DATSUN 610 1969 Owner's Guide
Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1969, Model line: 610, Model: DATSUN 610 1969Pages: 171, PDF Size: 10.63 MB
Page 31 of 171

inter
i
D
j
@
2l
Fig
C
3
Checking
the
ignition
timing
J
EARTH
LEAD
WIRE
SET
SCREW
OAmER
Fig
C
5
View
of
the
distributor
without
cap
Fig
C
7
Removing
the
retaining
pin
30
J
Fig
C
4
Adjusting
the
contact
points
gap
L
Fig
C
6
Removing
the
earn
2
1
1
I
7
V
J
J
1
Governor
weight
2
Oearance
for
start
and
nd
of
advanc
angle
1
Hook
4
GOllernor
spring
B
5
Com
plate
6
F7YWt
ight
pin
7
Hook
8
Goverrwrspring
A
9
Rotor
positioning
tip
@
Fig
C
8
Centrifugal
advance
mechanism
Page 32 of 171

CENTRIFUGAL
ADVANCE
MECHANISM
Special
equipment
is
required
to
check
the
advance
characteristics
It
is
possible
however
to
carry
out
an
exam
ination
of
the
caffi
assembly
and
the
weights
and
springs
to
ensure
that
the
earn
is
not
seizing
Lift
off
the
distributor
cap
and
turn
the
rotor
anti
clock
wise
When
the
rotor
is
released
is
should
return
to
the
fully
retarded
position
without
sticking
If
it
does
not
return
to
the
fully
retarded
position
it
will
be
necessary
to
check
for
dirt
and
weak
springs
It
should
be
noted
that
any
wear
in
the
mechanism
or
lose
of
spring
tension
will
upset
the
advance
characteristics
and
cause
unsatisfactory
engine
running
performance
over
the
speed
range
VACUUM
ADVANCE
MECHANISM
The
diaphragm
of
the
vacuum
advance
mechanism
is
mechanically
connected
to
the
contact
breaker
plate
The
rise
and
fall
of
inlet
manifold
depression
causes
the
diaphragm
to
move
the
contact
breaker
plate
to
advance
or
retard
the
ignition
If
the
vacuum
control
unit
fails
to
function
correctly
a
check
can
be
carried
out
to
ensure
that
the
contact
breaker
plate
is
moving
freely
and
that
the
three
steel
balls
at
the
top
and
oottom
of
the
plate
are
adequately
lubricated
Also
make
sure
that
the
vacuum
inlet
pipe
is
not
blocked
or
leaking
and
is
securely
tightened
Leakage
may
be
due
to
a
defective
diaphragm
which
should
be
renewed
along
with
any
other
faulty
part
of
the
mechanism
IGNITION
DlSTRffiUTOR
Removal
and
Dismantling
Disconnect
the
battery
leads
2
Disconnect
the
high
tension
lead
at
the
coil
3
Withdraw
the
high
tension
leads
from
the
distributor
cap
4
Detach
the
suction
pipe
from
the
vacuum
control
unit
5
Mark
the
position
of
the
distributor
and
rotor
remove
the
flange
mounting
bolts
and
withdraw
the
distributor
To
dismantle
the
distributor
proceed
as
follows
Take
off
the
distributor
cap
and
remove
the
rotor
Slacken
the
two
set
screws
holding
the
contact
breaker
upper
plate
Remove
the
primary
cable
terminals
and
withdraw
the
contact
set
from
the
distributor
Fig
C
S
Remove
the
vacuum
control
unit
c
Remove
the
two
screws
and
lift
out
the
contact
breaker
plate
detach
the
clamp
the
terminal
and
the
lead
To
remove
the
cam
take
out
the
centre
screw
as
shown
in
Fig
e
6
Drive
out
the
drive
pinion
retaining
pin
with
a
drift
and
hammer
Fig
e
and
remove
the
pinion
and
washer
Take
care
not
to
stretch
or
deform
the
governor
springs
when
detaching
them
from
the
weights
IGNITION
DISTRIBUTOR
Assembling
and
Installing
Assembly
is
a
reversal
of
the
dismantling
procedure
Lubricate
the
moving
contact
pivot
and
smear
the
lobes
of
the
cam
with
multi
purpose
grease
If
the
centrifugal
advance
mechanism
has
been
dismantled
the
governor
springs
and
cams
must
be
refitted
as
shown
in
Fig
e
8
The
governor
weight
pin
6
should
be
fitted
into
the
longer
of
the
two
slots
leaving
a
certain
amount
of
clearance
for
the
