ABS DATSUN B110 1973 Service User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 119 of 513
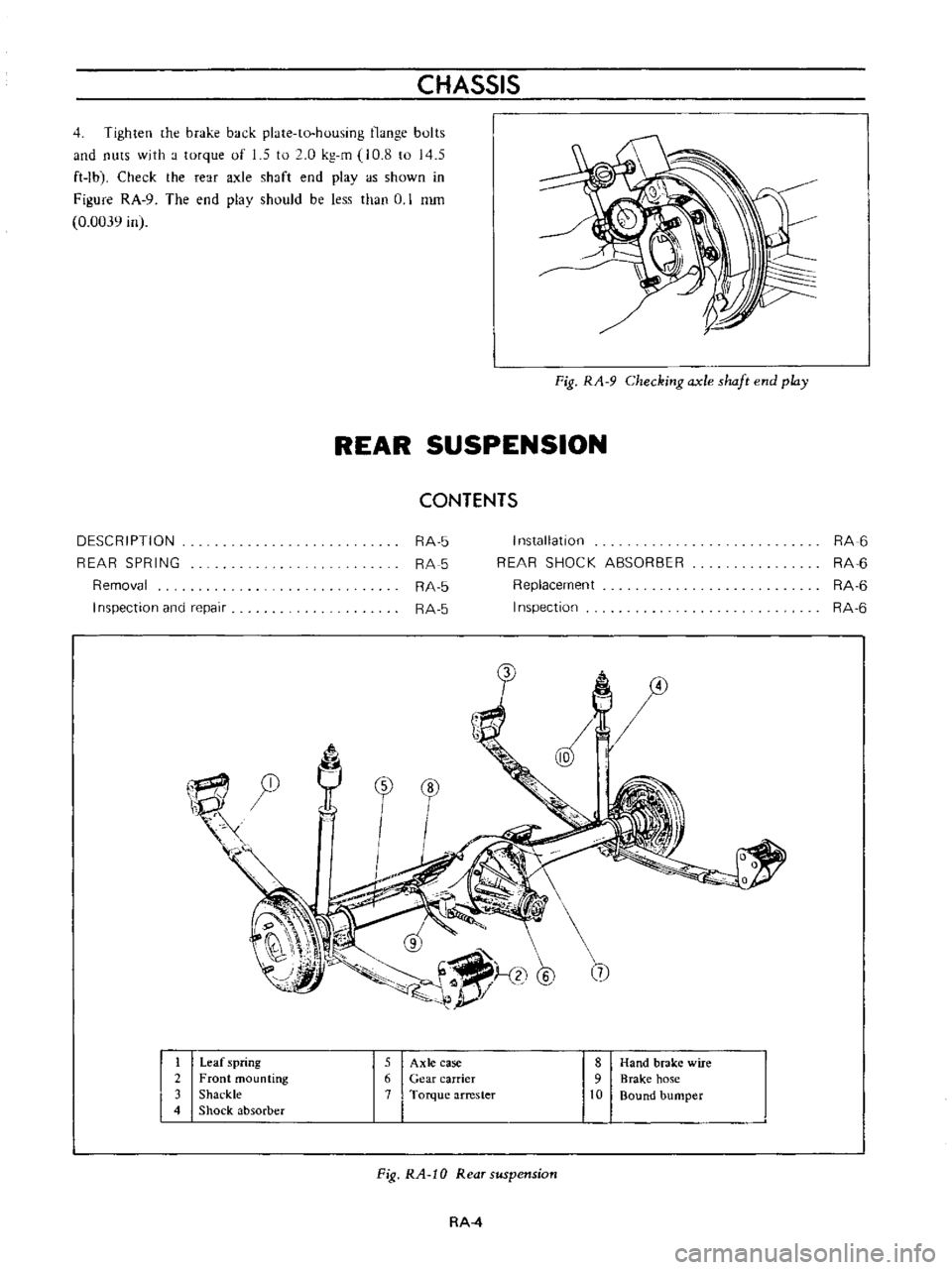
CHASSIS
4
Tighten
he
brake
back
plate
to
housing
nunge
bults
and
nuts
with
a
torque
of
1
5
to
2
0
kg
m
10
8
to
145
ft
Ibl
Check
the
rear
axle
shaft
end
playas
shown
in
Figure
RA
9
The
end
plav
should
be
less
than
U
I
nun
0
0039
in
Fig
RA
9
Checking
axle
shaft
end
play
REAR
SUSPENSION
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION
REAR
SPRING
Removal
I
nspection
and
repair
RA
5
RA
5
RA
5
RA
5
I
n5tallatlon
REAR
SHOCK
ABSORBER
Replacement
Inspection
RA
6
RA
6
RA
6
RA
6
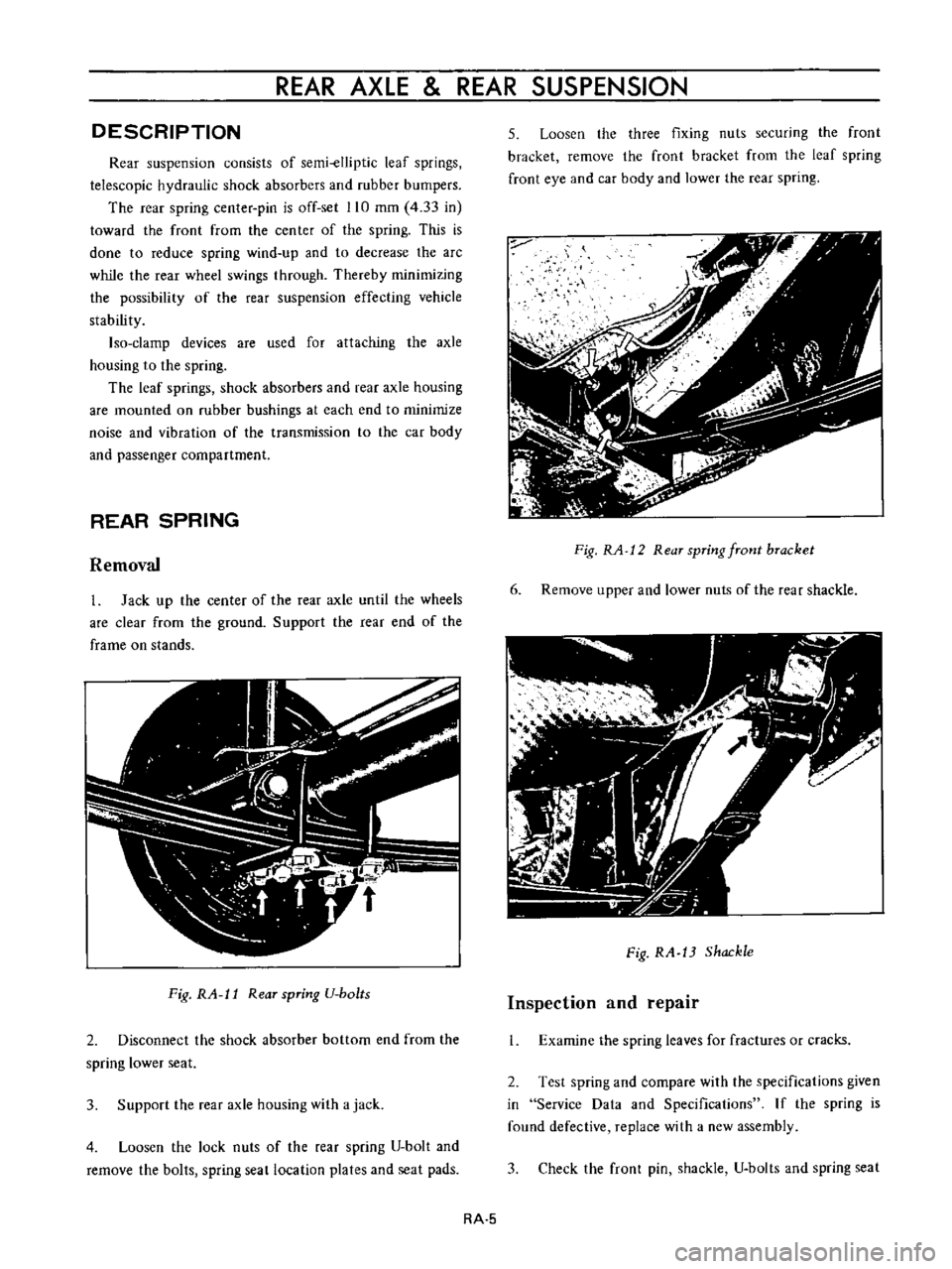
0
tr
1
1
@
5
@
7
I
Leaf
spring
5
Axle
case
8
Hand
brake
wire
2
Front
mounting
6
Gear
carrier
9
Brake
hose
3
Shackle
7
Torque
arrester
10
Bound
bumper
4
Shock
absorber
Fig
RA
10
Rear
suspension
RA
4
Page 120 of 513
REAR
AXLE
REAR
SUSPENSION
DESCRIPTION
Rear
suspension
consists
of
semi
elliptic
leaf
springs
telescopic
hydraulic
shock
absorbers
and
rubber
bumpers
The
rear
spring
center
pin
is
off
set
110
mm
4
33
in
toward
the
front
from
the
center
of
the
spring
This
is
done
to
reduce
spring
wind
up
and
to
decrease
the
arc
while
the
rear
wheel
swings
through
Thereby
minimizing
the
possibility
of
the
rear
suspension
effecting
vehicle
stability
Iso
clamp
devices
are
used
for
attaching
the
axle
housing
to
the
spring
The
leaf
springs
shock
absorbers
and
rear
axle
housing
are
mounted
on
rubber
bushings
at
each
end
to
minimize
noise
and
vibration
of
the
transmission
to
the
car
body
and
passenger
compartment
REAR
SPRING
Removal
1
Jack
up
the
center
of
the
rear
axle
until
