brakes CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 156 of 2438

TESTING APPLICATION ADJUSTER OPERATION
Place the vehicle on a hoist with a helper in the
driver's seat to apply the brakes. Remove the access
plug from the rear adjustment slot in each brake
support plate (Fig. 4) to provide access to the ad-
juster star wheel. Then, to eliminate the possibility
of maximum adjustment, where the adjuster does not
operate because the closest possible adjustment has
been reached. Back the star wheel off approximately
30 notches. It will be necessary to hold the adjuster
lever away from the star wheel to permit this adjust-
ment. Spin the wheel and brake drum in the reverse di-
rection, and with a greater than normal force apply
the brakes suddenly. This sudden application of force
will cause the secondary brake shoe to leave the an-
chor. The wrap up effect will move the secondary
shoe, and the cable will pull the adjuster lever up.
Upon application of the brake pedal, the lever should
move upward, turning the star wheel. Thus, a defi-
nite rotation of the adjuster star wheel can be ob-
served if the automatic adjuster is working properly.
If one or more adjusters do not function properly, the
respective drum must be removed for adjuster servic-
ing.
BLEEDING BRAKE SYSTEM
CAUTION: For bleeding of the Anti-Lock brake hy-
draulic system. See the Anti-Lock Brake system
service procedures in this group which refers to the
particular Anti-Lock brake system being serviced.
PRESSURE BLEEDING
Before removing the master cylinder cover, wipe it
clean to prevent dirt and other foreign matter from
dropping into the master cylinder. CAUTION: Use bleeder tank Special Tool C-3496-B
with adapter Special Tool C-4578 to pressurize the
system for bleeding.
Follow pressure bleeder manufacturer's instruc-
tions, for use of pressure bleeding equipment. When bleeding the brake system. Some air may be
trapped in the brake lines or valves far upstream. As
much as ten feet from the bleeder screw (Fig. 6).
Therefore, it is essential to have a fast flow of a large
volume of brake fluid when bleeding the brakes to
ensure all the air gets out.
The following wheel sequence for bleeding the
brake hydraulic system should be used to ensure ad-
equate removal of all trapped air from the hydraulic
system.
² Right rear wheel
² Left front wheel
² Left rear wheel
² Right front wheel
To bleed the brake system. Attach a clear plastic
hose to the bleeder screw starting at the right rear
wheel and feed the hose into a clear jar containing
fresh brake fluid (Fig. 7). Next, open the bleeder screw at least one full turn
or more to obtain an adequate flow of brake fluid
(Fig. 8).
CAUTION: Just cracking the bleeder screw often re-
stricts fluid flow, and a slow, weak fluid discharge
will NOT get all the air out.
After 4 to 8 ounces of fluid has been bled through
the brake system at this wheel. And an air-free flow
is maintained in the clear plastic hose and jar, this
will indicate a good bleed. Repeat the procedure at all the other remaining
bleeder screws. Then check the pedal for travel. If
pedal travel is excessive or has not been improved.
Enough fluid has not passed through the system to
Fig. 5 Brake Drum Adjustment With Tool C-3784
Fig. 6 Trapped Air in Brake Line
5 - 6 BRAKES Ä
Page 157 of 2438

expel all the trapped air. Be sure to monitor the fluid
level in the pressure bleeder. It must stay at the
proper level so air will not be allowed to reenter the
brake system through the master cylinder.
BLEEDING WITHOUT A PRESSURE BLEEDER
If a pressure bleeder is not available. A good brake
fluid flow can be obtained by manual bleeding of the
brake hydraulic system, following these steps. Manual bleeding of the brakes hydraulic sys-
tem will require the aid of a helper to correctly
perform manual brake bleeding procedure. The following wheel sequence for bleeding the
brake hydraulic system should be used to ensure ad-
equate removal of all trapped air from the hydraulic
system. ²
Right rear wheel
² Left front wheel
² Left rear wheel
² Right front wheel
(1) Pump the brake pedal three or four times and
hold it down before the bleeder screw is opened. (2) Then open the bleeder screw at least 1 full
turn. When the bleeder screw opens the brake pedal
will drop all the way to the floor. (3) Release the brake pedal only afterthe bleeder
screw is closed. (4) Repeat steps 1 through 3, four or five times, at
each bleeder screw. This should pass a sufficient
amount of fluid to expel all the trapped air from the
brake system. Be sure to monitor the fluid level in
the master cylinder, so it stays at a proper level so
air will not reenter the brake system through the
master cylinder. Test drive vehicle to be sure brakes are operating
correctly and that pedal is solid.
