tra DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
[x] Cancel search | Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 789 of 1285

CYLINDER BORE INSPECTION
The cylinder walls should be checked for out-of-
round and taper with Tool C-119 (Fig. 134). If the cyl-
inder walls are badly scuffed or scored, the cylinder
block should be rebored and honed, and new pistons
and rings fitted. Whatever type of boring equipment
is used, boring and honing operation should be
closely coordinated with the fitting of pistons and
rings in order that specified clearances may be main-
tained.Refer to Honing Cylinder Bores outlined
in the Standard Service Procedures for specifi-
cation and procedures.
Measure the cylinder bore at three levels in direc-
tions A and B (Fig. 134). Top measurement should be
10 mm (3/8 in.) down and bottom measurement
should be 10 mm (3/8 in.) up from bottom of bore.
For specifications, refer to Engine Specifications in
this section.
ADJUSTMENTS
ENGINE TORQUE STRUT ADJUSTMENT
The upper and lower torque struts need to be
adjusted together to assure proper engine positioning
and engine mount loading. Whenever a torque strut
bolt(s) is loosened, this procedure must be performed.
(1) Loosen the upper and lower torque strut
attaching bolt at the suspension crossmember and
shock tower bracket (Fig. 135).
(2) The engine position may now be adjusted by
positioning a suitable floor jack on the forward edge
of the transmission bell housing (Fig. 136).
NOTE: The floor jack must be positioned as shown
in (Fig. 136) to prevent minimal upward lifting of the
engine.(3) Carefully apply upward force, allowing the
upper engine to rotate rearward until the distance
between the center of the rearmost attaching stud on
the engine mount bracket (point ªAº) and the center
of the hole for the washer hose clip on the shock
tower bracket (point ªBº) is 119 mm (4.70 in.) (Fig.
137).
(4) With the engine held at the proper position,
tighten both the upper and lower torque strut bolts
to 118 N´m (87 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 135).
(5) Remove the floor jack.
Fig. 134 Checking Cylinder Bore Size
9 - 66 2.0L SOHC ENGINEPL
CLEANING AND INSPECTION (Continued)
Page 792 of 1285

DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Wear Limit 1.0 mm
(0.039 in.)
Ring Side ClearanceÐ
Compression Rings0.025±0.065 mm
(0.0010±0.0026 in.)
Wear Limit 0.10 mm
(0.004 in.)
Ring Side ClearanceÐOil
Ring Pack0.004±0.178 mm
(0.0002±0.0070 in.)
Ring WidthÐ
Compression Rings1.17±1.19 mm
(0.046±0.047 in.)
Ring WidthÐOil Ring
Pack2.854±3.008 mm
(0.1124±0.1184 in.)
Connecting Rod
Bearing Clearance 0.026±0.059 mm
(0.001±0.0023 in.)
Wear Limit 0.075 mm
(0.003 in.)
Bore DiameterÐPiston
Pin20.96±20.98 mm
(0.8252±0.8260 in.)
Bore DiameterÐ
Crankshaft End50.991±51.005 mm
(2.0075±2.0081 in.)
Side Clearance 0.13±0.38 mm
(0.005±0.015 in.)
Wear Limit 0.40 mm
(0.016 in.)
WeightÐTotal (Less
Bearing)543 grams
(1.20 lbs.)
Crankshaft
Connecting Rod Journal
Diameter47.9924±48.0076 mm
(1.8894±1.8900 in.)
Main Bearing Journal
Diameter51.9924±52.0076 mm
(2.0469±2.0475 in.)
Journal Out-of-Round
(Max.)0.0035 mm
(0.0001 in.)
Journal Taper (Max.) 0.0038 mm
(0.0001 in.)
End Play 0.09±0.24 mm
(0.0035±0.0094 in.)
Wear Limit 0.37 mm
(0.015 in.)
Main Bearing Diametrical
Clearance0.022±0.062 mm
(0.0008±0.0024 in.)DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Rocker Arm Shaft
Rocker Arm Shaft
Diameter19.966±19.984 mm
(0.7861±0.7868 in.)
Rocker Arm Shaft Retainers
IntakeÐWidth 28.43±28.49 mm
(1.1193±1.1217 in.)
ExhaustÐWidth1&529.15±29.25 mm
(1.1477±1.1516 in.)
ExhaustÐWidth 2, 3, and
440.40±40.50 mm
(1.5906±1.5945 in.)
Rocker Arm/Hydraulic Lash Adjuster
Rocker Arm Inside
Diameter20.00±20.02 mm
(0.787±0.788 in.)
Rocker Arm Shaft
Clearance0.016±0.054 mm
(0.0006±0.0021 in.)
Body Diameter 22.949±22.962 mm
(0.9035±0.9040 in.)
Plunger Travel Minimum
(Dry)2.2 mm
(0.087 in.)
Dry LashÐIntake 1.17 mm
(0.046 in.)
Dry LashÐExhaust 1.28 mm
(0.050 in.)
Rocker Arm Ratio 1.4 to 1
Cylinder Head Camshaft Bearing Diameter
Journal No. 1 41.20±41.221 mm
(1.622±1.6228 in.)
Journal No. 2 41.60±41.62 mm
(1.637±1.638 in.)
Journal No. 3 42.0±42.02 mm
(1.653±1.654 in.)
Journal No. 4 42.4±42.42 mm
(1.669±1.670 in.)
Journal No. 5 42.8±42.82 mm
(1.685±1.6858 in.)
