tra DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 733 of 1285

make sure the dye is thoroughly mixed as indicated
with a bright yellow color under a black light.
(3) Using a black light, inspect the entire engine
for fluorescent dye, particularly at the suspected area
of oil leak. If the oil leak is found and identified,
repair per service manual instructions.
(4) If dye is not observed, drive the vehicle at var-
ious speeds for approximately 24 km (15 miles), and
repeat inspection.
(5)If the oil leak source is not positively
identified at this time, proceed with the air leak
detection test method as follows:
²Disconnect the fresh air hose (makeup air) at
the cylinder head cover and plug or cap the nipple on
the cover.
²Remove the PCV valve hose from the cylinder
head cover. Cap or plug the PCV valve nipple on the
cover.
²Attach an air hose with pressure gauge and reg-
ulator to the dipstick tube.
CAUTION: Do not subject the engine assembly to
more than 20.6 kpa (3 PSI) of test pressure.
²Gradually apply air pressure from 1 psi to 2.5
psi maximum while applying soapy water at the sus-
pected source. Adjust the regulator to the suitable
test pressure that provides the best bubbles which
will pinpoint the leak source. If the oil leak is
detected and identified, repair per service manual
procedures.
²If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil
seal area, refer to the section, Inspection for Rear
Seal Area Leak.
(6) If no leaks are detected, turn off the air supply.
Remove the air hose, all plugs, and caps. Install the
PCV valve and CCV hose. Proceed to next step.
(7) Clean the oil off the suspect oil leak area using
a suitable solvent. Drive the vehicle at various
speeds approximately 24 km (15 miles). Inspect the
engine for signs of an oil leak by using a black light.
INSPECTION FOR REAR SEAL AREA LEAKS
Since it is sometimes difficult to determine the
source of an oil leak in the rear seal area of theengine, a more involved inspection is necessary. The
following steps should be followed to help pinpoint
the source of the leak.
If the leakage occurs at the crankshaft rear oil seal
area:
(1) Disconnect the battery.
(2) Raise the vehicle.
(3) Remove torque converter or clutch housing
cover and inspect rear of block for evidence of oil.
Use a black light to check for the oil leak. If a leak is
present in this area remove transmission for further
inspection.
(a) Circular spray pattern generally indicates
seal leakage or crankshaft damage.
(b) Where leakage tends to run straight down,
possible causes are a porous block, oil galley cup
plug, bedplate to cylinder block mating surfaces
and seal bore. See proper repair procedures for
these items.
(4) If no leaks are detected, pressurized the crank-
case as previously described.
CAUTION: Do not exceed 20.6 kPa (3 psi).
(5) If the leak is not detected, very slowly turn the
crankshaft and watch for leakage. If a leak is
detected between the crankshaft and seal while
slowly turning the crankshaft, it is possible the
crankshaft seal surface is damaged. The seal area on
the crankshaft could have minor nicks or scratches
that can be polished out with emery cloth.
CAUTION: Use extreme caution when crankshaft
polishing is necessary to remove minor nicks and
scratches. The crankshaft seal flange is especially
machined to complement the function of the rear oil
seal.
(6) For bubbles that remain steady with shaft
rotation, no further inspection can be done until dis-
assembled.
(7) After the oil leak root cause and appropriate
corrective action have been identified, refer to Crank-
shaft Oil SealÐRear for proper replacement proce-
dures.
9 - 10 ENGINEPL
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING (Continued)
Page 739 of 1285

CRANKSHAFT
A nodular cast iron crankshaft is used. The engine
has five main bearings. The number three main is
flanged to control thrust. The mains and connecting
rod journals have undercut fillet radiuses that are
deep rolled for added strength. To optimize bearing
loading, eight counterweights are used. Hydrody-
namic seals provide end sealing, where the crank-
shaft exits the block. Anaerobic gasket material is
used for parting line sealing. A sintered iron timing
belt sprocket is mounted on the crankshaft nose. This
sprocket transmits crankshaft movement, via timing
belt to the camshaft sprocket providing timed valve
actuation.
PISTONS
The engineDOES NOThave provision for a free
wheeling valve train. Non free wheeling valve train
means, in the event of a broken timing belt pistons
will contact the valves. The engine uses pressed-in
piston pins to attach forged powdered metal connect-
ing rods. The connecting rods are a cracked cap
design and are not repairable. Hex head cap screw
are used to provide alignment and durability in the
assembly. Pistons and connecting rods are serviced as
an assembly.
PISTON RINGS
The piston rings include a molybdenum faced top
ring for reliable compression sealing and a taper
faced intermediate ring for additional cylinder pres-
sure control. Oil Control Ring Package consist of two
steel rails and an expander spacer.
CYLINDER HEAD
The aluminum cylinder head features a Single
Over Head Camshaft (SOHC), four-valves per cylin-
der, cross flow design. The valves are arranged in
two inline banks, with the two intake per cylinder
facing toward the radiator. The exhaust valves facing
toward the dash panel. Rocker arm shafts mount
directly to the cylinder head. It incorporates powder
metal valve guides and seats. The hollow rocker arm
shafts supplies oil to the hydraulic lash adjusters,
camshaft and valve mechanisms.
