Solenoid DAEWOO LACETTI 2004 Service Service Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DAEWOO, Model Year: 2004, Model line: LACETTI, Model: DAEWOO LACETTI 2004Pages: 2643, PDF Size: 80.54 MB
Page 526 of 2643
1F – 280IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
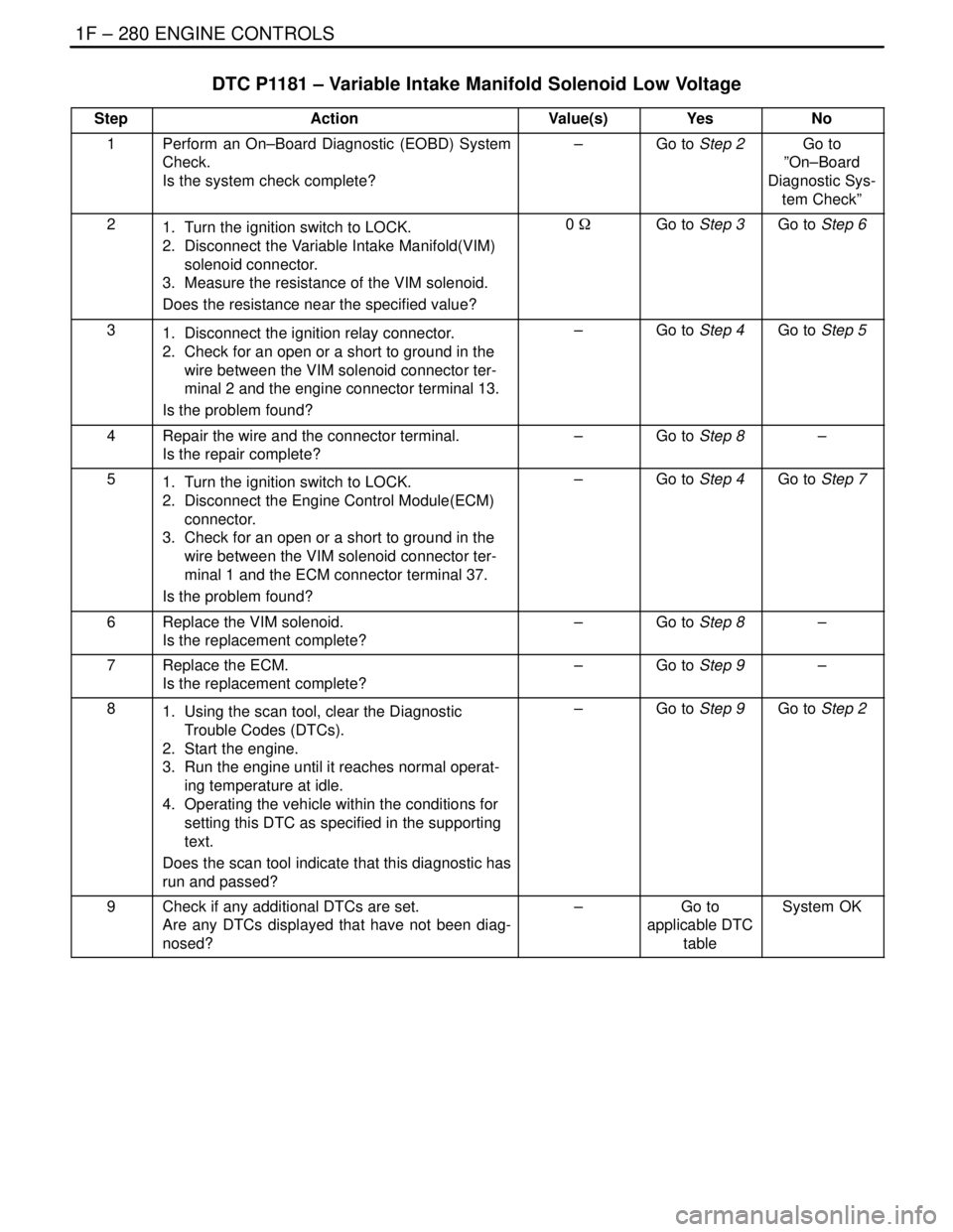
DTC P1181 – Variable Intake Manifold Solenoid Low Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the Variable Intake Manifold(VIM)
solenoid connector.
3. Measure the resistance of the VIM solenoid.
Does the resistance near the specified value?0 WGo to Step 3Go to Step 6
31. Disconnect the ignition relay connector.
2. Check for an open or a short to ground in the
wire between the VIM solenoid connector ter-
minal 2 and the engine connector terminal 13.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Repair the wire and the connector terminal.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8–
51. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the Engine Control Module(ECM)
connector.