Camshaft
Journal Diameter
No. 1 41.128±41.147 mm
(1.619±1.6199 in.)
No. 2 41.528±41.547 mm
(1.634±1.635 in.)
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 69
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 794 of 1285
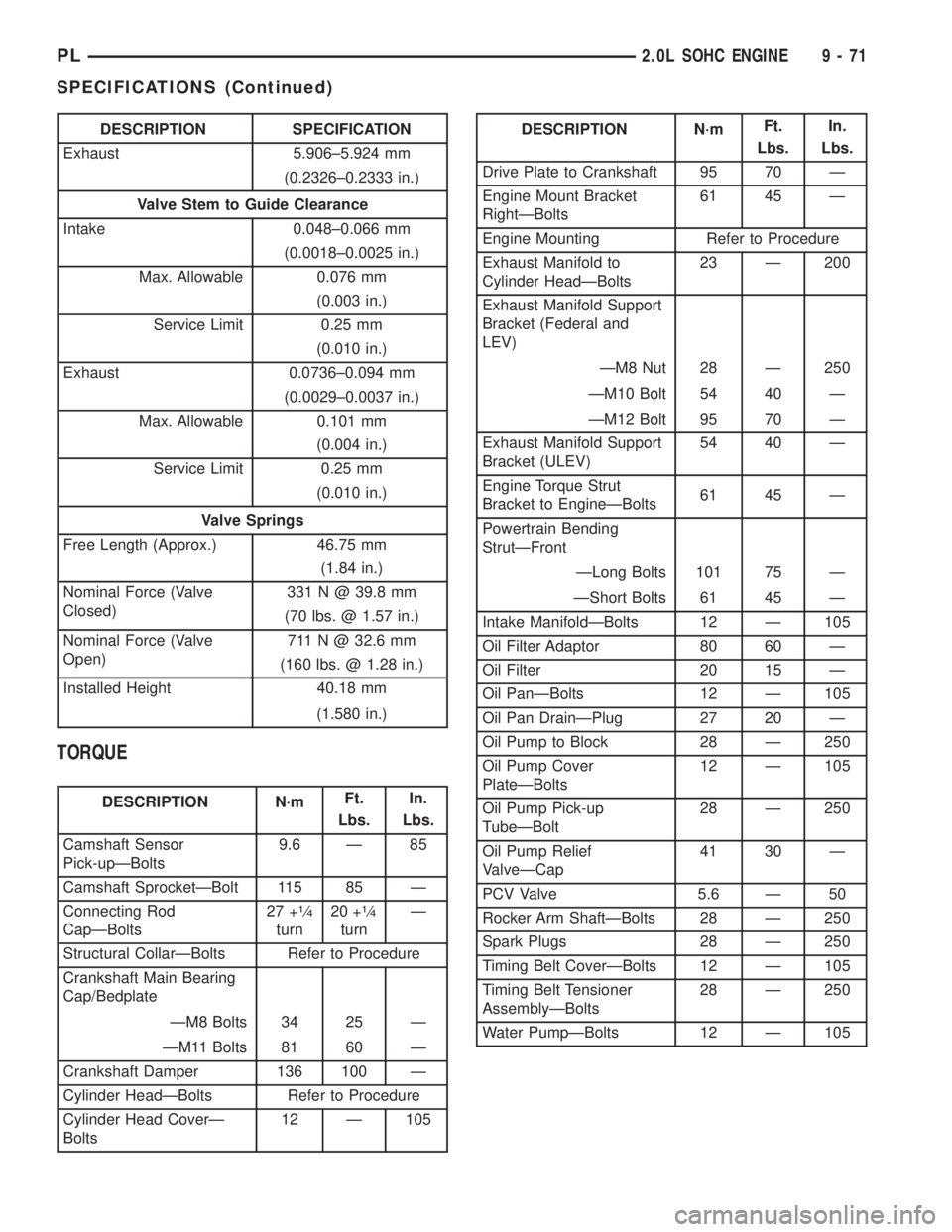
DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Exhaust 5.906±5.924 mm
(0.2326±0.2333 in.)
Valve Stem to Guide Clearance
Intake 0.048±0.066 mm
(0.0018±0.0025 in.)
Max. Allowable 0.076 mm
(0.003 in.)
Service Limit 0.25 mm
(0.010 in.)
Exhaust 0.0736±0.094 mm
(0.0029±0.0037 in.)
Max. Allowable 0.101 mm
(0.004 in.)
Service Limit 0.25 mm
(0.010 in.)
Valve Springs
Free Length (Approx.) 46.75 mm
(1.84 in.)
Nominal Force (Valve
Closed)331 N @ 39.8 mm
(70 lbs. @ 1.57 in.)
Nominal Force (Valve
Open)711 N @ 32.6 mm
(160 lbs. @ 1.28 in.)
Installed Height 40.18 mm
(1.580 in.)
TORQUE
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Camshaft Sensor
Pick-upÐBolts9.6 Ð 85
Camshaft SprocketÐBolt 115 85 Ð
Connecting Rod
CapÐBolts27 +
1¤4
turn20 +
1¤4
turnÐ
Structural CollarÐBolts Refer to Procedure
Crankshaft Main Bearing
Cap/Bedplate
ÐM8 Bolts 34 25 Ð
ÐM11 Bolts 81 60 Ð
Crankshaft Damper 136 100 Ð
Cylinder HeadÐBolts Refer to Procedure
Cylinder Head CoverÐ
Bolts12 Ð 105
DESCRIPTION N´mFt.
