alternator DATSUN PICK-UP 1977 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1977, Model line: PICK-UP, Model: DATSUN PICK-UP 1977Pages: 537, PDF Size: 35.48 MB
Page 183 of 537

REMOVAL
1
Disconnect
negative
battery
ter
minaL
2
Disconnect
two
lead
wires
and
connector
from
alternator
3
loosen
adjusting
bolt
4
Remove
alternator
drive
belt
5
Remove
parts
associated
with
alternator
from
engine
6
Remove
alternator
from
vehicle
DISASSEMBLY
1
Remove
pulley
nut
and
pulley
assembly
11
C
@@@
EE033
Fig
EE
27
Removing
pulley
ond
fan
2
Remove
brush
holder
fIxing
screws
and
remove
brush
holder
cover
Pull
brush
holder
fOIWard
and
remove
brushes
together
with
brush
holder
Note
Do
not
disconnect
N
tenninaJ
from
stator
coil
lead
wire
EE346
1
N
terminal
2
Brush
holder
3
Brush
holder
co
r
Fig
EE
28
Remouing
brush
Engine
Electrical
System
3
Remove
through
bolts
Separate
front
cover
with
rotor
from
rear
cover
with
stator
by
lightly
tapping
front
bracket
with
a
wooden
mallet
J
J
4
C
EE035
Fig
EE
29
Separating
front
cover
with
rotor
from
rear
cover
4
Remove
three
set
screws
from
bearing
retainer
and
separate
rotor
from
front
cover
DO
Q
EE036
Fig
EE
3D
Removing
rotor
5
Pull
rear
bearing
out
from
rotor
assembly
with
a
press
or
bearing
puller
L
I
EE037
Fig
EE
3I
Pulling
out
of
roar
bearing
EE
16
6
Remove
diode
cover
fIXing
screw
and
remove
diode
cover
Disconnect
three
stator
coil
lead
wires
from
diode
terminal
with
a
soldering
iron
7
Remove
A
tenninaJ
nut
and
diode
installation
nut
and
remove
diode
assembly
CD
AJ
f
e
ecA
O
1
Diode
assembly
o
2
Diode
cover
o
EE039
Fig
EE
32
Removing
diode
088embly
Note
Use
care
in
assembly
to
on
it
handling
diode
an
undue
st
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
Remove
alternator
from
car
and
connect
a
circuit
tester
between
F
tenninal
and
E
terminal
When
the
resistance
is
approxi
mately
5il
the
condition
of
brush
and
fIeld
coil
is
satisfactory
When
no
continuity
exists
in
brush
or
fIeld
coil
or
when
resistance
differs
significantly
between
those
parts
dis
assemble
and
inspect
A
o
E
O
1
ld
Q
EE040
Fig
EE
33
Inspecting
alternator
Page 185 of 537

If
current
flows
in
both
positive
and
negative
directions
diode
is
short
circuited
If
current
flows
in
one
direc
tion
only
diode
is
in
good
condition
Test
probe
of
a
circuit
t
ter
e
Gl
terminal
EEl
plate
EJ
plate
terminal
terminal
e
plate
e
plate
terminal
e
plate
@
plate
Xl
plate
e
plate
INSPECTION
OF
BRUSH
Check
movement
of
brush
and
if
movement
is
not
smooth
check
brush
holder
and
clean
if
necessary
Check
brush
for
wear
If
it
is
worn
down
to
less
than
the
specified
limit
replace
brush
assembly
Check
brush
pig
tail
and
if
dam
aged
replace
Brush
wear
limiting
line
