sensor DODGE NEON 1999 Service Workshop Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 1999, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 1999Pages: 1200, PDF Size: 35.29 MB
Page 274 of 1200

(2) Turn the ignition switch to the ON position.
The fuel gauge should be at its lowest position. Turn
the ignition switch OFF.
(3) Ground fuel gauge sending unit connector Pin
3. Refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams. Turn igni-
tion switch to the ON position. The fuel gauge should
be at its highest position. Turn ignition switch OFF
then ON, after a sending unit signal change to dis-
able the cluster electronic gauge dampening mecha-
nism.
(a) If OK, check the fuel gauge sending unit con-
nector for proper connection. If the connections are
OK, refer to Group 14 Fuel System for Fuel Level
Sensor Diagnosis.
(b) If not OK, connect the sending unit. Remove
the cluster and check for an open or short in the
sending unit wiring. The sending unit will be less
than 1080 ohms and greater than 50 ohms depend-
ing upon fuel level. If the sending unit wiring is
open or a short circuit, repair as necessary.
(c) If the sending unit wiring is OK, replace the
gauge assembly. If the condition persists, replace
the cluster printed circuit board.
FUEL GAUGE INCORRECTLY INDICATES
EMPTY
The fuel system uses both the instrument cluster
and the Powertrain Control Module (PCM) to moni-
tor the fuel level sending unit. If the PCM fuel mon-
itoring circuits senses an open circuit, the increased
circuit resistance will causes a false fuel gauge empty
reading. Check for continuity between cluster wire
harness connector Pin J2-10 and Pin 23 of the PCM(Fig. 9) and (Fig. 11). If there is no continuity, repair
as necessary. If there is continuity, refer to Fuel
Gauge test.
LOW FUEL WARNING CIRCUIT
The low fuel warning lamp receives its signal from
the fuel gauge drive circuit. Due to production varia-
tions, the point where the lamp illuminates, may
vary from 1/16 to 3/16 mark on the fuel gauge. There
is a built in time delay before the lamp illuminates.
This prevents the lamp from going on and off under
various road conditions.
(1) Verify that the fuel gauge is operating properly.
(2) Check the low fuel warning lamp assembly.
(3) If the lamp still does not function under a low
fuel condition replace the printed circuit board.
TACHOMETER CIRCUIT
(1) Remove the cluster. Refer to Cluster Removal.
(2) Check for battery voltage at Pin J1-6 of the
cluster wire harness connector (Fig. 9).
(3) With the ignition switch in the ON position,
check for battery voltage at Pin J1-5 connector.
(4) Check Pin J1-8 of the connector for continuity
to ground.
(5) Check for tachometer signal from the Power-
train Control Module by connecting an AC DIGITAL
VOLTMETER to Pin J1-7 of the connector and
ground. A reading of at least 1.0 volt should be
present with the engine running.
(a) If the voltage is NOT within specification, go
to Step 6.
(b) If the voltage is within specification, go to
Step 7.
(6) If there is less than 1.0 volt at Pin J1-7 of the
connector, check for continuity between Pin J1-7 and
Pin 73 of the Powertrain Control Module connector
(Fig. 11). Also, check the connector at the Powertrain
Control Module for damaged pins or terminal push
outs.
(7) If the voltage is less than 1.0 volt at Pin J1-7 of
the connector and there is continuity between Pin
J1-7 and Pin 73 of the PCM connector, replace the
Powertrain Control Module.
Fig. 10 Cluster Connector
Fig. 11 Powertrain Control Module Pin Location
PLINSTRUMENT PANEL AND SYSTEMS 8E - 5
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 275 of 1200

(8) If all tests performed test good, replace the dial
and gauge assembly.
(9) If the tachometer continues to be inoperative,
replace the print circuit board.
TEMPERATURE GAUGE
(1) Disconnect the coolant temperature sensor
(Fig. 12).
(2) Turn ignition switch ON. The temperature
gauge should be at its lowest position. Turn ignition
switch OFF.
(3) Ground temperature gauge sending unit con-
nector Pin 3. Refer to Group 8W, wiring Diagrams.
