wheel torque CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993 Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHEVROLET, Model Year: 1993, Model line: DYNASTY, Model: CHEVROLET DYNASTY 1993Pages: 2438, PDF Size: 74.98 MB
Page 1945 of 2438

bolts and nut on locating stud (Fig. 2). The right rear
crossmember stud is a pilot that correctly locates
the crossmember. Tighten down this bolt first,
then torque all 4 crossmember fasteners to 122
N Im (90 ft. lbs.).
CAUTION: Proper torque on the crossmember to
frame rail mounting bolts is very important.
(3) Torque the 4 bolts (Fig. 3) attaching the steering
gear assembly to front crossmember, to 68 N Im (50 ft.
lbs.). To ensure proper alignment of the steering
gear tighten left front bolt first. (4) Attach the engine damper strut from the engine
to the crossmember (if so equipped). (5) Attach the fluid tubes (Fig. 3) from the power
steering pump to the fittings on the steering gear.
Torque the fluid pressure line to steering gear tube nut
to 31 N Im (275 in. lbs.).
(6) Mount the outer tie rod ends to the steering
knuckles. Install the tie rod end to steering knuckle
attaching nuts. Torque the tie rod end to steering
knuckle nuts to 52 N Im (38 ft. lbs.). Install cotter pin
in tie rod end. (7) Install the front tire and wheel assemblies on
vehicle. Install the wheel lug nuts and torque to 129
N Im (95 ft. lbs.).
(8) Lower vehicle.
CAUTION: Do not use automatic transmission fluid. (9) Fill power steering pump fluid reservoir to the
(Full-Cold) proper level. (10) Start the engine and let run for a few seconds.
Then turn the engine off.
(11) Add fluid if necessary.
(12) Raise front wheels of vehicle off the ground.
(13) Start engine and turn steering wheel several
times from stop to stop to bleed air from fluid in
system. Stop engine, check fluid level, and inspect
system for leaks. Fill pump reservoir to correct
level with Mopar t, Power Steering Fluid, or
equivalent. See Checking Fluid Level.
(14) Lower front wheels of vehicle back on the
ground. (15) Adjust toe (Refer to Group 2 Suspension).
OUTER TIE ROD
REMOVAL
(1) Loosen inner tie rod to outer tie rod jam nut (Fig.
4). (2) Remove outer tie rod to steering knuckle cotter
pin and attaching nut (Fig. 4). (4) Remove the tie rod end from steering knuckles, using Puller Special Tool C-3894-A (Fig. 5).
(5) Remove outer tie rod from inner tie rod.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install outer tie rod onto inner tie rod. Make
sure jam nut is on inner tie rod (Fig. 4). (2) Do not tighten jam nut.
(3) Install outer tie rod onto steering knuckle. In-
stall tie rod to steering knuckle attaching nut and
torque to 52 N Im (38 ft.lbs.).
CAUTION: During this procedure do not allow the
steering gear boot to become twisted. (See Wheel
Alignment in the suspension section of this service
manual).
(4) Make toe adjustment by turning inner tie rod.
(5) Tighten the inner to outer tie rod jam nut to 75
N Im (55 ft. lbs.) torque. Lubricate tie rod boot groove
with silicone type lubricant before installing outer
boot clamp, making sure boot is not twisted.
Fig. 4 Outer Tie Rod
Fig. 5 Tie Rod End Removal
Ä STEERING 19 - 27
Page 1951 of 2438

(3) Position the steering column assembly in the
vehicle. Align the steering column assembly mounting
bracket slots on the brake pedal bracket attaching
studs (Fig. 13). Install, but loose assemblethe two
upper column bracket, washers and nuts.
(4) Make sure the front wheels are in the straight-
ahead position. Align and assemble the upper steering
coupler to lower steering coupler. Install the upper to
lower steering coupler retaining bolt and nut. Torque
the retaining bolt nut to 28 N Im (250 in. lbs.). Be sure
to install the upper to lower steering coupler
retaining bolt retention pin (Fig. 6). (5) Install the buttons which retain the multi func-
tion switch wiring harness to the steering column.