3. Check for an open or a short to ground in the
wire between the VIM solenoid connector ter-
minal 1 and the ECM connector terminal 37.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 7
6Replace the VIM solenoid.
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 8–
7Replace the ECM.
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 9–
81. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine.
3. Run the engine until it reaches normal operat-
ing temperature at idle.
4. Operating the vehicle within the conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 2
9Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 527 of 2643

ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 281
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P1182
VARIABLE INTAKE MANIFOLD SOLENOID HIGH
VOLTAGE
Circuit Description
The Engine Control Module(ECM) operates a solenoid to
control the Variable Intake Manifold(VIM) solenoid electri-
cal. The solenoid is normally closed. By providing a ground
path, the ECM energizes the solenoid.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S The VIM solenoid circuit is a short to battery condi-
tion exists.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
S The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illumi-
nate.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. The information will be
stored in the freeze frame and failure records buff-
ers.S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using the scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for 10 sec-
onds.
Diagnostic Aids
An intermittent problem may be caused by a poor connec-
tion, rubbed–through wire insulation, or a wire that is bro-
ken inside the insulation.
Page 528 of 2643
1F – 282IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
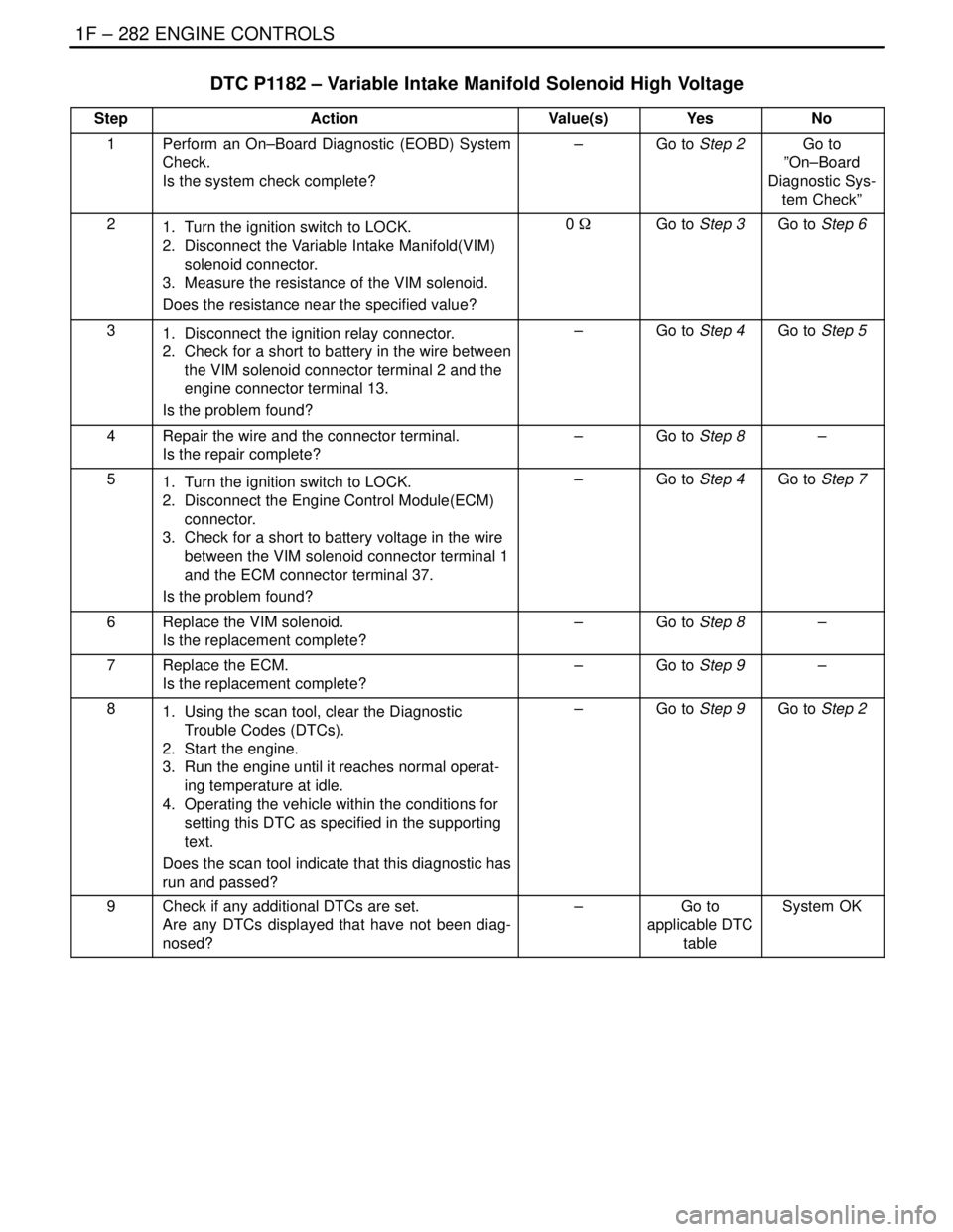
DTC P1182 – Variable Intake Manifold Solenoid High Voltage
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Is the system check complete?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the Variable Intake Manifold(VIM)
solenoid connector.