Lbs.In.
Lbs.
Drive Plate to Crankshaft 95 70 Ð
Engine Mount Bracket
RightÐBolts61 45 Ð
Engine Mounting Refer to Procedure
Exhaust Manifold to
Cylinder HeadÐBolts23 Ð 200
Exhaust Manifold Support
Bracket (Federal and
LEV)
ÐM8 Nut 28 Ð 250
ÐM10 Bolt 54 40 Ð
ÐM12 Bolt 95 70 Ð
Exhaust Manifold Support
Bracket (ULEV)54 40 Ð
Engine Torque Strut
Bracket to EngineÐBolts61 45 Ð
Powertrain Bending
StrutÐFront
ÐLong Bolts 101 75 Ð
ÐShort Bolts 61 45 Ð
Intake ManifoldÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Oil Filter Adaptor 80 60 Ð
Oil Filter 20 15 Ð
Oil PanÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Oil Pan DrainÐPlug 27 20 Ð
Oil Pump to Block 28 Ð 250
Oil Pump Cover
PlateÐBolts12 Ð 105
Oil Pump Pick-up
TubeÐBolt28 Ð 250
Oil Pump Relief
ValveÐCap41 30 Ð
PCV Valve 5.6 Ð 50
Rocker Arm ShaftÐBolts 28 Ð 250
Spark Plugs 28 Ð 250
Timing Belt CoverÐBolts 12 Ð 105
Timing Belt Tensioner
AssemblyÐBolts28 Ð 250
Water PumpÐBolts 12 Ð 105
PL2.0L SOHC ENGINE 9 - 71
SPECIFICATIONS (Continued)
Page 798 of 1285
EXHAUST SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
EXHAUST SYSTEM........................1
EXHAUST FLEX-JOINT COUPLING............1
CATALYTIC CONVERTER....................1
EXHAUST HEAT SHIELDS..................3
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EXHAUST SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART.......4
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
EXHAUST PIPE AND MUFFLER..............4CATALYTIC CONVERTER....................7
CLEANING AND INSPECTION
EXHAUST SYSTEM........................8
ADJUSTMENTS
EXHAUST SYSTEM ALIGNMENT.............8
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE SPECIFICATION CHART.............8
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
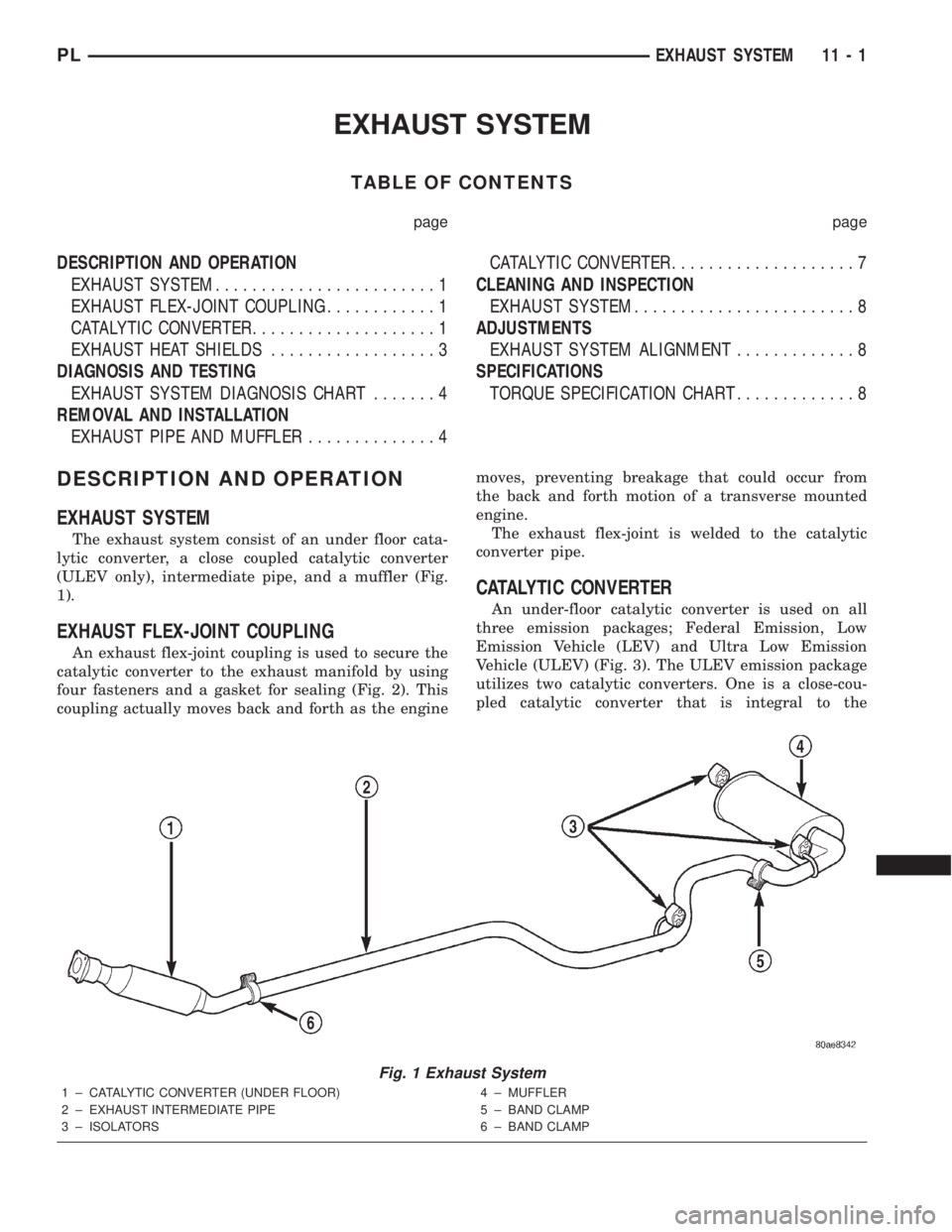
EXHAUST SYSTEM
The exhaust system consist of an under floor cata-
lytic converter, a close coupled catalytic converter
(ULEV only), intermediate pipe, and a muffler (Fig.
