torque CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996 Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: CHRYSLER, Model Year: 1996, Model line: VOYAGER, Model: CHRYSLER VOYAGER 1996Pages: 1938, PDF Size: 55.84 MB
Page 2 of 1938

FOREWORD
The information contained in this service manual has been prepared for the professional automotive tech-
nician involved in daily repair operations. This manual does not cover theory of operation, which is addressed
in service training material. Information describing the operation and use of standard and optional equipment
is included in the Owner 's Manual provided with the vehicle.
Information in this manual is divided into groups. These groups contain general information, diagnosis,
testing, adjustments, removal, installation, disassembly, and assembly procedures for the systems and compo-
nents. To assist in locating a group title page, use the Group Tab Locator on the following page. The solid bar
after the group title is aligned to a solid tab on the first page of each group. The first page of the group has
a contents section that lists major topics within the group. If you are not sure which Group contains the infor-
mation you need, look up the Component/System in the alphabetical index located in the rear of this manual.
Tightening torques are provided as a specific value throughout this manual. This value represents the
midpoint of the acceptable engineering torque range for a given fastener application. These torque values are
intended for use in service assembly and installation procedures using the correct OEM fasteners. When
replacing fasteners, always use the same type (part number) fastener as removed.
Chrysler International reserves the right to change testing procedures, specifications, diagnosis, repair
methods, or vehicle wiring at any time without prior notice or incurring obligation.
Page 4 of 1938

INTRODUCTION
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
BODY CODE PLATE...................... 1
FASTENER IDENTIFICATION................ 4
INTERNATIONAL VEHICLE CONTROL AND
DISPLAY SYMBOLS..................... 4METRIC SYSTEM........................ 7
TORQUE REFERENCES................... 7
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER.......... 1
VEHICLE SAFETY CERTIFICATION LABEL..... 1
VIN CHECK DIGIT........................ 1
GENERAL INFORMATION
VEHICLE SAFETY CERTIFICATION LABEL
A vehicle safety certification label (Fig. 1) is located
on the rear shut face of the driver's door. This label
indicates date of manufacture (month and year),
Gross Vehicle Weight Rating (GVWR), Gross Axle
Weight Rating (GAWR) front, Gross Axle Weight Rat-
ing (GAWR) rear and the Vehicle Identification Num-
ber (VIN). The Month, Day and Hour of manufacture
is also included.
When it is necessary to contact the manufacturer
regarding service or warranty, the information on the
Vehicle Safety Certification Label would be required.
VEHICLE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER
The Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) can be
viewed through the windshield at the upper left cor-
ner of the instrument panel, near the left windshield
pillar (Fig. 2). The VIN consists of 17 characters in a
combination of letters and numbers that provide spe-
cific information about the vehicle. Refer to VIN
Code Breakdown Chart for decoding information.
VIN CHECK DIGIT
To protect the consumer from theft and possible
fraud, the manufacturer is required to include a
Check Digit at the ninth position of the Vehicle Iden-
tification Number. The check digit is used by the
manufacturer and government agencies to verify the
authenticity of the vehicle and official documenta-
tion. The formula to use the check digit is not
released to the general public.
BODY CODE PLATE
LOCATION AND DECODING
The Body Code Plate (Fig. 3) is located in the
engine compartment on the radiator closure panel
crossmember. There are seven lines of information on
the body code plate. Lines 4, 5, 6, and 7 are not used
to define service information. Information reads from
left to right, starting with line 3 in the center of the
plate to line 1 at the bottom of the plate.Fig. 1 Vehicle Safety Certification Label
Fig. 2 Vehicle Identification Number (VIN Plate)
NSINTRODUCTION 1
Page 10 of 1938

METRIC SYSTEM
WARNING: USE OF AN INCORRECT FASTENER
MAY RESULT IN COMPONENT DAMAGE OR PER-
SONAL INJURY.
Figure art, specifications and torque references in
this Service Manual are identified in metric and SAE
format.
