oil type DATSUN 210 1979 Owner's Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1979, Model line: 210, Model: DATSUN 210 1979Pages: 548, PDF Size: 28.66 MB
Page 182 of 548

ASSEMBLY
To
assemble
reverse
the
order
of
disassembly
Carefully
observe
the
fol
lowing
instructions
CAUTION
B
tfore
installi
lg
IC
ignition
unit
make
sure
mating
surfaces
of
IC
ignition
unit
and
distriblitor
are
clean
and
free
from
dust
sand
and
moisture
Align
match
marks
so
that
parts
are
assembled
to
their
original
posi
tions
2
Ensure
that
reluctor
is
properly
oriented
when
installing
on
shaft
Al
ways
drive
in
roll
pin
with
its
slit
toward
the
outer
end
of
shaft
See
Fig
EE
64
Be
sure
to
use
a
new
roll
pin
DESCRIPTION
The
IC
ignition
unit
utilizes
a
semi
conductor
IC
device
and
is
mounted
on
the
side
surface
of
the
distributor
The
IC
ignition
unit
has
the
fol
lOwing
circuits
Spark
timing
signal
monitoring
circuit
This
circuit
detects
the
ignition
signal
sent
from
the
distributor
pick
up
coil
and
amplifies
the
signal
2
Lock
preventing
circuit
This
circuit
cuts
off
the
ignition
coil
primary
current
when
the
ignition
switch
is
ON
and
the
engine
is
sta
tionary
If
the
ignition
coil
primary
current
is
allowed
to
flow
under
such
condi
tions
excessive
current
will
be
drawn
because
of
low
internal
resistance
of
the
ignition
coil
Engine
Electrical
System
r
5
EE747
Fig
EE
64
Driuing
in
Roll
Pin
3
When
installing
pinion
on
shaft
be
sure
to
install
pinion
gear
correctly
to
position
where
it
was
installed
4
Apply
grease
to
the
top
of
rotor
shaft
as
required
5
Check
the
operation
of
governor
before
installing
distributor
on
engine
Ie
IGNITION
UNIT
This
can
result
in
an
abnormal
temperature
rise
in
the
ignition
coil
or
discharged
battery
These
malfunc
tions
can
be
prevented
by
this
lock
preventing
circuit
3
Duty
control
circuit
This
circuit
controls
the
ratio
of
the
ignition
coil
primary
current
ON
OFF
time
periods
in
one
cycle
of
ignition
operation
111is
is
equivalent
to
the
dwell
angle
of
the
conventional
point
type
dis
tributor
In
order
to
provide
high
performance
spark
ruing
over
a
wide
range
of
driving
speeds
this
duty
can
be
controlled
by
the
source
voltage
and
the
ambient
temperature
as
well
as
by
the
engine
rpm
4
Power
switching
circuit
This
circuit
is
used
to
make
or
break
directly
the
primary
circuit
cur
EE
24
6
Properly
eenterstatOr
and
reluc
tor
before
tightening