Turn ignition switch ON. The temperature gauge
should be at its highest position. After the seat belt
lamp goes out, the cluster should chime for about
eight seconds.
(a) If OK, check temperature sending unit con-
nector for proper connection. If connections are OK,
replace the sending unit.
(b) If not OK, and the high temperature chime
sounds but the gauge shows cold, replace the gauge
assembly. If gauge is still not working, replace the
printed circuit board.
SPEEDOMETER SYSTEM
The vehicle is equipped with a electronically driven
speedometer and odometer assemblies. A signal is
sent from a transmission-mounted vehicle speed sen-
sor to the speedometer circuitry through the wiring
harness.
SEAT BELT REMINDER SYSTEM TEST
For testing of this system refer to Group 8U,
Chime Warning/Reminder Systems.
SENDING UNIT
When a problem occurs with a cluster gauge check
for a defective sending unit or wiring. Do this before
disassembling the cluster.(1) Sending units and wiring can be checked by
grounding the connector leads at the sending unit in
the vehicle.
(2) With the ignition in the ON position, a
grounded input will cause the fuel or temperature
gauge to read at or above maximum.
SERVICE ENGINE SOON INDICATOR
Refer to Group 25, Emission Control Systems for
procedures.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR TEST
To test the vehicle speed sensor and related compo-
nents use a scan tool (DRB), and refer to the appro-
priate Powertrain Diagnostics Test Procedure
Manual.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
ASH RECEIVER RETAINER AND LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Open up and remove the ash receiver recepta-
cle.
(2) Remove the center bezel.
(3) Remove the two ash receiver retainer attaching
screws from the upper-rearward face and remove
retainer.
(4) For lamp replacement, remove the clamp and
lamp hood from the top of the retainer. Remove the
wiring clip at the forward edge of the retainer and
remove the lamp socket from the hood and replace
lamp.
INSTALLATION
For installation reverse the above procedures.
When installing the retainer ensure that the forward
tabs are inserted properly into the slots in the instru-
ment panel.
CENTER BEZEL
REMOVAL
(1) Open the ash receiver receptacle.
(2) Grasp the bezel and pull rearward disengaging
the clips.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
CIGAR LIGHTER RECEPTACLE
REMOVAL
(1) Remove the cigar lighter element.
(2) Reach underneath the instrument panel
through the bottom access hole and disconnect the
cigar lighter receptacle wiring connectors.
Fig. 12 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
8E - 6 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND SYSTEMSPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 283 of 1200

(2) Lift up the top cover and cluster bezel until the
clips disengage and separate to provide clearance
(Fig. 25).
(3) Rotate the ignition key cylinder to run/on posi-
tion. Insert a screw driver into the access hole at the
bottom of lower shroud to release the ignition key
cylinder.
(4) Pull out the ignition key cylinder.
(5) Remove the three lower to upper shroud
attaching screws through the bottom of the lower
shroud.
(6) Separate the upper and lower shrouds.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
TOP COVER AND CLUSTER BEZEL REMOVAL
REMOVAL
(1) Use care not to scratch the panel. Lift up on
the bottom outer areas of the cluster bezel and alongthe rearward edge of the top cover to disengage the
clips (Fig. 24).
(2) Pull the top cover and cluster bezel rearward
until the forward pins disengage from the instrument
panel.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures,
making sure that the forward pins engage the index
holes in the instrument panel. Position spring clips
in instrument panel and push firmly until seated.
TRANSMISSION RANGE INDICATOR LAMP
REMOVAL
(1) Raise the floor console (Fig. 16).
(2) Remove the attaching screw from each of the
two forward cup holders of the floor console. Remove
the screws at the rear of the console or inside of the
armrest console bin.
(3) Pull the parking brake lever all the way up.
(4) Lift the floor console at the rear high enough to
gain access to the lamp and socket.
(5) Remove the indicator lamp socket from bezel to
replace the lamp.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
TRUNK LAMP/LENS
REMOVAL
The trunk lamp snaps into the rear shelf panel
reinforcement under/below the package shelf.
(1) Remove the socket assembly by reaching up
above the sheet metal. Push the snap inward and
downward and remove the assembly.
(2) Remove the lamp from socket and pull the
socket from the lens. Replace as necessary.