CAMSHAFT
The nodular iron camshaft has five bearing jour-
nals and three cam lobes per cylinder. Provision for a
cam position sensor is provided on the camshaft at
the rear of cylinder head which also acts as thrust
plate. A hydrodynamic oil seal is used for oil control
at the front of the camshaft.
VALVES
Four valves per cylinder are actuated by roller
rocker arms/hydraulic lash adjusters assemblies
which pivot on rocker arm shafts. All valves have
chrome plated valve stems. Viton rubber valve stem
seals are integral with spring seats. Valve springs,
spring retainers, and locks are conventional design.
INTAKE MANIFOLD
The intake manifold is a molded plastic composi-
tion, attached to the cylinder head with five fasten-
ers. This long branch design enhances low and mid-
range torque.
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
The exhaust manifold is made of nodular cast iron
for strength and high temperatures. Exhaust gasses
exit the manifold into an articulated joint connection
and exhaust pipe.
COMPONENT REPLACEMENT
If any of the following parts have been changed or
replaced:
²Camshaft
²Camshaft Position Sensor
²Camshaft Position Sensor Target Magnet
²Cylinder Block
²Cylinder Head
²Water Pump
²Powertrain Control Module (PCM)
²Timing Belt and Timing Belt Tensioner
The camshaft and crankshaft timing relearn proce-
dure must be performed. Refer to the component
Removal and Installation procedure in this section.
9 - 16 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 740 of 1285
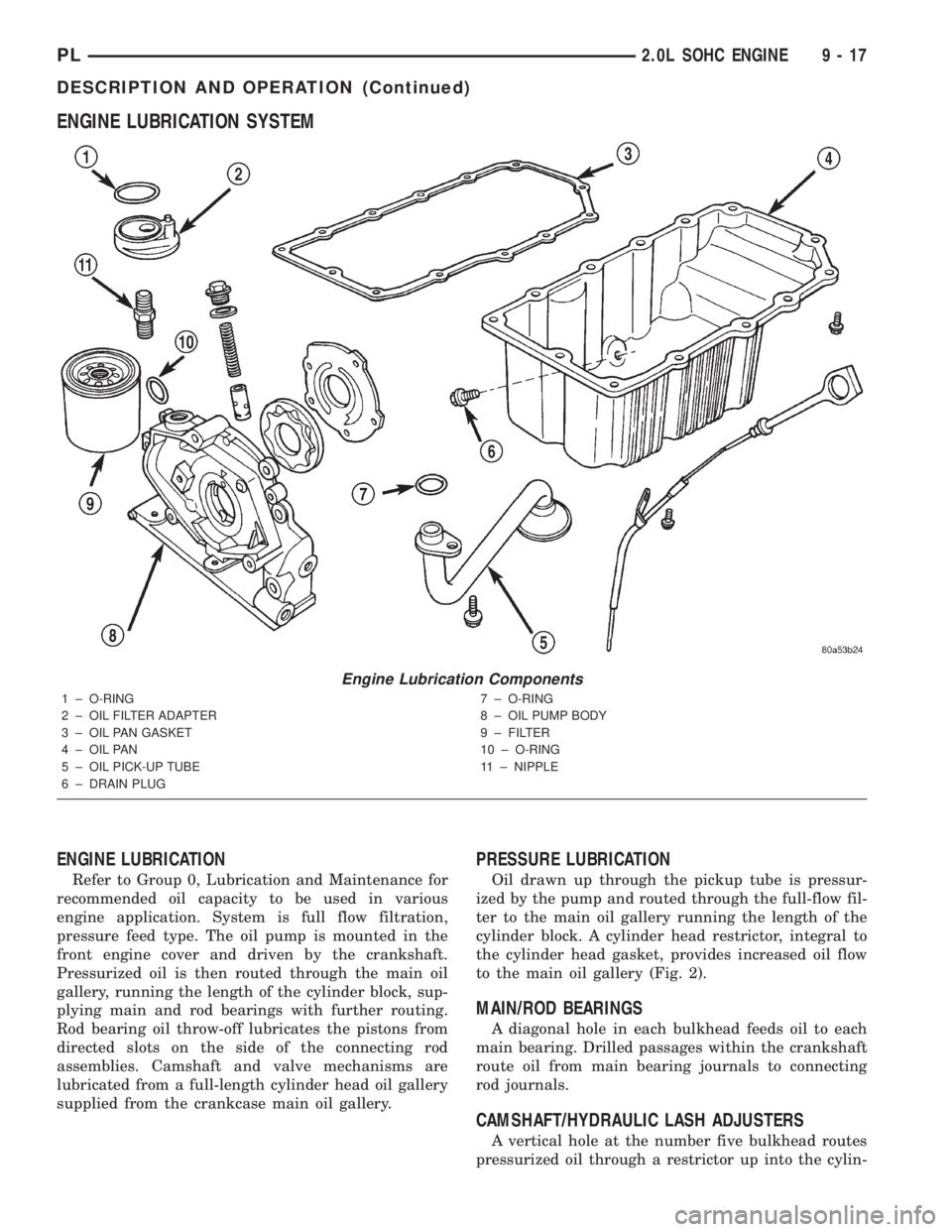
ENGINE LUBRICATION SYSTEM
ENGINE LUBRICATION
Refer to Group 0, Lubrication and Maintenance for
recommended oil capacity to be used in various
engine application. System is full flow filtration,
pressure feed type. The oil pump is mounted in the
front engine cover and driven by the crankshaft.