start
and
end
of
the
centrifugal
advance
movement
When
installing
the
distributor
take
care
to
align
the
body
and
rotor
with
the
marks
made
during
removal
The
rotor
must
be
positioned
in
its
original
location
it
will
turn
slightly
when
the
distributor
is
inserted
and
the
gear
teeth
mesh
Remove
and
replace
the
distributor
if
the
rotor
does
not
point
to
the
align
ment
mark
until
both
distributor
body
and
rotor
are
correctly
aligned
SPARKING
PLUGS
The
sparking
plugs
should
be
inspected
and
cleaned
at
regular
intervals
not
exceeding
every
10
000
km
6000
miles
New
sparking
plugs
should
be
fitted
at
approximately
20
000
km
12
000
miles
Remove
the
plugs
and
check
the
amount
of
electrode
wear
and
type
of
deposits
Brown
to
greyish
tan
deposits
with
slight
electrode
wear
indicate
that
the
plugs
are
satisfactory
and
working
in
the
correct
heat
range
Dry
fluffy
carbon
deposits
are
caused
by
too
rich
a
mixture
dirty
air
cleaner
excessive
idling
or
faulty
ignition
In
this
case
it
is
advisable
to
replace
the
plugs
with
plugs
having
a
higher
heat
range
Oily
wet
black
deposits
are
an
indication
of
oil
in
the
combustion
chambers
through
worn
pistons
and
rings
or
excessive
clearance
between
valve
guides
and
stems
The
engine
should
be
overhauled
and
hotter
plugs
installed
A
white
or
light
grey
centre
electrode
and
bluish
burned
side
electrode
indicates
engine
overheating
incorrect
ignition
timing
loose
plugs
low
fuel
pump
pressure
or
incorrect
grade
of
fuel
Colder
sparking
plugs
should
be
fitted
The
plugs
should
be
cleaned
on
a
blasting
machine
and
tested
Dress
the
electrodes
with
a
small
file
so
that
the
surfaces
of
both
electrodes
are
flat
and
parallel
Adjust
the
spark
plug
gap
to
0
8
0
9
mm
0
031
0
035
in
by
bending
the
earth
electrode
Refit
the
plugs
and
tighten
them
to
a
torque
reading
of
1
5
2
5
kgm
II
15Ib
ft
31
Page 33 of 171

TechnIcal
Data
IGNITION
DISTRIBUTOR
Type
L16
ll8
with
single
carbl
L16
L18
with
twin
arb
L14
Firing
order
Rotation
Ignition
timing
BTDC
0411
58K
0409
54K
0411
63
Dwen
angle
Hitachi
D411
58K
Hitachi
D409
54
K
Hitachi
0411
63
I
3
4
2
anticlockwise
100
at
600
r
p
m
140
at
650
c
p
m
80
at
600
r
p
m
49
550
Contact
point
gap
setting
Contact
spring
tension
0
45
0
55
mm
O
OI77
0
0217
in
0
50
0
65
kg
l
l
0
I
43
lb
Condenser
capacity
0
22
0
44
F
IGNITION
COil
Type
Spark
plugs
With
single
carb
With
twin
carb
Plug
gap
Tightening
torque
Hitachi
6
R
200
NGK
BP
5ES
NGK
BP
6ES
0
8
0
9
mm
0
031
0
035
in
1
5
2
5
kgm
II
15Ib
ft
1300cc
engine
IGNITION
TIMING
Adjustment
100
B
T
D
C
600
r
p
m
32
Page 34 of 171

Fuel
System
DESCRIPTION
FUEL
TANK
FUEL
PUMP
CARBURETTOR
IDLING
ADJUSTMENT
FAST
IDLE
OPENING
ADJUSTMENT
THROTTLE
VALVES
INTERLOCK
OPENING
DASHPOT
DESCRIPTION
The
diaphragm
type
fuel
pump
shown
in
Fig
D
1
feeds
fuel
from
the
tank
to
the
carburettor
in
a
regulated
supply
according
to
the
needs
of
the
engine
A
cartridge
type
fuel
strainer
prevents
any
dirt
from
reaching
the
pump
inlet
valve
The
carburettor
fitted
to
the
engine
is
either
a
down
draught
two
barrel
type
equipped
with
a
throttle
operated
acceleration
pump
and
power
valve
mechanism
See
Fig
D
2
or
a
twin
SU
carburettor
of
the
type
shown
in
Fig
D
3
In
the
two
barrel
type
carburettor
fuel
flows
from
the
passage
at
the
bottom
of
the
float
chamber
passes
through
the
primary
main
jet
and
mixes
with
air
introduced
through
the
main
air
bleed
screw
The
petrol
and
air
mixture
is
injected
into
the
venturi
through
the
main
nozzle
Each
time
the
accelerator
pedal
is
depressed
the
throttle
