YAMAHA WR 450F 2016 Owners Manual
Manufacturer: YAMAHA, Model Year: 2016, Model line: WR 450F, Model: YAMAHA WR 450F 2016Pages: 426, PDF Size: 10.86 MB
Page 391 of 426

ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-61
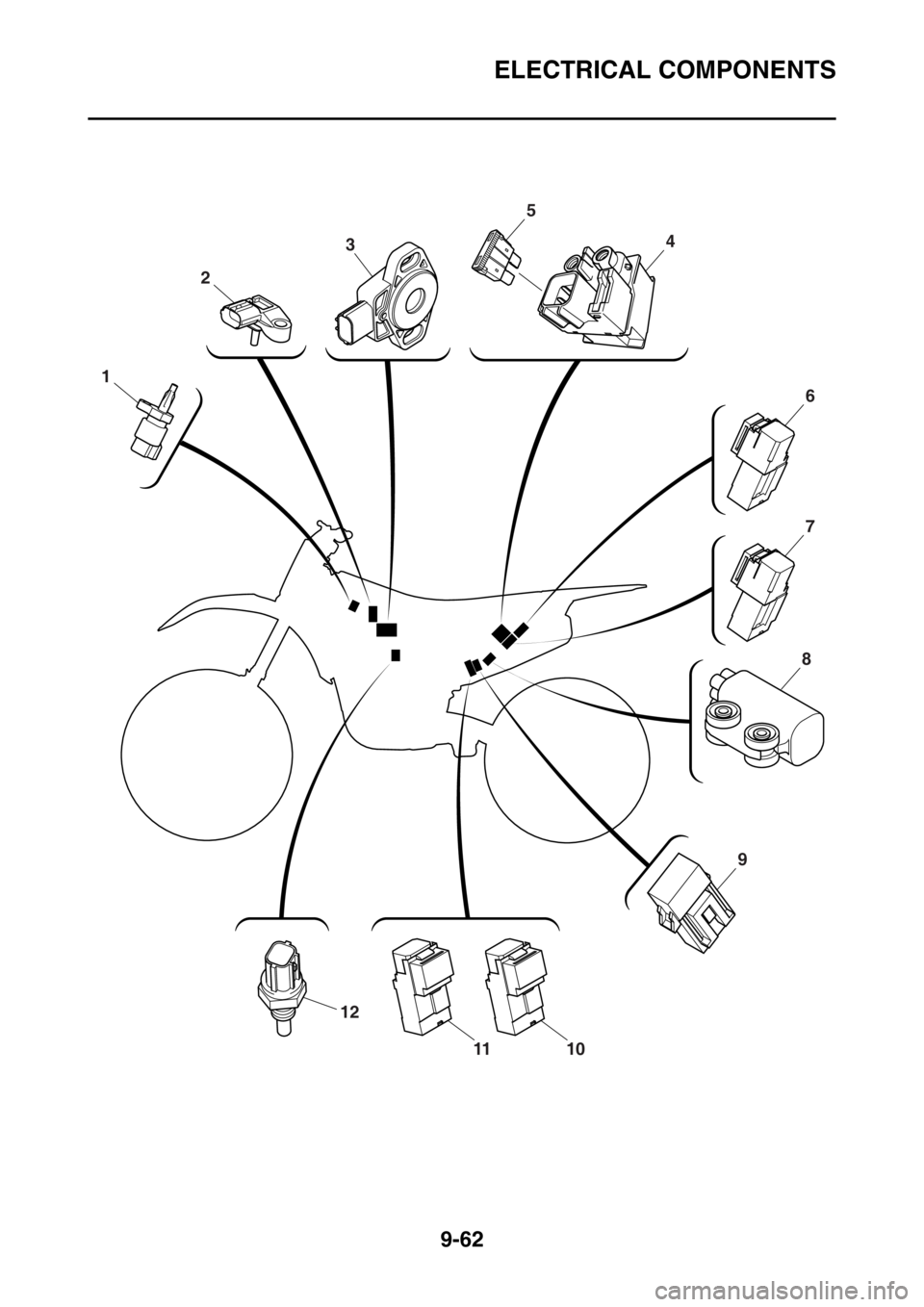
1. Rectifier/regulator
2. Clutch switch
3. Ignition coil
4. ECU (engine control unit)
5. Fuel sender
6. Fuel pump
7. Battery
8. Resistor
9. Neutral switch
10.Radiator fan motor
11.Injector
Page 392 of 426
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-62
12
1110
2
3
16
7
4
5
8
9
Page 393 of 426

ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-63
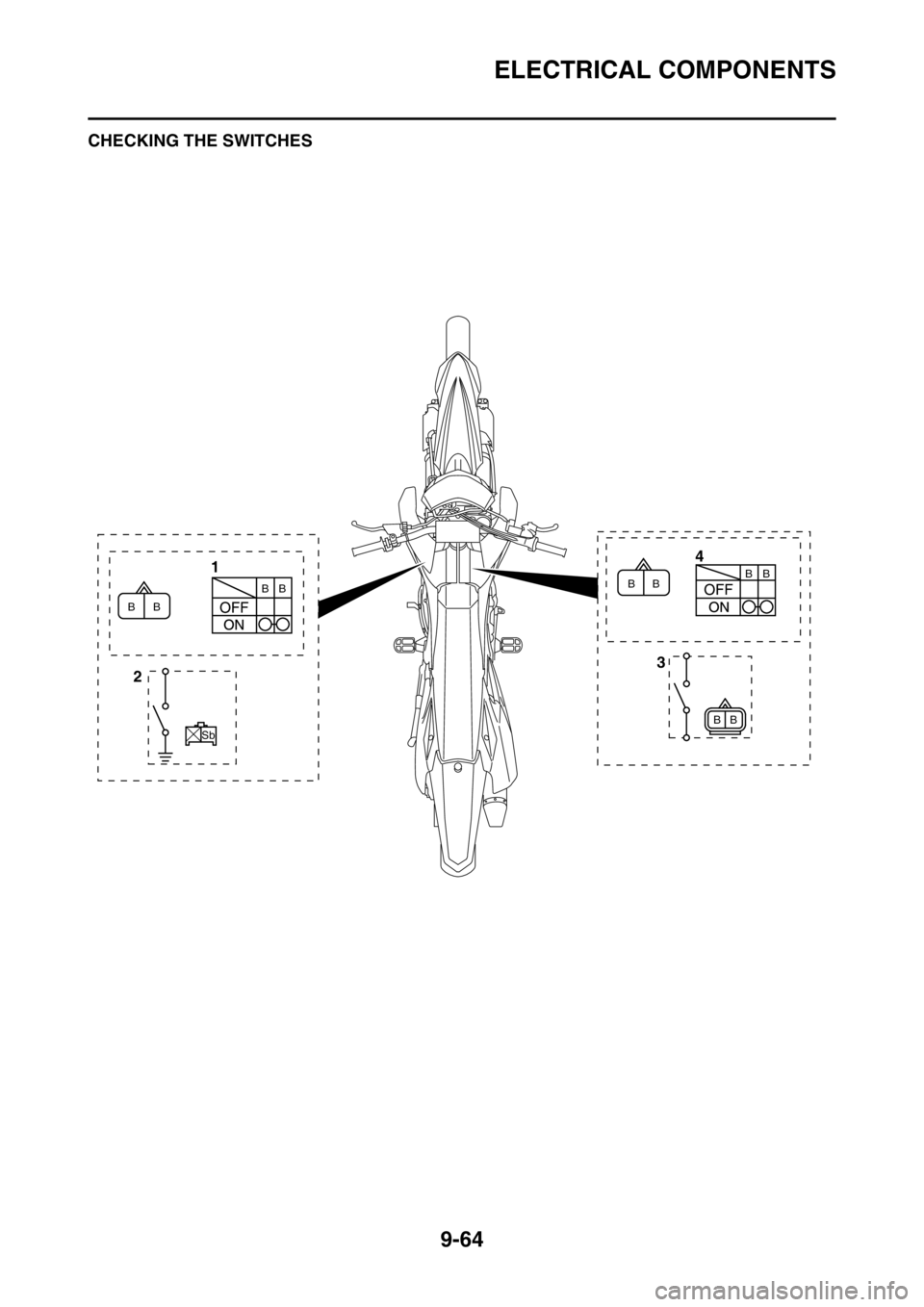
1. Intake air temperature sensor
2. Intake air pressure sensor
3. Throttle position sensor
4. Starter relay
5. Main fuse
6. Headlight relay
7. Starting circuit cut-off relay
8. Lean angle sensor
9. Radiator fan motor fuse
10.Radiator fan motor relay
11.Main relay
12.Coolant temperature sensor
Page 394 of 426
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-64
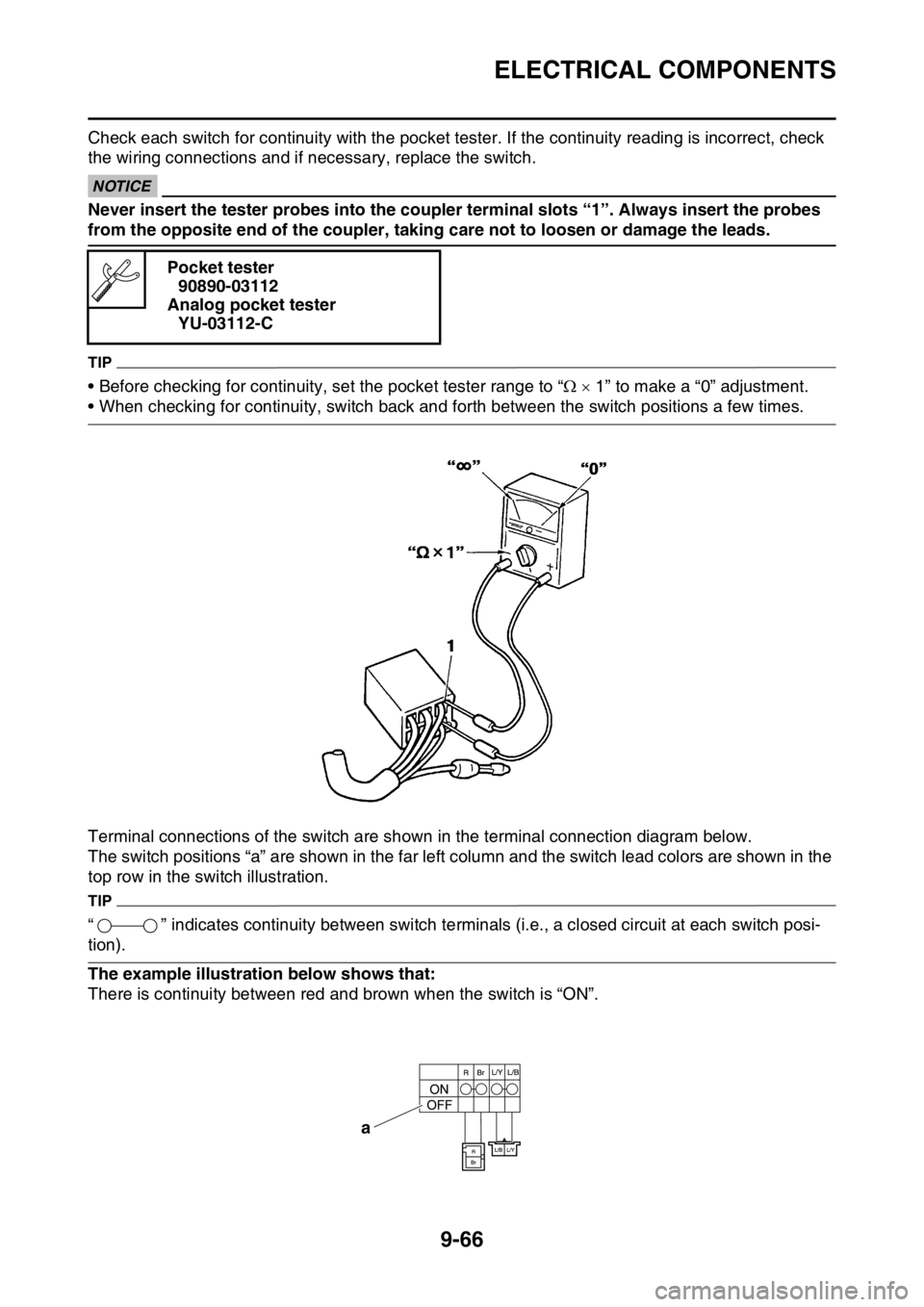
EAS2GC1384CHECKING THE SWITCHES
4
1
3
2
BB
Sb
BB
BB B
BB B
