are not a substitute for seat belts. Seat belts must
always be worn, even when the front seats are equipped with front airbags.
The intelligent technology of the proactive occupant protection system cannot overcome
the laws of physics, and functions only within the limits of the system. Never let the extra
convenience afforded by the proactive occupant protection system tempt you into taking
any risks when driving. The system cannot prevent a collision. The system is not a
substitute for the full concentration of the driver.
•Adapt your speed and distance from the vehicles ahead to suit visibility, weather, road
and traffic conditions.
•The system cannot detect objects in all situations.
•The proactive occupant protection system does not react to people, animals, objects
crossing in front of the vehicle, or objects which are hard to make out.
•Reflective objects such as safety barriers, tunnel entrances, heavy rain and ice can
impair the function of the proactive occupant protection system and thus prevent it
from detecting a collision risk.
•Incorrect system activation can occur.
WARNING
Accidents and injuries can occur if the driver is distracted.
•Never change settings in the Infotainment system when the vehicle is in motion.
WARNING
Failure to observe illuminated warning lamps and text messages can lead to your vehicle
breaking down in traffic, and can cause accidents and serious injuries.
•Never ignore any illuminated warning lamps or text messages.
•Stop the vehicle as soon as it is possible and safe to do so.
WARNING
Failure to observe illuminated indicator lamps and text messages can lead to your vehicle
being damaged.
NOTICE
Page 48 of 341
Types of front passenger front airbag system
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings⇒
Introduction
Never rely solely on the airbag system for your protection.
•Even if an airbag is triggered, it only offers auxiliary protection.
•The airbag system offers the best level of protection, and reduces the risk of injury,
when seat belts are properly worn ⇒ Seat belts.
•Before every trip, each vehicle occupant must adopt the correct sitting position,
correctly fasten the seat belt belonging to their seat and keep it fastened properly
throughout the trip. This applies to all vehicle occupants and also in urban traffic.
WARNING
The risk of injury increases if there are any objects between the vehicle occupants and the
deployment area of the airbag when it is triggered. This will alter the deployment zone of
the airbag, or the objects will be flung against the body.
•Never hold any objects in your hand or on your lap while the vehicle is in motion.
•Never transport any objects on the front passenger seat. The objects could enter the
deployment zone of the airbag during sudden braking or driving manoeuvres and then
be flung dangerously through the vehicle interior if the airbag is activated.
•Vehicle occupants sitting on the front seats and rear outer seats must never carry any
people, pets or objects in the deployment zone between themselves and the airbags.
Ensure that children and passengers keep to this rule.
WARNING
The airbag system can only be triggered once. The system will have to be replaced if the
airbags have been triggered.
•Airbags that have been triggered, and any affected system parts, must immediately be
replaced with new parts that are approved by Volkswagen for the vehicle.
•Repairs and modifications to your vehicle should only be carried out by a qualified
workshop. Qualified workshops have the necessary tools, diagnostic equipment, repair
information and qualified personnel.
•Never use recycled airbag components or components that have been taken from end-
of-life vehicles in your vehicle.
•Never alter any components of the airbag system.
WARNING
Fine dust particles or steam may be released when the airbags are triggered. This is
normal and does not mean that there is a fire in the vehicle.
•The fine dust can cause irritation to the skin and eye membranes and cause breathing
difficulties, particularly for people suffering from asthma or people who have (had)
other respiratory problems. To help reduce breathing difficulties, get out of the vehicle
or open the windows or doors for more fresh air.
•If you come into contact with the dust, you should wash your hands and face with a
mild soap and water before eating.
•Do not let the dust get into your eyes or into open wounds.
•If dust has entered your eyes, rinse them with water.
WARNING
Cleaning agents that contain solvents cause the surface of the airbag modules to become
porous. In an accident that triggers the airbag, loose plastic parts can cause serious
injury.
•Never clean the dash panel or the airbag covers with cleansers that contain solvents.
