CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Service Manual
Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 1291 of 1938
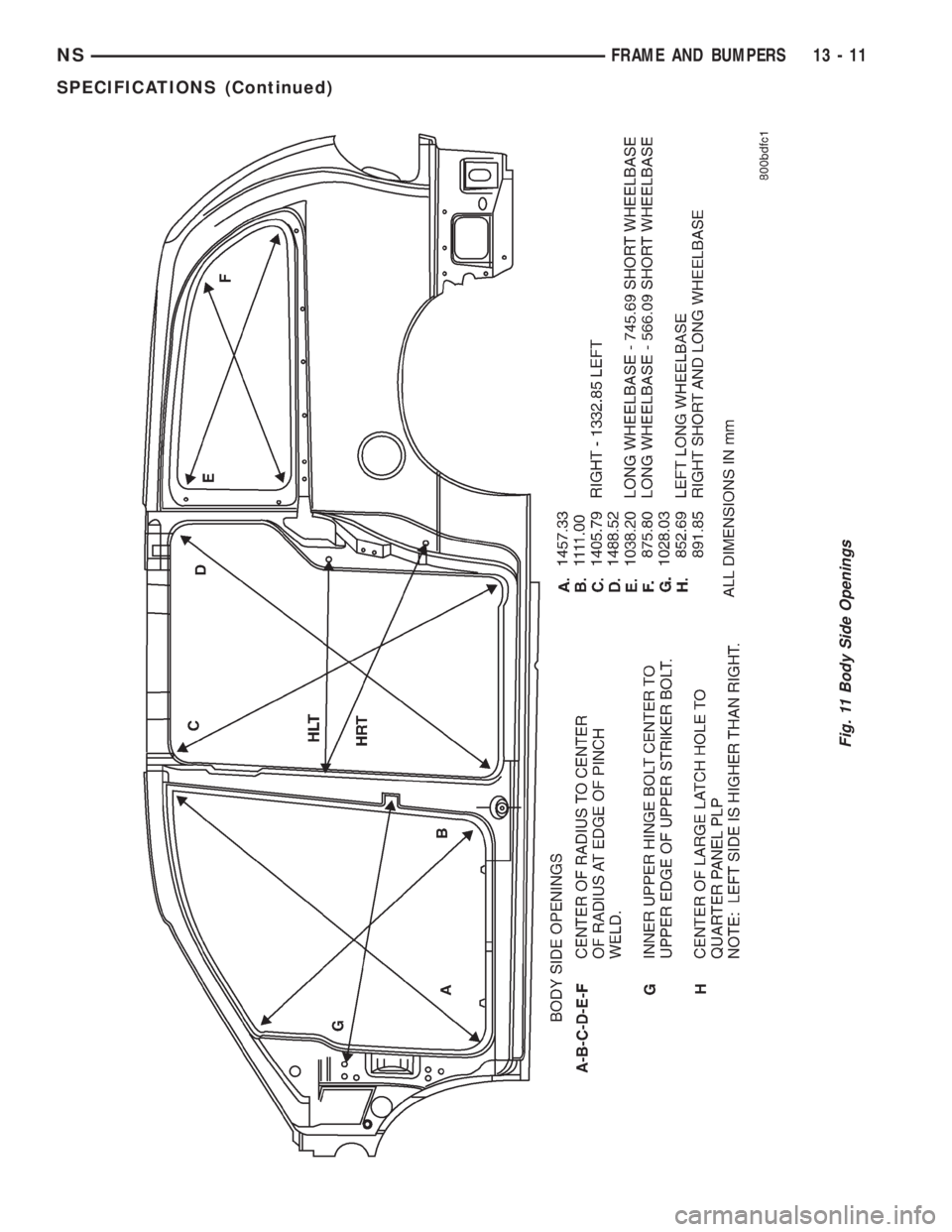
Fig. 11 Body Side Openings
NSFRAME AND BUMPERS 13 - 11
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 1292 of 1938

Page 1293 of 1938
FRAME AND BUMPERS
CONTENTS
page
FRAME................................ 1
FRAME
INDEX
page page
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
