DODGE NEON 2000 Service Repair Manual
Manufacturer: DODGE, Model Year: 2000, Model line: NEON, Model: DODGE NEON 2000Pages: 1285, PDF Size: 29.42 MB
Page 821 of 1285

Page 822 of 1285

FUEL SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM.................... 1FUEL INJECTION SYSTEM.................. 21
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FUEL REQUIREMENTS.....................1
GASOLINE/OXYGENATE BLENDS.............2
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM...................3
FUEL PUMP MODULE......................3
ELECTRIC FUEL PUMP.....................4
FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT................4
FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR....4
FUEL TANK..............................4
FUEL RAIL...............................4
FUEL INJECTORS.........................5
PRESSURE-VACUUM FILLER CAP............5
ONBOARD REFUELING VAPOR RECOVERY....6
CONTROL VALVE/PRESSURE RELIEF.........6
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS.................6
ROLLOVER VALVES.......................7
FUEL TUBES/LINES/HOSES AND CLAMPS......8
SERVICE PROCEDURES
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE...........................8INJECTOR CONNECTOR....................8
DRAINING FUEL TANK.....................9
HOSES AND CLAMPS......................9
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS.................9
REMOVAL AND INSTALLATION
AUTOMATIC SHUTDOWN RELAY............12
FUEL PUMP RELAY.......................12
FUEL PUMP MODULE.....................12
FUEL FILTER / PRESSURE REGULATOR......13
FUEL PUMP INLET STRAINER..............14
FUEL LEVEL SENSOR.....................14
FUEL INJECTORS........................15
FUEL TANK.............................16
FUEL FILLER NECK.......................17
ACCELERATOR PEDAL....................18
THROTTLE CABLE.......................19
SPECIFICATIONS
TORQUE...............................20
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION
FUEL REQUIREMENTS
OPERATION
Your engine is designed to meet all emissions reg-
ulations and provide excellent fuel economy and per-
formance when using high quality unleaded gasoline
having an octane rating of 87. The use of premium
gasoline is not recommended. The use of premium
gasoline will provide no benefit over high quality reg-
ular gasoline, and in some circumstances may result
in poorer performance.
Light spark knock at low engine speeds is not
harmful to your engine. However, continued heavyspark knock at high speeds can cause damage and
immediate service is required. Engine damage result-
ing from operation with a heavy spark knock may
not be covered by the new vehicle warranty.
Poor quality gasoline can cause problems such as
hard starting, stalling and hesitations. If you experi-
ence these symptoms, try another brand of gasoline
before considering service for the vehicle.
The American Automobile Manufacturers Associa-
tion, AAMA, has issued gasoline specifications to
define the minimum fuel properties necessary to
deliver enhanced performance and durability for your
vehicle. DaimlerChrysler Corporation recommends
the use of gasoline that meet the AAMA specifica-
tions if they are available.
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 1
Page 823 of 1285

REFORMULATED GASOLINE
Many areas of the country require the use of
cleaner burning gasoline referred to as ªreformulat-
edº gasoline. Reformulated gasoline contain oxygen-
ates, and are specifically blended to reduce vehicle
emissions and improve air quality.
DaimlerChrysler Corporation strongly supports the
use of reformulated gasoline. Properly blended refor-
mulated gasoline will provide excellent performance
and durability for the engine and fuel system compo-
nents.
GASOLINE/OXYGENATE BLENDS
Some fuel suppliers blend unleaded gasoline with
oxygenates such as 10% ethanol, MTBE, and ETBE.
Oxygenates are required in some areas of the country
during the winter months to reduce carbon monoxide
emissions. Fuels blended with these oxygenates may
be used in your vehicle.
CAUTION: DO NOT use gasoline containing METH-
ANOL. Gasoline containing methanol may damage
critical fuel system components.
MMT
MMT is a manganese-containing metallic additive
that is blended into some gasoline to increase octane.
Gasoline blended with MMT provide no performance
advantage beyond gasoline of the same octane num-
ber without MMT. Gasoline blended with MMT
reduce spark plug life and reduce emission system
performance in some vehicles. DaimlerChrysler rec-
ommends that gasoline without MMT be used in your
vehicle. The MMT content of gasoline may not be
indicated on the gasoline pump; therefore, you should
ask your gasoline retailer whether or not his/her gas-
oline contains MMT.
