battery DATSUN PICK-UP 1977 User Guide
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DATSUN, Model Year: 1977, Model line: PICK-UP, Model: DATSUN PICK-UP 1977Pages: 537, PDF Size: 35.48 MB
Page 171 of 537

DESCRIPTION
OPERATION
CONSTR
UCTI
ON
REMOVAL
DISASSEMBL
Y
CLEANING
AND
INSPECTION
TERMINAL
FIELD
COIL
BRUSHES
AND
BRUSH
LEAD
WIRE
BRUSH
SPRING
TENSION
ARMATURE
ASSEMBLY
DESCRIPTION
The
function
of
the
starting
system
which
consists
of
the
battery
ignition
switch
starting
motor
and
solenoid
is
to
crank
the
engine
The
electrical
energy
is
supplied
from
the
battery
the
solenoid
completes
the
circuit
to
operate
the
starling
motor
and
then
the
motor
carries
out
the
actual
crank
ing
of
the
engine
Engine
Electrical
System
STARTING
MOTOR
CONTENTS
EE
4
EE
6
EE
7
EE
7
EE
7
EE
8
EE
8
EE
B
EE
B
EE
B
EE
B
OVERRUNNING
CLUTCH
ASSEMBLY
BRUSH
HOLDER
TEST
FOR
GROUND
BEARING
METAL
MAGNETIC
SWITCH
ASSEMBLY
ASSEMBLY
TEST
PERFORMANCE
TEST
MAGNETIC
SWITCH
ASSEMBLY
TEST
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
5
@
EE
9
EE
9
EE
9
EE
9
EE
9
EE
9
EE
9
EE
O
EE
EE
11
I
Brush
2
Field
coil
3
Magnetic
switch
4
Pludgcr
5
Torsion
spring
6
Shifll
r
7
Overrunning
clutch
8
Pinion
9
Armature
9
EE315
Fig
EE
5
Sectioool
view
of
slarting
motor
Sl14
180B
EE
4
Page 172 of 537
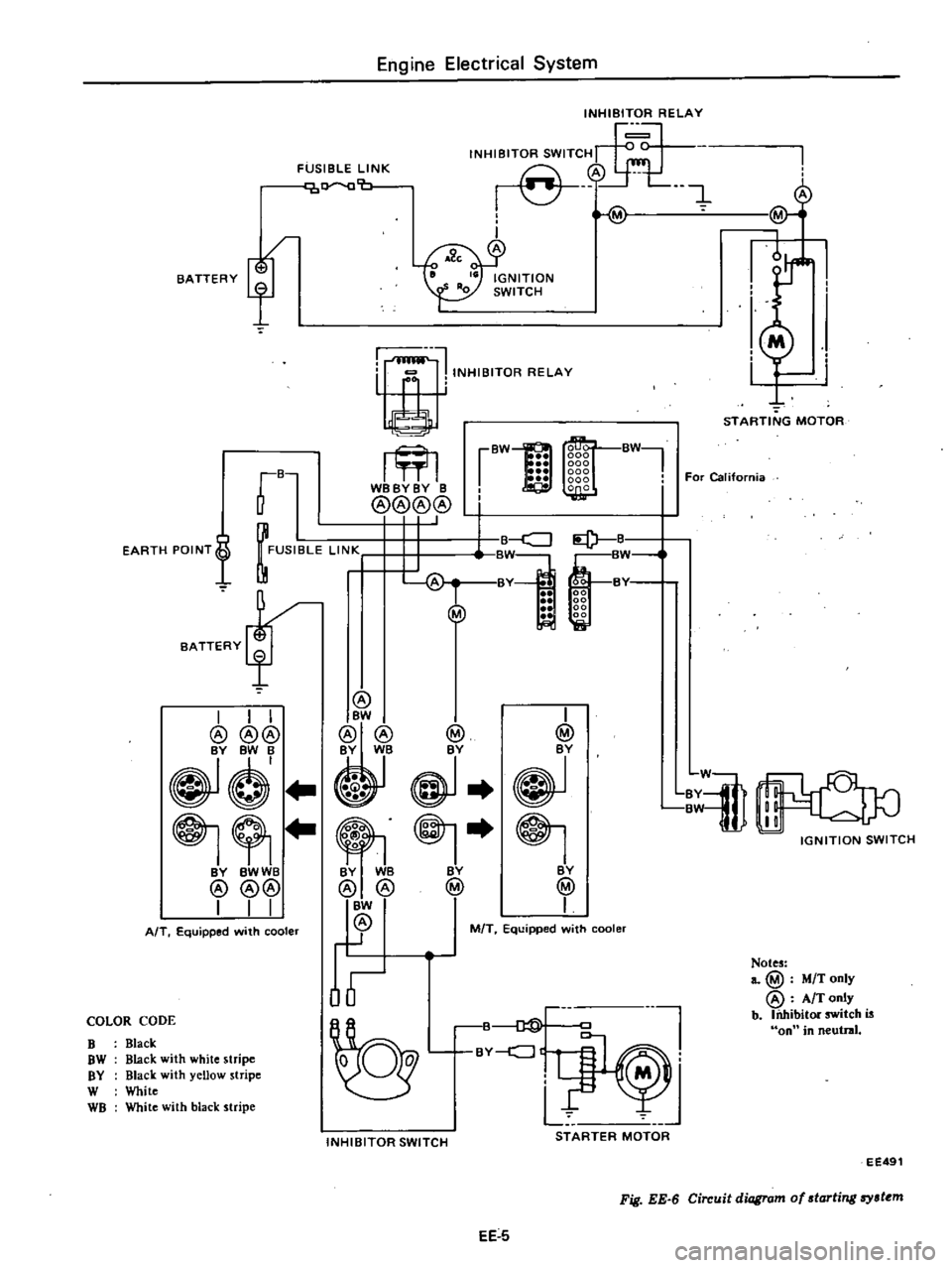
fB
WBBYBY
B
@@@@
I
I
FUSIBLE
lIN
r
T
H
BATTERY
rJ
BATTERY
f
EARTH
POINT
f
I
I
I
@@@
Y
BY
BWWB
@@@
I
I
I
AfT
E
quipped
with
cooler
COLOR
CODE
B
Black
OW
Black
with
white
stripe
BY
Black
with
yellow
stripe
W
White
WB
White
with
black
stripe
Engine
Electrical
System
FUSIBLE
LINK
1Y
O
b
INHIBITOR
RELAY
INHIBITOR
SWITCH
A
I
J
Y
@
I
A
l
rBW
j
CJ
B
W
BWI
000
000
ggg
For
California
I
Bd
f
00
00
00
00
Q
BW
B
Y
BY
WB
BY
@
@
@
BW
@
I
M
T
Equipped
with
cooler
@
I
@
BY
BY
@
I
STARTING
MOTOR
l
BY
BW
9
IGNITION
SWITCH
L
INHIBITOR
SWITCH
STARTER
MOTOR
Notes
a
@
M
T
only
@
A
T
only
b
Inhibitor
switch
is
on
in
neutral
EE
5
Fig
EE
6
Circuit
diagram
0
starting
systom
eE491
Page 173 of 537
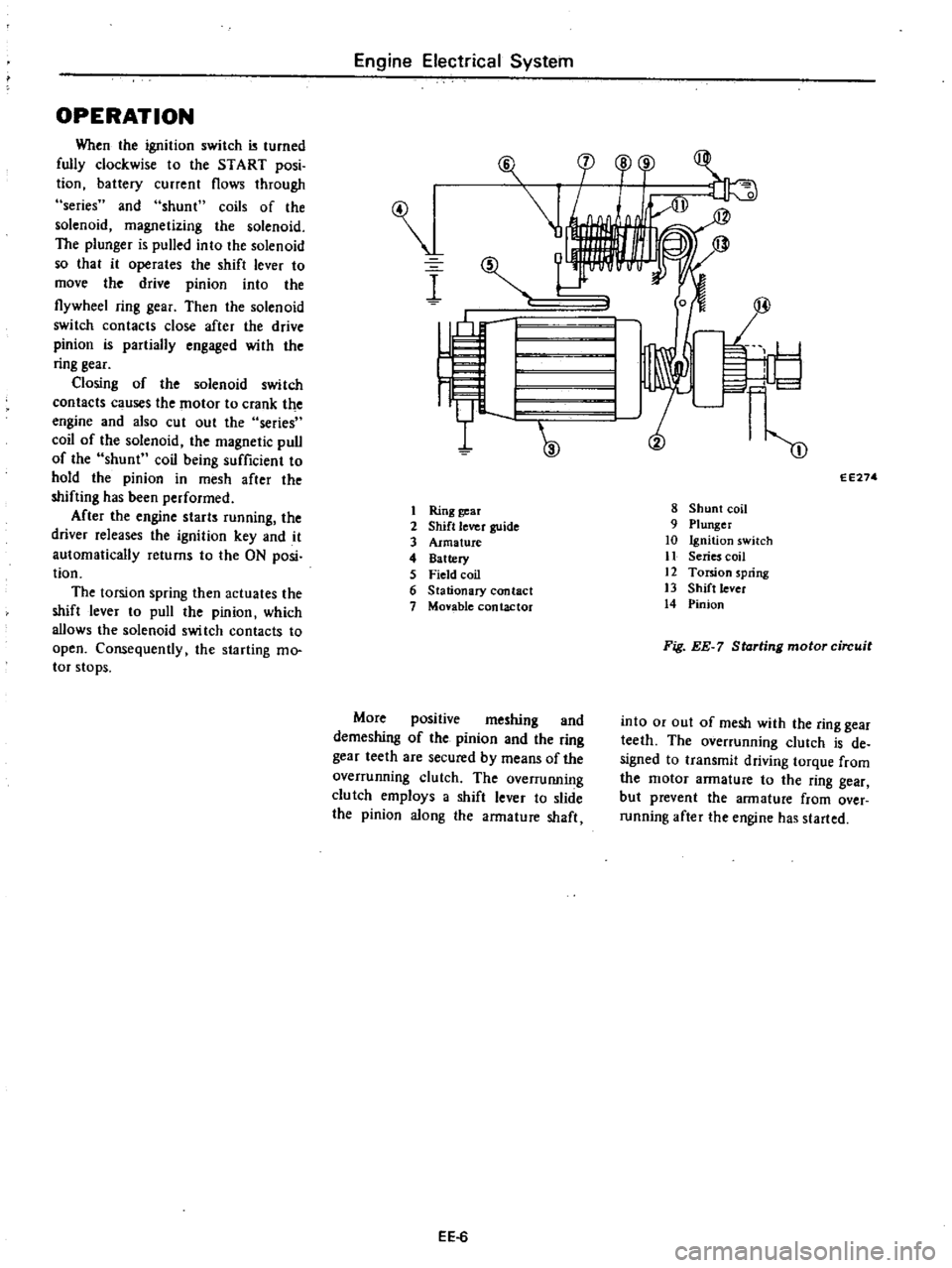
OPERATION
When
the
ignition