1).
EXHAUST FLEX-JOINT COUPLING
An exhaust flex-joint coupling is used to secure the
catalytic converter to the exhaust manifold by using
four fasteners and a gasket for sealing (Fig. 2). This
coupling actually moves back and forth as the enginemoves, preventing breakage that could occur from
the back and forth motion of a transverse mounted
engine.
The exhaust flex-joint is welded to the catalytic
converter pipe.
CATALYTIC CONVERTER
An under-floor catalytic converter is used on all
three emission packages; Federal Emission, Low
Emission Vehicle (LEV) and Ultra Low Emission
Vehicle (ULEV) (Fig. 3). The ULEV emission package
utilizes two catalytic converters. One is a close-cou-
pled catalytic converter that is integral to the
Fig. 1 Exhaust System
1 ± CATALYTIC CONVERTER (UNDER FLOOR)
2 ± EXHAUST INTERMEDIATE PIPE
3 ± ISOLATORS4 ± MUFFLER
5 ± BAND CLAMP
6 ± BAND CLAMP
PLEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 1
Page 799 of 1285
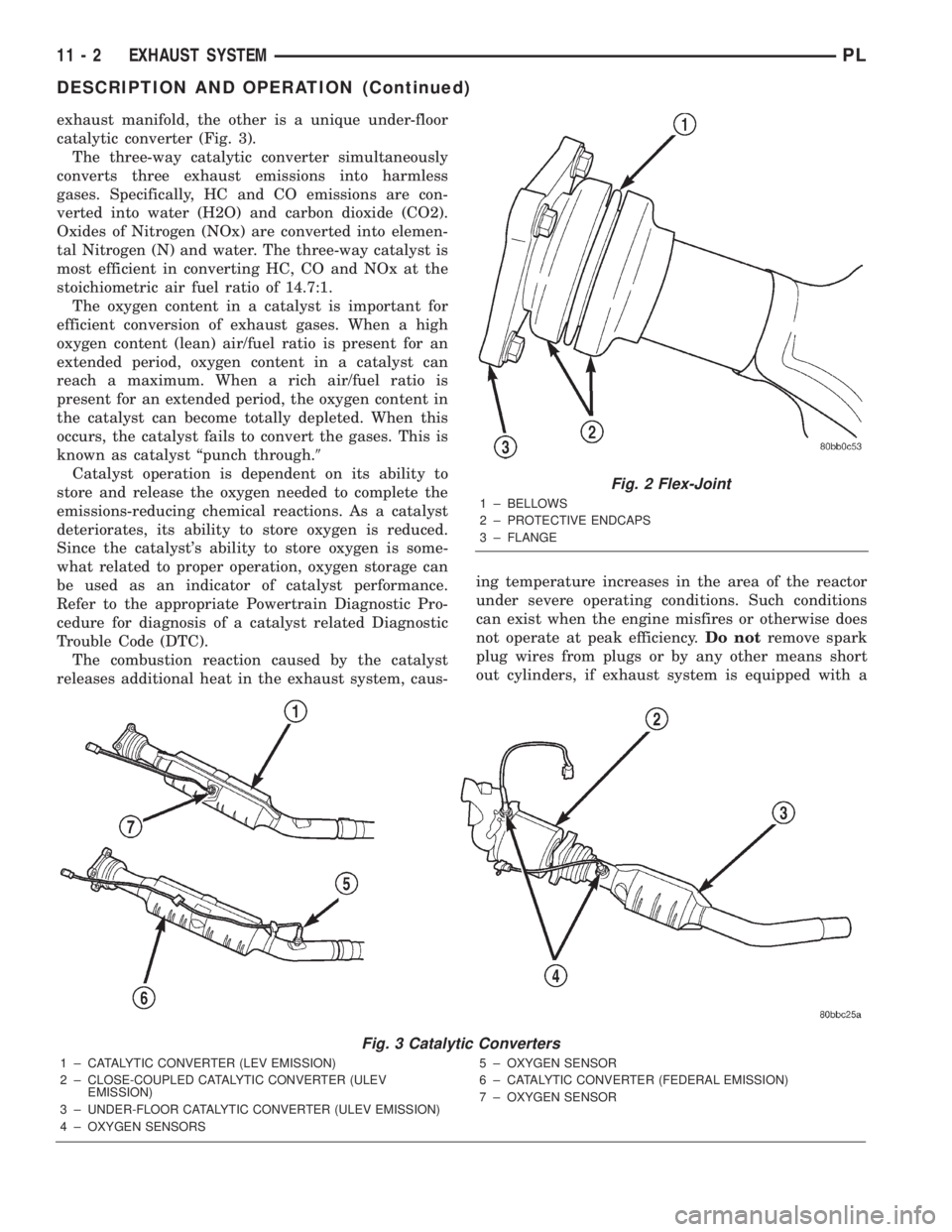
exhaust manifold, the other is a unique under-floor
catalytic converter (Fig. 3).