It is even more important to look for gasoline with-
out MMT in Canada because MMT can be used at
levels higher than allowed in the United States.
MMT is prohibited in Federal and California refor-
mulated gasoline.
SULFUR IN GASOLINE
If you live in the northeast United States, your
vehicle may have been designed to meet California
low emission standards with clean-burning, low-sul-
fur, California gasoline. Gasoline sold outside of Cal-
ifornia is permitted to have higher sulfur levels
which may affect the performance of the vehicle's cat-
alytic converter. This may cause the Check Engine or
Service Engine Soon light to illuminate.
Illumination of either light while operating on high
sulfur gasoline does not necessarily mean your emis-
sion control system is malfunctioning. DaimlerChrysler
recommends that you try a different brand of unleadedgasoline having lower sulfur to determine if the prob-
lem is fuel related prior to returning your vehicle to an
authorized dealer for service.
CAUTION: If the Check Engine or Service Engine
Soon light is flashing, immediate service is
required; see on-board diagnostics system section.
MATERIALS ADDED TO FUEL
All gasoline sold in the United States and Canada
are required to contain effective detergent additives.
Use of additional detergents or other additives is not
needed under normal conditions.
FUEL SYSTEM CAUTIONS
CAUTION: Follow these guidelines to maintain your
vehicle's performance:
²The use of leaded gas is prohibited by Federal
law. Using leaded gasoline can impair engine perfor-
mance, damage the emission control system, and
could result in loss of warranty coverage.
²An out-of-tune engine, or certain fuel or ignition
malfunctions, can cause the catalytic converter to
overheat. If you notice a pungent burning odor or
some light smoke, your engine may be out of tune or
malfunctioning and may require immediate service.
Contact your dealer for service assistance.
²When pulling a heavy load or driving a fully
loaded vehicle when the humidity is low and the tem-
perature is high, use a premium unleaded fuel to
help prevent spark knock. If spark knock persists,
lighten the load, or engine piston damage may result.
²The use of fuel additives which are now being
sold as octane enhancers is not recommended. Most
of these products contain high concentrations of
methanol. Fuel system damage or vehicle perfor-
mance problems resulting from the use of such fuels
or additives is not the responsibility of
DaimlerChrysler Corporation and may not be covered
under the new vehicle warranty.
NOTE: Intentional tampering with emissions control
systems can result in civil penalties being assessed
against you.
GASOLINE/OXYGENATE BLENDS
OPERATION
Some fuel suppliers blend unleaded gasoline with
materials that contain oxygen such as alcohol, MTBE
(Methyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) and ETBE (Ethyl Ter-
tiary Butyl Ether). Oxygenates are required in some
areas of the country during winter months to reduce
14 - 2 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 824 of 1285

carbon monoxide emissions. The type and amount of
oxygenate used in the blend is important.
The following are generally used in gasoline
blends:
Ethanol- (Ethyl or Grain Alcohol) properly
blended, is used as a mixture of 10 percent ethanol
and 90 percent gasoline. Gasoline blended with etha-
nol may be used in your vehicle.
MTBE/ETBE- Gasoline and MTBE (Methyl Ter-
tiary Butyl Ether) blends are a mixture of unleaded
gasoline and up to 15 percent MTBE. Gasoline and
ETBE (Ethyl Tertiary Butyl Ether) are blends of gas-
oline and up to 17 percent ETBE. Gasoline blended
with MTBE or ETBE may be used in your vehicle.
Methanol- Methanol (Methyl or Wood Alcohol) is
used in a variety of concentrations blended with
unleaded gasoline. You may encounter fuels contain-
ing 3 percent or more methanol along with other
alcohols called cosolvents.
DO NOT USE GASOLINE CONTAINING
METHANOL.
Use of methanol/gasoline blends may result in
starting and driveability problems and damage criti-
cal fuel system components.
Problems that are the result of using methanol/
gasoline blends are not the responsibility of
DaimlerChrysler Corporation and may not be covered
by the vehicle warranty.
Reformulated Gasoline
Many areas of the country are requiring the use of
cleaner-burning fuel referred to asReformulated
Gasoline. Reformulated gasoline are specially
blended to reduce vehicle emissions and improve air
quality.
DaimlerChrysler Corporation strongly supports the
use of reformulated gasoline whenever available.
Although your vehicle was designed to provide opti-
mum performance and lowest emissions operating on
high quality unleaded gasoline, it will perform
equally well and produce even lower emissions when
operating on reformulated gasoline.
