check engine DATSUN B110 1973 Service Manual PDF
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1973, Model line: B110, Model: DATSUN B110 1973Pages: 513, PDF Size: 28.74 MB
Page 380 of 513
r
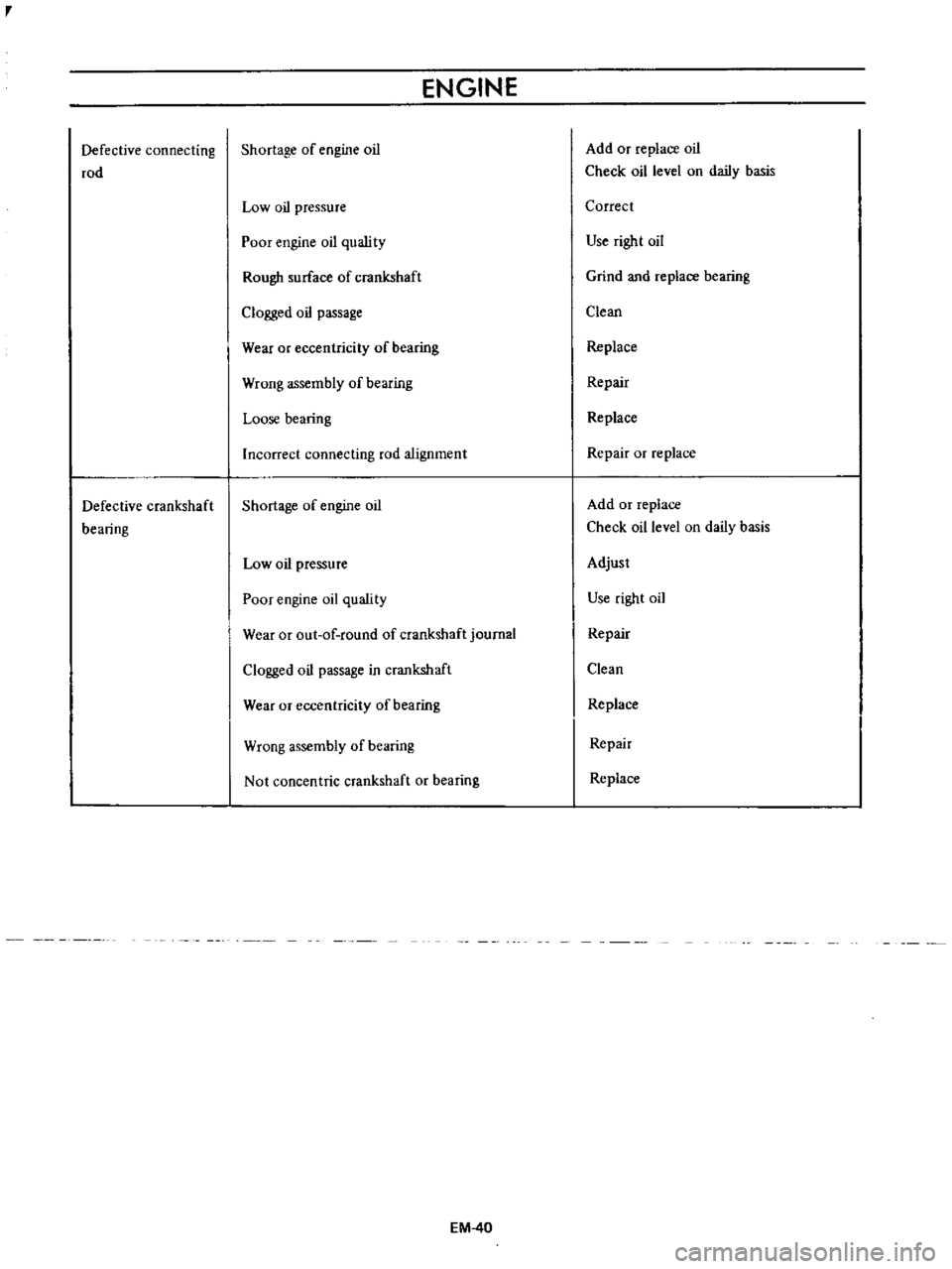
Defective
connecting
rod
Defective
crankshaft
bearing
ENGINE
Shortage
of
engine
oil
Low
oil
pressure
Poor
engine
oil
quslity
Rough
surface
of
crankshaft
Clogged
oil
passage
Wear
or
eccentricity
of
bearing
Wrong
assembly
of
bearing
Loose
bearing
Incorrect
connecting
rod
alignment
Shortage
of
engine
oil
Low
oil
pressure
Poor
engine
oil
quality
Wear
or
out
of
round
of
crankshaft
journal
Clogged
oil
passage
in
crankshaft
Wear
or
eccentricity
of
bearing
Wrong
assembly
of
bearing
Not
concentric
crankshaft
or
bearing
EM
40
Add
or
replace
oil
Check
oil
level
on
daily
basis
Correct
Use
right
oil
Grind
and
replace
bearing
Clean
Replace
Repair
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Add
or
replace
Check
oil
level
on
daily
basis
Adjust
Use
right
oil
Repair
Clean
Replace
Repair
Replace
Page 383 of 513
LUBRICATION
CIRCUIT
Oil
drawn
from
the
oil
pan
through
the
inlet
screen
and
tube
to
the
inlet
side
of
the
oil
pump
is
delivered
by
th
oil
pump
through
the
outlet
portion
of
the
oil
pump
and
the
oil
gallery
to
the
inlet
side
of
the
full
flow
oil
filter
and
to
the
main
oil
gallery
The
main
oil
gallery
supplies
oil
to
the
crankshaft
main
bearings
and
drilled
passages
in
the
crankshaft
and
thus
oil
is
fed
directly
from
the
main
bearings
to
the
connecting
rod
bearings
Oil
injected
from
jet
holes
on
connecting
rods
lubri
cates
the
cylinder
walls
and
pistion
pins
The
oil
distributed
from
the
main
gallery
enters
the
chain
teosioner
and
the
pad
is
held
against
the
chain
by
oil
pressure
and
spring
The
oil
also
lubricates
the
timing
chain
through
the
jet
hole
located
near
the
chain
Furthermore
lubricant
is
supplied
to
each
camshaft
bearing
through
each
crankshaft
main
bearing
and
finally
to
the
011
gallery
in
the
rocker
shaft
through
the
center
camshaft
bearing
The
rocker
arm
and
valve
are
lubricated
by
the
oil
through
the
oil
gallery
in
the
rockershaft
To
this
oil
gallery
lubricant
is
supplied
through
the
center
camshaft
bearing
as
shown
in
Figure
EL
I
OIL
PUMP
Description
The
oil
pump
assembly
is
installed
on
the
bottom
of
the
cylinder
block
and
driven
by
the
distributor
drive
shaft
assembly
The
oil
pump
is
of
a
rotor
type
The
oil
