length CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 201 of 2438
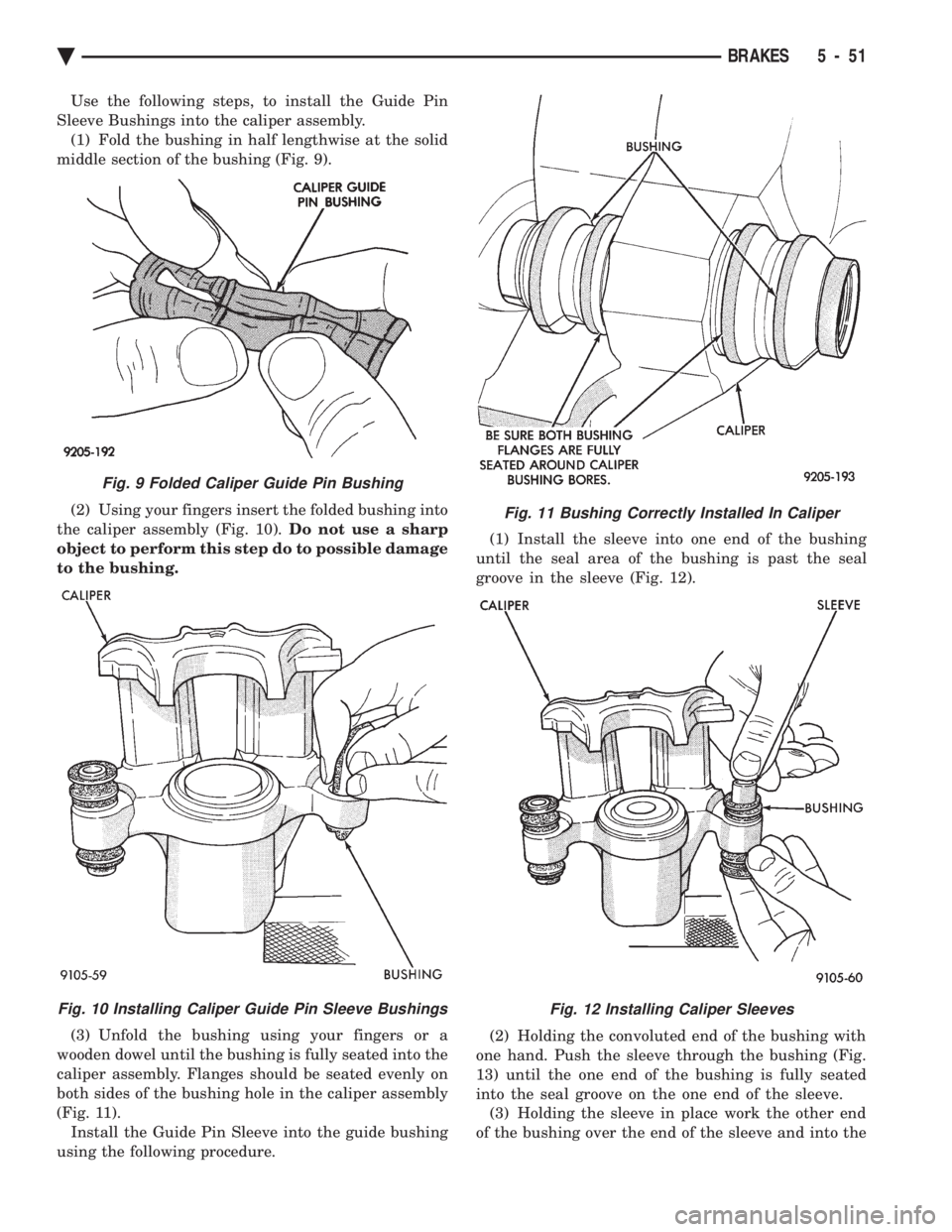
Use the following steps, to install the Guide Pin
Sleeve Bushings into the caliper assembly. (1) Fold the bushing in half lengthwise at the solid
middle section of the bushing (Fig. 9).
(2) Using your fingers insert the folded bushing into
the caliper assembly (Fig. 10). Do not use a sharp
object to perform this step do to possible damage
to the bushing.
(3) Unfold the bushing using your fingers or a
wooden dowel until the bushing is fully seated into the
caliper assembly. Flanges should be seated evenly on
both sides of the bushing hole in the caliper assembly
(Fig. 11). Install the Guide Pin Sleeve into the guide bushing
using the following procedure. (1) Install the sleeve into one end of the bushing
until the seal area of the bushing is past the seal
groove in the sleeve (Fig. 12).