Connect the multi-function switch wiring harness con-
nector to the multi-function switch. Torque the connec-
tor retaining bolt to 2 N Im (17 in. lbs) usin ga7mm
socket (Fig. 8). (6) Install the upper fixed shroud onto the steering
column assembly. (7) Be sure both breakaway capsules are fully seated
in the slots of the steering column upper support
bracket. Torque the 2 upper steering column assembly
to support bracket nuts to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.). Torque
the 2 lower steering column assembly to mounting
bracket nuts to 12 N Im (105 in. lbs.).
(8) Complete the wiring harness connections to the
remaining steering column switches (Fig. 9). Install
the lower fixed shroud onto the steering column.
(9) Route the PRNDL actuator assembly under left
steering column wing and along left side of steering
column. Insert the flange of the PRNDL actuator steering
column insert into the steering column jacket (Fig. 7).
Squeeze the legs of the steering column insert together
and install tabs under steering column jacket. Engage
lock bar to secure the actuator assembly into the steering
column jacket (Fig. 7). (10) Hook the PRNDL actuator cable eyelet to the
steering column actuator arm (Fig. 7). Move the shift
lever to neutral, check pointer location, should indicate neutral. If pointer does not indicate neutral adjust actua-
tor with tool (Fig. 14) to center pointer on N (Neutral) and
then check pointer location in other gears.
(11) Install the lock housing shrouds. The shroud
fasteners are Torx-headscrews. Install the tilt lever
(if equipped). (12) Install the lower dash panel cover.
(13) For steering wheel installation with speed con-
trol refer to Group 8 Electrical. For non-speed control,
place the steering wheel on the steering column shaft
with the master splines aligned. Install the steering
wheel to column shaft retaining nut. Tighten retaining
nut to 61 N Im (45 ft. lbs.) torque. Do not force the
steering wheel onto the column shaft by driving
it on with a heavy object. Pull steering wheel
down onto column shaft using ONLY the steering
wheel retaining nut.
(14) For vehicles equipped with a column shift. Pass
the transmission shift cable through its mounting bracket
on the steering column assembly. Connect the transmis-
sion shift cable to the shift lever on the steering column
assembly. Install the shift cable to mounting bracket
retaining clip (Fig. 2). The grommet must be installed
in the shift lever (Fig. 11) before the cable is in-
serted into the grommet. Use MopartMultipurpose
Lubricant, or an equivalent product, to aid installation of
shift link rod into grommet.
(15) Re-adjust the transmission shift linkage.
Whenever the steering column is loosened or
removed, the shift linkage MUST be adjusted and
tested. Refer to Group 21 Transmission for the shift
linkage adjustment procedure.
Fig. 13 Steering Column Mounting
Fig. 14 PRNDL Actuator Cable Adjustment
Ä STEERING 19 - 33
Page 1964 of 2438

CAUTION: Be sure crossover bellcrank does NOT
move when tightening adjusting screw (Fig. 10).
CAUTION: Proper torque to the crossover cable ad-
justing screw is very important (Fig. 10).
(6) Remove lock pin from gearshift housing and re-
install lock pin (so long end is up) in gear shift hous-
ing. Tighten lock pin to 8 N Im (70 in. lbs.).
(7) Check for shift into first and reverse.
(8) Gearshift mechanism and cables are now func-
tioning properly.
IN-CAR TRANSAXLE DISASSEMBLE/ASSEMBLE
The following items can be serviced without remov-
ing the transaxle from the vehicle:
² Gear shift housing
² Synchronizers
² Intermediate shaft speed gears
² Input shaft
² Reverse idler gear and shaft
² Shift forks and pads
² Shift rails ²
Roller detents
² Speedometer pinion
² All external covers
Observe following procedure:
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(2) Remove both shift cables from shift cover levers.
(3) Remove left front wheel and tire assembly and
left splash shield. (4) Place drain pan under transaxle and remove
transaxle rear end cover. (5) Push out the fifth fork roll pin and slide the fifth
fork and synchronizer sleeve off the rail/hub. (6) Remove the fifth hub snap ring, hub assembly
and speed gear. (7) Remove fifth gear nut and fifth input gear.
(8) Remove the bearing retainer plate, interlock
plate and shuttles.