The three-way catalytic converter simultaneously
converts three exhaust emissions into harmless
gases. Specifically, HC and CO emissions are con-
verted into water (H2O) and carbon dioxide (CO2).
Oxides of Nitrogen (NOx) are converted into elemen-
tal Nitrogen (N) and water. The three-way catalyst is
most efficient in converting HC, CO and NOx at the
stoichiometric air fuel ratio of 14.7:1.
The oxygen content in a catalyst is important for
efficient conversion of exhaust gases. When a high
oxygen content (lean) air/fuel ratio is present for an
extended period, oxygen content in a catalyst can
reach a maximum. When a rich air/fuel ratio is
present for an extended period, the oxygen content in
the catalyst can become totally depleted. When this
occurs, the catalyst fails to convert the gases. This is
known as catalyst ªpunch through.9
Catalyst operation is dependent on its ability to
store and release the oxygen needed to complete the
emissions-reducing chemical reactions. As a catalyst
deteriorates, its ability to store oxygen is reduced.
Since the catalyst's ability to store oxygen is some-
what related to proper operation, oxygen storage can
be used as an indicator of catalyst performance.
Refer to the appropriate Powertrain Diagnostic Pro-
cedure for diagnosis of a catalyst related Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC).
The combustion reaction caused by the catalyst
releases additional heat in the exhaust system, caus-ing temperature increases in the area of the reactor
under severe operating conditions. Such conditions
can exist when the engine misfires or otherwise does
not operate at peak efficiency.Do notremove spark
plug wires from plugs or by any other means short
out cylinders, if exhaust system is equipped with a
Fig. 2 Flex-Joint
1 ± BELLOWS
2 ± PROTECTIVE ENDCAPS
3 ± FLANGE
Fig. 3 Catalytic Converters
1 ± CATALYTIC CONVERTER (LEV EMISSION)
2 ± CLOSE-COUPLED CATALYTIC CONVERTER (ULEV
EMISSION)
3 ± UNDER-FLOOR CATALYTIC CONVERTER (ULEV EMISSION)
4 ± OXYGEN SENSORS5 ± OXYGEN SENSOR
6 ± CATALYTIC CONVERTER (FEDERAL EMISSION)
7 ± OXYGEN SENSOR
11 - 2 EXHAUST SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 800 of 1285
catalytic converter. Failure of the catalytic converter
can occur due to temperature increases caused by
unburned fuel passing through the converter. This
deterioration of the catalyst core can result in exces-
sively high emission levels, noise complaints, and
exhaust restrictions.
The use of catalysts also involves some non-auto-
motive problems. Unleaded gasoline must be used to
avoid poisoning the catalyst core. Do not allow engine
to operate above 1200 RPM in neutral for extended
periods over 5 minutes. This condition may result in
excessive exhaust system/floor pan temperatures
because of no air movement under the vehicle.
There is no regularly scheduled maintenance on
any DaimlerChrysler catalytic converter. If damaged,
the converter must be replaced.