EE127
Fig
EE
41
Bnlsh
wear
limil
Engine
Electrical
System
If
there
is
a
faulty
diode
replace
all
diodes
ix
diode
as
an
assembly
See
table
below
These
diodes
are
unserviceable
Conduction
o
o
o
SPRING
PRESSURE
TEST
With
brush
projected
approximate
ly
2
mm
0
079
in
from
brush
holder
measure
brush
spring
pressure
by
the
use
of
a
pring
balance
Normally
the
rated
pressure
of
a
new
brush
spring
is
255
to
345
gr
9
0
to
12
202
Morevover
when
brush
is
worn
pressure
decrease
approximately
20
g
0
7
02
per
1
mm
0
0039
in
wear
t
m
0
079
in
or
f
EEO
9
Fig
EE
42
M
CJ
uring
pring
preaure
EE
lB
ASSEMBLY
Reassemble
alternator
in
the
reverse
sequence
of
disassembly
noting
the
following
I
When
soldering
each
stator
coil
lead
wire
to
diode
assembly
terminal
carry
out
the
operation
as
fast
as
pas
sible
2
When
installing
diode
A
terminal
install
insulating
bush
correctly
1
Imulating
bush
2
A
terminal
bolt
3
Diode
cover
4
Rear
cover
5
Diode
a
sembly
EE347
Fig
EE
43
Sectional
view
of
diode
and
A
term
inal
3
Tighten
pulley
nut
with
tighten
ing
torque
of
3
5
to
4
0
kg
m
25
3
to
29
0
ft
Ib
When
pulley
is
tightened
make
sure
that
deflection
of
V
groove
is
less
than
0
3
mm
0
01
IS
in
q
ffl
t
EE051
Fig
EE
44
Tightening
pulley
nut
Page 186 of 537

Engine
Electrical
System
ALTERNATOR
TEST
Before
conducting
an
alternator
test
make
sure
th
tthe
battery
is
fully
charged
A
30
V
olt
voltmeter
and
suitable
test
probes
3re
necessary
for
the
test
Set
up
a
test
circuit
as
shown
in
Figure
EE45
and
test
auernator
in
the
manner
indica
ted
in
the
flow
chart
below
1
Disconnect
connectors
at
alternator
2
Connect
A
terminal
to
F
terminal
3
Connect
one
test
probe
from
voltmeter
positive
terminal
to
A
terminal
Connect
the
other
test
probe
to
ground
Make
sure
that
voltmeter
registers
battery
voltage
4
Turn
on
headlights
and
switch
to
High
Beam
5
Start
engine
6
Increase
engine
speed
gradually
until
it
is
approximately
1
100
rpm
and
take
the
voltmeter
reading
Measured
value
Below
12
5
Volts
Alternator
is
in
trouble
remove
and
check
it
for
condition
Measured
value
Over
12
5
Volts
Alternator
is
in
good
condition
Notes
a
Do
Dot
run
engine
at
the
speed
of
more
than
1
100
rpm
while
test
is
being
conducted
on
alternator
b
Do
not
race
engine
i
9
l
IV
I
Battery
EE052
Voltmeter
Fig
EE
45
Testing
alternator
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
Nominal
rating
V
A
LT138
IB
LTl35
36B
For
air
conditioner
1235
12
38
Negative
Negative
1
000
1
000
28
2
500
30
2
500
35
5
000
38
5
000
2
25
2
25
More
than
7
5
0
295
More
than
7
5
0
295
255
to
345
255
to
345
9
0
to
12
2
9
0
to
12
2
More
than
30
1
181
More
than
30
1
181
EE
19
Type
Ground
polarity
Minimum
revolution
when
generating
14V
with
no
load