INSTALLATION
For installation, reverse the above procedures.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
For Vehicle Soeed Sensor Removal and Installa-
tion, refer to Group 14±Fuel Systems for service
procedures.
Fig. 25 Upper/Lower Shroud
8E - 14 INSTRUMENT PANEL AND SYSTEMSPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 298 of 1200

VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION......................... 1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE.......... 3
SERVO CABLE.......................... 3
SPEED CONTROL SERVO.................. 1
SPEED CONTROL SWITCHES.............. 2
STOP LAMP SWITCH..................... 3
VACUUM RESERVOIR.................... 3
VEHICLE SPEED AND DISTANCE............ 3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING FOR DIAGNOSTIC CODES........ 4
ELECTRICAL TESTS AT POWERTRAIN
CONTROL MODULE..................... 7
OVERSHOOT/UNDERSHOOT FOLLOWING
SPEED CONTROL SET................... 6ROAD TEST............................ 3
SERVO VACUUM TEST.................... 6
SPEED CONTROL ELECTRICAL TEST........ 4
SPEED CONTROL SWITCH TEST............ 6
STOP LAMP SWITCH TEST................ 6
VACUUM SUPPLY TEST................... 8
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR................. 8
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE......... 10
SPEED CONTROL SERVO CABLE............ 9
SPEED CONTROL SERVO.................. 8
SPEED CONTROL SWITCH................. 8
STOP LAMP SWITCH.................... 8
VACUUM RESERVOIR................... 10
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR................ 10
GENERAL INFORMATION
INTRODUCTION
The speed control system is electronically con-
trolled and vacuum operated. The electronic control
is integrated into the powertrain control module
which is located in the engine compartment. The con-
trols are located on the steering wheel and consist of
five switches. The ON, OFF, and SET buttons are
located on the left side of the airbag module. The
RESUME/ACCEL, CANCEL and COAST buttons are
located on the right side of the airbag module (Fig.
1). For identification and location of the major com-
ponents (Fig. 2) and (Fig. 3).
The system is designed to operate at speeds above
30 mph (50 km/h).
WARNING: THE USE OF SPEED CONTROL IS NOT
RECOMMENDED WHEN DRIVING CONDITIONS DO NOT
PERMIT MAINTAINING A CONSTANT SPEED, SUCH AS
IN HEAVY TRAFFIC OR ON ROADS THAT ARE WIND-
ING, ICY, SNOW COVERED, OR SLIPPERY.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
SPEED CONTROL SERVO
The servo unit consists of a solenoid valve body,
and a vacuum chamber. The PCM controls the sole-noid valve body. The solenoid valve body controls the
application and release of vacuum to the diaphragm
of the vacuum servo. The servo unit cannot be
repaired and is serviced only as a complete assembly.
Fig. 1 Speed Control Switch
PLVEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 1
Page 300 of 1200

The individual switches cannot be repaired. If one
switch fails, the entire switch module must be
replaced.
STOP LAMP SWITCH
Vehicles equipped with the speed control option use
a dual function stop lamp switch. The switch is
mounted on the brake pedal mounting bracket under
the instrument panel. The PCM monitors the state of
the dual function stop lamp switch. Refer to Group 5,
Brakes for more information on stop lamp switch ser-
vice and adjustment procedures.
SERVO CABLE
The speed control servo cable is connected between
the speed control vacuum servo diaphragm and the
throttle body control linkage. This cable causes the
throttle control linkage to open or close the throttle
valve in response to movement of the vacuum servo
diaphragm.
POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
The speed control electronic control circuitry is
integrated into the Powertrain Control Module
(PCM). The PCM is located in the engine compart-
ment. The PCM speed control functions are moni-
tored by the On-Board Diagnostics (OBD). All OBD-
sensed systems are monitored by the PCM. Each
monitored circuit is assigned a Diagnostic Trouble
Code (DTC). The PCM will store a DTC in electronic
memory for any failure it detects. See On-Board
Diagnostic Tests in this group for more information.
The PCM cannot be repaired and must be replaced if
faulty.