Standard
air
gap
0
3
to
0
5
mm
0
012
to
0
020
in
0
3
to
0
5
mm
0
012
to
0
020
in
Fig
EE
65
EE748
Air
Gap
7
Adjust
ignition
timing
after
distri
butor
is
installed
on
engine
rent
of
the
ignition
coil
5
Current
limiting
circuit
This
circuit
controls
the
current
value
so
that
excessive
current
will
not
flow
through
the
power
switching
cir
cuit
To
ensure
efficient
operation
of
the
IC
ignition
unit
these
five
circuits
are
manufactured
in
one
assembly
as
shown
in
Fig
EE
66
The
semi
conductor
IC
is
utilized
for
all
these
circuits
except
the
power
switching
circuit
The
power
switching
circuit
uses
one
power
transistor
and
the
circuit
is
arranged
on
the
ceramic
substrate
together
with
resislors
capa
citors
and
diodes
Each
component
part
of
this
unit
is
highly
reliable
however
should
any
part
be
found
faulty
the
entire
as
sembly
musl
be
replaced
Page 186 of 548

JUDGMENT
OV
is
indicated
IC
ignition
unit
NG
But
condition
of
pick
up
coil
can
not
be
judged
Proceed
to
the
item
for
Pick
up
Coil
Check
Bat
tery
voltage
is
indicated
Condition
cannot
be
judged
Proceed
to
item
9
9
Remove
IC
ignition
unit
Refer
to
IC
ignition
Unit
for
re
moval
10
Measure
resistance
between
two
terminals
of
pick
up
coil
JUDGMENT
Approx
40011
are
indicated
The
ignition
coil
is
an
oil
filled
type
The
ignition
coil
case
is
filled
with
oil
which
has
good
insulating
and
heat
radiating
characteristics
The
ignition
coil
has
a
greater
ratio
between
the
primary
and
secondary
windings
to
step
up
battery
voltage
to
high
voltage
This
causes
stronger
sparks
to
jump
the
spark
plug
gap
The
cap
is
made
of
alkyd
resin
which
offers
high
resistance
to
electric
arc
and
increased
insulation
When
high
tension
cable
is
installed
to
ignition
coil
there
should
be
no
clearance
between
their
caps
Note
Do
not
disconnect
high
tension
cables
from
spark
plugs
during
en
gine
running
r
EE354
1
High
tension
cable
2
Rubber
cap
Fig
EE
74
Correct
Instalhltion
of
High
Tension
Cable
Engine
Electrical
System
Pick
up
coil
OK
IC
ignition
unit
NG
Approx
40011
are
not
indicated
Pick
up
coil
NG
Condition
of
IC
ignition
unit
can
not
be
judged
Proceed
to
item
11
II
Replace
faulty
pick
up
coil
with
new
one
12
Install
original
IC
ignition
unit
13
Check
parking
performance
JUDGMENT
Sparks
occur
IC
ignition
system
IC
ignition
unit
OK
No
spark
OCCUrs
IC
ignition
unit
NG
IGNITION
COIL
If
NG
replace
faulty
IC
ignition
unit
with