Pressurized oil is then routed through the main oil
gallery, running the length of the cylinder block, sup-
plying main and rod bearings with further routing.
Rod bearing oil throw-off lubricates the pistons from
directed slots on the side of the connecting rod
assemblies. Camshaft and valve mechanisms are
lubricated from a full-length cylinder head oil gallery
supplied from the crankcase main oil gallery.
PRESSURE LUBRICATION
Oil drawn up through the pickup tube is pressur-
ized by the pump and routed through the full-flow fil-
ter to the main oil gallery running the length of the
cylinder block. A cylinder head restrictor, integral to
the cylinder head gasket, provides increased oil flow
to the main oil gallery (Fig. 2).
MAIN/ROD BEARINGS
A diagonal hole in each bulkhead feeds oil to each
main bearing. Drilled passages within the crankshaft
route oil from main bearing journals to connecting
rod journals.
CAMSHAFT/HYDRAULIC LASH ADJUSTERS
A vertical hole at the number five bulkhead routes
pressurized oil through a restrictor up into the cylin-
Engine Lubrication Components
1 ± O-RING
2 ± OIL FILTER ADAPTER
3 ± OIL PAN GASKET
4 ± OIL PAN
5 ± OIL PICK-UP TUBE
6 ± DRAIN PLUG7 ± O-RING
8 ± OIL PUMP BODY
9 ± FILTER
10 ± O-RING
11 ± NIPPLE
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 17
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 741 of 1285

der head. The rocker shafts route oil to the rocker
arms/hydraulic lash adjuster assemblies.
SPLASH LUBRICATION
Oil returning to the pan from pressurized compo-
nents supplies lubrication to the valve stems. Cylin-
der bores and wrist pins are splash lubricated from
directed slots on the connecting rod thrust collars.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove oil pressure switch and install gauge
assembly C-3292 with adaptor.
(2) Run engine until thermostat opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not per-
form the 3000 RPM test in the next step.
(3) Oil Pressure:Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum3000 RPM170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
(4) If oil pressure is 0 at idle. Shut off engine,
check for pressure relief valve stuck open, a clogged
oil pick-up screen or a damaged oil pick-up tube
O-ring.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
CYLINDER BORE AND PISTON SIZING
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with recommended tool C-119 or
equivalent (Fig. 3). The cylinder bore out-of-roundand cylinder bore taper must within service limits.
Refer to Engine Specifications in this section. If the
cylinder walls are badly scuffed or scored, the cylin-
der block should be rebored and honed, and new pis-
tons and rings fitted. Whatever type of boring
equipment is used, boring and honing operations
should be closely coordinated with the fitting of pis-
tons and rings in order to maintain specified clear-
ances.Refer to Honing Cylinder Bores in the
Standard Service Procedures for procedures.
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 3). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 inch) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 inch.) up from bottom of bore.
Refer to Engine Specifications in this section for cyl-
inder block specifications.
SIZING PISTONS
Piston and cylinder wall must be clean and dry.
Piston diameter should be measured 90 degrees to
piston pin about 17.5 mm (11/16 inch) from the bot-
tom of the skirt as shown in (Fig. 4). Cylinder bores
should be measured halfway down the cylinder bore
and transverse to the engine crankshaft center line
shown in (Fig. 3). Correct piston to bore clearance
must be established in order to assure quiet and eco-
nomical operation. Refer to Engine Specifications in
this section for cylinder block and piston specifica-
tions.
DaimlerChrysler engines use pistons designed spe-
cifically for each engine model. Clearance and sizing
locations vary with respect to engine model.
Fig. 2 Engine Lubrication SystemÐ SOHC
Fig. 3 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
9 - 18 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 742 of 1285

NOTE: Pistons and cylinder bores should be mea-
sured at normal room temperature, 21ÉC (70ÉF).
FITTING PISTON RINGS
(1) Wipe cylinder bore clean. Insert ring and push
down with piston to ensure it is square in bore. The
ring gap measurement must be made with the ring
positioned below normal ring travel in the cylinder
bore. Check gap with feeler gauge (Fig. 5). Refer to
Engine Specifications in this section for piston ring
specifications.
(2) Check piston ring to groove side clearance (Fig.