rpm
Hot
output
current
Nrpm
Pulley
ratio
Brush
Length
Spring
pressure
mm
in
gr
oz
Slip
ring
outer
diameter
mm
in
Page 187 of 537

DESCRIPTION
MEASUREMENT
OF
REGULATOR
VOLTAGE
ADJUSTMENT
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
The
regulator
consists
basically
of
a
voltage
regulator
and
a
charge
relay
The
voltage
regulator
has
two
sets
of
contact
points
a
lower
set
and
an
upper
set
to
control
alternator
volt
age
An
armature
plate
placed
between
the
two
sets
of
contacts
moves
upward
or
downward
or
vibrates
The
lower
contacts
when
closed
complete
the
jCV
ID@
@
GJ
I
@
@
@
Engine
Electrical
System
REGULATOR
CONTENTS
EE
20
CHARGING
RELAY
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Including
alternatorl
EE
25
EE
23
EE
24
EE
20
EE
23
EE
23
field
circuit
direct
to
ground
and
the
upper
contacts
when
closed
complete
the
field
circuit
to
ground
through
a
resistance
field
coil
and
produce
alternator
output
The
charge
relay
i
similar
in
construction
to
the
voltage
regulator
When
the
upper
contacts
are
closed
charge
warning
lamp
goes
on
v
1
Charge
relay
2
Voltage
regulator
EE285
Fig
EE
46
View
of
removing
cover
As
regards
the
construction
the
voltage
regulator
is
very
similar
to
the
charge
relay
as
shown
in
Figure
EE47
@
r
J
CD
@
@
@
Q
@
ID@
ID@
J
t
L
T
@
r
b
r
CD
L
@
j
1
g
f
@
@
EEJ97
J
I1Jlccting
spring
2
Y
kt
g
p
3
Armaturc
4
Core
go
5
Low
Sllccd
lnlacl
h
Point
ap
7
High
speed
conlat
t
8
Contact
c
9
3111111
0
118
ill
di
10
41l1I11W
157in
c1ia
few
II
Cuil
12
lock
nut
J3
Adjllslin
screw
14
Adjll
sting
sprin
15
Yoke
9
Adjusting
screw
10
Lock
nut
11
Coil
12
4mm
0
157
in
dia
screw
13
3mm
0
118
in
dla
crew
14
Contact
iet
15
Voltage
cgulatm
contact
a
Cnl1
Tlll
tion
f
lltagl
l
j
llIOltllT
I
Point
gilp
2
Charge
relay
contllct
3
Core
gap
4
ArlllatlJre
5
Connecting
sprin
6
Yoke
gap
7
Yoh
B
Adjusting
pring
b
Construction
of
charge
relay
Fig
EE
47
Structural
vi
w
EE
20
Page 188 of 537
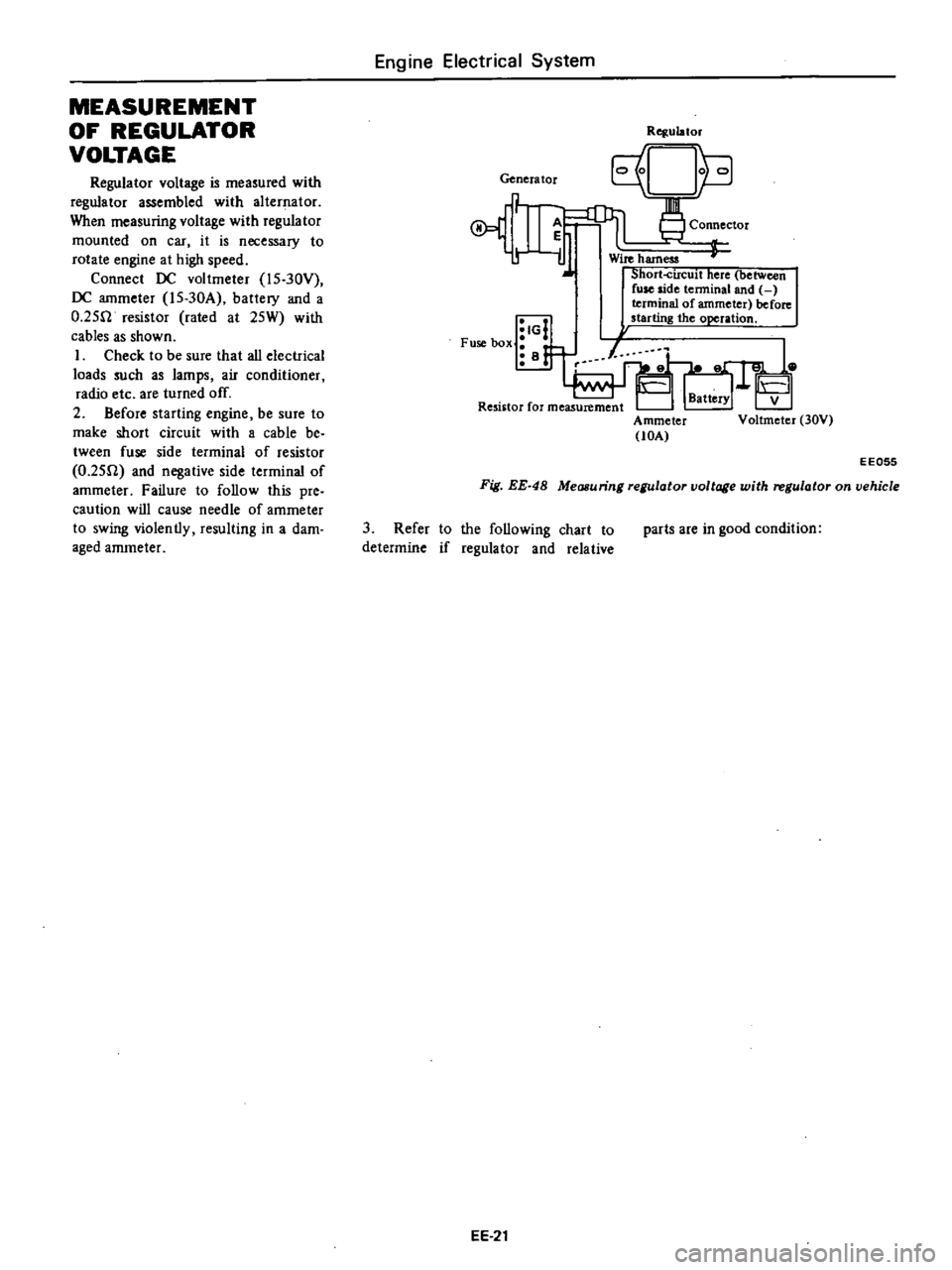
MEASUREMENT
OF
REGULATOR
VOLTAGE
Regulator
voltage
is
measured
with
regulator
assembled
with
alternator
When
measuring
voltage
with
regulator
mounted
on
car
it
is
necessary
to
rotate
engine
at
high
speed
Connect
DC
voltmeter
l5
30Y
DC
ammeter
l5
30A
battery
and
a
O
25fl
resistor
rated
at
25W
with
cables
as
shown
I
Check
to
be
sure
that
all
electrical
loads
such
as
lamps
air
conditioner
radio
etc
are
turned
off
2
Before
starting
engine
be
sure
to
make
short
circuit
with
a
cable
be
tween
fuse
side
terminal
of
resistor
O
25fl
and
negative
side
terminal
of
ammeter
Failure
to
follow
this
pre
caution
will
cause
needle
of
ammeter
to
swing
violently
resulting
in
a
dam
aged
ammeter
Engine
Electrical
System
Genera
tor
A
r
iJ