switch
turned
fully
clockwise
to
the
START
posi
tion
battery
current
flows
through
series
and
shunt
coils
of
the
solenoid
magnetizing
the
solenoid
The
plunger
is
pulled
into
the
solenoid
so
that
it
operates
the
shift
lever
to
move
the
drive
pinion
into
the
flywheel
ring
gear
Then
the
solenoid
switch
contacts
close
after
the
drive
pinion
is
partially
engaged
with
the
ring
gear
Closing
of
the
solenoid
switch
contacts
c
uses
the
motor
to
crank
the
engine
and
also
cut
out
the
series
coil
of
the
solenoid
the
magnetic
pull
of
the
shunt
coil
being
sufficient
to
hold
the
pinion
in
mesh
after
the
shifting
has
been
performed
After
the
engine
starts
running
the
driver
releases
the
ignition
key
and
it
automatically
returns
to
the
ON
posi
tion
The
torsion
spring
then
actuates
the
shift
lever
to
pull
the
pinion
which
allows
the
solenoid
swi
tch
contacts
to
open
Consequently
the
starting
mo
tor
stops
Engine
Electrical
System
I
I
Ring
gear
2
Shift
lever
guide
3
Armature
4
Battery
5
Field
coil
6
Stationary
contact
7
Monble
contactor
More
positive
meshing
and
demeshing
of
the
pinion
and
the
ring
gear
teeth
are
secured
by
means
of
the
overrunning
clutch
The
overruIUling
clutch
employs
a
shift
lever
to
slide
the
pinion
along
the
armature
shaft
EE
6
F
l
cp
o
r
1
I
I
W
m
EE274
8
Shunt
coil
9
Plunger
10
Ignition
switch
11
Series
coil
12
Torsion
spring
13
Shift
lever
14
Pinion
Fig
EE
7
Starting
motor
circuit
into
or
out
of
mesh
with
the
ring
gear
teeth
The
overrunning
clutch
is
de
signed
to
transmit
driving
torque
from
the
motor
armature
to
the
ring
gear
but
prevent
the
armature
from
over
running
after
the
engine
has
started
Page 174 of 537
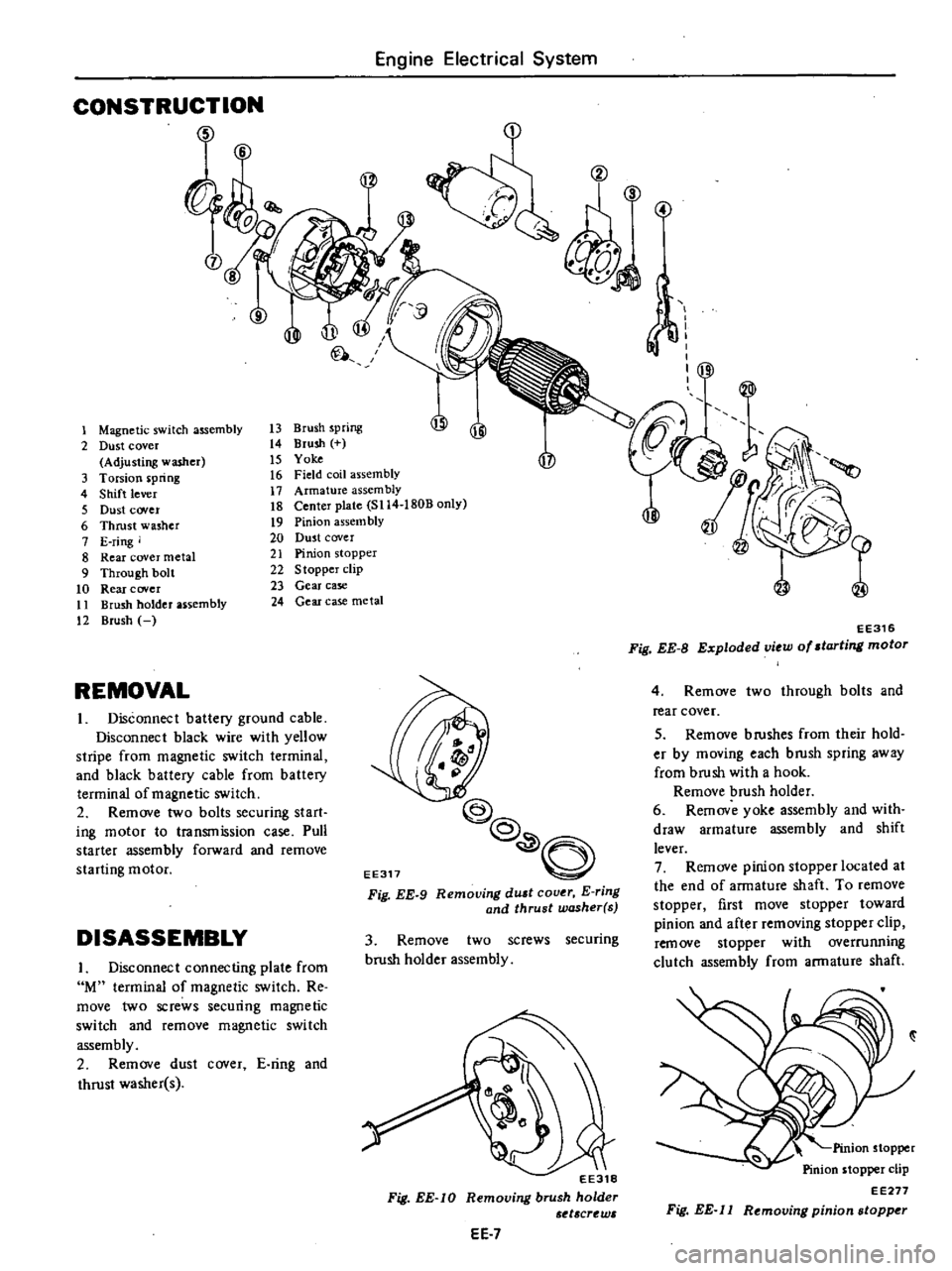
CONSTRUCTION
O
o
8
w
il
Engine
Electrical
System
V
1
Magnetic
switch
assembly
13
Brush
spring
jj
JI
2
Dust
cover
t4
Brush
Adjusting
washer
15
Yoke
P
3
Torsion
pring
t6
Field
coil
assembly
4
Shift
lever
17
Armature
assembly
5
Dust
cover
18
Center
plate
SI14
1808
only
6
Thrust
washer
19
Pinion
assem
bly
7
E
ring
20
Dust
cover
8
Rear
cover
metal
21
Pinion
stopper
9
Through
bolt
22