opens
and
the
accelerator
pump
forces
a
jet
of
petrol
into
the
air
stream
to
allow
the
engine
to
accelerate
smoothly
See
Fig
0
4
The
power
valve
mechanism
is
operated
automatically
according
to
the
demands
made
by
the
engine
Under
light
load
i
e
part
throttle
conditions
the
intake
manifold
depression
is
transmitted
below
the
throttle
valve
the
vacuum
pulls
a
piston
upwards
against
a
spring
and
leaves
the
power
valve
closed
allowing
additional
air
to
be
admitted
through
the
air
bleed
screw
and
thereby
weaken
the
petrol
and
air
mixture
When
the
vacuum
below
the
throttle
vaJve
is
lowered
during
full
load
conditions
the
piston
is
pushed
down
opening
the
power
valve
and
providing
additional
fuel
to
enrichen
the
mixture
The
model
HJ
L
38W6
SU
twin
carburettor
is
of
the
horizontal
variable
venturi
type
and
is
used
only
on
the
1600
and
1800
cc
engines
In
this
type
of
carburettor
a
constant
flow
of
intake
air
is
maintained
by
the
automatically
adjusted
venturi
opening
this
is
accomplished
by
the
suction
piston
sliding
in
accordance
with
changes
in
the
volume
of
intake
air
Referring
to
Fig
D
5
the
suction
chamber
is
mounted
above
the
venturi
The
suction
piston
slides
vertically
within
the
chamber
and
changes
the
venturi
opening
area
The
piston
is
operated
by
a
difference
between
the
upper
vacuum
pressure
which
is
applied
through
the
suction
poct
and
the
atmospheric
pressure
which
is
introduced
through
the
air
hole
from
the
air
cleaner
The
amount
by
which
the
throttle
is
opened
causes
the
suction
piston
to
rise
or
fall
under
the
intluence
of
the
engine
suction
The
pozzle
opening
therefore
changes
and
provides
an
optimum
air
fuel
mixture
at
all
engine
speeds
The
cartridge
type
fuel
strainer
utilizes
a
fibre
strainer
element
which
should
be
replaced
every
20
000
km
12
000
miles
Removal
of
the
fuel
strainer
is
a
simple
operation
but
as
it
cannot
be
drained
the
strainer
should
not
be
removed
when
CARBURETIOR
Removal
and
Overhaul
FLOAT
LEVEL
Adjustment
SU
TWIN
CARBURmORS
Adjustments
SU
TWIN
CARBURmORS
Dismantling
SU
TWIN
CARBURETTORS
Inspection
STARTING
INTERLOCK
VALVE
OPENING
HYDRAULIC
DAMPER
the
tank
is
full
unless
absolutely
necessary
A
viscous
paper
type
air
cleaner
element
is
fitted
which
does
not
require
cleaning
and
should
be
repl
ced
every
40
000
km
24
000
miles
The
air
cleaner
fitted
on
the
single
carburettor
is
equipped
with
an
idling
compensator
to
prevent
the
mixture
from
becoming
too
rich
at
high
idling
temperatures
Additional
fresh
air
is
introduced
into
the
inlet
manifold
by
the
action
of
a
bimettalic
strip
located
in
the
air
cleaner
When
the
temperature
under
the
bonnet
is
high
the
bimetal
is
heated
by
the
hot
inlet
air
and
lifts
to
allow
the
valve
to
open
The
idling
compensator
valve
partially
opens
at
550
I310F
and
is
fully
open
at
650C
l490F
The
unit
cannot
be
dismantled
as
it
is
pre
sealed
and
correctly
adjusted
for
valve
timing
Fig
D
6
shows
the
layout
of
the
idling
compensator
piping
FUEL
TANK
Replacing
The
fuel
tank
can
be
removed
in
the
following
manner
Remove
the
rear
seat
and
back
rest
2
Take
out
the
board
behind
the
back
rest
3
Take
out
the
luggage
compartment
lining
board
and
disconnect
the
cable
to
the
petrol
gauge
unit
4
Disconnect
the
petrol
filler
tube
from
the
tank
5
Remove
the
tank
retaining
bolts
and
disconnect
the
rubber
fuel
outlet
and
return
hoses
Installation
is
a
reversal
of
the
removal
procedure
always
ensure
that
the
fuel
lines
arc
carefully
checked
for
signs
of
damage
before
replacing
the
tank
FUEL
PUMP