3. Measure the resistance of the VIM solenoid.
Does the resistance near the specified value?0 WGo to Step 3Go to Step 6
31. Disconnect the ignition relay connector.
2. Check for a short to battery in the wire between
the VIM solenoid connector terminal 2 and the
engine connector terminal 13.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 5
4Repair the wire and the connector terminal.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 8–
51. Turn the ignition switch to LOCK.
2. Disconnect the Engine Control Module(ECM)
connector.
3. Check for a short to battery voltage in the wire
between the VIM solenoid connector terminal 1
and the ECM connector terminal 37.
Is the problem found?–Go to Step 4Go to Step 7
6Replace the VIM solenoid.
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 8–
7Replace the ECM.
Is the replacement complete?–Go to Step 9–
81. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine.
3. Run the engine until it reaches normal operat-
ing temperature at idle.
4. Operating the vehicle within the conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 2
9Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 591 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 345
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
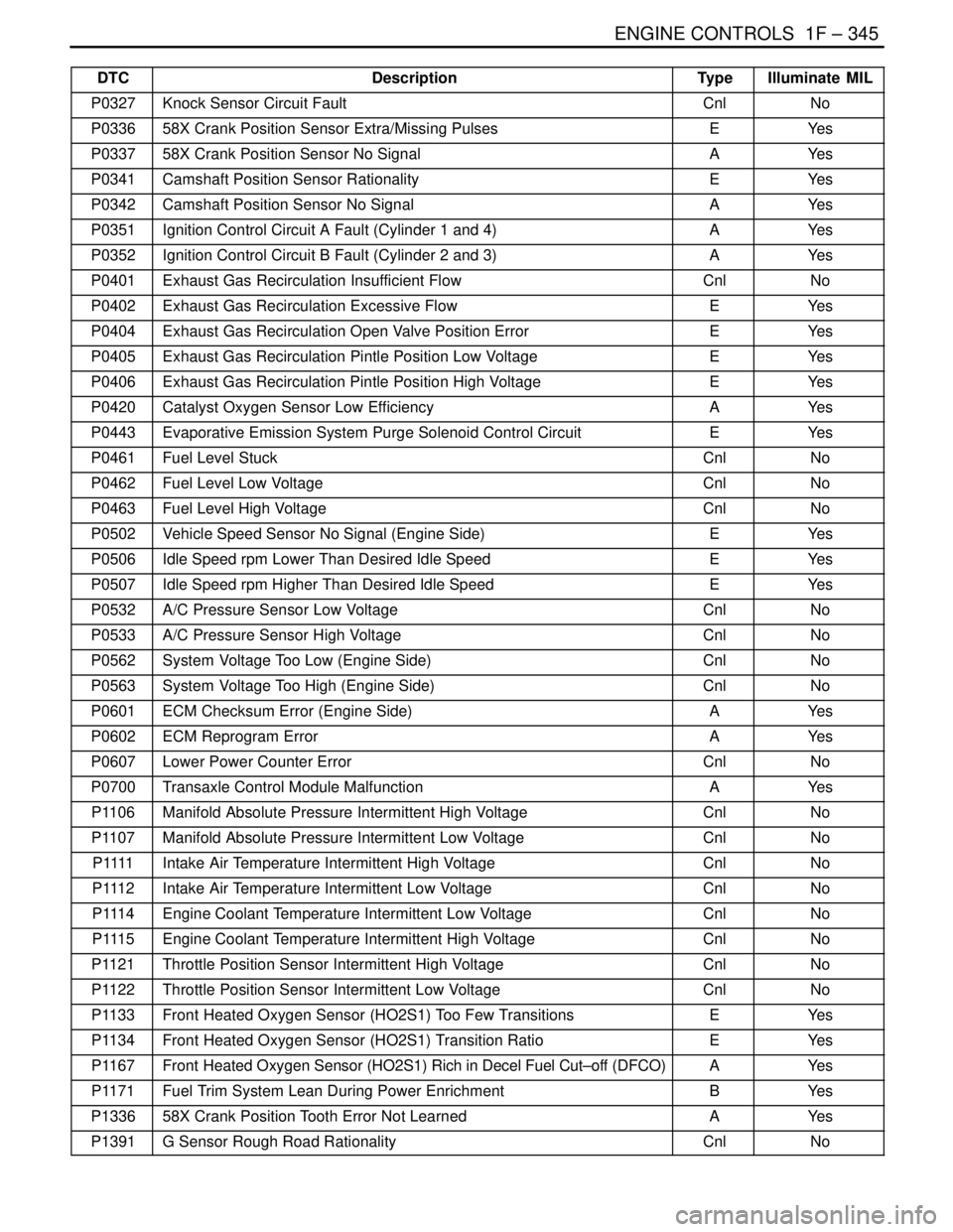
DTCIlluminate MIL Type Description
P0327Knock Sensor Circuit FaultCnlNo
P033658X Crank Position Sensor Extra/Missing PulsesEYe s
P033758X Crank Position Sensor No SignalAYe s
P0341Camshaft Position Sensor RationalityEYe s
P0342Camshaft Position Sensor No SignalAYe s
P0351Ignition Control Circuit A Fault (Cylinder 1 and 4)AYe s
P0352Ignition Control Circuit B Fault (Cylinder 2 and 3)AYe s
P0401Exhaust Gas Recirculation Insufficient FlowCnlNo
P0402Exhaust Gas Recirculation Excessive FlowEYe s
P0404Exhaust Gas Recirculation Open Valve Position ErrorEYe s
P0405Exhaust Gas Recirculation Pintle Position Low VoltageEYe s
P0406Exhaust Gas Recirculation Pintle Position High VoltageEYe s
P0420Catalyst Oxygen Sensor Low EfficiencyAYe s
P0443Evaporative Emission System Purge Solenoid Control CircuitEYe s
P0461Fuel Level StuckCnlNo
P0462Fuel Level Low VoltageCnlNo
P0463Fuel Level High VoltageCnlNo
P0502Vehicle Speed Sensor No Signal (Engine Side)EYe s
P0506Idle Speed rpm Lower Than Desired Idle SpeedEYe s
P0507Idle Speed rpm Higher Than Desired Idle SpeedEYe s
P0532A/C Pressure Sensor Low VoltageCnlNo
P0533A/C Pressure Sensor High VoltageCnlNo