(2) Holding the convoluted end of the bushing with
one hand. Push the sleeve through the bushing (Fig.
13) until the one end of the bushing is fully seated
into the seal groove on the one end of the sleeve. (3) Holding the sleeve in place work the other end
of the bushing over the end of the sleeve and into the
Fig. 11 Bushing Correctly Installed In Caliper
Fig. 12 Installing Caliper Sleeves
Fig. 9 Folded Caliper Guide Pin Bushing
Fig. 10 Installing Caliper Guide Pin Sleeve Bushings
Ä BRAKES 5 - 51
Page 213 of 2438

PARKING BRAKE HAND LEVER ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
REMOVAL (AG AND AJ BODY)
Remove ash receiver or courtesy light from rear of
console. Remove carpet from sides of console. Remove
parking brake trim cover from passenger side of con-
sole (pulls off). Load and lockout parking brake self adjuster (Fig.
6). Disconnect rear cables from equalizer bracket. Remove the 3 hold down nuts and remove hand le-
ver assembly through opening created by removing
console trim cover. Passenger seat might have to be
removed. Also, if metal tab at bottom of console pre-
vents removal of hand brake assembly, bend tab out
of the way. (Bend the tab back to original position af-
terR&Rof hand brake).
INSTALLATION (AG AND AJ BODY)
Install hand lever assembly through side opening
in console and bolt into place. Connect rear parking brake cables to equalizer.
Adjust parking brakes.
Install console trim cover, carpet, passenger seat
and rear ash receiver or courtesy light.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION PARKING BRAKE
SHOES
ALL WITH REAR DISK BRAKES
(1) Remove rear disc brake caliper assembly from
adapter and braking disc (See Disc Brake Shoe Re-
moval). (2) Remove rear braking disc from rear hub (See
Removing Braking Disk). (3) Remove grease cap.
(4) Remove cotter pin, lock nut, hub bearing re-
taining nut, and washer. (5) Remove hub and bearings.(See Wheel Bearing
Section) (6) Remove forward brake shoe assembly hold
down clip (Fig. 1). (7) Turn parking brake, brake shoe adjuster wheel
until adjuster is at shortest length. (8) Remove the parking brake, shoe adjuster as-
sembly (Fig. 2). (9) Remove upper parking brake, shoe to shoe
spring (Fig. 3). (10) Pull front parking brake shoe, away from an-
chor. Then remove front parking brake shoe and
lower spring (Fig. 4). (11) Remove rear parking brake shoe hold-down
clip. Then remove rear parking brake shoe assembly
(Fig. 5).
Fig. 1 Removing Brake Shoe Hold-Down Clip