During any maintenance or repair procedures, it is
important to salvage metric fasteners (nuts, bolts,
etc.) for reassembly. If the fastener is not salvage-
able, a fastener of equivalent specification should be
used.
The metric system is based on quantities of one,
ten, one hundred, one thousand and one million (Fig.
6).
The following chart will assist in converting metric
units to equivalent English and SAE units, or vise
versa.
Refer to the Conversion Chart to convert torque
values listed in metric Newton- meters (N´m). Also,
use the chart to convert between millimeters (mm)
and inches (in.)
TORQUE REFERENCES
Individual Torque Charts appear at the end of
many Groups. Refer to the Standard Torque Specifi-
cations Chart for torque references not listed in the
individual torque charts.
Fig. 6 Metric Prefixes
CONVERSION FORMULAS AND EQUIVALENT VALUES
NSINTRODUCTION 7
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 12 of 1938
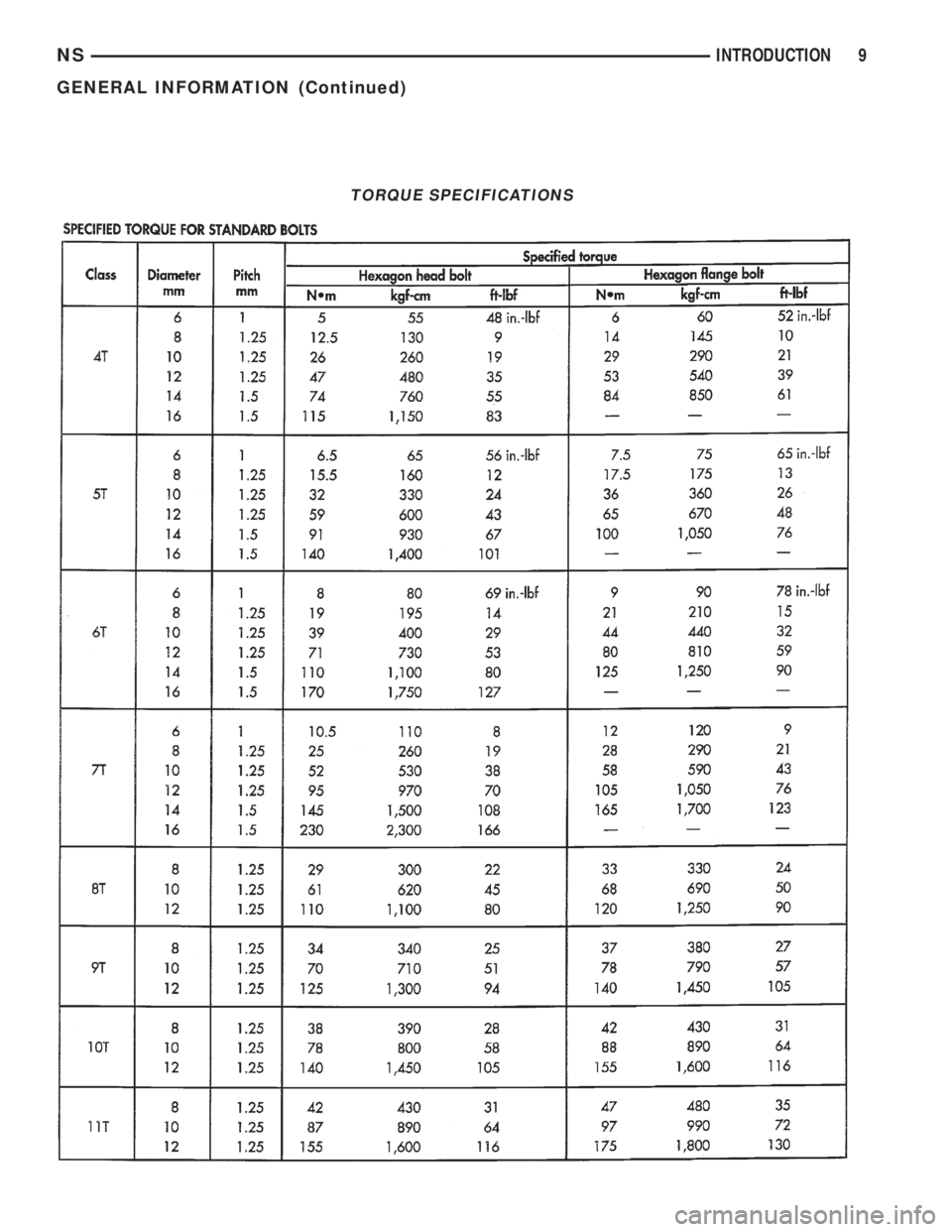
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
NSINTRODUCTION 9
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 24 of 1938

DISCONNECT CABLE CLAMPS AS FOLLOWS:
²Disconnect BLACK cable clamp from engine
ground on disabled vehicle.