Page 395 of 426

ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-65
1. Engine stop switch
2. Neutral switch
3. Clutch switch
4. Start switch
Page 396 of 426
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-66
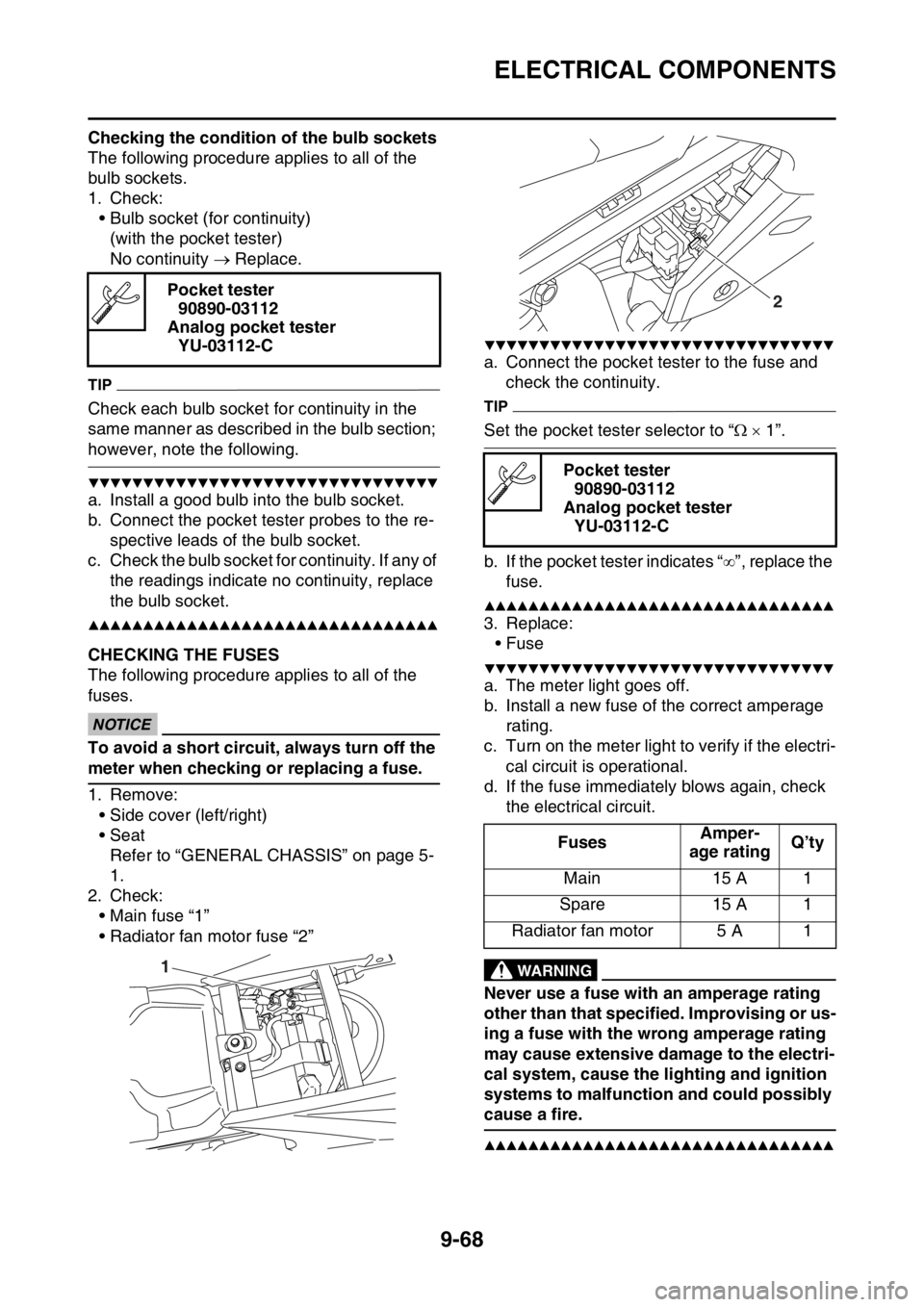
Check each switch for continuity with the pocket tester. If the continuity reading is incorrect, check
the wiring connections and if necessary, replace the switch.
ECA
NOTICE
Never insert the tester probes into the coupler terminal slots “1”. Always insert the probes
from the opposite end of the coupler, taking care not to loosen or damage the leads.
TIP
• Before checking for continuity, set the pocket tester range to “ 1” to make a “0” adjustment.
• When checking for continuity, switch back and forth between the switch positions a few times.
Terminal connections of the switch are shown in the terminal connection diagram below.
The switch positions “a” are shown in the far left column and the switch lead colors are shown in the
top row in the switch illustration.
TIP
“ ” indicates continuity between switch termin als (i.e., a closed circuit at each switch posi-
tion).