CAUTION: Before removing the gearshift housing
assembly, reverse the lock pin (so the long end is
down) and insert lock pin into the same threaded
hole. This procedure will save time when the gear
shift housing assembly is reinstalled. (9) Remove selector shaft housing bolts (note the two
pilot bolts) and remove housing. (10) Remove roller detents and springs, noting that
the rollers align with the shift rails. (11) Push out the 1-2 and 3-4 lug roll pins, remove
the reverse pivot lever and fifth rail C-Clip. If a roll
pin or C-Clip falls, be sure to remove it from the
bottom of the case. (12) Pull out the fifth shift rail and remove the fifth
shift lug and interlock pin. If the pin falls, be sure to
remove it from the bottom of the case. (13) Remove the intermediate shaft ball bearing
snap ring and the bearing support plate. (14) Remove reverse shift rail and lug assembly.
(15) Remove the reverse idler shaft and gear assem-
bly. (16) Rotate the 1-2 shift lug and rail, and 3-4 shift
lug towards the front of the vehicle. (17) Firmly grasp both the input and intermediate
shaft assemblies and pull them out of the transmission
with the 1-2 and 3-4 shift rails, lugs and forks. The differential assembly can only be serviced
by removing the complete transaxle from the
vehicle because bearing preload must be reset. The components listed in the first paragraph can now
be serviced. Refer to the appropriate subassembly
recondition section.
To reassemble the transaxle in the vehicle, reverse
the above procedure using the proper sealants. Fill the
transaxle with SAE 5W-30 engine oil to the bottom of
the fill hole in the end cover.
Fig. 9 Install Cables
Fig. 10 Adjusting Crossover Cable
21 - 4 TRANSAXLE Ä
Page 1995 of 2438

THREE SPEED TORQUEFLITE AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE INDEX
page page
Accumulator-Recondition ................... 67
Aluminum Thread Repair ................... 48
Assembly Subassembly Installation ........... 57
Band Adjustment ......................... 47
Bearing Adjustment Procedures .............. 81
Clutch and Servo Air Pressure Tests .......... 43
Differential Repair ........................ 76
Disassembly Subassembly Removal .......... 50
Fluid and Filter Change .................... 40
Fluid Drain and Refill ..................... 40
Fluid Leakage-Transaxle Torque Converter Housing Area .......................... 44
Fluid Level and Condition .................. 40
Front Clutch-Recondition ................... 62
Front Planetary & Annulus Gear-Recondition .... 65
Gearshift Linkage Adjustment ............... 46
General Information ....................... 35
Governor ............................... 48
Hydraulic Control Pressure Adjustments ....... 47
Hydraulic Pressure Tests ................... 42
Kickdown Servo (Controlled Load)-Recondition . . 67 Low/Reverse Servo-Recondition
.............. 66
Oil Cooler Flow Check .................... 48
Oil Coolers and Tubes Reverse Flushing ...... 48
Oil Pump-Recondition ..................... 62
Output Shaft Repair ...................... 71
Park/Neutral Position and Back-Up Lamp Switch . 47
Parking Pawl ............................ 71
Pump Oil Seal-Replacement ................ 61
Rear Clutch-Recondition ................... 64
Road Test .............................. 40
Selection of Lubricant ..................... 40
Special Additives ......................... 40
Three Speed Torqueflite General Diagnosis ..... 36
Throttle Pressure Linkage Adjustment ......... 46
Torque Converter Clutch Solenoid Wiring Connector ............................ 40
Transaxle and Torque Converter Removal ...... 48
Transfer Shaft Repair ..................... 68
Valve Body-Recondition .................... 57
Vehicle Speed Sensor Pinion Gear ........... 47
GENERAL INFORMATION
Safety goggles should be worn at all times
when working on these transaxles. This transaxle combines a fully automatic 3 speed
transmission, final drive gearing, and differential into
a front wheel drive system. The unit is a Metric
design. The identification markings and usage of the
transaxle are charted in Diagnosis and Tests. Transaxle operation requirements are differ-
ent for each vehicle and engine combination and
some internal parts will be different to provide
for this. Therefore, when replacing parts, refer to
the seven digit part number stamped on rear of
the transaxle oil pan flange. Within this transaxle, there are 3 primary areas:
(1) Main center line plus valve body.