²When using a Booster vehicle, disconnect
BLACK cable clamp from battery negative terminal.
Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery positive
terminal.
²Disconnect RED cable clamp from battery posi-
tive terminal on disabled vehicle.
TOWING RECOMMENDATIONS
WARNINGS AND CAUTIONS
WARNING: DO NOT ALLOW TOWING ATTACH-
MENT DEVICES TO CONTACT THE FUEL TANK OR
LINES, FUEL LEAK CAN RESULT.
DO NOT LIFT OR TOW VEHICLE BY FRONT OR
REAR BUMPER, OR BUMPER ENERGY ABSORBER
UNITS.
DO NOT GO UNDER A LIFTED VEHICLE IF NOT
SUPPORTED PROPERLY ON SAFETY STANDS.
DO NOT ALLOW PASSENGERS TO RIDE IN A
TOWED VEHICLE.
USE A SAFETY CHAIN THAT IS INDEPENDENT
FROM THE TOWING ATTACHMENT DEVICE.
CAUTION: Do not damage brake lines, exhaust sys-
tem, shock absorbers, sway bars, or any other
under vehicle components when attaching towing
device to vehicle.
Do not attach towing device to front or rear sus-
pension components.
Do not secure vehicle to towing device by the use
of front or rear suspension or steering components.
Remove or secure loose or protruding objects
from a damaged vehicle before towing.
Refer to state and local rules and regulations
before towing a vehicle.
Do not allow weight of towed vehicle to bear on
lower fascia, air dams, or spoilers.
RECOMMENDED TOWING EQUIPMENT
To avoid damage to bumper fascia and air dams
use of a flat bed towing device or wheel lift (Fig. 2) is
recommended. When using a wheel lift towing device,
be sure the disabled vehicle has at least 100 mm (4
in.) ground clearance. If minimum ground clearance
cannot be reached, use a towing dolly. If a flat bed
device is used, the approach angle should not exceed
15 degrees.
GROUND CLEARANCE
CAUTION: If vehicle is towed with wheels
removed, install lug nuts to retain brake drums or
rotors.
A towed vehicle should be raised until the lifted
wheels are a minimum 100 mm (4 in.) from the
ground. Be sure there is at least 100 mm (4 in.)
clearance between the tail pipe and the ground. If
necessary, remove the wheels from the lifted end of
the vehicle and lower the vehicle closer to the
ground, to increase the ground clearance at the rear
of the vehicle. Install lug nuts on wheel attaching
studs to retain brake drums or rotors.
LOCKED VEHICLE TOWING
When a locked vehicle must be towed with the
front wheels on the ground, use a towing dolly or flat
bed hauler.
FLAT TOWING WITH TOW BAR
²3-speed automatic transaxle vehicles can be flat
towed at speeds not to exceed 40 km/h (25 mph) for
not more than 25 km (15 miles). The steering column
must be unlocked and gear selector in neutral.
²4-speed electronic automatic transaxle vehicles
can be flat towed at speeds not to exceed 72 km/h (44
mph) for not more than 160 km (100 miles). The
steering column must be unlocked and gear selector
in neutral.