new
one
P1ck
up
coil
check
I
Make
sure
that
ignition
switch
is
in
OFF
position
2
Remove
IC
ignition
unit
Refer
to
IC
Ignition
Unit
for
removal
3
Measure
resistance
between
two
terminals
of
pick
up
coil
JUDGMENT
Approx
40011
are
indicated
OK
Approx
40011
are
not
indicated
NG
If
NG
replace
faulty
pick
up
coil
with
new
one
1
@
I
rJ
1
C
I
I
i
jllll
1
t
1
Rubber
cap
for
ignition
coil
2
Secondary
tenninal
3
Cap
4
Primary
terminal
5
Spring
6
Secondary
winding
EE
28
EE578
7
Primary
winding
8
Side
core
9
Insulator
10
Center
core
11
Segment
12
Case
Fig
EE
75
Ignition
Coit
Page 187 of 548

INSPECTION
I
Disconnect
high
tension
cables
from
spark
plugs
by
pulling
on
boot
not
on
cable
itself
2
Remove
spark
plugs
3
Check
electrodes
and
inner
and
outer
porcelains
of
plugs
noting
the
type
of
deposits
and
the
degree
of
electrode
erosion
Refer
to
Fig
EE
76
Normal
Brown
to
grayish
Ian
de
posits
and
slighl
electrode
wear
indicate
correct
spark
plug
heat
range
Carbon
fouled
Dry
fluffy
carbon
de
posits
on
the
insulator
and
elec
trode
are
mostly
caused
by
slow
speed
driving
in
city
weak
ignition
too
rich
fuel
mixture
dirty
air
cleaner
etc
H
is
advisable
to
replace
with
plugs
having
hotter
heat
range
Oil
fouled
Wet
black
deposits
show
excessive
oil
entrance
into
comb
us
tion
chamber
through
worn
rings
and
pistons
or
excessive
clearance
between
valve
guides
and
stems
If
the
same
condition
remains
after
repair
use
a
hotter
plug
Overheating
White
or
light
gray
insu
lator
with
black
or
gray
brown
spots
and
bluish
burnt
electrodes
indicate
engine
overheating
More
over
the
appearance
results
from
incorrect
ignition
timing
loose
spark
plugs
low
fuel
pump
pres
sure
wrong
selection
of
fuel
a
hotter
range
plug
etc
H
is
advisable
to
replace
with
plugs
having
colder
heat
range
4
After
cleaning
dress
electrodes
with
a
smaU
fme
file
to
flatten
the
surfaces
of
both
center
and
side
elec
trodes
in
parallel
Set
spark
plug
gap
to
specification
5
Install
spark
plugs
and
torque
each
plug
6
Connect
spark
plug
wires
CLEANING
AND
REGAP
Clean
spark
plugs
in
a
sand
blast
Engine
Electrical
System
SPARK
PLUG
Conventional
type
Normal
Overheating
Multi
gap
type
Nonnal
Overheating
type
cleaner
Avoid
excessive
blasting
Clean
and
remove
carbon
or
oxide
deposits
but
do
not
wear
away
porce
lain
If
deposits
are
too
stubborn
discard
plugs
After
cleaning
spark
plugs
renew
firing
surface
of
electrodes