P0562System Voltage Too Low (Engine Side)CnlNo
P0563System Voltage Too High (Engine Side)CnlNo
P0601ECM Checksum Error (Engine Side)AYe s
P0602ECM Reprogram ErrorAYe s
P0607Lower Power Counter ErrorCnlNo
P0700Transaxle Control Module MalfunctionAYe s
P1106Manifold Absolute Pressure Intermittent High VoltageCnlNo
P1107Manifold Absolute Pressure Intermittent Low VoltageCnlNo
P 1111Intake Air Temperature Intermittent High VoltageCnlNo
P1112Intake Air Temperature Intermittent Low VoltageCnlNo
P1114Engine Coolant Temperature Intermittent Low VoltageCnlNo
P1115Engine Coolant Temperature Intermittent High VoltageCnlNo
P1121Throttle Position Sensor Intermittent High VoltageCnlNo
P1122Throttle Position Sensor Intermittent Low VoltageCnlNo
P1133Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) Too Few TransitionsEYe s
P1134Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) Transition RatioEYe s
P1167Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1) Rich in Decel Fuel Cut–off (DFCO)AYe s
P1171Fuel Trim System Lean During Power EnrichmentBYe s
P133658X Crank Position Tooth Error Not LearnedAYe s
P1391G Sensor Rough Road RationalityCnlNo
Page 732 of 2643

1F – 486IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODE (DTC) P0443
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION SYSTEM PURGE SOLENOID
CONTROL CIRCUIT
System Description
The Evaporative Emission (EVAP) system includes the
following components:
S Fuel tank
S Fuel tank pressure sensor.
S Fuel pipes and hoses.
S Fuel vapor lines.
S Fuel cap
S EVAP canister.
S Purge lines.
S EVAP emission canister purge solenoid valve.
S EVAP service port.
The EVAP purge canister solenoid is controlled by the En-
gine Control Module (ECM). The ECM applies a ground to
the EVAP purge canister solenoid. The ECM determines
when to activate the EVAP canister purge solenoid de-
pending on operating conditions, including Throttle Posi-
tion (TP), engine speed, Engine Coolant Temperature
(ECT) and ambient temperature.
The Diagnostic Trouble Code will detect an open or short
circuit.
Conditions for Setting the DTC
S Ignition ON.
S Ignition voltage is greater than 11 v.
Action Taken When the DTC SetsS The Malfunction Indicator Lamp (MIL) will illuminate
after three consecutive trip with a fail.
S The ECM will record operating conditions at the
time the diagnostic fails. This information will be
stored in the Freeze Frame and Failure Records
buffers.
S A history DTC is stored.