The example illustration below shows that:
There is continuity between red and brown when the switch is “ON”.Pocket tester
90890-03112
Analog pocket tester YU-03112-C
a
Page 397 of 426

ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-67
EAS27990CHECKING THE BULBS AND BULB SOCK-
ETS
TIP
Do not check any of the lights that use LEDs.
Check each bulb and bulb socket for damage
or wear, proper connections, and also for con-
tinuity between the terminals.
Damage/wear Repair or replace the bulb,
bulb socket or both.
Improperly connected Properly connect.
No continuity Repair or replace the bulb,
bulb socket or both.
Types of bulbs
The bulbs used on this v ehicle are shown in the
illustration on the left.
• Bulbs “a” and “b” are used for the headlights
and usually use a bulb holder that must be de-
tached before removing the bulb. The majority
of these types of bulbs can be removed from
their respective socket by turning them coun-
terclockwise.
• Bulbs “c” is used for turn signal and can be re- moved from the socket by pushing and turn-
ing the bulb counterclockwise.
Checking the condition of the bulbs
The following procedure applies to all of the
bulbs.
1. Remove: •Bulb
EWA
WARNING
Since the headlight bulb gets extremely hot,
keep flammable products and your hands
away from the bulb until it has cooled down.
ECA
NOTICE
• Be sure to hold the socket firmly when re-moving the bulb. Never pull the lead, oth-
erwise it may be pulled out of the terminal
in the coupler.
• Avoid touching the glass part of the head- light bulb to keep it free from oil, otherwise
the transparency of the glass, the life of
the bulb, and the luminous flux will be ad-
versely affected. If the headlight bulb gets
soiled, thoroughly it with a cloth moist-
ened with alcohol or lacquer thinner.
2. Check: • Bulb (for continuity)(with the pocket tester)
No continuity Replace.
TIP
Before checking for continuity, set the pocket
tester to “0” and to the “ 1” range.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the positive tester probe to terminal
“1” and the negative tester probe to terminal
“2”, and check the continuity.
b. Connect the positive tester probe to terminal “1” and the negative tester probe to terminal
“3”, and check the continuity.
c. If either of the readings indicate no continu- ity, replace the bulb.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
Pocket tester90890-03112
Analog pocket tester YU-03112-C
Page 398 of 426
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-68
Checking the condition of the bulb sockets
The following procedure applies to all of the
bulb sockets.
1. Check:• Bulb socket (for continuity)(with the pocket tester)
No continuity Replace.
TIP
Check each bulb socket for continuity in the
same manner as described in the bulb section;
however, note the following.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Install a good bulb into the bulb socket.
b. Connect the pocket tester probes to the re-
spective leads of the bulb socket.
c. Check the bulb socket for continuity. If any of
the readings indicate no continuity, replace
the bulb socket.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
EAS2GC1385CHECKING THE FUSES
The following procedure applies to all of the
fuses.
ECA
NOTICE
To avoid a short circuit, always turn off the
meter when checking or replacing a fuse.
1. Remove: • Side cover (left/right)
• SeatRefer to “GENERAL CHASSIS” on page 5-
1.
2. Check: • Main fuse “1”
• Radiator fan motor fuse “2”
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect the pocket tester to the fuse and check the continuity.
TIP
Set the pocket tester selector to “ 1”.
b. If the pocket tester indicates “ ”, replace the
fuse.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
3. Replace: • Fuse
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. The meter light goes off.
b. Install a new fuse of the correct amperage rating.
c. Turn on the meter light to verify if the electri- cal circuit is operational.
d. If the fuse immediatel y blows again, check
the electrical circuit.
EWA
WARNING
Never use a fuse with an amperage rating
other than that specified. Improvising or us-
ing a fuse with the wrong amperage rating
may cause extensive damage to the electri-
cal system, cause the lighting and ignition
systems to malfunction and could possibly
cause a fire.
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
Pocket tester 90890-03112
Analog pocket tester YU-03112-C
1
Pocket tester90890-03112
Analog pocket tester YU-03112-C
Fuses Amper-
age rating Q’ty
Main 15 A 1
Spare 15 A 1
Radiator fan motor 5 A 1
2
Page 399 of 426

ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-69
4. Install:• Seat
• Side cover (left/right)Refer to “GENERAL CHASSIS” on page 5-
1.