TEST FOR FLUID CONTAMINATION
Indications of fluid contamination are swollen or
deteriorated rubber parts. Swollen rubber parts indicate the presence of petro-
leum in the brake fluid. To test for contamination, put small amount of
drained brake fluid in clear glass jar. If fluid sepa-
rates into layers, there is mineral oil contamination. If contaminated, drain and thoroughly flush sys-
tem. Replace master cylinder, proportioning valve,
caliper seals, wheel cylinder seals and all hoses.
WHEEL STUD NUT TIGHTENING
When tightening wheel stud nuts, a criss-cross
tightening sequence should be followed (Fig. 9).
Tighten all stud nuts to one-half specified torque.
Repeat, fully tightening to 129 N Im (95 ft. lbs.).
Fig. 9 Wheel Stud Nut Tightening Sequence
Fig. 7 Proper Method for Purging Air From Brake
System (Typical)
Fig. 8 Open Bleeder Screw at Least One Full Turn (Typical)
Ä BRAKES 5 - 7
Page 158 of 2438

FIG. 10 BRAKE LINE ROUTING NON ABS BRAKES
5 - 8 BRAKES Ä
Page 159 of 2438
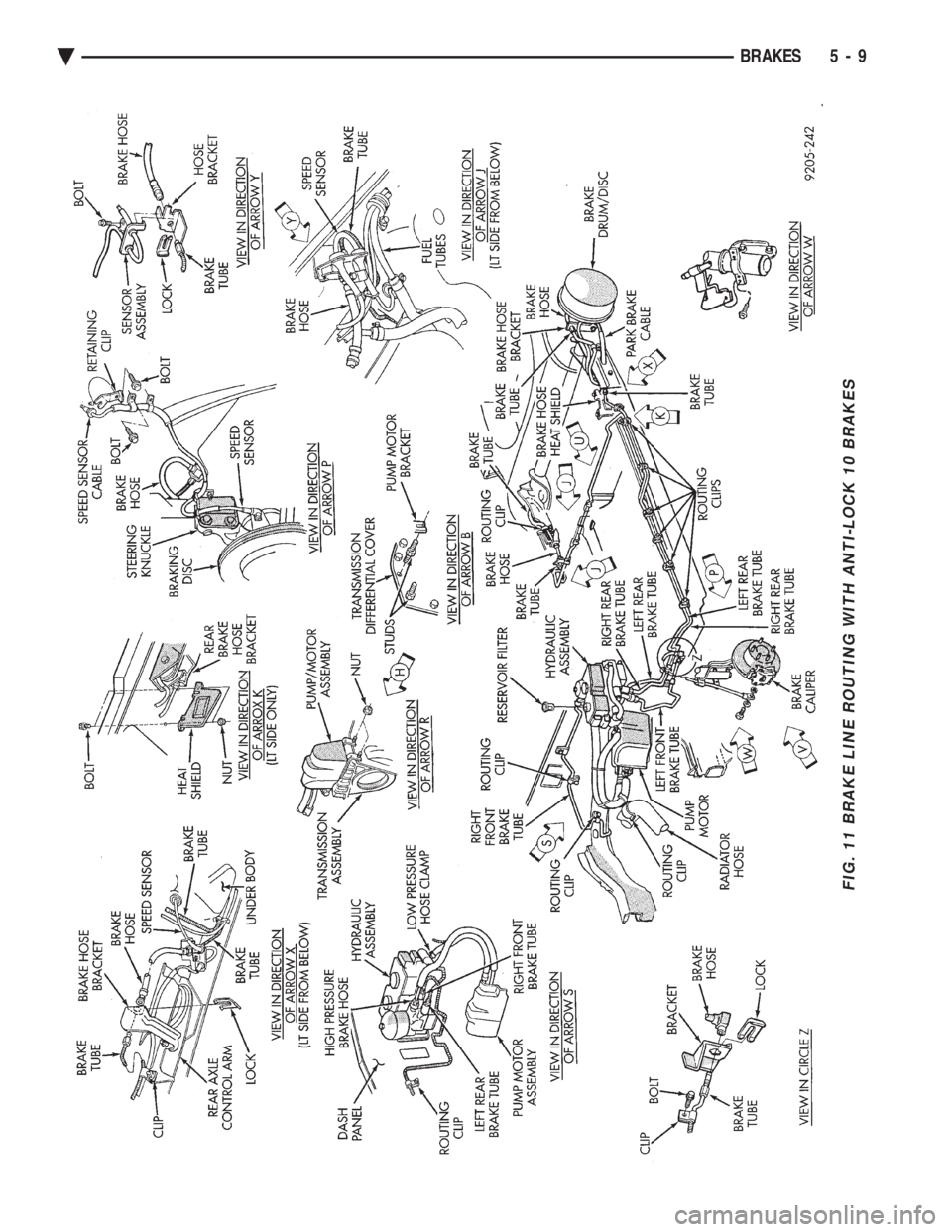
FIG. 11 BRAKE LINE ROUTING WITH ANTI-LOCK 10 BRAKES
Ä BRAKES 5 - 9
Page 160 of 2438

FIG. 12 BRAKE LINE ROUTING WITH ANTI-LOCK 6 BRAKES
5 - 10 BRAKES Ä
Page 161 of 2438

BRAKE HOSE AND TUBING
INSPECTION OF BRAKE HOSE AND TUBING
Flexible rubber hose is used at both front brakes and
at the rear axle. Inspection of brake hoses should be
performed whenever the brake system is serviced and
every 7,500 miles or 12 months, whichever comes first
(every engine oil change). Inspect hydraulic brake
hoses for severe surface cracking, scuffing, or worn
spots. Should the fabric casing of the rubber hose be
exposed due to cracks or abrasions in the rubber hose
cover, the hose should be replaced immediately. Even-
tual deterioration of the hose can take place with
possible burst failure. Faulty installation can cause