IG
Fuse
box
i
B
Rqulator
Connector
Wire
harness
Short
circuit
here
between
fuse
side
tenninal
and
terminal
of
ammeter
before
starting
the
operation
Ammeter
lOA
V
Voltmeter
30V
EE055
Fig
EE
48
Measuring
regulator
voltage
with
regulator
on
vehicle
3
Refer
to
the
following
chart
to
determine
if
regulator
and
relative
EE
21
parts
are
in
good
condition
Page 190 of 537
ADJUSTMENT
VOLTAGE
REGULATOR
When
regulating
voltage
as
meas
ured
above
deviates
from
rated
value
adjust
regulator
in
accordance
with
the
following
instructions
I
Inspect
contact
surface
and
if
rough
lightly
polish
with
fine
emery
paper
1
500
or
600
2
Measure
each
gap
and
adjust
if
necessary
Adjust
core
gap
and
point
gap
in
that
order
No
adjustment
is
required
for
yoke
gap
3
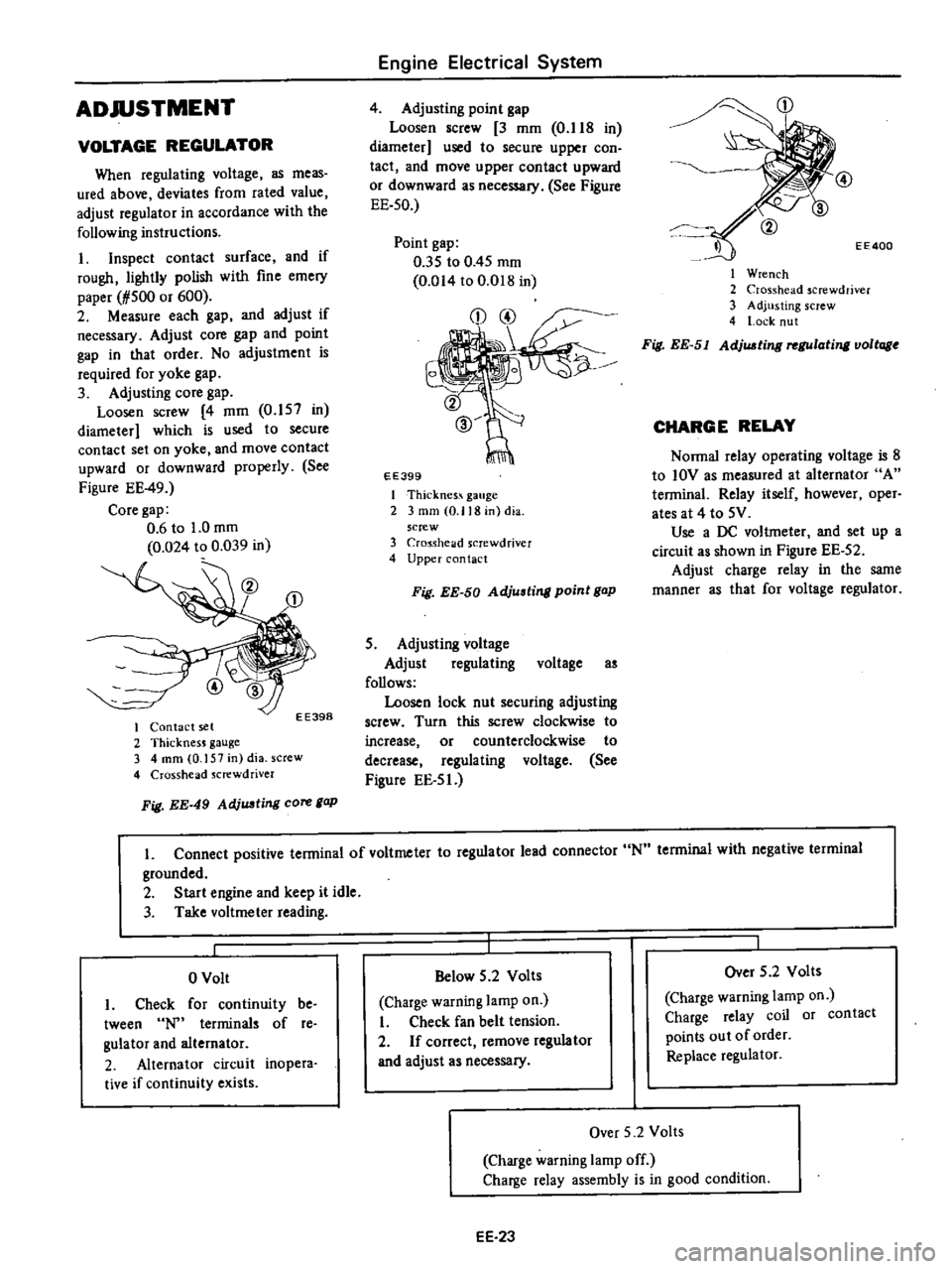
Adjusting
core
gap
Loosen
screw
4
mm
0
157
in
diameter
which
is
used
to
secure
contact
set
on
yoke
and
move
contact
upward
or
downward
properly
See
Figure
EE
49
Core
gap
0
6
to
1
0
mm
0
024
to
0
039
in
EE398
I
Contact
set
2
ThicknesJ
gauge
3
4
mm
0
157
in
dia
screw
4
Crosshead
Jcrewdriver
Fig
EE
49
AdjUJJting
core
gap
Engine
Electrical
System
4
Adjusting
point
gap
Loosen
screw
3
mm
O
lIS
in
diameter
used
to
secure
upper
con
tact
and
move
upper
contact
upward
or
downward
as
necessary
See
Figure
EE
50
Point
gap
035
to
0
45
mm
0
014
to
O
D1S
in
EE399
I
Thicknes
gauge
2
3
mm
0
118
in
dia
screw
3
Cro
Sshelld
screwdriver
4
Upper
contact
Fig
EE
50
Adjusting
point
gap
5
Adjusting
voltage
Adjust
regulating
voltage
as
follows
Loosen
lock
nut
securing
adjusting
screw
Turn
this
screw
clockwise
to
increase
or
counterclockwise
to
decrease
regulating
voltage
See
Figure
EE
5
J
CD
EE400
I
Wrench
2
Crosshead
screwdriver
3
Adjusting
screw
4
l
ock
nut
Fig
EE
51
AdjUJJting
rel
Ulating
voltage
CHARGE
RELAY
Nonna
relay
operating
voltage
is
S
to
IOV
as
measured
at
alternator
A
tenninal
Relay
itself
however
oper
ates
at
4
to
5V
Use
a
DC
voltmeter
and
set
up
a
circuit
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
52
Adjust
charge
relay
in
the
same
manner
as
that
for
voltage
regulator
L
Connect
positive
tenninal
of
voltmeter
to
regulator
lead
connector
N
tenninal
with
negative
terminal
grounded
2
Start
engine
and
keep
it
idle
3
Take
voltmeter
reading
o
Volt
I
Check
for
continuity
be
tween
terminals
of
re
gulator
and
alternator
2
Alternator
circuit
inopera
tive
if
continuity
exists
Below
5
2
Volts
Charge
warning
lamp
on
I
Check
fan
belt
tension
2
If
correct
remove
regulator
and
adjust
as
necessary
Over
5
2
Volts
Charge
warning
lamp
on
Charge
relay
coil
or
contact
points
out
of
order
Replace
regulator
Over
5
2
Volts
Charge
warning
lamp
off
Charge
relay
assembly
is
in
good
condition
EE
23