USE THE DRB SCAN TOOL TO REPROGRAM
THE NEW PCM WITH THE VEHICLES ORIGI-
NAL IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) AND
THE ORIGINAL VEHICLES MILEAGE. IF THIS
STEP IS NOT DONE A DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODE (DTC) MAY BE SET.
VACUUM RESERVOIR
The reservoir contains a one-way check valve to
trap engine vacuum in the reservoir. When engine
vacuum drops, as in climbing a grade while driving,
the reservoir supplies the vacuum needed to main-
tain proper speed control operation. The vacuum res-
ervoir cannot be repaired and must be replaced if
faulty.
VEHICLE SPEED AND DISTANCE
The 4 speed automatic Transmission Control Mod-
ule (TCM) supplies the speed input to the PCM. The
PCM determines acceleration rates. The speed con-
trol software in the PCM uses vehicle speed and
acceleration to control to the set speed.Vehicles with a 3 speed automatic or manual trans-
mission have a vehicle speed sensor (VSS) mounted
to an adapter near the transmission output shaft.
The sensor is driven through the adapter by a speed-
ometer pinion gear. The VSS pulse signal is moni-
tored by the PCM to determine vehicle speed and to
maintain speed control set speed. Refer to the appro-
priate Powertrain Diagnostic Procedures manual for
diagnosis and testing of this component. Refer to
group 14, Fuel System for Removal/Installation
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
ROAD TEST
Perform a vehicle road test to verify reports of
speed control system malfunction. The road test
should include attention to the speedometer. Speed-
ometer operation should be smooth and without flut-
ter at all speeds.
Flutter in the speedometer indicates a problem
which might cause surging in the speed control sys-
tem. The cause of any speedometer problems should
be corrected before proceeding. Refer to Group 8E,
Instrument Panel and Gauges for speedometer diag-
nosis.
If a road test verifies a surge following a set and
the speedometer operates properly see ªOvershoot/
Undershoot on speed control setº.
If a road test verifies an inoperative system, and
the speedometer operates properly, check for:
²A Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC). If a DTC
exists, conduct tests per the Powertrain Diagnostic
Procedures service manual.
²A misadjusted brake (stop) lamp switch. This
could also cause an intermittent problem.
²Loose or corroded electrical connections at the
servo. Corrosion should be removed from electrical
terminals and a light coating of Mopar Multipurpose
Grease, or equivalent, applied.
²Leaking vacuum reservoir.
²Loose or leaking vacuum hoses or connections.
²Defective one-way vacuum check valve.
²Secure attachment at both ends of the speed
control servo cable.
²Smooth operation of throttle linkage and throttle
body air valve.
²Conduct electrical test at PCM.
²Failed speed control servo. Do the servo vacuum
test.
CAUTION: When test probing for voltage or conti-
nuity at electrical connectors, care must be taken
not to damage connector, terminals or seals. If
these components are damaged, intermittent or
complete system failure may occur.
PLVEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEM 8H - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 301 of 1200

CHECKING FOR DIAGNOSTIC CODES
When trying to verify a speed control system elec-
tronic malfunction: Connect a DRB scan tool if avail-
able to the data link connector. The connector is
located at left side of the steering column, and at
lower edge of the panel.
(1) A speed control malfunction may occur without
a diagnostic code being indicated.
Refer to Group 25, for further information and use-
age of the DRB scan tool and a more complete list of
Diagnostic Trouble Code.
SPEED CONTROL SLOWS DOWN BY ITSELF
Test vehicle speed sensor, refer to group 8E. If sen-
sor fails replace sensor, if it passes perform the fol-
lowing test:
(1) Perform the speed control switch test on the
DECEL switch, if it fails replace switch.
(2) If the switch passes, conduct the vacuum sup-
ply test.
(3) If it passes, conduct the servo vacuum test. If it
fails replace servo.
(4) If continuity, replace the PCM.
SPEED CONTROL ELECTRICAL TEST
Electronic speed control systems may be tested
using two different methods. One involves use of aDRB. If this test method is desired, refer to the Pow-
ertrain Diagnostic Test Procedures for charging and
speed control system manual.
The other test method uses a volt/ohm meter. The
volt/ohm meter method is described in the following
tests.