twisting and wheel, tire or chassis interference. The steel brake tubing should be inspected periodi-
cally for evidence of physical damage or contact with
moving or hot components.
INSTALLATION OF BRAKE HOSE
Always use factory recommended brake hose to en-
sure quality, correct length and superior fatigue life.
Care should be taken to make sure that the tube and
hose mating surfaces are clean and free from nicks and
burrs. Front right and left side hoses are not
interchangeable. Connections should be correct and properly made.
Use new copper seal washers on all connections using
Banjo Bolts and tighten all fittings to their specified
torques. The flexible front hydraulic brake hose should al-
ways be installed on the vehicle by first attaching the
Banjo connector to the caliper assembly. Then bolt the
intermediate hose bracket to the strut assembly allow-
ing the bracket to position the hose to prevent twisting.
Attach the hose to the body bracket and steel brake
tubing. Tighten all fittings to specified torque. The
body bracket and hose end are keyed so that they will
only fit one way. Install rear brake hoses first to the trailing arm
tubes and then to the floor pan tubes. Minimize hose
twisting. Vehicles equipped with rear disc brakes have
brake hoses attached to the caliper on each side. The
brake hose should be first attached by the Banjo bolt to
the caliper and then secured to the hose bracket with
the retaining clip. The attach the steel brake tubing to
the hose fitting.
REPAIR AND INSTALLATION OF BRAKE TUB- ING
Only double wall 4.75mm (3/16 in.) steel tubing
should be used for replacement. Care should be taken
when replacing brake tubing, to be sure the proper
bending and flaring tools and procedures are used, to
avoid kinking. Do not route the tubes against sharp edges, moving components or into hot areas. All
tubes should be properly attached with recommended
retaining clips.