the
wheels
are
clear
from
the
ground
Support
the
rear
end
of
the
frame
on
stands
Fig
RA
l1
Rear
spring
U
bo
ts
2
Disconnect
the
shock
absorber
bottom
end
from
the
spring
lower
seat
3
Support
the
rear
axle
housing
with
a
jack
4
Loosen
the
lock
nuts
of
the
rear
spring
U
bolt
and
remove
the
bolts
spring
seat
location
plates
and
seat
pads
5
Loosen
the
three
fixing
nuts
securing
the
front
bracket
remove
the
front
bracket
from
the
leaf
spring
front
eye
and
car
body
and
lower
the
rear
spring
Fig
RA
12
Rear
spring
front
bracket
6
Remove
upper
and
lower
nuts
of
the
rear
shackle
Fig
RA
13
Shackle
Inspection
and
repair
1
Examine
the
spring
leaves
for
fractures
or
cracks
2
Test
spring
and
compare
with
the
specifications
given
in
Service
Data
and
Specifications
If
the
spring
is
found
defective
replace
with
a
new
assembly
3
Check
the
front
pin
shackle
U
bolts
and
spring
seat
RA
5
Page 121 of 513

CHASSIS
for
wear
cra
ks
straightness
and
damaged
thread
s
If
defective
parts
are
found
replace
with
new
ones
4
Inspect
all
rubber
pans
for
wear
damage
separation
and
deformation
Replace
them
if
necessary
Installation
Install
the
rear
spring
in
reverse
sequence
of
removal
noting
the
following
matters
Coat
the
front
bracket
pin
front
bracket
bushing
shackle
pin
and
shackle
bushing
with
a
soap
solution
prior
to
assembly
2
The
front
pin
securing
nut
and
shock
absorber
lower
end
securing
nut
should
be
tightened
with
the
vehicle
unladen
Note
Make
sure
that
the
flange
of
the
shackle
bushing
is
clamped
evenly
on
both
sides
REAR
SHOCK
ABSORBER
Replacement
lack
up
the
center
of
the
rear
axle
and
support
the
axle
housing
with
stands
Fig
RA
14