WARNING
Page 49 of 341
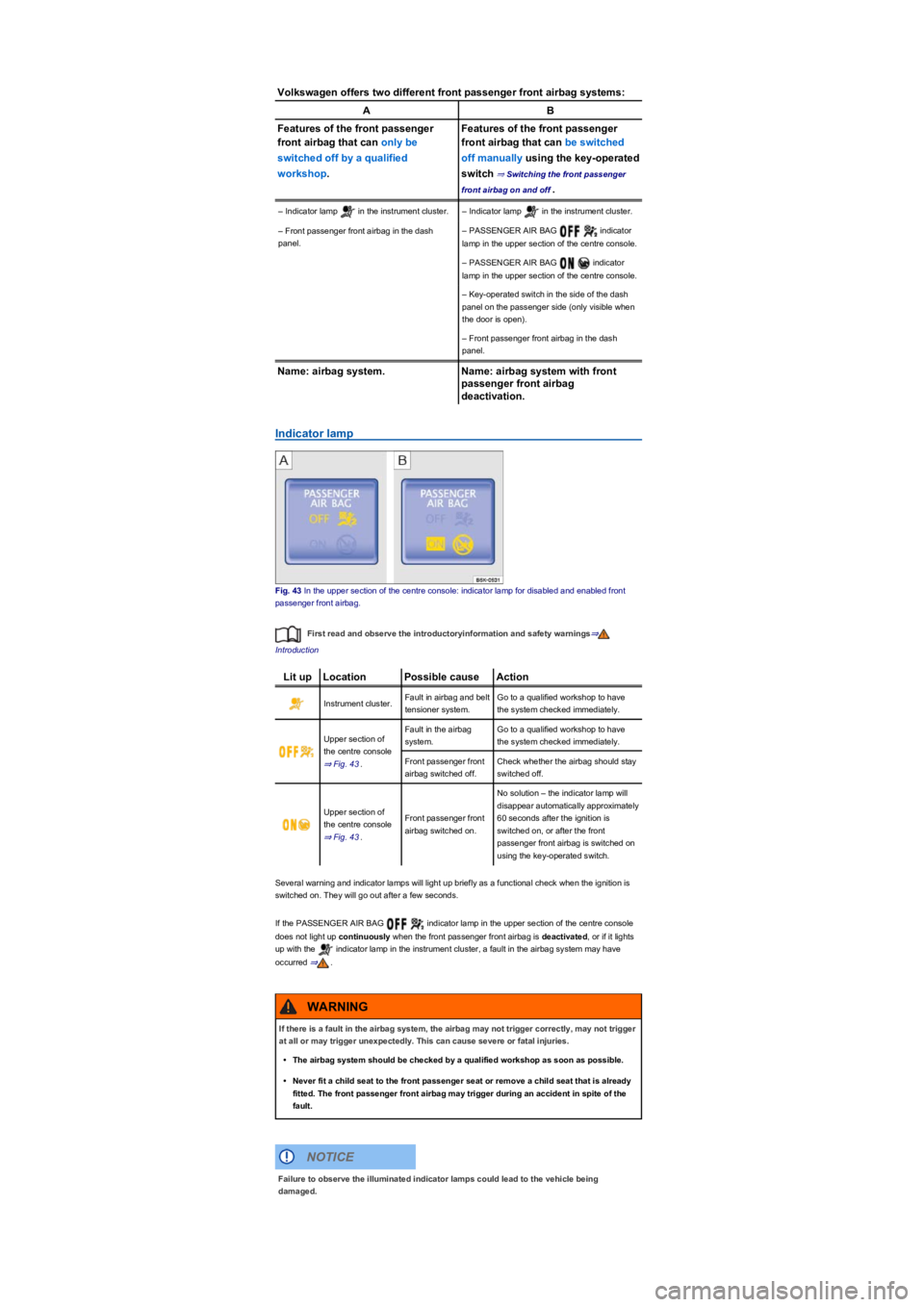
Volkswagen offers two different front passenger front airbag systems:
AB
Features of the front passenger
front airbag that can only be
switched off by a qualified
workshop.
Features of the front passenger
front airbag that can be switched
off manually using the key-operated
switch ⇒ Switching the front passenger
front airbag on and off.
– Indicator lamp in the instrument cluster.– Indicator lamp in the instrument cluster.
– Front passenger front airbag in the dash
panel.
– PASSENGER AIR BAG indicator
lamp in the upper section of the centre console.
– PASSENGER AIR BAG indicator
lamp in the upper section of the centre console.
– Key-operated switch in the side of the dash
panel on the passenger side (only visible when
the door is open).
– Front passenger front airbag in the dash
panel.
Name: airbag system.Name: airbag system with front
passenger front airbag
deactivation.
Indicator lamp
Fig. 43 In the upper section of the centre console: indicator lamp for disabled and enabled front
passenger front airbag.
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings⇒
Introduction
Lit upLocationPossible causeAction
Instrument cluster.Fault in airbag and belt
tensioner system.
Go to a qualified workshop to have
the system checked immediately.
Upper section of
the centre console
⇒ Fig. 43.
Fault in the airbag
system.
Go to a qualified workshop to have
the system checked immediately.
Front passenger front
airbag switched off.
Check whether the airbag should stay
switched off.
Upper section of
the centre console
⇒ Fig. 43.
Front passenger front
airbag switched on.
No solution – the indicator lamp will
disappear automatically approximately
60 seconds after the ignition is
switched on, or after the front
passenger front airbag is switched on
using the key-operated switch.