pressure
is
regulated
by
the
regulator
valve
camshaft
Removal
Engine
in
vehicle
Drain
engine
oil
2
Remove
the
frunt
stabilizer
3
Remove
the
splash
shield
board
4
Detach
the
oil
pump
body
together
with
drive
gear
spindle
ENGINE
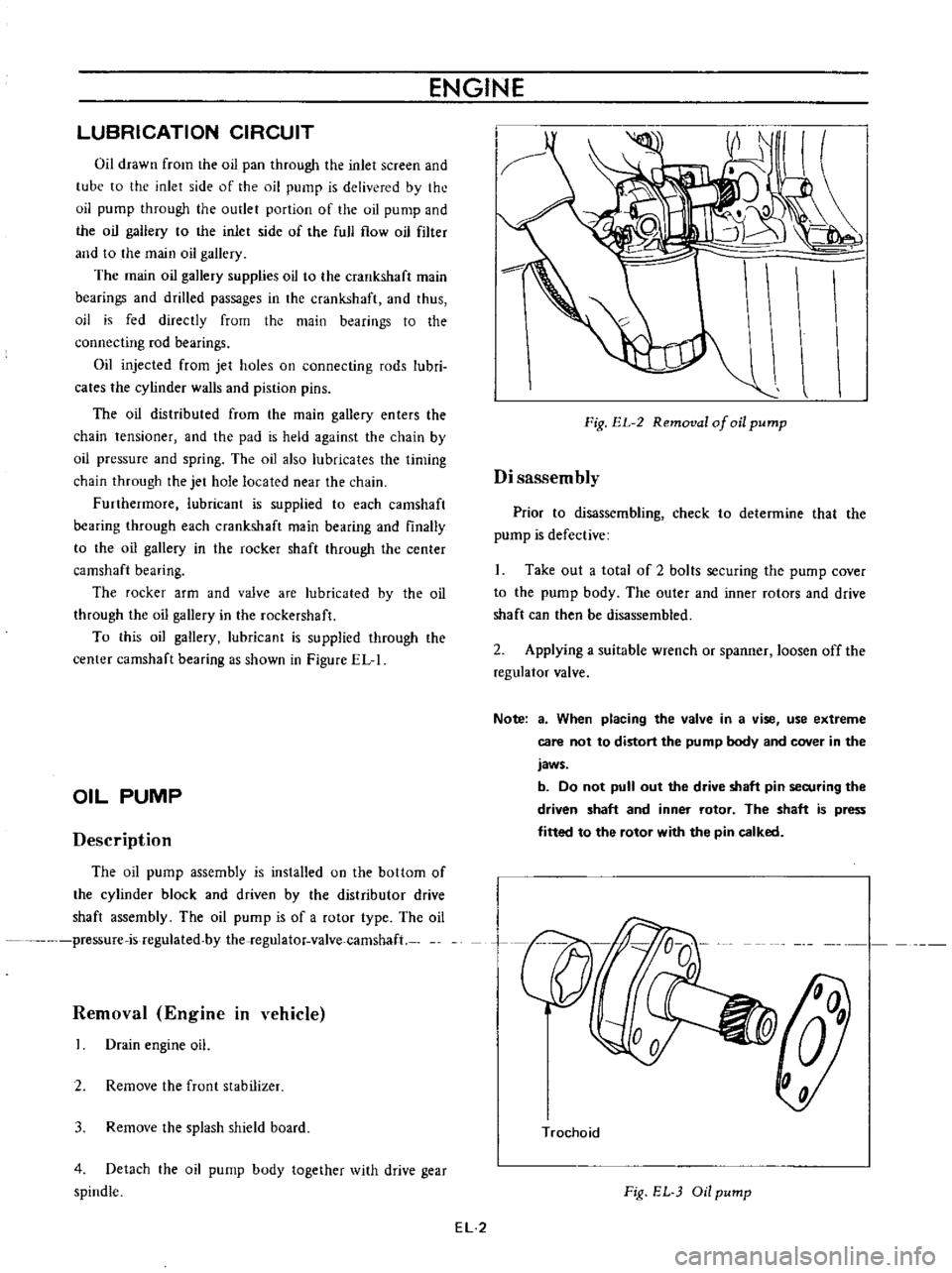
Fig
EL
2
Removal
of
oil
pump
Disassembly
Prior
to
disassembling
check
to
determine
that
the
pump
is
defective
Take
out
a
total
of
2
bolts
securing
the
pump
cover
to
the
pump
body
The
outer
and
inner
rotors
and
drive
shaft
can
then
be
disassembled
2
Applying
a
suitable
wrench
or
spanner
loosen
off
the
regulator
valve
Note
a
When
placing
the
valve
in
a
vise
use
extreme
care
not
to
distort
the
pump
body
and
cover
in
the
jaws
b
Do
not
pull
out
the
drive
shaft
pin
securing
the
driven
shaft
and
inner
rotor
The
shaft
is
press
fitted
to
the
rotor
with
the
pin
calked
n
Trochoid
Fig
EL
Oil
pump
EL
2
Page 384 of 513
ENGINE
LUBRICATION
SYSTEM
Inspection
and
repair
Clean
the
disassembled
parts
with
cleaning
solvent
and
inspect
for
defects
Inspect
the
drive
rotor
shaft
for
excessive
wear
and
scores
and
check
the
following
clearances
Side
clearance
between
Quter
and
inner
rotors
0
12
mm
0
0047
in
or
below
Tip
clearance
0
04
to
0
I2mm
0
0016
to
0
0047
in
Clearance
between
outer
rotor
and
body
0
15
to
0
21
rom
0
0059
to
0
0083
in
Adjusting
regulator
Insert
valve
in
the
body
and
measure
the
distance
A
from
the
valve
end
to
the
spring
contacting
face
inside
the
plug
See
Figure
EL
4
2
The
distance
from
the
spring
contacting
face
inside
the
valve
to
the
valve
end
amounts
to
18
mm
0
7086
in
3
On
inspecting
the
above
dimensions
determine
the
thickness
of
adjusting
shim
Shim
thickness
A
18
mm
0
7086
in
spring
length
at
compression
load
3
67
kg
8
091bs
Assembly
Assembling
the
oil
pump
is
the
reverse
order
of
disassembly
Note
3
Be
sure
no
traces
of
grinding
chips
lint
or
dirt
remain
b
Be
sure
gasket
is
not
turned
up
and
discon
tinued
OIL
PRESSURE
REGULATOR
VALVE
The
oil
pressure
regulator
valve
is
not
adjustable
At
the
released
position
the
valve
permits
oil
passing
through
a
passage
on
the
pump
cover
to
the
inlet
side
of
the
pump
Measure
the
regulator
valve
spring
dimension
to
ensure
that
the
spring
is
provided
with
the
correct
tension
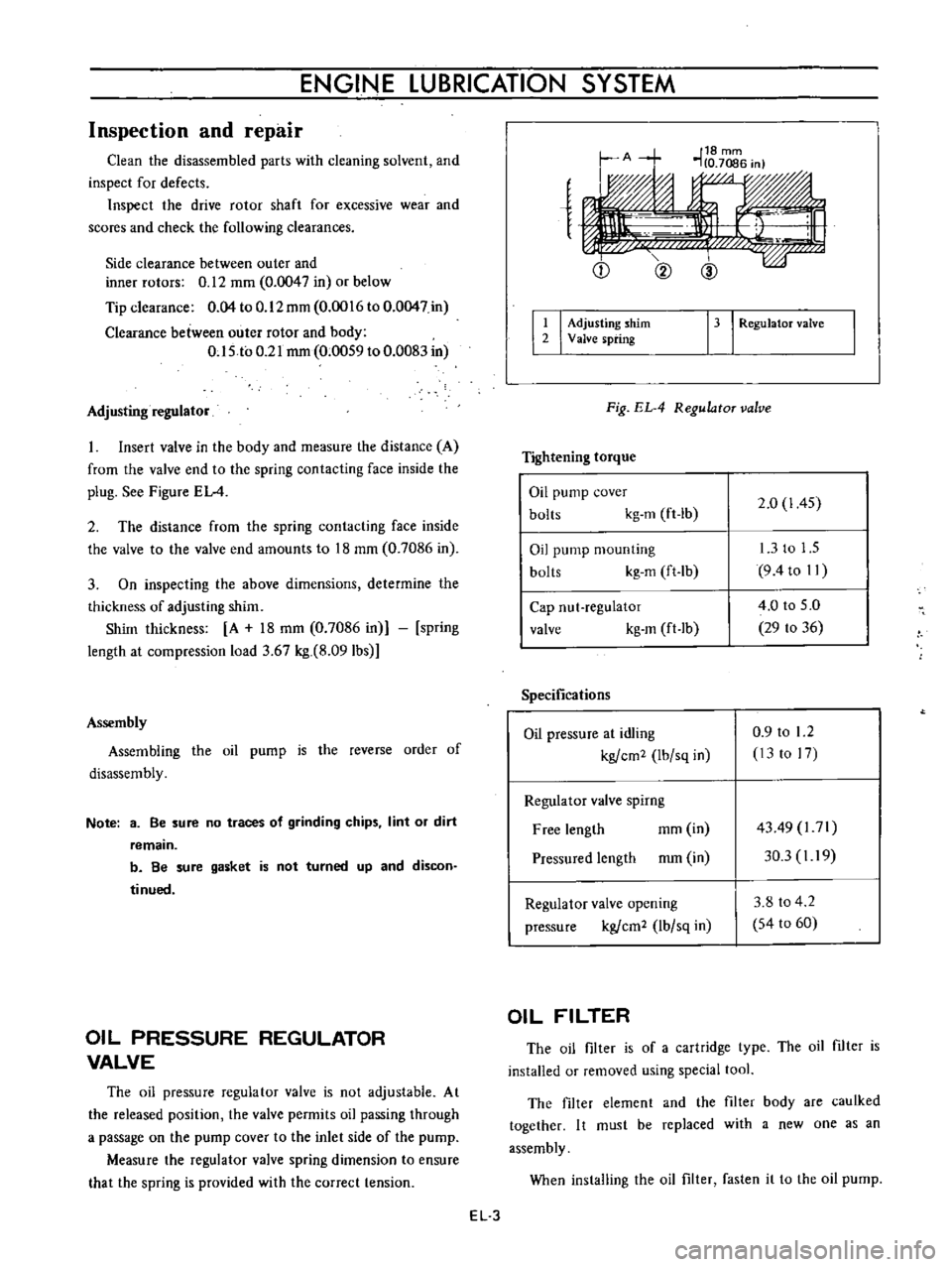
e
Q
@
I
I
Adjusting
shim
2
Valve
spring
13
I
RegulatoT
valve
Fig
EL
4
RegulatoT
valve
Tightening
torque
Oil
pump
cover
bolts
kg
m
ft
lb
2
0
1
45