(2) Transfer shaft center line (includes governor and
parking sprag). (3) Differential center line. Center distances be-
tween the main rotating parts in these 3 areas are held
precise. This maintains a low noise level through
smooth accurate mesh of the gears. The torque converter, transaxle area, and differential
are housed in an integral aluminum die casting. The
differential oil sump is common with thetransaxle
sump. Separate filling of the differential is NOT nec-
essary. The torque converter is attached to the crankshaft
through a flexible driving plate. Cooling of the con-
verter is accomplished by circulating the transaxle
fluid through an oil-to-water type cooler located in the
radiator side tank and/or an oil-to air heat ex- changer. The torque converter assembly is a sealed
unit that cannot be disassembled.
The transaxle fluid is filtered by an internal filter
attached to the lower side of the valve body assem-
bly. Engine torque is transmitted to the torque con-
verter then, through the input shaft to multiple-disc
clutches in the transaxle. The power flow depends on
the application of the clutches and bands. Refer to
Elements in Use Chart in Diagnosis and Tests sec-
tion. The transaxle consists of two multiple-disc
clutches, an overrunning clutch, two servos, a hy-
draulic accumulator, two bands, and two planetary
gear sets. They provide three forward ratios and a re-
verse ratio. The common sun gear of the planetary
gear sets is connected to the front clutch by a driving
shell. The drive shell is splined to the sun gear and
to the front clutch retainer. The hydraulic system
consists of an oil pump, and a single valve body
which contains all of the valves except the governor
valves. The transaxle sump and differential sump are
both vented through the dipstick.Output torque
from the main center line is delivered through heli-
cal gears to the transfer shaft.This gear set is a
factor of the final drive (axle) ratio. The shaft also
carries the governor and parking sprag. An integral
helical gear on the transfer shaft drives the differen-
tial ring gear. The final drive gearing is completed
with one of three gear sets producing overall top gear
ratios of 2.78, 3.02, or 3.22 depending on model and
application.
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 35
Page 2009 of 2438

If equipped, unplug torque converter clutch
plug, located near the dipstick.
CAUTION: Raise vehicle. Remove front wheels. Refer
to Suspension, Group 2 to remove or install wheel
hub nut and both drive shafts. Remove torque converter dust cover. Mark
torque converter and drive plate with chalk, for
reassembly. Remove torque converter mounting
bolts.
Fig. 1 Remove Upper and Lower Oil Cooler Hoses
Fig. 2 Engine Support Fixture
Fig. 3 Remove Bell Housing Upper Bolts
Fig. 4 Remove or Install Left Splash Shield
Fig. 5 Remove or Install Access Plug in Right Splash Shield to Rotate Engine Crankshaft
Fig. 6 Remove or Install Wire to Neutral/Park Safety Switch
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 49
Page 2054 of 2438
During the road test, the transaxle should be oper-
ated in each position to check for slipping and any
variation in shifting. If vehicle operates properly at highway speeds, but
has poor acceleration, the torque converter stator
overrunning clutch may be slipping. If through-gear
acceleration is normal, but high throttle opening is
required to maintain highway speeds, the torque con-
verter stator clutch may have seized. Both of these
stator defects require replacement of the torque con-
verter. The clutch that is slipping can be determined by
noting the transaxle operation in all selector posi-
tions. Then comparing which internal units are ap-
plied in those positions. The Elements in Use Chart
provides a basis for road test analysis. The process of elimination can be used to detect
any unit which slips and to confirm proper operation
of good units. Road test analysis can usually diag-
nose slipping units, but the actual cause of the mal-
function usually can not be decided. Practically any
condition can be caused by leaking hydraulic circuits
or sticking valves.
HYDRAULIC PRESSURE TESTS
Pressure testing is a very important step in the di-
agnostic procedure. These tests usually reveal the
cause of most transaxle problems. Before performing pressure tests, be certain that
fluid level and condition, and shift cable adjustments
have been checked and approved. Fluid must be at
operating temperature (150 to 200 degrees F.). Install an engine tachometer, raise vehicle on hoist
which allows front wheels to turn, and position ta-
chometer so it can be read. Attach 150 psi gauges to ports required for test be-
ing conducted. A 300 psi gauge (C-3293) is required
for reverse pressure test. Test port locations are shown in (Figure 1).