Page 192 of 537

Engine
Electrical
System
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Including
alternator
Condition
Probable
cause
No
output
Sticking
brushes
Dirty
brushes
and
slip
rings
Loose
connections
or
broken
leads
Open
sta
tor
winding
Open
rotor
winding
Open
diodes
Shorted
rotor
Shorted
stator
Grounded
A
terminal
Broken
fan
belt
Excessive
output
Broken
neutral
wire
COIOf
of
wire
is
yellow
Voltage
fegulator
breakdown
Poor
grounding
of
alternator
and
voltage
regulator
En
terminal
Broken
ground
wire
color
of
wire
is
black
Low
output
Loose
or
worn
fan
belt
Sticking
brushes
Low
brush
spring
tension
Voltage
regulator
breakdown
Dirty
slip
rings
Partial
short
ground
or
open
in
stator
winding
Partially
shorted
or
grounded
rotor
winding
Open
or
damaged
diode
Noisy
alternator
Loose
mounting
Loose
drive
pulley
Broken
ball
bearing
Improperly
seated
brushes
EE
25
Corrective
action
Correct
or
replace
brushes
and
brush
springs
Clean
Retighten
or
soldef
connections
Replace
leads
if
necessary
Repair
Of
replace
stator
Replace
rotor
Replace
Replace
rotor
Repair
or
replace
Replace
insulator
Replace
Replace
Check
regulator
operation
and
repair
or
replace
as
required
Retighten
terminal
connection
Replace
Retighten
or
replace
Correct
or
replace
brushes
and
springs
if
necessary
Replace
brush
springs
Check
regulator
OpefatiOn
and
repair
or
replace
as
required
Clean
Replace
stator
Replace
rotor
Replace
diode
Retighten
bolts
Retighten
Replace
Seat
correctly
Page 193 of 537
NON
CALIFORNIA
MODELS
Engine
Electrical
System
IGNITION
CIRCUIT
CONTENTS
EE
26
CALIFORNIA
MODELS
EE
2B
NON
CALIFORNIA
MODELS
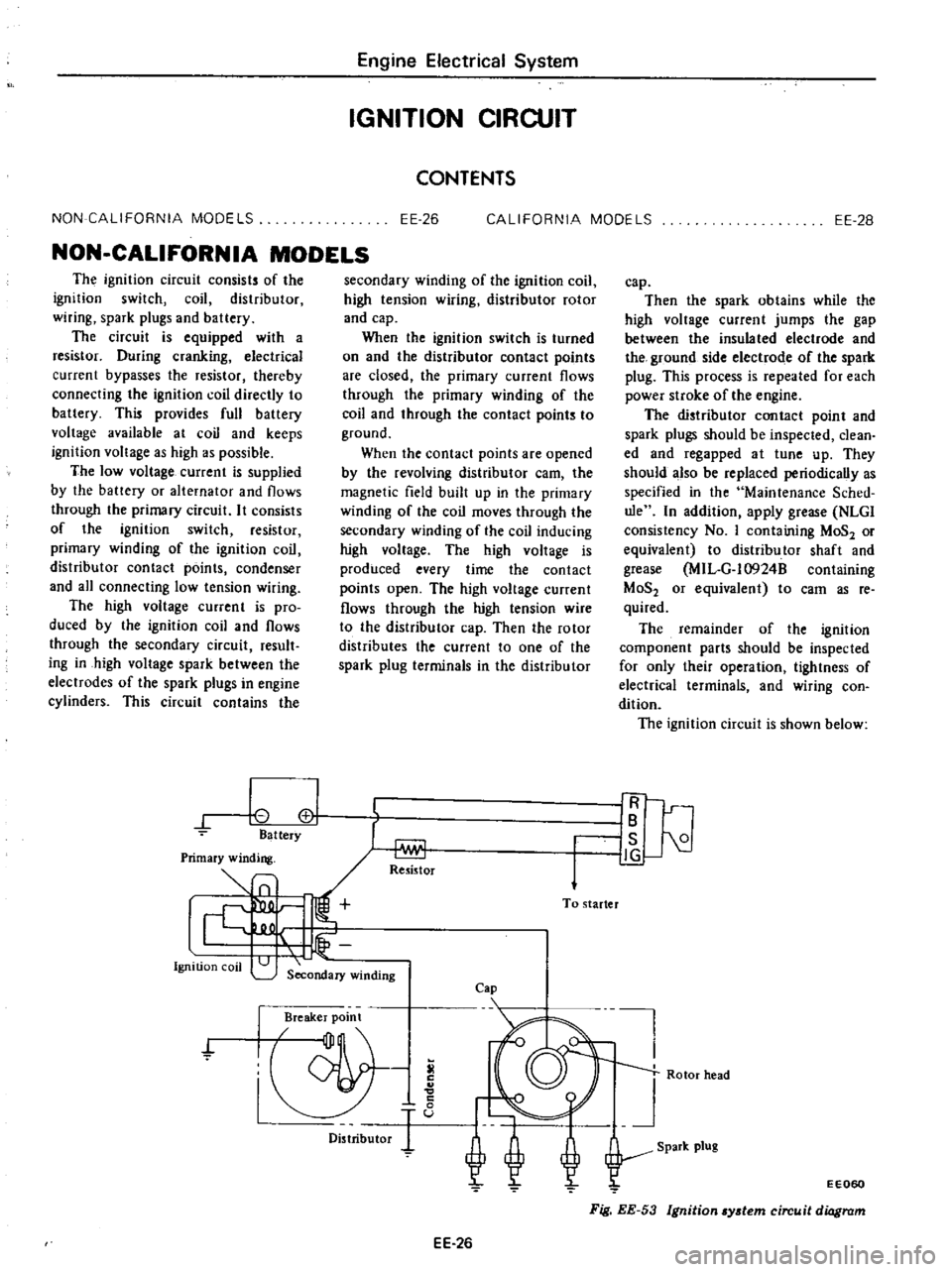
The
ignition
circuit
consists
of
the
ignition
switch
coil
distributor
wiring
spark
plugs
and
battery
The
circuit
is
equipped
with
a
resistor
During
cranking
electrical
current
bypasses
the
resistor
thereby
connecting
the
ignition
coil
directly
to
battery
This
provides
full
battery
voltage
available
at
coil
and
keeps
ignition
voltage
as
high
as
possible
The
low
voltage
current
is
supplied
by
the
battery
or
alternator
and
flows
through
the
primary
circuit
It
consists
of
the
ignition
switch
resistor
primary
winding
of
the
ignition
coil
distributor
contact
points
condenser
and
all
connecting
low
tension
wiring
The
high
voltage
current
is
pro
duced
by
the
ignition
coil
and
flows
through
the
secondary
circuit
result
ing
in
high
voltage
spark
between
the
electrodes
of
the
spark
plugs
in
engine
cylinders
This
circuit
contains
the
0
cl
Battery
Ignition
coil
secondary
winding
of
the
ignition
coil
high
tension
wiring
distributor
rotor
and
cap
When
the
ignition
switch
is
turned
on
and
the
distributor
contact
points
are
closed