Removing
the
shock
absorber
ower
end
2
Remove
the
lower
end
of
the
rear
shock
absorber
from
the
spring
seat
See
Figure
RA
14
FiK
RA
15
Removing
shock
absorber
upper
bracket
3
Remove
the
rear
shock
absorber
installing
nut
located
under
the
rear
seat
back
4
Install
rear
shock
absorber
in
reverse
sequence
of
removal
Inspection
Test
the
shock
absorber
and
compare
with
the
specifications
given
in
Service
Data
and
Specifications
Replace
if
necessary
2
Check
for
leakage
cracks
and
the
shafl
for
straightness
3
Inspect
the
rubber
bushings
for
damage
cracks
and
excessive
deformation
Replace
the
defective
parts
jf
necessary
RA
6
Page 122 of 513
REAR
AXLE
REAR
SUSPENSION
SERVICE
DATA
AN
D
SPECIFICATIONS
Shock
absorber
Applied
model
Sedan
Coupe
Van
Stroke
x
max
length
mm
in
167x506
6
57xI9
9
180
x
440
7
09
x
17
3
180
x
468
7
09
x
18
4
Damping
force
at
0
3mjs
Rebound
Compression
kg
Ib
kg
lb
58
128
38
83
8
68
I
50
45
99
2
90
198
45
99
2
Rear
spring
Length
x
widlh
x
thickness
NO
ofleaves
mm
in
6
I
1
llOx50x72
O
6
1
I
ll
x50x7
2
6
3
1
110
x
50
x
13
1
0
24
1
43
7x
1
97x
0
28
2
0
24
2
43
7xI
97x
0
28
1
0
52
1
1
110x50x
6
2
43
7X
1
97
x
0
24
1
7
1
0
28
2
11
1
0
43
1
0
24
1
43
7x
1
97x
0
28
2
Heavy
duty
spring
Camber
Free
mm
in
109
t3
4
29
1
0
1181
11
0
433
109
1
3
4
29
1
0
1181
11
0
433
131
1
5
5
15
tO
1969
11
0
433
Loaded
wi
th
specified
load
mm
in
Specified
load
kg
Ib
In
423
In
423
295
650
Spring
eye
diameter
Front
mm
in
35
1
378
35
1
378
35
1
378
Rear
mm
in
23
0
906
23
0
906
23
0
906
Rear
axle
End
play
mm
in
Less
than
0
1
0
0039
Rear
axle
end
shim
mm
in
0
Q75
0
003
Wheel
bearing
coUar
pressing
force
ton
Ib
3
to
5
6
600
to
11
000