TEST ONE-SELECTOR IN LOW 1ST GEAR
(1) Attach pressure gauge to the low/reverse clutch
tap. (2) Move selector lever to the L position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle
speed to 20 mph. (4) Low/reverse clutch pressure should read 115 to
145 psi.
ELEMENTS IN USE AT EACH POSITION OF THE SELECTOR LEVER
Fig. 4 Oil Level Indicator Location
21 - 94 TRANSAXLE Ä
Page 2055 of 2438

(5) This test checks pump output, pressure regula-
tion and condition of the low/reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit and shift schedule.
TEST TWO-SELECTOR IN DRIVE 2ND GEAR
(1) Attach gauge to the underdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the 3position.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle
speed of 30 mph. (4) Underdrive clutch pressure should read 110 to
145 psi. (5) This test checks the underdrive clutch hydrau-
lic circuit as well as the shift schedule.
TEST THREE-OVERDRIVE CLUTCH CHECK
(1) Attach gauge to the overdrive clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the circle Dposition.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle
speed of 20 mph. (4) Overdrive clutch pressure should read 74 to 95
psi. (5) Move selector lever to the 3position and in-
crease indicated vehicle speed to 30 mph. (6) The vehicle should be in second gear and over-
drive clutch pressure should be less than 5 psi. (7) This test checks the overdrive clutch hydraulic
circuit as well as the shift schedule.
TEST FOUR-SELECTOR IN CIRCLE DRIVE, OVERDRIVE GEAR
(1) Attach gauge to the 2/4 clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the circle Dposition.
(3) Allow vehicle front wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle
speed of 30 mph. (4) The 2/4 clutch pressure should read 75 to 95
psi. (5) This test checks the 2/4 clutch hydraulic circuit.
TEST FIVE-SELECTOR IN CIRCLE DRIVE,
OVERDRIVE
(1) Attach gauge to the torque converter clutch off
pressure tap. (2) Move selector lever to the circle Dposition.
(3) Allow vehicle wheels to turn and increase
throttle opening to achieve an indicated vehicle speed
of 50 mph.
CAUTION: Both wheels must turn at the same speed. (4) Torque converter clutch off pressure should be
less than 5 psi. (5) This test checks the torque converter clutch
hydraulic circuit.
TEST SIX-SELECTOR IN REVERSE
(1) Attach gauge to the reverse clutch tap.
(2) Move selector lever to the reverse position.
(3) Read reverse clutch pressure with output sta-
tionary (foot on brake) and throttle opened to achieve
1500 rpm. (4) Reverse clutch pressure should read 165 to 235
psi. (5) This test checks the reverse clutch hydraulic
circuit.
TEST RESULT INDICATIONS
(1) If proper line pressure is found in any one test,
the pump and pressure regulator are working properly. (2) Low pressure in all positions indicates a defec-
tive pump, a clogged filter, or a stuck pressure regula-
tor valve. (3) Clutch circuit leaks are indicated if pressures do
not fall within the specified pressure range. (4) If the overdrive clutch pressure is greater than 5
psi in step (6) of Test Three, a worn reaction shaft seal
ring is indicated.
CLUTCH AIR PRESSURE TESTS
Inoperative clutches can be located using a series of
tests by substituting air pressure for fluid pressure
(Figs. 2 and 3). The clutches may be tested by applying
air pressure to their respective passages after the valve
body has been removed and Tool 6056 has been in-
stalled. To make air pressure tests, proceed as follows: The compressed air supply must be free of all
dirt and moisture. Use a pressure of 30 psi. Remove oil pan and valve body. See Valve body
removal.
OVERDRIVE CLUTCH
Apply air pressure to the overdrive clutch apply
passage and watch for the push/pull piston to move
Fig. 1 Pressure Taps
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 95
Page 2059 of 2438

CAUTION: If the vehicle is equipped with two oil
coolers (one in the radiator tank, one in front of the
radiator) they must be flushed separately. Do not
attempt to flush both coolers at one time. (1) Disconnect the cooler lines at the transmission.