FLAT BED TOWING TIE DOWNS
CAUTION: Do not tie vehicle down by attaching
chains or cables to suspension components or
engine mounts, damage to vehicle can result.
NS vehicles can be tied to a flat bed device using
the reinforced loops located under the front and rear
bumpers on the drivers side of the vehicle. There are
also four reinforced elongated holes for T or R-hooks
located on the bottom of the front frame rail torque
Fig. 2 Recommended Towing Devices
0 - 8 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCENS
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 28 of 1938

MAINTENANCE SCHEDULES
INDEX
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE............... 2
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULEÐ
DIESEL ENGINE....................... 2SCHEDULEÐA (DIESEL).................. 2
SCHEDULEÐB (DIESEL).................. 3
UNSCHEDULED INSPECTION.............. 2
GENERAL INFORMATION
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULE
Refer to the 1998 GS Service Manual for Gasoline
Engine and non-engine related Maintenance Sched-
ules.
MAINTENANCE SCHEDULEÐDIESEL ENGINE
The following are engine related Maintenance
items which are unique to Diesel engine-equipped
vehicles. Refer to the 1998 GS Service Manual for
Gasoline Engine and non-engine related Maintenance
Schedules.
The service intervals are based on odometer read-
ings in kilometers. There are two maintenance sched-
ules that show proper service intervals. Use the
schedule that best describes the conditions the vehi-
cle is operated under.Schedule-Alists all the sched-
uled maintenance to be performed under normal
operating conditions.Schedule-Bis the schedule for
vehicles that are operated under one or more of the
following conditions:
²Day and night temperatures are below freezing.
²Stop and go driving.
²Long periods of engine idling.
²Driving in dusty conditions.
²Short trips of less than 5 miles.
²Operation at sustained high speeds during hot
weather above 32ÉC (90ÉF).
²Taxi, police or delivery service.
²Trailer towing.
UNSCHEDULED INSPECTION
At Each Stop for Fuel
²Check engine oil level, add as required.
²Check windshield washer solvent and add if
required.
Once a Month
²Check tire pressure and look for unusual wear
or damage.
²Inspect battery and clean and tighten terminals
as required.²Check fluid levels of coolant reservoir, brake
master cylinder, power steering and transaxle and
add as needed.
²Check all lights and all other electrical items for
correct operation.
²Check rubber seals on each side of the radiator
for proper fit.
At Each Oil Change
²Inspect exhaust system.
²Inspect brake hoses
²Inspect the CV joints and front suspension com-
ponents
²Rotate the tires at each oil change interval
shown on ScheduleÐA (7,500 miles) or every other
interval shown on ScheduleÐ B (6,000 miles).
²Check the coolant level, hoses, and clamps.
²If your mileage is less than 7,500 miles (12 000
km) yearly, replace the engine oil filter at each oil
change.
²Replace engine oil filter.
SCHEDULEÐA (DIESEL)
1 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Check all fluid levels.
²Check correct torque, intake manifold mounting
nuts.
²Check correct torque, exhaust manifold mount-
ing nuts.
²Check correct torque, turbocharger mounting
nuts.
²Check correct torque, water manifold bolts.
10 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
20 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
0 - 2 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCENS/GS
Page 29 of 1938

²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
30 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
40 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element.**
50 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
60 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check glow plug operation.
²Replace drive belt.
²Check engine smoke.
²Replace engine coolant.
70 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
80 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element.**
90 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
100 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
EVERY 40 000 KM AFTER 80 000 KM
²Replace fuel filter/water separator element.**
**The fuel filter/water separator element should be
replaced once a year if the vehicle is driven less than
40 000 km annually or if power loss from fuel star-
vation is detected.
EVERY 10 000 KM AFTER 100 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
EVERY 20 000 KM AFTER 100 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
SCHEDULEÐB (DIESEL)
500 KM
²Check correct torque, intake manifold mounting
nuts.