TYPES OF TUBING FLARES
Two different tubing flares (Fig. 13) are used on 93
M.Y. vehicles. On some ABS brake systems the tub-
ing connections made to the hydraulic assembly use
an ISO flare. All other ABS brake system compo-
nent, tubing connections are made using a double in-
verted flare. On non-ABS brake systems all
component tubing connections use only the double in-
verted flare. No ISO flares are used.
CAUTION: ALWAYS USE THE PROPER FLARING
TOOL AND PROCEDURE, FOR THE TYPE OF
BRAKE SYSTEM THAT IS BEING SERVICED TO IN-
SURE THE INTEGRITY OF THE HYDRAULIC SYS-
TEM.
TO REPAIR OR FLARE TUBING
Using Tubing Cutter, Special Tool C-3478-A or
equivalent, cut off damaged seat or tubing (Fig. 14).
Ream out any burrs or rough edges showing on in-
side of tubing (Fig. 15). This will make the ends of
tubing square (Fig. 15) and ensure better seating of
flared end tubing. PLACE TUBE NUT ON TUB-
ING BEFORE FLARING THE TUBING.
DOUBLE INVERTED TUBING FLARES.
To make a double inverted tubing flare (Fig. 13 &
16). Open handles of Flaring Tool, Special Tool
C-4047 or equivalent. Then rotate jaws of tool until
the mating jaws of tubing size are centered between
vertical posts on tool. Slowly close handles with tub-
Fig. 13 Identifying Hydraulic Brake Tubing Flares
Ä BRAKES 5 - 11
Page 162 of 2438
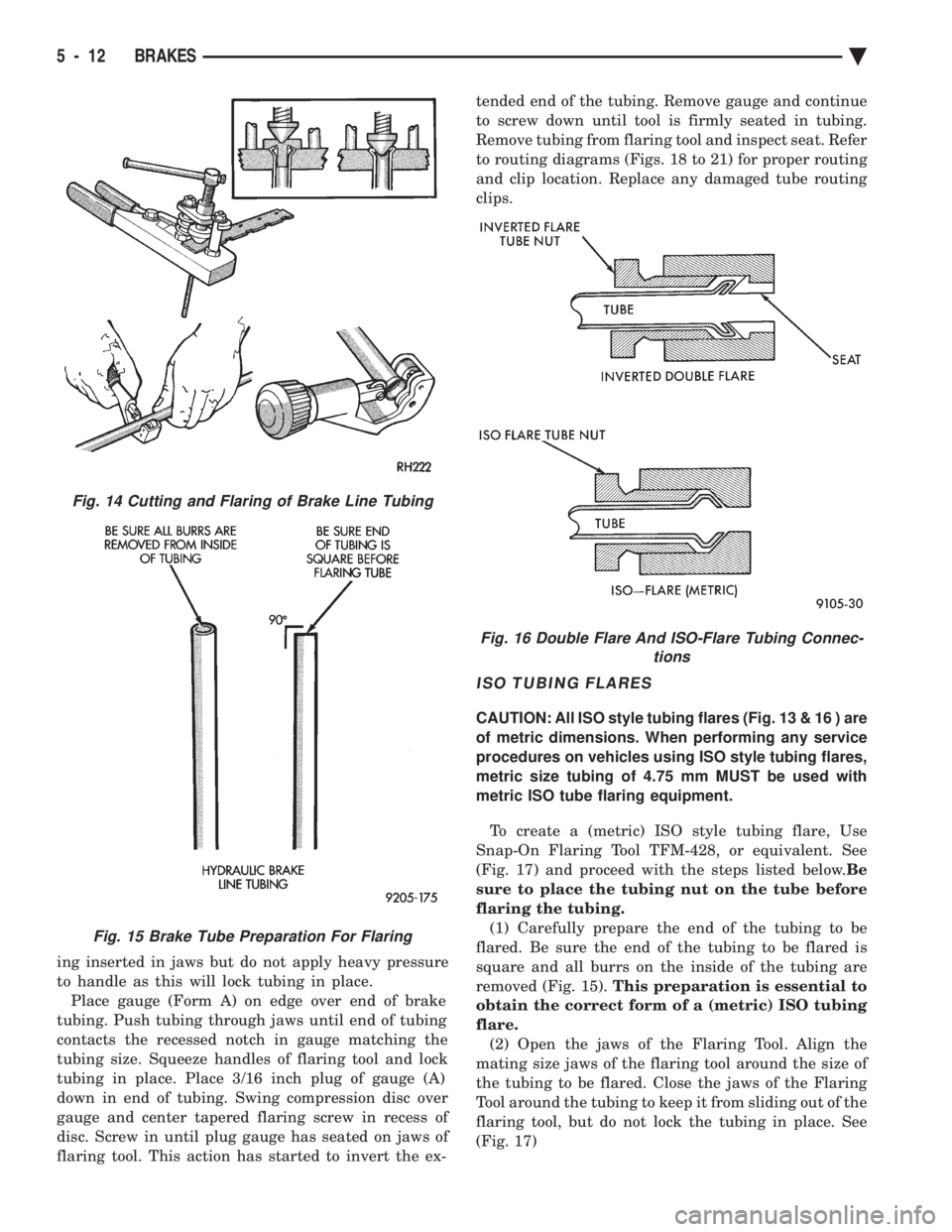
ing inserted in jaws but do not apply heavy pressure
to handle as this will lock tubing in place.Place gauge (Form A) on edge over end of brake
tubing. Push tubing through jaws until end of tubing
contacts the recessed notch in gauge matching the
tubing size. Squeeze handles of flaring tool and lock
tubing in place. Place 3/16 inch plug of gauge (A)
down in end of tubing. Swing compression disc over
gauge and center tapered flaring screw in recess of
disc. Screw in until plug gauge has seated on jaws of
flaring tool. This action has started to invert the ex- tended end of the tubing. Remove gauge and continue
to screw down until tool is firmly seated in tubing.
Remove tubing from flaring tool and inspect seat. Refer
to routing diagrams (Figs. 18 to 21) for proper routing
and clip location. Replace any damaged tube routing