Conditions for Clearing the MIL/DTC
S The MIL will turn off after four consecutive ignition
cycles in which the diagnostic runs without a fault.
S A history DTC will clear after 40 consecutive warm–
up cycles without a fault.
S DTC(s) can be cleared by using a scan tool.
S Disconnecting the ECM battery feed for more than
10 seconds.
Diagnostic Aids
Using Freeze Frame and/or Failure Records data may aid
in locating an intermittent condition. If the DTC cannot be
duplicated, the information included in the Freeze Frame
and/or Failure Records data can be useful in determining
how many miles since the DTC set. The Fail Counter and
the Pass Counter can also be used to determine how
many ignition cycles the diagnostic reported a pass and/or
a fail. Operate the vehicle within the same freeze frame
conditions (rpm, load, vehicle speed, temperature, etc.)
that were noted. This will isolate when the DTC failed.
Page 733 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 487
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
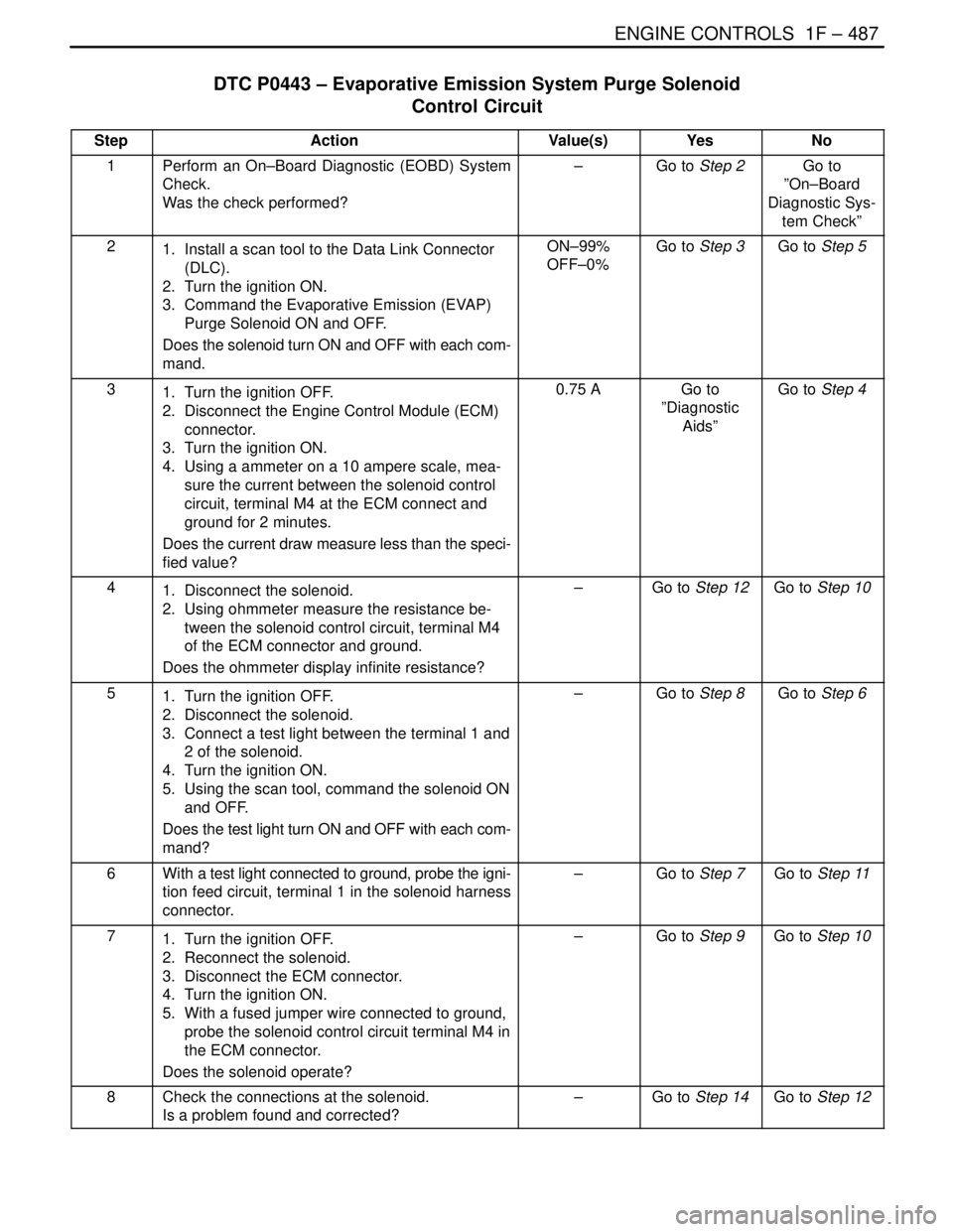
DTC P0443 – Evaporative Emission System Purge Solenoid
Control Circuit
StepActionValue(s)YesNo
1Perform an On–Board Diagnostic (EOBD) System
Check.