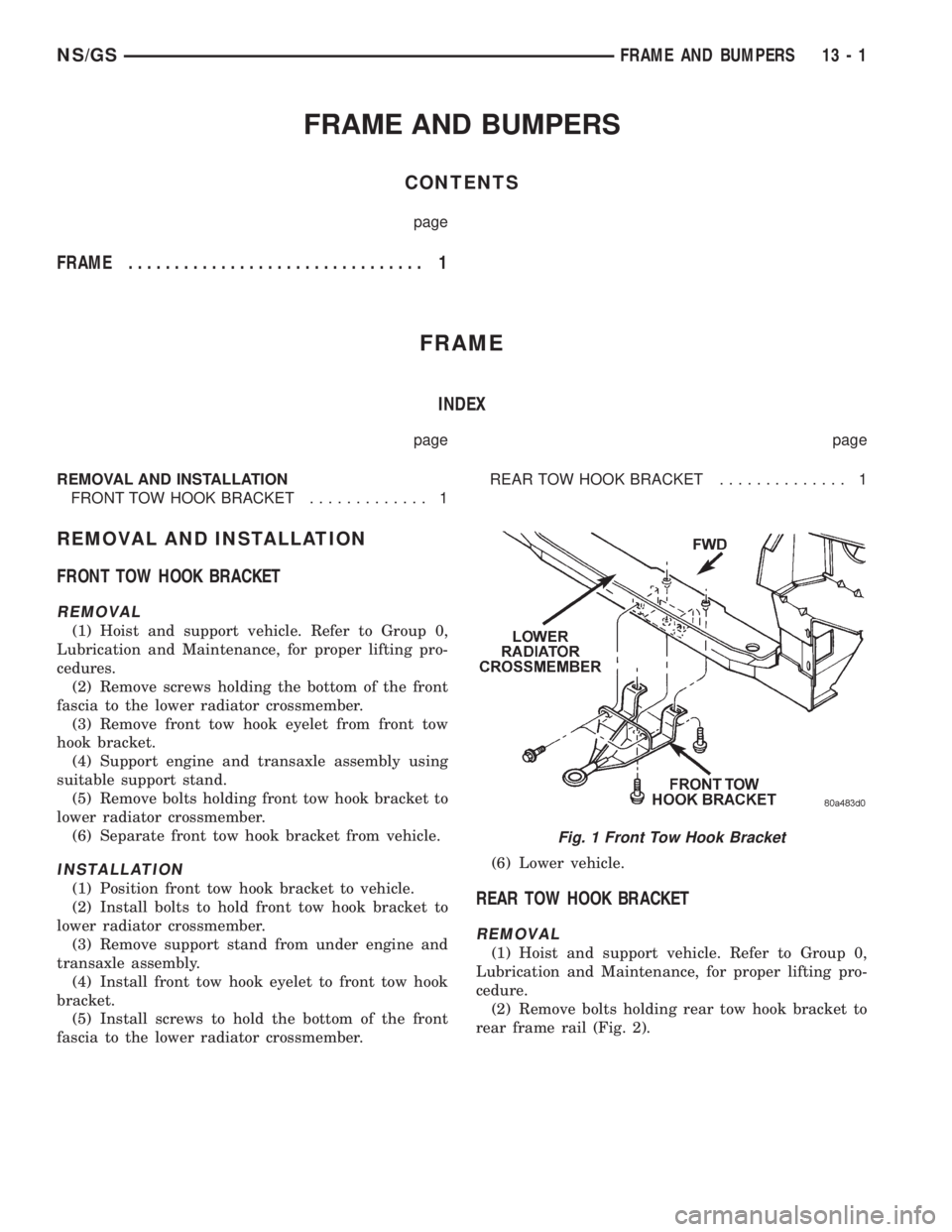
FRONT TOW HOOK BRACKET............. 1REAR TOW HOOK BRACKET.............. 1
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
FRONT TOW HOOK BRACKET
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle. Refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance, for proper lifting pro-
cedures.
(2) Remove screws holding the bottom of the front
fascia to the lower radiator crossmember.