Stopper
clip
10
Rear
cover
23
Gear
case
tl
Brush
holder
assembly
24
Gear
case
metal
12
Brush
REMOVAL
Disconnect
battery
ground
cable
Disconnect
black
wire
with
yellow
stripe
from
magnetic
switch
terminal
and
black
battery
cable
from
battery
terminal
of
magnetic
switch
2
Remove
two
bolts
securing
start
ing
motor
to
transmission
case
Pull
starter
assembly
forward
and
remove
starting
motor
DISASSEMBLY
I
Disconnect
connecting
plate
from
M
terminal
of
magnetic
switch
Re
move
two
screws
securing
magnetic
switch
and
remove
magnetic
switch
assembly
2
Remove
dust
cover
E
ring
and
thrust
washer
s
EE317
@
@
O
Fig
EE
9
Remouing
dUlt
cover
E
ring
and
thrust
washer
s
3
Remove
two
screws
securing
brush
holder
assembly
EE318
Fig
EE
IO
Removing
brush
holder
d
crt
w
EE
7
S
4
f
I
jl
I
EE316
Fig
EE
B
Exploded
view
of
starting
motor
4
Remove
two
through
bolts
and
rear
cover
5
Remove
b
rushes
from
their
hold
er
by
moving
each
brush
spring
away
from
brush
with
a
hook
Remove
brush
holder
6
Remov
yoke
assembly
and
with
draw
armature
assembly
and
shift
lever
7
Remove
pinion
stopper
located
at
the
end
of
armature
shaft
To
remove
stopper
first
move
stopper
toward
pinion
and
after
removing
stopper
clip
remove
stopper
with
overrunning
clutch
assembly
from
armature
shaft
Pinion
stopper
Pinion
stopper
clip
EE277
Fig
EE
l1
Removing
pinion
stopper
Page 177 of 537

No
load
test
Connect
starting
motor
in
series
with
specified
12
volts
battery
and
an
ammeter
capable
of
indicating
1
000
amperes
Starter
motor
Diagnoses
of
test
1
Low
speed
with
no
load
and
high
current
draw
may
result
from
the
following
1
Tight
dirty
or
worn
bearings
2
Bent
armature
shaft
or
loosened
field
probe
3
Shorted
armature
Check
armature
further
4
A
grounded
armature
or
field
a
Remove
input
tenninal
b
Raise
two
negative
side
brushes
from
commutator
c
Using
a
circuit
tester
place
one
probe
onto
input
tenninal
and
the
other
onto
yoke
d
I
f
tester
indicates
continuity
raise
the
other
two
brushes
and
check
field
and
armature
separately
to
determine
whether
field
or
armature
is
grounded
2
F
allure
to