Materials Added to Fuel
Indiscriminate use of fuel system cleaning agents
should be avoided. Many of these materials intended
for gum and varnish removal may contain active sol-
vents of similar ingredients that can be harmful to
fuel system gasket and diaphragm materials.
FUEL DELIVERY SYSTEM
OPERATION
The fuel delivery system consists of: the electric
fuel pump, fuel filter/fuel pressure regulator, fuel
tubes/lines/hoses, fuel rail, fuel injectors, fuel tank,
accelerator pedal and throttle cable.A fuel return system is used on all models (all
engines). Fuel is returned through the fuel pump
module and back into the fuel tank through the fuel
filter/fuel pressure regulator. A separate fuel return
line from the engine to the tank is no longer used
with any engine.
The fuel tank assembly consists of: the fuel tank,
filler tube, fuel gauge sending unit/electric fuel pump
module, a rollover valve(s) and a pressure-vacuum
filler cap.
Also to be considered part of the fuel system is the
evaporation control system or Onboard Refueling
Vapor recovery (ORVR). This is designed to reduce
the emission of fuel vapors into the atmosphere. The
description and function of the Evaporative Control
System is found in the Emission Control Systems
section.
FUEL PUMP MODULE
DESCRIPTION
The fuel pump module is installed in the fuel tank
(Fig. 1).
OPERATION
The fuel pump module contains the following:
²Electric fuel pump
²Fuel pump reservoir
²Inlet strainer
²Fuel filter/pressure regulator
²Fuel gauge sending unit
²Fuel supply line connection
Fig. 1 Fuel Pump Module
1 ± FUEL FILTER/PRESSURE REGULATOR
2 ± FUEL LEVEL SENSOR
3 ± FUEL RESERVOIR
4 ± INLET STRAINER
5 ± FLOAT
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 3
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 825 of 1285

The inlet strainer, fuel pressure regulator and fuel
level sensor are the only serviceable items. If the fuel
pump requires service, replace the fuel pump module.
ELECTRIC FUEL PUMP
DESCRIPTION
The electric fuel pump is located in and is part of
the fuel pump module. It is a positive displacement,
gerotor type, immersible pump with a permanent
magnet electric motor. The fuel pump module is sus-
pended in fuel in the fuel tank.
OPERATION
The pump draws fuel through a strainer and
pushes it through the motor to the outlet. The pump
contains a check valve. The valve, in the pump out-
let, maintains pump pressure during engine off con-
ditions. The fuel pump relay provides voltage to the
fuel pump. The fuel pump has a maximum dead-
headed pressure output of approximately 880 kPa
(130 psi). The regulator adjusts fuel system pressure
to approximately 338 kPa (49 psi).
FUEL GAUGE SENDING UNIT
DESCRIPTION
The fuel gauge sending unit (fuel level sensor) is
attached to the side of the fuel pump module. The
sending unit consists of a float, an arm, and a vari-
able resistor (track). The resistor track is used to
send electrical signals to the instrument cluster for
fuel gauge operation and are then transmitted to the
engine controller for OBDII emission requirements.
OPERATION
For fuel gauge operation:As fuel level
increases, the float and arm move up. This increases
the sending unit resistance, causing the fuel gauge to
read full. As fuel level decreases, the float and arm
move down. This decreases the sending unit resis-
tance causing the fuel gauge to read empty.
After this fuel level signal is sent to the instru-
ment cluster, the instrument cluster will transmit
the data across the J1850 bus circuit to the PCM.
For OBD II emission requirements:The voltage
signal is sent to the instrument cluster to indicate
fuel level. The cluster transmits the fuel level to the
PCM where it is used to prevent a false setting of
misfire and fuel system monitor trouble codes. This
occurs if the fuel level in the tank is less than
approximately 15 percent of its rated capacity.
FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
DESCRIPTION
A combination fuel filter and fuel pressure regula-
tor is used on all gas powered engines. It is located
on the top of the fuel pump module. A separate frame
mounted fuel filter is not used.
OPERATION
Fuel Pressure Regulator Operation:The pres-
sure regulator is a mechanical device that is cali-
brated to maintain fuel system operating pressure of
approximately 338 kPa (49 psi) at the fuel injectors.
It contains a diaphragm, calibrated springs and a
fuel return valve. The internal fuel filter (Fig. 2) is
also part of the assembly.