(2) Using a hand suction gun filled with mineral
spirits, reverse flush the cooler. Force mineral spirits
into the From Cooler line of the cooler (Fig. 7) and
catch the exiting spirits from the To Coolerline.
Observe for the presence of debris in the exiting
fluid. Continue until fluid exiting is clear and free
from debris.
(3) Using compressed air in intermittent spurts,
blow any remaining mineral spirits from the cooler,
again in the reverse direction. (4) To remove any remaining mineral spirits from
the cooler, one (1) quart of automatic transmission
fluid should be pumped through the cooler before re-
connecting. (5) If at any stage of the cleaning process, the
cooler does not freely pass fluid, the cooler must be
replaced.
OIL COOLER FLOW CHECK
After the new or repaired transmission has been
installed, filled to the proper level with automatic
transmission fluid. The flow should be checked using
the following procedure: (1) Disconnect the From coolerline at the trans-
mission and place a collecting container under the
disconnected line. (2) Run the engine at curb idle speed , with the
shift selector in neutral. (3) If the fluid flow is intermittent or it takes more
than 20 seconds to collect one quart of automatic
transmission fluid, the cooler should be replaced. CAUTION: With the fluid set at the proper level,
fluid collection should not exceed (1) quart or inter-
nal damage to the transmission may occur.
(4) If flow is found to be within acceptable limits,
reconnect the cooler line. Then fill transmission to
the proper level, using the approved type of auto-
matic transmission fluid.
TRANSAXLE REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
Transaxle removal does NOT require engine re-
moval. See Group 7-Cooling, to drain engine cooling sys-
tem and remove coolant return extension (3.0 liter
engine only). (1) The transaxle and torque converter must be re-
moved as an assembly; otherwise, the torque con-
verter drive plate, pump bushing or oil seal may be
damaged. The drive plate will not support a load;
therefore, none of the weight of the transaxle should
be allowed to rest on the drive plate during removal. (2) Disconnect negative battery cable.
(3) Disconnect transaxle shift linkage.
(4) Install engine support fixture and support en-
gine (Fig.1).
(5) Remove upper bell housing upper bolts.
(6) Raise vehicle. Remove front wheels. Refer to
Suspension, Group 2 to remove wheel hub nut and
both drive shafts. (7) Remove left plastic splash to gain access to the
transaxle (Fig. 2). (8) Remove torque converter dust shield to gain ac-
cess to torque converter bolts (Fig. 3). (9) Mark torque converter and drive plate with
chalk, for reassembly. Remove torque converter
mounting bolts. (10) Disconnect electrical connectors at transmis-
sion range switch and Park/Neutral Position Switch
(Fig. 4).
Fig. 7 Cooler Line Location
Fig. 1 Engine Support Fixture (Typical)
Ä TRANSAXLE 21 - 99
Page 2151 of 2438

ponents. Under extremes of suspension and steering
travel tire damage may occur.
WARNING: FAILURE TO EQUIP THE VEHICLE WITH
TIRES HAVING ADEQUATE SPEED RATING CAN
CAUSE SUDDEN TIRE FAILURE.
ROTATION
DIRECTIONAL TREAD PATTERN TIRES
Some vehicles are fitted with special high-perfor-
mance tires having a directional tread pattern de-
signed to improve traction on wet pavement. To obtain the full benefits of this design, the tires
must be installed so that they rotate in the correct
direction. This is indicated by arrows on the tire
sidewalls. When wheels and tires are being installed, extra
care is needed to ensure that this direction of rota-
tion is maintained. Refer to Owner's Manual for rotation schedule.
NONDIRECTIONAL TIRES
Tires on the front and rear axles of vehicles oper-
ate at different loads and perform different steering,
driving, and braking functions. For these reasons,
they wear at unequal rates, and tend to develop ir-
regular wear patterns. These effects can be reduced
by timely rotation of tires. Rotation will increase
tread life, help to maintain mud, snow, and wet trac-
tion levels, and contribute to a smooth, quiet ride. The suggested rotation method is the forward-cross
tire rotation method. This method takes advantage of
current tire industry practice which now allows cross
rotation of radial-ply tires. Refer to the owner's man-
ual (usually found in the glove box) for additional in-
formation. Other rotation methods may be used, but
may not have all the benefits of the recommended
method. Always check air pressure and wheel nut tightness
after rotation. Do NOT use oil or grease on studs
or nuts. Refer to Owner's Manual for rotation schedule.