operate
with
high
current
draw
may
be
caused
by
the
Engine
Electrical
System
Specified
current
draw
and
revolu
tion
in
these
test
are
shown
in
Specifications
Switch
6
Battery
Et
Voltmeter
Ammeter
Ee026
Fig
EE
20
No
load
l
ting
following
I
A
grounded
or
open
field
coil
Inspect
the
connection
and
trace
circuit
with
a
circuit
tester
2
Armature
coil
does
not
operate
Inspect
commutator
for
excessive
burning
In
this
case
arc
may
occur
on
damaged
commutator
when
motor
is
operated
with
no
load
3
Burned
out
commutator
bar
Weak
brush
spring
tension
broken
brush
spring
rubber
bush
thrust
out
of
mica
in
commu
tat
or
or
a
loose
contact
between
biush
and
com
mutator
would
cause
commutator
bar
to
burn
3
Low
current
draw
and
low
no
load
speed
would
cause
high
internal
resistance
due
to
loose
con
nections
damaged
leads
dirty
corn
mutator
and
causes
listed
on
item
2
3
EE10
MAGNETIC
SWITCH
ASSEMBLY
TEST
Switch
o
Fv
IB
I
I
D
Battery
Starter
motor
EE351
FiN
EE
21
Circuit
ofmagndic
awitch
assembly
ted
If
the
starting
motor
check
is
OK
check
magnetic
switch
as
sembly
Connect
cables
between
negative
battery
tenninal
and
start
ing
motor
M
terminal
positive
battery
terminal
and
starting
motor
S
terminal
connecting
a
switch
in
series
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
21
With
the
switch
on
push
pinion
back
to
remove
all
slack
and
measure
the
clearance
l
between
pinion
front
edge
and
pinion
stopper
The
clearance
should
be
held
within
0
3
to
1
5
mm
0
012
to
0
059
in
If
neces
sary
adjust
it
by
changing
or
adding
adjusting
washer
s
Adjusting
washers
are
available
in
to
two
different
sizes
0
5
mm
0
020
in
and
O
S
mm
0
031
in
0
3
to
I
S
rom
0
012
to
0
059
in
l
EE029
Fig
EE
22
MeO
uring
clearance
t
Page 178 of 537

Engine
Electrical
System
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
Type
System
voltage
No
load
Terminal
voltage
Current
Revolution
v
V
A
rpm
Brush
length
Outer
diameter
of
commutator
mm
in
mm
in
Brush
spring
tension
kg
Ib
Clearance
between
bearing
metal
and
armature
shaft
mm
in
Clearance
L
between
pinion
front
edge
and