Fuel is supplied to the filter/regulator by the elec-
tric fuel pump through an opening tube at the bot-
tom of filter/regulator.
The fuel pump module contains a check valve to
maintain some fuel pressure when the engine is not
operating. This will help to start the engine.
If fuel pressure at the pressure regulator exceeds
approximately 49 psi, an internal diaphragm closes
and excess fuel pressure is routed back into the tank
through the pressure regulator. A separate fuel
return line is not used with any gas powered engine.
FUEL TANK
OPERATION
All models pass a full 360 degree rollover test
without fuel leakage. To accomplish this, fuel and
vapor flow controls are required for all fuel tank con-
nections.
All models are equipped with either one or two
rollover valves mounted into the top of the fuel tank
(or pump module).
An evaporation control system is connected to the
rollover valve(s) to reduce emissions of fuel vapors
into the atmosphere. When fuel evaporates from the
fuel tank, vapors pass through vent hoses or tubes to
a charcoal canister where they are temporarily held.
When the engine is running, the vapors are drawn
into the intake manifold. Certain models are also
equipped with a self-diagnosing system using a Leak
Detection Pump (LDP). Refer to the Emission Control
System for additional information.
FUEL RAIL
DESCRIPTION
The fuel rail supplies the necessary fuel to each
individual fuel injector and is mounted to the intake
manifold (Fig. 3).
14 - 4 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 826 of 1285

OPERATION
The fuel pressure regulator is no longer mounted
to the fuel rail on any engine. It is now located on
the fuel tank mounted fuel pump module. Refer toFuel Filter/Fuel Pressure Regulator in the Fuel
Delivery System section of this group for information.
The fuel rail is not repairable.
FUEL INJECTORS
DESCRIPTION
The injectors are positioned in the intake manifold
with the nozzle ends directly above the intake valve
port (Fig. 4).
OPERATION
The fuel injectors are 12 ohm electrical solenoids
(Fig. 5). The injector contains a pintle that closes off
an orifice at the nozzle end. When electric current is
supplied to the injector, the armature and needle
move a short distance against a spring, allowing fuel
to flow out the orifice. Because the fuel is under high
pressure, a fine spray is developed in the shape of a
hollow cone. The spraying action atomizes the fuel,
adding it to the air entering the combustion chamber.
Fuel injectors are not interchangeable between
engines.
PRESSURE-VACUUM FILLER CAP
OPERATION
The loss of any fuel or vapor out of the filler neck
is prevented by the use of a safety filler cap. The cap
will release pressure only under significant pressure
of 10.9 to 13.45 kPa (1.58 to 1.95 psi). The vacuum
release for all gas caps is between 1.94 and 2.94 kPa
(0.28 and 0.43 psi). The cap must be replaced by a
similar unit if replacement is necessary.
Fig. 2 Side ViewÐFilter/Regulator
1 ± INTERNAL FUEL FILTER
2 ± FUEL FLOW TO FUEL INJECTORS
3 ± FUEL FILTER/FUEL PRESSURE REGULATOR
4 ± O-RINGS
5 ± EXCESS FUEL BACK TO TANK
6 ± FUEL INLET
7 ± CALIBRATED SPRINGS
8 ± RUBBER GROMMET AT PUMP MODULE
9 ± LOCKING TAB
Fig. 3 Fuel Rail
Fig. 4 Fuel Injector LocationÐTypical
1 ± FUEL RAIL
2 ± INTAKE MANIFOLD
3 ± FUEL INJECTORS
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 5
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 827 of 1285

WARNING: REMOVE FILLER CAP TO RELIEVE
TANK PRESSURE BEFORE REMOVING OR REPAIR-
ING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
ONBOARD REFUELING VAPOR RECOVERY
OPERATION
The emission control principle used in the ORVR
system is that the fuel flowing into the filler tube
(appx. 1º I. D.) creates an aspiration effect which
draws air into the fill tube. During refueling, the fuel
tank is vented to the vapor canister to capture escap-
ing vapors. With air flowing into the filler tube, there
are no fuel vapors escaping to the atmosphere. Once
the refueling vapors are captured by the canister, the
vehicle's computer controlled purge system draws
vapor out of the canister for the engine to burn. The
vapors flow is metered by the purge solenoid so that
there is no or minimal impact on driveability or
tailpipe emissions.