EAS2GC1386CHECKING AND CHARGING THE BATTERYEWA
WARNING
Batteries generate explosive hydrogen gas
and contain electrolyte which is made of
poisonous and highly caustic sulfuric acid.
Therefore, always follow these preventive
measures:
• Wear protective eye gear when handling or working near batteries.
• Charge batteries in a well-ventilated area.
• Keep batteries away from fire, sparks or
open flames (e.g., welding equipment,
lighted cigarettes).
• DO NOT SMOKE when charging or han- dling batteries.
• KEEP BATTERIES AND ELECTROLYTE
OUT OF REACH OF CHILDREN.
• Avoid bodily contact with electrolyte as it can cause severe burns or permanent eye
injury.
FIRST AID IN CASE OF BODILY CONTACT:
EXTERNAL
• Skin — Wash with water.
• Eyes — Flush with water for 15 minutes and get immediate medical attention.
INTERNAL
• Drink large quantities of water or milk fol-
lowed with milk of magnesia, beaten egg
or vegetable oil. Get immediate medical at-
tention.
ECA
NOTICE
• This is a VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Ac-id) battery. Never remove the sealing caps
because the balance between cells will not
be maintained and battery performance
will deteriorate.
• Charging time, charging amperage and charging voltage for a VRLA (Valve Regu-
lated Lead Acid) battery are different from
those of conventional batteries. The VRLA
(Valve Regulated Lead Acid) battery
should be charged according to the appro-
priate charging method. If the battery is
overcharged, the electrolyte level will drop
considerably. Therefore, take special care
when charging the battery.
TIP
Since VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) bat-
teries are sealed, it is not possible to check the
charge state of the battery by measuring the
specific gravity of the electrolyte. Therefore, the
charge of the battery has to be checked by
measuring the voltage at the battery terminals.
1. Remove:• Side cover (left/right)
• SeatRefer to “GENERAL CHASSIS” on page 5-
1.
2. Disconnect: • Battery leads
(from the battery terminals)
ECA
NOTICE
First, disconnect the negative battery lead
“1”, and then positive battery lead “2”.
3. Remove:• Battery
4. Check: • Battery charge
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
a. Connect a pocket tester to the battery termi- nals.
TIP
• The charge state of a VRLA (Valve Regulated Lead Acid) battery can be checked by mea-
suring its open-circuit voltage (i.e., the voltage
when the positive battery terminal is discon-
nected).
• No charging is necessary when the open-cir-
cuit voltage equals or exceeds 12.8 V.
b. Check the charge of the battery, as shown in the charts and the following example.
• Positive tester probe
positive battery terminal
• Negative tester probe
negative battery terminal
1
2
Page 400 of 426
ELECTRICAL COMPONENTS
9-70
▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲▲
5. Charge:• Battery
(refer to the appropriate charging method)
EWA
WARNING
Do not quick charge a battery.
ECA
NOTICE
• Do not use a high-rate battery charger since it forces a high-amperage current
into the battery quickly and can cause bat-
tery overheating and battery plate dam-
age.
• If it is impossible to regulate the charging current on the battery charger, be careful
not to overcharge the battery. • When charging a battery, be sure to re-
move it from the vehicle. (If charging has
to be done with the battery mounted on the
vehicle, disconnect the negative battery
lead from the battery terminal.)
• To reduce the chance of sparks, do not
plug in the battery charger until the battery
charger leads are connected to the bat-
tery.
• Before removing the battery charger lead clips from the battery terminals, be sure to
turn off the battery charger.
• Make sure the battery charger lead clips are in full contact with the battery terminal
and that they are not shorted. A corroded
battery charger lead clip may generate
heat in the contact area and a weak clip
spring may cause sparks.
• If the battery becomes hot to the touch at
any time during the charging process, dis-
connect the battery charger and let the
battery cool before reconnecting it. Hot
batteries can explode!
• As shown in the following illustration, the open-circuit voltage of a VRLA (Valve Reg-
ulated Lead Acid) battery stabilizes about
30 minutes after charging has been com-
pleted. Therefore, wait 30 minutes after
charging is completed before measuring
the open-circuit voltage.
▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼▼
Charging method using a variable-cur-
rent (voltage) charger
a. Measure the open-circuit voltage prior to charging.
TIP
Voltage should be measur ed 30 minutes after
the engine is stopped.