(3) Remove front tow hook eyelet from front tow
hook bracket.
(4) Support engine and transaxle assembly using
suitable support stand.
(5) Remove bolts holding front tow hook bracket to
lower radiator crossmember.
(6) Separate front tow hook bracket from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position front tow hook bracket to vehicle.
(2) Install bolts to hold front tow hook bracket to
lower radiator crossmember.
(3) Remove support stand from under engine and
transaxle assembly.
(4) Install front tow hook eyelet to front tow hook
bracket.
(5) Install screws to hold the bottom of the front
fascia to the lower radiator crossmember.(6) Lower vehicle.REAR TOW HOOK BRACKET
REMOVAL
(1) Hoist and support vehicle. Refer to Group 0,
Lubrication and Maintenance, for proper lifting pro-
cedure.
(2) Remove bolts holding rear tow hook bracket to
rear frame rail (Fig. 2).
Fig. 1 Front Tow Hook Bracket
NS/GSFRAME AND BUMPERS 13 - 1
Page 1294 of 1938
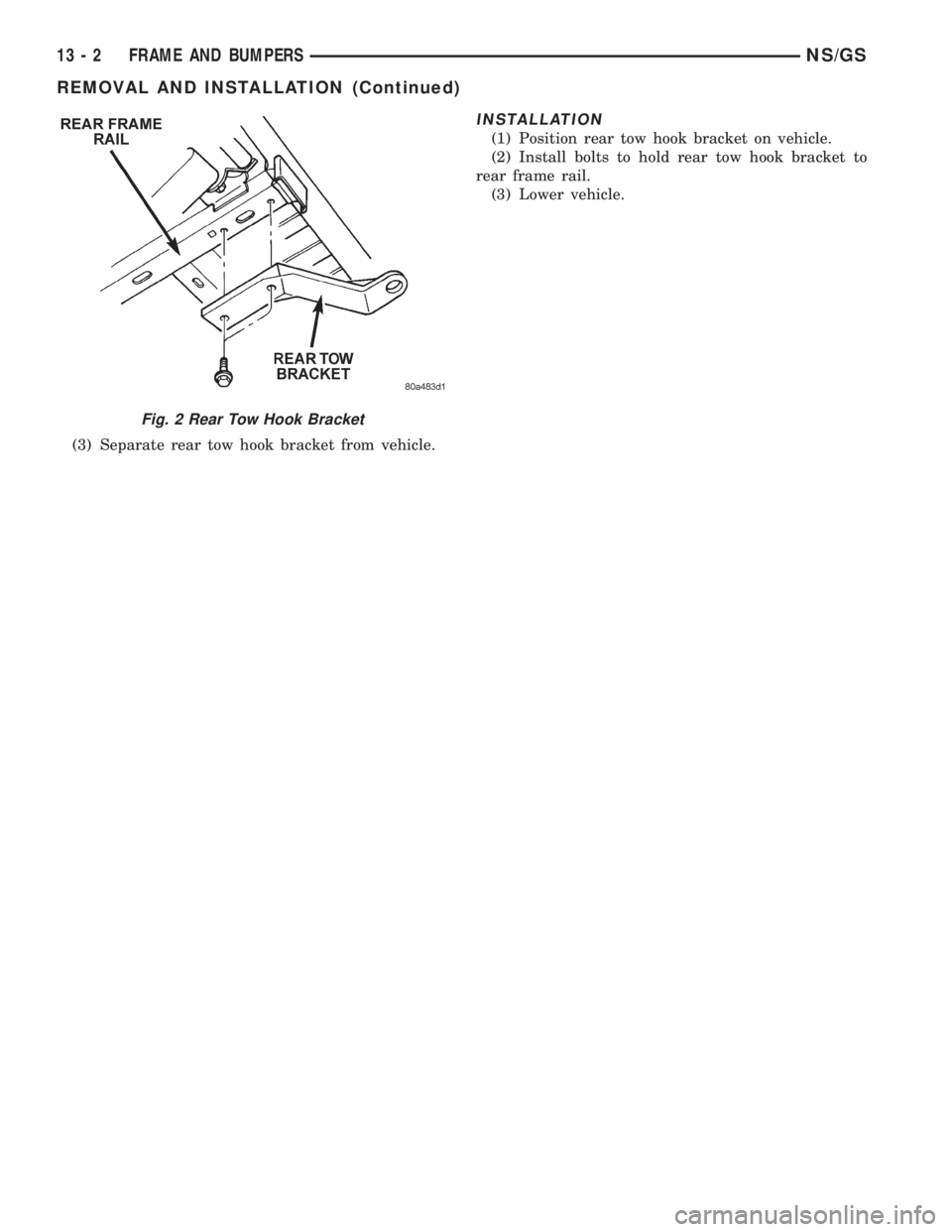
(3) Separate rear tow hook bracket from vehicle.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position rear tow hook bracket on vehicle.