clips.
ISO TUBING FLARES
CAUTION: All ISO style tubing flares (Fig. 13 & 16 ) are
of metric dimensions. When performing any service
procedures on vehicles using ISO style tubing flares,
metric size tubing of 4.75 mm MUST be used with
metric ISO tube flaring equipment.
To create a (metric) ISO style tubing flare, Use
Snap-On Flaring Tool TFM-428, or equivalent. See
(Fig. 17) and proceed with the steps listed below. Be
sure to place the tubing nut on the tube before
flaring the tubing. (1) Carefully prepare the end of the tubing to be
flared. Be sure the end of the tubing to be flared is
square and all burrs on the inside of the tubing are
removed (Fig. 15). This preparation is essential to
obtain the correct form of a (metric) ISO tubing
flare. (2) Open the jaws of the Flaring Tool. Align the
mating size jaws of the flaring tool around the size of
the tubing to be flared. Close the jaws of the Flaring
Tool around the tubing to keep it from sliding out of the
flaring tool, but do not lock the tubing in place. See
(Fig. 17)
Fig. 14 Cutting and Flaring of Brake Line Tubing
Fig. 15 Brake Tube Preparation For Flaring
Fig. 16 Double Flare And ISO-Flare Tubing Connec- tions
5 - 12 BRAKES Ä
Page 163 of 2438

(3) Position the tubing in the jaws of the Flaring
Tool so that it is flush with the top surface of the
flaring tool bar assembly. (See Fig. 17). (4) Install the correct size adaptor for the brake
tubing being flared, on the feed screw of the yoke as-
sembly. Center the yoke and adapter over the end of
the tubing. Apply lubricant to the adapter area that
contacts brake tubing. Making sure the adapter pilot
is fully inserted in the end of the brake tubing.
Screw in the feed screw of the yoke assembly until
the adaptor has seated squarely on the surface of the
bar assembly (Fig. 17). This process has created the
(metric) ISO tubing flare.STOP LAMP SWITCH ADJUSTMENT (ALL
VEHICLES)
The stop lamp switch incorporates a self adjusting
feature. If adjustment or replacement is required,
proceed as follows: Install the switch in the retaining
bracket and push the switch forward as far as it will
go. The brake pedal will move forward slightly (Fig.