Fig. 2 Removing Adjuster Assembly
Ä BRAKES 5 - 63
Page 344 of 2438
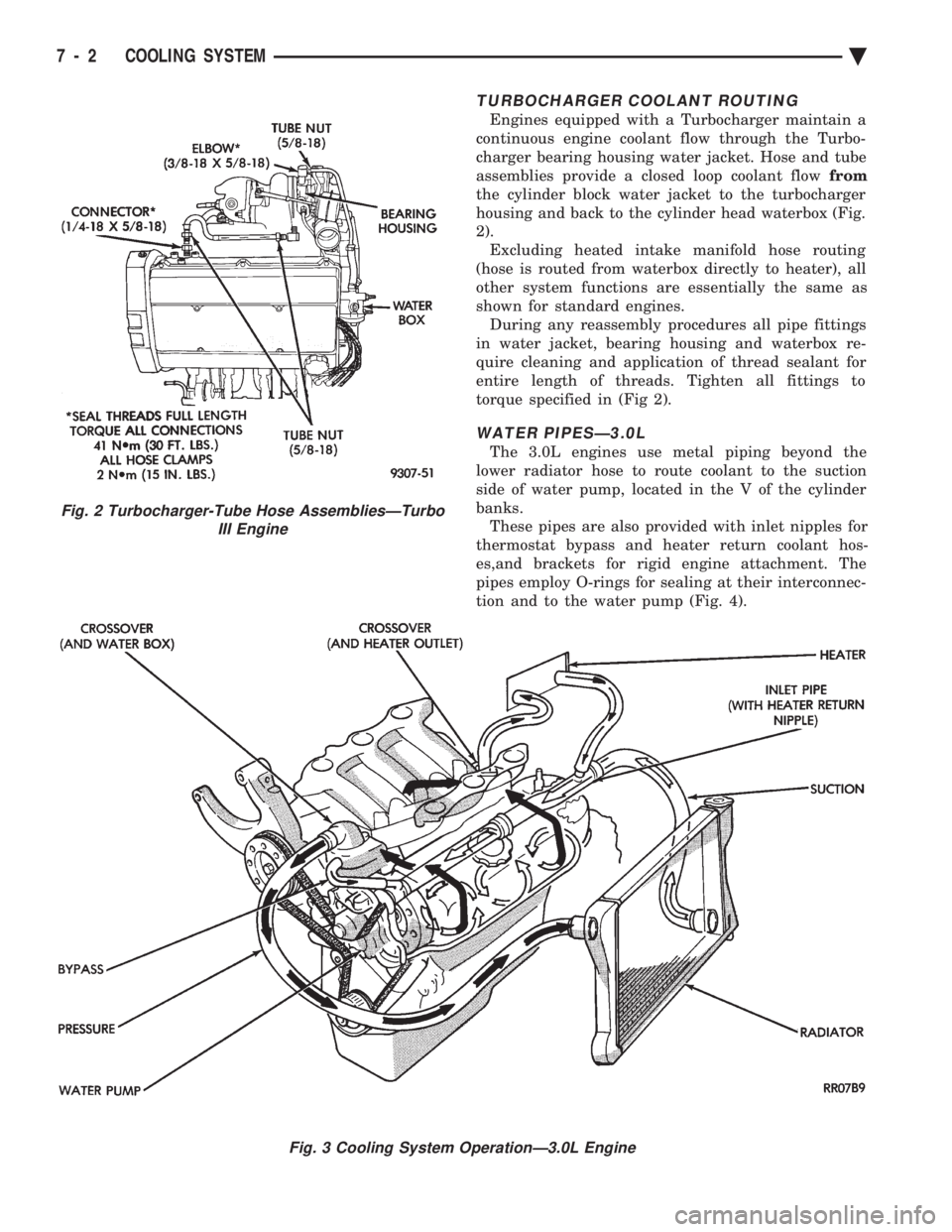
TURBOCHARGER COOLANT ROUTING
Engines equipped with a Turbocharger maintain a
continuous engine coolant flow through the Turbo-
charger bearing housing water jacket. Hose and tube
assemblies provide a closed loop coolant flow from
the cylinder block water jacket to the turbocharger
housing and back to the cylinder head waterbox (Fig.
2). Excluding heated intake manifold hose routing
(hose is routed from waterbox directly to heater), all
other system functions are essentially the same as
shown for standard engines. During any reassembly procedures all pipe fittings
in water jacket, bearing housing and waterbox re-
quire cleaning and application of thread sealant for
entire length of threads. Tighten all fittings to
torque specified in (Fig 2).
WATER PIPESÐ3.0L
The 3.0L engines use metal piping beyond the
lower radiator hose to route coolant to the suction
side of water pump, located in the V of the cylinder
banks. These pipes are also provided with inlet nipples for
thermostat bypass and heater return coolant hos-
es,and brackets for rigid engine attachment. The
pipes employ O-rings for sealing at their interconnec-
tion and to the water pump (Fig. 4).
Fig. 2 Turbocharger-Tube Hose AssembliesÐTurbo III Engine
Fig. 3 Cooling System OperationÐ3.0L Engine
7 - 2 COOLING SYSTEM Ä
Page 420 of 2438

VARIANCE SETTING PROCEDURE
There are two methods for setting variance while
in variance set mode. If the CAL symbol is on proce-
dure 2 must be used.
PROCEDURE 1
(1) Turn ignition switch to the on position.
(2) Press and hold the Comp/Temp button till the
display is turned OFF. (3) While continuing to hold Comp/Temp button
depress and hold US/Metric button until the VAR
symbol lights in approximately 5 seconds. (4) Release buttons.
(5) To determine the zone number which, corre-
sponds with your geographic area refer to Fig. 4.
(6) Press the US/Metric button until the zone num-
ber matches the display. (7) Press the Comp/Temp button to finish setting
of variation. (8) Variation is complete.
PROCEDURE 2 (1) Move away from any large metal objects like
buildings, or bridges. With the engine running and
the doors closed point vehicle true north. (2) Press and hold Comp/Temp button. The display
will go blank. (3) While continuing to hold Comp/Temp button
depress and hold the US/Metric button until the
VAR symbol lights in approximately 5 seconds. (4) Release buttons.