6). Refer to Engine Specifications in this section for
piston ring specifications.
FITTING CONNECTING RODS
(1) Follow the procedure specified in the Standard
Service Procedures Section for Measuring Main Bear-
ing Clearance and Connecting Rod Bearing Clear-ance (Fig. 7). Refer to Engine Specifications in this
section for connecting rod specifications.
CAUTION: Do not rotate crankshaft or the Plasti-
gage may be smeared.
NOTE: The rod bearing bolts should not be reused.
(2) Before installing theNEWbolts the threads
should be oiled with clean engine oil.
(3) Install each bolt finger tight than alternately
torque each bolt to assemble the cap properly.
(4) Tighten the bolts to 27 N´m PLUS 1/4 turn (20
ft. lbs. PLUS 1/4 turn)Do not use a torque
wrench for last step.
(5) Using a feeler gauge, check connecting rod side
clearance (Fig. 8). Refer to Engine Specifications in
this section for connecting rod specifications.
FITTING CRANKSHAFT BEARINGS
Refer to Measuring Main Bearing Clearance in
Standard Service Procedures. Refer to Engine Speci-
fications in this section for crankshaft specifications.
Fig. 4 Piston Measurements
1 ± PISTON O. D. MEASUREMENT LOCATION
Fig. 5 Piston Ring Gap
1 ± FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 6 Piston Ring Side Clearance
1 ± FEELER GAUGE
Fig. 7 Connecting Rod Bearing Clearance
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 19
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 743 of 1285

CRANKSHAFT END PLAY
DIAL INDICATOR METHOD
(1) Mount a dial indicator to front of engine, locat-
ing probe on nose of crankshaft (Fig. 9).
(2) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel.
(3) Zero the dial indicator.
(4) Move crankshaft all the way to the front of its
travel and read the dial indicator. Refer to Engine
Specifications in this section for crankshaft specifica-
tions.
FEELER GAGE METHOD
(1) Move crankshaft all the way to the rear of its
travel using a lever inserted between a main bearing
cap and a crankshaft cheek, using care not to dam-
age any bearing surface. Donotloosen main bearing
cap.(2) Use a feeler gauge between number three
thrust bearing and machined crankshaft surface to
determine end play.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
TORQUE STRUTS
UPPER TORQUE STRUT
REMOVAL
(1) Remove bolts attaching strut to shock tower
bracket and engine mount bracket (Fig. 10).
(2) Remove the upper torque strut.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the upper torque strut into mounting
locations.
(2) Install the mounting bolts and perform the
torque strut adjustment procedure.
LOWER TORQUE STRUT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.
(2) Remove right side splash shield.
(3) Remove bolts attaching lower strut to cross-
member and strut bracket (Fig. 10).
(4) Remove lower torque strut.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position lower torque strut into mounting loca-
tions.
(2) Install mounting bolts and perform torque
strut adjustment procedure.
(3) Install splash shield and lower vehicle
TORQUE STRUT ADJUSTMENT
The upper and lower torque struts need to be
adjusted together to assure proper engine positioning
and engine mount loading. Whenever a torque strut
bolt(s) is loosened, this procedure must be performed.
(1) Loosen the upper and lower torque strut
attaching bolt at the suspension crossmember and
shock tower bracket.
(2) The engine position may now be adjusted by
positioning a suitable floor jack on the forward edge
of the transmission bell housing (Fig. 11).
NOTE: The floor jack must be positioned as shown
in (Fig. 11) to prevent minimal upward lifting of the
engine.