Testing
Pressure
and
capacity
tests
can
be
carried
out
with
the
pump
installed
in
the
following
manner
Static
pressure
test
Disconnect
the
fuel
line
at
the
carburettor
install
an
adaptor
tee
fitting
and
suitable
pressure
gauge
to
the
fuel
line
between
carburettor
and
fuel
pump
Start
the
engine
and
run
it
at
varying
speeds
The
reading
on
the
gauge
should
be
0
18
0
24
kg
sq
cm
2
6
34
Ib
sq
in
If
the
pressure
is
below
the
specified
figure
then
either
one
part
of
the
pump
has
worn
excessively
or
general
wear
has
occured
to
all
the
working
parts
The
faults
may
include
a
ruptured
diaphragm
worn
and
warped
valves
33
Page 35 of 171
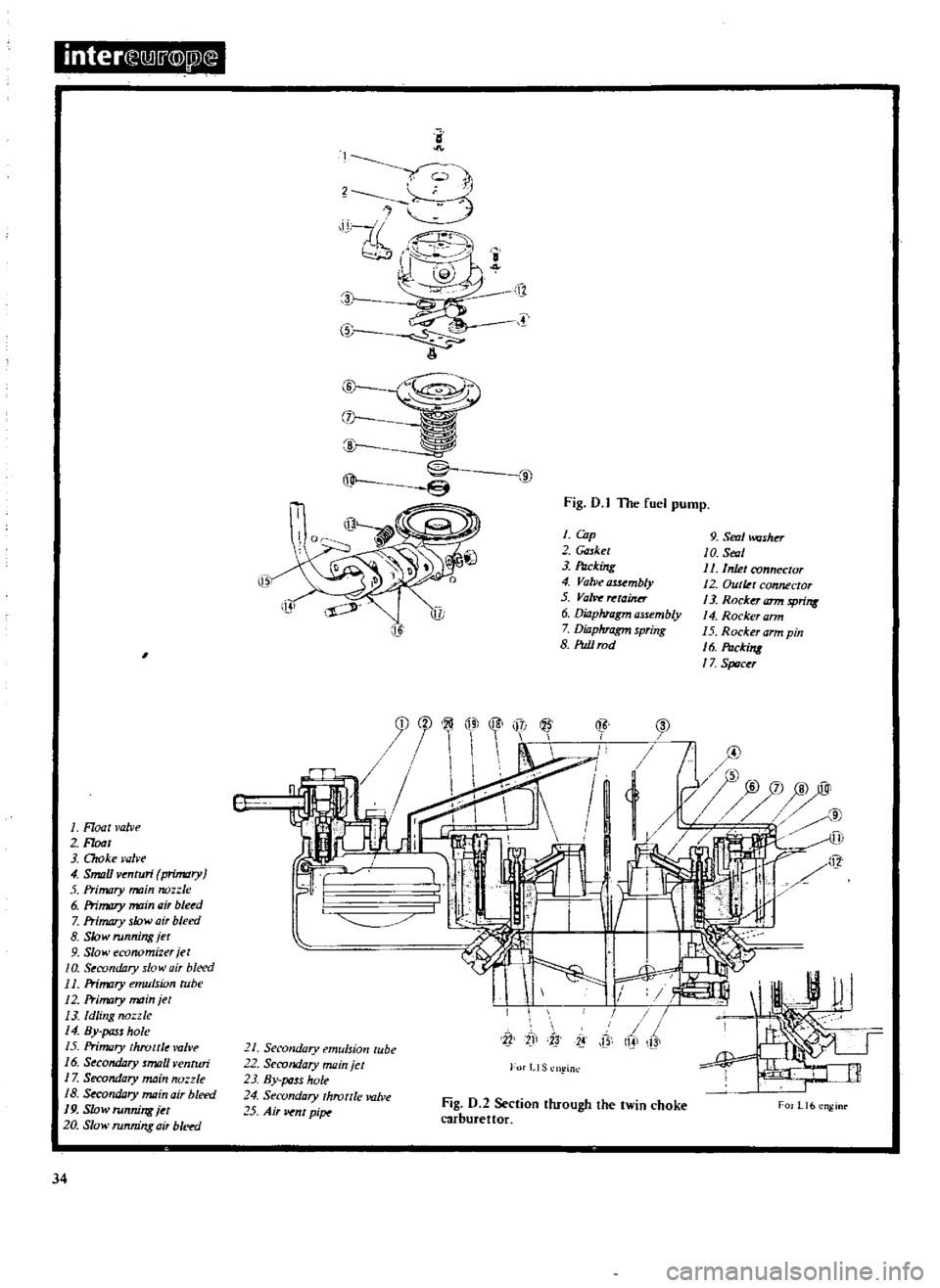
inter
1
j
Q
I
JJtE
1
Float
valve
2
Float
3
C1roke
aU
l
4
SmaU
venturi
primary
5
PritniJry
main
nozzle
6
Primary
main
ai
blud
7
Primmy
slow
air
bleed
8
Slow
running
jet
9
Slow
economizer
jet
10
condory
slow
ai
bleed
11
Primlry
emulsion
tube
12
Primary
main
jet
13
Idling
nozzle
14
By
pass
hole
15
Primary
throttle
vah
l
16
Secondary
smo
lllenturi
1
Z
Secondary
main
nozzle
18
Secondary
1ni1
n
air
bleed
19
Slow
running
jet
20
Slow
running
air
bhYd
34
1
G
o
1
u
40
j
t
1
fE
SV
11
t
9
Fig
D
l
The
fuel
pump
I
Cop
2
Gasket
3
Packing
4
Valve
ouembly
5
YaM
tain
6
Diaphragm
assembly
7
DiaphTagm
spring
8
Prdl
rod
9
Seal
washer
10
Seal
11
nletconnector
12
Outln
connector
J
J
Rocker
arm
sprint
J
4
Rocker
ann
15
Rocker
ann
pin
J
6
Packing
7
Spacer
If
C1l
T
l
I
I
@
51
lID
ID
I
9J
lJi
22
ill
21
23
3
f
II
I
21
Secondary
emulsio
tube
22
Secondary
main
jet
23
Bv
pass
hole
24
Secondary
thro
e
valve
25
Air
Tf
pi
I
or
LIt
Fig
D
l
Section
through
the
twin
choke
carburettor
For
LIb
ml
Page 36 of 171

and
seats
or
a
weak
diaphragm
return
spring
A
pressure
above
the
specified
figure
may
be
due
to
an
excessively
strong
and
tight
diaphragm
Capacity
test
The
capacity
test
can
be
carried
out
when
the
static
pressure
has
been
tested
and
conforms
with
the
specified
figure
of
0
18
kg
sq
cm
2
6Ib
sq
inJ
Disconnect
the
fuel
line
at
the
carburettor
and
place
a
container
under
the
end
of
the
pipe
to
act
as
a
fuel
sump
Start
the
engine
and
run
it
at
a
speed
of
1000
Lp
m
The
amount
of
fuel
delivered
from
the
pump
in
one
minutc
should
be
1000
cc
2
1
US
pt
If
petrol
does
not
flow
from
the
opcned
end
of
the
pipe
at
the
correct
rate
then
either
the
fuel
pipe
is
clogged
or
the
pump
is
not
operating
correctly
If
the
latter
cause
is
suspected
the
pump
must
be
removed
and
inspected
as
described
below
FUEL
PUMP
Removing
and
Dismantling
Before
removing
the
pump
take
off
the
petrol
tank
cap
and
disconnect
the
pump
inlet
and
outlet
pipes
Blow
through
the
pipes
with
compressed
air
to
make
sure
that
they
are
not
clogged
Remove
the
pump
retaining
nuts
withdraw
the
pump
and
dismantle
it
in
the
following
order
Referring
to
Fig
D
l
Take
out
the
screws
holding
the
two
body
halves
together
and
scparate
the
upper
body
from
the
lower
body
2
Remove
the
cap
and
cap
gasket
3
Unscrew
the
eI
bow
and
connector
4
Take
off
the
valve
retainer
and
remove
the
two
valves
5
To
remove
the
diaphragm
diaphragm
spring
and
lower
body
sealing
washer
press
the
diaphragm
down
against
the
force
of
the
spring
and
tilt
the
diaphragm
at
the
same
time
so
that
the
pull
rod
can
be
unhooked
from
the
rocker
arm
link
Fig
D
7
The
rocker
arm
pin
can
be
driven
out
with
a
suitable
drift
FUEL
PUMP
Inspection
and
Assembly
Check
the
uppcr
and
lower
body
halves
for
cracks
Inspect
the
valve
and
valve
spring
assembly
for
signs
of
wear
and
make
sure
that
the
diaphragm
is
not