TREAD WEAR INDICATORS
Tread wear indicators (Fig. 3) are molded into the
bottom of the tread grooves. When tread is 1.6 mm
(1/16 in.), the tread wear indicators will appear as a
13 mm (1/2 in.) band. Tire replacement is necessary when indicators ap-
pear in two or more grooves, or if localized balding
occurs.
REPAIRING LEAKS
For proper repairing, a radial tire must be removed
from the wheel. Repairs should only be made if the
defect or puncture is in the tread area otherwise the
tire should be replaced. Deflate tire completely before dismounting tire
from the wheel. Use lubrication such as a mild soap
solution when dismounting or mounting tire. Use
tools free of burrs or sharp edges which could dam-
age the tire or wheel rim. Before mounting tire on wheel, make sure all rust
scale is removed from the rim and repaint if neces-
sary. Install wheels on vehicle, progressively tightening
wheel nuts to 129 N Im (95 ft. lbs.) torque (See
Wheels).
TIRE NOISE OR VIBRATION
Radial-ply tires are sensitive to force impulses
caused by improper mounting, wheel irregularities,
or imbalance. To determine if the tires are causing the noise or
vibration, drive the vehicle over a smooth portion of
highway at different speeds and note the effect of ac-
celeration and deceleration on noise level. Differen-
tial and exhaust noise will change in intensity as
speed varies, while tire noise will usually remain
constant.
TIRE WEAR PATTERNS
Under inflation results in faster wear on shoulders
of tire. Over inflation causes faster wear at center of tread.
Excessive camber causes the tire to run at an angle
to the road. One side of tread is worn more than the
other. Excessive toe-in or toe-out causes wear on the
tread edges of the tire, from dragging of tire. There
is a feathered effect across the tread (Fig. 4).
Fig. 3 Tread Wear Indicators
Ä WHEELSÐTIRES 22 - 3
Page 2155 of 2438
It is recommended that a two plane dynamic bal-
ancing machine be used when a wheel and tire as-
sembly require balancing. Static balancing should be
used only when a two plane dynamic balancing is not
available. For static imbalance, find location of heavy spot
causing imbalance and counterbalance wheel directly
opposite the heavy spot. Determine weight required
to counterbalance the area of imbalance. Place half
of this weight on the inner rim flange. Then place
the other half on the outer rim flange (Fig. 3). Off-
vehicle balancing is preferred.
TIRE AND WHEEL RUN OUT
Radial run out is the difference between the high
and low points on the tire or wheel periphery. Lateral run out is the wobble of the tire or wheel.
Radial run out of more than 1.5 mm (.060 inch)
measured at the center line of the tread may cause
the vehicle to shake. Lateral run out of more than 2.0 mm (.080 inch)
measured near the shoulder of the tire may cause the
vehicle to shake. Sometimes radial run out can be reduced by relo-
cating the wheel and tire assembly on the mounting
studs (See Method 1). If this does not reduce run out
to an acceptable level, the tire can be rotated on the
wheel. (See Method 2).