Oil
pump
mounting
bolts
kg
m
ft
lb
13
to
1
5
9
4to
II
Cap
nut
regulator
valve
kg
m
ft
lb
4
0
to
5
0
29
to
36
Specifications
Oil
pressure
at
idling
kgfcm2
Ibfsq
in
0
9
to
1
2
13
to
17
Regulator
valve
spirng
Free
length
mm
in
Pressured
length
mm
in
4349
l71
30
3
I
19
Regulator
valve
opening
pressure
kgfcm2
lbfsq
in
3
8
to
4
2
54
to
60
OIL
FILTER
The
oil
filter
is
of
a
cartridge
type
The
oil
filter
is
installed
or
removed
using
special
tool
The
filter
element
and
the
filter
body
are
caulked
together
I
t
must
be
replaced
with
a
new
one
as
an
assembly
When
installing
the
oil
filter
fasten
it
to
the
oil
pump
EL
3
Page 396 of 513
FUEl
SYSTEM
FUEL
STRAINER
DESCRIPTION
The
fuel
strainer
is
of
a
cartridge
type
It
uses
paper
element
as
strainer
element
which
can
be
checked
for
condition
from
outside
This
strainer
cannot
be
cleaned
Replace
the
strainer
at
the
specified
service
interval
or
if
it
becomes
clogged
or
restricted
REMOVAL
Disconnect
inlet
and
outlet
fuel
lines
from
fuel
strainer
and
remove
fuel
strainer
Note
Before
disconnecting
fuel
lines
use
a
container
to
receive
the
remaining
fuel
in
lines
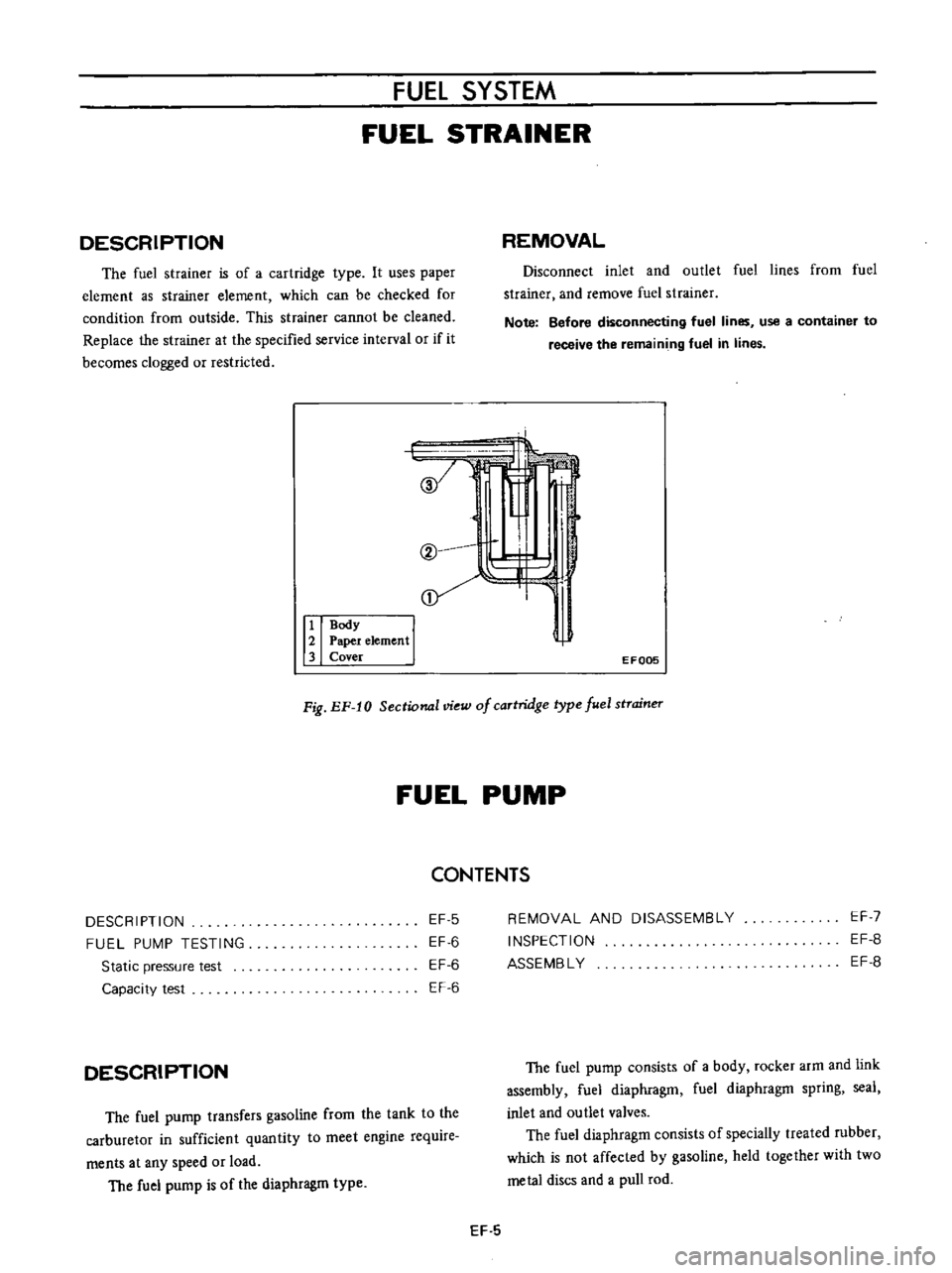
r
@
I
I
Il
QY
I
I
I
elementl
3
Cover
@
EF005
Fig
EF
10
Sectional
view
of
caTtridge
type
fuel
stTaineT
FUEL
PUMP
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION
FUEL
PUMP
TESTING
Static
pressure
test
Capacity
test
EF
5
EF
6
EF
6
EF
6
DESCRIPTION
The
fuel
pump
transfers
gasoline
from
the
tank
to
the
carburetor
in
sufficient
quantity
to
meet
engine
require
ments
at
any
speed
or
load
The
fuel
pump
is
of
the
diaphragm
type
REMOVAL
AND
DISASSEMBLY
INSPECTION
ASSEMBLY
EF
7
EF
B
EF
B
The
fuel
pump
consists
of
a
body
rocker
arm
and
link
assembly
fuel
diaphragm
fuel
diaphragm
spring
seal
inlet
and
outlet
valves
The
fuel
diaphragm
consists
of
specially
treated
rubber
which
is
not
affected
by
gasoline
held
together
with
two
metal
discs
and
a
pull
rod
EF
5
Page 399 of 513

ENGINE
INSPECTION
Check
the
upper
and
lower
bodies
for
cracks
2
Check
the
valve
assembly
for
wear
of
the
valve
and
valve
spring
Blow
the
valve
assembly
by
breath
to
examine
its
function
3
Check
the
diaphragm
for
small
holes
cracks
and
wear
4
Check
the
rocker
arm
for
wear
at
the
portion
in
contact
with
the
camshaft
5
Check
the
rocker
arm
pin
for
wear
since
a
worn
pin
may
cause
oil
leakage
6
Check
all
other
components
for
any
abnormalities
and
replace
with
new
parts