holed
or
cracked
also
make
sure
that
the
rocker
arm
is
not
worn
at
the
point
of
contact
with
the
camshaft
The
rocker
arm
pin
may
cause
oil
leakage
if
worn
and
should
be
renewed
Assembly
is
a
reversal
of
the
dismantling
procedure
noting
the
following
points
Fit
new
gaskets
and
lubricate
the
rocker
arm
link
and
the
rocker
arm
pin
before
installing
The
pump
can
be
tested
by
holding
it
approximately
I
metre
3
feet
above
the
level
of
fuel
and
with
a
pipe
connected
between
the
pump
and
fuel
strainer
Operate
the
rocker
ann
by
hand
the
pump
is
operating
correctly
if
fuel
is
drawn
up
soon
after
the
rocker
ann
is
released
CARBURETTOR
IDLING
ADJUSTMENT
The
idling
speed
cannot
be
adjusted
satisfactorily
if
the
ignition
timing
is
incorrect
if
the
spark
plugs
are
dirty
or
if
the
valve
clearances
are
not
correctly
adjusted
Before
adjusting
the
idling
speed
set
the
hot
valve
clearances
t
o
0
25
mm
0
0098
in
for
the
intake
valves
and
0
30
mm
0
0118
in
for
the
exhaust
valves
as
described
in
the
ENGINE
section
Idling
adjustment
is
carried
out
with
the
throttle
stop
screw
in
conjunction
with
the
idling
adjustment
screw
See
Fig
D
8
Run
the
engine
until
it
attains
its
normal
operating
temperature
and
then
switch
off
Starting
from
the
fully
closed
position
unscrew
the
idling
adjustment
screw
by
approximately
three
turns
Screw
the
throttle
stop
screw
in
by
two
or
tftr
e
turns
and
start
th
engine
Unscrew
the
throttle
stop
screw
until
the
engine
commences
to
run
unevenly
then
screw
in
the
idling
adjustment
screw
so
that
the
engine
runs
smoothly
at
the
highest
speed
Readjust
the
throttle
stop
screw
to
drop
the
engine
speed
of
approximately
600
r
p
m
is
obtained
WARNING
Do
not
attempt
to
screw
the
idling
adjustment
screw
down
completely
or
the
tip
of
the
screw
may
be
damaged
FAST
IDLE
OPENING
ADJUSTMENT
The
choke
valve
is
synchronized
with
the
throttle
valve
and
connected
to
it
by
levers
as
shown
in
Fig
D
9
The
fast
idle
opening
can
be
check
by
fully
closing
the
choke
valve
and
measuring
the
clearance
between
the
primary
throttle
valve
and
the
wall
of
the
throttle
chamber
This
clearance
being
shown
as
A
in
the
illustration
The
clearance
for
the
carburettor
types
is
as
follows
Carburettor
type
Throttle
opening
angle
180
180
190
Dimension
A
213304
361
13304
4
I
13282
331
1
55mm
0
06lin
1
55mm
0
06Iin
1
3
mm
0
051
in
35
Page 37 of 171
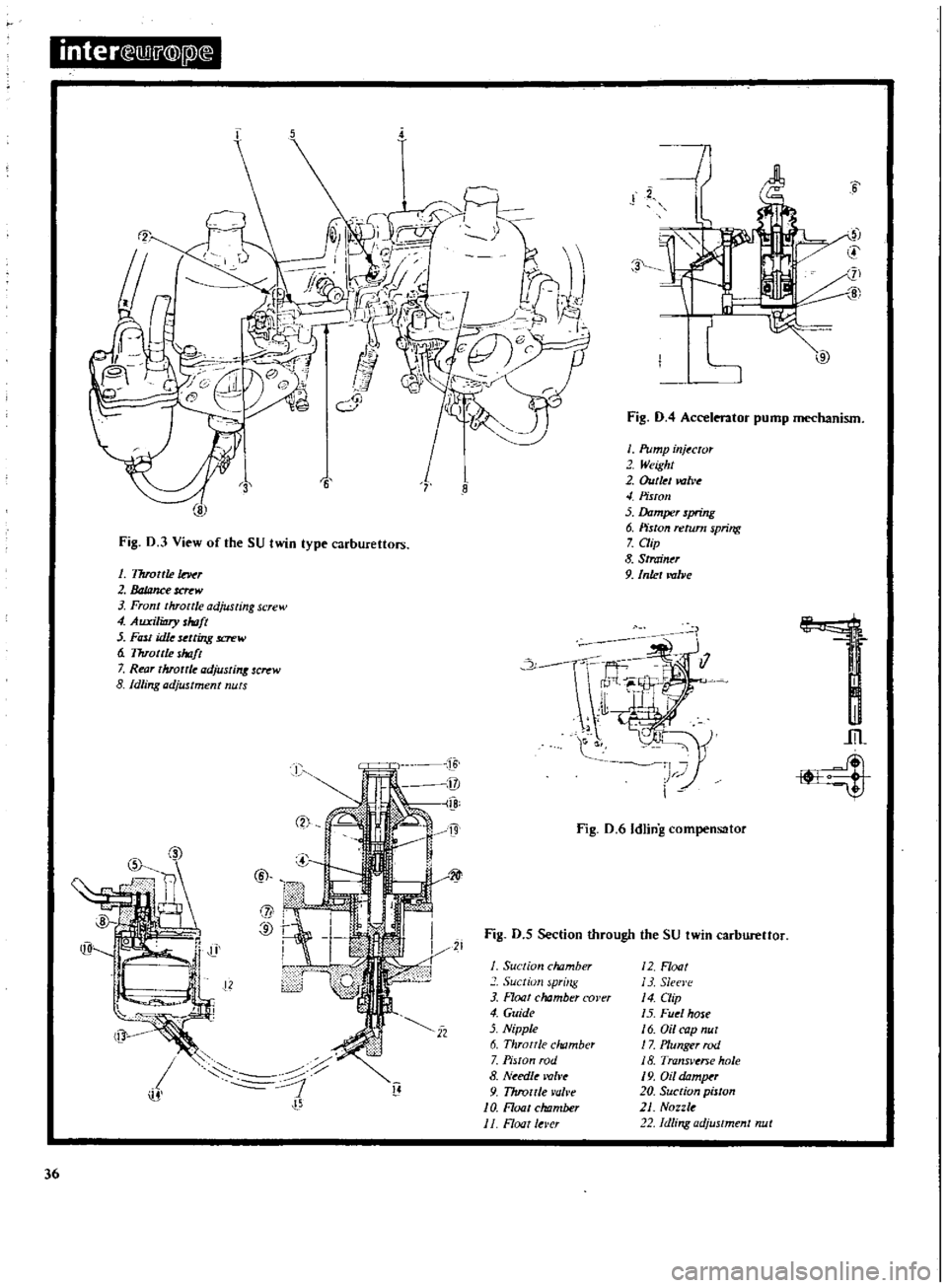
inter
ill
j
@
pl
T
i
5
12
Fig
D
3
View
of
the
SU
twin
type
carburettors
1
Throttle
r
2
JaJana
crew
Front
throttle
adjusting
screw
4
AuxiliDry
shoft
5
Ftnt
idle
selling
lCn
W
6
Throttle
shaft
7
Rear
throttle
adjusrint
screw
8
Idling
adjustment
nuts
m
11
j
G
36
B
l
D
i
I
lli
9
3
J6
6
Fig
D
4
Accelerator
pump
mechanism
J
Pump
injuror
2
Weight
2
Outklvolve
4
Piston
5
Damper
spring
6
Piston
return
spring
7
Clip
8
Strainu
9
Inlet
lmlJe
I
Fig
D
6
Idling
compensator
1
lit
21
Fig
D
5
Section
through
the
SU
twin
carbureUor
J
Suction
chamber
Suctiull
spring
3
Hoat
chamber
corer
4
Guide
5
Nipple
6
Throttle
chamber
7
Piston
rod
8
Needle
valve
9
T7trollle
l
ob
e
J
O
Float
chtzmber
J
1
Float
Iel
cr
J
2
Float
13
Sleel
e
4
aip
5
Fuel
hose
6
Oil
cap
nut
1
7
Plunger
rod
18
Transvtne
hole
J
9
Oil
domJX
20
Suction
piston
21
Nozzle
Idling
adjustment
nut
Page 38 of 171

Carburettor
type
Throttle
opening
angle
190
200
Dimension
A
213282
341
213282
221
l
3mm
0
051
in
I
4mm
0
056in
If
adjustment
is
required
the
choke
connecting
rod
can
be
carefully
bent
until
the
required
clearance
is
obtained
THROTTLE
VALVES
INTERLOCK