Tightening
torque
Axle
shaft
to
housing
flange
bolt
nuts
kg
m
ft
lb
1
5
to
2
0
10
9
to
14
5
L7
to
2
5
12
3
to
18
1
Differential
carrier
to
housing
bolts
Spring
V
bolts
3
2
to
4
0
23
1
to
28
9
RA
7
Page 123 of 513

CHASSIS
Wheel
nuts
8
0
to
9
0
7
8
to
65
1
Spring
front
bracket
to
body
bolt
nuts
Sedan
and
Coupe
Van
6
to
0
1
6
to
14
5
6
to
I
11
6
to
15
2
Spring
shackle
pin
nuts
1
6
to
0
11
6
to
14
5
Spring
front
pin
nut
Sedan
and
Coupe
Van
6
to
2
0
1
6
to
14
5
3
2
to
4
0
23
1
to
28
9
Shock
absorber
upper
nuts
Sedan
and
Van
Coupe
3
6
to
4
5
26
0
to
32
5
0
to
1
7
2
to
8
6
Shock
absorber
lower
nuts
Sedan
and
Van
Coupe
3
6
to
4
5
26
0
to
32
5
0
to
I
2
7
2
to
8
6
0
6
to
0
8
4
3
to
5
8
Torque
arrester
to
body
bolts
SERVICE
JOURNAL
OR
BULLETIN
REFERENCE
DATE
JOURNAL
or
BULLETIN
No
PAGE
No
SUBJECT
RA
8
Page 158 of 513
WHEEL
AND
TIRE
Note
In
replacing
tire
take
extra
care
not
to
damage
tire
bead
rim
flange
and
bead
seat
Do
not
use
tire
irons
to
force
beads
away
from
wheel
rim
flange
that
is
always
use
tire
replace
ment
device
whenever
tire
is
removed
WT005
2
Discard
when
any
of
the
following
trouble
occurs
I
Broken
or
damaged
bead
wire
2
Ply
or
tread
separation
3
Worn
febric
damage
on
tubeless
tire
4
Cracked
or
damaged
side
wall
etc
Fig
WT
4
Wheel
rim
run
out
heck
points
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Condition
Probable
cause
Corrective
action
Wheel
wobbles
Improper
t
re
pressure
Measure
and
adjust
correctly
Damaged
tire
9f
distorted
wheel
rim
Repair
or
replace
UnbalanceiLwheel
Balance
correctly
Loose
wheel
nuts
Retighten
Worn
qr
damaged
wheel
bearing
or
excessive
play
of
wheel
bearing
Correct
play
or