²Check correct torque, exhaust manifold mount-
ing nuts.
²Check correct torque, turbocharger mounting
nuts.
²Check correct torque, water manifold bolts.
1 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Check all fluid levels.
5 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
10 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
15 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
20 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
²Check drive belt tension.
²Check glow plug operation.
25 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
30 000 KM
²Change engine oil.
²Change engine oil filter.
²Replace air filter element.
NS/GSLUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCE 0 - 3
GENERAL INFORMATION (Continued)
Page 32 of 1938

NS vehicles can be tied to a flat bed device using
the reinforced loops located under the front and rear
bumpers on the drivers side of the vehicle. There are
also four reinforced elongated holes for T or R-hooks
located on the bottom of the front frame rail torque
boxes behind the front wheels and forward of the
rear wheels inboard of the rocker panel weld seam.
TOWINGÐFRONT WHEEL LIFT
Chrysler International recommends that a vehicle
be towed with the front end lifted, whenever possible.
A 90 cm (36 in.) length of 4x4 wood beam can be
placed between the wheel lift device and the bottom
of the fascia to prevent damage to vehicle during the
lifting operation. The beam can removed after lifting
the front of the vehicle.
TOWINGÐREAR WHEEL LIFT
If a vehicle cannot be towed with the front wheels
lifted, the rear wheels can be lifted provided the fol-
lowing guide lines are observed.
CAUTION: Do not use steering column lock to
secure steering wheel during towing operation.
²On AWD vehicles, all four wheels must be free to
rotate. Use towing dollies at unlifted end of vehicle.
²Unlock steering column and secure steering
wheel in straight ahead position with a clamp device
designed for towing.
²4-speed electronic automatic transaxle vehicles
can be flat towed at speeds not to exceed 72 km/h (44
mph) for not more than 160 km (100 miles). The
steering column must be unlocked and gear selector