as
required
ASSEMBLY
Assembly
is
done
in
reverse
order
of
disassembly
For
reassembly
and
reinstallation
the
following
matters
should
be
noted
Use
new
gasket
2
Lubricate
the
rocker
arm
link
rocker
arm
pin
and
lever
pin
before
installation
3
To
test
the
function
position
the
fuel
pump
assem
bly
about
I
meter
3
3
ft
above
fuel
level
with
a
pipe
connecting
the
fuel
pump
and
the
fuel
strainer
and
operate
the
rocker
afm
by
hand
If
fuel
is
drawn
up
soon
after
the
rocker
arm
is
released
the
function
of
the
pump
is
satisfactory
CARBURETOR
CONTENTS
DESCRIPTION
STRUCTURE
AND
OPERATION
EF
8
EF
9
EF
10
EF
11
EF
12
EF
12
EF
12
EF
14
EF
14
EF
15
EF
15
EF
16
EF
16
Primary
system
Secondary
system
Anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
Float
system
Electric
automatic
choke
ADJUSTMENT
Idling
adjustment
Fuel
level
adjustment
Fast
idle
adjustment
Vacuum
break
adjustment
Choke
un
loader
adjustment
DESCRIPTION
The
carburetors
are
of
a
downdraft
type
which
is
designed
and
built
to
increase
power
and
fuel
economy
as
Bi
metal
setting
Adjustment
of
interlock
opening
of
primary
and
secondary
throttle
valves
Dash
pot
adjustment
MAJOR
SERVICE
OPERATIONS
Removal
Disassembly
Cleaning
and
inspection
Assembly
and
installation
JETS
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
EF
17
EF
18
EF
18
EF
19
EF
19
EF
19
EF
21
EF
22
EF
22
EF
22
EF
22
well
as
to
reduce
the
emission
of
exhaust
gases
These
carburetors
present
several
distinct
features
of
importance
to
the
car
owners
A
summary
of
features
is
as
follows
EF
8
Page 403 of 513
ENGINE
Step
system
The
construction
of
this
system
corresponds
to
the
idling
and
slow
system
of
the
primary
system
This
system
aims
at
the
power
filling
up
of
the
gap
when
fuel
supply
is
transferred
from
the
primary
system
to
the
secondary
system
The
step
port
is
located
near
the
auxiliary
valve
in
its
fully
closed
state
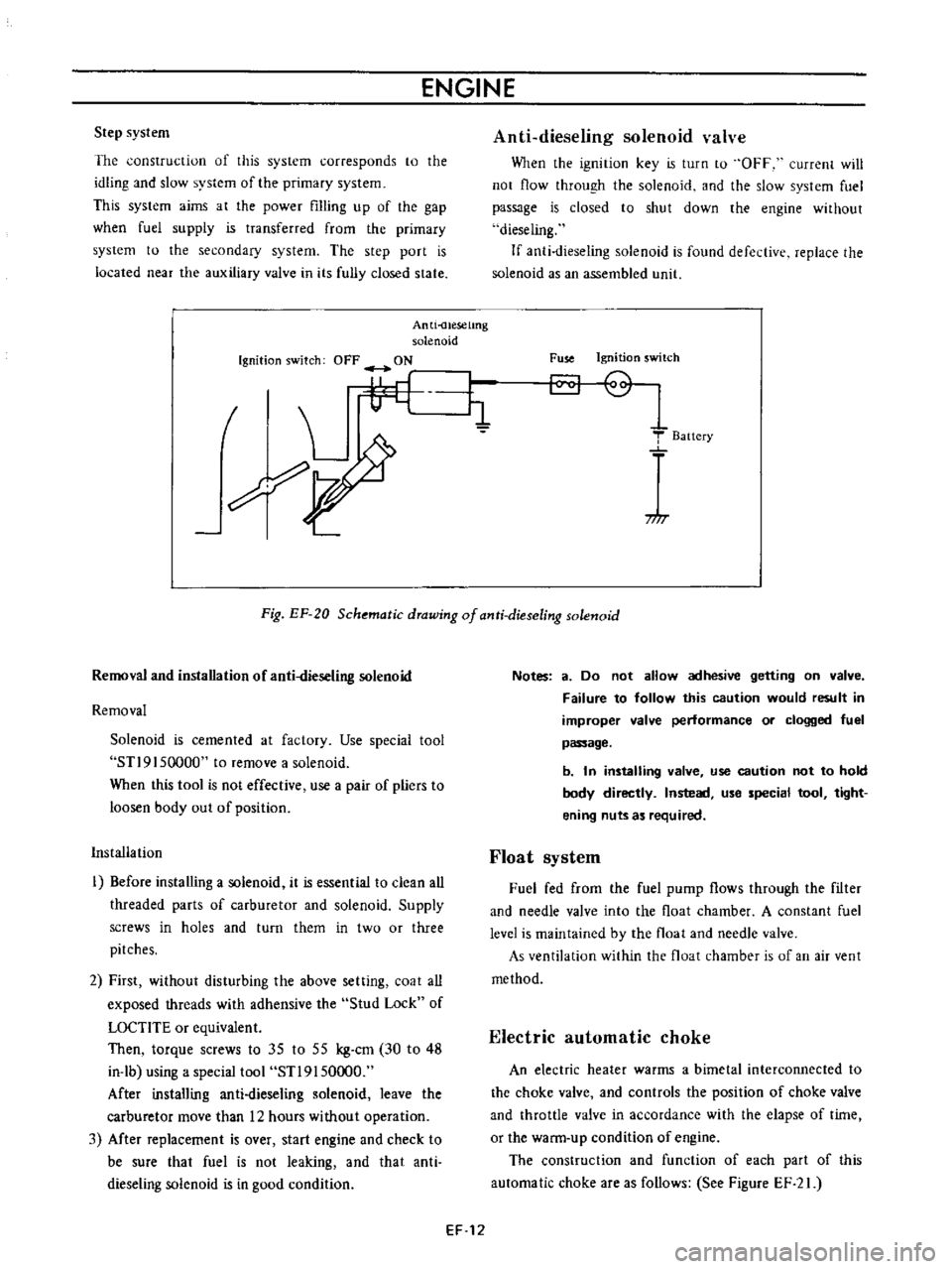
Anti
uesetmg
solenoid
Ignition
switch
OFF
ON
I
L
i1
7
I
Anti
dieseling
solenoid
valve
When
the
ignition
key
is
turn
to
OFF
current
will
not
flow
through
the
solenoid
and
the
slow
system
fuel
passage
is
closed
to
shut
down
the
engine
without
dieseling
If
anti
dieseling
solenoid
is
found
defective
replace
the
solenoid
as
an
assembled
llnit
Fuse
Ignition
switch
T
Baitery
717
Fig
EF
20
Schematic
drawing
of
anti
dieseling
solenoid
Removal
and
installation
of
anti
dieseling
solenoid
Removal