(2) Install bolts to hold rear tow hook bracket to
rear frame rail.
(3) Lower vehicle.
Fig. 2 Rear Tow Hook Bracket
13 - 2 FRAME AND BUMPERSNS/GS
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 1295 of 1938

FUEL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM................... 4
FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM................. 29GENERAL INFORMATION................... 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
CRUISING RANGE........................ 3
E-85 GENERAL INFORMATION.............. 2
ETHANOL FUEL (E-85).................... 2
FUEL REQUIREMENTS.................... 1
FUEL REQUIREMENTS.................... 2GASOLINE/OXYGENATE BLENDS............ 2
INTRODUCTION......................... 1
PCM REPLACEMENT..................... 1
REPLACEMENT PARTS.................... 3
STARTING.............................. 2
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
Throughout this group, references may be made to
a particular vehicle by letter or number designation.
A chart showing the breakdown of these designations
is included in the Introduction Section at the front of
this service manual.
The Evaporation Control System, is also considered
part of the fuel system. The system reduces the emis-
sion of fuel vapor into the atmosphere.
The description and function of the Evaporation
Control System is found in Group 25 of this manual.
PCM REPLACEMENT
USE THE DRB SCAN TOOL TO REPROGRAM
THE NEW PCM WITH THE VEHICLES ORIGI-
NAL IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) AND
THE VEHICLES ORIGINAL MILEAGE. IF THIS
STEP IS NOT DONE A DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODE (DTC) MAY BE SET.
FUEL REQUIREMENTS
Your vehicle was designed to meet all emission reg-
ulations and provide excellent fuel economy when
using high quality unleaded gasoline.
Use unleaded gasolines having a minimum posted
octane of 87.
If your vehicle develops occasional light spark
knock (ping) at low engine speeds this is not harm-
ful. However; continued heavy knock at high speeds
can cause damage and should be reported to your
dealer immediately. Engine damage as a result of
heavy knock operation may not be covered by the
new vehicle warranty.
In addition to using unleaded gasoline with the
proper octane rating, those that contain detergents,
corrosion and stability additives are recommended.
Using gasolines that have these additives will help
improve fuel economy, reduce emissions, and main-
tain vehicle performance.
Poor quality gasoline can cause problems such as
hard starting, stalling, and stumble. If you experi-
ence these problems, try another brand of gasoline
before considering service for the vehicle.
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 1
Page 1296 of 1938

GASOLINE/OXYGENATE BLENDS
Some fuel suppliers blend unleaded gasoline with
materials that contain oxygen such as alcohol, MTBE
(Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) and ETBE (Ethyl Ter-
tiary Butyl Ether). Oxygenates are required in some
areas of the country during winter months to reduce
carbon monoxide emissions. The type and amount of
oxygenate used in the blend is important.
The following are generally used in gasoline
blends:
Ethanol- (Ethyl or Grain Alcohol) properly
blended, is used as a mixture of 10 percent ethanol
and 90 percent gasoline. Gasoline blended with etha-
nol may be used in your vehicle.
MTBE/ETBE- Gasoline and MTBE (Methyl Ter-
tiary Butyl Ether) blends are a mixture of unleaded
gasoline and up to 15 percent MTBE. Gasoline and
ETBE (Ethyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) are blends of gas-
oline and up to 17 percent ETBE. Gasoline blended
with MTBE or ETBE may be used in your vehicle.