(5) Press the Comp/Temp button to finish setting
of variation. (6) Variation is complete.
DEMAGNETIZING PROCEDURE
Do not attach magnetic devices, such as magnetic
CB antennas to the vehicle roof, as they can cause
the compass to give false readings. Every vehicle has its own magnetic field. This
magnetic field is created by the various processes a
steel roof goes through when the vehicle is built. A
magnetic field also can be created if the roof is sub-
jected to A magnet, example:
² Magnetic c.b. antenna
² Magnetic tipped screwdriver and etc.
If the roof becomes magnetized use a demagnetiz-
ing Tool 6029 to demagnetize the roof. In this demagnetizing procedure you will use the
demagnetizing tool to demagnetize the roof and
mounting screws in the overhead console. It is impor-
tant that you follow the instructions below exactly.
The mounting screws and the mounting brackets
around the compass area are steel, and therefore aid
in the degaussing of the roof panel. (1) Be sure the ignition switch is in the OFF posi-
tion before you begin the demagnetizing procedure. (2) Open the sun glass compartment to gain access
to the overhead console mounting screws. (3) Plug the demagnetizing tool into a standard
110/115 volt AC outlet, keeping the demagnetizing
tool at least 12 inches away from the compass area
when plugging it in. (4) Slowly approach the console mounting screw
with the plastic coated tip of the tool for at least 2
seconds. (5) With the demagnetizing tool still energized,
slowly back it away from the screw until the tip is at
least 12 inches from the screw head. (6) After you have pulled at least 12 inches from
the last screw, remove the demagnetizing tool from
inside of the vehicle and disconnect it from the elec-
trical outlet. (7) Place an 8 1/2 in. X 11 in. piece of paper
lengthwise on the roof of vehicle directly above com-
pass. The purpose of the paper is to protect the roof
panel from scratches and define the area to be de-
magnetized.
Fig. 4 Variance Settings
8C - 4 OVERHEAD CONSOLE Ä
Page 433 of 2438

(4) Drive the vehicle 1 to 3 complete circles. The
CAL light will then go off, showing the compass is
calibrated. If the compass portion of the display:
² It does not display.
² Readings are not accurate after calibration.
² The vehicle may have too much magnetism for the
compass to be accurate.
² The compass circuitry is not working properly.
² Refer to Variance Procedure, Demagnetizing Pro-
cedure and/or Compass Diagnostics.
VARIANCE PROCEDURE
Variance is the difference between magnetic North
and geographic North. In some areas the difference
between magnetic and geographic North is great
enough to cause the compass to give false readings. If
this occurs, the variance must be set. To set the variance, depress and hold down both
the Comp/Temp button and the U.S./Metric button.
The display will go off and after 5 seconds the VAR
light will come on. Release both buttons. Using the
zone map (Fig. 5) to find your geographic location,
note the zone which, you are in. Press the U.S./Met-
ric button until the zone number appears on the dis-
play. Press the Comp/Temp button to enter your zone
number. Do not attach magnetic devices, such as magnetic
CB antennas to the vehicle roof, as they can cause
the compass to give false readings.
DEMAGNETIZING PROCEDURE
Every vehicle has its own magnetic field. This
magnetic field is created by the various processes a
steel roof goes through when the vehicle is built. A
magnetic field also can be created if the roof is sub-
jected to a magnet, example:
² Magnetic c.b. antenna
² Magnetic tipped screwdriver and etc.
If the roof becomes magnetized use a demagnetizer
tool 6029 to demagnetize the roof. In this demagnetizing procedure you will use the
demagnetizing tool to demagnetize the roof and
mounting screws in the overhead console. It is impor-
tant that you follow the instructions below exactly.
The mounting screws and the mounting brackets
around the compass area are steel, and therefore aid
in the demagnetizing of the roof panel. (1) Be sure the ignition switch is in the OFF posi-
tion before you begin the demagnetize procedure. (2) Open the sun glass compartment to gain access
to the overhead console mounting screws. (3) Plug the demagnetizing tool into a standard
110/115 volt AC outlet, keeping the demagnetizing
tool at least 12 inches away from the compass area
when plugging it in. (4) Slowly approach the console mounting screw
with the plastic coated tip of the tool for at least 2
seconds. (5) With the demagnetizing tool still energized,
slowly back it away from the screw until the tip is at
least 12 inches from the screw head. (6) After you have pulled at least 12 inches from
the last screw, remove the demagnetizing tool from
inside of the vehicle and disconnect it from the elec-
trical outlet. (7) Place an 8 1/2 X 11 inch piece of paper length-
wise on the roof of vehicle directly above compass.