Fig. 8 Connecting Rod Side Clearance
Fig. 9 Checking Crankshaft End PlayÐ Dial
Indicator
9 - 20 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)
Page 744 of 1285
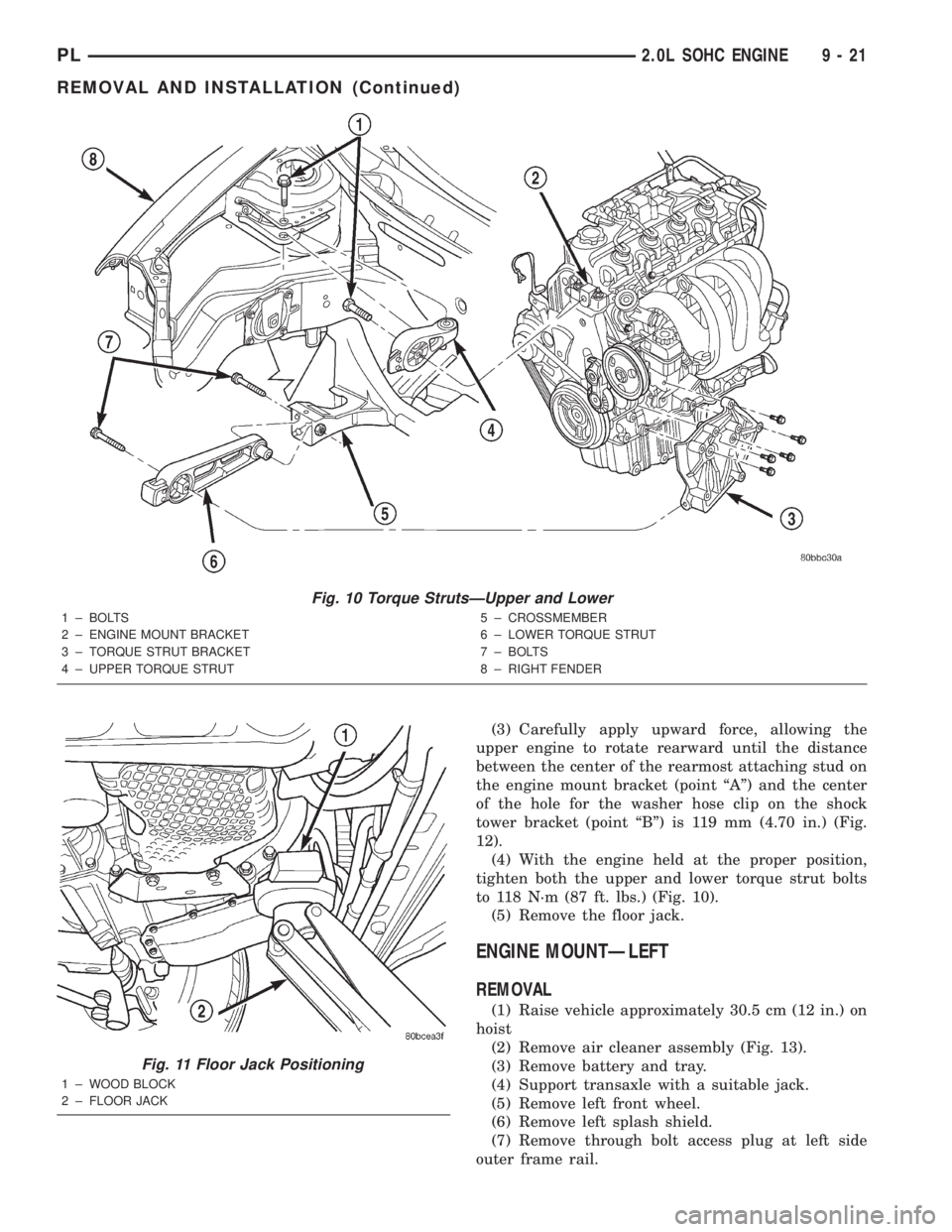
(3) Carefully apply upward force, allowing the
upper engine to rotate rearward until the distance
between the center of the rearmost attaching stud on
the engine mount bracket (point ªAº) and the center
of the hole for the washer hose clip on the shock
tower bracket (point ªBº) is 119 mm (4.70 in.) (Fig.
12).
(4) With the engine held at the proper position,
tighten both the upper and lower torque strut bolts
to 118 N´m (87 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 10).
(5) Remove the floor jack.
ENGINE MOUNTÐLEFT
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle approximately 30.5 cm (12 in.) on
hoist
(2) Remove air cleaner assembly (Fig. 13).
(3) Remove battery and tray.
(4) Support transaxle with a suitable jack.
(5) Remove left front wheel.
(6) Remove left splash shield.
(7) Remove through bolt access plug at left side
outer frame rail.
Fig. 10 Torque StrutsÐUpper and Lower
1 ± BOLTS
2 ± ENGINE MOUNT BRACKET
3 ± TORQUE STRUT BRACKET
4 ± UPPER TORQUE STRUT5 ± CROSSMEMBER
6 ± LOWER TORQUE STRUT
7 ± BOLTS