pinion
stopper
mm
in
TROUBLE
DIAGNOSES
AND
CORRECTIONS
Condition
Starting
motor
will
not
operate
Noisy
starting
motor
Starting
motor
cranks
slowly
Probable
cause
Discharged
battery
Damaged
solenoid
switch
Loose
connections
of
terminal
Damaged
brushes
Starti
g
motor
inoperative
Loose
securing
bolt
Worn
pinion
gear
Poor
lubrication
Worn
commutator
Worn
brushes
Discharged
battery
Loose
connection
of
terminal
Worn
brushes
Locked
brushes
EE
ll
Manual
transmission
Automatic
transmission
Optional
for
manual
transmission
SII4
ISOB
S114
170B
12
12
Less
than
60
More
than
7
000
More
than
6
000
More
than
39
1
54
More
than
12
0
47
1
4
to
I
S
3
1
to
4
0
Less
than
0
2
O
OOS
0
3
to
1
5
0
012
to
0
059
Corrective
action
Charge
or
replace
battery
Repair
or
replace
solenoid
switch
Clean
and
tighten
terminal
Replace
brushes
Remove
starting
motor
and
make
test
Tighten
Replace
Add
oil
Replace
Replace
Charge
Clean
and
tighten
Replace
Inspect
brush
spring
tension
or
repair
brush
holder
Page 179 of 537

Condition
Engine
Electrical
System
Probable
cause
Starting
motor
cranks
slowly
Dirty
or
worn
commutator
Armature
rubs
field
coil
Damaged
solenoid
switch
Starting
motor
operates
but
does
not
crank
engine
Worn
pinion
Locked
pinion
guide
Worn
ring
gear
Starting
motor
will
not
disengage
even
if
ignition
switch
is
turned
off
Damaged
solenoid
switch
Damaged
gear
teeth
The
charging
circuit
consists
of
the
battery
alternator
regulator
and
necessary
wiring
to
connect
these
parts
The
purpose
of
this
system
is
to
convert
mechanical
energy
from
the
engine
into
electrical
energy
which
is
used
to
operate
all
electrically
operat
ed
units
and
to
keep
the
battery
fully
charged
When
the
ignition
switch
is
set
to
ON
current
flows
from
the
battery
to
ground
through
the
ignition
switch
voltage
regulator
IG
terminal
primary
side
contact
point
PI
movable
contact
point
P2
voltage
regulator
IF
terminal
alternator
IF
terminal
rotor
field
coil
and
alternator
E
terminal
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
23
by
full
line
arrow
marks
Then
the
rotor
in
the
alternator
is