The purpose of the paper is to protect the roof panel
from scratches and define the area to be demagne-
tized. (8) Plug in the demagnetizing tool, keeping it at
least 2 feet away from the compass unit. (9) Slowly approach the center of the roof panel at
the windshield with the demagnetizing tool plugged
in. (10) Contact the roof panel with the tip of the tool.
Using slow sweeping motions of 1/2 inch between
sweeps. Move the tool approximately 4 inches either
side of the centerline and at least 11 inch back from
the windshield. (11) With the demagnetizing tool still energized,
slowly back away from the roof panel until the tip is
at least 2 feet from the roof before unplugging the
tool.
Fig. 5 Variance Zone Map
Ä OVERHEAD CONSOLE 8C - 17
Page 436 of 2438
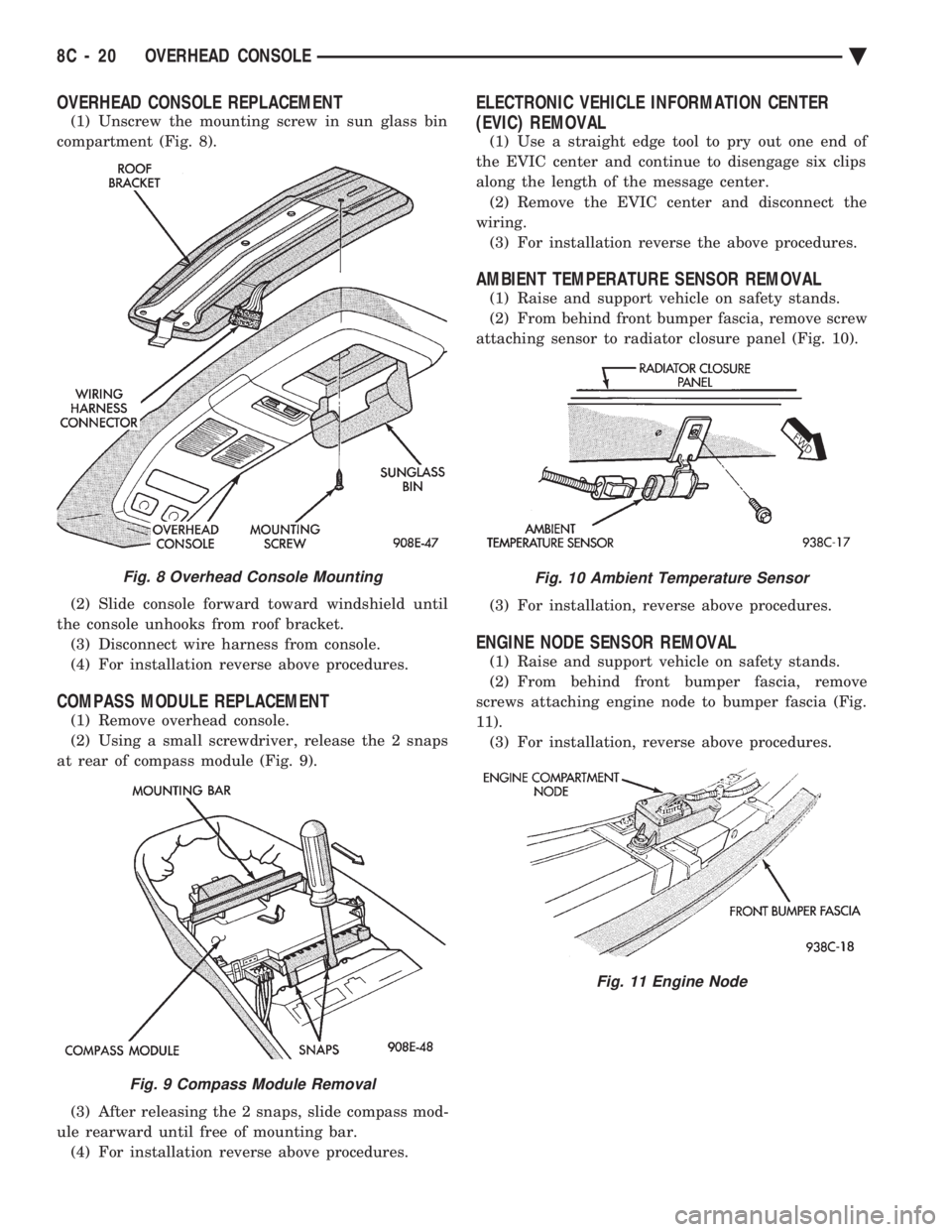
OVERHEAD CONSOLE REPLACEMENT
(1) Unscrew the mounting screw in sun glass bin
compartment (Fig. 8).