As fuel starts to flow through the fill tube, it opens
the normally closed check valve and enters the fuel
tank. Vapor or air is expelled from the tank through
the control valve to the vapor canister. Vapor is
absorbed in the canister until vapor flow in the lines
stops, either following shut-off or by having the fuel
level in the tank rise high enough to close the control
valve. The control valve contains a float that rises to
seal the large diameter vent path to the canister. At
this point in the fueling of the vehicle, the tank pres-
sure increase, the check valve closes (preventing tank
fuel from spiting back at the operator), and fuel then
rises up the filler tube to shut-off the dispensing noz-
zle.If the engine is shut-off while the On-Board diag-
nostics test is running, low level tank pressure can
be trapped in the fuel tank and fuel can not be added
to the tank until the pressure is relieved. This is due
to the leak detection pump closing the vapor outlet
from the top of the tank and the one-way check valve
not allowing the tank to vent through the fill tube to
atmosphere. Therefore, when fuel is added, it will
back-up in the fill tube and shut off the dispensing
nozzle. The pressure can be eliminated in two ways:
1. Vehicle purge must be activated and for a long
enough period to eliminate the pressure. 2. Removing
the fuel cap and allowing enough time for the system
to vent thru the recirulation tube.
CONTROL VALVE/PRESSURE RELIEF
OPERATION
If the fuel tank should over-pressurize, the control
valve incorporates a pressure relief port that allows
pressure relief capability under extreme conditions.
Example, if the canister vent line was to get pinched
or obstructed, the relief valve would vent the pres-
sure.
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
DESCRIPTION
Different types of quick-connect fittings are used to
attach various fuel system components. These are: a
single-tab type, a two-tab type or a plastic retainer
ring type. Some are equipped with safety latch clips.
Refer to the Removal/Installation section for more
information.
CAUTION: The interior components (o-rings, spac-
ers) of quick-connect fitting are not serviced sepa-
rately. Do not attempt to repair damaged fittings or
fuel lines/tubes. If repair is necessary, replace the
complete fuel tube assembly.
Fuel tubes connect fuel system components with
plastic quick-connect fuel fittings. The fitting con-
tains non-serviceable O-ring seals (Fig. 6).
CAUTION: Quick-connect fittings are not serviced
separately. Do not attempt to repair damaged quick-
connect fittings or fuel tubes. Replace the complete