8 ± RIGHT FENDER
Fig. 11 Floor Jack Positioning
1 ± WOOD BLOCK
2 ± FLOOR JACK
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 21
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 745 of 1285
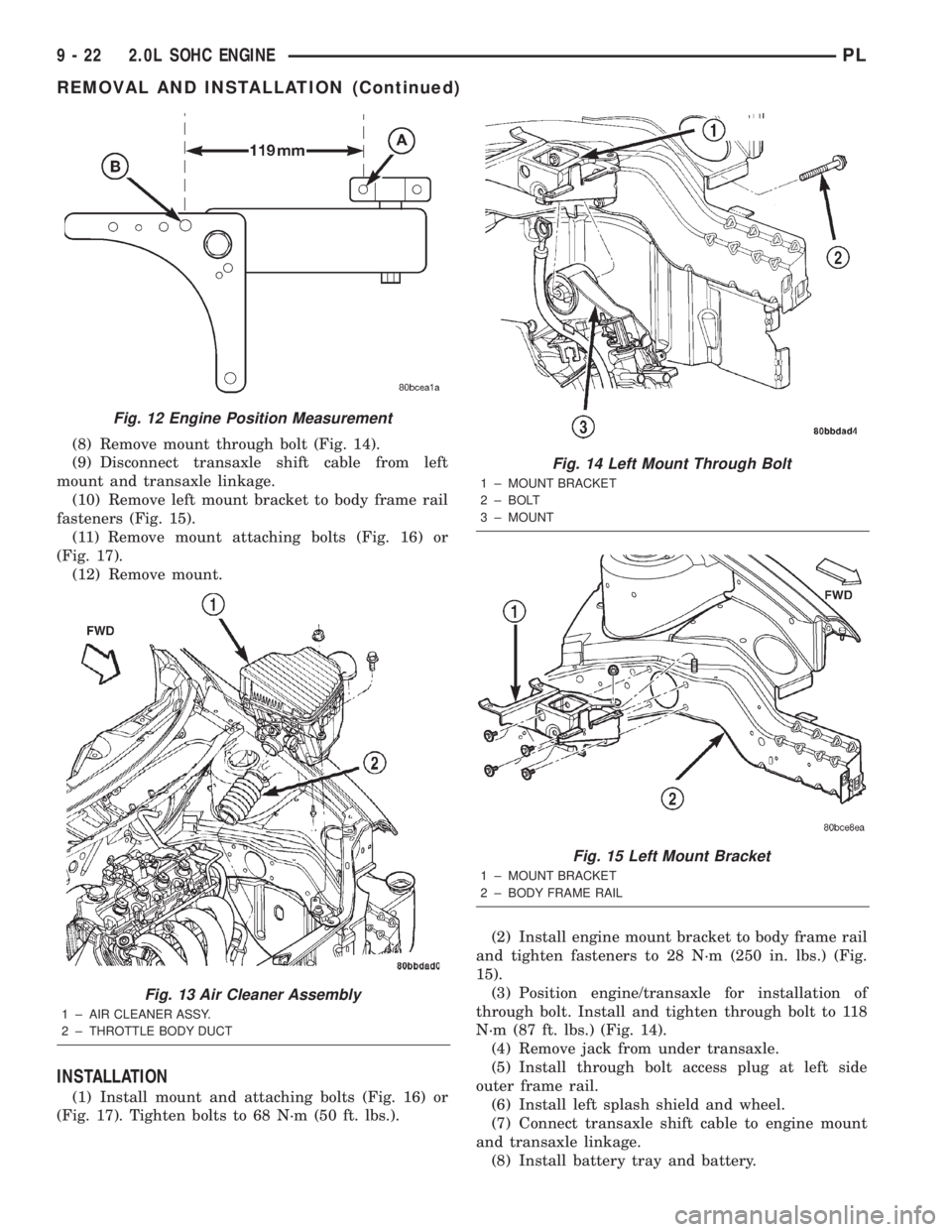
(8) Remove mount through bolt (Fig. 14).
(9) Disconnect transaxle shift cable from left
mount and transaxle linkage.
(10) Remove left mount bracket to body frame rail
fasteners (Fig. 15).
(11) Remove mount attaching bolts (Fig. 16) or
(Fig. 17).
(12) Remove mount.
INSTALLATION
(1) Install mount and attaching bolts (Fig. 16) or
(Fig. 17). Tighten bolts to 68 N´m (50 ft. lbs.).(2) Install engine mount bracket to body frame rail
and tighten fasteners to 28 N´m (250 in. lbs.) (Fig.
15).
(3) Position engine/transaxle for installation of
through bolt. Install and tighten through bolt to 118
N´m (87 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 14).
(4) Remove jack from under transaxle.
(5) Install through bolt access plug at left side
outer frame rail.
(6) Install left splash shield and wheel.
(7) Connect transaxle shift cable to engine mount
and transaxle linkage.
(8) Install battery tray and battery.
Fig. 12 Engine Position Measurement
Fig. 13 Air Cleaner Assembly
1 ± AIR CLEANER ASSY.