in neutral.
TOWINGÐTOW HOOKS
WARNING: Do not use the tow hook to lift the vehi-
cle off the ground.
A tow-hook bolt, located in the rear interior trim
storage compartment (with jack), is provided with
your vehicle. The tow hook is used for towing the
vehicle with all four wheels on the ground only. It
can be attached to the vehicle through an opening in
the lower front fascia. The tow hook must be fully
seated to the attach bracket through the lower front
fascia as shown. If the tow hook is not fully seated to
the attach bracket the vehicle should not be towed.
NOTE: The tow hook bolt protective plug must be
removed from the tow hook bracket prior to bolt
attachment. The tow hook is used ONLY for towing
the vehicle with all four wheels on the ground.
Fig. 2
0 - 6 LUBRICATION AND MAINTENANCENS/GS
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 35 of 1938
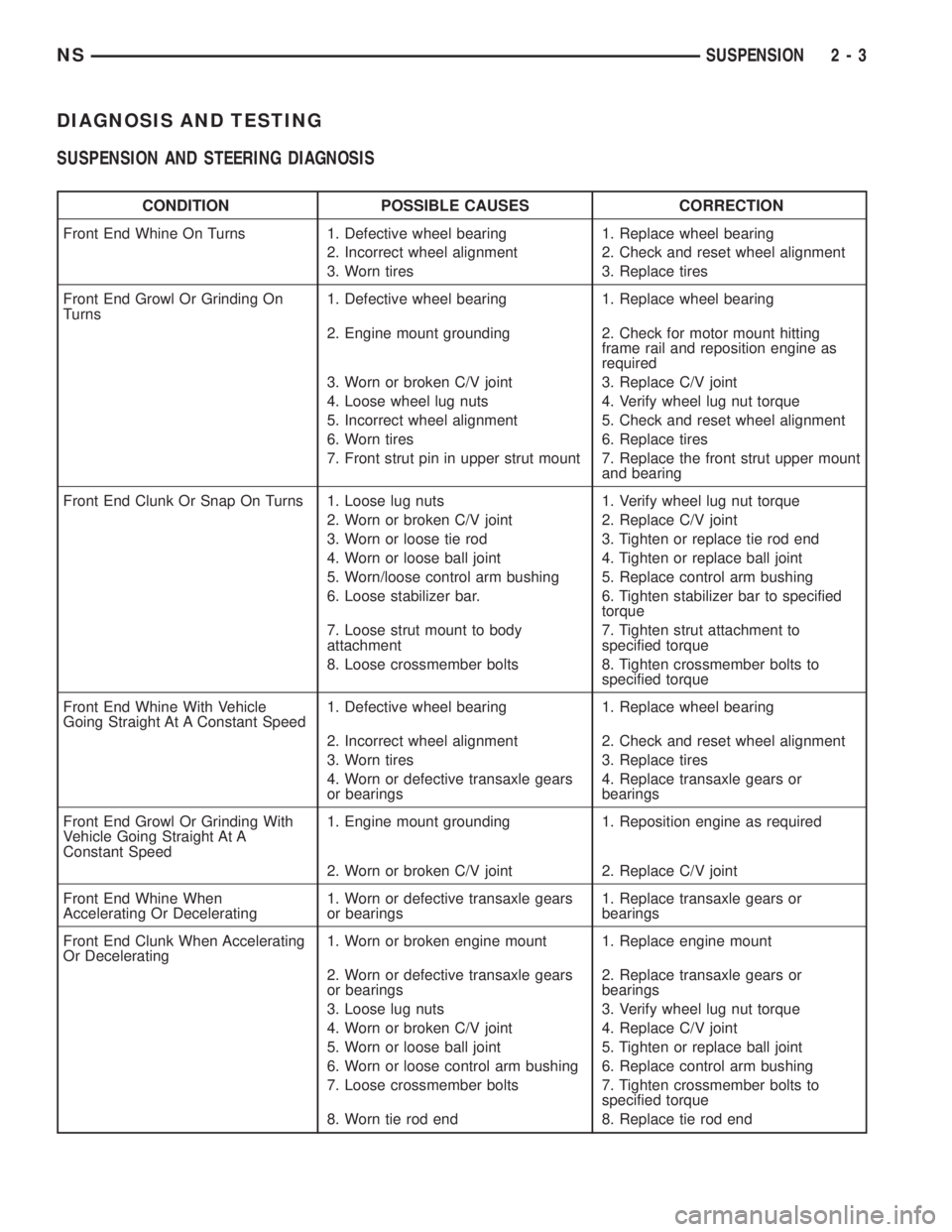
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
SUSPENSION AND STEERING DIAGNOSIS
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Front End Whine On Turns 1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Incorrect wheel alignment 2. Check and reset wheel alignment
3. Worn tires 3. Replace tires
Front End Growl Or Grinding On
Turns1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Engine mount grounding 2. Check for motor mount hitting
frame rail and reposition engine as
required
3. Worn or broken C/V joint 3. Replace C/V joint
4. Loose wheel lug nuts 4. Verify wheel lug nut torque
5. Incorrect wheel alignment 5. Check and reset wheel alignment
6. Worn tires 6. Replace tires
7. Front strut pin in upper strut mount 7. Replace the front strut upper mount
and bearing
Front End Clunk Or Snap On Turns 1. Loose lug nuts 1. Verify wheel lug nut torque
2. Worn or broken C/V joint 2. Replace C/V joint
3. Worn or loose tie rod 3. Tighten or replace tie rod end
4. Worn or loose ball joint 4. Tighten or replace ball joint
5. Worn/loose control arm bushing 5. Replace control arm bushing
6. Loose stabilizer bar. 6. Tighten stabilizer bar to specified
torque
7. Loose strut mount to body
attachment7. Tighten strut attachment to
specified torque