excited
On
the
other
hand
current
flows
from
the
battery
to
ground
through
the
ignition
switch
warning
lamp
voltage
regula
tor
L
terminal
lamp
side
contact
point
P4
movable
contact
point
P5
and
voltage
regulator
E
termi
nal
as
shown
by
dotted
line
arrow
CHARGING
CIRCUIT
marks
Then
the
warning
lamp
lights
When
the
alternator
begins
to
op
erate
three
phase
alternating
current
is
induced
in
the
stator
armature
coil
This
alternating
current
is
rectified
by
the
positive
and
negative
silicon
diodes
The
rectified
direct
current
output
reaches
the
alternator
A
and
E
terminals
On
the
other
hand
the
neutral
point
voltage
reaches
N
and
E
terminals
nearly
a
half
of
the
output
voltage
and
current
flows
from
voltage
regulator
N
terminal
to
E
terminal
or
ground
through
the
coil
VCI
as
shown
in
Figure
EE
24
by
the
dotted
line
arrow
marks
Then
the
coil
VCI
is
excited
and
the
movable
contact
point
IPS
comes
into
contact
with
voltage
winding
side
contact
point
P6
This
action
causes
to
turn
off
the
warning
lamp
and
complete
the
voltage
winding
circuit
as
shown
by
the
full
line
arrow
marks
When
the
alternator
speed
is
in
creased
or
the
voltage
starts
to
rise
excessively
the
movable
contact
point
EE
12
Corrective
action
Clean
and
repair
Replace
assembly
Repair
or
replace
Replace
Repair
Replace
Repair
or
replace
Replace
damaged
gear
P2
is
separated
from
the
primary
side
contact
PI
by
the
magnetic
force
of
coil
VC2
Therefore
registor
RI
is
applied
into
the
rotor
circuit
and
output
voltage
is
decreased
AJ
the
output
voltage
is
decreased
the
movable
contact
point
P2
and
primary
side
contact
Pin
comes
into
contact
once
again
and
the
alternator
voltage
increases
Thus
the
rapid
vibration
of
the
movable
contact
point
IPl
maintains
an
alternator
output
voltage
constant
When
the
alternator
speed
is
further
increased
or
the
voltage
starts
to
rise
excessively
the
movable
contact
point
P2
comes
into
contact
with
secondllJ
side
contact
point
P3
Then
the
rotor
current
is
shut
off
and
alternator
output
voltage
is
decreased
immediately
This
action
causes
movable
contact