the
primary
current
flows
through
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
and
through
the
contact
points
to
ground
When
the
contact
points
are
opened
by
the
revolving
distributor
earn
the
magnetic
field
built
up
in
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
moves
through
the
secondary
winding
of
the
coil
inducing
high
voltage
The
high
voltage
is
produced
every
time
the
contact
points
open
The
high
voltage
current
flows
through
the
high
tension
wire
to
the
distributor
cap
Then
the
rotor
distributes
the
current
to
one
of
the
spark
plug
terminals
in
the
distributor
Re5istor
To
starter
Secondary
winding
Cap
Breaker
point
f
Distributor
EE
26
cap
Then
the
spark
obtains
while
the
high
voltage
current
jumps
the
gap
between
the
insulated
electrode
and
the
ground
side
electrode
of
the
spark
plug
This
process
is
repeated
for
each
power
stroke
of
the
engine
The
distributor
contact
point
and
spark
plugs
should
be
inspected
clean
ed
and
regapped
at
tune
up
They
should
also
be
replaced
periodically
as
specified
in
the
Maintenance
Sched
ule
In
addition
apply
grease
NLGl
consistency
No
I
containing
MoS2
or
equivalent
to
distributor
shaft
and
grease
MIL
G
l0924B
containing
MoS2
or
equivalent
to
cam
as
reo
quired
The
remainder
of
the
ignition
component
parts
should
be
inspected
for
only
their
operation
tightness
of
electrical
terminals
and
wiring
con
dition
The
ignition
circuit
is
shown
below
IR
IB
I
is
21
J
g
Rotor
head
EE060
Fig
EE
53
Ignition
ydem
circuit
diagram
Page 195 of 537
Primary
winding
1
Ignition
coo
I
Secondary
winding
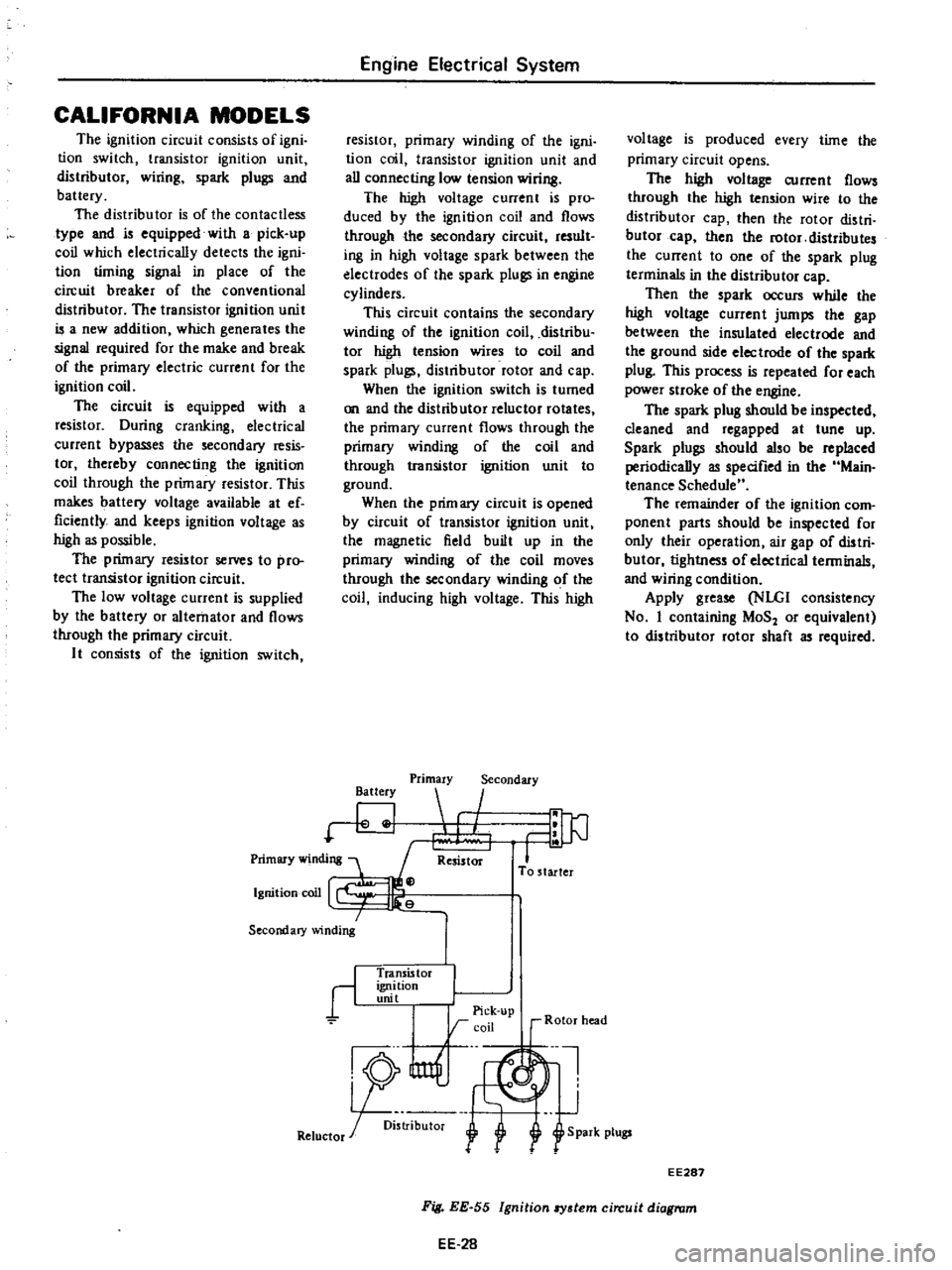
CALIFORNIA
MODELS
The
ignition
circuit
consists
of
igni
tion
switch
transistor
ignition
unit
distributor
wiring
spark
plugs
and
battery
The
distributor
is
of
the
contactless
type
and
is
equipped
with
a
pick
up
coil
which
electrically
detects
the
igni
tion
timing
signal
in
place
of
the
circuit
breaker
of
the
conventional
distributor
The
transistor
ignition
unit
is
a
new
addition
which
generates
the
signal
required
for
the
make
and
break
of
the
primary
electric
current
for
the
ignition
coil
The
circuit
is
equipped
with
a
resistor
During
cranking
electrical
current
bypasses
the
secondary
resis
tor
thereby
connecting
the
ignition
coil
through
the
primary
resistor
This
makes
battery
voltage
available
at
ef
ficiently
and
keeps
ignition
voltage
as
high
as
possible
The
primary
resistor
selVeS
to
pro
tect
transistor
ignition
circuit
The
low
voltage
current
is
supplied
by
the
battery
or
alternator
and
flows
through
the
primary
circuit
It
consists
of
the
ignition
switch
Engine
Electrical
System
resistor
primary
winding
of
the
igni
tion
coil
transistor
ignition
unit
and
all