OPENING
ADJUSfMENT
Open
the
primary
throttle
valve
500
from
the
fully
closed
position
as
shown
in
Fig
D
I
O
At
this
angle
the
connecting
link
2
should
be
at
the
extreme
right
of
the
groove
in
the
primary
throttle
arm
The
linkage
between
the
primary
and
the
secondary
throttles
is
operating
correctly
if
the
clearance
C
between
the
primary
throttle
valve
and
the
wall
of
the
chamber
is
as
follows
Carburettor
type
213304
361
213304
421
213282
331
213282
341
Dimension
C
6
3
mm
0
248
in
6
3
mm
0
248
in
74
mm
0
291
in
74
mm
0
291
in
Adjustment
can
be
made
if
necessary
by
bending
the
connecting
link
until
the
required
clearance
is
obtained
DASHPOT
ADJUSfMENT
This
adjustment
is
only
required
on
carburettors
fitted
to
vehicles
with
automatic
transmission
Correct
contact
must
be
made
between
the
throttle
lever
and
the
dashpot
stem
See
Fig
D
II
Adjustment
can
be
carried
out
if
necessary
by
slackening
the
locknut
2
and
then
rotating
the
dashpot
in
either
direction
so
that
the
throttle
ann
touches
the
stem
at
a
throttle
valve
opening
angle
of
110
At
this
angle
the
clearance
B
between
the
throttle
valve
and
the
wall
of
the
chamber
should
be
as
follows
Carburettor
type
213304
421
213282
341
Dimension
B
0
780mm
90
0307
in
0
586mm
0
0231
in
Retighten
the
locknut
after
completing
the
adjustment
CARBURETTOR
Removal
and
Overhaul
The
carburettor
can
be
removed
from
the
engine
in
the
following
manner
Remove
the
air
cleaner
assembly
2
Disconnect
the
fuel
and
vacuum
pipes
and
the
choke
wire
from
the
carburettor
3
Remove
the
throttle
lever
and
take
off
the
nuts
and
washers
securing
the
carburettor
to
the
manifold
4
Lift
the
carburettor
away
from
the
manifold
and
discard
the
gasket
To
dismantle
the
carburettor
for
a
complete
overhaul
remove
the
primary
and
secondary
main
jets
and
needle
valves
these
are
accessible
from
the
exterior
of
the
carburettor
Remove
the
choke
connecting
rod
pump
lever
return
spring
and
set
screws
and
take
off
the
choke
chamber
The
primary
and
secondary
emulsion
tubes
can
be
with
drawn
after
removing
the
main
air
bleed
screws
If
the
accelerator
pump
is
to
be
checked
take
off
the
pump
cover
but
take
care
not
to
lose
the
return
spring
and
inlet
valve
ball
situated
at
the
lower
part
of
the
piston
Separate
the
throttle
chamber
from
the
float
chamber
by
removing
the
retaining
screws
leave
the
throttle
valve
intact
unless
otherwise
required
All
parts
of
the
carburettor
must
be
ctifefully
cleaned
and
sediment
gum
or
other
deposits
removed
Clean
the
jets
by
blowing
through
them
with
compressed
air
Never
push
wire
through
the
j
ts
or
passages
or
the
orifices
will
be
enlarged
and
the
calibration
affected
Check
all
parts
for
signs
of
wear
and
exchange
them
if
necessary
Examine
the
float
needle
and
seat
for
wear
and
make
sure
that
the
throttle
and
choke
bores
in
the
throttle
body
and
cover
are
not
worn
or
out
of
round
If
the
idling
adjustment
needles
have
burrs
or
ridges
they
must
be
replaced
Inspect
the
gaskets
to
make
sure
that
they
are
not
hard
and
brittle
or
distorted
Oean
the
filter
screen
if
it
is
clogged
or
change
it
if
it
is
otherwist
unsatisfactory
Check
the
operation
of
the
accelerator
pump
by
pouring
petrol
into
the
float
chamber
and
operating
the
throttle
lever
Petrol
should
spurt
from
the
pump
discharge
jet
if
the
pump
is
working
correctly
If
petrol
cannot
be
ejected
from
the
jet
when
the
lever
is
actuated
clean
the
discharge
jet
by
blowing
through
it
with
compressed
air
CARBURETTOR
Assembly
and
Installation
The
assembly
and