2 ± THROTTLE BODY DUCT
Fig. 14 Left Mount Through Bolt
1 ± MOUNT BRACKET
2 ± BOLT
3 ± MOUNT
Fig. 15 Left Mount Bracket
1 ± MOUNT BRACKET
2 ± BODY FRAME RAIL
9 - 22 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 746 of 1285
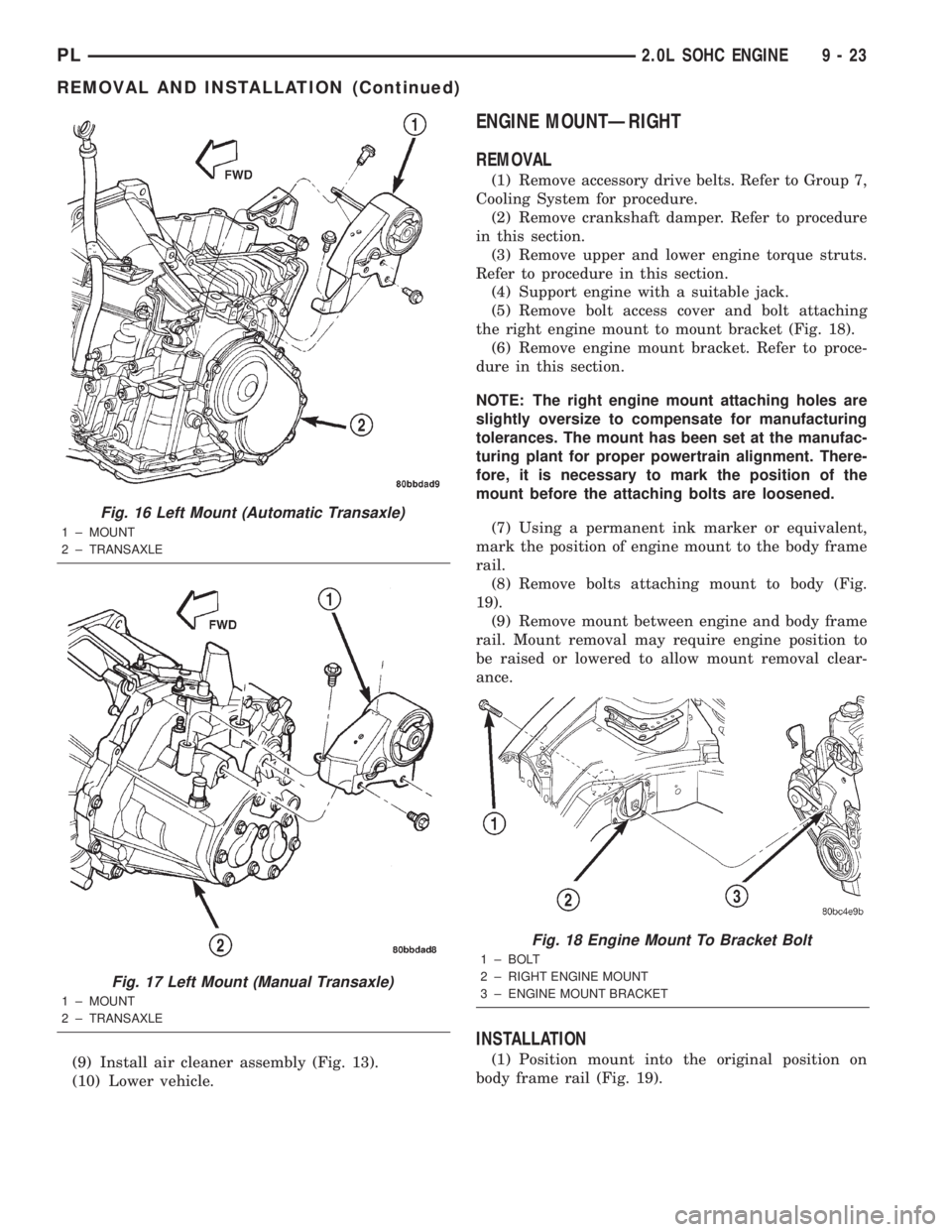
(9) Install air cleaner assembly (Fig. 13).
(10) Lower vehicle.
ENGINE MOUNTÐRIGHT
REMOVAL
(1) Remove accessory drive belts. Refer to Group 7,
Cooling System for procedure.
(2) Remove crankshaft damper. Refer to procedure
in this section.
(3) Remove upper and lower engine torque struts.
Refer to procedure in this section.
(4) Support engine with a suitable jack.
(5) Remove bolt access cover and bolt attaching
the right engine mount to mount bracket (Fig. 18).
(6) Remove engine mount bracket. Refer to proce-
dure in this section.
NOTE: The right engine mount attaching holes are
slightly oversize to compensate for manufacturing
tolerances. The mount has been set at the manufac-
turing plant for proper powertrain alignment. There-
fore, it is necessary to mark the position of the
mount before the attaching bolts are loosened.
(7) Using a permanent ink marker or equivalent,
mark the position of engine mount to the body frame
rail.
(8) Remove bolts attaching mount to body (Fig.
19).
(9) Remove mount between engine and body frame
rail. Mount removal may require engine position to
be raised or lowered to allow mount removal clear-
ance.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position mount into the original position on
body frame rail (Fig. 19).