Methanol- Methanol (Methyl or Wood Alcohol) is
used in a variety of concentrations blended with
unleaded gasoline. You may encounter fuels contain-
ing 3 percent or more methanol along with other
alcohols called cosolvents.
DO NOT USE GASOLINES CONTAINING
METHANOL.
Use of methanol/gasoline blends may result in
starting and driveability problems and damage criti-
cal fuel system components.
Problems that are the result of using methanol/
gasoline blends are not the responsibility of Chrysler
Corporation and may not be covered by the vehicle
warranty.
Reformulated Gasoline
Many areas of the country are requiring the use of
cleaner-burning fuel referred to asReformulated
Gasoline. Reformulated gasolines are specially
blended to reduce vehicle emissions and improve air
quality.
Chrysler Corporation strongly supports the use of
reformulated gasolines whenever available. Although
your vehicle was designed to provide optimum perfor-
mance and lowest emissions operating on high qual-
ity unleaded gasoline, it will perform equally well
and produce even lower emissions when operating on
reformulated gasoline.
Materials Added to Fuel
Indiscriminate use of fuel system cleaning agents
should be avoided. Many of these materials intended
for gum and varnish removal may contain active sol-
vents of similar ingredients that can be harmful to
fuel system gasket and diaphragm materials.
E-85 GENERAL INFORMATION
The information in this section is for Flexible Fuel
Vehicles (FFV) only. These vehicles can be identified
by the unique Fuel Filler Door Label that states
Ethanol (E-85) or Unleaded Gasoline Only. This sec-
tion only covers those subjects that are unique to
these vehicles. Please refer to the other sections of
this manual for information on features that are
common between Flexible Fuel and gasoline only
powered vehicles.
ETHANOL FUEL (E-85)
E-85 is a mixture of approximately 85% fuel etha-
nol and 15% unleaded gasoline.
WARNING: Ethanol vapors are extremely flammable
and could cause serious personal injury. Never
have any smoking materials lit in or near the vehi-
cle when removing the fuel filler tube cap (gas cap)
or filling the tank. Do not use E-85 as a cleaning
agent and never use it near an open flame.
FUEL REQUIREMENTS
Your vehicle will operate on both unleaded gasoline
with an octane rating of 87, or E-85 fuel, or any mix-
ture of these two.
For best results, a refueling pattern that alternates
between E-85 and unleaded gasoline should be
avoided. When you do switch fuels, it is recom-
mended that
²you do not switch when the fuel gauge indicates
less than 1/4 full
²you do not add less than 5 gallons when refuel-
ing
²you operate the vehicle immediately after refuel-
ing for a period of at least 5 minutes
Observing these precautions will avoid possible
hard starting and/or significant deterioration in driv-
ability during warm up.
NOTE: When the ambient temperature is above
90ÉF, you may experience hard starting and rough
idle following start up even if the above recommen-
dations are followed.
STARTING
The characteristics of E-85 fuel make it unsuitable
for use when ambient temperatures fall below 0ÉF. In
the range of 0ÉF to 32ÉF, you may experience an
increase in the time it takes for your engine to start,
and a deterioration in drivability (sags and/or hesita-
tions) until the engine is fully warmed up.
14 - 2 FUEL SYSTEMNS
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1297 of 1938

CRUISING RANGE
Because E-85 fuel contains less energy per gallon
than gasoline, you will experience an increase in fuel
consumption. You can expect your MPG and your
driving range to decrease by about 30% compared to
gasoline operation.
REPLACEMENT PARTS
Many components in your Flexible Fuel Vehicle
(FFV) are designed to be compatible with ethanol.Always be sure that your vehicle is serviced with cor-
rect ethanol compatible parts.
CAUTION: Replacing fuel system components with
non-ethanol compatible components can damage
your vehicle and may void the warranty.