replace
Improper
front
wheel
alignment
Adjust
Worn
or
damaged
ball
joint
and
link
bushing
Replace
Excessive
steering
linkage
play
or
worn
steering
lin
age
Adjust
or
replace
Loose
stcerin
linkage
connection
Retighten
the
nuts
with
the
rated
lightening
torque
or
replace
worn
parts
if
any
Broken
suspension
spring
Replace
Defective
shock
absorber
Replace
Unevenly
or
excessively
worn
tire
Improper
tire
rotation
Conduct
tire
rotation
periodically
Standard
every
10
000
km
6
000
miies
Improper
tire
pressure
Measure
and
adjust
correctly
Unbalanced
wheel
Balance
or
replace
Improperly
adjusled
brake
Readjust
correctly
WT5
Page 161 of 513
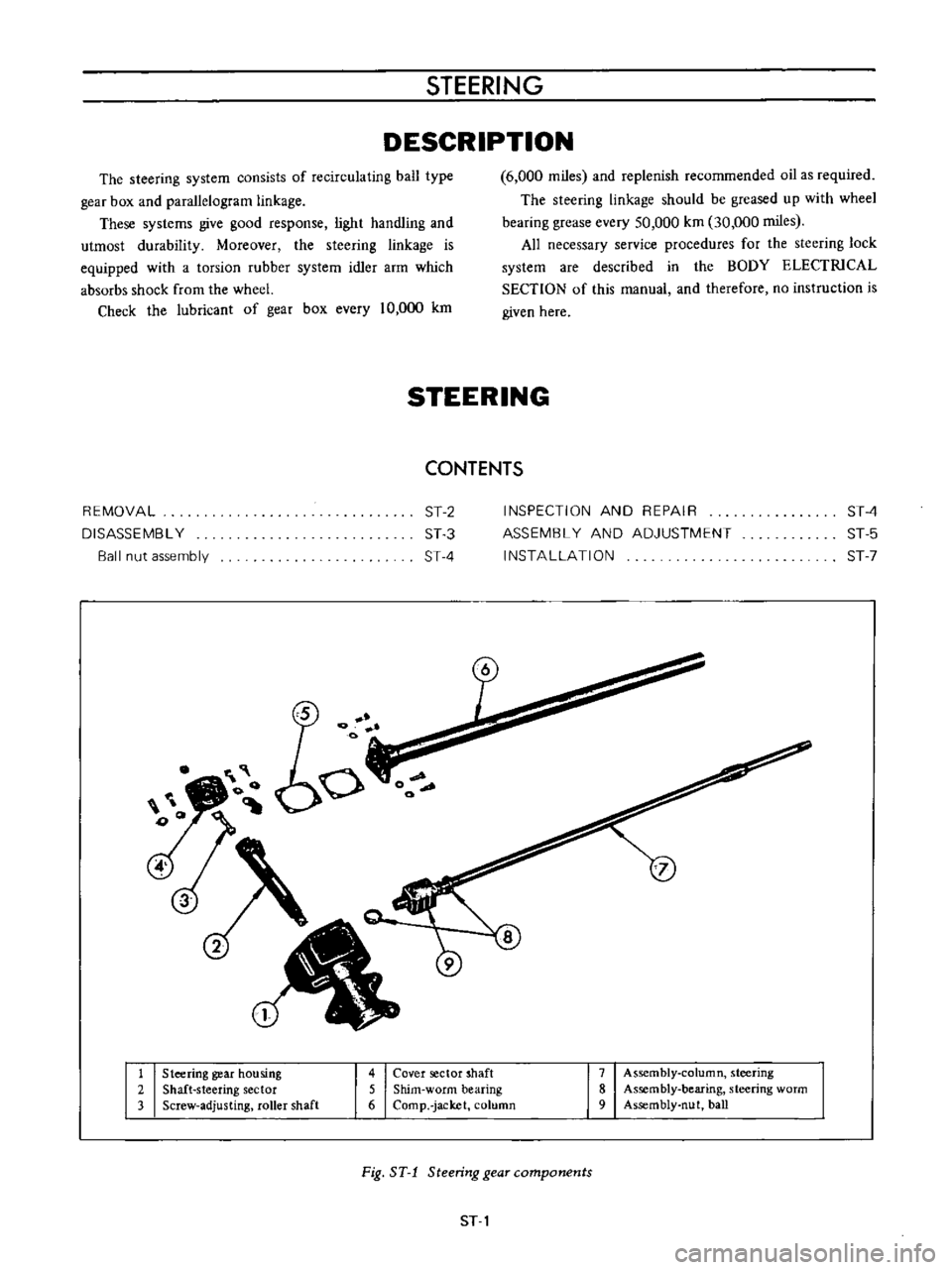
STEERING
DESCRIPTION
The
steering
system
consists
of
recirculating
ball
type
gear
box
and
parallelogram
linkage
These
systems
give
good
response
light
handling
and
utmost
durability
Moreover
the
steering
linkage
is
equipped
with
a
torsion
rubber
system
idler
arm
which
absorbs
shock
from
the
wheel
Check
the
lubricant
of
gear
box
every
10
000
km
6
000
miles
and
replenish
recommended
oil
as
required
The
steering
linkage
should
be
greased
up
with
wheel
bearing
grease
every
50
000
km
30
000
miles
All
necessary
service
procedures
for
the
steering
lock
system
are
described
in
the
BODY
ELECTRICAL
SECTION
of
this
manual
and
therefore
no
instruction
is
given
here
STEERING
CONTENTS
REMOVAL
DISASSEMBL
Y
Ball
nut
assembly
ST
2
ST
3
ST
4
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
ASSEMBL
Y
AND
ADJUSTMENT
INSTALLATION
ST
4
ST
5
ST
7
1
Steering
gear
housing
2
Shaft
steering
sector
3
Screw
adjusting
roller
shaft
4
Cover
sector
shaft
5
Shim
worm
bearing
6