with
file
mentioned
above
Then
check
spark
plug
gap
with
wire
feeler
gauge
All
spark
plugs
new
or
used
should
have
the
gap
checked
and
reset
by
bending
ground
electrode
EEOSO
Fig
EE
77
Setting
Spark
Plug
Gap
Except
FU
model
EE
29
Carbon
fouled
EE079
Worn
Carbon
fouled
Worn
EE601
Fig
EE
76
Spark
Plug
EE586
Fig
EE
78
Setting
Spark
Plug
Gap
FU
models
Page 189 of 548
Engine
Electrical
System
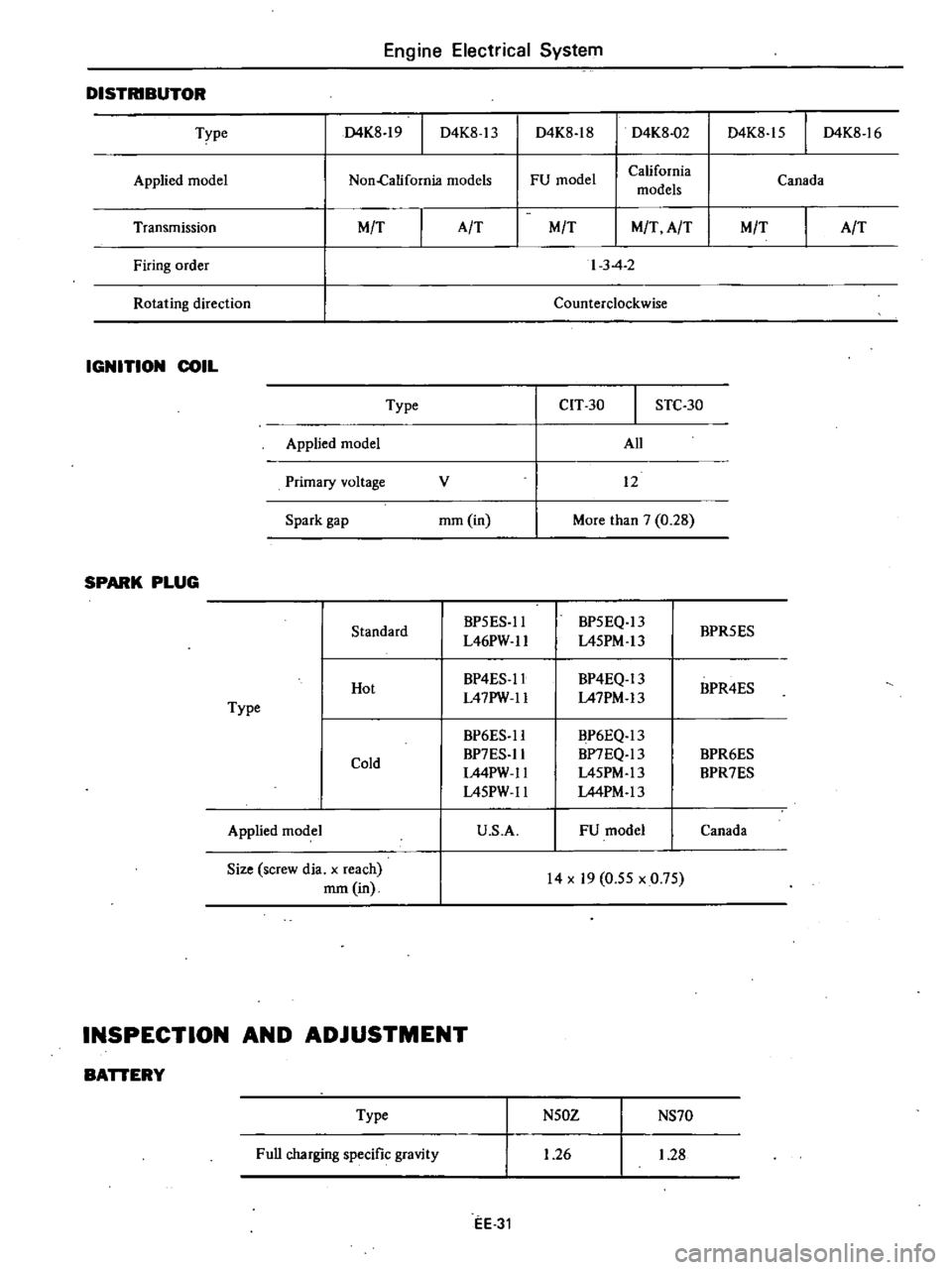
DISTRIBUTOR
D4K8
18
D4K8
15
I
D4K8
16
Type
D4K8
19
I
D4K8
13
D4K8
02
Applied
model
FU
model
California
models
Canada
Non
California
models
Transmission
MfT
Firing
order
Rotating
direction
IGNITION
COIL
Type
Applied
model
Primary
voltage
Spark
gap
SPARK
PLUG
Standard
Hot
Type
Cold
Applied
model
Size
screw
dia
x
reach
mm
in
AfT
MfT
MfT
AfT
MfT
AfT
I
3
4
2
Counterclockwise
cn
30
STC
30
All
v
12
mm
in
More
than
7
0
28
BP5ES
II
BP5EQ
13
BPR5ES
L46PW
1I
L45PM
13
BP4ES
1I
BP4EQ
13
BPR4ES
L47PW
1I
L47PM
13
BP6ES
1I
BP6EQ
13
BP7ES
1I
BP7EQ
13
BPR6ES
L44PW
1I
L45PM
13
BPR7ES
L45PW
1I
L44PM
13
U
S
A
FU
model
Canada
14
x
19
0
55
x
0
75
INSPECTION
AND
ADJUSTMENT
BATTERY
Type
Full
charging
specific
gravity
N50Z
NS70
1
26
1
28
EE
31
Page 190 of 548

Engine
Electrical
System
STARTING
MOTOR
Type
S1I4
160B
I
Sl14
163E
S114
253
Outer
diameter
of
commutator
mm
in
More
than
32
1
26
More
than
29
L14
Minimum
length
of
brush
mm
in
12
0
47
II
0
43
Brush
spring
tension
kg
Ib
1
4
to
1
8
3
1
to
4
0
1
6to
2
0
3
5
to
4
4
Clearance
between
bearing
metal
and
armature
shaft
mm
in
Less
than
0
2
0
008
Clearance
R
between
pinion
front
edge
and
pinioIl
stopper
mm
in
0
3
to
2
5
0
012
to
0
098
Difference
T
in
height
of
pinion
nun
in
0
3
to
1
5
0
012
to
0
059
ALTERNATOR
Type
LRI5049
Minimum
length
of
brush
mm
in
More
than
7
5
0
295
Brush
spring
pressure
gr
oz
255
to
345
8
99
to
12
17
Slip
ring
outer
diameter
nun
in
More
than
30
1
18
DISTRIBUTOR
Air
gap
mm
in
D4K8
19
I
D4K8
l3
I
D4K8
18
I
D4K8
02
D4K8
15
I
D4K8
16
0
3
to
0
5
0
012
to
0
020
Type
Cap
il1s
ation
resistance
M
1
More
than
50
Rotor
head
insulation
resistance
Mil
More
than
50
Cap
carbon
point
length
mm
in
10
0
39
Vacuum
advance
0
105
4
13
0
170
6
69
0
80
3
15
0
105
4
13
0
70
2
76
0
170
6
69
Distributor
degree
distributor
9
250
3
225
12
265
9
300
15
300
6
5
300
mmHg
inHg
9
84
8
86
10
43
11
81
11
81
11
81
Centrifugal
advance
0
550
6
550
0
550
0
550
0
750
0
750
Distributor
degree
distributor