18). Gently pull back on the brake pedal bringing the
striker back toward the switch until the brake pedal
will go back no further. This will cause the switch to
ratchet backward to the correct position. Very little
movement is required, and no further adjustment is
necessary.
Fig. 17 ISO Tubing Flare ProcessFig. 18 Stop Lamp Switch
BASIC DIAGNOSIS GUIDE
Ä BRAKES 5 - 13
Page 164 of 2438
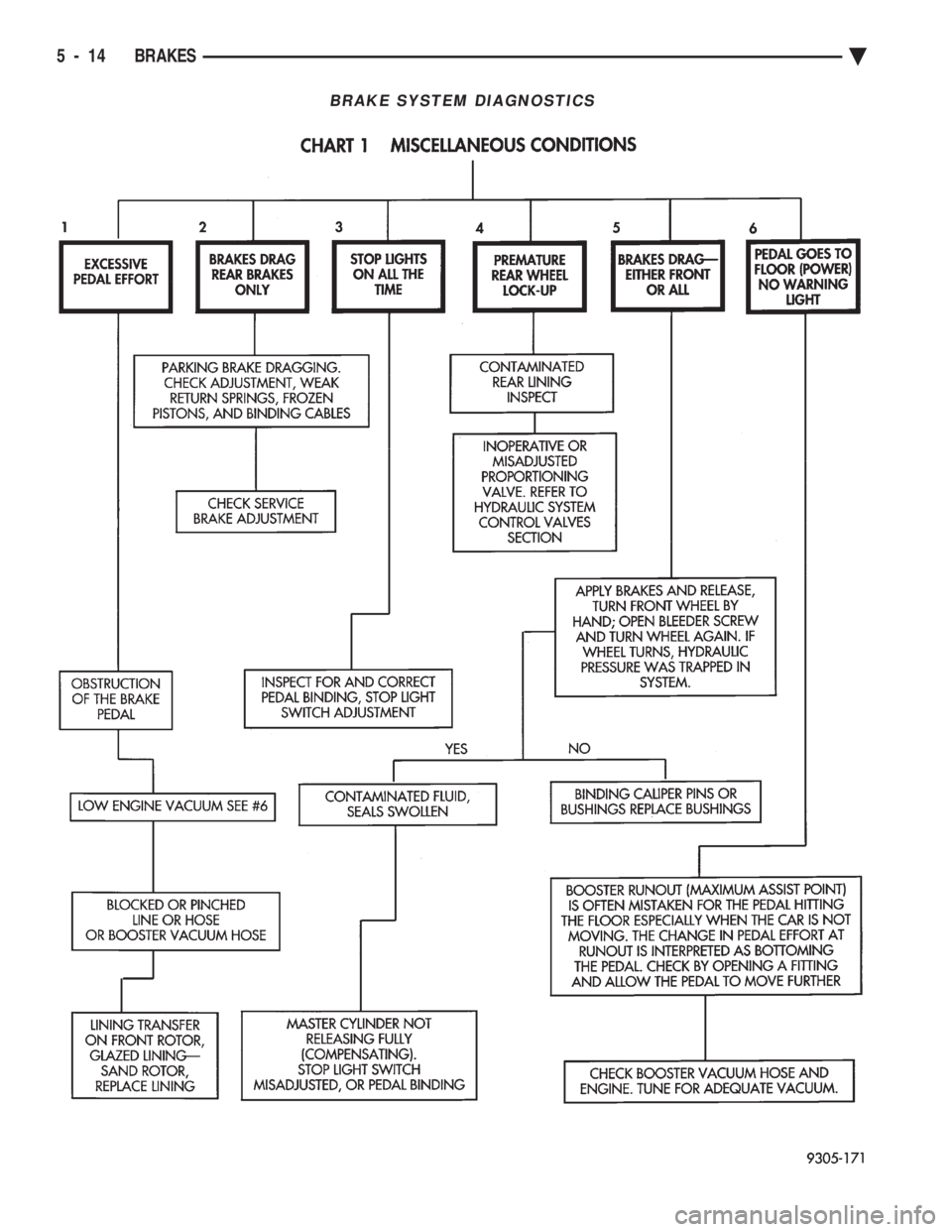
BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS
5 - 14 BRAKES Ä
Page 165 of 2438
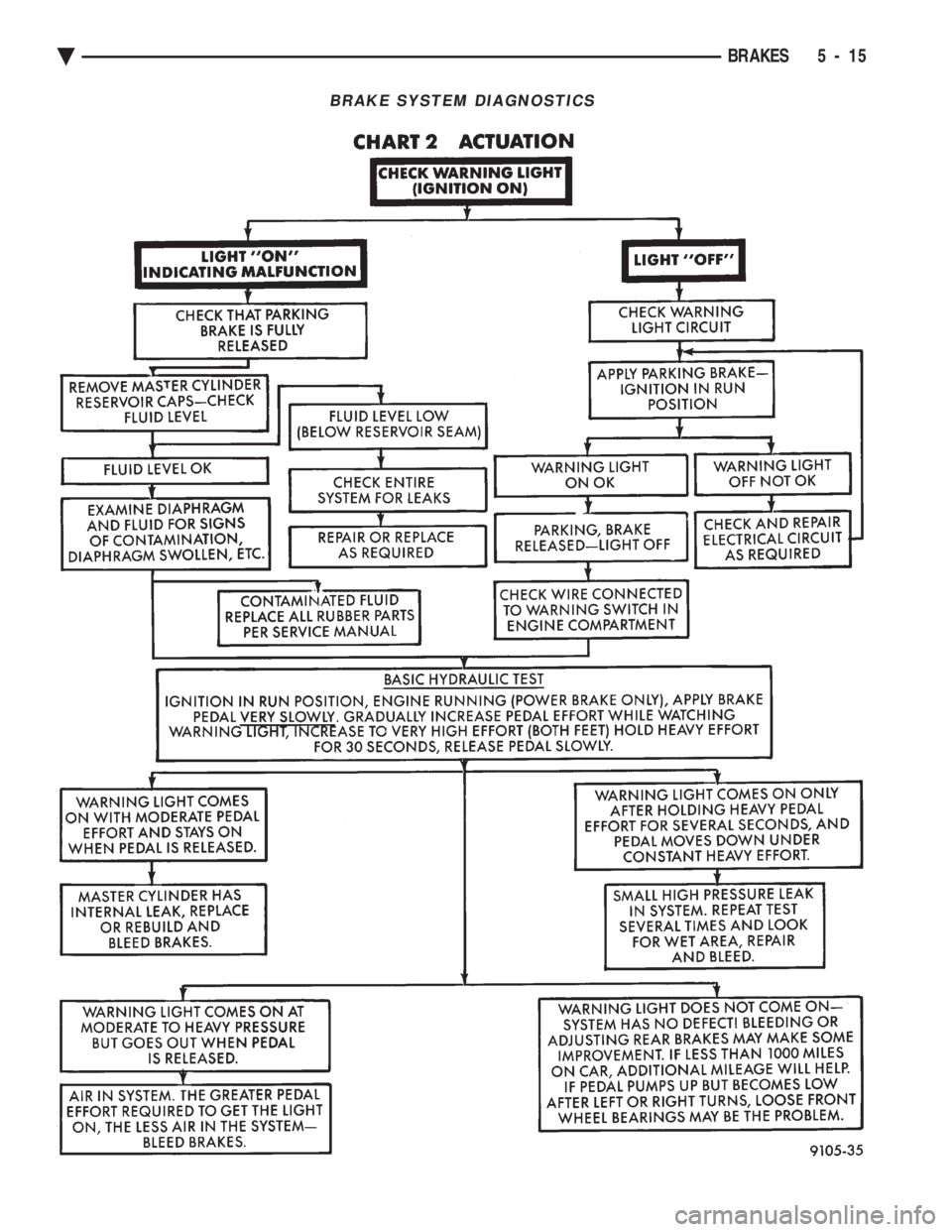
BRAKE SYSTEM DIAGNOSTICS
Ä BRAKES 5 - 15