steering CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 1919 of 2438

STEERING
CONTENTS
page page
ACUSTAR STANDARD AND TILT STEERING COLUMN ............................ 28
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION SHIFTER/IGNITION INTERLOCK .......................... 36
GENERAL INFORMATION .................. 1 POWER STEERING GEAR
................ 25
POWER STEERING PUMPS ................ 1
SPECIFICATIONS AND TIGHTENING REFERENCE .......................... 42
GENERAL INFORMATION
Safety goggles should be worn at all times
when working on any steering gear or pump. Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the breakdown of these designations
is included in the Introduction Section at the front of
this service manual. The power steering system consists of these four
major components. Power Steering Pump, Power
Steering Gear, Pressure Hose, and Return Line.
Turning of the steering wheel is converted into lin-
ear travel through the meshing of the helical pinion teeth with the rack teeth. Power assist steering is
provided by an open center, rotary type control valve.
It is used to direct oil from the power steering pump
to either side of the integral steering rack piston. Road feel is controlled by the diameter of a torsion
bar which initially steers the vehicle. As steering ef-
fort increases as in a turn, the torsion bar twists,
causing relative rotary motion between the rotary
valve body and valve spool. This movement directs
oil behind the integral rack piston, which in turn,
builds up hydraulic pressure and assists in the turn-
ing effort.
POWER STEERING PUMPS
INDEX
page page
Checking Power Steering Fluid Level .......... 9
Flow Control Valve Fitting O-Ring Seal ........ 23
General Information ........................ 1
Power Steering Hoses ..................... 11
Power Steering Pressure Switch ............. 10
Power Steering Pump Fluid Reservoirs ........ 22 Power Steering Pump Pressure Test
........... 9
Power Steering Pump Pulley Service .......... 20
Power Steering Pump Removal .............. 12
Power Steering Pump Service ................ 2
Power Steering PumpÐInitial Operation ....... 24
Steering Components Service Diagnosis ........ 2
GENERAL INFORMATION
Hydraulic pressure for operation of the power
steering gear is provided by a belt driven power
steering pump. The power steering pump is a con-
stant flow rate and displacement, vane type pump.
Different styles of Saginaw power steering pumps are
used depending on the engine application of the ve-
hicle. On all four cylinder and 3.0-liter V-6 applications
the Saginaw Ham Can power steering pump is used
(Fig. 1). On the 3.3 & 3.8-liter V-6 and Turbo III applica-
tions, different versions of the Saginaw T/C style
power steering pump is used (Fig. 2). The 3.3 & 3.8 liter V-6 engine application uses the T/C style power
steering pump with a remote mounted reservoir for
the power steering fluid. On the Turbo III application
of the T/C style power steering pump, the power
steering fluid reservoir is integral to the power steer-
ing pump. On the integral reservoir type pump (Fig. 1) the
pump housing and internal components are combined
with the reservoir to form a one-piece mechanism. The Saginaw T/C style power steering pump (Fig.
2), consists of the power steering pump internal com-
ponents and pump housing. The Saginaw T/C style
power steering pump though has no internal reser-
voir for the power steering fluid. Depending on vehi-
Ä STEERING 19 - 1
Page 1920 of 2438

cle and or engine application the Saginaw T/C style
power steering pump is used on, it will be equipped
with a plastic integral or remote mounted power
steering fluid reservoir. Drive tangs on the power steering gear pinion, mate
loosely with the stub shaft of the steering gear. This
will allow manual steering control to be maintained, if
the drive belt on the power steering pump should
break. However, under these conditions, steering effort
will significantly increase.
STEERING COMPONENTS SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
POWER STEERING PUMP SERVICE
The service procedures for the Saginaw power steer-
ing pump are limited to the areas and components
listed below. No repair procedures are to be done
on internal components of the Saginaw power
steering pumps.
² Repair of power steering fluid leaks from areas of
the power steering pump sealed by O-rings is allowed
(See Pump Leak Diagnosis). However power steering
pump shaft seal leakage will require replacement of
the pump.
² Power steering fluid reservoirs, related components
and attaching hardware.
² Power steering fluid reservoir filler cap/dipstick as-
semblies. Because of unique shaft bearings, flow control levels
or pump displacements, power steering pumps may be
used only on specific vehicle applications. Be sure that
all power steering pumps are only replaced with a
pump that is the correct replacement for that specific
application. Hydraulic pressure is provided for operation of the
power steering gear by the belt driven power steering
pumps (Fig . 1 & 2). It is a constant displacement, vane
type pump. The power steering pump is connected to
the steering gear by a power steering fluid pressure
hose and return hose.
Rectangular pumping vanes in the shaft driven rotor,
move power steering fluid from the intake to the cam ring
pressure cavities of the power steering pump. As the rotor
begins to turn, centrifugal force throws the vanes against
the inside surface of the cam ring to pickup residual oil.
This oil is then forced into the high pressure area. As more
oil is picked up by the vanes. That additional oil is forced
into the cavities of the thrust plate through two crossover
holes in the cam ring and pressure plate. The crossover
holes empty into the high pressure area between the
pressure plate and the housing end cover.
As the high pressure area is filled, oil flows under
the vanes in the rotor slots, forcing the vanes to follow
the inside surface of the cam ring. As the vanes
reach the restricted area of the cam ring, oil is
forced out from between the vanes. When excess oil
flow is generated during high-speed operation, a regu-
lated amount of oil returns to the pump intake side
through a flow control valve. The flow control valve
reduces the power required to drive the pump
and holds down temperature build-up.
Fig. 1 Saginaw Ham Can Power Steering Pump
Fig. 2 Saginaw T/C Style Power Steering Pump
19 - 2 STEERING Ä
Page 1921 of 2438