14
2
300
14
2
300
13
5
2
400
13
5
2
400
10
2
400
10
2
400
rpm
EE
32
Page 191 of 548

Engine
Electrical
System
IGNITION
COIL
Type
CIT
30
STC
30
Primary
resistance
at
200C
680F
U
0
84
to
1
02
Secondary
resistance
at
200C
680F
KU
8
2
to
12
4
SPARK
PLUG
BP5ES
ll
L46PW
ll
BP5EQ
13
L46PM
13
BPR5ES
BP4E
ll
L47PW
ll
BP4EQ
13
L47PM
13
BPR4ES
Type
BP6ES
I1
L44PW
I1
BP6EQ
13
L45PM
13
BPR6ES
BP7ES
II
L45PW
II
BP7EQ
13
L44PM
13
BPR7ES
Plug
gap
mm
in
1
0
to
1
1
1
1
to
1
3
0
8
to
0
9
0
039
to
0
043
0
043
to
0
051
0
031
to
0
035
TIGHTENING
TORQUE
Magnetic
switch
terminal
SI14
160B
S114
163E
S1l4
253
kg
em
in
Ib
Magnetic
switch
attaching
bolts
Starting
motor
Gear
case
attaching
bolts
Pulley
nut
Alternator
through
bolts
Spark
plug
kg
cm
in
Ib
75
to
100
65
to
87
115
to
160
100
to
139
38
to
51
3
to
44
kg
em
in
lb
kg
m
ft
Ib
kg
cm
in
Ib
kg
m
ft
Ib
64
to
85
56
to
74
4
5
to
6
0
33
to
43
60
to
70
52
to
61
1
5
to
2
5
II
to
18
EE
33
Page 247 of 548

Manual
Transmission
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
GENERAL
SPECIFICATIONS
Transmission
model
F4W60L
FS5W60L
Item
No
of
speeds
4
5
Synchromesh
type
Warner
Shift
type
t
3
I
I
R
2
4
2
4
R
r
I
I
1
3
5
1st
3
513
3
513
2nd
2
170
2
170
3rd
1
378
1
378
Gear
ratio
4th
1
000
1
000
5th
0
846
Rev
3
764
3
464
Final
gear
ratio
3
700
3
700
155
13
6
15
13
4PR
16
5
Speedometer
Tire
155SRI3
16
5
gear
ratio
175
70SR13
16
5
Oil
capacity
liter
US
pt
Imp
pt
1
3
2
U
2
Y
I
1
2
2
i
i
i
MT31
Page 254 of 548

The
3N71
B
trammission
is
a
fully
automatic
unit
consisting
primarily
of
a
3
element
hydraulic
torque
converter
and
two
planetary
gear
sets
Two
multiple
disc
c1utclies
a
multiple
disc
brake
brake
band
and
one
way
clutch
provide
the
friction
elements
necessary
to
obtain
the
desired
function
of
the
two
planetary
gear
ets
A
hydraulic
control
system
is
used
to
operate
the
friction
elements
and
automatic
shift
controls
TORQUE
CONVERTER
The
torque
converter
is
attached
to
the
crankshaft
through
a
flexible
drive
plate
Heat
generat
in
the
t
rque
converter
is
dissipated
by
circulating
the
transmission
fluid
through
an
oil
to
water
type
cooler
in
the
radiator
lower
tank
The
welded
comtruction
of
the
torque
co
verter
prevents
di
3
ssembly
or
service
unless
highly
specialized
equipment
is
available
Qj
gJ
Autpmatic
Trimsmissi6n
DEScRIPTION
FLUID
RECOMMENDAnON
Use
DEXRON
type
automatic
transmission
fluid
only
IDENTIFICATION
NUMBER