If any information is needed concerning wiring,
refer to Group 8W, Wiring Diagrams (Fig. 4).
CAUTION: When test probing for voltage or conti-
nuity at electrical connectors, care must be taken
not to damage connector, terminals, or seals. If
these components are damaged, intermittent or
complete system failure may occur.
When electrical connections are removed, corrosion
should be removed from electrical terminals and a
light coating of Mopar Multi-Purpose Grease, or
equivalent, applied. Inspect connectors for damage
terminals.
A poor connection can cause a complete or inter-
mittent malfunction and is also the only connection
in the circuit, that can not be tested. For this reason,
a loose connection may be misdiagnosed as a compo-
nent malfunction.
SPEED CONTROL DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE CODES
Hex Code DRB Scan Tool Display Description of Diagnostic Trouble Code
23No Vehicle Speed Sensor
SignalNo vehicle distance (speed) sensor signal detected during
road load conditions.
OFSpeed Control Solenoid
CircuitsAn open or shorted condition detected in the Speed Control
vacuum or vent solenoid circuits.
56MUX S/C Switch High Speed Control switch input above the maximum acceptable
voltage.
57MUX S/C Switch Low Speed Control switch input below the minimum acceptable
voltage.
52S/C Power Relay Or 12V
Driver CircuitMalfunction detected with power feed to speed control servo
solnoids.
Check Engine Lamp will illuminate during engine operation if this Diagnostic Trouble Code was recorded.
8H - 4 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 305 of 1200

(c) If continuity is OK between cavity 62 and
cavity 1, repair open circuit between cavity 2 of the
stop lamp switch connector and ground.
(6) Using an ohmmeter, check continuity from cav-
ity 76 on PCM connector to ground with the trans-
mission in park or neutral. If no continuity, test TRS/
Park-Neutral switch and switch wiring
(7) Turn speed control and ignition switch OFF.
(8) Unplug the BLACK 40-way connector from the
Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
(9) Using an ohmmeter, check continuity from cav-
ity 3 of servo connector to cavity 5 on the PCM con-
nector.
(a) If continuity is OK, replace PCM. Check cir-
cuit for short to ground before replacing PCM.
(b) If no continuity, remove stop lamp switch
and conduct Stop Lamp Switch Test. If test fails,
adjust or replace as necessary.
(c) If switch passes, measure continuity from
cavity 4 of stop lamp switch connector to cavity 3
of servo connector. Repair open circuit if necessary.
(d) If continuity is OK, measure continuity from
cavity 3 of stop lamp switch to cavity 5 of PCM
connector. Repair open circuit as necessary.
(e) Install PCM connectors onto PCM and speed
control servo connector to servo.
VACUUM SUPPLY TEST
(1) Disconnect vacuum hose at the servo and
install a vacuum gauge in the hose (Fig. 9).
(2) Start engine and observe gauge at idle. Vac-
uum gauge should read at least ten inches of mer-
cury. Shut off engine, the vacuum should continue to
hold 10 inches of mercury.
(3) If vacuum does not meet this requirement,
check and correct the following vacuum leaks in the
vacuum lines, check valve, vacuum reservoir or poor
engine performance.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
For diagnosis and testing of the Vehicle Speed Sen-
sor (VSS), refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diag-
nostic Procedures service manual. Also refer to the
DRB scan tool.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
SPEED CONTROL SERVO
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connector from servo.
(2) Disconnect vacuum hoses from servo
(3) Remove 2 nuts retaining cable to servo.
(4) Remove hair pin holding cable to servo.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install hairpin to cable at servo.
(2) Install 2 nuts at cable to servo and servo
bracket, tighten to 7 N´m (60 ins. lbs.).
(3) Connect electrical connector to servo.
(4) Connect vacuum hose to servo
SPEED CONTROL SWITCH
The speed control switches are mounted in the
steering wheel and wired through the clock spring
device under the airbag module (Fig. 1).
WARNING: IF REMOVAL OF AIRBAG MODULE IS
NECESSARY, REFER TO GROUP 8M, RESTRAINT
SYSTEMS.
REMOVAL
(1) Turn off ignition.
(2) Remove two screws from side of each switch.