n
to
separate
from
secondary
contact
P3
Thus
the
rapid
vibration
of
the
movable
contact
point
P2
or
breaking
and
completing
the
rotor
circuit
maintains
an
alternator
output
voltage
constant
Page 180 of 537
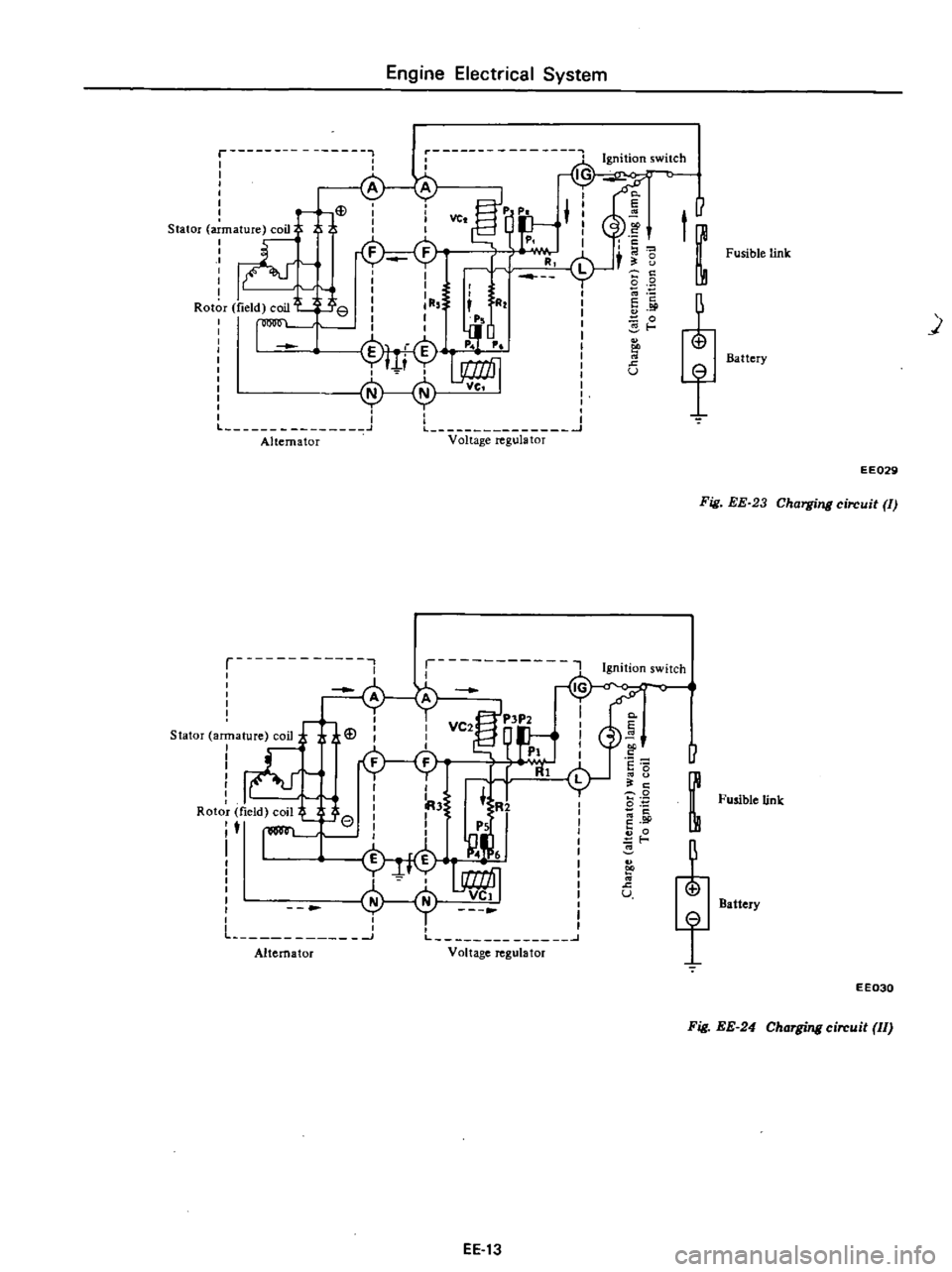
Engine
Electrical
System
r
l
I
I
I
i
r
Ye
Ff
p
Stator
ma
ture
coiJ
FF
vw
I
I
RI
L
Rot
r
field
C
oil
e
R
I
I
I
I
I
J
1
J
Alternator
Voltage
regulator
11
t
c
I
Fusible
link
t
8
c
J
5
9
i
c
c
0
Battery
t
u
J
EE029
Fig
EE
23
Charging
circuit
II
p
ns
1
Slator
ar
ature
coil
teJ
U
2iI
I
r
R
l
I
I
A3
R2
0
Fusible
link
Roto
field
coil
e
I
I
t
I
I
PS
M
g
j
t
i
H
U
Battery
Lh
A
l
a
o
J
L
V
It
g
t
f
EE030
Fig
EE
24
Charging
circuit
II
EE
13
Page 183 of 537

REMOVAL
1
Disconnect
negative
battery
ter
minaL
2
Disconnect
two
lead
wires
and
connector
from
alternator
3
loosen
adjusting
bolt
4
Remove
alternator
drive
belt
5
Remove
parts
associated
with
alternator
from
engine
6
Remove
alternator
from
vehicle
DISASSEMBLY
1
Remove
pulley
nut
and
pulley
assembly
11
C
@@@
EE033
Fig
EE
27
Removing
pulley
ond
fan
2
Remove
brush
holder
fIxing
screws
and
remove
brush
holder
cover
Pull
brush
holder
fOIWard
and
remove
brushes
together
with
brush
holder
Note
Do
not
disconnect
N
tenninaJ
from
stator
coil
lead
wire
EE346
1
N
terminal
2
Brush
holder
3
Brush
holder
co
r
Fig
EE
28
Remouing
brush
Engine
Electrical
System
3
Remove
through
bolts
Separate
front
cover
with
rotor
from
rear
cover
with
stator
by
lightly
tapping
front
bracket
with
a
wooden
mallet
J
J
4
C
EE035
Fig
EE
29
Separating
front
cover
with
rotor
from
rear
cover
4
Remove
three
set
screws
from
bearing
retainer
and
separate
rotor
from
front
cover
DO
Q
EE036
Fig
EE
3D
Removing
rotor
5
Pull
rear
bearing
out
from
rotor
assembly
with
a
press
or
bearing
puller
L
I
EE037
Fig
EE
3I
Pulling
out
of
roar
bearing
EE
16
6
Remove
diode
cover
fIXing
screw
and
remove
diode
cover
Disconnect
three
stator
coil
lead
wires
from
diode
terminal
with
a
soldering
iron
7
Remove
A
tenninaJ
nut
and
diode
installation
nut
and
remove
diode
assembly
CD
AJ
f
e
ecA
O
1
Diode
assembly
o
2
Diode