POWER STEERING SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
Ä STEERING 19 - 3
Page 1922 of 2438
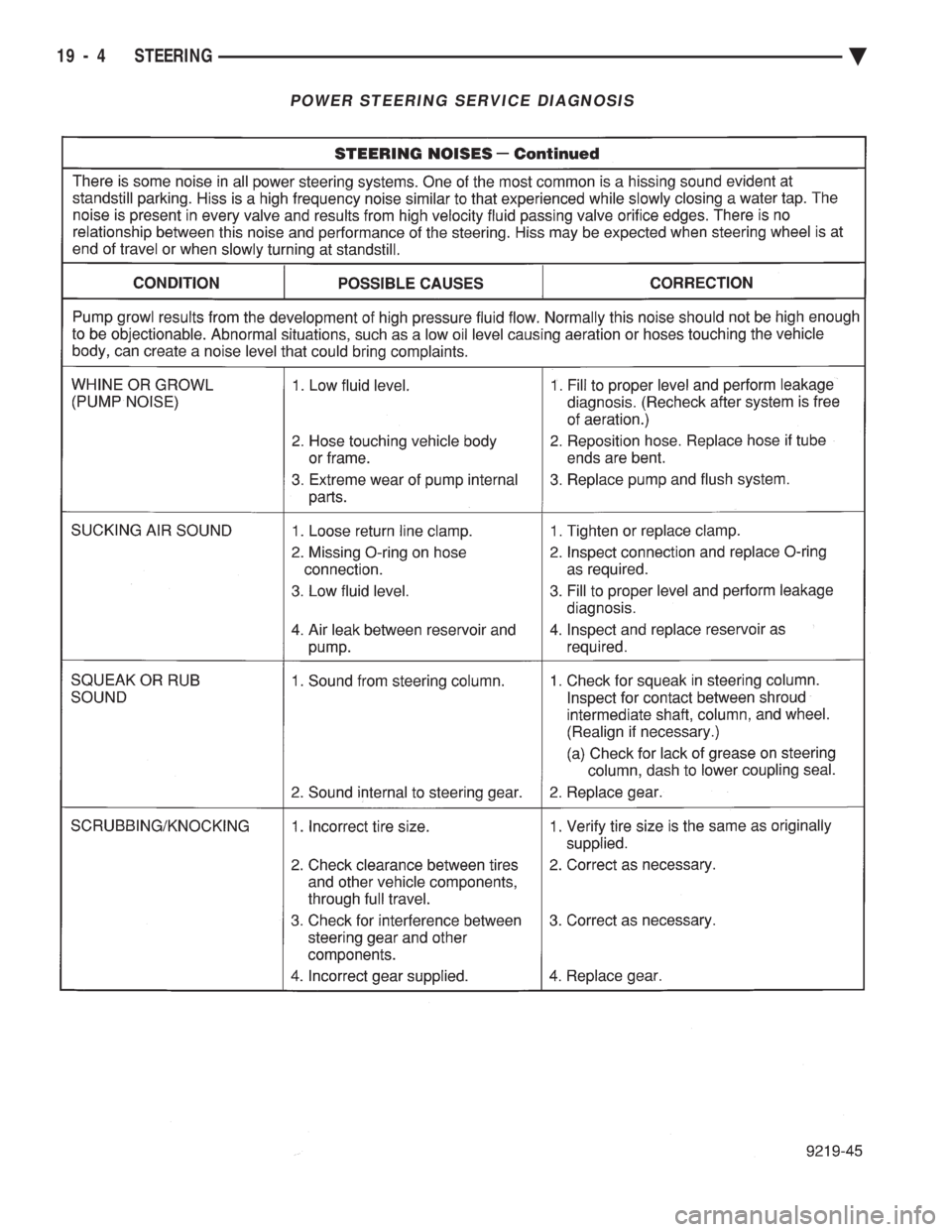
POWER STEERING SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
19 - 4 STEERING Ä
Page 1923 of 2438

POWER STEERING SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
Ä STEERING 19 - 5
Page 1924 of 2438

POWER STEERING SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
19 - 6 STEERING Ä
Page 1925 of 2438