Was the check performed?–Go to Step 2Go to
”On–Board
Diagnostic Sys-
tem Check”
21. Install a scan tool to the Data Link Connector
(DLC).
2. Turn the ignition ON.
3. Command the Evaporative Emission (EVAP)
Purge Solenoid ON and OFF.
Does the solenoid turn ON and OFF with each com-
mand.ON–99%
OFF–0%Go to Step 3Go to Step 5
31. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the Engine Control Module (ECM)
connector.
3. Turn the ignition ON.
4. Using a ammeter on a 10 ampere scale, mea-
sure the current between the solenoid control
circuit, terminal M4 at the ECM connect and
ground for 2 minutes.
Does the current draw measure less than the speci-
fied value?0.75 AGo to
”Diagnostic
Aids”Go to Step 4
41. Disconnect the solenoid.
2. Using ohmmeter measure the resistance be-
tween the solenoid control circuit, terminal M4
of the ECM connector and ground.
Does the ohmmeter display infinite resistance?–Go to Step 12Go to Step 10
51. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Disconnect the solenoid.
3. Connect a test light between the terminal 1 and
2 of the solenoid.
4. Turn the ignition ON.
5. Using the scan tool, command the solenoid ON
and OFF.
Does the test light turn ON and OFF with each com-
mand?–Go to Step 8Go to Step 6
6With a test light connected to ground, probe the igni-
tion feed circuit, terminal 1 in the solenoid harness
connector.–Go to Step 7Go to Step 11
71. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Reconnect the solenoid.
3. Disconnect the ECM connector.
4. Turn the ignition ON.
5. With a fused jumper wire connected to ground,
probe the solenoid control circuit terminal M4 in
the ECM connector.
Does the solenoid operate?–Go to Step 9Go to Step 10
8Check the connections at the solenoid.
Is a problem found and corrected?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 12
Page 734 of 2643
1F – 488IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
9Check the connections at the ECM.
Is a problem found and corrected?–Go to Step 14Go to Step 13
10Repair the faulty solenoid control circuit.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14–
11Repair the faulty solenoid ignition feed circuit.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14
121. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace the solenoid.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14–
131. Turn the ignition OFF.
2. Replace ECM.
Is the repair complete?–Go to Step 14–
141. Using the scan tool, clear the Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs).
2. Start the engine and idle at normal operating
temperature.
3. Operate the vehicle within the Conditions for
setting this DTC as specified in the supporting
text.
Does the scan tool indicate that this diagnostic has
run and passed?–Go to Step 15Go to Step 2
15Check if any additional DTCs are set.
Are any DTCs displayed that have not been diag-
nosed?–Go to
Applicable DTC
tableSystem OK
Page 821 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 575
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
StepNo Yes Value(s) Action
5Replace the sensor in the affected circuit, if a Diag-
nostic Trouble Code (DTC) was stored for this circuit
(except for the DTCs P0171 and P0172.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
6Does an intermittent Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) or DTC occur?–Go toStep 7Go toStep 8
71. Check for a faulty relay, electronic control mod-
ule (ECM) driven solenoid, or switch.
2. Check for improper installation of electrical de-
vices, such as lights, two–way radios, electric
motors, etc.
3. Inspect the ignition control wires for proper
routing (away from ignition wires, ignition sys-
tem components, and the generator).
4. Check for a short–to–ground in the MIL circuit
or the DLC ”test” terminal.
5. Inspect the ECM ground connections.
6. Correct or repair the affected circuits as need-
ed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
81. Check for a loss of DTC memory.
2. 2. Disconnect the Throttle Position Sensor.
3. Run the engine at idle until the MIL comes on.
4. Turn the ignition OFF.
Is DTC P0122 stored in memory?–Go toStep 10Go toStep 9
9Replace the ECM.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
10Does the vehicle stall while driving?–Go toStep 11Go toStep 12
11Monitor the Front Heated Oxygen Sensor (HO2S1)
and the injector base pulse width with the scan tool.
Does the scan tool display a steady low voltage
(about 0 mv) for the HO2S1 sensor with the control
module commanding an injector base pulse width of
the value specified?8 msGo toStep 9Go toStep 12
121. Check for an open diode across the A/C clutch
and for other open diodes.