METHOD 1 (RELOCATE WHEEL ON HUB)
Check accuracy of the wheel mounting surface;ad-
just wheel bearings. Drive vehicle a short distance to eliminate tire flat
spotting from a parked position. Make sure all wheel nuts are properly torqued
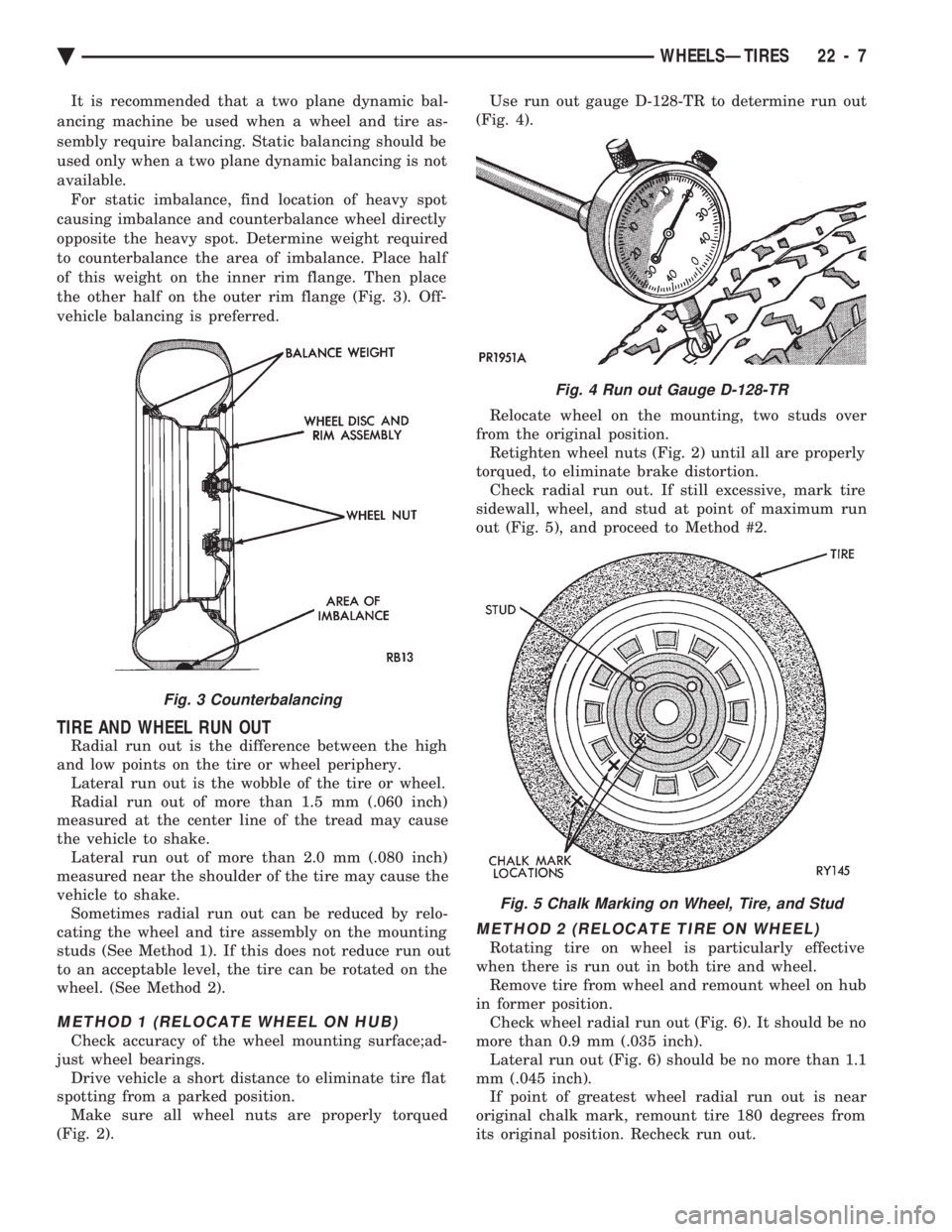
(Fig. 2). Use run out gauge D-128-TR to determine run out
(Fig. 4).
Relocate wheel on the mounting, two studs over
from the original position. Retighten wheel nuts (Fig. 2) until all are properly
torqued, to eliminate brake distortion. Check radial run out. If still excessive, mark tire
sidewall, wheel, and stud at point of maximum run
out (Fig. 5), and proceed to Method #2.
METHOD 2 (RELOCATE TIRE ON WHEEL)
Rotating tire on wheel is particularly effective
when there is run out in both tire and wheel. Remove tire from wheel and remount wheel on hub
in former position. Check wheel radial run out (Fig. 6). It should be no
more than 0.9 mm (.035 inch). Lateral run out (Fig. 6) should be no more than 1.1
mm (.045 inch). If point of greatest wheel radial run out is near
original chalk mark, remount tire 180 degrees from
its original position. Recheck run out.
Fig. 3 Counterbalancing
Fig. 4 Run out Gauge D-128-TR
Fig. 5 Chalk Marking on Wheel, Tire, and Stud
Ä WHEELSÐTIRES 22 - 7