Solenoid
is
cemented
at
factory
Use
special
tool
STl9
I
50000
to
remove
a
solenoid
When
this
tool
is
not
effective
use
a
pair
of
pliers
to
loosen
body
out
of
position
Installation
I
Before
installing
a
solenoid
it
is
essential
to
clean
all
threaded
parts
of
carburetor
and
solenoid
Supply
screws
in
holes
and
turn
them
in
two
or
three
pitches
2
First
without
disturbing
the
above
setting
coat
all
exposed
threads
with
adhensive
the
Stud
Lock
of
LOCTlTE
or
equivalent
Then
torque
screws
to
35
to
55
kg
cm
30
to
48
in
lb
using
a
special
tool
STl9150000
After
installing
anti
dieseling
solenoid
leave
the
carburetor
move
than
12
hours
without
operation
3
Mter
replacement
is
over
start
engine
and
check
to
be
sure
that
fuel
is
not
leaking
and
that
anti
dieseling
solenoid
is
in
good
condition
Notes
a
Do
not
allow
adhesive
getting
on
valve
Failure
to
follow
this
caution
would
result
in
improper
valve
performance
or
clogged
fuel
passage
b
In
installing
valve
use
caution
not
to
hold
body
directly
Instead
use
special
tool
tight
ening
nuts
as
required
Float
system
Fuel
fed
from
the
fuel
pump
flows
through
the
filter
and
needle
valve
into
the
float
chamber
A
constant
fuel
level
is
maintained
by
the
float
and
needle
valve
As
ventilation
within
the
float
chamber
is
of
an
air
vent
method
Electric
automatic
choke
An
electric
heater
warms
a
bimetal
interconnected
to
the
choke
valve
and
controls
the
position
of
choke
valve
and
throttle
valve
in
accordance
with
the
elapse
of
time
or
the
warm
up
condition
of
engine
The
construction
and
function
of
each
part
of
this
automatic
choke
are
as
follows
See
Figure
EF
21
EF
12
Page 405 of 513
ENGINE
AD
JUSTMENT
Idling
adjustment
Idle
mixture
adjustment
requires
the
use
of
a
CO
meter
When
preparing
to
adjust
idle
mixture
it
is
essential
to
have
the
meter
thoroughly
warmed
and
calibrated
Warm
up
the
engine
sufficiently
2
Continue
engine
operation
for
one
minute
under
idling
speed
3
Adjust
throttle
adjusting
screw
so
that
engine
speed
is
800
rpm
in
N
position
for
automatic
transmission
4
Check
ignition
timing
if
necessary
adjust
it
to
the
specifications
Ignition
timing
50
800
rpm
5
Adjust
idle
adjusting
screw
so
that
ca
percentage
is
1
5
t
0
5
6
Repeat
the
adjustments
as
described
in
steps
3
and
5
above
so
that
ca
percentage
is
1
5
to
5
at
800
rpm
Cautions
a
On
automatic
transmission
equipped
model
check
must
be
done
in
the
0
position
Be
sure