Fig. 16 Left Mount (Automatic Transaxle)
1 ± MOUNT
2 ± TRANSAXLE
Fig. 17 Left Mount (Manual Transaxle)
1 ± MOUNT
2 ± TRANSAXLE
Fig. 18 Engine Mount To Bracket Bolt
1 ± BOLT
2 ± RIGHT ENGINE MOUNT
3 ± ENGINE MOUNT BRACKET
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 23
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 748 of 1285
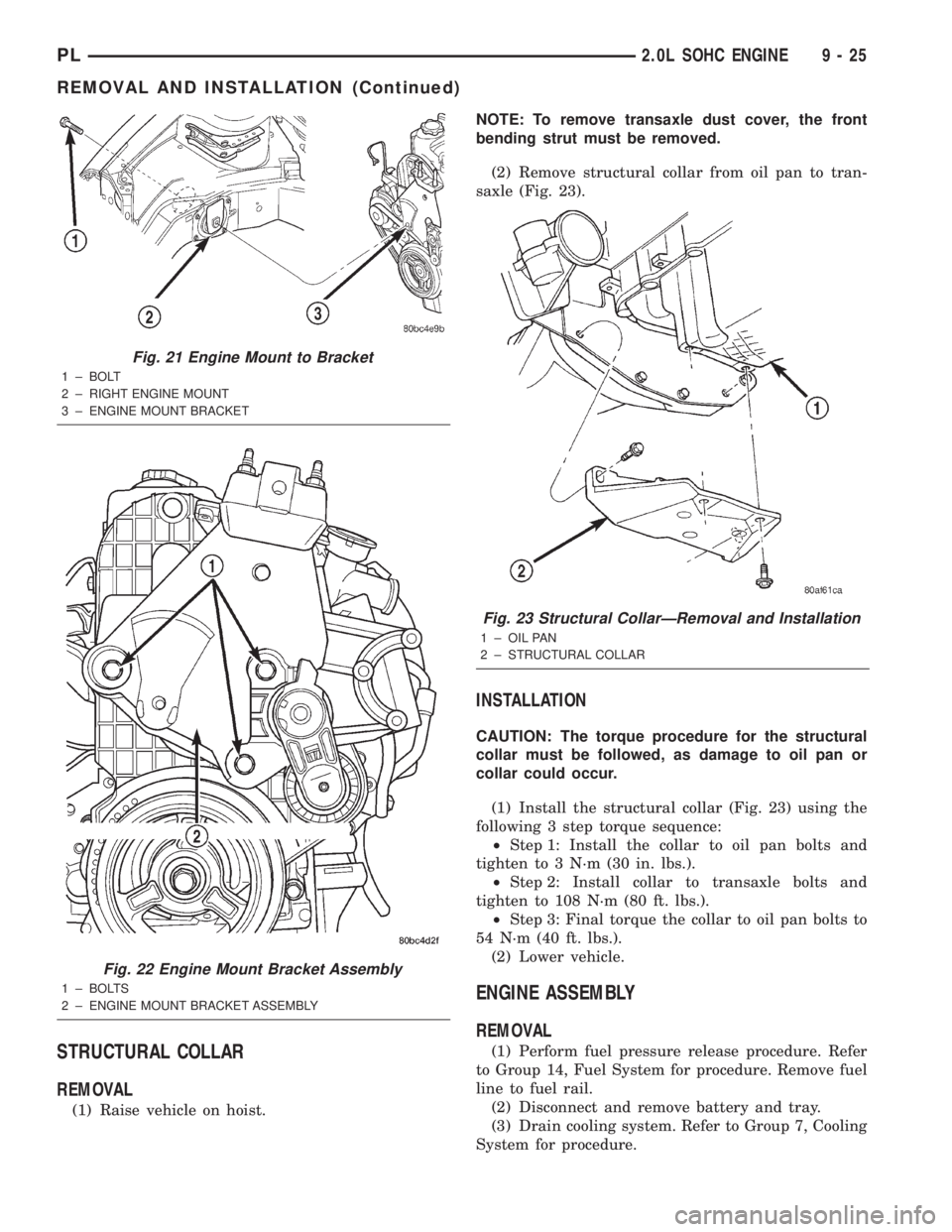
STRUCTURAL COLLAR
REMOVAL
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist.NOTE: To remove transaxle dust cover, the front
bending strut must be removed.
(2) Remove structural collar from oil pan to tran-
saxle (Fig. 23).
INSTALLATION
CAUTION: The torque procedure for the structural
collar must be followed, as damage to oil pan or
collar could occur.
(1) Install the structural collar (Fig. 23) using the
following 3 step torque sequence:
²Step 1: Install the collar to oil pan bolts and
tighten to 3 N´m (30 in. lbs.).
²Step 2: Install collar to transaxle bolts and
tighten to 108 N´m (80 ft. lbs.).
²Step 3: Final torque the collar to oil pan bolts to
54 N´m (40 ft. lbs.).
(2) Lower vehicle.
ENGINE ASSEMBLY
REMOVAL
(1) Perform fuel pressure release procedure. Refer
to Group 14, Fuel System for procedure. Remove fuel
line to fuel rail.
(2) Disconnect and remove battery and tray.
(3) Drain cooling system. Refer to Group 7, Cooling
System for procedure.
Fig. 21 Engine Mount to Bracket
1 ± BOLT
2 ± RIGHT ENGINE MOUNT
3 ± ENGINE MOUNT BRACKET
Fig. 22 Engine Mount Bracket Assembly
1 ± BOLTS
2 ± ENGINE MOUNT BRACKET ASSEMBLY
Fig. 23 Structural CollarÐRemoval and Installation
1 ± OIL PAN
2 ± STRUCTURAL COLLAR
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 25
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)