Stamped
position
The
plate
is
attached
to
the
right
han
side
of
transmission
case
AT
M
Fig
AT
l
Identification
Number
Identification
of
number
arranaemanta
JAPAJllUTOIlATlC
TRAJISIIISSIO
C8
Ull
MODEL
X
0
12
3
NO
7
6
0
1
2
34
Number
designation
76
0
I
2
34
L
Serial
productioo
number
for
the
month
Month
of
production
1
Jan
2
Feb
X
Oct
Y
Nov
Z
Dec
Lut
IJgUre
denotins
the
year
A
D
IJ
III
J
W
f
r
lrr
G
1
Transmission
case
2
Oil
pump
3
Front
clutch
4
Band
brake
5
Rear
dutch
6
Front
planetary
geat
7
Rear
planetary
gear
8
One
way
clutch
9
Low
4
Reverse
brake
10
Oil
distributor
11
Governor
12
utput
shaft
13
Rear
extension
14
Oil
pan
IS
Control
valve
16
Input
shaft
17
Torque
converter
18
Converter
housi
19
Drive
pia
te
Tightening
torque
T
of
bolts
and
nuts
kg
m
ft
lb
@
T
4
to
5
29
to
36
@
T
14
to
16
101
to
116
@
T
4
5
to
5
5
33
to
40
@
T
0
6
to
0
8
4
3
to
5
8
@
T
0
5
to
0
7
3
6
to
5
1
T
2
0
to
2
5
14
to
18
@
T
1
3
to
1
8
9
to
13
@
T
0
55
ta
0
75
4
0
to
5
4
CD
T
0
25
to
0
35
1
8
to
2
5
AT312
Fig
AT
2
3N71B
Automatic
Trammiuion
AT
2
Page 255 of 548

Automatic
Transmission
HYDRAULIC
CONTROL
UNIT
AND
VALVES
The
hydraulic
or
a
tomatic
control
system
is
comprised
of
four
4
basic
groups
the
pressure
supply
system
the
pressure
regulating
system
the
flow
control
valves
and
the
friction
elements
PRESSURE
SUPPLY
SYSTEM
The
pressure
supply
system
consists
of
a
gear
type
oil
pwnp
driven
by
the
engine
through
the
torque
converter
The
pump
provides
pressure
for
aU
hydraulic
and
lubrication
needs
PRESSURE
REGULATOR
VALVES
The
pressure
regulating
valves
con
trol
the
output
pressure
of
the
oil
pump
Pre
ure
rellulator
valve
The
pressure
regulator
valve
con
trois
mainline
pressure
based
on
throttle
opening
for
the
operation
of
the
band
clutches
and
brake
Governor
valve
The
governor
valve
transmits
re
gulated
pressure
based
on
car
peed
to
the
shift
valves
to
control
upshifts
and
downshifts
Vacuum
throttle
valve
The
vacuum
throttle
valve
transmits
regulated
pressure
based
on
engine
load
vacuum
This
pressure
controls
the
pressure
regulator
valve
Also
this
pressure
is
applied
to
one
end
of
the
shift
valves
in
opposition
to
governor
pressure
which
acts
on
the
other
end
of
the
shift
valves
controlling
upshift
and
downshift
speeds
FLOW
CONTROL
VALVES
Manual
valve
The
manual
valve
is
moved
manual
Iy
by
the
car
operator
to
select
the
different
drive
ranges
1
2
ShHt
valve