to
apply
parking
brake
and
to
lock
both
front
and
rear
wheels
with
wheel
chocks
b
Hold
brake
pedal
while
stepping
down
on
accelerator
pedal
Otherwise
car
will
rush
out
dangerously
7
On
automatic
transmission
equipped
model
make
sure
that
the
adjustment
has
been
made
with
the
selector
lever
in
N
position
And
then
check
the
specifications
with
the
lever
in
D
position
Insure
that
CO
percent
and
idle
speed
are
as
follows
Idle
rpm
650
ca
percentage
with
lever
in
D
position
15
to
5
If
necessary
adjust
by
progressively
turning
throttle
adjusting
screw
and
idle
adjusting
screw
until
correct
adjustments
are
made
Notes
a
Do
not
attempt
to
screw
down
the
id
Ie
adjusting
screw
completely
to
avoid
damage
to
the
EF
14
tip
which
will
tend
to
cause
malfunctions
b
After
idle
adjustment
has
been
made
shift
the
lever
to
N
or
p
position
for
automatic
transmission
c
Remove
wheel
chocks
before
starting
the
car
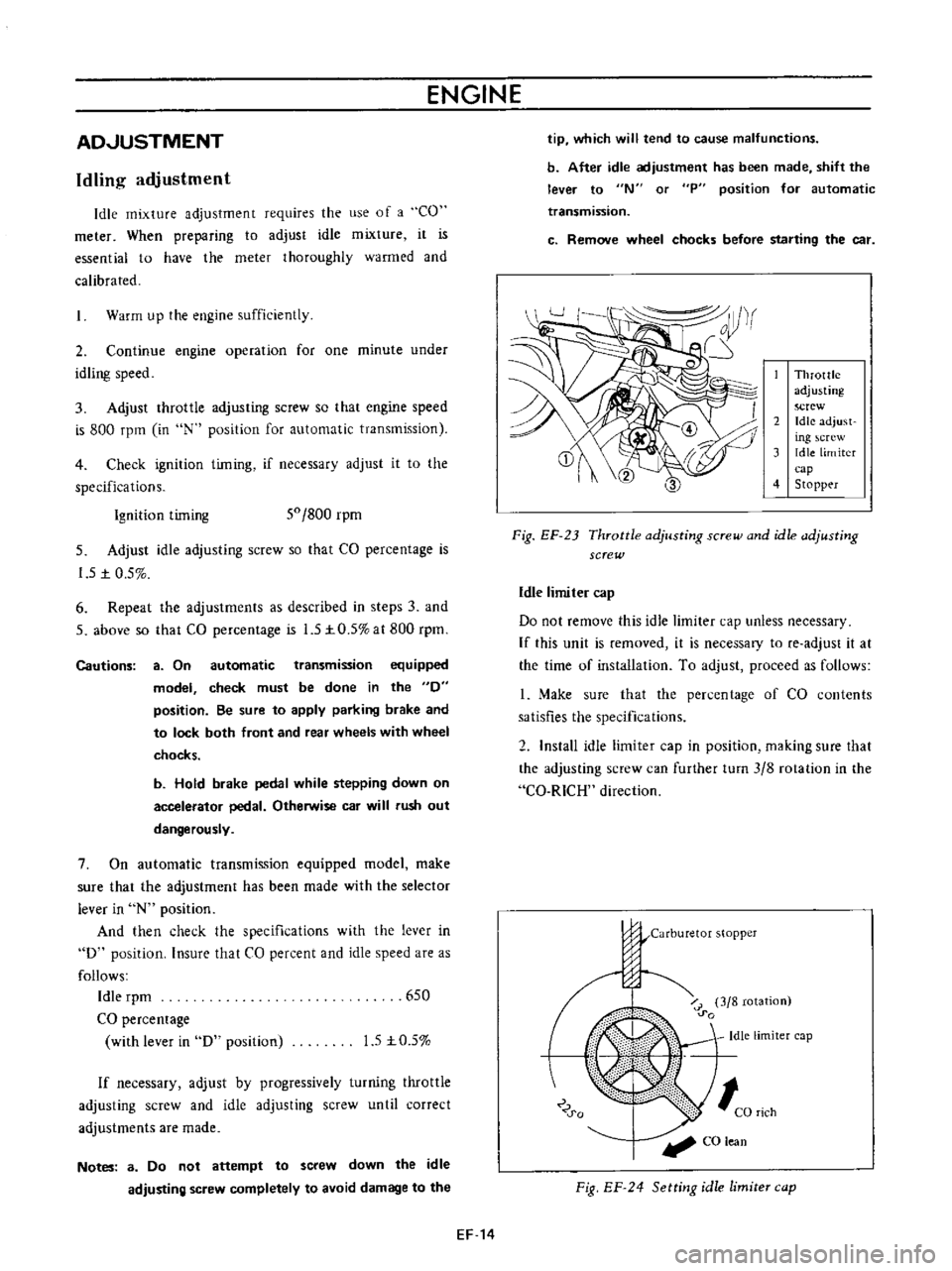
Throttle
adjusting
screw
2
Idle
adjust
ing
crew
3
Idle
limiter
cap
4
Stopp
r
Fig
EF
23
Throttle
adjusting
screw
and
idle
adjusting
screw
Idle
limiter
cap
Do
not
remove
this
idle
limiter
cap
unless
necessary
If
this
unit
is
removed
it
is
necessary
to
fe
adjust
it
at
the
time
of
installation
To
adjust
proceed
as
follows
1
Make
sure
that
the
percentage
of
CO
contents
satisfies
the
specifications
2
Install
idle
limiter
cap
in
position
making
sure
that
the
adjusting
screw
can
further
turn
3
8
rotation
in
the
Ca
RICH
direction
j
j
Carburetor
stopper
o
u
o
i
r
3
8
rotation
0
0
Idle
limiter
cap
0
0
CO
lean
Fig
EF
24
Setting
idle
limite
cap
Page 406 of 513
CD
r
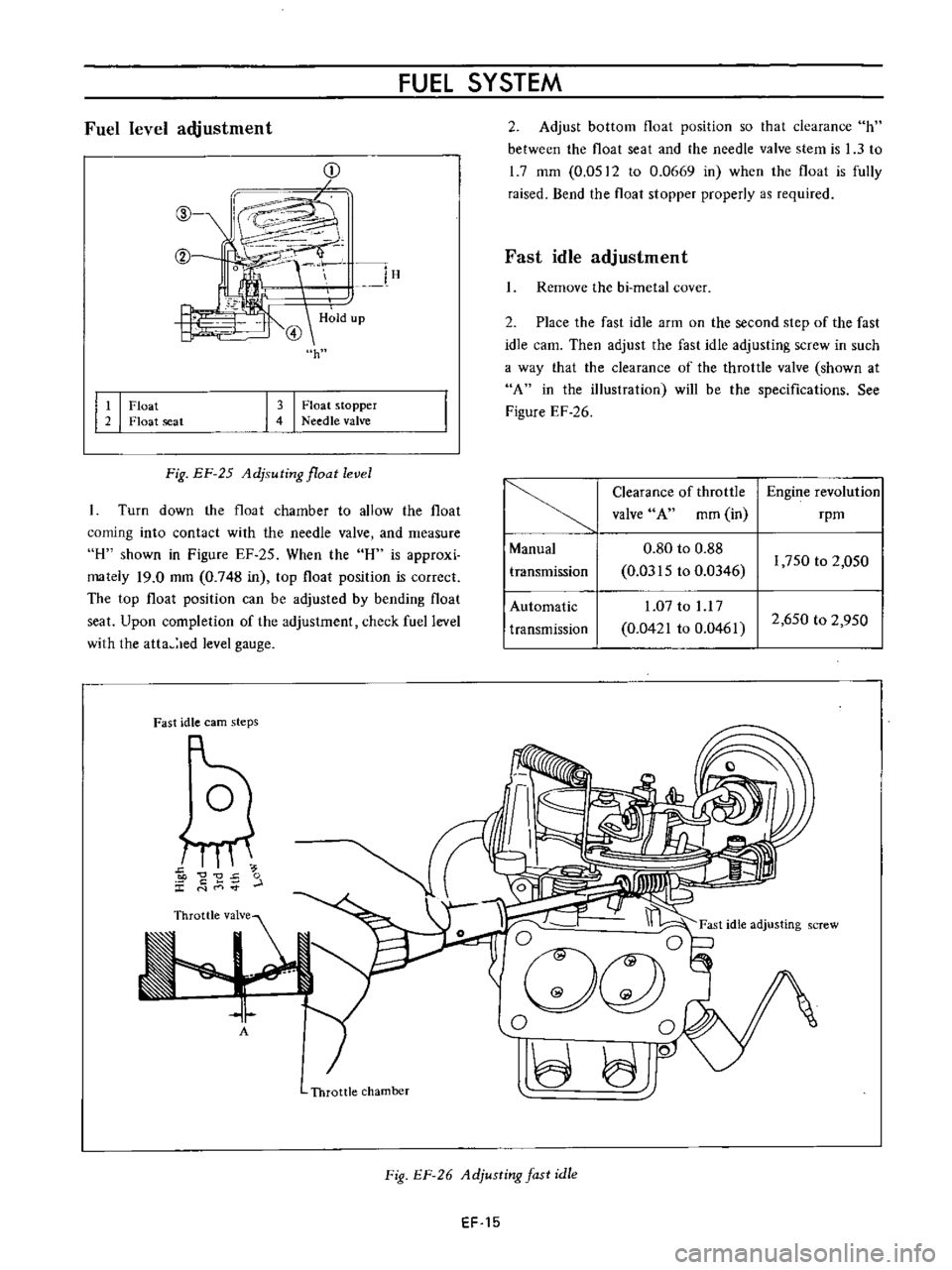
Fuel
level
adjustment
@
@
It
I
Float
2
Float
seat
FUEL
SYSTEM
2
Adjust
bottom
float
position
so
that
clearance
h
between
the
float
seat
and
the
needle
valve
stem
is
1
3
to
1
7
mm
0
0512
to
0
0669
in
when
the
float
is
fully
raised
Bend
the
float
stopper
properly
as
required
l
lH
H
ld
up
@
h
Fast
idle
adjustment
Remove
the
bi
metal
cover
3
I
Float
stopper
4
Needle
valve
2
Place
the
fast
idle
arm
on
the
second
step
of
the
fast
idle
earn
Then
adjust
the
fast
idle
adjusting
screw
in
such
a
way
that
the
clearance
of
the
throttle
valve
shown
at
A
in
the
illustration
will
be
the
specifications
See
Figure
EF
26
Fig
EF
25
Adjsuting
float
level
Turn
down
the
float
chamber
to
allow
the
float
coming
into
contact
with
the
needle
valve
and
measure
H
shown
in