Several warning and indicator lamps will light up briefly as a functional check when the ignition is
switched on. They will go out after a few seconds.
If the PASSENGER AIR BAG indicator lamp in the upper section of the centre console
does not light up continuously when the front passenger front airbag is deactivated, or if it lights
up with the indicator lamp in the instrument cluster, a fault in the airbag system may have
occurred ⇒.
If there is a fault in the airbag system, the airbag may not trigger correctly, may not trigger
at all or may trigger unexpectedly. This can cause severe or fatal injuries.
•The airbag system should be checked by a qualified workshop as soon as possible.
•Never fit a child seat to the front passenger seat or remove a child seat that is already
fitted. The front passenger front airbag may trigger during an accident in spite of the
fault.
WARNING
Failure to observe the illuminated indicator lamps could lead to the vehicle being
damaged.
NOTICE
Page 50 of 341

Description and function of the airbags
First read and observe the introductoryinformation and safety warnings⇒
Introduction
The airbags can protect vehicle occupants during frontal and side collisions by reducing their
movement in the direction of the collision.
When an airbag is triggered, it is inflated by a gas generator. This causes the airbag covers to
break, and the airbags inflate forcefully to cover their deployment zones within milliseconds. Once a
vehicle occupant wearing a seat belt starts to sink into the inflated airbag, the gas inside the airbag
starts to escape to cushion the occupant and slow down their movement. This can reduce the risk
of severe and fatal injuries. A triggered airbag will not always prevent other injuries from occurring,
such as swelling, bruising, burning and grazing. The deployment of the airbag can also produce
frictional heat.
Airbags provide no protection for the arms or lower body. Exception: in vehicles with a knee airbag,
the knee area of the driver will be protected.
The most important factors for triggering the airbag are the type of accident, the angle of impact,
the vehicle speed and the type of object with which the vehicle collides. Therefore, visible damage
to the vehicle does not always mean that the airbag should have been triggered.
Whether or not the airbag triggers is determined by the vehicle deceleration rate caused by the
collision and registered by the electronic control unit. If this rate is below the reference value
programmed into the control unit, the airbags will not be triggered, even though the vehicle may be
badly damaged as a result of the collision. Vehicle damage, repair costs or even the lack of vehicle
damage in an accident do not necessarily give an indication of whether an airbag should inflate or
not. It is not possible to define a range of vehicle speeds and reference values, since the
circumstances will vary considerably between one collision and another. It is therefore impossible to
cover every possible kind and angle of impact that would trigger the airbags. Important factors in
the triggering of the airbag include the nature (hard or soft) of the object that the vehicle hits, the
angle of impact, and the vehicle speed.
Airbags only serve as a supplement to the three-point seat belt in some accident situations when
the vehicle braking is sufficient to trigger the airbags. Airbags can only be triggered once and only
in certain situations. The seat belts are always there to provide protection in situations in which the
airbags are not triggered or have already been triggered. For example, if the vehicle collides with a
further vehicle following the initial collision, or is hit by another vehicle.
The airbag system is part of the vehicle's overall passive safety concept. The airbag system can
only work effectively when the occupants are wearing their seat belts correctly and have assumed a
proper sitting position ⇒ Sitting position.
Components of the vehicle safety concept
The following vehicle safety equipment makes up the vehicle's safety concept to reduce the risk of
severe and fatal injuries. Some of this equipment may not be fitted in your particular vehicle. It may
not be available at all in some countries.
•Optimised seat belts for all seats.
•Belt tensioners for the driver and front passenger and also on the rear outer seats if in
conjunction with side airbags.
•Belt tension limiter for the driver, front passenger and, if applicable, for the rear outer seats.
•Belt height adjuster for the front seats.
•Warning lamp and belt status display.
•Front airbags for driver and front passenger.
•Side airbags for the driver, front passenger and, if applicable, for the rear outer seats.
•Curtain airbags on the left and right.
•If applicable, knee airbag for the driver.
•Airbag indicator lamp .
•Indicator lamp PASSENGER AIR BAG in the upper section of the centre console.
•Indicator lamp PASSENGER AIR BAG in the upper section of the centre console.
•Control units and sensors.
•Whiplash-optimised and height-adjustable head restraints.
•Adjustable steering column.
•If applicable, anchor points for child seats on the rear outer seats and on the front passenger
seat.
•If applicable, securing points for the top tether for child seats.
Situations when the front, knee, side and curtain airbags will not be
triggered:
•If the ignition is switched off during a collision.
•If the level of deceleration measured by the control unit is too low during a collision at the front
of the vehicle.
•During a minor side collision.
•During rear collisions.