(3) Rock switch away from airbag and steering
wheel.
(4) Disconnect two-way electrical connector.
(5) Repeat for the other switch.
INSTALLATION
For installation reverse above procedures.
STOP LAMP SWITCH
REMOVAL
Remove the switch from the bracket by depressing
the brake pedal and rotating the switch in a counter-
clockwise direction approximately 30 degrees. Pull
the switch rearward and remove from bracket. Dis-
connect wiring harness connector.
INSTALLATION
Before installing the switch, reset the adjustable
switch plunger by pulling on the plunger head until
Fig. 9 Vacuum Gauge TestÐTypical
8H - 8 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 307 of 1200

POWERTRAIN CONTROL MODULE
For Removal/Installation refer to Powertrain Con-
trol Module in Group 14, Fuel Injection System.
USE THE DRB SCAN TOOL TO REPROGRAM
THE NEW PCM WITH THE VEHICLES ORIGI-
NAL IDENTIFICATION NUMBER (VIN) AND
THE ORIGINAL VEHICLES MILEAGE. IF THIS
STEP IS NOT DONE A DIAGNOSTIC TROUBLE
CODE (DTC) MAY BE SET.
VACUUM RESERVOIR
REMOVAL
(1) Raise and support vehicle.
(2) Remove bolt on top of vacuum reservoir.
(3) Remove vacuum hoses.
(4) Remove vacuum reservoir.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install vacuum reservoir, install push pin and
tighten screw to 5 N.m (44 in. lbs.)..
(2) Install vacuum hoses.
(3) Lower vehicle.
VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR
For Removal/Installation, refer to Vehicle Speed
Sensor in Group 14, Fuel Injections.
Fig. 12 Throttle Cable Attachment to Throttle
BodyÐAutomatic Transmission
Fig. 13 Disconnecting Throttle Cable
8H - 10 VEHICLE SPEED CONTROL SYSTEMPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 352 of 1200

RESTRAINT SYSTEM
CONTENTS
page page
GENERAL INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS............ 1
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE............... 1
CLOCKSPRING.......................... 2
DRIVER AND PASSENGER AIRBAG MODULE . . 2
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
AIRBAG SYSTEM TEST................... 3
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CLEANUP PROCEDURE................... 3HANDLING AIRBAG MODULE.............. 3
MAINTENANCE INSPECTION............... 4
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE (ACM)......... 4
CLOCKSPRING.......................... 8
DRIVER AIRBAG MODULE................. 9
PASSENGER AIRBAG MODULE............. 9
STEERING WHEEL...................... 10
ADJUSTMENTS
CLOCKSPRING CENTERING PROCEDURE.... 11
GENERAL INFORMATION
WARNINGS AND PRECAUTIONS
WARNING: THIS SYSTEM IS A SENSITIVE, COM-
PLEX ELECTRO±MECHANICAL UNIT. DISCONNECT
AND ISOLATE THE BATTERY NEGATIVE CABLE
BEFORE BEGINNING AIRBAG SYSTEM COMPO-
NENT REMOVAL OR INSTALLATION PROCEDURES.
THIS WILL DISABLE THE AIRBAG SYSTEM. FAIL-
URE TO DISCONNECT THE BATTERY COULD
RESULT IN ACCIDENTAL AIRBAG DEPLOYMENT
AND POSSIBLE PERSONAL INJURY.
ALLOW SYSTEM CAPACITOR TO DISCHARGE
FOR TWO MINUTES BEFORE REMOVING AIRBAG
COMPONENTS.
DO NOT PLACE AN INTACT UNDEPLOYED AIR-
BAG FACE DOWN ON A SOLID SURFACE, THE AIR-
BAG WILL PROPEL INTO THE AIR IF
ACCIDENTALLY DEPLOYED AND COULD RESULT
IN PERSONAL INJURY. WHEN CARRYING OR HAN-
DLING AN UNDEPLOYED AIRBAG MODULE, THE
TRIM SIDE OF THE AIRBAG SHOULD BE POINTING
AWAY FROM THE BODY TO MINIMIZE POSSIBILITY
OF INJURY IF ACCIDENTAL DEPLOYMENT
OCCURS.