Figure
EF
25
When
the
H
is
approxi
mately
19
0
mm
0
748
in
top
float
position
is
correct
The
top
float
position
can
be
adjusted
by
bending
float
seat
Upon
completion
of
the
adjustment
check
fuel
level
with
the
atta
led
level
gauge
Clearance
of
throttle
Engine
revolution
valve
A
mm
in
rpm
Manual
0
80
to
0
88
transmission
0
0315
to
0
0346
1
750
to
2
050
Automatic
1
07
to
l
l
7
transmission
0
0421
to
0
0461
2
650
to
2
950
Fast
idle
earn
steps
5
C
0
J
t
E
r
L
E
I
I
Ogc
l
0
0
JO
A
Throttle
chamber
Fig
EF
26
Adjusting
fast
idle
EF
15
Page 410 of 513

FUEl
SYSTEM
MA
JOR
SERVICE
OPERATIONS
A
completely
adjusted
and
serviced
carburetor
will
provide
the
engine
with
proper
mixture
at
all
speeds
Periodical
overhauling
which
cleans
all
components
and
passages
will
recover
the
originally
designed
performance
producing
the
engine
with
proper
gasoline
and
air
ratio
at
all
speeds
Passages
and
holes
of
the
carburetor
must
be
cleaned
carefully
Use
only
carburetor
solvent
and
com
pressed
air
to
clean
aU
passages
and
discharge
holes
Never
use
wire
or
other
pointed
tool
otherwise
accurately
calibrated
carburetor
will
be
affected
Removal
Remove
the
air
cleaner
2
Disconnect
the
fuel
line
vacuum
line
automatic
choke
harness
and
anti
dieseling
solenoid
harness
from
carburetor
3
Remove
the
throttle
lever
4
Remove
four
nuts
and
washers
retaining
the
carbuTe
tor
to
the
manifold
if
necessary
5
Lift
the
carburetor
and
remove
from
the
manifold
6
Remove
and
discard
the
gasket
used
between
the
carburetor
and
manifold
Disassembly
The
main
jets
and
needle
valves
on
both
primary
and
secondary
sides
are
accessible
from
outside
of
the
carbure
tor
for
disassembly
2
Remove
throttle
return
spring
3
Remove
pump
lever
shaft
take
out
pump
lever
and
pump
connecting
rod
4
Remove
rubber
pipe
from
choke
piston
5
Loosen
off
bolts
securing
servo
diaphragm
in
posi
tion
take
out
diaphragm
6
Back
off
total
of
five
bolts
which
hold
choke
in
position
and
remove
rods
of
starter
system
take
out
choke
chamber
In
removing
chamber
exercise
care
to
avoid
damaging
float
EF
19
ilia
Fig
EF
32
Removing
choke
dwmherand
seroo
diaphragm
7
The
primary
and
secondary
emulsion
tubes
can
be
disassembled
by
removing
the
main
air
bleeds
on
the
individual
sides
In
removing
injector
weight
piston
return
spring
and
ball
care
should
be
excercised
to
prevent
them
from
being
scattered
and
lost
OQ
fI
Fig
EF
33
Removing
emulsion
tubes
8