fuel tube/quick-connect fitting assembly.
The quick-connect fitting consists of the O-rings,
retainer and casing (Fig. 6). When the fuel tube
enters the fitting, the retainer locks the shoulder of
the nipple in place and the O-rings seal the tube.
Fig. 5 Fuel Injector
1 ± FUEL INJECTOR
2 ± NOZZLE
3 ± TOP (FUEL ENTRY)
14 - 6 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 828 of 1285
ROLLOVER VALVES
DESCRIPTION
All vehicles have rollover valve(s) on top of the fuel
tank.
OPERATION
The valves prevent fuel flow through the fuel tank
vent valve hoses should the vehicle rollover.
The rollover valves on the fuel tank are not ser-
viceable.
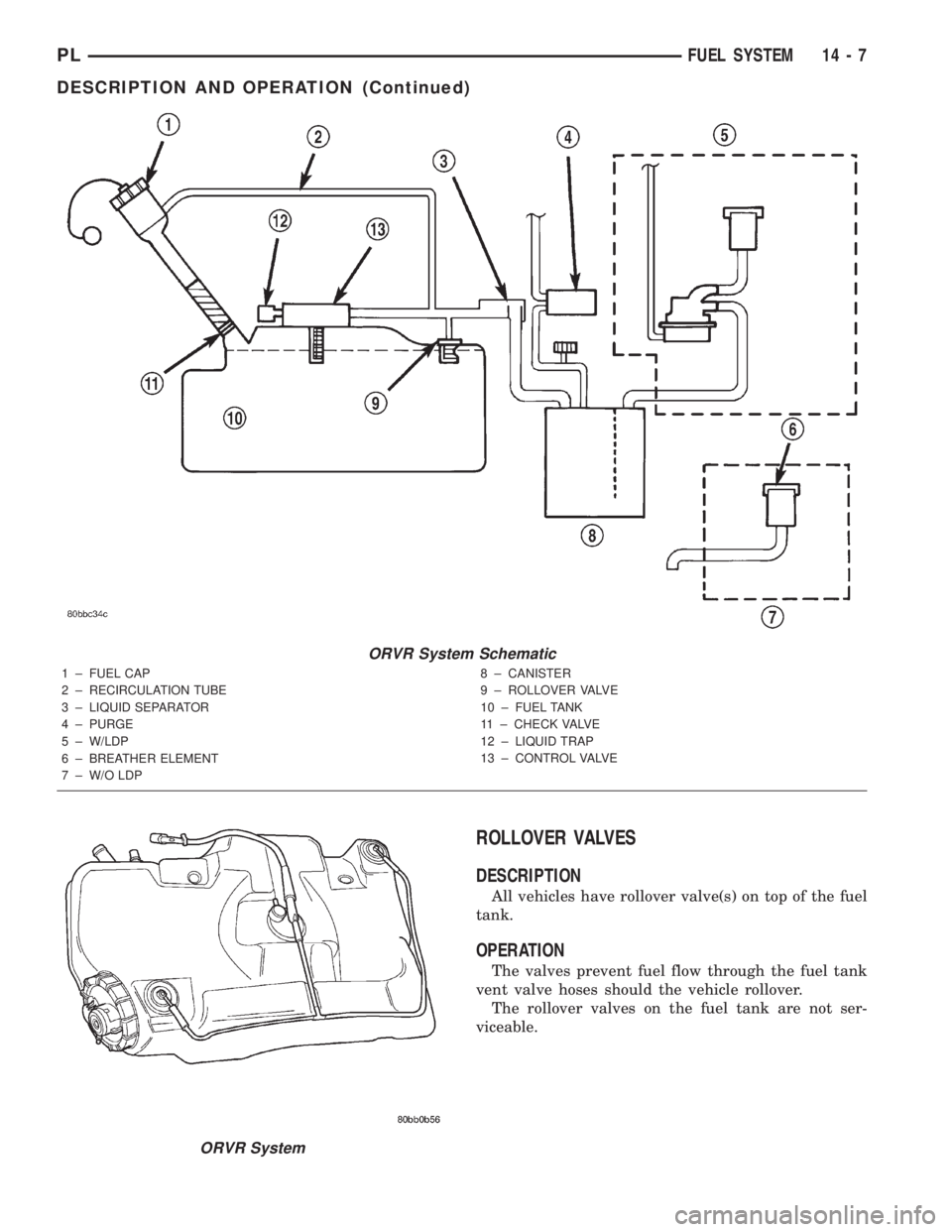
ORVR System Schematic
1 ± FUEL CAP
2 ± RECIRCULATION TUBE
3 ± LIQUID SEPARATOR
4 ± PURGE
5 ± W/LDP
6 ± BREATHER ELEMENT
7 ± W/O LDP8 ± CANISTER
9 ± ROLLOVER VALVE
10 ± FUEL TANK
11 ± CHECK VALVE
12 ± LIQUID TRAP
13 ± CONTROL VALVE
ORVR System
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 7
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 829 of 1285

FUEL TUBES/LINES/HOSES AND CLAMPS
OPERATION
Also refer to Quick-Connect Fittings.
WARNING: THE FUEL SYSTEM IS UNDER A CON-
STANT PRESSURE (EVEN WITH THE ENGINE OFF).
BEFORE SERVICING ANY FUEL SYSTEM HOSES,
FITTINGS OR LINES, THE FUEL SYSTEM PRES-
SURE MUST BE RELEASED. REFER TO THE FUEL
SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE PROCEDURE IN
THIS GROUP.
Inspect all hose connections such as clamps, cou-
plings and fittings to make sure they are secure and
leaks are not present. The component should be
replaced immediately if there is any evidence of deg-
radation that could result in failure.
Never attempt to repair a plastic fuel line/tube.
Replace as necessary.
Avoid contact of any fuel tubes/hoses with other
vehicle components that could cause abrasions or
scuffing. Be sure that the plastic fuel lines/tubes areproperly routed to prevent pinching and to avoid heat
sources.
The lines/tubes/hoses used on fuel injected vehicles
are of a special construction. This is due to the
higher fuel pressures and the possibility of contami-
nated fuel in this system. If it is necessary to replace
these lines/tubes/hoses, only those marked EFM/EFI
may be used.
If equipped:The hose clamps used to secure rub-
ber hoses on fuel injected vehicles are of a special
rolled edge construction. This construction is used to
prevent the edge of the clamp from cutting into the
hose. Only these rolled edge type clamps may be
used in this system. All other types of clamps may
cut into the hoses and cause high-pressure fuel leaks.