cover
o
EE039
Fig
EE
32
Removing
diode
088embly
Note
Use
care
in
assembly
to
on
it
handling
diode
an
undue
st
INSPECTION
AND
REPAIR
Remove
alternator
from
car
and
connect
a
circuit
tester
between
F
tenninal
and
E
terminal
When
the
resistance
is
approxi
mately
5il
the
condition
of
brush
and
fIeld
coil
is
satisfactory
When
no
continuity
exists
in
brush
or
fIeld
coil
or
when
resistance
differs
significantly
between
those
parts
dis
assemble
and
inspect
A
o
E
O
1
ld
Q
EE040
Fig
EE
33
Inspecting
alternator
Page 186 of 537

Engine
Electrical
System
ALTERNATOR
TEST
Before
conducting
an
alternator
test
make
sure
th
tthe
battery
is
fully
charged
A
30
V
olt
voltmeter
and
suitable
test
probes
3re
necessary
for
the
test
Set
up
a
test
circuit
as
shown
in
Figure
EE45
and
test
auernator
in
the
manner
indica
ted
in
the
flow
chart
below
1
Disconnect
connectors
at
alternator
2
Connect
A
terminal
to
F
terminal
3
Connect
one
test
probe
from
voltmeter
positive
terminal
to
A
terminal
Connect
the
other
test
probe
to
ground
Make
sure
that
voltmeter
registers
battery
voltage
4
Turn
on
headlights
and
switch
to
High
Beam
5
Start
engine
6
Increase
engine
speed
gradually
until
it
is
approximately
1
100
rpm
and
take
the
voltmeter
reading
Measured
value
Below
12
5
Volts
Alternator
is
in
trouble
remove
and
check
it
for
condition
Measured
value
Over
12
5
Volts
Alternator
is
in
good
condition
Notes
a
Do
Dot
run
engine
at
the
speed
of
more
than
1
100
rpm
while
test
is
being
conducted
on
alternator
b
Do
not
race
engine
i
9
l
IV
I
Battery
EE052
Voltmeter
Fig
EE
45
Testing
alternator
SERVICE
DATA
AND
SPECIFICATIONS
Nominal
rating
V
A
LT138
IB
LTl35
36B
For
air
conditioner
1235
12
38
Negative
Negative
1
000
1
000
28
2
500
30
2
500
35
5
000
38
5
000
2
25
2
25
More
than
7
5
0
295
More
than
7
5
0
295
255
to
345
255
to
345
9
0
to
12
2
9
0
to
12
2
More
than
30
1
181
More
than
30
1
181
EE
19
Type
Ground
polarity
Minimum
revolution
when
generating
14V
with
no
load
rpm
Hot
output
current
Nrpm
Pulley
ratio
Brush
Length
Spring
pressure
mm
in
gr
oz
Slip
ring
outer
diameter
mm
in