2. Repair or replace any components as needed.
Is the repair complete?–System OK–
Page 861 of 2643
ENGINE CONTROLS 1F – 615
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
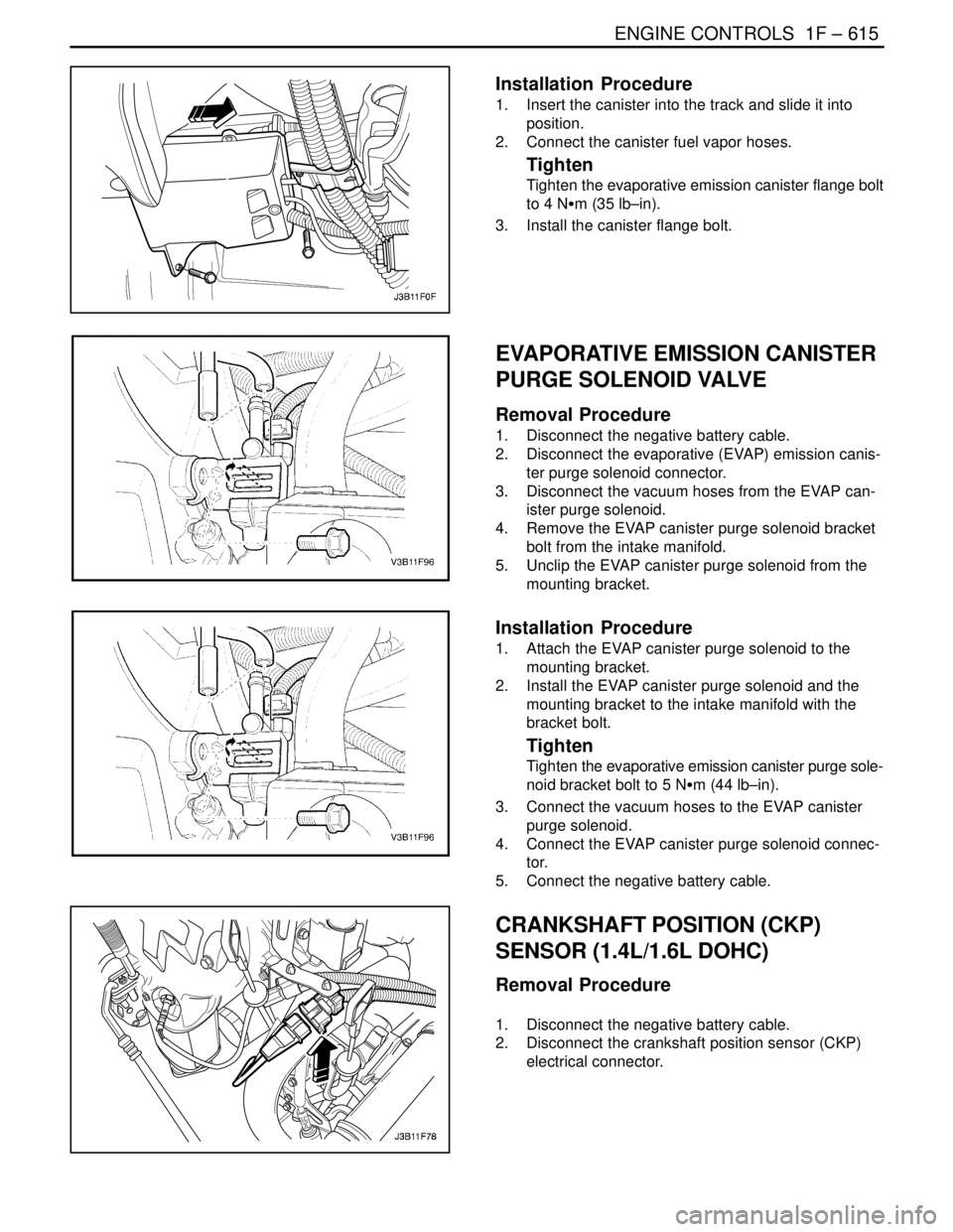
Installation Procedure
1. Insert the canister into the track and slide it into
position.
2. Connect the canister fuel vapor hoses.
Tighten
Tighten the evaporative emission canister flange bolt
to 4 NSm (35 lb–in).
3. Install the canister flange bolt.
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CANISTER
PURGE SOLENOID VALVE
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the evaporative (EVAP) emission canis-
ter purge solenoid connector.
3. Disconnect the vacuum hoses from the EVAP can-
ister purge solenoid.
4. Remove the EVAP canister purge solenoid bracket
bolt from the intake manifold.
5. Unclip the EVAP canister purge solenoid from the
mounting bracket.
Installation Procedure
1. Attach the EVAP canister purge solenoid to the
mounting bracket.
2. Install the EVAP canister purge solenoid and the
mounting bracket to the intake manifold with the
bracket bolt.
Tighten
Tighten the evaporative emission canister purge sole-
noid bracket bolt to 5 NSm (44 lb–in).
3. Connect the vacuum hoses to the EVAP canister
purge solenoid.