(2) Slide console forward toward windshield until
the console unhooks from roof bracket. (3) Disconnect wire harness from console.
(4) For installation reverse above procedures.
COMPASS MODULE REPLACEMENT
(1) Remove overhead console.
(2) Using a small screwdriver, release the 2 snaps
at rear of compass module (Fig. 9).
(3) After releasing the 2 snaps, slide compass mod-
ule rearward until free of mounting bar. (4) For installation reverse above procedures.
ELECTRONIC VEHICLE INFORMATION CENTER
(EVIC) REMOVAL
(1) Use a straight edge tool to pry out one end of
the EVIC center and continue to disengage six clips
along the length of the message center. (2) Remove the EVIC center and disconnect the
wiring. (3) For installation reverse the above procedures.
AMBIENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) From behind front bumper fascia, remove screw
attaching sensor to radiator closure panel (Fig. 10).
(3) For installation, reverse above procedures.
ENGINE NODE SENSOR REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle on safety stands.
(2) From behind front bumper fascia, remove
screws attaching engine node to bumper fascia (Fig.
11). (3) For installation, reverse above procedures.
Fig. 8 Overhead Console Mounting
Fig. 9 Compass Module Removal
Fig. 10 Ambient Temperature Sensor
Fig. 11 Engine Node
8C - 20 OVERHEAD CONSOLE Ä
Page 439 of 2438

(3) Plug the demagnetizing tool into a standard
110/115 volt AC outlet, keeping the demagnetizing
tool at least 12 inches away from the compass area
when plugging it in. (4) Slowly approach the console mounting screw
with the plastic coated tip of the tool for at least 2
seconds. (5) With the demagnetizing tool still energized,
slowly back it away from the screw until the tip is at
least 12 inches from the screw head. (6) After you have pulled at least 12 inches from
the last screw, remove the demagnetizer tool from in-
side of the vehicle and disconnect it from the electri-
cal outlet. (7) Place an 8 1/2 X 11 inch piece of paper length-
wise on the roof of vehicle directly above compass.
The purpose of the paper is to protect the roof panel
from scratches and define the area to be demagne-
tized. (8) Plug in the demagnetizing tool, keeping it at
least 2 feet away from the compass unit. (9) Slowly approach the center of the roof panel at
the windshield with the demagnetizing tool plugged
in. (10) Contact the roof panel with the tip of the tool
and using slow sweeping motions of 1/2 inch between sweeps. Move the tool approximately 4 inches either
side of the centerline and at least 11 inches back
from the windshield. (11) With the demagnetizing tool still energized,
slowly back away from the roof panel until the tip is
at least 2 feet from the roof before unplugging the
tool. (12) Recalibrate compass.
COMPASS DIAGNOSTICS
To place the unit into the diagnostics mode, turn
the vehicle ignition off. Depress the Comp/Temp but-
ton while turning on the ignition/run switch. The
display will then show DO. There are 3 tests that
can be performed when in the diagnostics mode.
Press the U.S./Metric button to choose test desired.
Refer to Fig. 4 and 5.
Test 1 (d1) determines the magnetic field strength
at the compass. The compass displays compensation
numbers which, correspond to the current magnetic
field strength at the compass. The letter N is dis-
played in the compass portion of the display. While a
number which, corresponds to the magnetic field
strength in the North/South direction is displayed.
The temperature portion of the display or the letter
W is displayed in the compass portion of the display.
A number which, corresponds to the magnetic field
strength in the East/West direction is displayed in
the temperature portion of the display. For proper
compass operation the numbers should be between 1
and 14. A number of 7 or 8 is ideal (no vehicle mag-
netism) while numbers approaching 1 or 14 show
that the vehicle is highly magnetic. If the numbers
show that the vehicle is highly magnetic, perform
the demagnetized procedure in this Group and retest
for magnetism at compass. If the numbers show that
the vehicle is highly magnetic, perform the demagne-
tizing procedure in this section and retest for magne-
tism at compass. The compass is not on the CCD bus,
if not functioning properly, refer to the Overhead
Console and Thermometer diagnosis. Test 2 (d2) checks the electronic circuits of the
compass, temperature, and CCD bus. If the test
passes d2 will be displayed, and if the test fails F2
will be displayed. Refer to AG and AJ Body Diagnos-
tic Procedure Manual for further testing procedures.