REPLACE AIRBAG SYSTEM COMPONENTS WITH
MOPARTREPLACEMENT PARTS. SUBSTITUTE
PARTS MAY APPEAR INTERCHANGEABLE, BUT
INTERNAL DIFFERENCES MAY RESULT IN INFE-
RIOR OCCUPANT PROTECTION.
WEAR SAFETY GLASSES, RUBBER GLOVES,
AND LONG SLEEVES CLOTHING WHEN CLEANING
POWDER RESIDUE FROM VEHICLE AFTER AIRBAG
DEPLOYMENT. SODIUM HYDROXIDE POWDER
RESIDUE EMITTED FROM A DEPLOYED AIRBAGCAN CAUSE SKIN IRRITATION. FLUSH AFFECTED
AREA WITH COOL WATER IF IRRITATION IS EXPE-
RIENCED. IF NASAL OR THROAT IRRITATION IS
EXPERIENCED, EXIT THE VEHICLE FOR FRESH AIR
UNTIL THE IRRITATION CEASES. IF IRRITATION
CONTINUES, SEE A PHYSICIAN.
DO NOT USE A REPLACEMENT AIRBAG THAT IS
NOT IN THE ORIGINAL PACKAGING, IMPROPER
DEPLOYMENT AND PERSONAL INJURY CAN
RESULT.
THE FACTORY INSTALLED FASTENERS,
SCREWS AND BOLTS USED TO FASTEN AIRBAG
COMPONENTS, ARE SPECIFICALLY DESIGNED
FOR THE AIRBAG SYSTEM. DO NOT USE SUBSTI-
TUTE FASTENERS, USE ONLY ORIGINAL EQUIP-
MENT FASTENERS LISTED IN THE PARTS
CATALOG WHEN FASTENER REPLACEMENT IS
REQUIRED.
NOTE: Airbags should be stored in a cool dry loca-
tion away from excessive heat and static electrical
activity with the fabric airbag facing UP, or a prema-
ture deployment can result.
If the Driver/Passenger Airbag Module is defective
and not deployed, refer to Chrysler Corporation cur-
rent return list for proper handling procedures.
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE
The Airbag Control Module (ACM) contains the
safing sensor and energy reserve capacitor. The saf-
ing sensor is located inside the ACM. The module is
mounted on the tunnel/floor pan between the gear
PLRESTRAINT SYSTEM 8M - 1
Page 353 of 1200
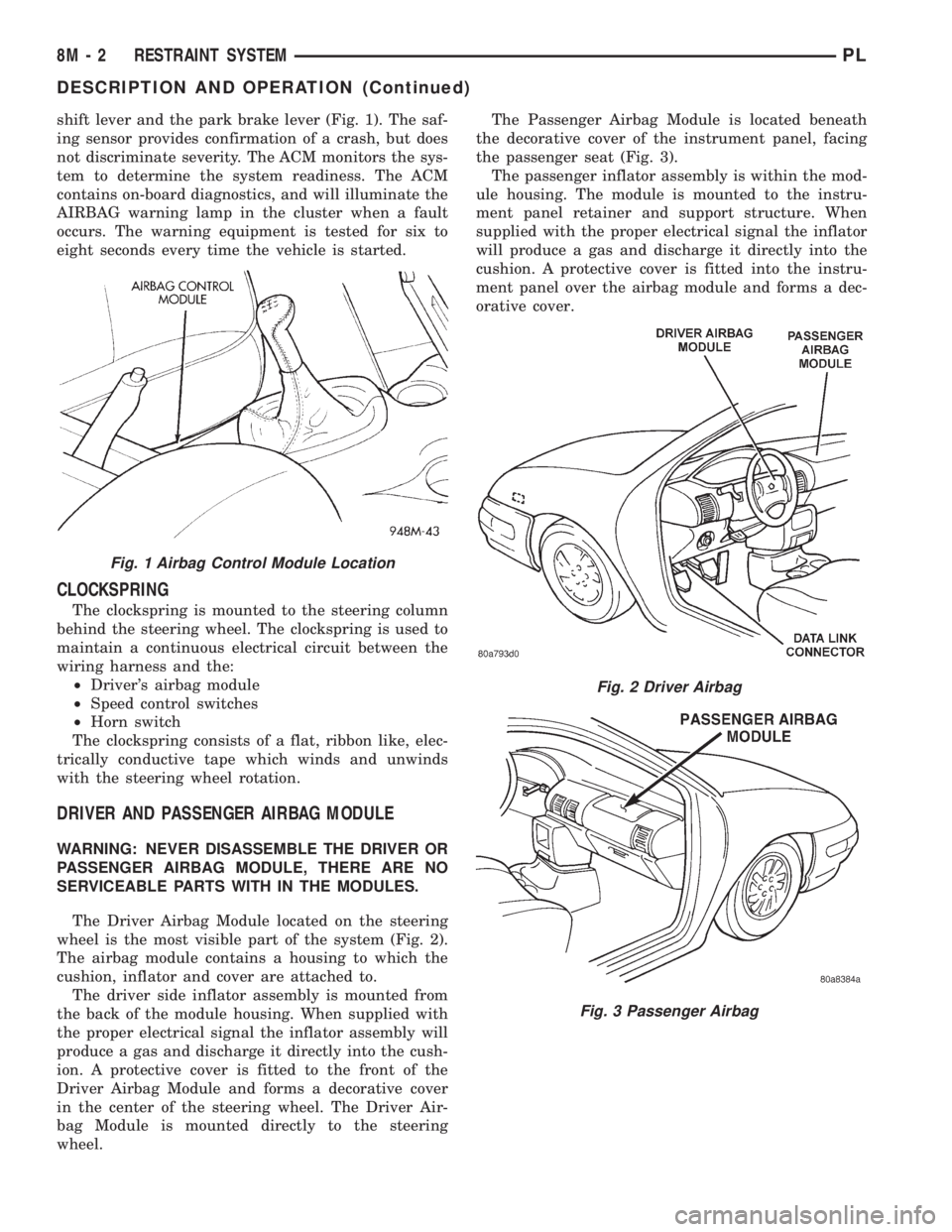
shift lever and the park brake lever (Fig. 1). The saf-
ing sensor provides confirmation of a crash, but does
not discriminate severity. The ACM monitors the sys-
tem to determine the system readiness. The ACM
contains on-board diagnostics, and will illuminate the