CAUTION: Due to exterior physical similarities of
some catalytic converters with pipe assemblies,
extreme care should be taken with replacement
parts.
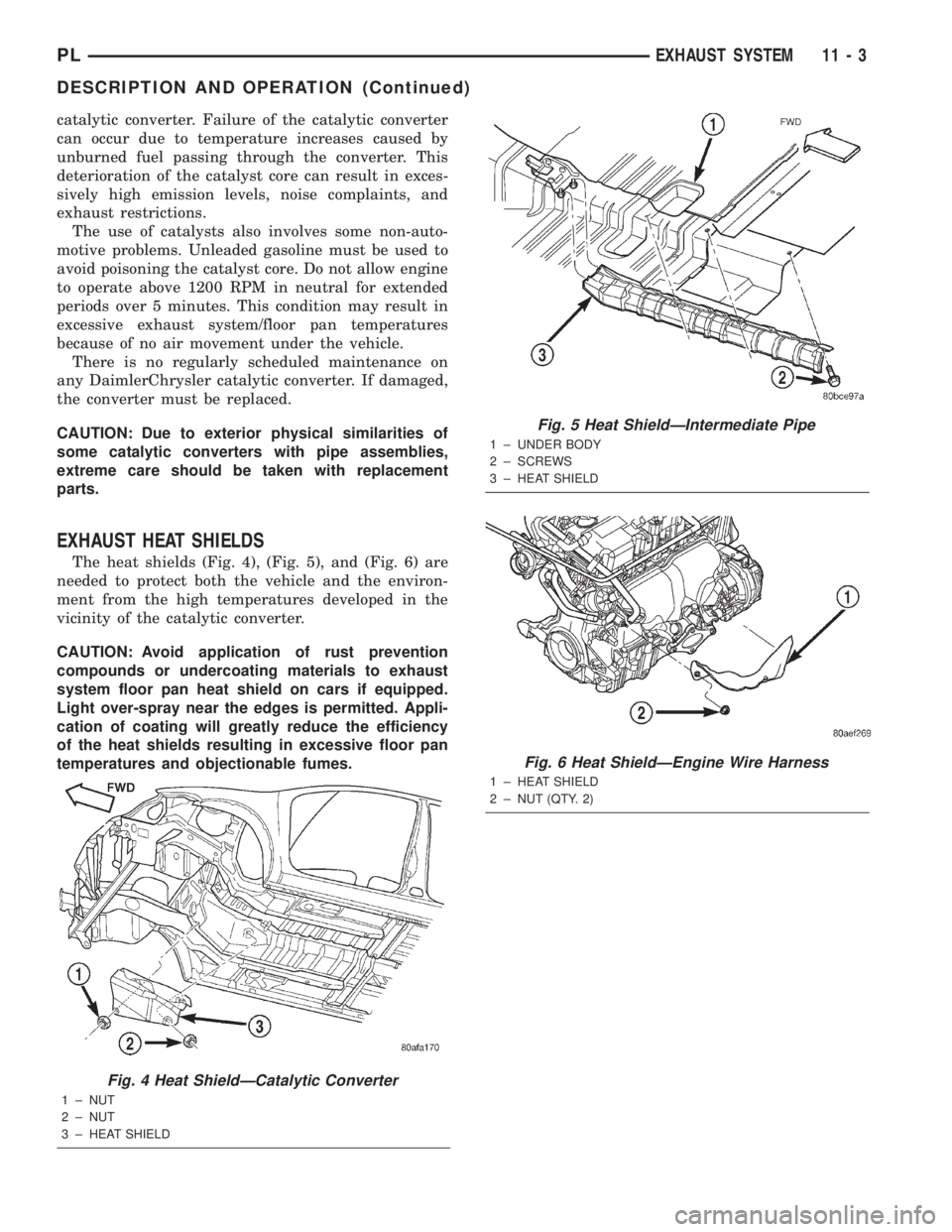
EXHAUST HEAT SHIELDS
The heat shields (Fig. 4), (Fig. 5), and (Fig. 6) are
needed to protect both the vehicle and the environ-
ment from the high temperatures developed in the
vicinity of the catalytic converter.
CAUTION: Avoid application of rust prevention
compounds or undercoating materials to exhaust
system floor pan heat shield on cars if equipped.
Light over-spray near the edges is permitted. Appli-
cation of coating will greatly reduce the efficiency
of the heat shields resulting in excessive floor pan
temperatures and objectionable fumes.
Fig. 4 Heat ShieldÐCatalytic Converter
1 ± NUT
2 ± NUT
3 ± HEAT SHIELD
Fig. 5 Heat ShieldÐIntermediate Pipe
1 ± UNDER BODY
2 ± SCREWS
3 ± HEAT SHIELD
Fig. 6 Heat ShieldÐEngine Wire Harness
1 ± HEAT SHIELD
2 ± NUT (QTY. 2)
PLEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 801 of 1285

DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING
EXHAUST SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS CHART
CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSES CORRECTION
EXCESSIVE
EXHAUST NOISE
(UNDER HOOD)1. Exhaust manifold cracked or broken. 1. Replace manifold.
2. Manifold to cylinder head leak. 2. Tighten manifold and/or replace gasket.
3. Exhaust Flex joint to manifold leak. 3. Tighten fasteners or replace gasket.
4. Exhaust flex joint. 4. Replace catalytic converter assembly.
5. Pipe and shell noise from front exhaust
pipe.5. Characteristic of single wall pipes.
EXCESSIVE
EXHAUST NOISE1. Leaks at pipe joints. 1. Tighten or replace clamps at leaking
joints.
2. Burned, blown, or rusted out exhaust
pipe or muffler.2. Replace muffler or exhaust pipes.
3. Restriction in muffler or tailpipe. 3. Remove restriction, if possible or replace
as necessary.
4. Catalytic converter material in muffler. 4. Replace muffler and converter assembly.
Check fuel injection and ignition systems for
proper operation.
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
EXHAUST PIPE AND MUFFLER
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER WORK AROUND OR ATTEMPT
TO SERVICE ANY PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM
UNTIL IT IS COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE
TAKEN WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC
CONVERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CON-
VERTER RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT
PERIOD OF ENGINE OPERATING TIME.
(1) Raise vehicle on hoist and apply penetrating oil
to band clamp fastener of component being removed.
NOTE: Do not use petroleum-based lubricants
when removing/installing muffler or exhaust pipe
isolators as it may compromise the life of the part.
A suitable substitute is a mixture of liquid dish
soap and water.
(2) Remove exhaust system ground strap.