The
1
2
shift
valve
automaticaIly
shifts
the
transmission
from
first
to
second
or
from
second
to
first
depend
ing
upon
governor
and
throttle
pres
sure
along
with
accelerator
position
solenoid
downshift
valve
See
Hy
draulic
Control
Circuits
Drive
2
2
3
ShHt
valve
The
2
3
shift
valve
automaticaIly
shifts
the
transmission
from
second
to
top
gear
or
from
top
to
second
de
pending
upon
governor
and
throttle
pressure
or
accelerator
position
sole
noid
downshift
valve
See
Hydraulic
Control
Circuits
Drive
3
Range
2
3
Tlmlnll
valve
For
2
3
shifts
a
restrictive
orifice
slows
the
application
fluid
to
the
front
clutch
while
the
slower
reacting
band
is
allowed
to
release
This
prevents
a
hard
2
3
or
3
2
shift
Under
heavy
load
however
the
engine
will
tend
to
run
away
during
the
2
3
or
3
2
shift
pause
therefore
a
2
3
timing
valve
using
throttle
and
governor
pressure
is
used
to
bypass
the
restrictive
orifice
during
such
heavy
load
conditions
Solenoid
down
hHt
valve
The
solenoid
downshift
valve
is
activated
electrically
when
the
ac
celerator
is
f1oor
d
causing
a
forced
downshift
from
top
to
second
top
to
first
or
second
to
first
gear
depending
upon
car
speed
governor
pressure
AT
3
Pre
ure
modified
valve
The
pressure
modifier
valve
assists
the
mainline
pressure
regulator
valve
in
lowering
mainline
pressure
during
high
speed
light
load
conditions
such
as
steady
speed
cruise
Governor
pres
sure
working
against
a
spring
opens
the
valve
which
aUows
modified
throt
tle
pressure
to
work
against
the
pres
sure
regulator
valve
spring
lowering
mainline
pressure
Lower
operating
pressure
under
light
load
reduces
oil
temperature
and
increases
transmis
sian
life
Throttle
back
up
valve
The
throttle
back
up
valve
assists
the
vacuum
throttle
valve
to
increase
line
pressure
when
the
manual
valve
is
shifted
either
to
2
or
I
range
Second
lock
valve
The
second
lock
valve
is
used
to
bypa
the
1
2
shift
valve
to
maintain
the
band
apply
pressure
in
2
posi
tion
The
valve
is
also
used
as
an
oil
passage
for
the
1
2
shift
valve
band
apply
pressure
in
D2
D3
and
12
Range
CLUTCHES
AND
BAND
SERVOS
The
servo
pistons
of
the
clutches
low
reverse
brake
and
band
are
moved
hydraulically
to
engage
the
clutches
brake
and
apply
the
band
The
clutch
and
brake
istons
are
released
by
spring
tension
and
band
piston
is
released
by
spring
tension
and
hy
draulic
pressure
Page 285 of 548
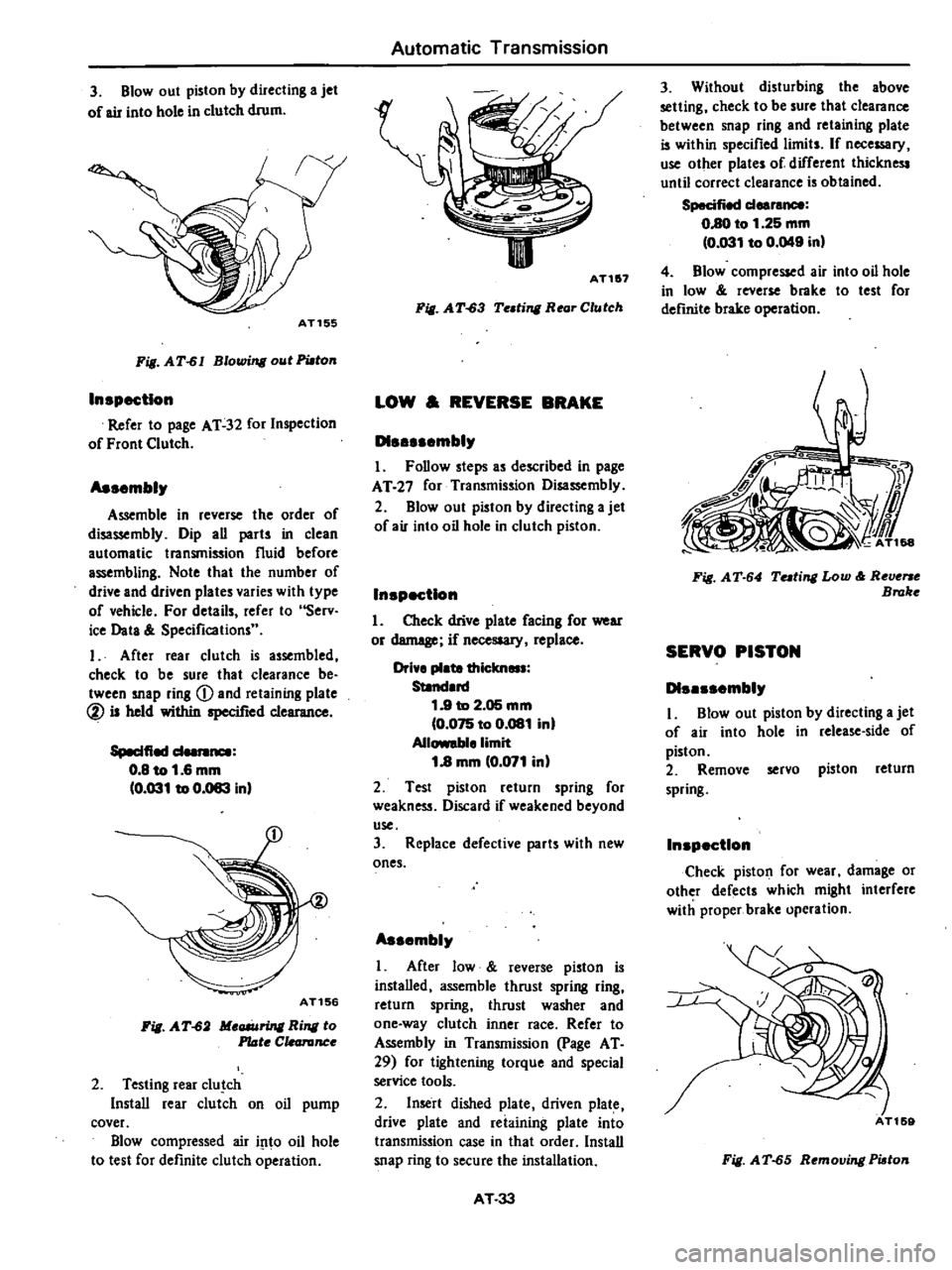