Use new original equipment type hose clamps.
Tighten hose clamps to 3 N´m (25 in. lbs.) torque.
SERVICE PROCEDURES
FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE
(1) Remove Fuel Pump relay from Power Distribu-
tion Center (PDC). For location of relay, refer to label
on underside of PDC cover.
(2) Start and run engine until it stalls.
(3) Attempt restarting engine until it will no
longer run.
(4) Turn ignition key to OFF position.
CAUTION: Steps 1, 2, 3 and 4 must be performed to
relieve high pressure fuel from within fuel rail. Do
not attempt to use following steps to relieve this
pressure as excessive fuel will be forced into a cyl-
inder chamber.
(5) Place a rag or towel below fuel line quick-con-
nect fitting at fuel rail.
(6) Return fuel pump relay to PDC.
(7) One or more Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTC's)
may have been stored in PCM memory due to fuel
pump relay removal. The DRB IIItscan tool must be
used to erase a DTC.
INJECTOR CONNECTOR
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect electrical connectors at the fuel
injectors. To remove connector refer to (Fig. 8). Pull
the red colored slider away from injector (1). While
pulling the slider, depress tab (2) and remove connec-
tor (3) from injector. The factory fuel injection wiring
harness is numerically tagged (INJ 1, INJ 2, etc.) for
injector position identification. If harness is not
tagged, make note of wiring location before removal.
Fig. 6 Plastic Quick-Connect Fittings
1 ± CASING
2 ± WINDOW
3 ± RETAINER TAB
4 ± NIPPLE
5 ± O RINGS
6 ± WINDOW
7 ± RETAINER ªEARº
14 - 8 FUEL SYSTEMPL
DESCRIPTION AND OPERATION (Continued)
Page 830 of 1285

INSTALLATION
(1) Connect electrical connectors at all fuel injec-
tors. To install connector, refer to (Fig. 8). Push con-
nector onto injector (1) and then push and lock red
colored slider (2). Verify connector is locked to injec-
tor by lightly tugging on connector.
DRAINING FUEL TANK
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE SERVICING FUEL SYSTEM COMPONENTS.
SERVICE VEHICLES IN WELL VENTILATED AREAS
AND AVOID IGNITION SOURCES. NEVER SMOKE
WHILE SERVICING THE VEHICLE.
(1) Remove fuel filler cap.
(2) Perform the Fuel System Pressure Release pro-
cedure.
(3) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(4) Raise vehicle and support.
(5) Remove quick connect cap from drain port.
(6) Drain fuel tank into holding tank or a properly
labeledGasolinesafety container.
(7) Replace quick connect cap.
HOSES AND CLAMPS
Inspect all hose connections (clamps and quick con-
nect fittings) for completeness and leaks. Replace
cracked, scuffed, or swelled hoses. Replace hoses that
rub against other vehicle components or show sign of
wear.
Fuel injected vehicles use specially constructed
hoses. When replacing hoses, only use hoses marked
EFM/EFI.
When installing hoses, ensure that they are routed
away from contact with other vehicle components
that could rub against them and cause failure. Avoid
contact with clamps or other components that cause
abrasions or scuffing. Ensure that rubber hoses are
properly routed and avoid heat sources.
The hose clamps have rolled edges to prevent the
clamp from cutting into the hose. Only use clamps
that are original equipment or equivalent. Other
types of clamps may cut into the hoses and cause
high pressure fuel leaks. Tighten hose clamps to 1
N´m (10 in. lbs.) torque.
QUICK-CONNECT FITTINGS
REMOVAL
When disconnecting a quick-connect fitting, the
retainer will remain on the fuel tube nipple.
WARNING: RELEASE FUEL SYSTEM PRESSURE
BEFORE DISCONNECTING A QUICK-CONNECT FIT-
TINGS. REFER TO THE FUEL PRESSURE RELEASE
PROCEDURE.
(1) Disconnect negative cable from battery or aux-
iliary jumper terminal.
(2) Perform Fuel Pressure Release Procedure.
Refer to the Fuel Pressure Release Procedure in this
section.
Fig. 7 Fuel Injectors
Fig. 8 Remove/Install Injector Connector
PLFUEL SYSTEM 14 - 9
SERVICE PROCEDURES (Continued)