connecting
low
tension
wiring
The
high
voltage
current
is
pro
duced
by
the
ignition
coil
and
flows
through
the
secondary
circuit
result
ing
in
high
voltage
spark
between
the
electrodes
of
the
spark
plugs
in
engine
cylinders
This
circuit
contains
the
secondary
winding
of
the
ignition
coil
distribu
tor
high
tension
wires
to
coil
and
spark
plugs
distributor
rotor
and
cap
When
the
ignition
switch
is
turned
on
and
the
distributor
reluctor
rotates
the
primary
current
flows
through
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
and
through
transistor
ignition
unit
to
ground
When
the
prim
ary
circuit
is
opened
by
circuit
of
transistor
ignition
unit
the
magnetic
field
built
up
in
the
primary
winding
of
the
coil
moves
through
the
secondary
winding
of
the
coil
inducing
high
voltage
This
high
Battery
Primary
Secondary
I
Resistor
To
starter
r
Transis
tor
ignition
unit
I
I
Pick
up
rcoil
r
Rotor
head
nl
J
R5
U1f
1
Retuctor
r
oi
l
f
S
park
plugs
voltage
is
produced
every
time
the
primary
circuit
opens
The
high
voltage
current
flows
through
the
high
tension
wire
to
the
distributor
cap
then
the
rotor
distri
butor
cap
then
the
rotor
distributes
the
current
to
one
of
the
spark
plug
terminals
in
the
distributor
cap
Then
the
spark
occurs
while
the
high
voltage
current
jumps
the
gap
between
the
insulated
electrode
and
the
ground
side
electrode
of
the
spark
plug
This
process
is
repeated
for
each
power
stroke
of
the
engine
The
spark
plug
should
be
inspected
cleaned
and
regapped
at
tune
up
Spark
plugs
should
also
be
replaced
periodically
as
specified
in
the
Main
tenance
Schedule
The
remainder
of
the
ignition
com
ponent
parts
should
be
inspected
for
only
their
operation
air
gap
of
distri
butor
tightness
of
electrical
terminals
and
wiring
condition
Apply
grease
NLGI
consistency
No
I
containing
MoS
or
equivalent
to
distributor
rotor
shaft
as
required
EE287
EE
28
Fig
EE
55
Ignition
8Y3tem
circuit
diagram
Page 219 of 537

Engine
Removal
Installation
ENGINE
REMOVAL
AND
INSTAllATION
REMOVAL
INSTALLATION
ENGINE
MOUNTING
INSULATORS
REMOVAL
It
is
much
easier
to
remove
engine
and
transmission
as
a
single
unit
than
to
remove
them
separately
After
re
moval
engine
can
be
separated
from
transntission
assembly
Notes
a
Be
sure
to
hoist
engine
and
jack
up
transmission
in
a
safe
manner
b
Use
fender
cove
to
protect
vehicle
body
1
Remove
battery
2
Scribe
hood
hinge
location
for
proper
reinstallation
and
remove
hood
Note
Have
an
assistant
help
you
so
as
to
prevent
damage
to
body
3
Drain
radiator
coolant
4
Disconnect
upper
and
lower
radiator
hoses
from
engine
5
Remove
two
oil
cooler
hoses
from
lower
end
of
radiator
Auto
ma
tic
transmission
models
only
6
Remove
radiator
shroud