3
Blowout
piston
by
directing
a
jet
of
air
into
hole
in
clutch
drum
AT155
Fig
AT
61
Blowing
out
PWton
In
pectlon
Refer
to
page
AT
32
for
Inspection
of
Front
Clutch
As
mbly
Assemble
in
reverse
the
order
of
disassembly
Dip
all
parts
in
clean
automatic
transmission
fluid
before
assembling
Note
that
the
number
of
drive
and
driven
plates
varies
with
type
of
vehicle
For
details
refer
to
Serv
ice
Data
Specifications
I
After
rear
clutch
is
assembled
check
to
be
sure
that
clearance
be
tween
snap
ring
Q
and
retaining
plate
@
is
held
within
specified
clearance
Speelfied
d
0
8
to
1
6
mm
0
031
to
0
083
inl
AT156
Fig
AT
62
Meaiuring
Ring
to
Plate
C
canInce
2
Testing
rear
c1u
ch
Install
rear
clutch
on
oil
pump
cover
Blow
compressed
air
i
1to
oil
hole
to
test
for
definite
clutch
operation
Automatic
Transmission
II
AT1
7
Fill
A
T
63
Te
ting
Rear
Clutch
LOW
REVERSE
BRAKE
D1
mbly
I
Follow
steps
as
described
in
page
AT
27
for
Transmission
Disassembly
2
Blowout
piston
by
directing
a
jet
of
air
into
oil
hole
in
clutch
piston
In
pectlon
1
Check
drive
plate
facing
for
wear
or
demege
if
necesaary
replace
Drive
plate
thielm
Standard
1
9
to
2
05
mm
0
075
to
0
081
in
Allowable
limit
1
8
mm
0
071
inl
2
Test
piston
return
spring
for
weakness
Discard
if
weakened
beyond
use
3
Replace
defective
parts
with
new
ones
As
mbly
I
After
low
reverse
piston
is
installed
assemble
thrust
spring
ring
return
spring
thrust
washer
and
one
way
clutch
inner
race
Refer
to
Assembly
in
Transmission
page
AT
29
for
tightening
torque
and
special
service
tools
2
Insert
dished
plate
driven
plate
drive
plate
and
reiaining
plate
into
transmission
case
in
that
order
Install
snap
ring
to
secure
the
installation
AT
33
3
Without
disturbing
the
above
setting
check
to
be
sure
that
clearance
between
snap
ring
and
retaining
plate
is
within
specified
limits
If
nece
ry
use
other
plates
of
different
thickness
until
correct
clearance
is
obtained
Specified
deereM8
0
80
to
1
25
mm
0
031
to
0
049
inl
4
Blow
compressed
air
into
oil
hole
in
low
roverse
brake
to
test
for
deftnite
brake
operation
Fill
AT
64
Tuting
Low
Reverse
Broke
SERVO
PISTON
D1
mbly
I
Blowout
piston
by
dilecting
a
jet
of
air
into
hole
in
release
side
of
piston
2
Remove
servo
piston
return
spring
In
p
ctlon
Check
piston
for
wear
damage
or
other
defects
which
might
interfere
with
proper
brake
opcration
Fig
AT
65
Removing
Piaton