8. Loose crossmember bolts 8. Tighten crossmember bolts to
specified torque
Front End Whine With Vehicle
Going Straight At A Constant Speed1. Defective wheel bearing 1. Replace wheel bearing
2. Incorrect wheel alignment 2. Check and reset wheel alignment
3. Worn tires 3. Replace tires
4. Worn or defective transaxle gears
or bearings4. Replace transaxle gears or
bearings
Front End Growl Or Grinding With
Vehicle Going Straight At A
Constant Speed1. Engine mount grounding 1. Reposition engine as required
2. Worn or broken C/V joint 2. Replace C/V joint
Front End Whine When
Accelerating Or Decelerating1. Worn or defective transaxle gears
or bearings1. Replace transaxle gears or
bearings
Front End Clunk When Accelerating
Or Decelerating1. Worn or broken engine mount 1. Replace engine mount
2. Worn or defective transaxle gears
or bearings2. Replace transaxle gears or
bearings
3. Loose lug nuts 3. Verify wheel lug nut torque
4. Worn or broken C/V joint 4. Replace C/V joint
5. Worn or loose ball joint 5. Tighten or replace ball joint
6. Worn or loose control arm bushing 6. Replace control arm bushing
7. Loose crossmember bolts 7. Tighten crossmember bolts to
specified torque
8. Worn tie rod end 8. Replace tie rod end
NSSUSPENSION 2 - 3
Page 36 of 1938
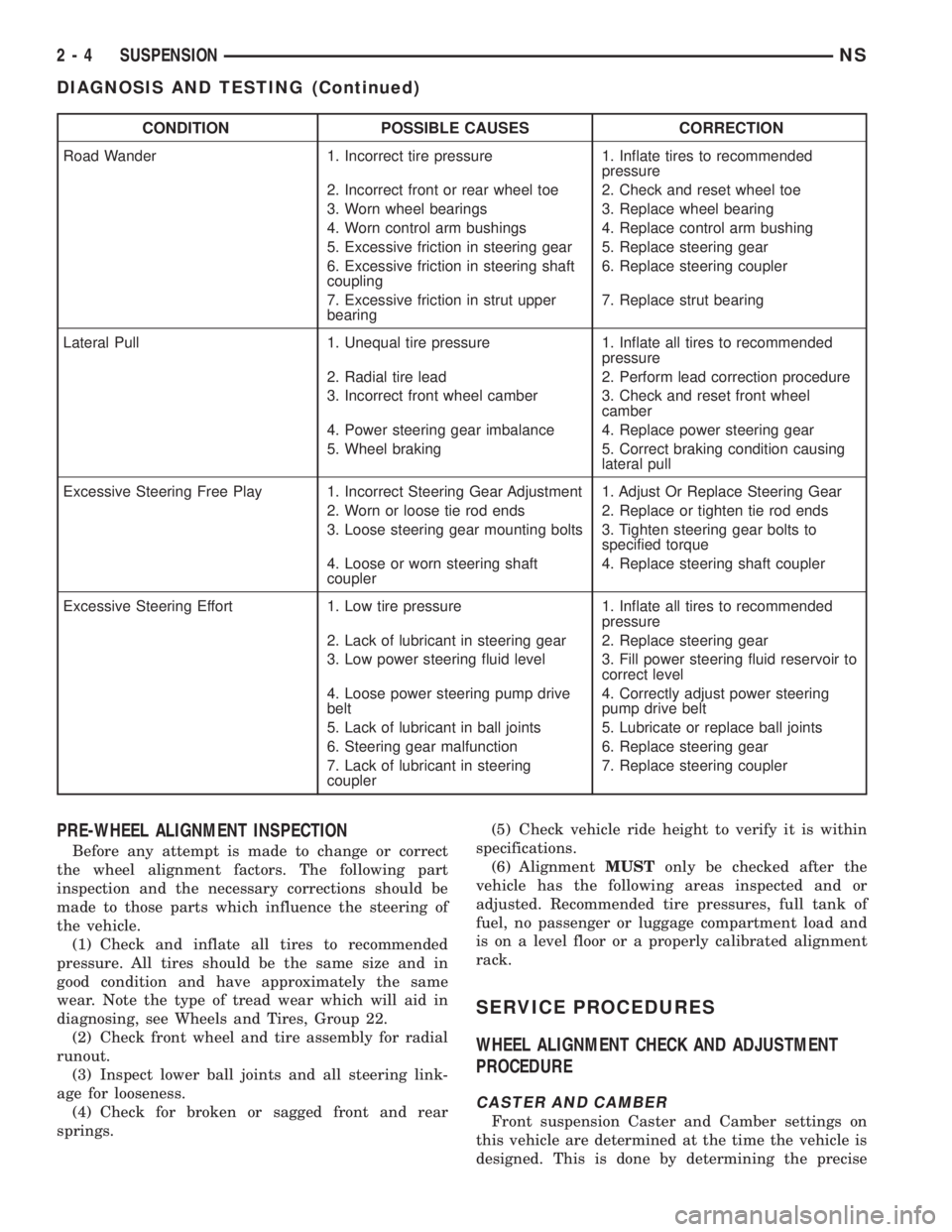
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
Road Wander 1. Incorrect tire pressure 1. Inflate tires to recommended
pressure
2. Incorrect front or rear wheel toe 2. Check and reset wheel toe
3. Worn wheel bearings 3. Replace wheel bearing
4. Worn control arm bushings 4. Replace control arm bushing
5. Excessive friction in steering gear 5. Replace steering gear
6. Excessive friction in steering shaft
coupling6. Replace steering coupler
7. Excessive friction in strut upper
bearing7. Replace strut bearing
Lateral Pull 1. Unequal tire pressure 1. Inflate all tires to recommended
pressure
2. Radial tire lead 2. Perform lead correction procedure
3. Incorrect front wheel camber 3. Check and reset front wheel
camber
4. Power steering gear imbalance 4. Replace power steering gear
5. Wheel braking 5. Correct braking condition causing
lateral pull