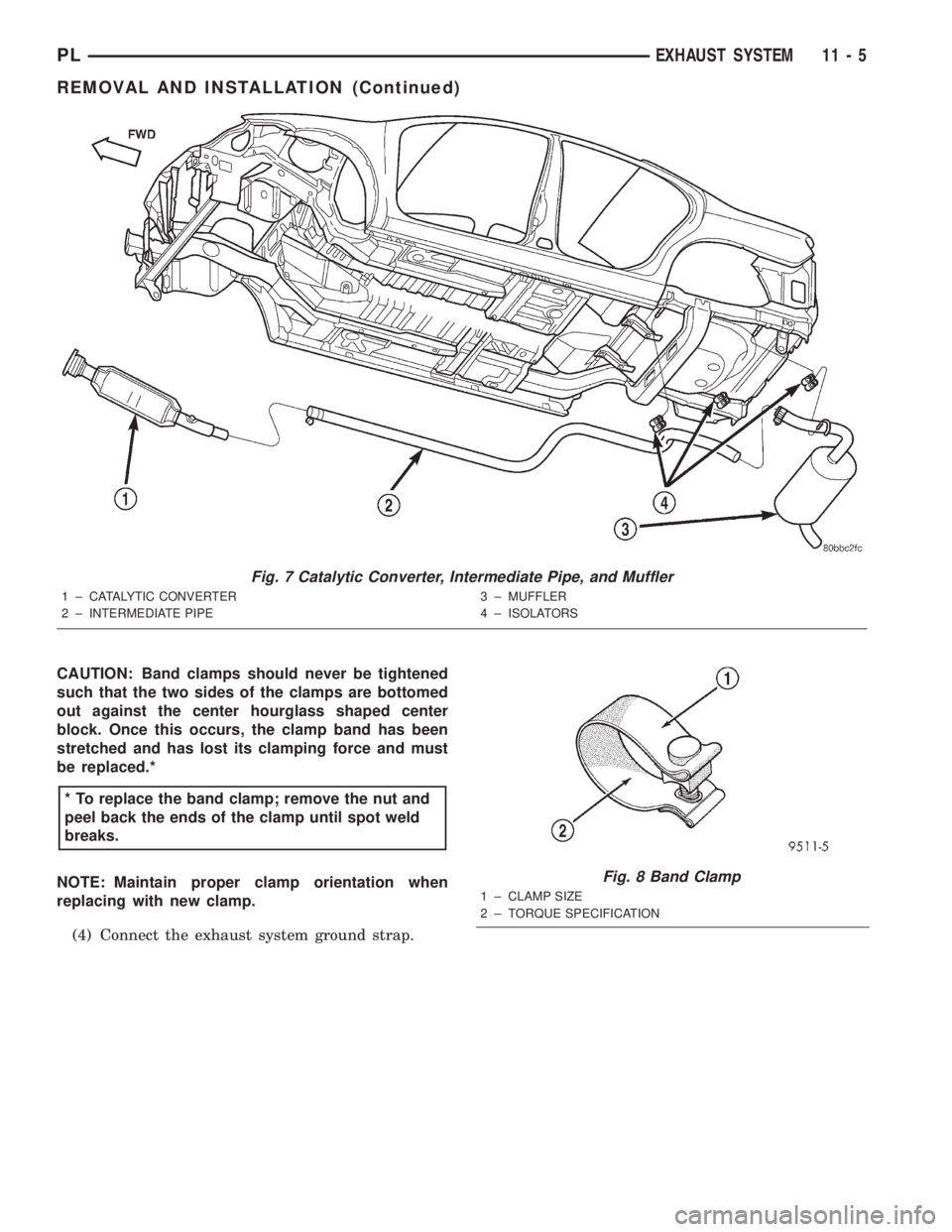
(3) Loosen band clamp and remove support isola-
tors at muffler. Remove muffler from exhaust pipe
(Fig. 7).(4) Loosen band clamp at the catalytic converter to
intermediate pipe joint (Fig. 7)
(5) Remove intermediate pipe support isolator.
Separate at slip joint and remove intermediate pipe
(Fig. 7).
(6) Clean ends of pipes and muffler to assure mat-
ing of all parts. Discard broken or worn isolators,
rusted or overused clamps, supports, and attaching
parts.
NOTE: When replacement is required on any com-
ponent of the exhaust system, you must use origi-
nal equipment parts (or their equivalent).
INSTALLATION
When assembling exhaust systemdo nottighten
clamps until components are aligned and clearances
are checked.
(1) Assemble intermediate pipe to catalytic con-
verter and the isolator support to the underbody (Fig.
7).
(2) Install the muffler to intermediate pipe and the
isolator supports to the underbody.
(3) Working from the front of system; align each
component to maintain position and proper clearance
with underbody parts (Fig. 9). Tighten band clamps
to 47 N´m (35 ft. lbs.) (Fig. 8).
11 - 4 EXHAUST SYSTEMPL
Page 802 of 1285
CAUTION: Band clamps should never be tightened
such that the two sides of the clamps are bottomed
out against the center hourglass shaped center
block. Once this occurs, the clamp band has been
stretched and has lost its clamping force and must
be replaced.*
NOTE: Maintain proper clamp orientation when
replacing with new clamp.
(4) Connect the exhaust system ground strap.
Fig. 7 Catalytic Converter, Intermediate Pipe, and Muffler
1 ± CATALYTIC CONVERTER
2 ± INTERMEDIATE PIPE3 ± MUFFLER
4 ± ISOLATORS
* To replace the band clamp; remove the nut and
peel back the ends of the clamp until spot weld
breaks.
Fig. 8 Band Clamp
1 ± CLAMP SIZE
2 ± TORQUE SPECIFICATION
PLEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 5
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 804 of 1285

CATALYTIC CONVERTER
REMOVAL
WARNING: THE NORMAL OPERATING TEMPERA-
TURE OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM IS VERY HIGH.
THEREFORE, NEVER ATTEMPT TO SERVICE ANY
PART OF THE EXHAUST SYSTEM UNTIL IT IS
COOLED. SPECIAL CARE SHOULD BE TAKEN
WHEN WORKING NEAR THE CATALYTIC CON-
VERTER. THE TEMPERATURE OF THE CONVERTER
RISES TO A HIGH LEVEL AFTER A SHORT PERIOD
OF ENGINE OPERATION TIME.