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 1298 of 1938

FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
INDEX
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM.................. 4
FUEL INJECTORS........................ 5
FUEL LEVEL SENSOR..................... 5
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR.............. 5
FUEL PUMP MODULE..................... 4
FUEL TANK............................. 5
PRESSURE-VACUUM FILLER CAP........... 6
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS................ 6
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
FUEL INJECTORS........................ 9
FUEL LEVEL SENSOR..................... 9
FUEL PUMP PRESSURE TEST 2.4/3.3/3.8L..... 6
SERVICE PROCEDURES
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDUREÐ2.4/3.3/3.8L............... 11
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDUREÐ3.0L ENGINE............. 11
HOSES AND CLAMPS.................... 12QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS............... 12
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ACCELERATOR PEDAL................... 26
FUEL FILTER........................... 12
FUEL INJECTOR RAILÐ2.4L............... 18
FUEL INJECTOR RAILÐ3.0L............... 19
FUEL INJECTOR RAILÐ3.3/3.8L............ 21
FUEL INJECTORSÐ3.0L.................. 25
FUEL INJECTORÐ2.4L................... 24
FUEL INJECTORÐ3.3/3.8L................. 26
FUEL LEVEL SENSOR.................... 15
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR............. 14
FUEL PUMP INLET STRAINER............. 15
FUEL PUMP MODULE.................... 13
FUEL TANK............................ 17
THROTTLE CABLE...................... 27
SPECIFICATIONS
FUEL TANK CAPACITY................... 28
TORQUE.............................. 28
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
The front wheel drive van uses a plastic fuel tank
located on the left side of the vehicle.
The Fuel Delivery System consists of: the electric
fuel pump module, fuel filter, tubes/lines/hoses, fuel
rail, and fuel injectors.
The in-tank fuel pump module contains the fuel
pump and pressure regulator. The pump is serviced
as part of the fuel pump module. Refer to Fuel Pump
Module.
The fuel filter is a replaceable in-line filter. The fil-
ter attaches to a bracket mounted on top of the fuel
tank. Refer to the Maintenance Schedules in the
Introduction section of this manual for recommended
fuel filter replacement intervals.
A returnless fuel system is used on all vehicles.
Fuel is returned through the fuel pump module and
back to the fuel tank. A separate fuel return line
from the tank to the engine is no longer used.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
The fuel pump module is installed in the top of the
fuel tank (Fig. 1). The fuel pump module contains the
following:
²Electric fuel pump
²Fuel pump reservoir
²Inlet strainer²Fuel pressure regulator
²Fuel gauge sending unit
²Fuel supply line connection
The inlet strainer, fuel pressure regulator
and fuel level sensor are the only serviceable
items. If the fuel pump or electrical wiring har-
ness requires service, replace the fuel pump
module.
ELECTRIC FUEL PUMP
The electric fuel pump is located in and is part of
the fuel pump module. It is a positive displacement,
gerotor type, immersible pump with a permanent
magnet electric motor. The pump draws fuel through
a strainer and pushes it through the motor to the
outlet. The pump contains one check valve. The
Fig. 1 Fuel Pump Module
14 - 4 FUEL SYSTEMNS
Page 1299 of 1938

check valve, in the pump outlet, maintains pump
pressure during engine off conditions. The fuel pump
relay provides voltage to the fuel pump.
The fuel pump has a maximum deadheaded pres-
sure output of approximately 635 kPa (95 psi). The
regulator adjusts fuel system pressure to approxi-
mately 338 kPa (49 psi).
FUEL PUMP ELECTRICAL CONTROL
Voltage to operate the electric pump is supplied
through the fuel pump relay. For an electrical opera-
tional description of the fuel pump refer to fuel Pump
RelayÐPCM Output.
ELECTRICAL PUMP REPLACEMENT
The electric fuel pump is not serviceable. If the
fuel pump or electrical wiring harness needs replace-
ment, the complete fuel pump module must be
replaced. Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release
procedure before servicing the fuel pump.
FUEL LEVEL SENSOR
The level sensor is attached to the side of the fuel
pump module. The level sensor consists of a float, an
arm, and a variable resistor. As the fuel level
increases, the float and arm move up. This decreases
the sending unit resistance, causing the fuel gauge
on the instrument panel to read full.
FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
The fuel system uses a nonadjustable pressure reg-
ulator that maintains fuel system pressure at
approximately 338 kPa (49 psi), 3.3l uses approxi-
mately 379 kPa (55 psi). The fuel pressure regulator
contains a diaphragm, calibrated spring and a fuel
return valve. The spring pushes down on the dia-
phragm and closes off the fuel return port. System
fuel pressure reflects the amount of fuel pressure
required to open the return port.
The pressure regulator is a mechanical device that
is NOT controlled by the PCM or engine vacuum.
FUEL INJECTORS
The fuel injectors are 12 ohm electrical solenoids
(Fig. 2). The injector contains a pintle that closes off
an orifice at the nozzle end. When electric current is
supplied to the injector, the armature and needle
move a short distance against a spring, allowing fuel
to flow out the orifice. Because the fuel is under high
pressure, a fine spray is developed in the shape of a
hollow cone. The spraying action atomizes the fuel,
adding it to the air entering the combustion chamber.
The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold.
Fuel injectors are not interchangeable between
engines.The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold
with the nozzle ends directly above the intake valve
port (Fig. 3).
FUEL TANK
The fuel tanks of all Chrysler Motors built vehicles
are equipped with fuel and vapor controls that allow
the vehicle to pass a full 360É rollover without fuel
leakage.
Front Wheel Drive fuel delivery systems contain a
fuel tank rollover valve. The valve is mounted on top
of the fuel tank. The valve functions as a tank pres-
sure control valve while the vehicle is upright, but
contains a check valve that prevents fuel from escap-
ing from the fuel tank when the vehicle is turned
over.
The fuel filler cap acts as a pressure/vacuum relief
valve. When air pressure inside the fuel tank gets too
high or too low, the fuel filler cap opens to relieve the
difference in pressure.
An evaporation control system restricts fuel evapo-
ration into the atmosphere and reduces unburned
Fig. 2 Fuel Injector
Fig. 3 Fuel Injector LocationÐTypical
NSFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 1300 of 1938
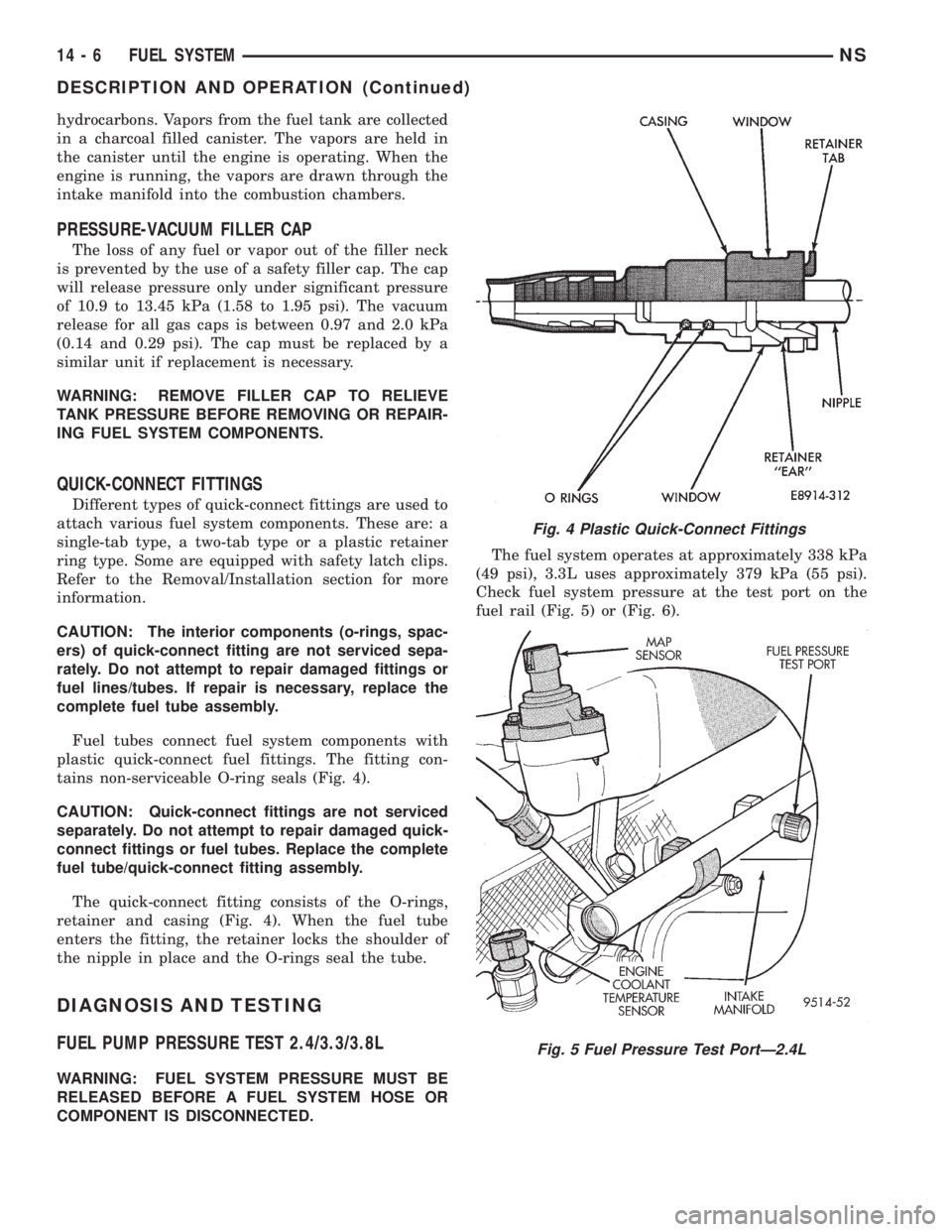