7
Remove
four
bolts
securing
radia
tor
and
detach
radiator
Note
Always
tighten
securing
bolt
at
upper
right
hand
side
together
with
body
harness
terminal
8
Remove
carburetor
air
cleaner
as
follows
Remove
fresh
air
duct
Remove
hot
air
duct
Loosen
air
cleaner
band
bolt
and
air
cleaner
supporting
bolts
Disconnect
air
cleaner
ta
air
pump
hose
Disconnect
air
cleaner
to
rocker
cover
hose
at
rocker
cover
Disconnect
air
cleaner
to
air
control
valve
hose
California
models
only
CONTENTS
ER
2
ER
3
ER
3
FRONT
INSULATOR
REAR
INSULATOR
TIGHTENING
TORQUE
ER
4
ER
4
ER
4
Disconnect
air
deaner
to
A
B
valve
hose
Disconnect
air
cleaner
ta
vacuum
hoses
Note
Protect
carburetor
from
dust
and
foreign
matter
by
placing
cover
over
air
inlet
opening
9
Disconnect
fuel
pump
to
fuel
fdter
hose
and
return
hose
10
Disconnect
carbon
canister
hose
on
engine
side
II
Disconnect
air
pump
air
C1eaner
to
al
p
p
hose
12
Disconnect
following
cables
wires
and
hoses
Engine
ground
cable
Accelerator
wire
at
carburetor
High
tension
cable
between
ignition
coil
and
distributor
Wire
to
distributor
at
body
ter
minal
Wire
to
oil
pressure
switch
Wires
to
thermal
transmitter
Wires
to
B
C
p
D
cut
solenoid
Non
California
models
only
auto
choke
heater
and
anti
dieseling
solenoid
Wires
to
alternator
Wires
to
starter
motor
Heater
inlet
and
outlet
hoses
if
so
equipped
Vacuum
hose
of
Master
Vac
at
in
taJce
manifold
Wires
for
back
up
lamp
switch
Cable
to
speedometer
13
Remove
transmission
control
linkage
from
transmission
Manual
transmission
models
I
Detach
rubber
boot
2
Remove
E
ring
and
control
lever
pin
from
transmission
striking
rod
guide
and
remove
control
lever
ER
2
Fig
ER
l
Automatic
transmission
models
I
Disconnect
selector
range
lever
from
manual
shaft
2
Disconnect
wires
at
inhibitor
switch
and
down
shift
solenoid
14
Air
conditioner
equipped
models
need
following
procedures
1
After
removing
flexible
hose
support
remove
four
comi
ressor
se
curing
bolts
Then
move
the
com
pressor
to
battery
support
2
Remove
vacuum
hoses
of
F
LC
D
solenoid
valve
3
Remove
F
LC
D
actuator
15
Remove
two
bolts
securing
clutch
operating
cylinder
Then
dis
connect
operating
cylinder
and
flexi
ble
tube
as
an
assembly
Manual
transmission
models
only
16
Disconnect
front
exhaust
tube
from
exhaust
manifold
17
Remove
propeller
shaft
I
Disconnect
propeller
shaft
center
bearing
bracket
from
third
crossmember
2
Disconnect
propeller
shaft
from
companion
flange
of
differential
carrier
3
Remove
propeller
shaft
from
transmission
and
plug
up
rear
end
of
extension
housing
of
transmission
to
prevent
oil
leakage
18
Attach
a
suitable
wire
or
chain
to
lift
engine
19
Remove
front
engine
mounting
bolts
at
engine
mounting
front
sup
port