AIRBAG warning lamp in the cluster when a fault
occurs. The warning equipment is tested for six to
eight seconds every time the vehicle is started.
CLOCKSPRING
The clockspring is mounted to the steering column
behind the steering wheel. The clockspring is used to
maintain a continuous electrical circuit between the
wiring harness and the:
²Driver's airbag module
²Speed control switches
²Horn switch
The clockspring consists of a flat, ribbon like, elec-
trically conductive tape which winds and unwinds
with the steering wheel rotation.
DRIVER AND PASSENGER AIRBAG MODULE
WARNING: NEVER DISASSEMBLE THE DRIVER OR
PASSENGER AIRBAG MODULE, THERE ARE NO
SERVICEABLE PARTS WITH IN THE MODULES.
The Driver Airbag Module located on the steering
wheel is the most visible part of the system (Fig. 2).
The airbag module contains a housing to which the
cushion, inflator and cover are attached to.
The driver side inflator assembly is mounted from
the back of the module housing. When supplied with
the proper electrical signal the inflator assembly will
produce a gas and discharge it directly into the cush-
ion. A protective cover is fitted to the front of the
Driver Airbag Module and forms a decorative cover
in the center of the steering wheel. The Driver Air-
bag Module is mounted directly to the steering
wheel.The Passenger Airbag Module is located beneath
the decorative cover of the instrument panel, facing
the passenger seat (Fig. 3).
The passenger inflator assembly is within the mod-
ule housing. The module is mounted to the instru-
ment panel retainer and support structure. When
supplied with the proper electrical signal the inflator
will produce a gas and discharge it directly into the
cushion. A protective cover is fitted into the instru-
ment panel over the airbag module and forms a dec-
orative cover.
Fig. 1 Airbag Control Module Location
Fig. 2 Driver Airbag
Fig. 3 Passenger Airbag
8M - 2 RESTRAINT SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)