hydrocarbons. Vapors from the fuel tank are collected
in a charcoal filled canister. The vapors are held in
the canister until the engine is operating. When the
engine is running, the vapors are drawn through the
intake manifold into the combustion chambers.
PRESSURE-VACUUM FILLER CAP
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of the filler neck
is prevented by the use of a safety filler cap. The cap
will release pressure only under significant pressure
of 10.9 to 13.45 kPa (1.58 to 1.95 psi). The vacuum
release for all gas caps is between 0.97 and 2.0 kPa
(0.14 and 0.29 psi). The cap must be replaced by a
similar unit if replacement is necessary.
WARNING: REMOVE FILLER CAP TO RELIEVE
TANK PRESSURE BEFORE REMOVING OR REPAIR-
ING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components. These are: a
single-tab type, a two-tab type or a plastic retainer
ring type. Some are equipped with safety latch clips.
Refer to the Removal/Installation section for more
information.
CAUTION: The interior components (o-rings, spac-
ers) of quick-connect fitting are not serviced sepa-
rately. Do not attempt to repair damaged fittings or
fuel lines/tubes. If repair is necessary, replace the
complete fuel tube assembly.
Fuel tubes connect fuel system components with
plastic quick-connect fuel fittings. The fitting con-
tains non-serviceable O-ring seals (Fig. 4).
CAUTION: Quick-connect fittings are not serviced
separately. Do not attempt to repair damaged quick-
connect fittings or fuel tubes. Replace the complete
fuel tube/quick-connect fitting assembly.
The quick-connect fitting consists of the O-rings,
retainer and casing (Fig. 4). When the fuel tube
enters the fitting, the retainer locks the shoulder of
the nipple in place and the O-rings seal the tube.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
FUEL PUMP PRESSURE TEST 2.4/3.3/3.8L
WARNING: FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE MUST BE
RELEASED BEFORE A FUEL SYSTEM HOSE OR
COMPONENT IS DISCONNECTED.The fuel system operates at approximately 338 kPa
(49 psi), 3.3L uses approximately 379 kPa (55 psi).
Check fuel system pressure at the test port on the
fuel rail (Fig. 5) or (Fig. 6).
Fig. 4 Plastic Quick-Connect Fittings
Fig. 5 Fuel Pressure Test PortÐ2.4L
14 - 6 FUEL SYSTEMNS
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)