Fig. 3 Variance Zone MapFig. 4 Overhead Console Connector
Ä OVERHEAD CONSOLE 8C - 23
Page 445 of 2438

When testing secondary cables for punctures and
cracks with an oscilloscope follow the equipment
manufacturers instructions. If an oscilloscope is not available, secondary cables
can be tested as follows:
CAUTION: Do not leave any one spark plug cable
disconnected any longer than necessary during test-
ing. Excessive heat could damage the catalytic con-
verter. Total test time must not exceed ten minutes.
(a) With the engine not running, connect one end
of a test probe to a good ground. Use a probe made of
insulated wire with insulated alligator clips on each
end. (b) With engine running, move test probe along
entire length of all cables (approximately 0 to 1/8
inch gap). If punctures or cracks are present there
will be a noticeable spark jump from the faulty area
to the probe. Check the coil cable the same way.
Replace cracked, leaking or faulty cables.
When replacing cables, install the new high
tension cable and nipple assembly over cap or
coil tower. When entering the terminal into the
tower, push lightly, then pinch the large diam-
eter of nipple to release air trapped between the
nipple and tower. Continue pushing on the cable
and nipple until cables are properly seated in the
cap towers. A snap should be heard as terminal
goes into place. Use the same procedure to install cable in coil tower.
Wipe the spark plug insulator clean before reinstalling
cable and cover. Use the following procedure when removing the high
tension cable from the spark plug. First, remove the
cable from the retaining bracket. Then grasp the ter-
minal as close as possible to the spark plug. Rotate the
cover and pull the cable straight back. Pulling on the
cable itself will damage the conductor and termi-
nal connection. Do not use pliers and do not pull
the cable at an angle. Doing so will damage the
insulation, cable terminal or the spark plug in-
sulator. Wipe spark plug insulator clean before
reinstalling cable and cover. Resistance type cable is identified by the words
Electronic Suppression printed on the cable jacket.
Use an ohmmeter to check resistance type cable for
open circuits, loose terminals or high resistance as
follows: (a) Remove cable from spark plug.
(b) Lift distributor cap from distributor with
cables intact. Do not remove cables from cap. The
cables must be removed from the spark plugs. (c) Connect the ohmmeter between spark plug end
terminal and the corresponding electrode inside the
cap, make sure ohmmeter probes are in good contact.
Resistance should be within tolerance shown in the cable resistance chart. If resistance is
not within tolerance, remove cable at cap tower
and check the cable. If resistance is still not within
tolerance, replace cable assembly. Test all spark
plug cables in same manner.
To test coil to distributor cap high tension cable,
remove distributor cap with the cable intact. Do not
remove cable from the cap. Connect the ohmmeter
between center contact in the cap and remove the ca-
ble at coil tower and check cable resistance. If resis-
tance is not within tolerance, replace the cable.
SPARK PLUGS
Resistor spark plugs are used in all engines and
have resistance values of 6,000 to 20,000 ohms when
checked with at least a 1000 volt tester. Remove the spark plugs and examine them for
burned electrodes and fouled, cracked or broken por-
celain insulators. Keep plugs arranged in the order
in which they were removed from the engine. An iso-
lated plug displaying an abnormal condition indi-
cates that a problem exists in the corresponding
cylinder. Replace spark plugs at the intervals recom-
mended in Group O. Undamaged low milage spark plugs can be cleaned
and reused. Refer to the Spark Plug Condition sec-
tion of this group. After cleaning, file the center elec-
trode flat with a small point file or jewelers file.
Adjust the gap between the electrodes (Fig. 6) to the
dimensions specified in the chart at the end of this
section. Always tighten spark plugs to the specified torque.
Over tightening can cause distortion and change
spark plug gap. Tighten spark plugs to 28 N Im (20 ft.
lbs.) torque.