POWER STEERING SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
Ä STEERING 19 - 7
Page 1926 of 2438

POWER STEERING SERVICE DIAGNOSIS
19 - 8 STEERING Ä
Page 1927 of 2438

When steering conditions exceed maximum pres-
sure requirements, such as when the wheels are
turned against the stops. The pressure built up in
the steering gear exerts pressure on the spring end of
the flow control valve. The high pressure lifts the re-
lief valve ball from its seat and allows oil to flow
through a trigger orifice located in the outlet fitting.
This reduces pressure on the spring end of the flow
control valve which then opens and allows the oil to
return to the intake side of the pump. This action
limits maximum pressure output of the pump to a
safe level. Under normal power steering pump operating con-
ditions, pressure requirements of the pump are below
maximum, causing the pressure relief valve to re-
main closed.
CHECKING POWER STEERING FLUID LEVEL
WARNING: FLUID LEVEL SHOULD BE CHECKED
WITH ENGINE OFF TO PREVENT INJURY FROM
MOVING PARTS. DO NOT USE AUTOMATIC TRANS-
MISSION FLUID IN THE POWER STEERING SYS-
TEM. DO NOT OVERFILL THE POWER STEERING
SYSTEM.
Wipe reservoir filler cap free of dirt, before check-
ing power steering fluid level. The dipstick should in- dicate FULL COLD when fluid is at normal ambient
temperature, approximately 21ÉC to 27ÉC (70ÉF to
80ÉF). In all pumps add fluid as necessary to obtain
proper level, using only MopartPower Steering
Fluid, or equivalent. DO NOT USE ANY TYPE
OF AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION FLUID.
POWER STEERING PUMP PRESSURE TEST
The following procedure can be used to test the op-
eration of the power steering system on the vehicle. (1) Check power steering pump drive belt tension
and adjust as necessary. (2) Disconnect power steering fluid pressure hose,
at steering gear or power steering pump. Use a con-
tainer for dripping fluid. (3) Connect Pressure Gauge, Special Tool C-3309-E
(Fig. 1) to both hoses using adapter fittings. Connect
spare pressure hose to gear or pump. (4) Completely open valve on Special Tool
C-3309-E (Fig. 1). (5) Start engine and let idle.
(6) Check power steering fluid level, and add fluid
as necessary. (7) Gauge should read below 862 kPa (125 psi), if
above, inspect the hoses for restrictions and repair as
necessary. The initial pressure should be in the
range of 345-552 kPa (50-80 psi).
PUMP LEAKAGE DIAGNOSIS
Ä STEERING 19 - 9
Page 1928 of 2438

CAUTION: The following test procedure involves test-
ing power steering pump maximum pressure output
and flow control valve operation. Do not leave valve
closed for more than 5 seconds as the pump could be
damaged.
(8) Close valve fully three times and record highest
pressure indicated each time. All three readings
must be above specifications and within 345 kPa
(50 psi) of each other. Power steering pump maximum relief pressure
is 8275 to 8975 kPa (1200 to 1300 psi.).
² Power steering pump pressures above specifications
but not within 345 kPa (50 psi) of each other, replace
pump.
² Pressures within 345 kPa (50 psi) of each other but
below specifications, replace pump.
CAUTION: Do not force the pump to operate against
the stops for more than 5 seconds at a time because,
pump damage will result.
(9) Open test valve. Turn steering wheel to the
extreme left and right positions until against the stops,
recording the highest indicated pressure at each posi-
tion. Compare pressure gauge readings to power steer-
ing pump specifications. If highest output pressures
are not the same against either stop, the steering gear
is leaking internally and must be replaced.
POWER STEERING PRESSURE SWITCH
New for 1993 M.Y., is the use of an idle quality power
steering pressure switch on some front wheel drive
passenger car applications. The purpose of this switch is to signal the power
train control module, that the power steering system is
putting additional load on the engine. This type of
condition exists when turning the front tires of the
vehicle, when the vehicle is stationary and the engine
is at idle speed. When this condition is sensed by the
power train control module, through a signal from the power steering pressure switch, engine idle
speed is increased. This increase in engine idle speed
compensates for the additional load, thus maintain-
ing the require engine idle speed and idle quality.
The power steering pressure switch is mounted to
the power steering pressure hose on the applications
that require its usage. Refer to (Fig. 1 and 2) below
for the pressure switch location on the different en-
gine applications.
REMOVE
(1) Locate power steering pressure switch on power
steering pressure hose. Refer to (Fig. 1 and 2) for the
engine application showing the location of the power
steering switch. (2) Remove vehicle wiring harness connector from
the power steering pressure switch. (3) Remove power steering pressure switch, from
power steering pressure hose.
Fig. 1 Power Steering Pressure Switch Location 3.0L
Fig. 2 Power Steering Pressure Switch Location 3.3 & 3.8L
Fig. 1 Pressure Test Gauge
19 - 10 STEERING Ä