Excessive Steering Free Play 1. Incorrect Steering Gear Adjustment 1. Adjust Or Replace Steering Gear
2. Worn or loose tie rod ends 2. Replace or tighten tie rod ends
3. Loose steering gear mounting bolts 3. Tighten steering gear bolts to
specified torque
4. Loose or worn steering shaft
coupler4. Replace steering shaft coupler
Excessive Steering Effort 1. Low tire pressure 1. Inflate all tires to recommended
pressure
2. Lack of lubricant in steering gear 2. Replace steering gear
3. Low power steering fluid level 3. Fill power steering fluid reservoir to
correct level
4. Loose power steering pump drive
belt4. Correctly adjust power steering
pump drive belt
5. Lack of lubricant in ball joints 5. Lubricate or replace ball joints
6. Steering gear malfunction 6. Replace steering gear
7. Lack of lubricant in steering
coupler7. Replace steering coupler
PRE-WHEEL ALIGNMENT INSPECTION
Before any attempt is made to change or correct
the wheel alignment factors. The following part
inspection and the necessary corrections should be
made to those parts which influence the steering of
the vehicle.
(1) Check and inflate all tires to recommended
pressure. All tires should be the same size and in
good condition and have approximately the same
wear. Note the type of tread wear which will aid in
diagnosing, see Wheels and Tires, Group 22.
(2) Check front wheel and tire assembly for radial
runout.
(3) Inspect lower ball joints and all steering link-
age for looseness.
(4) Check for broken or sagged front and rear
springs.(5) Check vehicle ride height to verify it is within
specifications.
(6) AlignmentMUSTonly be checked after the
vehicle has the following areas inspected and or
adjusted. Recommended tire pressures, full tank of
fuel, no passenger or luggage compartment load and
is on a level floor or a properly calibrated alignment
rack.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
WHEEL ALIGNMENT CHECK AND ADJUSTMENT
PROCEDURE
CASTER AND CAMBER
Front suspension Caster and Camber settings on
this vehicle are determined at the time the vehicle is
designed. This is done by determining the precise
2 - 4 SUSPENSIONNS
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)