4. Connect the EVAP canister purge solenoid connec-
tor.
5. Connect the negative battery cable.
CRANKSHAFT POSITION (CKP)
SENSOR (1.4L/1.6L DOHC)
Removal Procedure
1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor (CKP)
electrical connector.
Page 870 of 2643

1F – 624IENGINE CONTROLS
DAEWOO V–121 BL4
Because of the constant measuring and adjusting of the
air/fuel ratio, the fuel injection system is called a ”closed
loop” system.
The ECM uses voltage inputs from several sensors to de-
termine how much fuel to provide to the engine. The fuel
is delivered under one of several conditions, called
”modes.”
Starting Mode
When the ignition is turned ON, the ECM turns the fuel
pump relay on for two seconds. The fuel pump then builds
fuel pressure. The ECM also checks the Engine Coolant
Temperature (ECT) sensor and the Throttle Position (TP)
sensor and determines the proper air/fuel ratio for starting
the engine. This ranges from 1.5 to 1 at –97 °F (–36 °C)
coolant temperature to 14.7 to 1 at 201 °F (94 °C) coolant
temperature. The ECM controls the amount of fuel deliv-
ered in the starting mode by changing how long the fuel in-
jector is turned on and off. This is done by ”pulsing” the fuel
injectors for very short times.
Clear Flood Mode
If the engine floods with excessive fuel, it may be cleared
by pushing the accelerator pedal down all the way. The
ECM will then completely turn off the fuel by eliminating
any fuel injector signal. The ECM holds this injector rate
as long as the throttle stays wide open and the engine is
below approximately 400. If the throttle position becomes
less than approximately 80 percent, the ECM returns to
the starting mode.
Run Mode
The run mode has two conditions called ”open loop” and
”closed loop.”
Open Loop
When the engine is first started and it is above 400 rpm,
the system goes into ”open loop” operation. In ”open loop,”
the ECM ignores the signal from the HO2S and calculates
the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the ECT sensor and
the MAP sensor. The sensor stays in ”open loop” until the
following conditions are met:
S The HO2S sensor has a varying voltage output,
showing that it is hot enough to operate properly.
S The ECT sensor is above a specified temperature.
S A specific amount of time has elapsed after starting
the engine.
Closed Loop
The specific values for the above conditions vary with dif-
ferent engines and are stored in the Electronically Eras-
able Programmable Read–Only Memory (EEPROM).
When these conditions are met, the system goes into
”closed loop” operation. In ”closed loop,” the ECM calcu-
lates the air/fuel ratio (fuel injector on–time) based on the
signal from the oxygen sensor. This allows the air/fuel ratio
to stay very close to 14.7 to 1.Acceleration Mode
The ECM responds to rapid changes in throttle position
and airflow and provides extra fuel.
Deceleration Mode
The ECM responds to changes in throttle position and air-
flow and reduces the amount of fuel. When deceleration
is very fast, the ECM can cut off fuel completely for short
periods of time.
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
When battery voltage is low, the ECM can compensate for
a weak spark delivered by the ignition module by using the
following methods:
S Increasing the fuel injector pulse width.
S Increasing the idle speed rpm.
S Increasing the ignition dwell time.
Fuel Cut–Off Mode
No fuel is delivered by the fuel injectors when the ignition
is OFF. This prevents dieseling or engine run–on. Also, the
fuel is not delivered if there are no reference pulses re-
ceived from the central power supply. This prevents flood-
ing.
EVAPORATIVE EMISSION CONTROL
SYSTEM OPERATION
The basic Evaporative (EVAP) Emission control system
used is the charcoal canister storage method. This meth-
od transfers fuel vapor from the fuel tank to an activated
carbon (charcoal) storage device (canister) to hold the va-
pors when the vehicle is not operating. When the engine
is running, the fuel vapor is purged from the carbon ele-
ment by intake airflow and consumed in the normal com-
bustion process.
Gasoline vapors from the fuel tank flow into the tube la-
beled TANK. These vapors are absorbed into the carbon.
The canister is purged by the engine control module
(ECM) when the engine has been running for a specified
amount of time. Air is drawn into the canister and mixed
with the vapor. This mixture is then drawn into the intake
manifold.
The ECM supplies a ground to energize the EVAP emis-
sion canister purge solenoid valve. This valve is Pulse
Width Modulated (PWM) or turned on and off several
times a second. The EVAP emission canister purge PWM
duty cycle varies according to operating conditions deter-
mined by mass airflow, fuel trim, and intake air tempera-
ture.
Poor idle, stalling, and poor driveability can be caused by
the following conditions:
S An inoperative EVAP emission canister purge sole-
noid valve.
S A damaged canister.
S Hoses that are split, cracked, or not connected to
the proper tubes.