installation
of
the
carburettor
is
a
reversal
of
the
dismantling
and
removal
procedures
noting
the
following
points
Always
replace
the
gaskets
if
they
are
not
satisfactory
and
take
care
that
the
carburettor
linkage
operates
smoothly
and
is
not
bent
or
distorted
The
performance
of
the
carburettor
will
depend
on
the
condition
of
the
jets
and
air
bleeds
As
previously
stated
these
pacts
should
be
cleaned
using
petrol
and
compressed
air
only
Replacement
jets
or
air
bleed
screws
can
be
used
to
provide
greater
economy
or
to
increase
output
whatever
the
require
ment
When
the
carburettor
is
installed
adjust
the
idling
speed
as
previously
described
37
Page 39 of 171
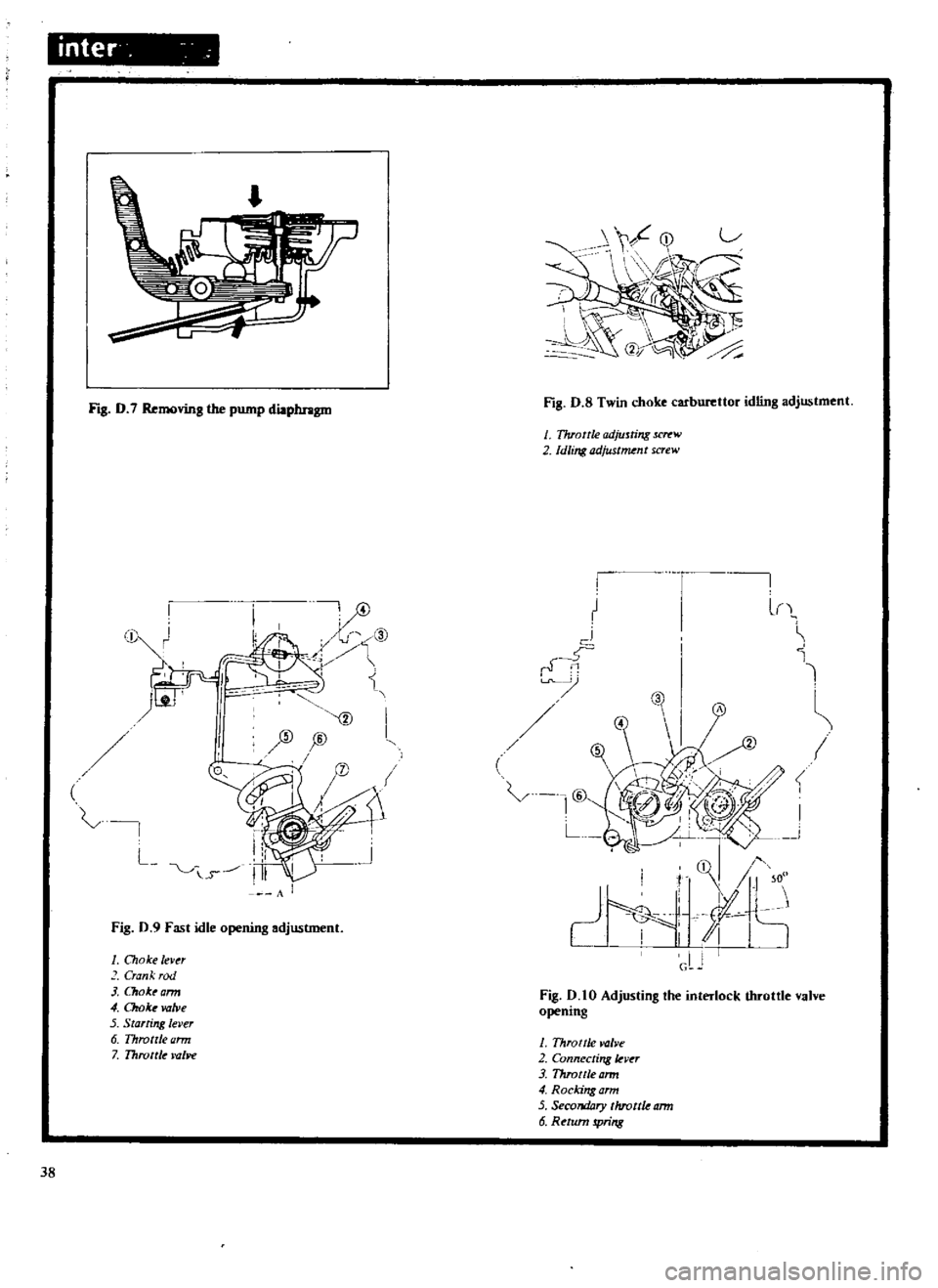
inter
Fig
D
7
Removing
the
pump
diaphragm
Fig
D
S
Twin
choke
carburettor
idling
adjustment
I
TJuottle
odjuJting
Jl
1l
W
2
Idling
adjust
nt
screw
t
c
l
1
cl
rf
C
L
t
0
i
I
SID
jID
L
v
i
s
A
Fig
0
9
Fast
idle
opening
adjustment
I
Choke
lever
Crank
rod
1
a
ok
arm
4
Chob
valve
5
Starring
lever
6
Throttle
ann
7
Throttle
lYl
J1e
Fig
0
10
Adjusting
the
interlock
throttle
valve
opening
J
Throttle
valve
2
Connecling
kv
r
3
Throttle
ann
4
Rocking
ann
5
Secondary
throttle
ann
6
Return
pring
38
Page 40 of 171

FLOAT
LEVEL
Adjustment
A
constant
fuel
level
in
the
float
chamber
is
maintained
by
the
float
and
ball
valve
Fig
D
12
If
the
fuel
level
is
not
in
accordance
with
the
level
gauge
line
it
will
be
necessary
to
care
fully
bend
the
float
seat
until
the
float
upper
position
is
correctly
set
Fig
D
13
The
clearance
H
between
the
valve
stem
and
float
seat
should
be
1
0
mm
0
039
in
with
the
float
fully
lifted
as
shown
Adjustment
can
be
carried
out
by
carefully
bending
the
float
stopper
Fig
D
14
until
the
required
clearance
is
obtained
SU
TWIN
CARBURETTORS
Adjustments
It
is
essential
that
the
two
carburettors
are
correctly
adjusted
if
peak
m3l1ce
and
economical
fuel
consumption
is
to
be
realized
Incorrect
carburettor
a
ljustment
will
have
an
adverse
affect
during
idling
and
on
acceleration
etc
Carburettor
synchronization
and
idling
adjustment
Run
the
engine
until
it
reaches
its
normal
operating
temperature
remove
the
air
cleaner
and
slacken
the
front
and
rear
throttle
adjusting
screws
the
balance
screw
and
the
fast
idling
setting
screw
Make
sure
that
the
front
and
rear
throttle
shafts
are
not
connected
Fully
tighten
the
idling
adjustment
nuts
of
the
front
and
rear
carburettors
Fig
D
15
the
back
off
each
nut
by
an
equal
amount
and
by
one
and
a
half
to
two
tUrns
Screw
in
the
front
and
rear
throttle
adjusting
screws
by
a
few
turns
and
start
the
engine
Allow
the
engine
to
reach
its
normal
operating
temperature
before
proceding
to
the
next
stage
Adjust
the
front
and
rear
throttle
adjusting
screws
until
the
engine
speed
is
reduced
to
approximately
600
700
r
p
m
The
engine
should
turn
over
smoothly
and
consistently
Apply
a
flow
meter
to
the
front
carburettor
air
cleaner
flange
and
turn
the
adjustment
screw
on
the
flow
meter
so
that
the
upper
end
of
the
float
in
the
glass
tube
is
in
line
with
the
scale
Uft
off
the
flow
meter
and
apply
it
to
the
rear
carburettor
air
cleaner
flange
without
altering
the
setting
of
the
flow
meter
adjusting
screw
If
the
position
of
the
flow
meter
float
is
not
aligned
with
the
scale
adjust
the
rear
carburettor
throttle
adjusting
screw
to
align
the
float
with
the
mark
on
the
scale
With
the
carburettor
flow
correctly
adjusted
turn
the
idling
adjustment
nuts
of
both
carburettors
approximately
1
8
of
a
turn
either
way
to
obtain
a
fast
and
stable