NOTE: Vehicles equipped with the ULEV emission
package are equipped with an additional catalytic
converter that is integral to the exhaust manifold.
Refer to Exhaust Manifold in Group 9, Engine for
procedure.
(1) Remove muffler and exhaust pipe. Refer to pro-
cedure in this section.
(2) Disconnect downstream oxygen sensor electri-
cal connector.
(3) Remove exhaust manifold support bracket
(Federal and LEV only) (Fig. 10).
(4) Remove catalytic converter to exhaust manifold
attaching fasteners and remove converter from vehi-
cle (Fig. 11) or (Fig. 12).
(5) Remove and discard flange gasket.
NOTE: When replacement is required on any com-
ponent of the exhaust system, original equipment
parts (or equivalent) must be used.
INSTALLATION
NOTE: When assembling exhaust system do not
tighten clamps until all components are aligned and
clearances are checked.(1) Assemble catalytic converter to exhaust mani-
fold connection. Use a new flange gasket.
1 ± HEAT SHIELD
2 ± FLOOR PAN
3 ± BAND CLAMP
4 ± FLOOR PAN
5 ± TANK STRAP
6 ± FUEL TANK
7 ± SPARE TIRE TUB
8 ± REAR SUSPENSION CROSSMEMBER
9 ± FLOOR PAN
10 ± SPARE TIRE TUB
11 ± MUFFLER12 ± BUMPER BEAM
13 ± HEAT SHIELD
14 ± OXYGEN SENSOR CLEARANCE (LEV)
15 ± FLOOR PAN
16 ± FEDERAL & LEV
17 ± OXYGEN SENSOR CLEARANCE (FEDERAL)
18 ± HEAT SHIELD
19 ± FLOOR PAN
20 ± CROSSMEMBER
21 ± TAIL PIPE
22 ± FASCIA
Fig. 10 Exhaust Manifold Support BracketÐFederal
& LEV
1 ± BRACKET
2 ± BOLT (M10)
3 ± BOLT (M12)
4 ± NUT
Fig. 11 Catalytic Converter to Exhaust Manifold
ConnectionÐFederal & LEV
1 ± PRESSED-IN STUDS
2 ± NUTS
3 ± GASKET
PLEXHAUST SYSTEM 11 - 7
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)
Page 811 of 1285

CAUTION: After removing the steering knuckle from
the ball joint stud, do not pull outward on the knuckle.
Pulling the steering knuckle outward at this point can
separate the inner C/V joint on the driveshaft. Refer to
FRONT DRIVESHAFTS in the DIFFERENTIAL AND
DRIVELINE group for further information.
NOTE: Use caution when separating the ball joint
stud from the steering knuckle, so the ball joint seal
does not get cut.
(6) Separate each ball joint stud from the steering
knuckle by prying down on lower control arm and up
against the ball joint boss on the steering knuckle
(Fig. 3).
(7) If the vehicle is equipped with a power steering
fluid cooler, remove the two screws securing the
cooler to the front suspension crossmember. They are
located behind the cooler and can be accessed from
above. Allow the cooler to hang out of the way.
(8) Using wire or cord, support and tie off the
power steering gear to the underbody of the vehicle,
so when the crossmember is lowered, the gear does
not fall away being held to the vehicle by only the
steering column coupler and the fluid hoses.
(9) Loosen and remove the four bolts attaching the
power steering gear to the front suspension cross-
member (Fig. 4). Remove the power steering gear
from the front suspension crossmember.
(10) Remove the bolt mounting the engine torque
strut to the right forward corner of the front suspen-
sion crossmember (Fig. 5).
NOTE: Before removing the front suspension
crossmember from the vehicle, the location of thecrossmember must be scribed on the body of the
vehicle (Fig. 9). Do this so that the crossmember
can be relocated upon reinstallation against the
body of vehicle in the same location as before
removal. If the front suspension crossmember is
not reinstalled in exactly the same location as
before removal, the preset front wheel alignment
settings (caster and camber) will be lost.
(11) Using an awl, scribe a line (Fig. 6) marking
the location of where the front suspension crossmem-
ber is mounted against the body of the vehicle.
(12) Position a transmission jack under the center
of the front suspension crossmember and raise it to
support the bottom of the crossmember.
(13) Loosen and completely remove the two front
bolts (one right and one left) attaching the front sus-
pension crossmember to the frame rails of vehicle.
The right side bolt can be viewed in the mounting
bolt figure (Fig. 5). The left side bolt is located in the
same location on the other side of the vehicle.
(14) Loosen the two rear bolts (one right and one
left) attaching the front suspension crossmember and
lower control arms to the body of the vehicle until
they release from the threaded tapping plates in the
body of the vehicle. Remove the rear bolts from the
body of the vehicle, but do not completely remove the
rear bolts because they are designed to disengage
from the body threads yet stay within the lower con-
trol arm rear isolator bushing. This allows the lower
control arm to stay in place on the crossmember. The
right side bolt can be viewed in the mounting bolt
figure (Fig. 5). The left side bolt is located in the
same location on the other side of the vehicle.
(15) Lower the front suspension crossmember.
Fig. 2 Ball Joint Bolt And Nut
1 ± NUT
2 ± BOLT
3 ± BALL JOINT
Fig. 3 Pry Bar Usage
1 ± STEERING KNUCKLE
2±PRYBAR
3 ± LOWER CONTROL ARM
4 ± BALL JOINT STUD
13 - 6 FRAME AND BUMPERSPL
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION (Continued)