Comp
jacket
column
7
Assembly
column
steering
8
Assembly
bearing
steering
worm
9
Assembly
nut
ball
Fig
ST
1
Steering
gear
components
ST
1
Page 168 of 513
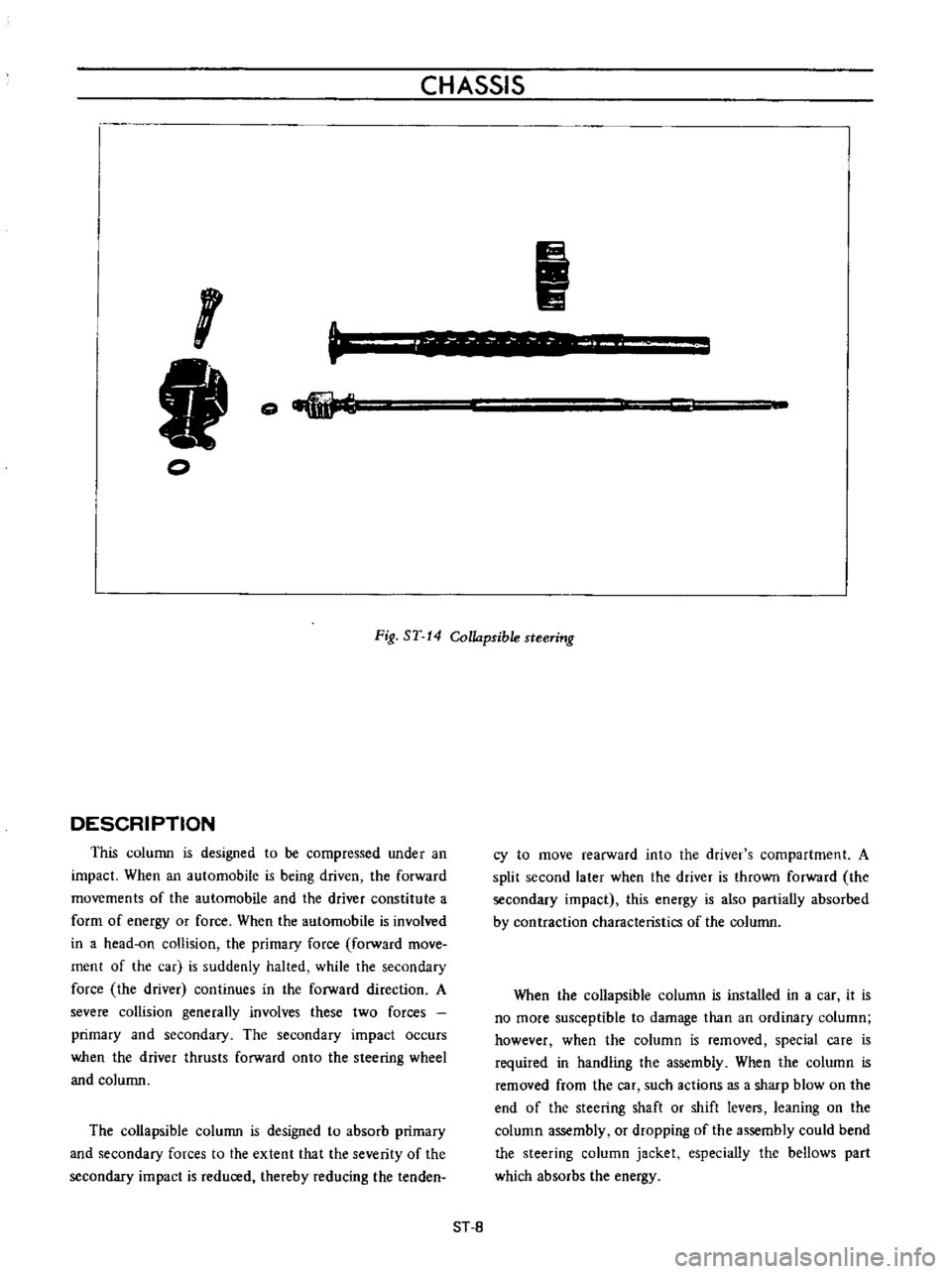
CHASSIS
I
l
I
I
2
fa
r
o
Fig
ST
14
Collapsible
steering
DESCRIPTION
This
column
is
designed
to
be
compressed
under
an
impact
When
an
automobile
is
being
driven
the
forward
movements
of
the
automobile
and
the
driver
constitute
a
form
of
energy
or
force
When
the
automobile
is
involved
in
a
head
on
collision
the
primary
force
forward
move
ment
of
the
car
is
suddenly
halted
while
the
secondary
force
the
driver
continues
in
the
forward
direction
A
severe
collision
generally
involves
these
two
forces
primary
and
secondary
The
secondary
impact
occurs
when
the
driver
thrusts
forward
onto
the
steering
wheel
and
column
The
collapsible
column
is
designed
to
absorb
primary
and
secondary
forces
to
the
extent
that
the
severity
of
the
secondary
impact
is
reduced
thereby
reducing
the
tenden
cy
to
move
rearward
into
the
driver
s
compartment
A
split
second
later
when
the
driver
is
thrown
forward
the
secondary
impact
this
energy
is
also
partially
absorbed
by
contraction
characteristics
of
the
column
When
the
collapsible
column
is
installed
in
a
car
it
is
no
more
susceptible
to
damage
than
an
ordinary
column
however
when
the
column
is
removed
special
care
is
required
in
handling
the
assembly
When
the
column
is
removed
from
the
car
such
actions
as
a
sharp
blow
on
the
end
of
the
steering
shaft
or
shift
levers
leaning
on
the
column
assembly
or
dropping
of
the
assembly
could
bend
the
steering
column
jacket
especially
the
bellows
part
which