To
check
the
accelerator
pump
the
pump
cover
is
removed
Be
careful
not
to
lose
the
return
spring
and
inlet
valve
ball
provided
at
the
lower
part
of
the
piston
during
disassemb
ly
Removal
of
bi
metal
cover
is
a
simple
matter
of
removing
three
set
screws
When
it
becomes
necessary
to
take
out
float
pull
shaft
from
float
Note
Under
no
circumstances
should
bi
metal
be
moved
with
excessive
force
since
this
may
cause
a
perma
nent
set
in
bi
metal
making
starting
difficult
Page 411 of 513

ENGINE
Y
Q
0
Fig
EF
34
Disassembling
accelerator
pump
and
hi
metal
cover
1
EC013
Fig
EF
35
Removing
throttle
chamber
9
The
throttle
chamber
can
be
detached
from
the
float
chamber
by
removing
three
set
screws
Do
not
remove
anti
dieseling
solenoid
unless
it
is
necessary
to
change
If
necessary
refer
to
the
item
of
Anti
dieseling
solenoid
page
EF
12
10
It
is
preferable
to
leave
throttle
valve
intact
unless
otherwise
required
If
throttle
valve
must
be
disassembled
to
remedy
a
defect
secondary
throttle
valve
must
be
installed
with
gap
to
be
free
Otherwise
stable
idling
and
slow
speed
performance
will
not
be
obtained
I
o
rJ
01
o
o
Fig
EF
36
Removing
throttle
valve
II
In
disassembling
and
reassembling
interlocking
links
take
care
so
that
each
linkage
has
a
smooth
action
and
that
it
is
not
fitted
in
any
forced
position
Cleaning
and
inspection
Dirt
gum
water
or
carbon
contamination
in
or
on
the
exterior
moving
parts
of
carburetor
are
often
responsible
for
unsatisfactory
performance
For
this
reason
efficient
carburetion
depends
upon
careful
cleaning
and
inspection
while
servicing
1
Blow
aU
passages
and
castings
with
compressed
air
and
blow
off
all
parts
until
dry
Note
Do
not
pass
drills
or
wires
through
calibrated
jets
or
pssages
as
this
may
enlarge
orifice
and
seriously
affect
carburetor
calibration
2
Check
all
parts
for
wear
Replace
worn
part
Especial
ly
the
following
matters
should
be
noted
I
Check
float
needle
and
seat
for
wear
Replace
the
assembly
if
worn
2
Check
the
throttle
and
choke
bores
in
throttle
body
and
cover
casting
for
wear
or
out
of
round
3
Inspect
idle
adjusting
needles
fur
burrs
or
ridges
Replace
as
required
3
Inspect
gaskets
to
ensure
that
they
do
not
appear
hard
or
brittle
and
that
the
edges
are
not
turned
or
distorted
If
any
such
condition
is
detected
they
must
be
replaced
4
Check
fIlter
screen
for
clogging
Clean
and
if
it
is
distorted
or
remains
plugged
replace
EF
20