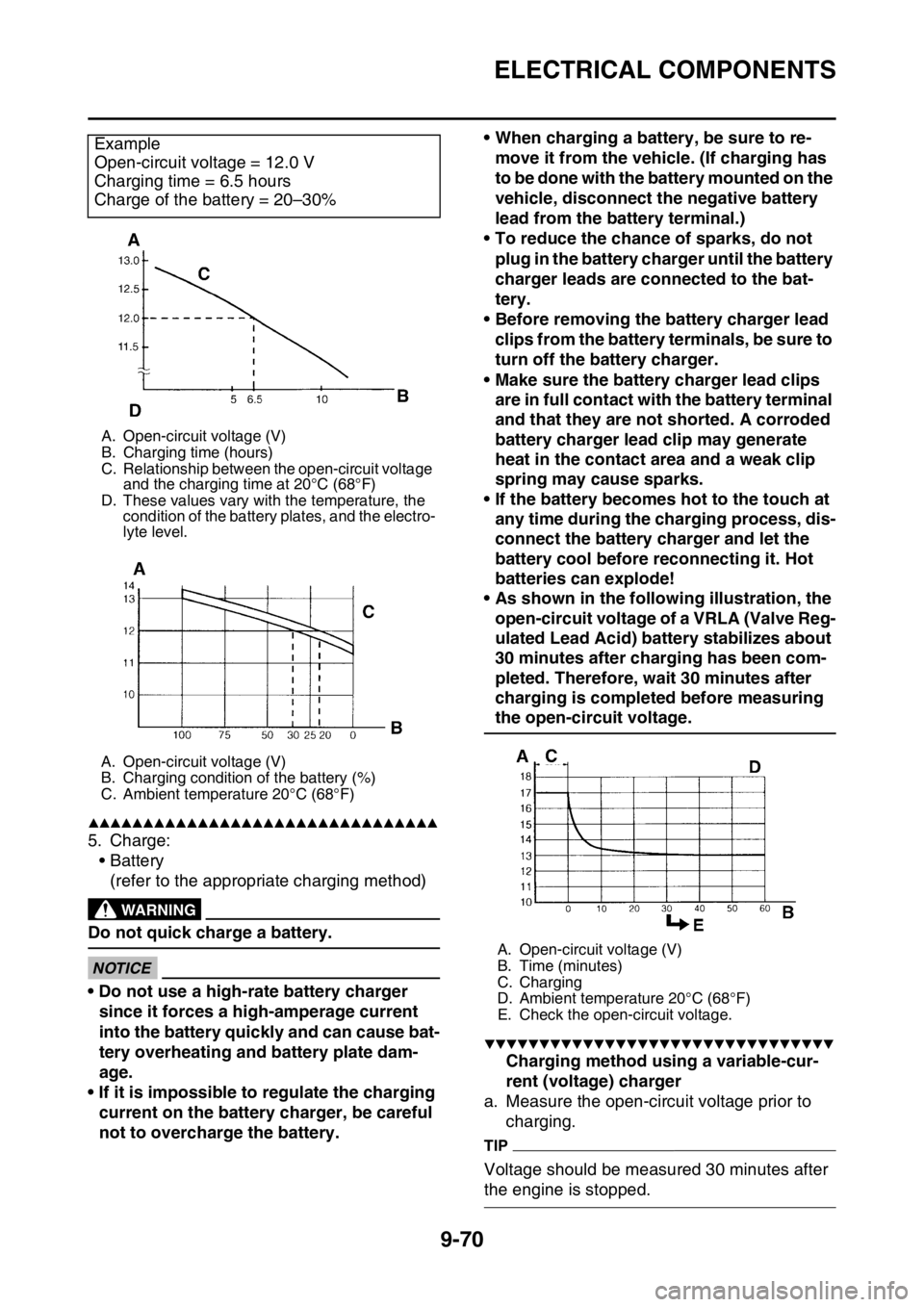
Example
Open-circuit voltage = 12.0 V
Charging time = 6.5 hours
Charge of the battery = 20–30%
A. Open-circuit voltage (V)
B. Charging time (hours)
C. Relationship between the open-circuit voltage
and the charging time at 20°C (68°F)
D. These values vary wit h the temperature, the
condition of the battery plates, and the electro-
lyte level.
A. Open-circuit voltage (V)
B. Charging condition of the battery (%)
C. Ambient temperature 20°C (68°F)
A. Open-circuit voltage (V)
B. Time (minutes)
C. Charging
D. Ambient temperature 20°C (68°F)
E. Check the open-circuit voltage.