absorbs
the
energy
ST
8
Page 171 of 513
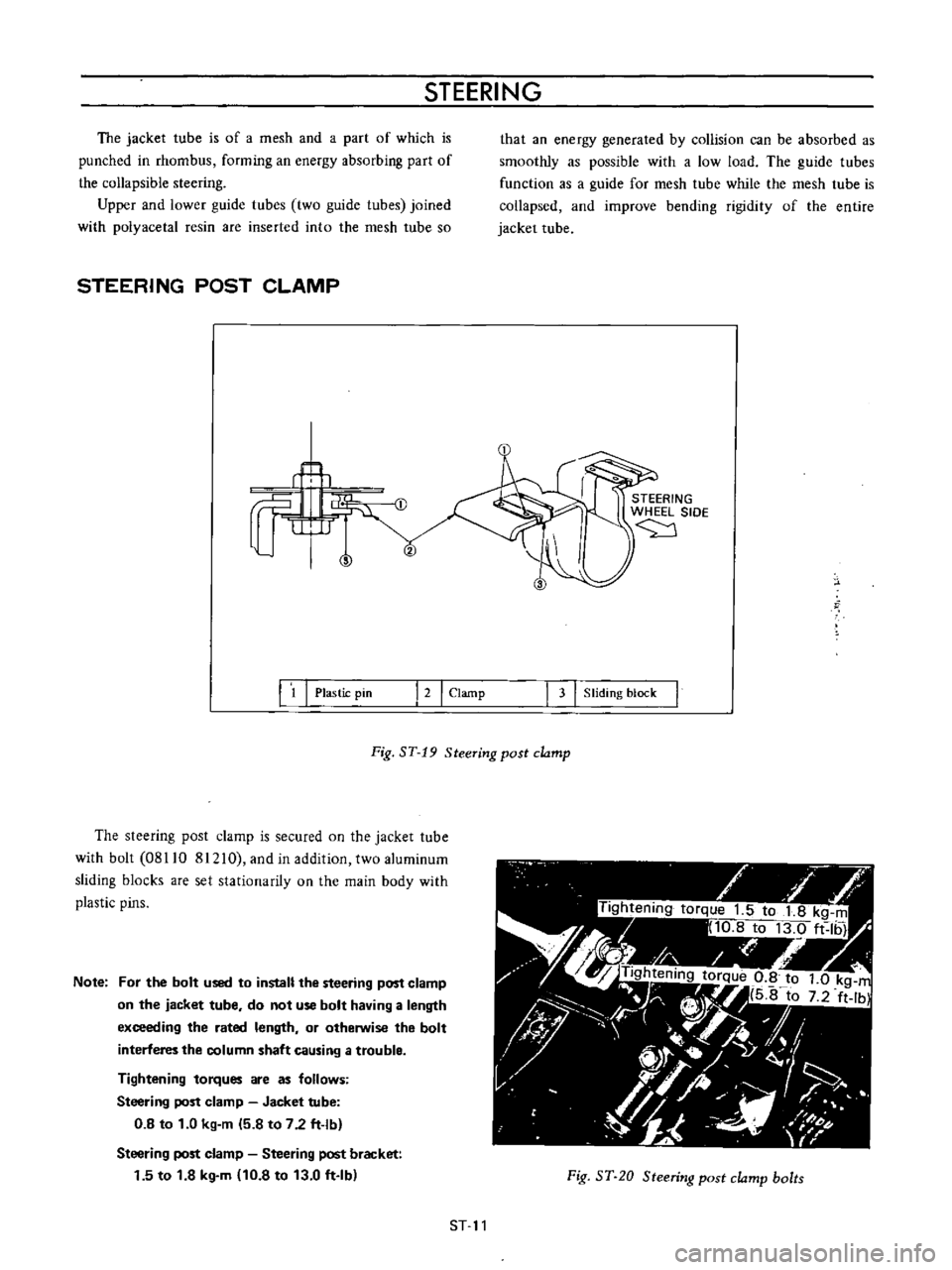
STEERING
The
jacket
tube
is
of
a
mesh
and
a
part
of
which
is
punched
in
rhombus
forming
an
energy
absorbing
part
of
the
collapsible
steering
Upper
and
lower
guide
tubes
two
guide
tubes
joined
with
polyacetal
resin
are
inserted
into
the
mesh
tube
so
STEERING
POST
CLAMP
that
an
energy
generated
by
collision
can
be
absorbed
as
smoothly
as
possible
with
a
low
load
The
guide
tubes
function
as
a
guide
for
mesh
tube
while
the
mesh
tube
is
collapsed
and
improve
bending
rigidity
of
the
entire
jacket
tube
1
1
Plastic
pin
I
2
I
Clamp
1
3
I
Sliding
block
Fig
ST
19
Steering
post
clamp
The
steering
post
clamp
is
secured
on
the
jacket
tube
with
bolt
08110
81210
and
in
addition
two
aluminum
sliding
blocks
are
set
stationarity
on
the
main
body
with
plastic
pins
Note
For
the
bolt
used
to
install
the
steering
post
clamp
on
the
jacket
tube
do
not
use
bolt
having
a
length
exceeding
the
rated
length
or
otherwise
the
bolt
interferes
the
column
shaft
causing
a
trouble
Tightening
torques
are
as
follows
Steering
post
clamp
Jacket
tube
0
8
to
1
0
kg
m
5
8
to
7
2
ft
lb
Steering
post
clamp
Steering
post
bracket
1
5
to
1
8
kg
m
10
8
to
13
0
ft
Ib
Fig
ST
20
Steering
post
clamp
bolts
ST
11
Page 172 of 513
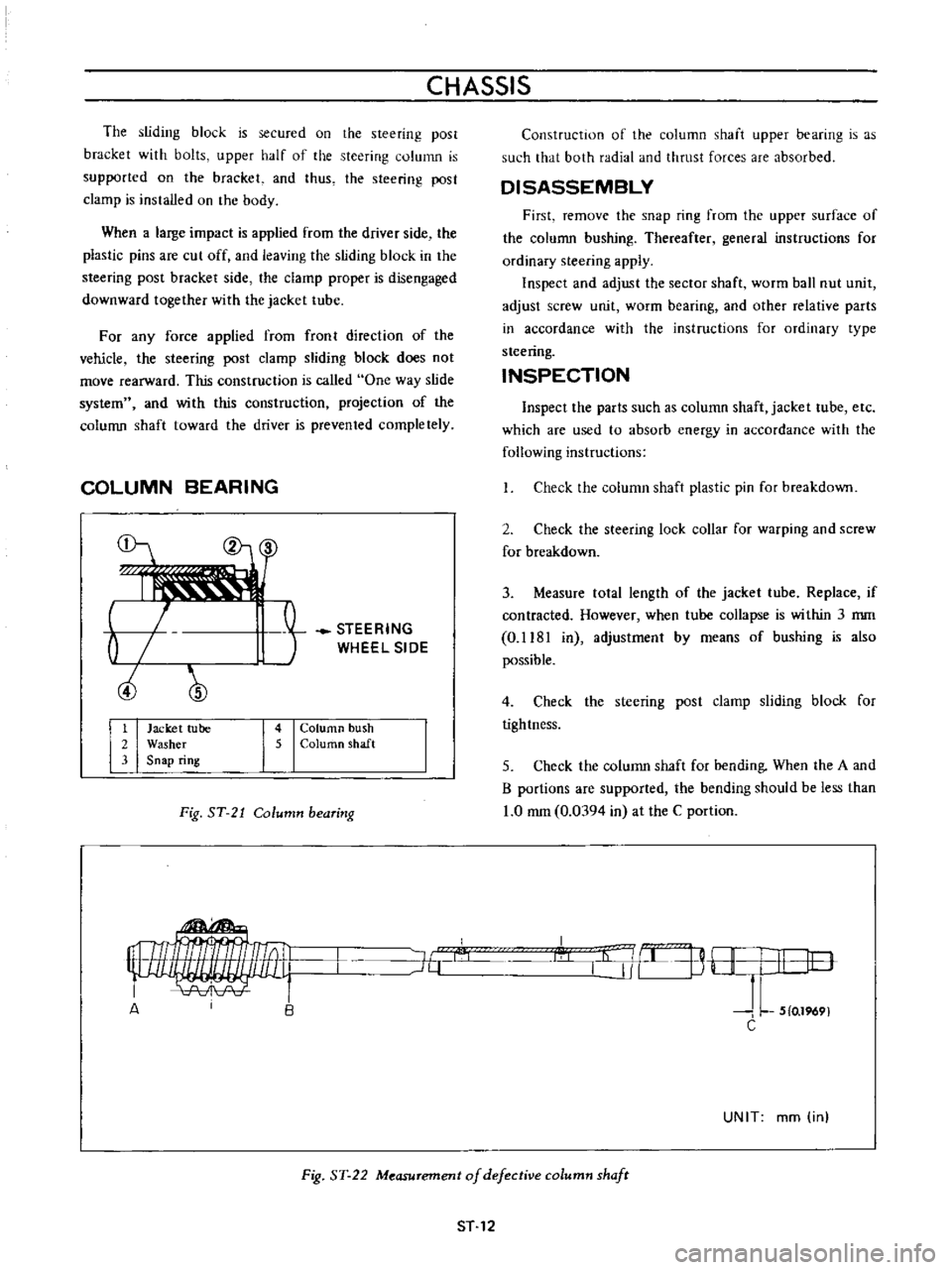
CHASSIS
The
sliding
block
is
secured
on
the
steering
post
bracket
with
bolts
upper
half
of
the
steering
column
is
supported
on
the
bracket
and
thus
the
steering
post
clamp
is
installed
on
the
body
When
a
large
impact
is
applied
from
the
driver
side
the
plastic
pins
are
cut
off
and
leaving
the
sliding
block
in
the
steering
post