SPARK PLUG CONDITION
NORMAL OPERATING CONDITIONS
The few deposits present will be probably light tan
or slightly gray in color with most grades of commer-
cial gasoline (Fig. 7). There will not be evidence of
electrode burning. Gap growth will not average more
than approximately 0.025 mm (.001 in) per 1600 km
(1000 miles) of operation. Spark plugs that have nor-
mal wear can usually be cleaned, have the electrodes
filed and regapped, and then reinstalled. Some fuel refiners in several areas of the United
States have introduced a manganese additive (MMT)
CABLE RESISTANCE CHART
Ä IGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 3
Page 447 of 2438

(Fig. 9). This short circuits the electrodes. Spark
plugs with electrode gap bridging can be cleaned us-
ing standard procedures.
SCAVENGER DEPOSITS Fuel scavenger deposits may be either white or yel-
low (Fig. 10). They may appear to be harmful, but
are a normal condition caused by chemical additives
in certain fuels. These additives are designed to
change the chemical nature of deposits and decrease
spark plug misfire tendencies. Accumulation on the
ground electrode and shell area may be heavy but
the deposits are easily removed. Spark plugs with
scavenger deposits can be considered normal in con-
dition and be cleaned using standard procedures.
CHIPPED ELECTRODE INSULATOR A chipped electrode insulator usually results from
bending the center electrode while adjusting the
spark plug electrode gap. Under certain conditions,
severe detonation also can separate the insulator
from the center electrode (Fig. 11). Replace spark
plugs with chipped electrode insulators. PREIGNITION DAMAGE
Excessive combustion chamber temperature can
cause preignition damage. The center electrode dis-
solves first and the ground electrode dissolves some-
what later (Fig. 12). Insulators appear relatively
deposit free. Determine if the spark plug has the cor-
rect heat range rating for the engine, if ignition tim-
ing is over advanced or if other operating conditions
are causing engine overheating. The heat range rat-
ing refers to the operating temperature of a particu-
lar type spark plug. Spark plugs are designed to
operate within specific temperature ranges depend-
ing upon the thickness and length of the center elec-
trode and porcelain insulator.
SPARK PLUG OVERHEATING Overheating is indicated by a white or gray center
electrode insulator that also appears blistered (Fig.
13). The increase in electrode gap will be consider-
ably in excess of 0.001 in per 1000 miles of operation.
This suggests that a plug with a cooler heat range
rating should be used. Over advanced ignition tim-
Fig. 9 Electrode Gap Bridging
Fig. 10 Scavenger Deposits
Fig. 11 Chipped Electrode Insulator
Fig. 12 Preignition Damage
Ä IGNITION SYSTEMS 8D - 5
Page 470 of 2438

SCAVENGER DEPOSITS Fuel scavenger deposits may be either white or yel-
low (Fig. 12). They may appear to be harmful, but
are a normal condition caused by chemical additives
in certain fuels. These additives are designed to
change the chemical nature of deposits and decrease
spark plug misfire tendencies. Accumulation on the
ground electrode and shell area may be heavy but
the deposits are easily removed. Spark plugs with
scavenger deposits can be considered normal in con-
dition and be cleaned using standard procedures.
CHIPPED ELECTRODE INSULATOR A chipped electrode insulator usually results from
bending the center electrode while adjusting the
spark plug electrode gap. Under certain conditions,
severe detonation also can separate the insulator
from the center electrode (Fig. 13). Spark plugs with
chipped electrode insulators must be replaced.
PREIGNITION DAMAGE
Excessive combustion chamber temperature can
cause preignition damage. First, the center electrode
dissolves and the ground electrode dissolves some- what later (Fig. 14). Insulators appear relatively de-
posit free. Determine if the spark plug has the
correct heat range rating for the engine, if ignition
timing is over advanced or if other operating condi-
tions are causing engine overheating. The heat range
rating refers to the operating temperature of a par-
ticular type spark plug. Spark plugs are designed to
operate within specific temperature ranges depend-
ing upon the thickness and length of the center elec-
trode and porcelain insulator.
SPARK PLUG OVERHEATING
Overheating is indicated by a white or gray center
electrode insulator that also appears blistered (Fig.
15). The increase in electrode gap will be consider-
ably in excess of 0.001 in per 1000 miles of operation.
This suggests that a plug with a cooler heat range
rating should be used. Over advanced ignition tim-
ing, detonation and cooling system malfunctions also
can cause spark plug overheating.
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
The camshaft position sensor provides fuel injection
synchronization and cylinder identification informa-
Fig. 12 Scavenger Deposits
Fig. 13 Chipped Electrode Insulator
Fig. 14 Preignition Damage
Fig. 15 Spark Plug Overheating
8D - 28 IGNITION SYSTEMS Ä