engine
speed
Both
nuts
must
be
turned
by
an
equal
amount
Back
off
the
front
and
rear
throttle
adjusting
screws
and
adjust
the
engine
speed
to
the
specified
value
of
650
r
p
m
for
the
standard
engine
or
700
r
p
m
with
vehicles
fitted
with
automatic
transmission
Make
sure
that
the
air
flow
of
both
carburettors
remains
unchanged
Screw
in
the
balance
screw
until
the
screw
head
contacts
the
throttle
shafts
without
changing
the
idling
speed
setting
Move
the
throttle
connecting
shaft
and
accelerate
the
engine
a
few
times
then
check
that
the
idling
speed
is
unchanged
Turn
the
fast
idle
setting
screw
to
increase
the
engine
speed
to
approximately
1500
r
p
m
and
recheck
with
the
flow
meter
that
the
air
flow
for
both
carburettors
is
correctly
matched
If
the
air
flow
is
uneven
it
will
be
necessary
to
readjust
the
balance
screw
Finally
back
off
the
fast
idle
setting
screw
Fig
D
16
and
decrease
the
engine
speed
Apply
the
flow
meter
to
the
carburettors
to
confirm
that
the
float
positions
are
even
Re
adjust
if
necessary
by
means
of
the
throttle
adjusting
screws
Stop
the
engine
and
fit
the
air
cleaner
SU
TWIN
CARBURETTOR
Dismantling
Piston
and
suction
chamber
Dismantling
Unscrew
the
plug
and
withdraw
the
piston
damper
Fig
D
17
Remove
the
four
set
screws
and
lift
out
the
suction
chamber
withdraw
the
spring
nylon
washer
and
the
piston
Take
care
not
the
damage
the
jet
needle
and
the
interior
of
the
suction
chamber
Do
not
remove
the
jet
needle
from
the
piston
unless
absolutely
necessary
If
a
replacement
is
to
be
fitted
ensure
that
the
shoulder
of
the
needle
is
flush
with
the
lower
face
of
the
piston
This
operation
can
be
accomplished
by
holding
a
strai
edge
over
the
shoulder
of
the
needle
and
then
tightening
the
set
screw
as
shown
in
Fig
D
18
Wash
the
suction
chamber
and
piston
with
dean
solvent
and
dry
with
compressed
air
Lubricate
the
piston
rod
with
a
light
oil
Do
NOT
lubricate
the
large
end
of
the
piston
or
the
interior
of
the
suction
chamber
NOZZLE
Dismantling
The
nozzle
See
Fig
D
19
can
be
removed
quite
easily
but
should
not
be
dismantled
unless
absolutely
necessary
as
reassembly
of
the
nozzle
sleeve
washer
and
nozzle
sleeve
set
screw
is
an
extremely
intricate
operation
To
remove
the
nozzle
detach
the
connecting
plate
from
the
nozzle
head
pulling
lightly
on
the
starter
lever
to
ease
the
operation
Loosen
the
retaining
clip
take
off
the
fuel
line
and
remove
the
nozzle
Be
careful
not
to
damage
either
the
jet
needle
oc
the
nozzle
Remove
the
idle
adjusting
nut
and
spring
The
nozzle
sleeve
can
be
removed
if
necessary
by
taking
out
the
set
screw
but
as
previously
stated
should
not
be
dismantled
unless
absolutely
necessary
SU
TWIN
CARBUREfTOR
Assembly
Assemble
the
piston
assembly
into
position
but
do
not
fill
with
damper
oil
Assemble
the
nozzle
sleeve
washec
and
set
screw
by
temporarily
tightening
the
set
screw
Set
the
piston
to
its
fully
closed
position
and
insert
the
nozzle
until
it
contacts
the
nozzle
sleeve
When
the
nozzle
jet
contacts
the
jet
needle
the
nozzle
sleeve
must
be
slightly
adjusted
so
that
it
is
at
right
angles
to
the
centre
axis
and
positioned
to
leave
the
nozzle
jet
clear
of
the
jet
needle
Raise
the
piston
without
disturbing
the
setting
and
allow
it
to
drop
The
piston
should
drop
smoothly
until
the
stop
pin
strikes
the
venturi
with
a
liaht
metallic
click
See
below
under
Centering
the
jet
Tighten
the
nozzle
sleeve
set
screw
remove
the
nozzle
install
the
idle
adjustinJ
spring
and
adjusting
nut
on
the
nozzle
sleeve
and
refit
the
nozzle
39