bracket
side
the
clamp
proper
is
disengaged
downward
together
with
the
jacket
tube
For
any
force
applied
from
front
direction
of
the
vehicle
the
steering
post
clamp
sliding
block
does
not
move
rearward
This
construction
is
called
One
way
slide
system
and
with
this
construction
projection
of
the
column
shaft
toward
the
driver
is
prevented
completely
COLUMN
BEARING
b
ciJ
STEERING
WHEEL
SIDE
1
Jacket
tube
2
Washer
3
Snap
ring
4
Column
bush
5
ColurtlO
shaft
Fig
ST
21
Column
bearing
Construction
of
the
column
shaft
upper
bearing
is
as
such
that
both
radial
and
thrust
forces
are
absorbed
DISASSEMBLY
First
remove
the
snap
ring
from
the
upper
surface
of
the
column
bushing
Thereafter
general
instructions
for
ordinary
steering
apply
Inspect
and
adjust
the
sector
shaft
worm
ball
nut
unit
adjust
screw
unit
worm
bearing
and
other
relative
parts
in
accordance
with
the
instructions
for
ordinary
type
steering
INSPECTION
Inspect
the
parts
such
as
column
shaft
jacket
tube
etc
which
are
used
to
absorb
energy
in
accordance
with
the
following
instructions
Check
the
column
shaft
plastic
pin
for
breakdown
2
Check
the
steering
lock
collar
for
warping
and
screw
for
breakdown
3
Measure
tolal
length
of
the
jacket
tube
Replace
if
contracted
However
when
tube
collapse
is
within
3
mm
0
1181
in
adjustmenl
by
means
of
bushing
is
also
possible
4
Check
the
steering
post
clamp
sliding
block
for
tightness
5
Check
the
column
shaft
for
bending
When
the
A
and
B
portions
are
supported
the
bending
should
be
less
than
1
0
mm
0
0394
in
at
the
C
portion
I
l
j
B
H
I
I
lO
J
L
5
0
1969
C
J6
A
UNIT
mm
in
Fig
ST
22
Measurement
of
defective
column
shafr
ST
12